🌿 Structure and Function of a Leaf (NSSCO Biology)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
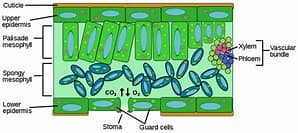
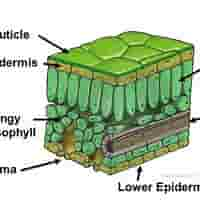
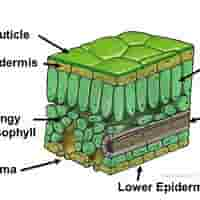
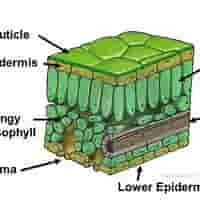
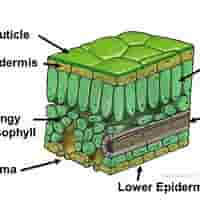
structure of upper epidermis
A single layer of transparent cells without chloroplasts.
functions of upper epidermis [ 3 ]
Protects the inner cells of the leaf.
Allows light to pass through to the photosynthetic cells beneath.
Secretes the cuticle for water conservation.
significance of upper epidermis
Transparency ensures maximum light reaches the mesophyll for photosynthesis
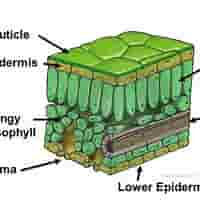
structure of cuticle
A waxy, waterproof layer covering the upper epidermis.
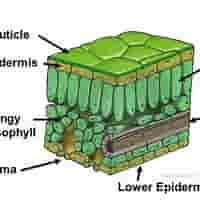
functions of cuticle
Reduces water loss by evaporation.
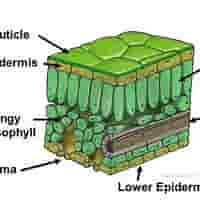
significance of cuticle
Prevents excessive drying of the leaf in hot or dry conditions
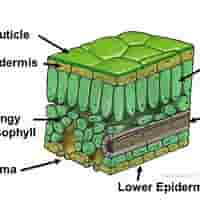
structure of lower epidermis
Transparent cells forming the bottom layer of the leaf. May also secrete cuticle.
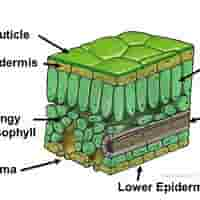
functions of lower epidermis
Protects inner tissues.
Allows light to pass through.
Contains stomata for gas exchange.
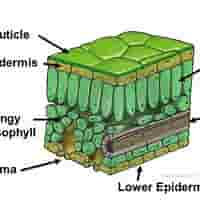
significance of lower epidermis
Protects while supporting controlled gas exchange via stomata.
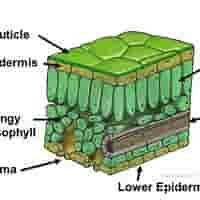
structure of mesophyll
Made up of two types of cells: Palisade Mesophyll & Spongy Mesophyll
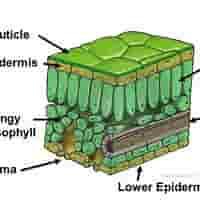
structure of palisade mesophyll
Tightly packed, column-shaped cells with many chloroplasts, just beneath the upper epidermis.
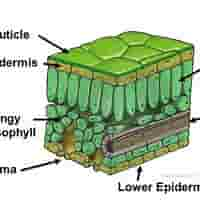
function of palisade mesophyll
Main site of photosynthesis.
significance of palisade mesophyll
Close to light and packed with chloroplasts to maximize photosynthesis.
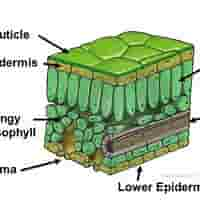
structure of spongy mesophyll
Loosely arranged cells with air spaces between them
functions of spongy mesophyll
Gas exchange between cells and air (CO₂ in, O₂ out).
Some photosynthesis also occurs here
significance of spongy mesophyll
Air spaces allow diffusion of gases and movement of water vapor for transpiration.
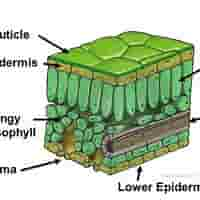
Vascular Bundles (Veins) - structure
Includes xylem and phloem.
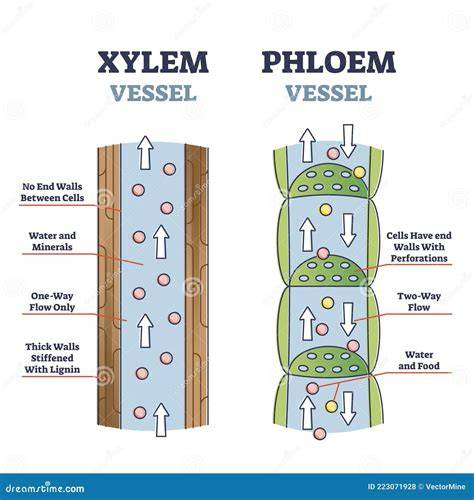
structure of xylem
Tubes called xylem vessels.
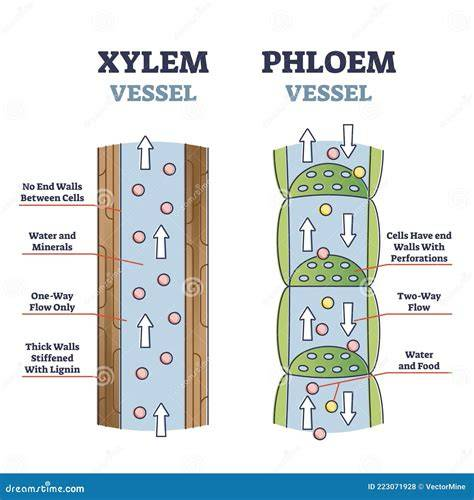
function of xylem
Transports water and mineral ions from roots to leaves.
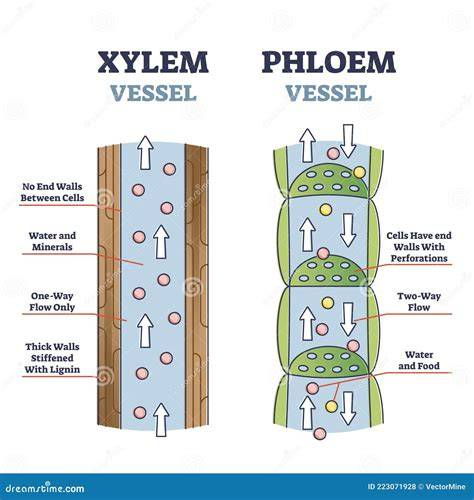
significance of xylem
Water is essential for photosynthesis and keeping cells turgid.
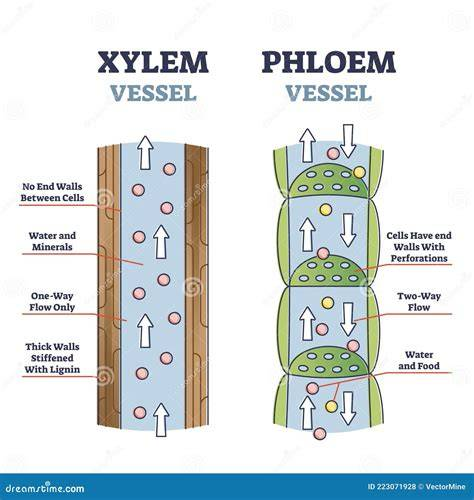
stucture of phloem
Living tubes
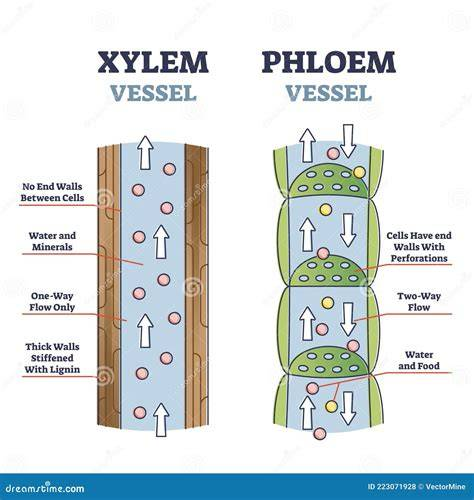
functions of phloem
Transports organic substances like sucrose and amino acids via translocation.
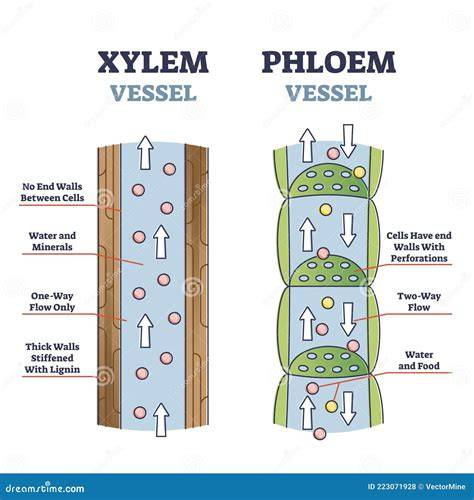
significance of phloem
Moves products of photosynthesis to other parts of the plant.
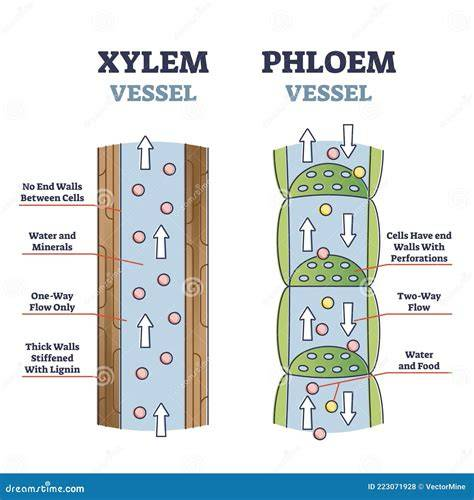
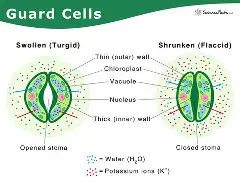
structure of stomata
Small pores in the lower epidermis, each surrounded by two guard cells.

functions of stomata
Allow carbon dioxide in for photosynthesis.
Allow oxygen and water vapor out.
Enable transpiration.

significance of stomata
Control gas exchange and water loss, vital for survival and cooling the plant.

structure of guard cells
Bean-shaped cells with some chloroplasts.

functions of guard cells
Open and close the stomata.
Perform some photosynthesis.
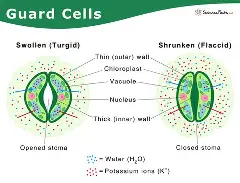
significance of guard cells
Regulate gas exchange and water loss, helping the plant respond to environment.