Cloning
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
What does grown in vitro mean?
Grown in glass, often referring to the glassware in lab procedures
Describe the process of micropropagation (tissue culture).
Tips of stems/ roots/ side shoots are removed from the plant to be cloned - explants
Explants are trimmed to about 0.5-1.0 mm
Then, explants are washed in mild bleach to kill any microorganisms
In sterile conditions, explants are placed in an agar medium that contains nutrients (glucose, nitrogen source or nitrates) and plant hormones to encourage cell division and growth
Cells in explant divide by mitosis to form a callus
When there are many cells, they are separated into smaller pieces again and grown under sterile conditions
Some explants are put on different growth mediums with different concentrations of plant hormones to encourage the cells to differentiate and produce roots, shoots and leaves
The grown roots and shoots (plantlets) are transferred to greenhouses and transplanted into compost
Greenhouses are kept very moist to reduce water loss
What are the advantages of micropropagation?
Large numbers of genetically identical plants can be produced rapidly
Species that are difficult to grow from seed or cuttings can be propagated instead
Plants can be produced at any time of the year
Large number of plants can be stored easily - kept in the cold at early stages of production and developed when needed
genetic modifications can be introduced into thousands of plants quickly after modifying only a small amount of plants
Why are cloning animals beneficial?
allows reliable and quick production of animals with desirable characteristics
helps build population of rare animals that are threatened with extinction
Describe the stages in the production of cloned mammals.
Haploid nucleus of an unfertilised egg is removed, forming an enucleated egg cell
Diploid nucleus from a mature body cell of a donor fuses with the enucleated egg cell by an electric pulse
A second electric pulse is then used to trigger the cell division of mitosis to produce an embryo
The developing embryo is implanted in the uterus of a surrogate mother
The surrogate mother then gives birth to a baby who is identical to the donor
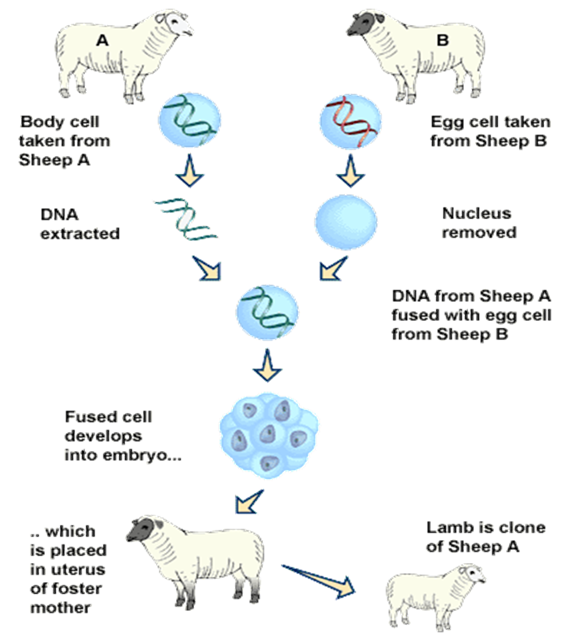
What is a real-life example of cloned mammals?
Dolly the sheep
What are some concerns of reproductive cloning using the example of Dolly the sheep?
Technique has a low success rate (Dolly was produced after 237 attempts)
As the body cell of the donor most likely has already lived a few years, the embryo tends to not develop normally, meaning a shorter lifespan
Often an increase in birth size
Defects in organs like the heart, liver, kidney and brain
Their immune system may not function as it should
What is therapeutic cloning?
It is when cells are taken from an early embryo (before 10 days) so before the cells have started to differentiate and uses embryonic stem cells for disease treatment