Heterotrophs
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
heterotrophy
organic sources of carbon synthesized by others to derive energy - eat organic material
found across all groups: prokaryotes, protists, plants, fungi, animals
can be: herbivores, carnivores, or detritivores
must balance ease of getting food and quality
herbivores
organisms which eat plants
high ease, low quality (too high CN)
high CN means hard to ingest and digest, needs many adaptations and relationship w symbionts
must eat a lot
koala example
eat a lot to compensate for low quality food
long digestive system, gut microbes, and sleep a lot
herbivore adaptation
in order to gain max nutrients from plants
insect mandibles for slicing and manipulation, rodents long incisors to gnaw tough material, ruminants complex digestive system
herbivory challenges
plant defences such as physical (thorns), chemical (cyanide)
but animals can adapt to these - such as caterpillars resistance to cardiac glycosides, or giraffes long tongue to thorns
carnivores
organisms which eat animals
high quality food (high CN), but harder to get food
most prey species give same nutrition
little digestive adaptations, but selection for efficiency
carnivory adaptations
speed, claws or talons, canine teeth
detritivores
organisms which ingest and digest dead organic matter via internal processes - all are decomposers
easy to get food but quality is variable (plant material has low quality, feces or dead animals have slightly higher, etc)
very important in decomp and nutrient cycling
detritivores limitations
not limited by abundance but by abiotic factors and chemical composition
ex soil moisture is very important for soil dwelling organisms
nitrogen use efficiency
plants are able to reabsorb nitrogen before dropping leaves
this affects CN ratio in dead material
decomposers
do not ingest dead organic matter but can directly absorb nutrients through chemical and biological processes
not all are detritivores
ex fungi, slime mold
food quality
balance of 5 elements which make up biomass or organisms
carbon (structure), oxygen (water), hydrogen (water), nitrogen (amino/nucleic acids), and phosphorus (cellular processes, ATP)
relative abundance of C and N
plants have high ratio, nitrogen is limiting
animals have low ratio, carbon is limiting
indicates what type and how much one needs to consume
mixotrophy
gain energy from photosynthesis and consuming organic material
includes algae, bacteria and protist species, as well as hemi-parasitic plants (obtain food from living host) and carnivorous plants
omnivores
gain energy from both plant and animal matter
myco-heterotroph plants
pine-sap and ghost pipe
no photosynthesis (chloroplasts), instead are associated with and obtain food from fungal hyphae via myccorhizae
epiphytes
grow on other plants but don’t parasitize on them
not even mixotroph
just grow on them for better access to resources
insectivorous plants
obtain additional nutrients from trapped insects
still photosynthesize
energy limits
in plants photosynthesis reaches a plateau above Isat
in animals in saturates at a specific density - functional response curves
what influences organism feeding rate
physical ability, time to digest, time to find food, time to handle/process food, consider safety which searching
all use energy or are invested energy
functional response curve type 1
least common
feeding rate increases linearly due to quick food processing
but then food level abruptly levels off
ex zooplankton, filter feeders
mostly restricted by density of food they are eating
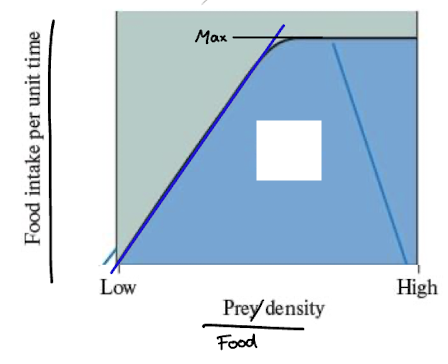
functional response curve type 2
feeding rate increases linearly at low food density and slows through moderate and levels off
limited. by searching for food as well as handling times at low density
ex moose, wolves, bears, parasitoid wasps
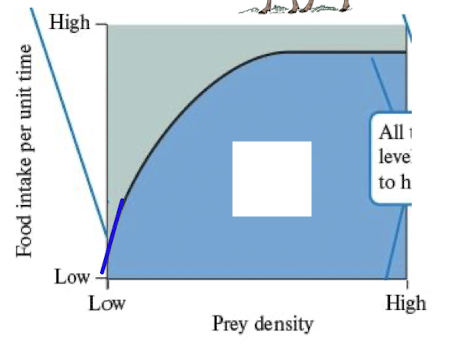
functional response curve type 3
s shaped feeding rate - increases rapidly
limited by age, exposure to prey and encounter rate
ex juveniles learning to hunt, prey switching, or searching for rare prey
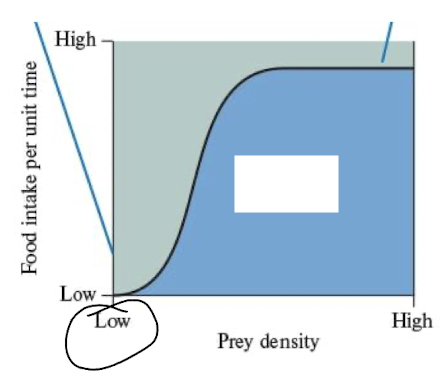
optimal foraging strategy
describes how organisms feed as an optimizing process - maximizes or minimizes some quantity such as energy intake or predation risk
what, when, where
marginal value theorem
an organism should spend time in a patch that maximizes their energy gained in the patch
when energy gain levels off they should leave the patch
longer travels time = more time spent in
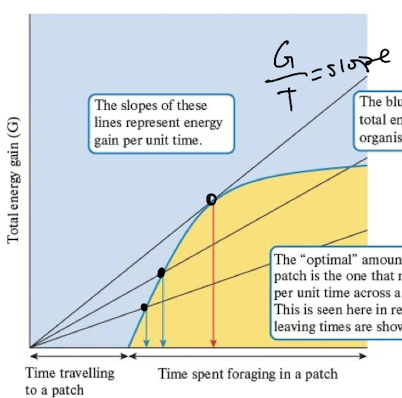
net energy gain
gain from one prey species including time spent, energy gain, number of prey encountered per unit time, energy lost searching and handling time
can be altered to include n species
a species can be predicted to prey on one species if the energy gain is more than the energy lost searching for more species (etc)
ex bluegill sunfish
most abundant prey are 1mm long
optimal foraging theory predicts 4 mm long max energy rate
actual intake from prey is 4mm as seen in natural habitat
optimal foraging by plants
limited by nutrients in soil, water and sunlight - while they are sessile, they can grown to locations of these factors
roots grow down with gravity (positive gravitropism), they also branch and use root hairs
thigmotaxis
response of an organism to touch
ex, searching for climbing surface to reach light
not all plants, but ex legumes