Semiconductor Diodes Lecture
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of 40 Q&A flashcards covering semiconductor diode fundamentals, models, equations, wave-shaping circuits, special-purpose diodes, and troubleshooting.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What type of charge carriers dominate in an n-type semiconductor?
Electrons (negative charge carriers).
Which dopant is commonly used to create n-type silicon?
Phosphorus.
What type of charge carriers dominate in a p-type semiconductor?
Holes (positive charge carriers).
Which dopant is commonly used to create p-type silicon?
Aluminum.
How many terminals does a typical semiconductor diode have?
Two (anode and cathode).
In which direction does a diode conduct significant current?
Forward-bias direction, from anode to cathode.
What happens to diode current when no external voltage (0 V) is applied?
Ideally zero current; the diode is not in an operating condition.
How does the depletion region change under reverse-bias?
It widens, preventing current flow (except leakage).
What small current flows under reverse-bias due to minority carriers?
Reverse saturation current (IS).
How does the depletion region change under forward-bias?
It narrows, allowing majority carriers to cross the junction.
State Shockley’s diode equation.
ID = IS (e^{VD/(n·VT)} − 1).
What ideality-factor value (n) is usually assumed for a silicon diode in basic calculations?
n = 1.
What is the approximate thermal voltage (VT) at room temperature (25 °C)?
About 25 mV.
What is the typical cut-in (threshold) voltage for a silicon diode?
Approximately 0.7 V.
When forward voltage greatly exceeds VT, how does the diode current vary?
It rises exponentially; the “−1” term becomes negligible.
What is the diode breakdown region?
Reverse-bias region where current rises sharply once a limit voltage is exceeded.
How is DC or static resistance (RD) of a diode defined?
RD = VD ⁄ ID at a chosen Q-point.
How is AC or dynamic resistance (rd) obtained on the diode curve?
As the slope of the tangent at the Q-point: rd = ΔVD ⁄ ΔID.
What is average AC resistance (rav)?
Slope of a secant between operating limits: rav = ΔVD ⁄ ΔID over the signal swing.
In the ideal diode model (Model I), how does the diode behave under forward-bias?
Like a closed switch (zero voltage drop).
In the constant voltage-drop model (Model II), what fixed voltage is assigned to a conducting silicon diode?
Approximately 0.7 V.
What extra element does the piecewise-linear model (Model III) add beyond Model II?
A series resistance modeling rav of the diode.
What graphical method is used to find a diode’s operating point in a circuit?
Load-line analysis.
What does the intersection of the load line and the diode characteristic represent?
The Q-point (operating point) values of VD and ID.
Which circuit uses one diode to convert AC to pulsating DC by passing only one half-cycle?
Half-wave rectifier.
Name two full-wave rectifier configurations.
Bridge rectifier and center-tapped transformer rectifier.
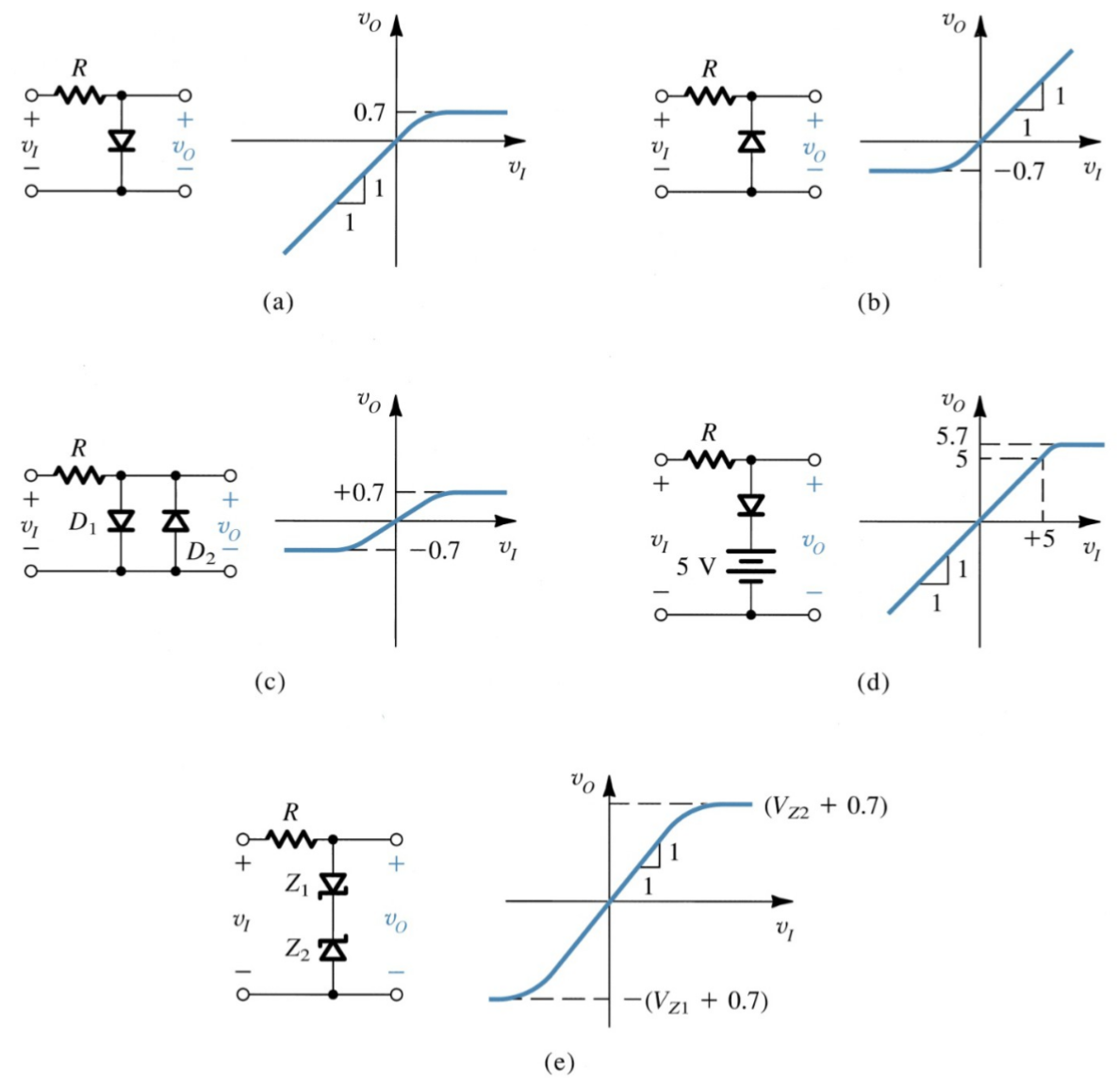
What wave-shaping circuit removes part of a signal above or below a reference level?
Clipper.
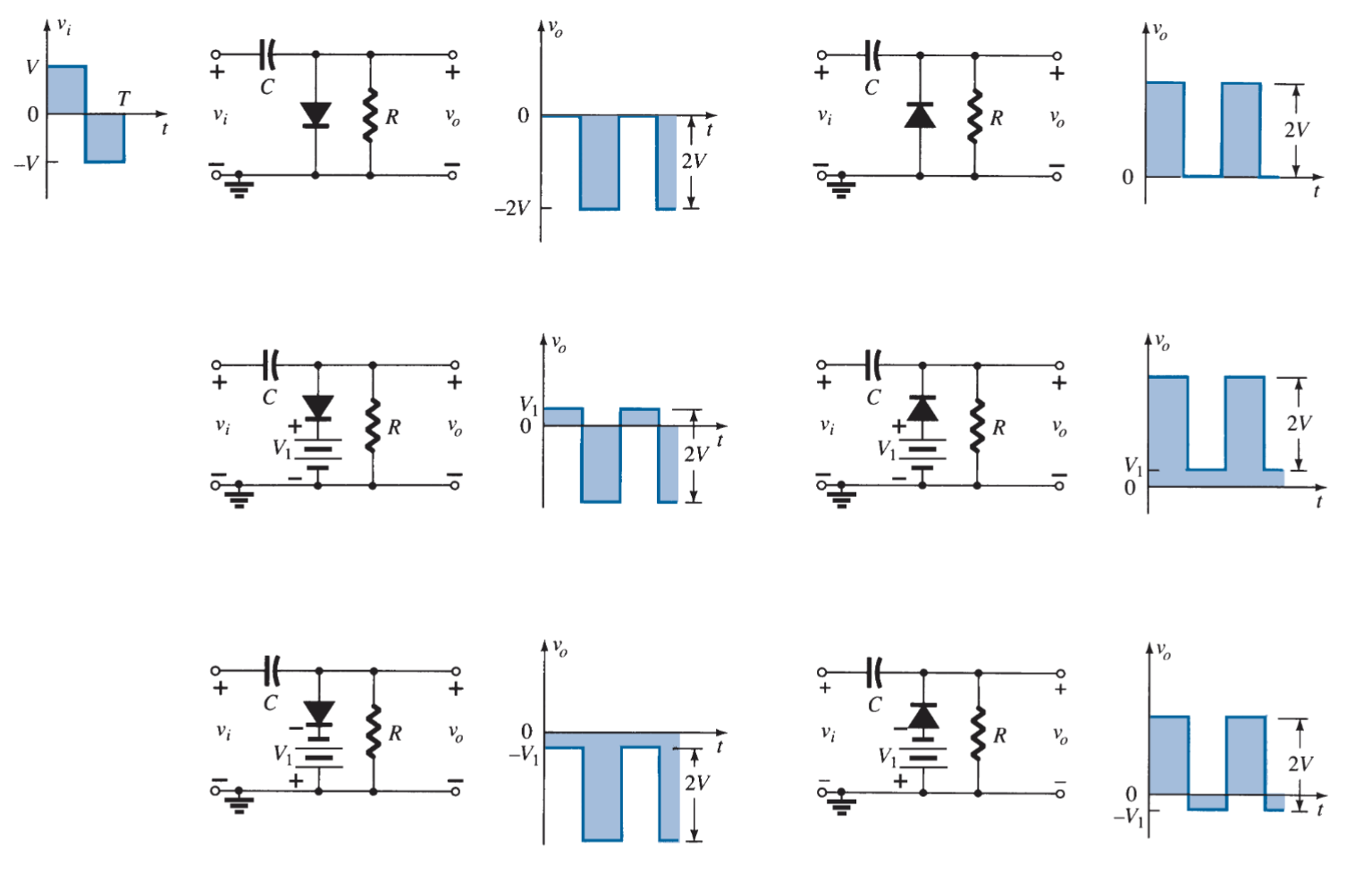
Which circuit shifts an entire waveform up or down without altering its shape?
Clamper.
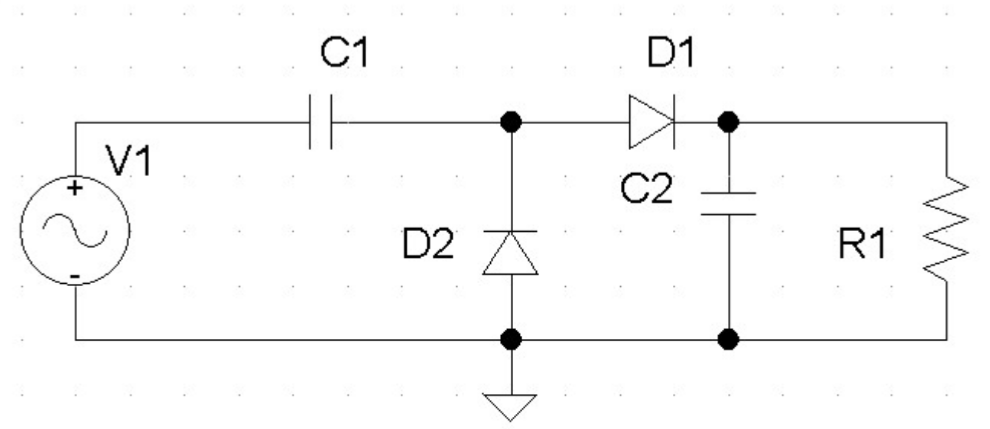
What does a voltage doubler circuit accomplish?
Produces an output DC voltage roughly twice the peak AC input.
What phenomenon enables an LED to emit visible light when forward-biased?
Electroluminescence.
What is the approximate forward voltage of a red LED?
About 1.6 V – 1.7 V.
Which diode is designed to provide voltage-variable capacitance for tuning circuits?
Varactor (voltage-variable capacitance) diode.
Which silicon diode has a very low forward drop (~0.2 V) due to its metal-semiconductor junction?
Schottky diode.
What is the primary function of a current-regulator diode?
To act as a constant-current source.
Which heavily doped pn-junction diode shows negative resistance via quantum tunneling?
Tunnel diode.
What does the acronym PIN stand for in a PIN diode?
p-type, Intrinsic, n-type.
Which property makes a step-recovery diode useful at microwave frequencies?
Extremely fast switching caused by abrupt charge storage release.
List three common tests used to troubleshoot diodes.
Voltage measurements, ohmmeter tests, and diode testers.
Name two typical diode failure modes detected during troubleshooting.
Anode-cathode short and anode-cathode open.
What does a low front-to-back ratio indicate about a diode’s condition?
The diode is partially conducting in reverse-bias; it is defective.