Containment - lecture 1&2 - Introduction and assignment theory
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
endemic EXAM
endemic is a current burden (naturally present in communities)
epidemic
epidemic is when the disease is on the rise
pandemic
pandemic is worldwide increase in the disease.
communicable disease
an illness that is transmitted from a person animal or inanimate source to another person either directly, with the assistance of an intermediate host or by a vector.
zooonotic disease
transmitted from human to animals and vice versa
the animals also get sick
difference isolation and quarantine
isolation - lock someone up when you have a confirmed case
quarantine - it is suspected that someone may have a case.
Spanish flu
1918 and 1919
killed 100 million people
1/3rd of world population infected
biggest take away was quarantine led to less affected areas
spain was the first to report about it.
most important scientific findings in infectious diseases
antibiotics (penicillin)
vaccines → edward jenner invented first vaccine (1796)
before Jenner in ottoman / china already experiments with vaccines were done.
vaccines are very succesful, control eliminate and even eradicate diseases but there is increasing societal resistance
HIV - Aids
infectious disease but treatment is chronic
HIV learned a lot from tuberculosis
mobilizing global funds is very important
VCT - voluntary counseling and testing (people do not know when they have it)
behaviour change groups
swine flu (mexican)
ruined more than that we learned
little people died, we got complacent
containment strategies
inteventions that control, eliminate and eradicate disease
EIDM
evidence informed decision making
evidence matters
context matters - what works where for whom?
integration of Evidence, Epistemiological justice (TDR) - all knowledge matters when we design things.
5 steps in health intervention
these are the 5 steps of Jenkins
what is the problem
what factors cause the problem (show references in assignment, tools to identify causes epidemiological triangle and the problem tree).
how can these factors be changed
what overall intervention strategies are most appropriate and cost effective (including what do people want and what are their needs)
what needs to be done to reach the goals? with what (sub)populations shall work be done, and in what sequence, to solve the problem?
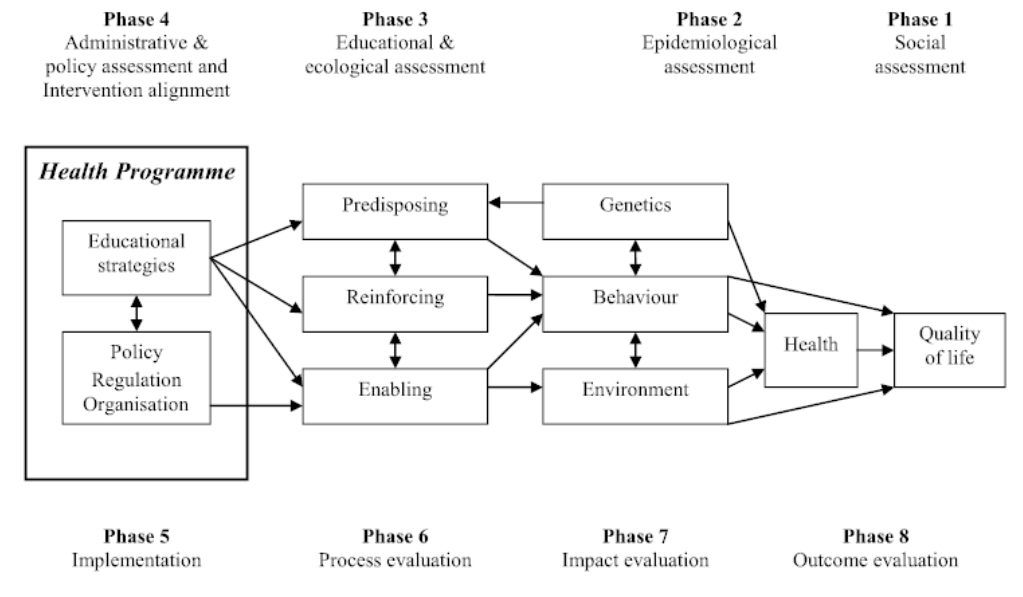
precede / proceed model
framework for designing, implementing, and evaluating health promotion programs
this is a planning and evaluation framework for developing health promotion programs. starting with the desired outcome and working backward.
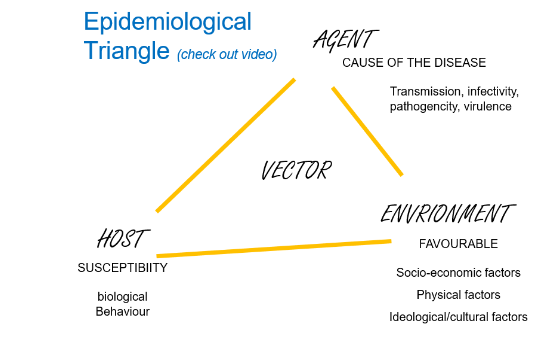
epidemiological triangle
disease is always the interaction between a host, agent and in an environment.
how susceptible is the host (host is where reproduction of the agent takes place). individual level.
environment needs to be favourable. (climate, health system, public transport, education level of the country). societal level.
vector - not always present, can be a mosquito, needle etc.
how can the factors of the epidemiological triangle be changed
change / kill agent
raise host resistance (vaccines)
modify environment (remove mosquito breeding places etc.)
separate agent from host
interrupt transmission (isolation)
social determinants of health
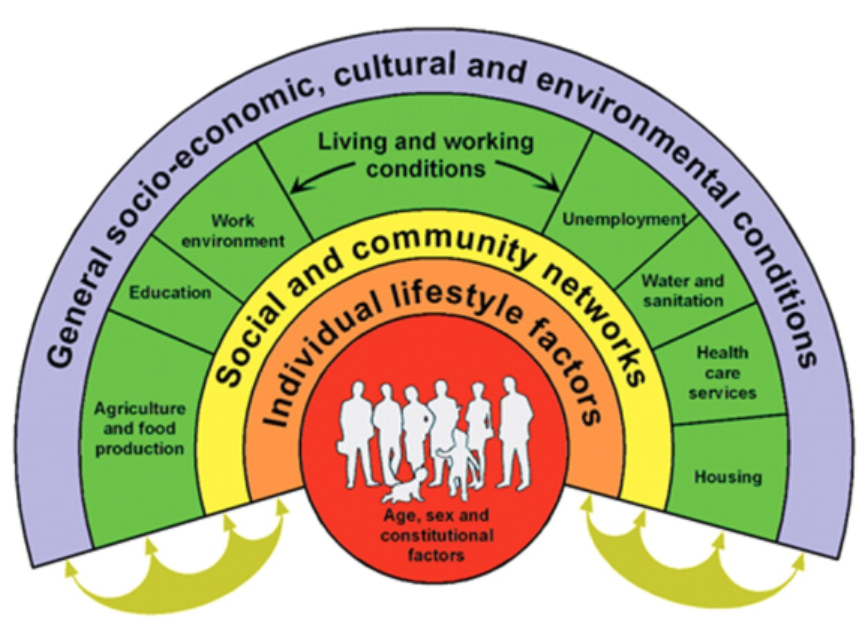
problem tree
helps to understand where to intervene
primary, secondary, tertiary prevention
P → prevent a health problem (vaccination, sleeping under bed net)
S → early detection and treatment, hardly any symptoms (pap smear, breast cancer screening).
T → preventing the disease from getting worse
selecting best intervention
also called multi criteria decision making
choose the right intervention, that can be implemented with limited negative side effects.
important criteria
medical effectiveness (vaccination better than face mask, more evidence for this). look at most effective intervention
cost effectiveness