Constitutional Right to Privacy and Abortion Cases
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
What was the Connecticut law challenged in Griswold v. Connecticut (1965)?
The law prohibited the use of any drug, medicinal article, or instrument for preventing conception, imposing fines or imprisonment for violations.

Who were the key figures involved in the Griswold v. Connecticut case?
Estelle Griswold, executive director of Planned Parenthood League of Connecticut, and Dr. C. Lee Buxton, a doctor and professor at Yale Medical School.
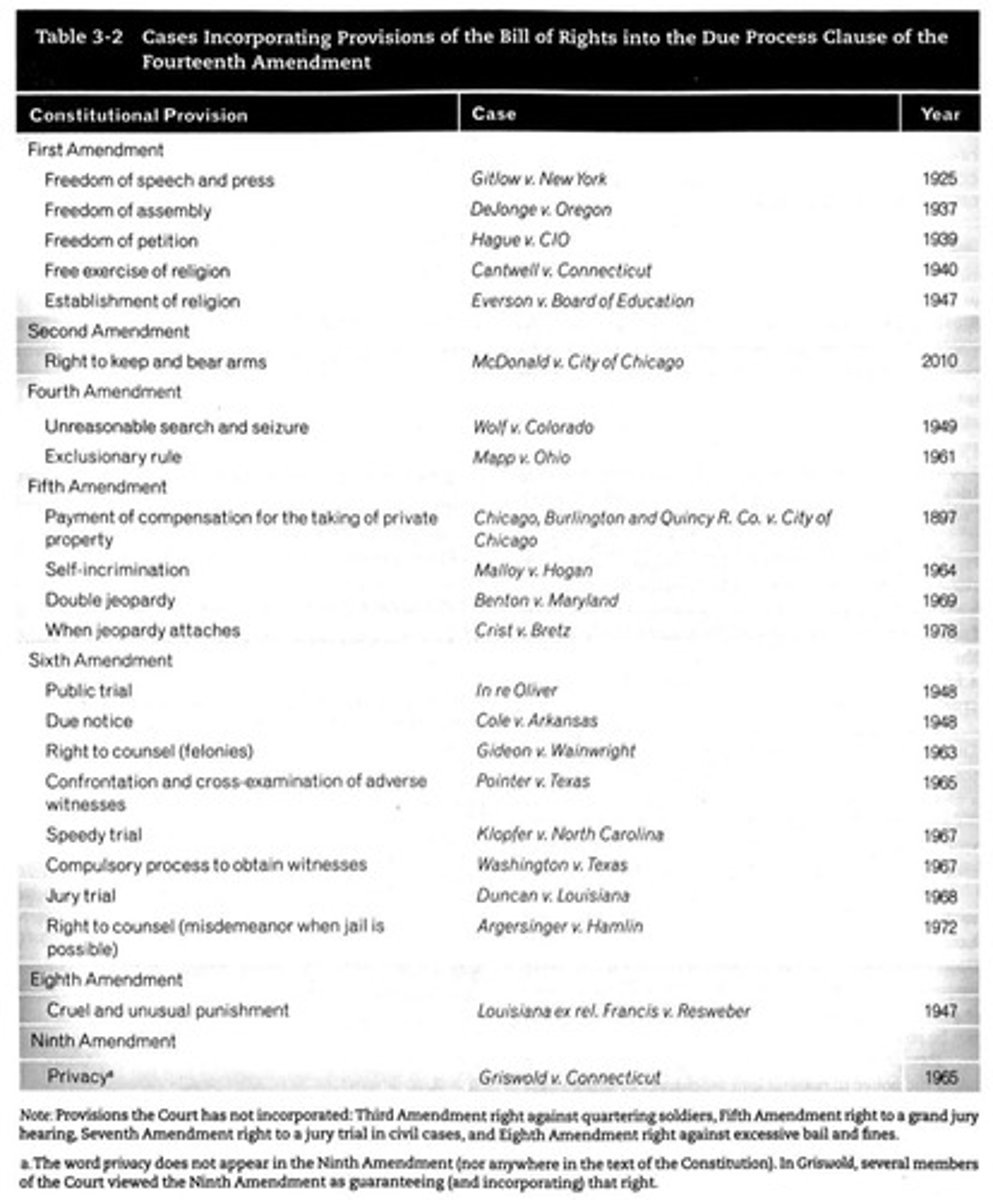
What constitutional violation did Griswold and Buxton claim in their appeal?
They claimed that the Connecticut law violated the right to marital privacy.
What are the key amendments cited by the Supreme Court in Griswold v. Connecticut?
1st Amendment (right to speech), 3rd Amendment (no forced quartering of soldiers), 4th Amendment (no unreasonable search and seizure), and 9th Amendment (rights not enumerated in the Constitution belong to the people).
What is meant by 'penumbra' in the context of Griswold v. Connecticut?
Penumbra refers to the area of partial illumination between full shadow and full light, suggesting implied rights like privacy.
What is the significance of the 14th Amendment in relation to privacy rights?
The 14th Amendment's Due Process Clause protects against state deprivation of life, liberty, or property, which has been interpreted to include privacy rights.
What is 'Substantive Due Process'?
Substantive Due Process refers to the constitutional doctrine that protects certain fundamental rights from government interference.
What is 'Selective Incorporation'?
Selective Incorporation is the legal doctrine that ensures that certain rights in the Bill of Rights are applied to the states through the 14th Amendment.
What is the Glucksberg two-step test?
1. The right must be clearly defined. 2. The right must be deeply rooted in American tradition and history.
How was the Glucksberg test applied in Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization?
The Glucksberg test was used to evaluate the constitutional right to abortion.
What were the facts of the Roe v. Wade case?
Jane Roe, an unmarried and pregnant Texas resident, challenged a Texas law that made abortion a felony unless to save the mother's life.
What was the Supreme Court's ruling in Roe v. Wade (1973)?
The Court ruled 7-2 that there is a constitutional right to an abortion under the right to privacy.
What does the Fourteenth Amendment's concept of personal liberty include according to Roe v. Wade?
It includes a right of personal privacy and guarantees certain areas or zones of privacy.
What is the relationship between Griswold v. Connecticut and Roe v. Wade?
Griswold v. Connecticut established the right to marital privacy, which laid the groundwork for the right to privacy in Roe v. Wade.
What is the primary question addressed in the Griswold v. Connecticut case?
Whether there is a constitutional right to privacy in the Bill of Rights.
What was the outcome of the Griswold v. Connecticut case?
The Supreme Court ruled that the law violated the right to marital privacy.
What does the term 'unenumerated rights' refer to?
Rights that are not explicitly listed in the Constitution but are implied by the liberty guarantee.
What established rights are recognized under 'Substantive Due Process'?
Privacy, child-rearing, and marriage are recognized as established rights.
What was the legal basis for Roe's challenge against the Texas law?
Roe contended that the Texas law violated her personal liberty and right to privacy.
What does the term 'personal liberty' encompass in the context of the Fourteenth Amendment?
It encompasses rights that protect individuals from state interference in personal decisions.
What is the significance of the 9th Amendment in privacy rights?
It suggests that rights not specifically enumerated in the Constitution are still retained by the people.
What was the ruling ratio in Roe v. Wade?
The ruling was 7-2 in favor of recognizing a constitutional right to an abortion.
What implications did the Roe v. Wade decision have on state laws regarding abortion?
It established that states cannot impose undue restrictions on a woman's right to choose to have an abortion.
What is the constitutional right established in Roe v. Wade?
Yes, there is a constitutional right to an abortion.
From which amendment does the right to an abortion derive?
The Fourteenth Amendment's Due Process Clause.
What does the Fourteenth Amendment's Due Process Clause state?
It states that no State shall deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law.
What legal concept supports the right to an abortion in Roe v. Wade?
Substantive due process.
What is the significance of the right of personal privacy in Roe v. Wade?
It encompasses a woman's decision whether or not to terminate her pregnancy.
What level of scrutiny is applied in cases regarding abortion rights?
Strict scrutiny.
What are the two state interests recognized in Roe v. Wade?
1) Preserving and protecting the health of the pregnant woman. 2) Protecting the potentiality of human life.
How does the state's interest in protecting the fetus change during pregnancy?
Each interest grows in substantiality as the woman approaches term and becomes compelling at a certain point.
What is the legal framework used in Roe v. Wade to assess abortion rights?
The trimester framework.
What is the state's interest in the first trimester of pregnancy according to Roe v. Wade?
There is no legitimate state interest in either the mother or the fetus.
What is the state's interest in the second trimester of pregnancy?
The state has an interest in maternal health and can impose reasonable regulations.
What is the state's interest in the third trimester of pregnancy?
The state has a compelling interest in protecting the potentiality of human life.
What does Roe v. Wade say about the viability of the fetus?
The state has no legitimate interest in the fetus during the second trimester since it is not viable.
What balancing act is discussed in Roe v. Wade?
The balancing of the state's interest in protecting the fetus versus the woman's right to choose.
What is meant by 'strict scrutiny' in the context of Roe v. Wade?
It refers to the highest standard of review used by courts to evaluate laws that infringe on fundamental rights.
What does the term 'fundamental right' refer to in Roe v. Wade?
It refers to rights that are considered essential to the order and liberty of a free society.
What does Roe v. Wade imply about state action regarding abortion?
Restrictions upon state action include a right of personal privacy.
What does the phrase 'zones of privacy' refer to in Roe v. Wade?
Certain areas of personal privacy protected by the Constitution.
What is the significance of the phrase 'compelling interest' in Roe v. Wade?
It indicates that the state's interest must be strong enough to justify restrictions on personal rights.
How does Roe v. Wade address the issue of fetal protection?
It recognizes the state's interest in protecting potential human life, which increases as the pregnancy progresses.
What is the overall impact of Roe v. Wade on abortion rights?
It established a constitutional right to abortion and set guidelines for state regulation based on the trimester framework.
What is the legal standard applied to abortion restrictions in the first trimester according to Roe v. Wade?
Low level of scrutiny.
What is the legal standard applied to abortion restrictions in the second trimester according to Roe v. Wade?
Reasonable regulations with a state interest in maternal health.
What is the legal standard applied to abortion restrictions in the third trimester according to Roe v. Wade?
High level of scrutiny, with the state having an interest in regulating or prohibiting abortions due to the fetus being potential human life.
What exception exists for third trimester abortions according to Roe v. Wade?
Abortions may be performed if necessary to preserve the life or health of the mother.
What was the holding regarding spousal consent in post-Roe cases?
Spousal consent is unconstitutional.
What was the ruling on blanket parental consent for minors in post-Roe cases?
Blanket parental consent for minors is unconstitutional.
What did the court rule regarding the requirement for attending physicians to exercise care for the health of the mother regardless of viability?
This requirement is unconstitutional.
What was the ruling on the requirement that all post-first-trimester abortions be performed in a hospital?
This requirement is unconstitutional.
What was the court's decision on informed consent requirements aimed at discouraging abortions?
These requirements are unconstitutional.
What is the ruling on a 24-hour waiting period following written informed consent?
This requirement is unconstitutional.
What did the court decide regarding written consent being informed and freely given?
This requirement is constitutional.
What is the ruling on mandatory reporting and record keeping for public health purposes?
This requirement is constitutional, with assurances of confidentiality.
What was the court's decision on requiring a second physician to be present for post-viability abortions?
This requirement is constitutional.
What did Webster v. Reproductive Health (1989) uphold regarding Missouri restrictions?
The court upheld restrictions prohibiting abortions in public facilities and by public employees where the health of the mother was not at stake.
What did the court require regarding the viability determination of a post-20 week fetus in Webster v. Reproductive Health?
The physician must make a viability determination.
Did Planned Parenthood v. Casey (1992) overturn Roe v. Wade?
No, it did not overturn Roe v. Wade.
What was the outcome of the vote regarding the overturning of Roe v. Wade in the case of Webster v. Reproductive Health?
There were four votes to overturn or substantially reduce the standard of Roe v. Wade.
What significant question does Planned Parenthood v. Casey (1992) address?
Whether there is a constitutional right to an abortion.
What is the state's interest in the second trimester according to Roe v. Wade?
The state has an interest in maternal health.
What does the term 'viability' refer to in the context of Roe v. Wade?
The point at which the fetus can survive outside the womb, typically occurring in the third trimester.
What is the significance of Roe v. Wade in the context of abortion law?
It established the legal framework for abortion rights in the United States.
What is the primary focus of the legal scrutiny applied to abortion restrictions in the third trimester?
The potential human life of the fetus.
What is the role of the Supreme Court in relation to abortion regulations as established by Roe v. Wade?
To apply scrutiny to state regulations concerning abortion based on the trimester framework.
Is there a constitutional right to an abortion according to the Supreme Court?
Yes, as determined by a 5-4 decision.
What framework did Planned Parenthood v. Casey (1992) abandon?
The trimester framework was abandoned in favor of a viability standard.
What are the three key principles established by Planned Parenthood v. Casey (1992) regarding abortion?
1. Women have the right to choose an abortion before viability without undue state interference. 2. States can restrict abortions after viability with exceptions for the woman's life or health. 3. States have legitimate interests in protecting the woman's health and the life of the fetus from the outset of pregnancy.
Does the Supreme Court use the same legal standard for pre-viability abortions as in Roe v. Wade?
No, it uses a different standard.
What legal standards are applied to abortion restrictions according to Planned Parenthood v. Casey (1992)?
The standards include strict scrutiny, rational basis, and the undue burden standard (intermediate scrutiny).
What constitutes an undue burden in the context of abortion laws?
An undue burden exists if a law's purpose or effect is to place a substantial obstacle in the path of a woman seeking an abortion before viability.
What is the level of scrutiny applied to abortion restrictions in Roe v. Wade (1973)?
High scrutiny is applied to restrictions on abortions.
What is the level of scrutiny applied to abortion restrictions in Planned Parenthood v. Casey (1992)?
Intermediate scrutiny is applied, specifically the undue burden standard.
What was the Supreme Court's ruling on spousal consent laws in Planned Parenthood v. Casey (1992)?
Spousal consent laws were deemed unconstitutional.
What was the Supreme Court's decision ratio in Planned Parenthood v. Casey (1992) regarding state interests across trimesters?
The decision was 7-2, stating that state interests are not the same across trimesters.
What is the significance of the viability standard established in Planned Parenthood v. Casey (1992)?
It allows for state restrictions on abortions after viability, provided there are exceptions for the woman's life or health.
What does the term 'strict scrutiny' refer to in the context of abortion laws?
Strict scrutiny is a high level of judicial review used to evaluate laws that infringe on fundamental rights.
What does the term 'rational basis' refer to in legal standards?
Rational basis is a low level of scrutiny applied to laws that do not affect fundamental rights.
What is the difference between pre-viability and post-viability abortion laws?
Pre-viability laws are subject to the undue burden standard, while post-viability laws can impose restrictions as long as they include exceptions for the woman's life or health.
What is the historical context of Roe v. Wade (1973) in relation to abortion rights?
Roe v. Wade established a woman's constitutional right to choose an abortion, applying high scrutiny to restrictions.
What did the Supreme Court affirm regarding state interests in Planned Parenthood v. Casey (1992)?
The Court affirmed that states have legitimate interests in protecting the health of the woman and the life of the fetus from the outset of pregnancy.
What is the legal significance of the phrase 'liberty finds no refuge in a jurisprudence of doubt'?
This phrase emphasizes the importance of clear legal standards in protecting individual rights, particularly regarding abortion.
What is the impact of the undue burden standard on abortion laws?
It invalidates laws that create substantial obstacles for women seeking abortions before viability.
How did the rulings in Roe v. Wade and Planned Parenthood v. Casey differ in terms of abortion restrictions?
Roe v. Wade applied high scrutiny to restrictions, while Casey introduced the undue burden standard, allowing for more state regulation after viability.
What does the term 'intermediate scrutiny' mean in the context of abortion law?
Intermediate scrutiny is a standard of review that requires laws to serve an important government interest and be substantially related to that interest.
What role did the Supreme Court play in shaping abortion rights through its rulings?
The Supreme Court's rulings established and clarified the constitutional right to abortion and the standards for evaluating related laws.
What was the ruling regarding spousal consent in the context of abortion laws post-Roe?
Spousal consent was ruled unconstitutional.
What was the ruling on parental consent for minors in the context of abortion laws post-Roe?
Parental consent for minors was ruled unconstitutional.
What was the ruling on informed consent requirements in the context of abortion laws post-Roe?
Informed consent requirements were ruled unconstitutional.
What was the ruling on the 24-hour waiting period following written, informed consent in abortion laws?
The 24-hour waiting period was ruled constitutional.
What was the ruling on reporting and record keeping for public health purposes in abortion laws?
Reporting and record keeping for public health purposes were ruled constitutional.
What was the issue in Stenberg v. Carhart (2000)?
The issue was a state ban on partial birth abortions.
What was the ruling in Stenberg v. Carhart (2000)?
The ruling struck down the state ban on partial birth abortions.
What was the issue in Gonzales v. Carhart (2007)?
The issue was a federal ban on partial birth abortions.
What was the ruling in Gonzales v. Carhart (2007)?
The ruling upheld the federal ban on partial birth abortions.
What was the issue in Whole Women's Health v. Hellerstedt (2016)?
The issue involved state restrictions on abortion, including physician admitting privileges.
What was the ruling in Whole Women's Health v. Hellerstedt (2016)?
The ruling struck down state restrictions on physician admitting privileges and facility standards.
What was the issue in June Medical Services v. Russo (2020)?
The issue was similar to Whole Women's Health, concerning Louisiana's abortion laws.