HMW Fall Exam
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Virgin Soil Epidemic
Communities at risk due to lack of previous contact with diseases, making them immunologically defenseless
policies to discourage population growth
- increase contraceptives and abortion practices
- increase education
- delayed reproduction
- punishments to those who have children (fines)
- genocide, famine, war, etc.
Policies to encourage population growth
- tax breaks for people with children
- encouraging immigration
- free childcare and cheaper birth
- gender equality
- paid work leave
China's One child policy
Families were restricted to only have one child in order to control population size
GMOs
Genetically modified organisms that are modified for various purposes, but can have nutritional and environmental concerns
Origin of Islam
Muhammad received revelations from Angel Gabriel from God. These revelations are known as the Quran, Islam's holy text)
five pillars of islam
key practices of muslims:
Shahadah: reciting the Muslim profession of faith
Salat: saying prayers in the proper way five times each day
Zakat: paying an alms (or charity) tax to benefit the poor and the needy
Sawm: fasting during the month of Ramadan.
Hajj: pilgrimage to Mecca
Columbian Exchange
Trade of plants, food, diseases, and ideas between Central America and Europe in the 1500s
Thomas Malthus
English cleric who believed increased food production only increases population, not standard of living
Marquis de Condorcet
French philosopher who advocated for conservation, prevention of waste, female education, anti-slavery, and pro-women's suffrage
- Faith in science & technology
- Belief that technological advancements will improve population's access to food and stabilize population growth
Green Revolution
Agricultural revolution led by Norman Borlaug, increasing food production through technological advancements
Agricultural Revolution
Period in the 17th-19th centuries of increased food production, leading to population growth and eventually the industrial revolution
Irish Potato Famine
British took all of ireland's food, leaving them only with the diseased potatoes to eat
Agricultural Collectives
Common ownership of resources and pooling of labor and income, seen in Stalin's 5-year plans and Chinese famine
Stalin's 5 year plans
Joseph Stalin, the dictator of the Soviets, wanted rapid industrialization of agriculture in 1928
About 20 million died; peasants farm and sell food at low prices - the food is then exported out at high prices
Chinese Famine
Mao wanted to control agricultural production, so they put people into agricultural collectives and forced them to work and cultivate food; horrible conditions
Fertility Rate
average number of children to a woman
Birth/ death rate
number of births/deaths per 1000 people
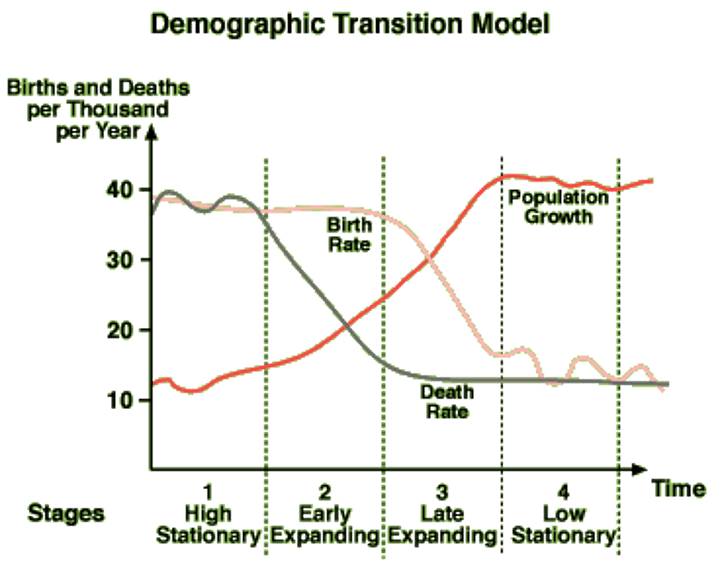
Demographic Transition
birth and death rates dropping after time, causing population to level off
population pyramids
the more steady the line, the more stable the population; if the line is very curvy, interpret it in terms of birth/ death rate; includes gender studies as well.
Sunni and Shia
2 main branches of islam:
Sunni: believe in elections of their leader (85% of muslims)
Shia: believe Muhammad's successor should be blood related (15%)
Origins of Protestant Reformation
Criticism of Catholic Church, Martin Luther's 95 theses stating that faith alone could bring salvation (good deeds not necessarily needed)
Martin Luther
German theologian who argued for faith alone as means of salvation; criticized Catholic Church and wasn't a nobleman
King Henry VIII
King of England who started the Church of England after the pope denied him a divorce
english reformation
creation of the church of england
Pope Leo X
Head of Catholic Church during Protestant Reformation, known for selling forgiveness for sins (he took peoples' money). also was against martin luther.
Catherine de Medici
French queen regent who instigated St. Bartholomew's Day Massacre, a conflict between Catholics and Protestants
French Wars of Religion
religious civil wars between Protestantism and Catholicism
England's path to democracy
Magna Carta, Petition of Right, Charles I Execution, English Civil War, Oliver Cromwell, Glorious Revolution, English Bill of Rights, Regency Period, Reform Act of 1832
Magna Carta
First document stating the king is not above the law, containing laws applicable to all of England.
Barons forced King John to sign it, but it was later nullified by the Pope
Petition of Right
Charles I reaffirmed the Magna Carta, asserting 4 principles:
1. no taxes without he consent of parliament
2. no subject may be imprisoned without cause shown
3. no soldiers may be quartered upon the citizens
4. martial law may not be used in time of peace
Charles I Execution & the English Civil War
Conflict between Puritans/Parliament and the king, resulting in Charles I's execution
Oliver Cromwell
Leader of Parliament's forces during English Civil War.
He had many rivals, so after his death, he was dug up and his head was put on a stake.
Glorious Revolution
James II succeeded by his daughter Mary II, who established the English Bill of Rights
English Bill of Rights
Established freedom of parliament and individual freedoms, similar to the US Bill of Rights
Regency Period
Period where a king chooses a prime minister to handle most of the work.
Bc king isn't doing much work, this leads to the parliament selecting the prime minister.
Reform Act of 1832
Reforms for voting rights for the lower/middle class; broadening property qualification and expanding suffrage over time
Liberal Democracy
system that gives government the power to protect individual liberty but also prevents those who govern from abusing power. Main focus is individual freedom.
Illiberal Democracy
A procedural democracy, with elections, but without real competition, and lacking some civil rights and liberties.
Theocracy
A government guided by religious leaders
Oligarchy
A government ruled by a small group of powerful people
Authoritarianism
one person rules without participation of the people
totalitarianism
one ruler has total control and focuses on one guiding idea
absolutism
A form of government in which the ruler is an absolute dictator (not restricted by a constitution or laws or opposition. chosen by god)
fascism
A political system headed by a dictator that calls for extreme nationalism and militarism and no tolerance of opposition (cult-like)
Meritocracy
people get success or power because of their abilities, not because of their money or social position (ex: imperial system in china where everyone must pass a special test to determine their worth)
feudalism
a system in which people were given land and protection by people of higher rank, and worked and fought for them in return
Influence of Confucianism and bushido code on China/Japan
Confucius states that order and stability can be achieved by implementing virtues and shame instead of just having law and punishment.
The Bushido code is a moral code (followed by samurais) made up of virtues, which is the basis of Confusius' ideology.
Locke
believed in natural rights and government's role in protecting
Machiavelli
Political theorist who emphasized the importance of military strength and being feared as a leader (better to be feared than loved)
Mercantilism
Belief that wealth leads to a more powerful state, promoting economic activity and trade
Less wealthy countries had to give many of their products to their mother countries (like the game we played in class)
Guilds
Groups of people working together for mutual aid or common goals
Capitalism (market economy) - Adam Smith
Economic system where trade and industry are controlled by private owners for profit, advocated by Adam Smith.
Adam Smith was the father of capitalism and believed that government shouldn't interfere with the natural course of free trade
Socialism
advocates for equal sharing of resources; Robert Owen advocated for this.
Communism
envisions a classless society with common ownership of all resources. This idea was created by Friedrich Engels and Karl Marx.
Marxism
predicts class struggles: lower class will revolt against upper class. This thought was produced by Karl Marx, and he also advocated for a classless society with Engkes.
Industrial Revolution & its effects
Period of technological advancements and mass production, leading to population growth and social changes
poor laws
government is responsible for aiding poor citizens financially
corn laws
taxes placed on imported food so domestic food was favored
combination acts/ riot acts
allows local officials to punish people who form unions or riot against higher classes
Hobbes
believed in a strong monarchy to maintain order.
The Enlightenment
a period in Europe when these ideas of societal order were passed around for people to understand equality and rights