ISS Sem 2 Final
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/84
Last updated 4:25 PM on 5/19/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
1
New cards
economics
the study of how we make decisions in a world with limited resource
2
New cards
What is the fundamental economic problem?
scarcity
3
New cards
what is scarcity?
the fact that there are limited quantities of resources to meet unlimited wants
4
New cards
what is TINSTAAFL
there is no such thing as a free lunch
5
New cards
what are the three basic economic questions?
1. What to produce
2. how to produce
3. for whom to produce
6
New cards
what are the factors of production
1. land/natural resources
2. capital
3. labor
4. entrepreneur
7
New cards
what is(are) land(natural resources)?
gifts of nature; not made by humans
8
New cards
examples of capital
tools, equipment, and factories used to produce (not just money)
9
New cards
what is labor?
people with efforts, abilities, and skills to produce
10
New cards
what is an entrepreneur?
risk-taker in search of profits (uses other three factors)
11
New cards
trade offs
exchanging one thing for the use of another
12
New cards
opportunity cost
what you can’t buy or do when you choose to do or buy one thing rather than another; cost of trade off
13
New cards
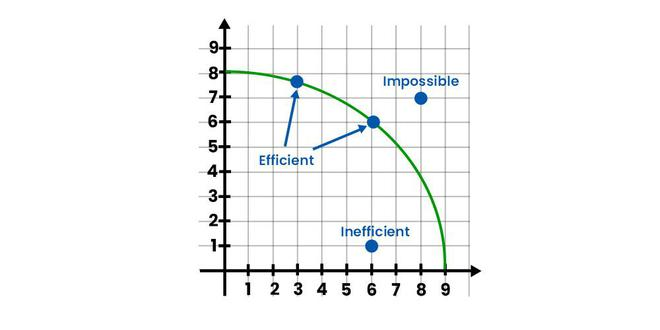
production possibilities graph
\
14
New cards
good
something you can use or consume
* food, shoes, car
* food, shoes, car
15
New cards
service
something that someone does for you
* ex: haircut, oil change
* ex: haircut, oil change
16
New cards
demand (2 def)
1. combination of the desire, willingness, and ability to buy a good or service
2. the amount of goods and services consumers are willing to buy at various prices at a particular time
17
New cards
law of demand
consumers will buy more of a product at lover prices and less at higher prices
18
New cards
shortage
when quantity demanded exceeds quantity supply
19
New cards
surplus
when quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded
20
New cards
Law of diminishing marginal utility
the more of an item that you use or consume, the less satisfaction you get from each additional unit consumed or used
* ex: eating a pizza
* ex: eating a pizza
21
New cards
demand scheduele
table that lists the various quantities of a product or service that someone is willing to buy over a range of possible prices
22
New cards
demand curve
curve that shows the quantities demanded at all possible prices
23
New cards
change in quantity demanded
only a change in price can cause a change
* when price ↑ quantity demand ↓
* when price ↓ quantity demand ↑
* when price ↑ quantity demand ↓
* when price ↓ quantity demand ↑
24
New cards
change in demand
A change in consumer demand for a specific product or service that is not influenced by the price of the product or service
25
New cards
law of supply
principle that more will be offered for sale at higher prices than at lower prices
26
New cards
supply
the amount of a product offered for sale at all possible prices
27
New cards
supply scheduele
listing of the various quantities of a particular product supplied at all possible prices in the market
28
New cards
supply curve
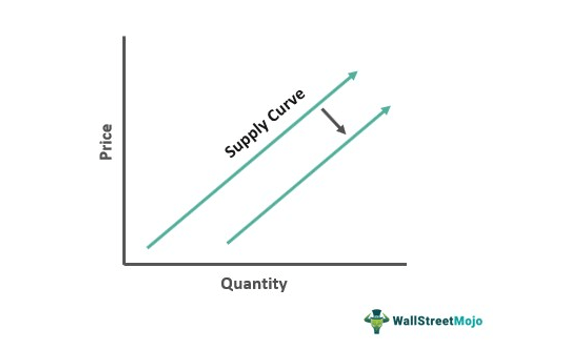
graph showing the different amounts of a product supplied over a range of possible prices
29
New cards
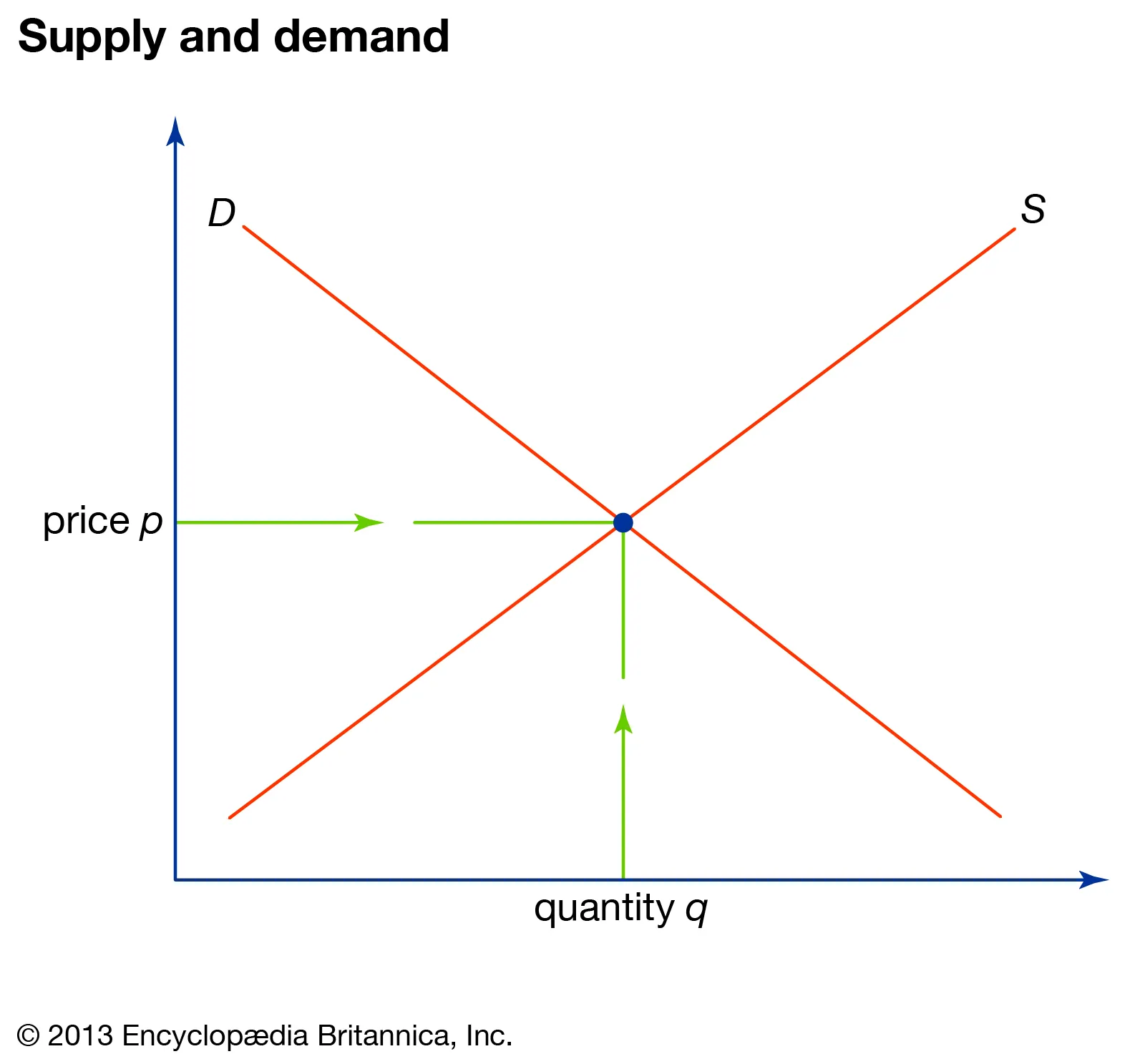
equilibrium
quantity demanded = quantity supplied
30
New cards
economy systems
1. traditional
2. command
3. market
4. mixed
31
New cards
traditional system
decisions made according to long-established ways of behaving
32
New cards
command system
government controls the economy
33
New cards
market system
private individuals own the factors of production and are free to make their own choices about production, distribution, and consumption
34
New cards
mixed system
capitalism dominates with varying degrees of gov. regulation and manipulation
35
New cards
cardinal directions
1. North
2. South
3. East
4. West
36
New cards
absolute location
the description of where something is located using some system of giving an exact spot
37
New cards
which way do latitude lines go?
horizontal
38
New cards
which way do longitude lines go?
vertical
39
New cards
5 themes of geography
1. location
2. place
3. human-environment interaction
4. movement
5. region
40
New cards
place
tells what the physical features and humans features of the place
* **What is it like?**
* **What is it like?**
41
New cards
human-environment interaction
the interaction between human society and the ecosystem and physical environment
* **How are humans and the environment shaping each other?**
* **How are humans and the environment shaping each other?**
42
New cards
movement
**why/where/how do people, objects, and information move?**
43
New cards
what are push and pull factors?
what makes people want to leave or go to a certain place
* push = emigrate
* pull = immigrate
* push = emigrate
* pull = immigrate
44
New cards
What are some examples of push factors?
* loss of job
* political or religious persecution
* war
* disease
* etc.
* political or religious persecution
* war
* disease
* etc.
45
New cards
what are some examples of pull factors?
* safety
* peace
* resources
* work
* culture and ideals
* peace
* resources
* work
* culture and ideals
46
New cards
region
an area defined by similar characteristics
47
New cards
What does GPS stand for?
global positioning system
48
New cards
how does GPS work?
listens to the signals of multiple satellites to get an accurate location
49
New cards
how many satellites have to be visible for GPS to work?
4
50
New cards
what is a biome?
a large region with a certain climate and certain types of living things
51
New cards
what biomes are found in South America?
* Amazon Rainforest
* Andes Mountains
* Atacama Desert
* Brazilian Highlands
* Gran Chaco
* Patagonian Desert.
* Andes Mountains
* Atacama Desert
* Brazilian Highlands
* Gran Chaco
* Patagonian Desert.
52
New cards
why are rainforests located where they are?
there’s a lot of direct sunlight at the equator which causes a lot of evaporation → rainforests
53
New cards
why are deserts located at 30° N+S latitude?
the circulation patterns of air put all the hot dry air at these places and the intense sunlight adds to that
54
New cards
describe the desert biome
very dry with little water
55
New cards
describe the taiga biome
characterized by it’s long, cold winters and short summers
56
New cards
describe the savanna biome
characterized by grasslands with scattered trees and shrubs and has a dry and wet season.
57
New cards
describe the deciduous forest biome
characterized by trees that lose their leaves seasonally, and have moderate temperatures that vary throughout the year
58
New cards
characteristics of grass
* spread their pollen by wind
* grow very fast
* leaves grow from the base, not the top
* grow very fast
* leaves grow from the base, not the top
59
New cards
why has grass been important in human history?
it has supported cattle and other resources needed for survival
60
New cards
why is grass important to us today?
it includes some of our most important crops
61
New cards
describe the jungle biome
* densely forested area with high levels of precipitation and humidity
* characterized by tall trees, thick vegetation, and a diverse range of plant and animal species
* characterized by tall trees, thick vegetation, and a diverse range of plant and animal species
62
New cards
how does plate tectonics work?
plates under the Earth that can move and cause changes in Earth’s surface
63
New cards
what drives the process of plate movement?
convection currents
64
New cards
what are the two types of plates?
continental plates and oceanic plates
65
New cards
what do convergent plates form?
mountains and volcanoes
66
New cards
what do divergent plates form
mountain valleys and rifts
67
New cards
what’s the ring of fire?
a region around the Pacific Ocean where a lot of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur because of the movement of tectonic plates
68
New cards
why do we study tectonic plates?
to better understand processes and outcomes like mountains, earthquakes, and volcanoes and their effect on people’s lives and culture
69
New cards
African slave trade
* “pawnship”
* slaves were often accepted into the new tribe
* slaves were often accepted into the new tribe
70
New cards
Where is Guatemala on a map?
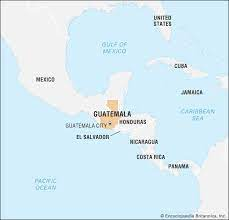
71
New cards
Where is Venezuela on a map?
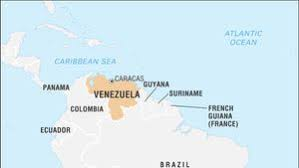
72
New cards
Where is Brazil on a map?
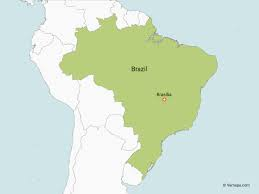
73
New cards
Where is Argentina on a map?
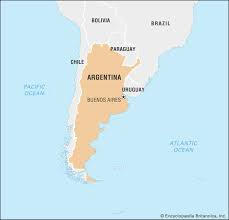
74
New cards
Where is Nigeria on a map?
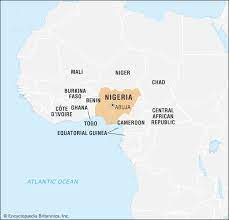
75
New cards
Where is Egypt on a map?
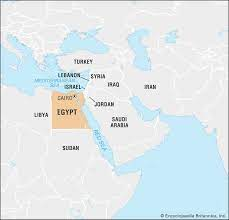
76
New cards
Where is Libya on a map?
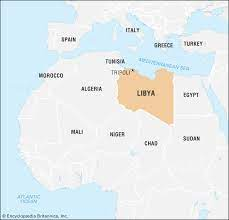
77
New cards
Where is Ethiopia on a map?
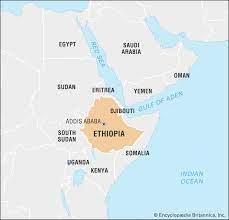
78
New cards
Where is India on a map?
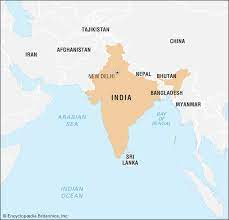
79
New cards
Where is North Korea on a map?
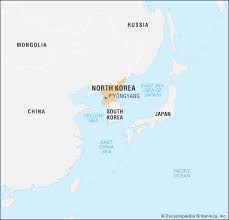
80
New cards
Where is Japan on a map?
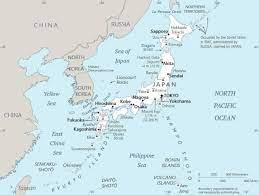
81
New cards
Where is Vietnam on a map?
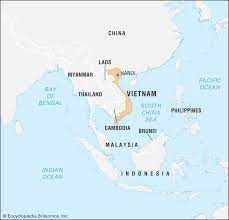
82
New cards
Where is the Panama Canal?
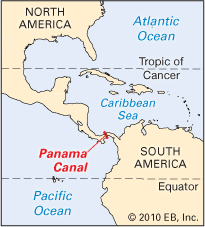
83
New cards
Where is the Amazon River?
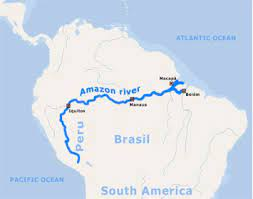
84
New cards
Where is the Nile River?
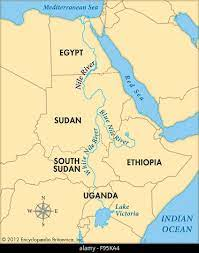
85
New cards
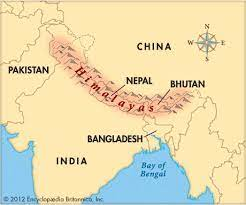
Where are the Himalayas?