Biology 1801 Test 3- John Walker (AppState)
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
Total radiant energy hitting earth from sun/day ≈
1 million Hiroshima A-bombs
One factor that has allowed life to evolve & thrive on earth is the abundance of _______ _______!
free energy
What major groups can photosynthesize?
(algae/protists, plants, bacteria)
Photosynthesis is not universal to _____ _____
all cells
Respiration?
A metabolic process wherein, the living cells of an organism obtains energy (in the form of ATP) by taking in oxygen and liberating carbon dioxide from the oxidation of complex organic substances.
Which groups of organisms conduct photosynthesis?
Plants, Protists, Bacteria
___________ is the use of sunlight to manufacture carbohydrates
Photosynthesis
Organisms that make organic molecules from inorganic ones are __________ ("self-feeders")
autotrophs
___________ ("different-feeders") must consume organic molecules
Heterotrophs
____________ converts electromagnetic energy to chemical energy
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis requires?
1. Sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water
2. Produces oxygen as a by-product
What is oxidized?
Electrons have been pulled closer to the hydrogen
idk
What is reduced?
Electrons have been pulled closer to the carbon
idk
Photosynthesis in Plants?
Chloroplasts, Chlorophyll, Mesophyll & mesophyll cells, Stomata
Chloroplasts?
organelles in plants and algae that carry out photosynthesis. Endosymbiosis theory origin of this organelle (DNA, Binary fission)
Chlorophyll? and where it is located
main pigment (green) and is located in the chloroplast
Stomata?
carbon dioxide enters and oxygen exits leaf
_________ from atmosphere goes in through stomata
CO2
Stomata?
Pores that let CO2 come in
The source of CO2 used in photosynthesis is?
the atmosphere
Photosynthesis consists of two sets of reactions
1. The light-dependent reactions produce O2, ATP, NADPH
2. The Calvin cycle reactions produce sugar from CO2
The light dependent reactions and Calvin cycle reactions react where?
The light dependent reactions take place in the Thykoid membranes and the Calvin cycle reactions take place in the Stroma
Photosynthetic ___________ are located in the ___________ membranes
pigments, thylakoid
Most common pigment in thylakoids = __________ and reflects/absorbs what lights?
chlorophyll, and reflects green light and absorbs red and blue light
True or False: Is the chlorophyll responsible for the green color in plants
True
_________ ________ is the electromagnetic radiation that humans can see
Visible light
_________ wavelengths have more energy than longer wavelengths
Shorter
There are two major classes of pigment in plants:
1. The chlorophylls (chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b) that absorb red and blue light and reflect and transmit green light
2. The carotenoids absorb blue and green light and reflect and transmit yellow, orange, and red light
What light color has the highest energy?
Blue light
What light color has the lowest energy?
Red Light
A plant appears green because?
Chlorophyll absorbs red and blue light, and green light is reflected by chlorophyll.
Each pigment has an __________ __________
absorption spectrum
Produces the _______ __________ (rate of photosynthesis at each wavelength)
action spectrum
______ and _______ are the most effective at driving photosynthesis
blue and red photons
Carotenoids _______ the range of wavelengths that can drive photosynthesis
extend
Chlorophyll & accessory pigments have _______ consisting of ring structures that can absorb light energy
"heads"
When Light Is Absorbed, Electrons Enter an Excited State?
1. Chlorophyll can absorb red or blue photons
2. Red photons bump an electron up one energy level
3. Blue photons bump an electron up two energy levels
4. Green photons are intermediate, so are not absorbed
Exam!!! Energy (not the electrons but the excitement) can be transferred to nearby molecules is what?
Resonance Energy Transfer
A photosystem consists of two major elements?
1. An antenna complex- Is composed of 200-300 chlorophyll and accessory pigment molecules
2. A reaction center- Energy is transferred from one molecule to the next until it reaches the reaction center (by resonance)
__ finally transferred to a specialized chlorophyll molecule
E
Transfers an excited electron to an electron acceptor, 2 ways?
1. Redox
2. Transformed to chemical E
Which comes first (photosystem I or photosystem II)
Photosystem II
How does the photosystem II work?
1. Excited electrons passed to ETC
2. ETC pumps Protons into thylakoid lumen Drives ATP Synthase
3. Reaction center splits water (oxidized) Generates O2
4. Replaces electrons in reaction center
Oxidation of water yields oxygen gas (This is the only protein complex that can oxidize water into atmosphere)
Manganese cluster:
How does the photosystem I work?
1. Electrons from electronic transport chain re-excited
2. Passed to NADP+ reductase
3. NADP+ is reduced to form NADPH Terminal electron acceptor (end of electronic transport chain)
The __ _________ is a model of how photosystems I and II interact
PS II energy pumps protons, produces ATP
PS I energy excites electrons to produce NADPH
Z scheme
Since electrons pass from water to NADP+ in a linear fashion, it is called _________ ________ _______
noncyclic electron flow
________ __________ ________ also occurs in green algae and land plants and increases ATP
Cyclic electron flow
ATP and NADPH are produced by photosystems I and II in the?
stroma
What is used to drive Calvin cycle in stroma
Energy
Carbon fixation?
add inorganic carbon to an organic compound
Can the Calvin Cycle occur in the dark? Yes or No?
Yes
The Calvin cycle has three phases:
1. Fixation
2. Reduction
3. Regeneration
What is the output of the Calvin cycle
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P)
Fixation?
CO2 attached to a five-carbon compound called ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP - 5C + 1CO2)
Reduction?
The 3PGA are phosphorylated by ATP and reduced by NADPH
Regeneration?
The remaining G3P is used in reactions that use ATP to regenerate RuBP
The CO2-fixing enzyme is ________ and thought to be the most abundant enzyme on earth
Rubisco
What does O2 fixation cause?
Photorespiration
What competes at rubisco's active sites
CO2 & O2
Where did all the oxygen come from in the atmosphere?
The photosystems
_______________ consumes oxygen, ATP, and releases fixed CO2
Photorespiration
Rate _________ when concentration of CO2 is ________ and O2 is higher
increases, lower
______ stomata allow CO2 to diffuse into the leaf and O2 to diffuse out and lose H2O in the process
Open
When conditions are hot and dry, _________ must close to prevent evaporation of water in this process what builds up and what drops
stomata, O2, and CO2
C4 plants, such as sugarcane and maize, use a different enzyme to initially fix CO2 and form what?
four-carbon compound (malate)
What is (CAM)
Crassulacean acid metabolism
Why does the stomata open at night and what happens when the stomata is closed during the day?
Fixation of CO2, and releases CO2 to be able to run the Calvin cycle
Both ___ and _____ pathways function to concentrate CO2 to drive the Calvin cycle
C4, CAM
Because energy is required, ___ plants are most efficient in normal conditions
C3
CO2 is realsed in what?
bundled sheath cells
What does G3P make?
Sugar (glucose)
All __________ use respiration
organisms
Which type of organisms carry out cellular respiration?
All organisms use cellular respiration.
Glucose is reduced or oxidized?
Oxidized
Oxygen is oxidized or reduced?
Reduced
In cellular respiration which molecule is oxidized?
Glucose
Are involved in the synthesis, modification, and breakdown of several types of cellular molecules and contain their own DNA, divide by binary fission
Intermembrane space and mitochondrial matrix
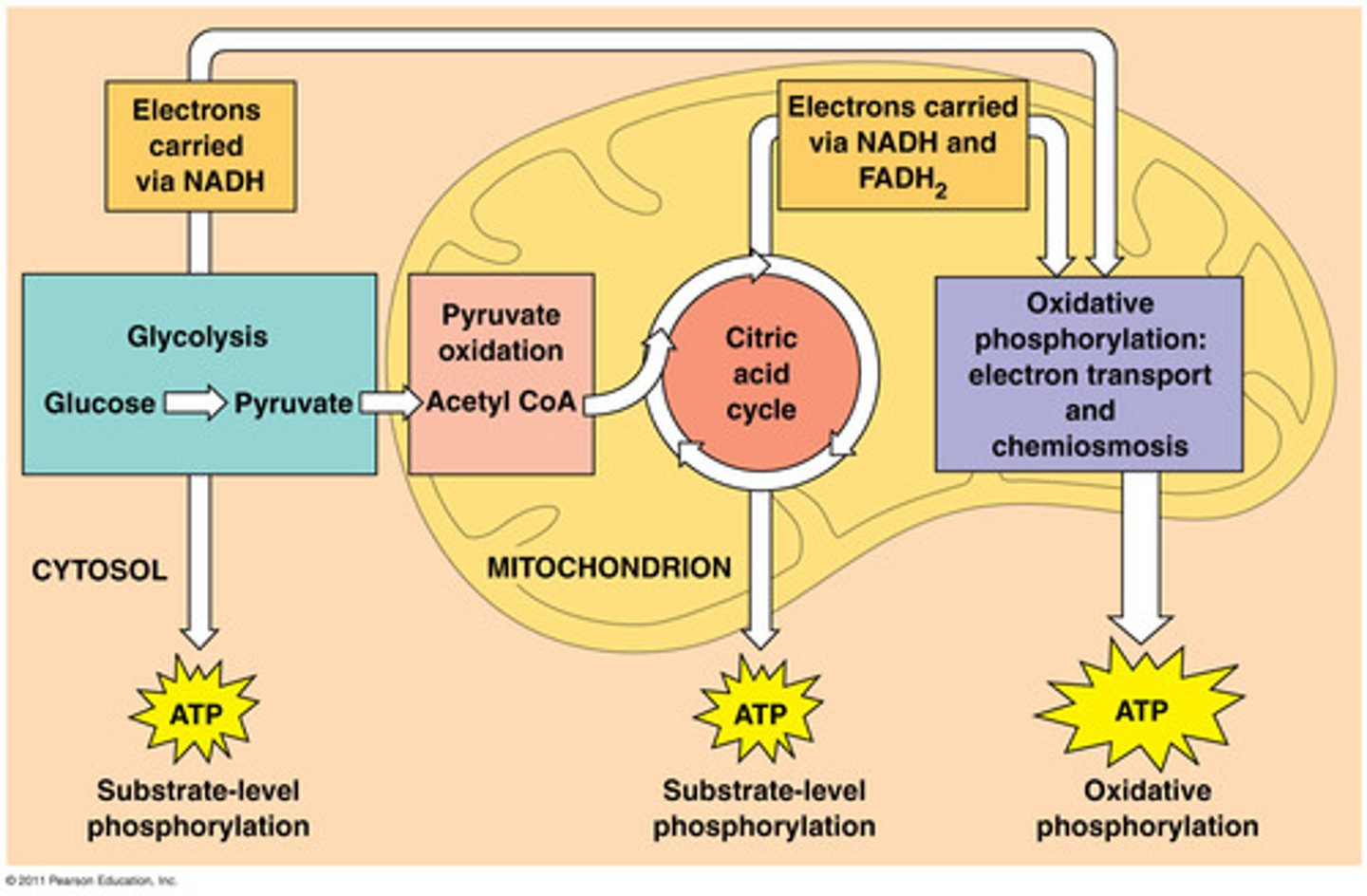
Cellular respiration is a set of four processes?
1. glycolysis- glucose broken down into two pyruvate
2. pyruvate processing- pyruvate is oxidized to form acetyl
3. citric acid cycle- acetyl is oxidized to fully CO2
4. electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation- ETC produces proton gradient that is used to make ATP
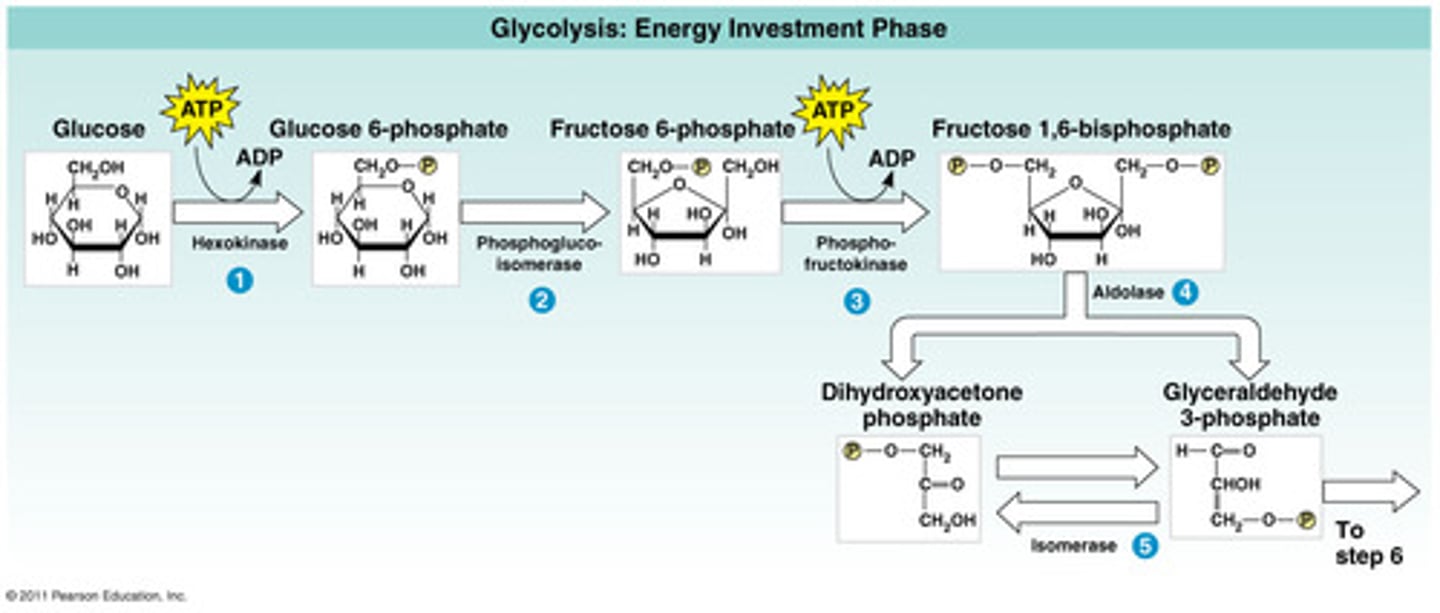
There are two phases of glycolysis
1. The energy investment phase- uses 2 ATP's
2. The energy payoff phase- produces 4 ATP and 2 NADH
Overview of Cellular Respiration
Energy Investment Phase
Energy Payoff Phase
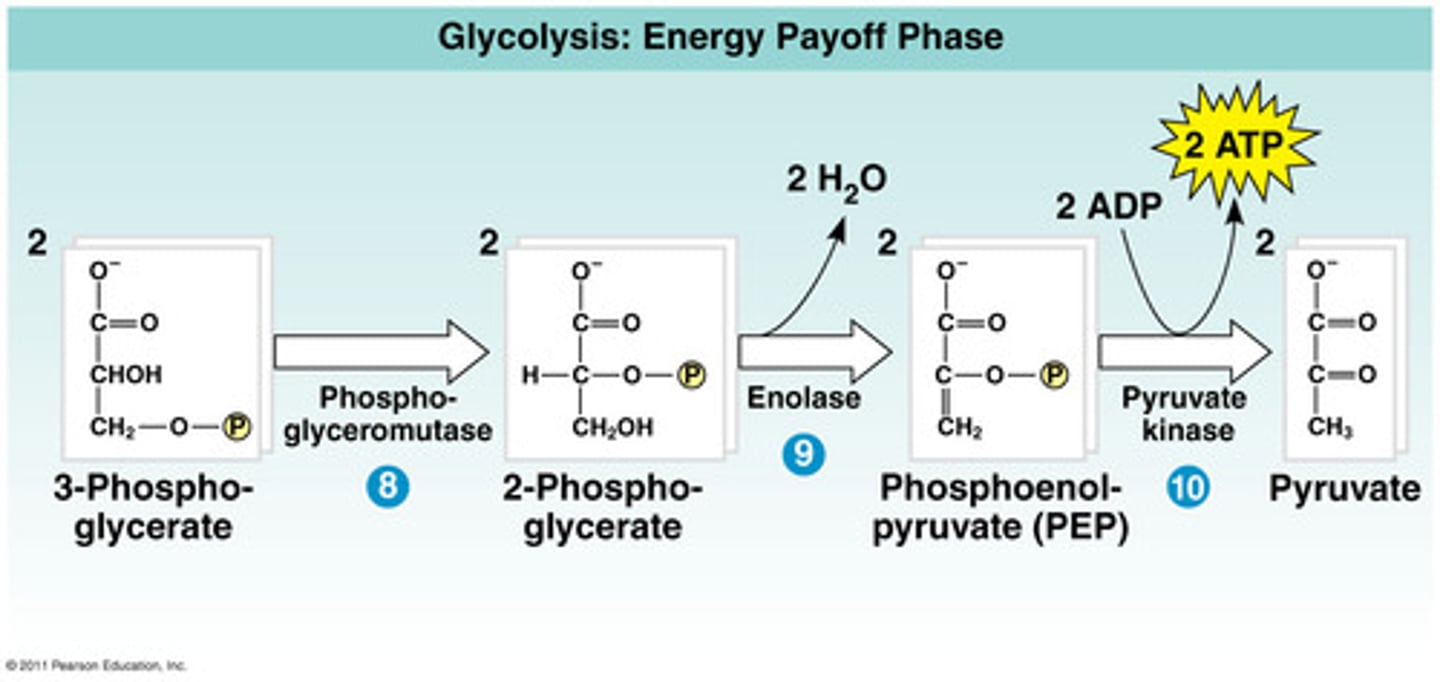
What is substrate level phosphorylation
When a phosphoryl group is transferred from a substrate to ADP or GDP to form ATP or GTP, coupled with the release of free energy.
Chemiosmotic
The process of moving ions to the other side of a biological membrane, and as a result, an electrochemical gradient is generated. This can then be used to drive ATP synthesis.
There is feedback inhibition of ___________ by ATP
Glycolysis
____________ produced during glycolysis is transported into mitochondrial matrix (cytosol in prokaryotes)
Pyruvate
___________ ________ __________ of pyruvate dehydrogenase occurs when products of glycolysis and pyruvate processing are high
Inhibitory allosteric phosphorylation
In the citric acid cycle, each acetyl CoA (2C) from pyruvate processing is completely oxidized into _______ _____
two CO2
In Oxidizing Acetyl CoA to CO2 potential energy is used to
1. Reduce three NAD+ to NADH
2. Reduce one FAD to FADH2
3. Phosphorylate one ADP (or GDP) to form ATP (or GTP)
and also 2 acetyl Co A = 2 cycles per glucose
Citric Acid Cycle
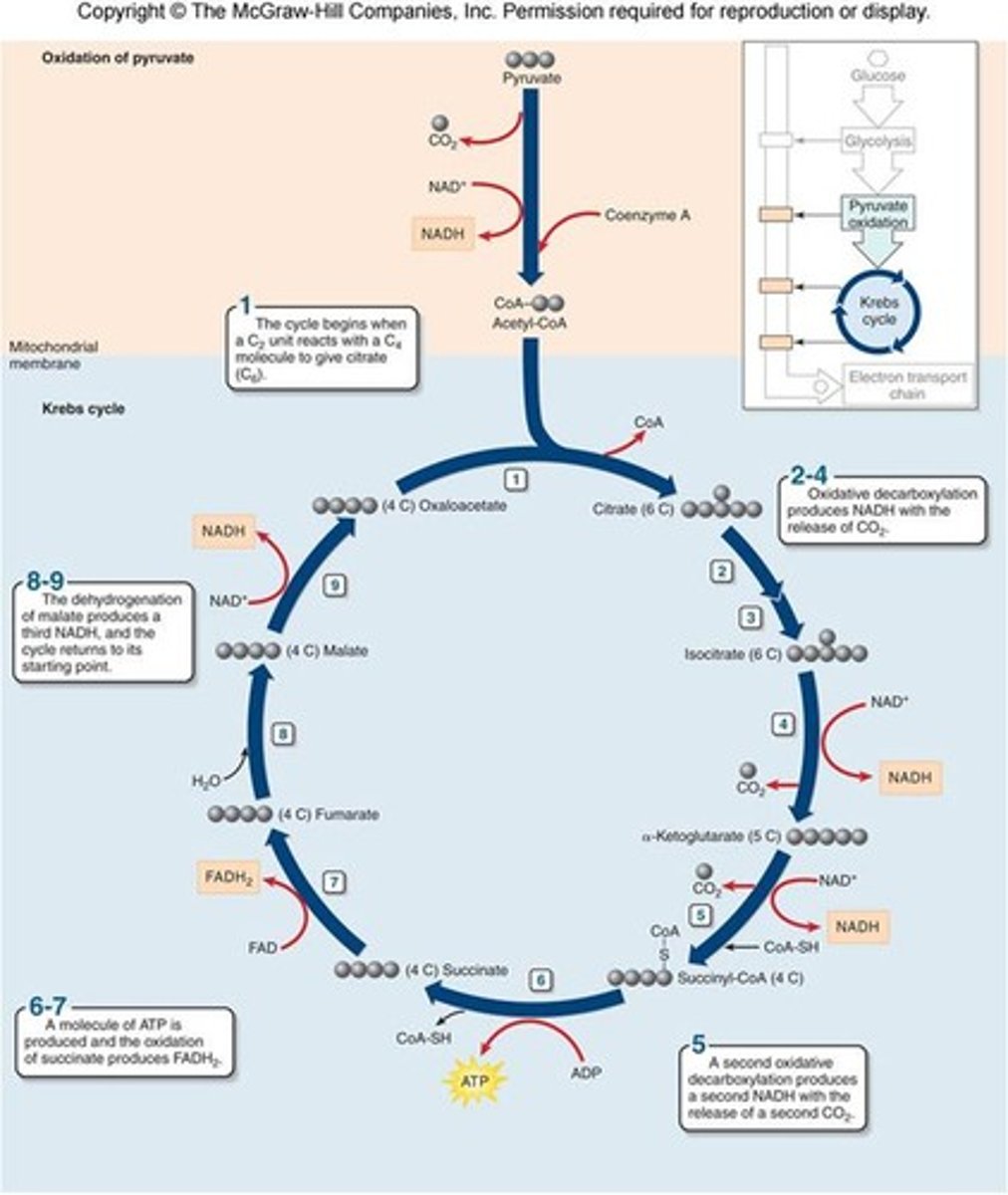
The citric acid cycle can be turned off at multiple points which is?
feedback inhibition
In the citric acid cycle the reaction rates are low when ATP or NADH are _________
abundant
Most of _________ __________ ________ is contained in the electrons transferred to NADH and FADH2
glucose's original energy
The electrons (and protons) are ultimately transferred to oxygen to form _______
water
The molecules that oxidize NADH and FADH2 are called the ______________ ___________ _________
electron transport chain (ETC)
What does the terminal electron acceptor form?
water
The ETC has 4 protein complexes
Complex I, Complex II, Complex III, Complex IV
___ is used to pump protons across the mitochondrial inner membrane into the inter membrane space and forms a strong electrochemical gradient
ETC
____ __________ is the enzyme that synthesizes ATP
ATP synthase