AP Environmental Science Unit 4
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
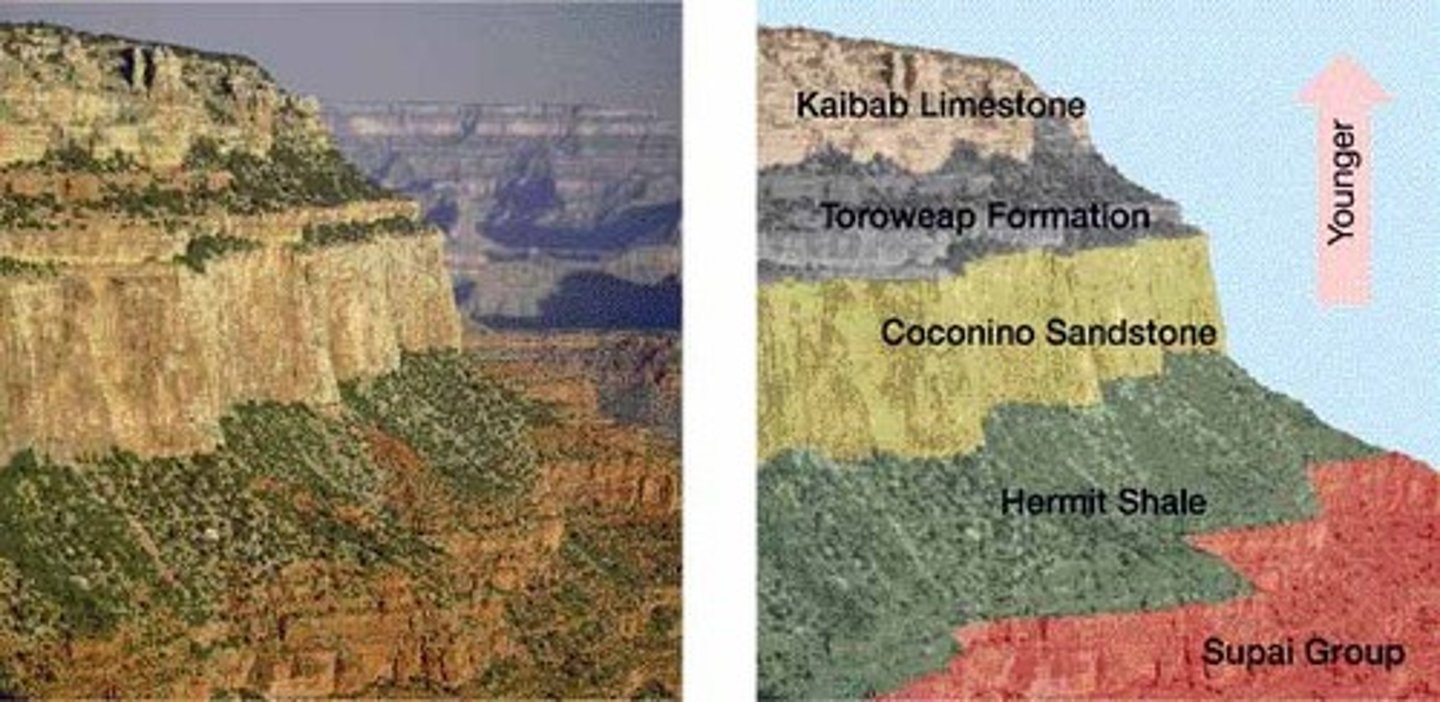
superposition
The principle that any given rock layer is probably older than those above it and younger than those below it
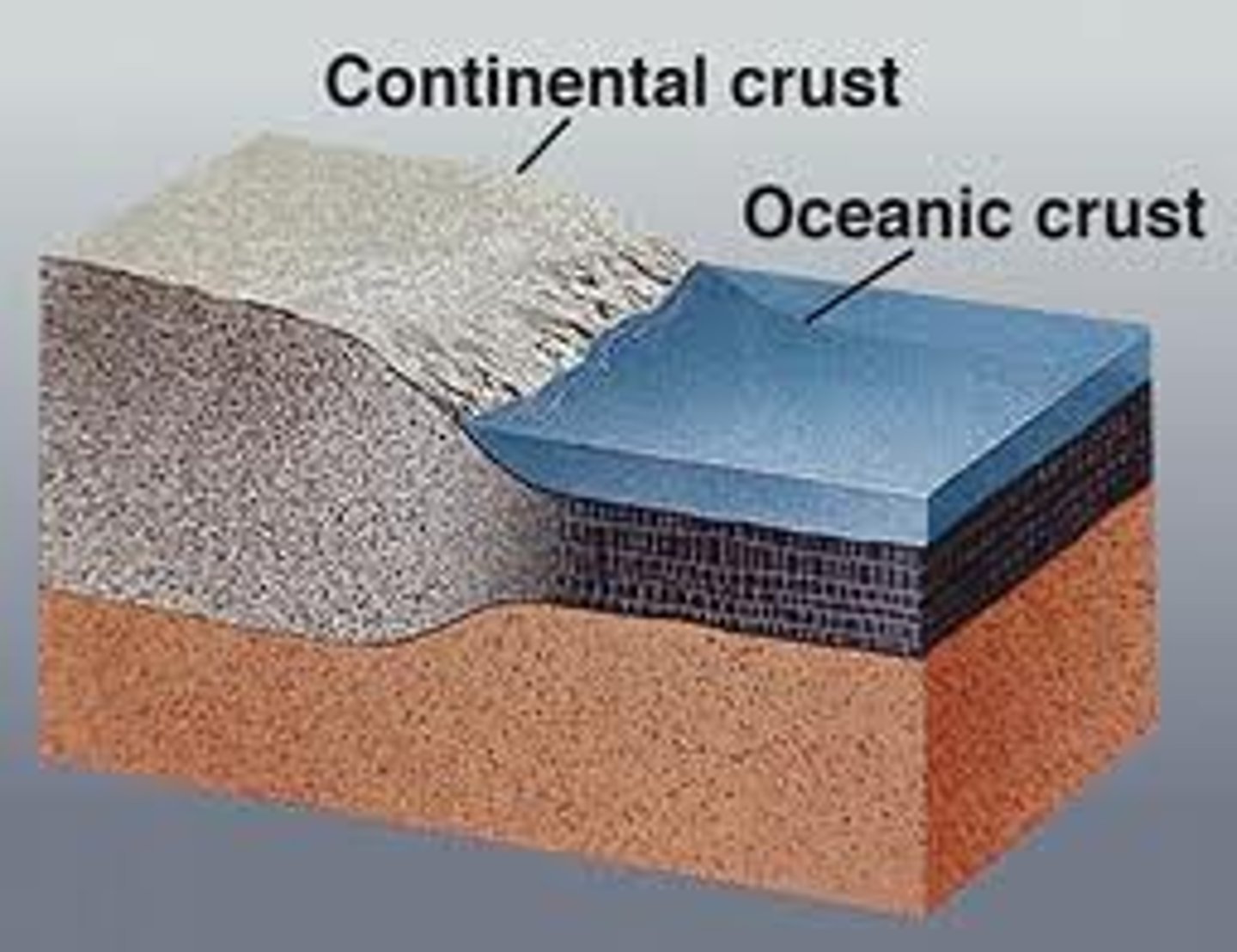
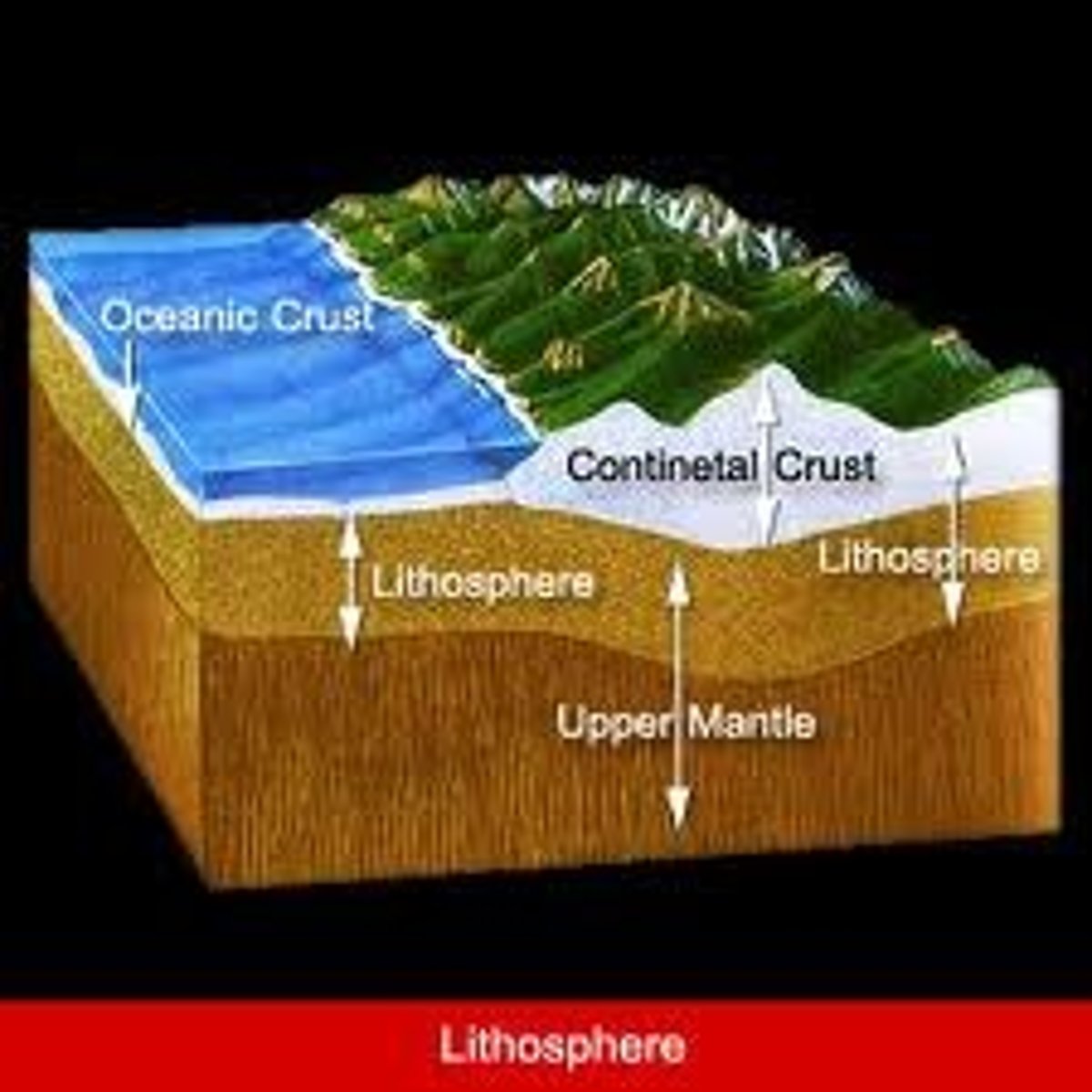
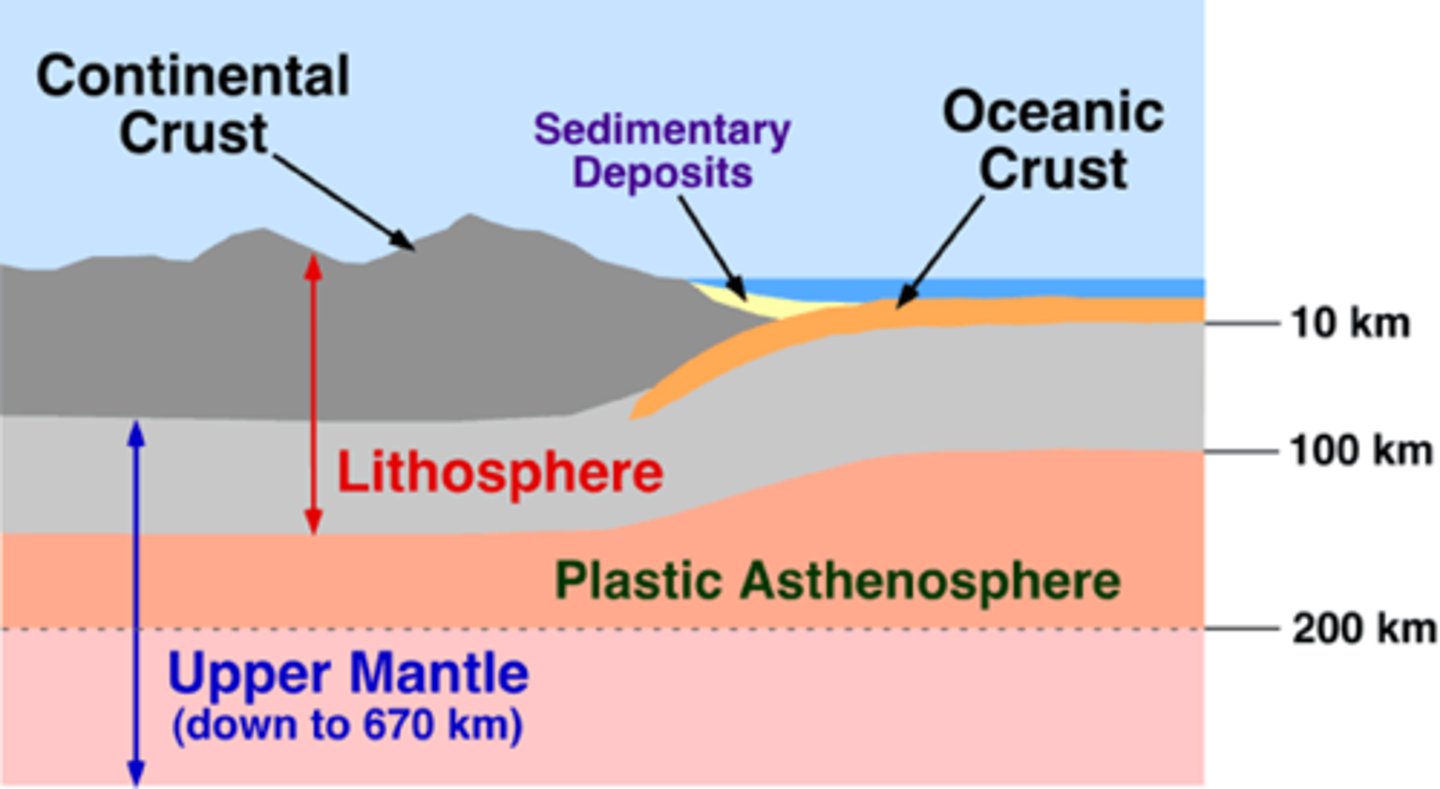
continental crust
Extends from surface of Earth down to 20-30 miles. Continental crust (granite) is less dense then ocean crust (basalt).
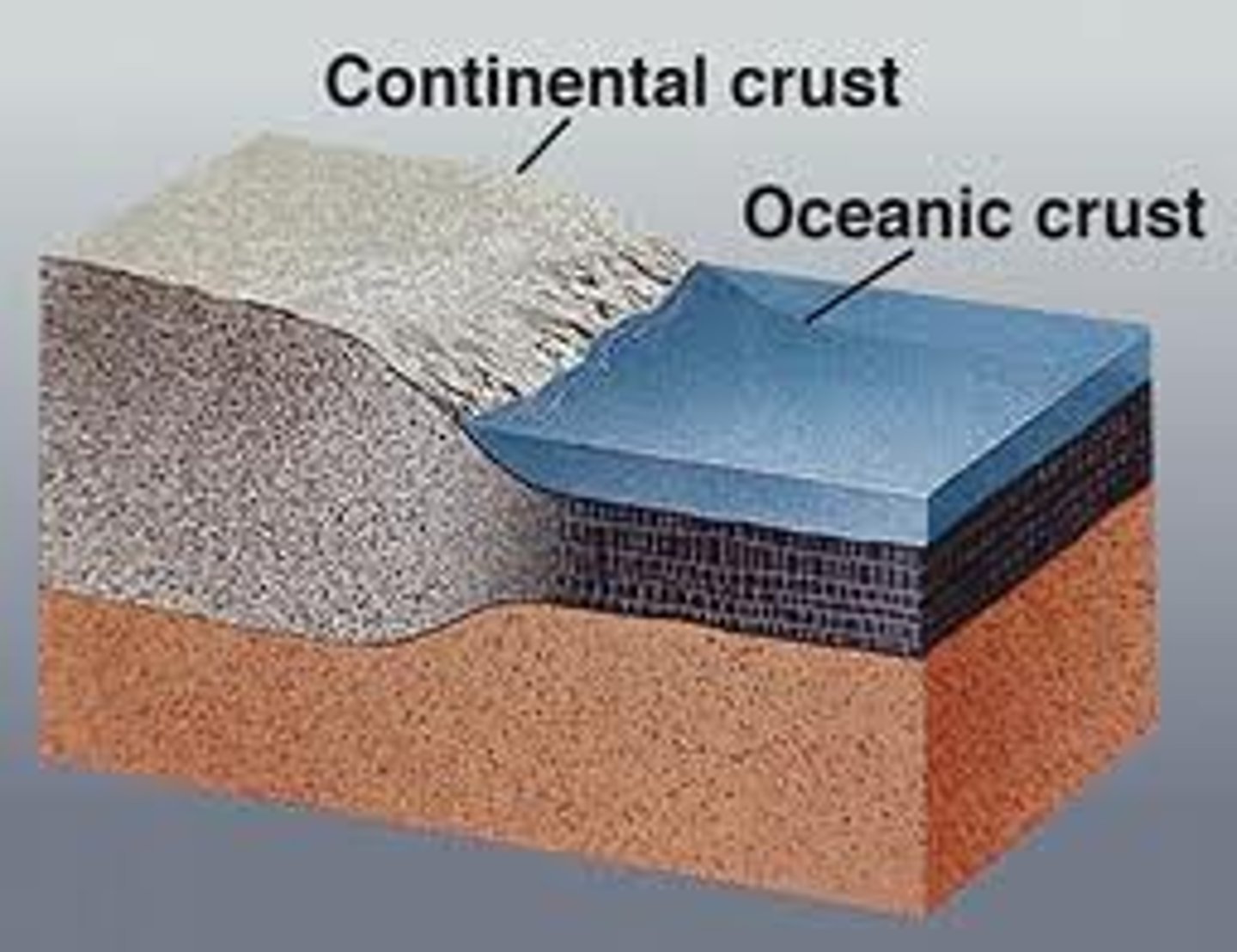
oceanic crust
Extends down from the surface of the Earth to 7 miles. Crust is layered and very uniform. Composed of basalt.
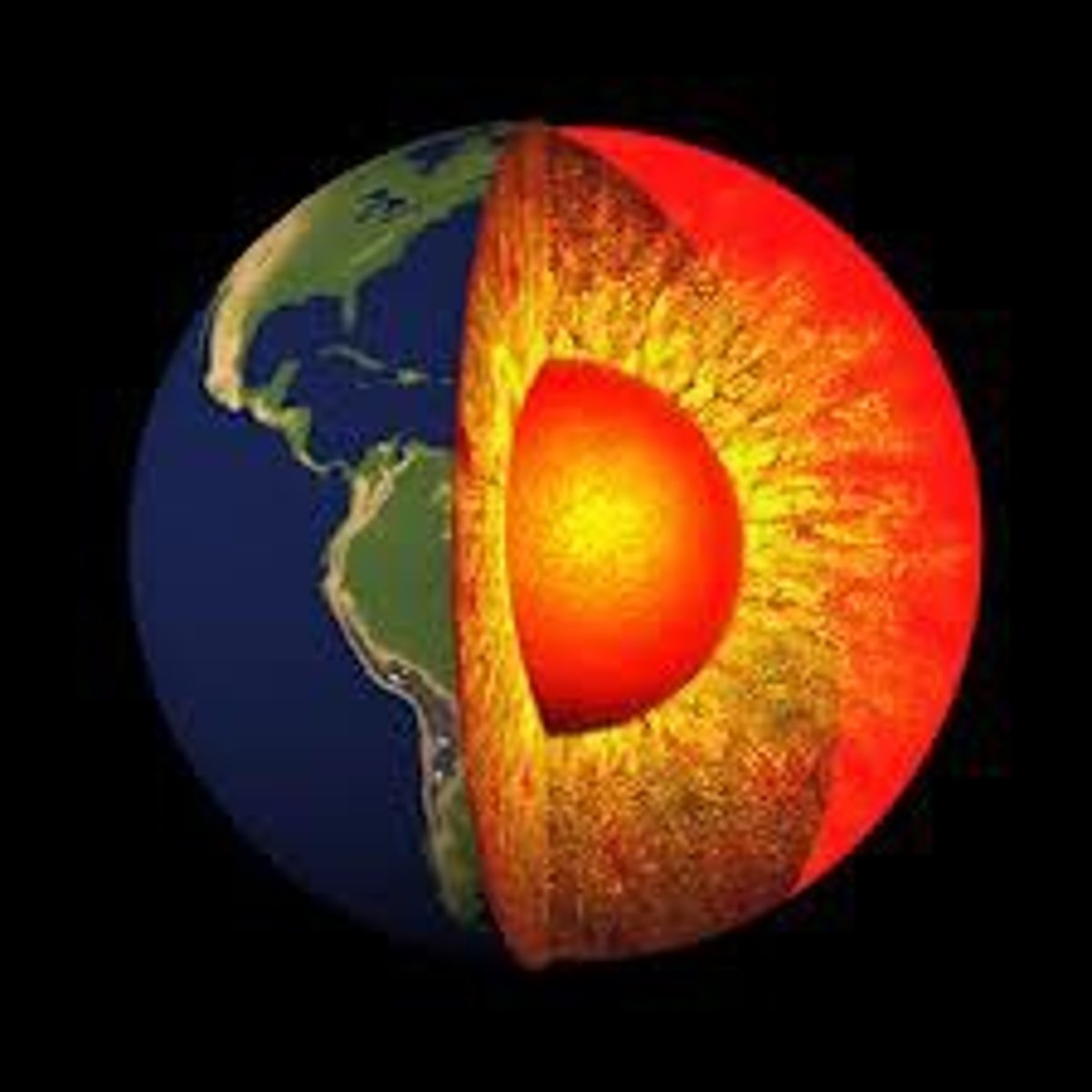
mantle
Contains most of Earth's mass. Composed of iron, magnesium, aluminum, and silicon-oxygen compounds
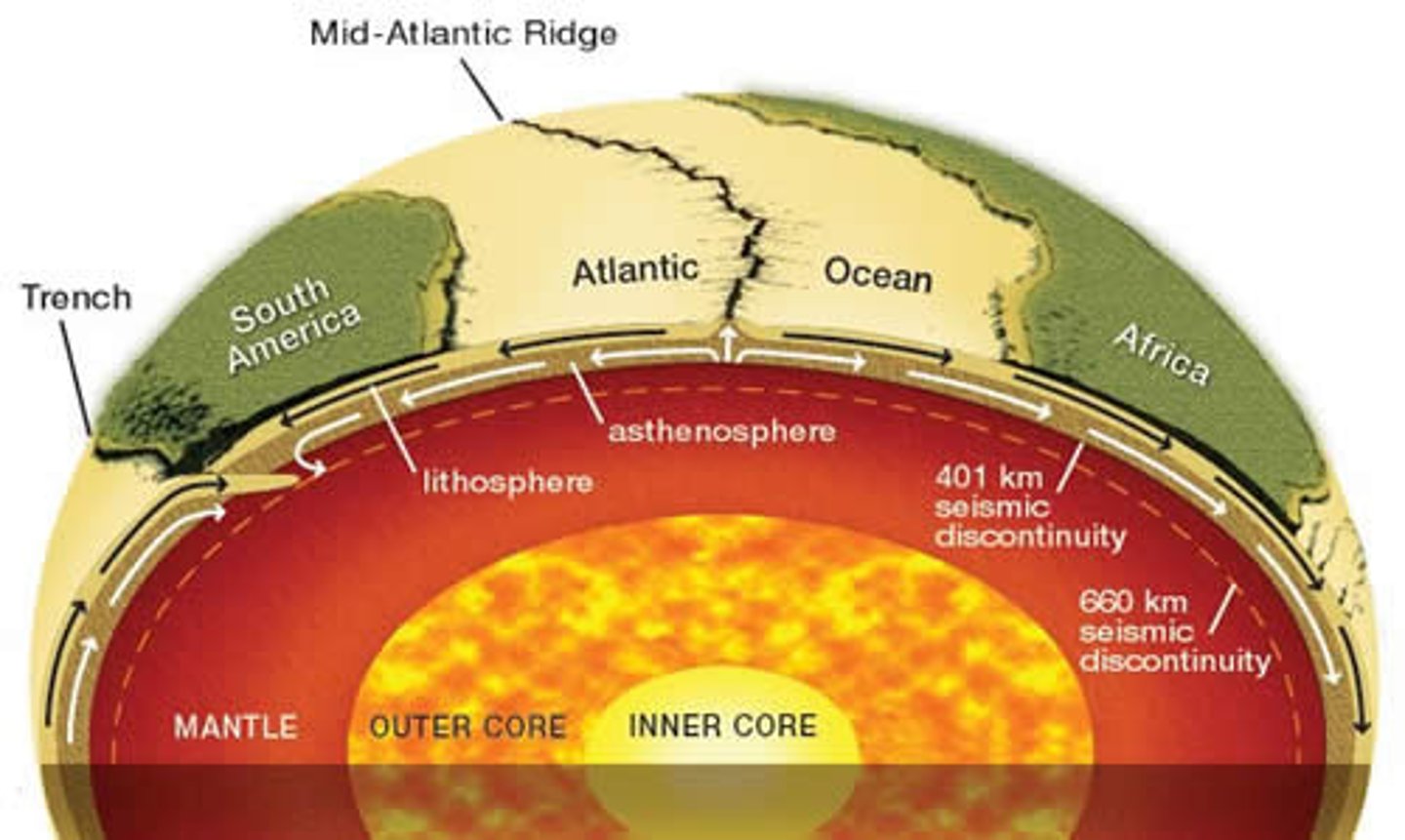
core
Composed mostly of iron and is so hot that the outer core is molten. The inner core is under such extreme pressure that it remains solid.
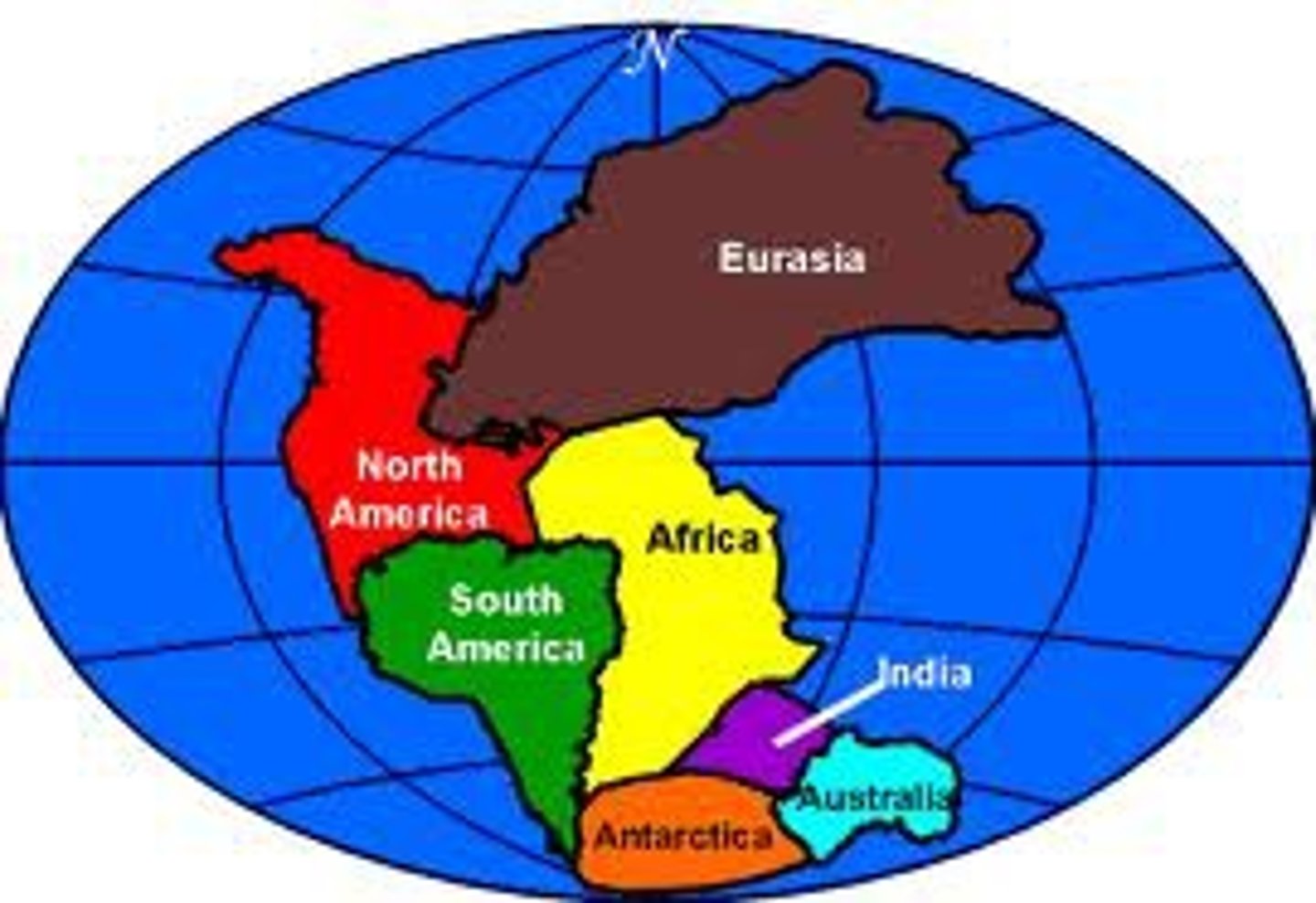
Continental Drift Theory
1915- Alfred Wegener proposed that all present-day continents originally formed one landmass (Pangaea).
lithosphere
Lithosphere (crust and upper mantle) is divided into massive sections known as plates, which float and move on the asthenosphere.
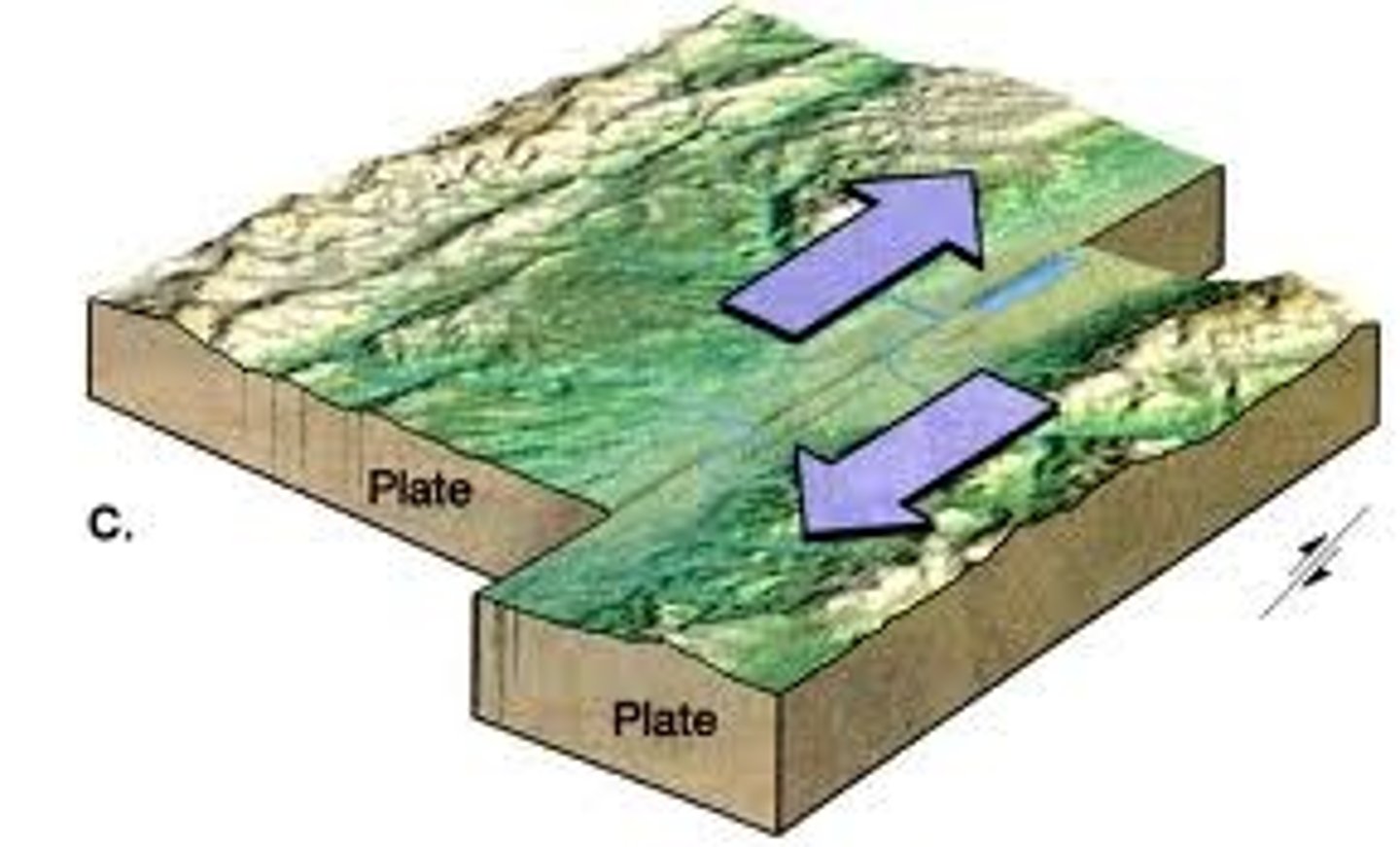
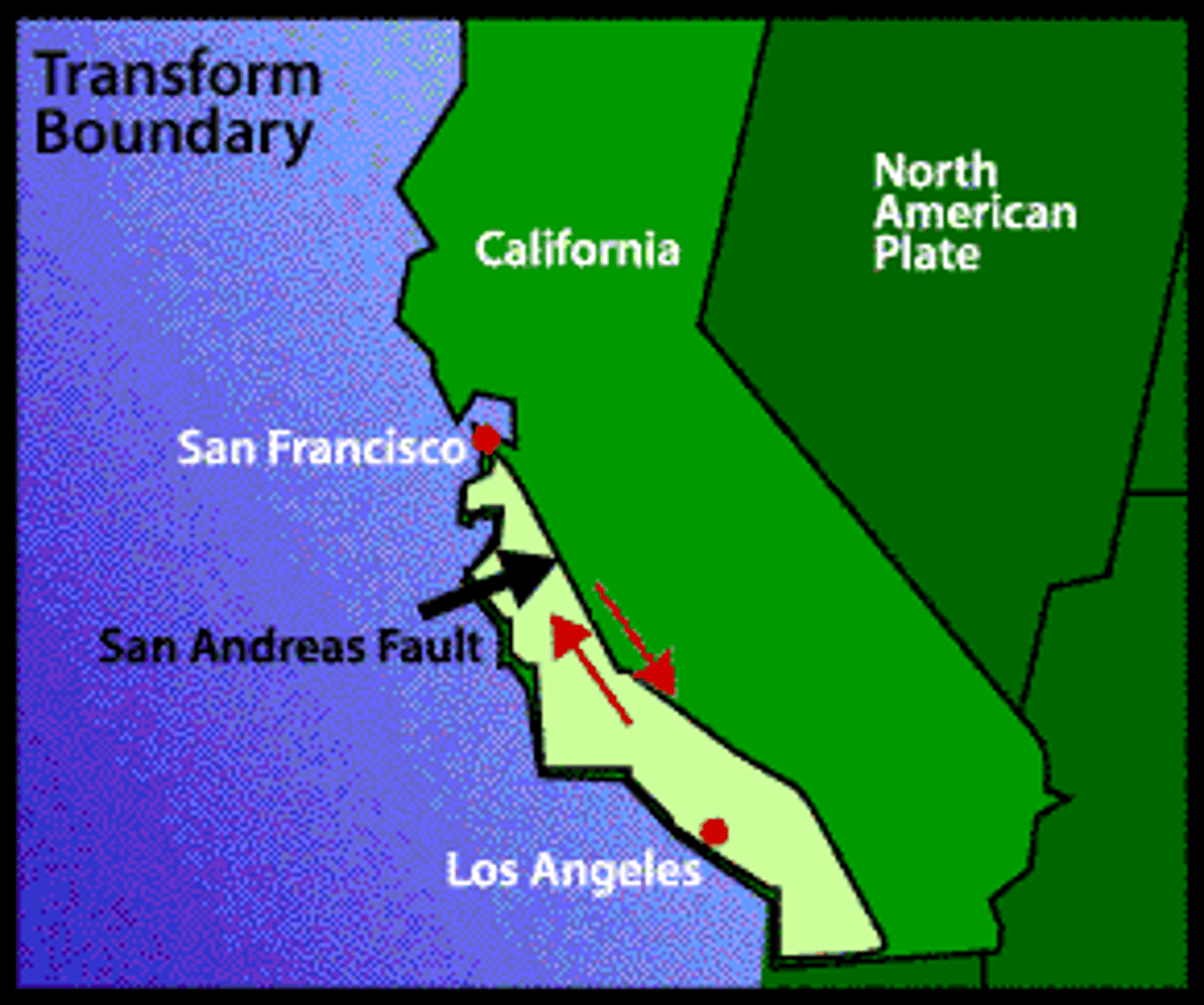
transform boundaries
Occur where plates slide PAST each other.
San Andreas Fault
Found near the western coast of North America. Where the Pacific and North American plates move relative to each other.
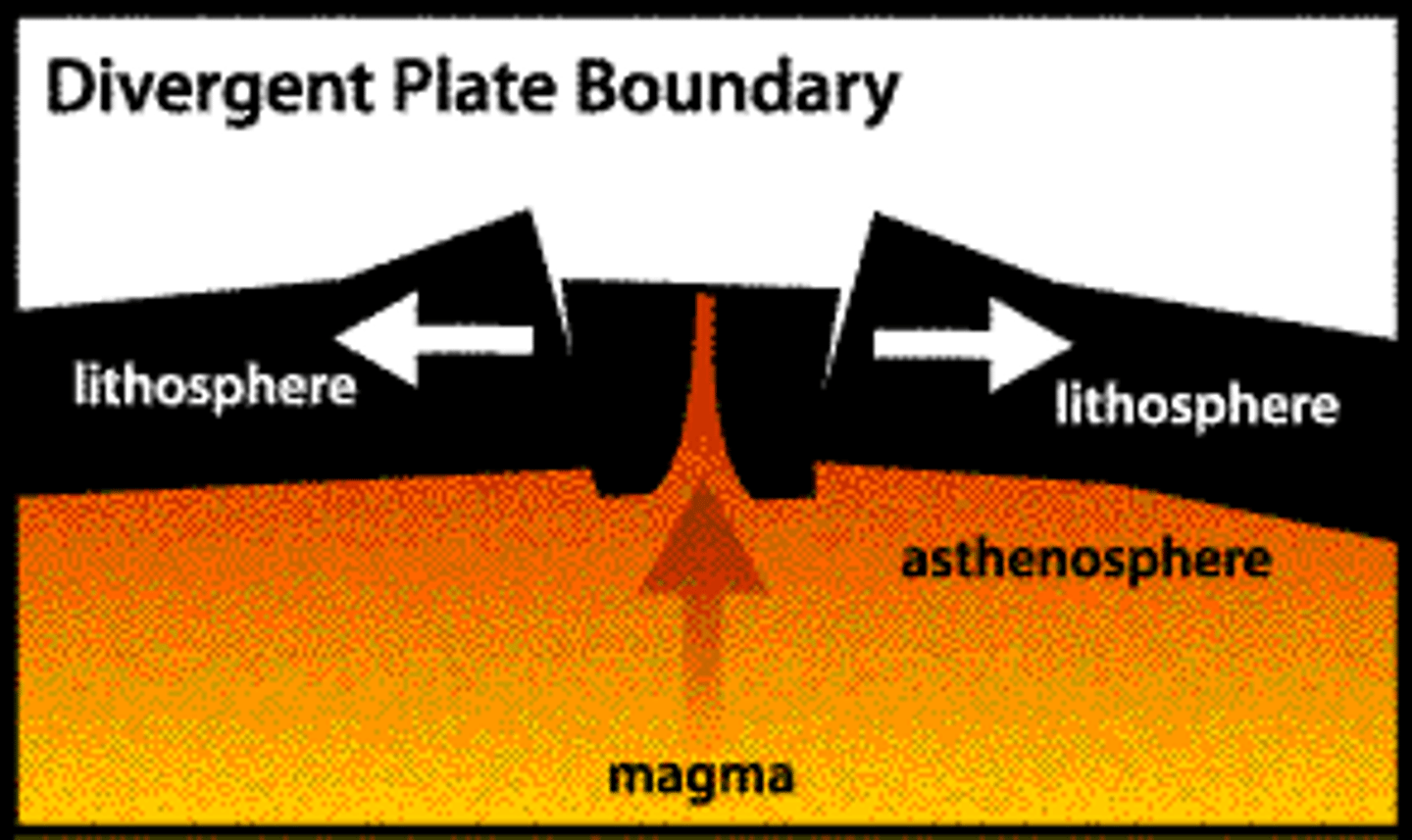
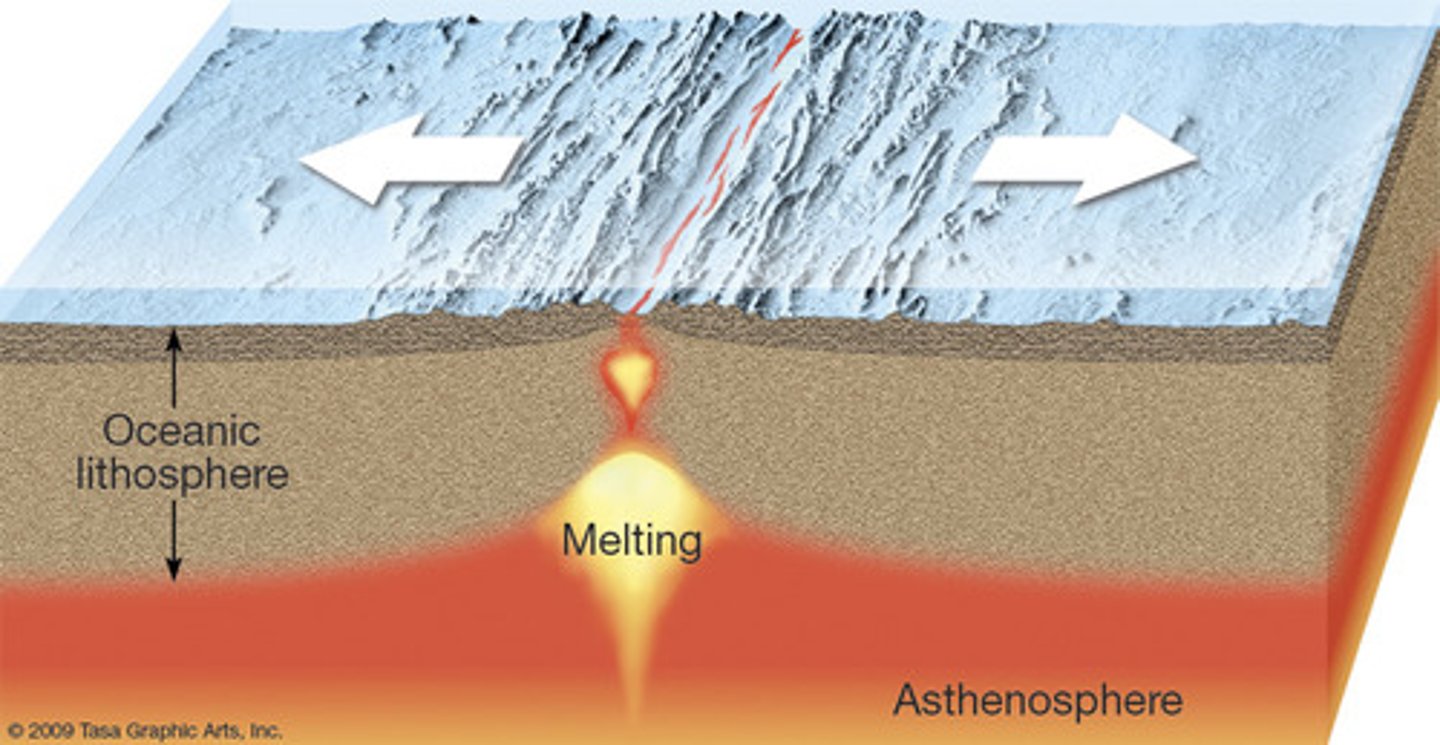
divergent boundaries
Occur where two plates slide APART from each other with the space that was created being filled with molten magma from below.
Mid-Atlantic Ridge and Pacific Rise
Examples of oceanic divergent boundaries.
East African Great Rift Valley
Examples of areas of continental divergent boundaries
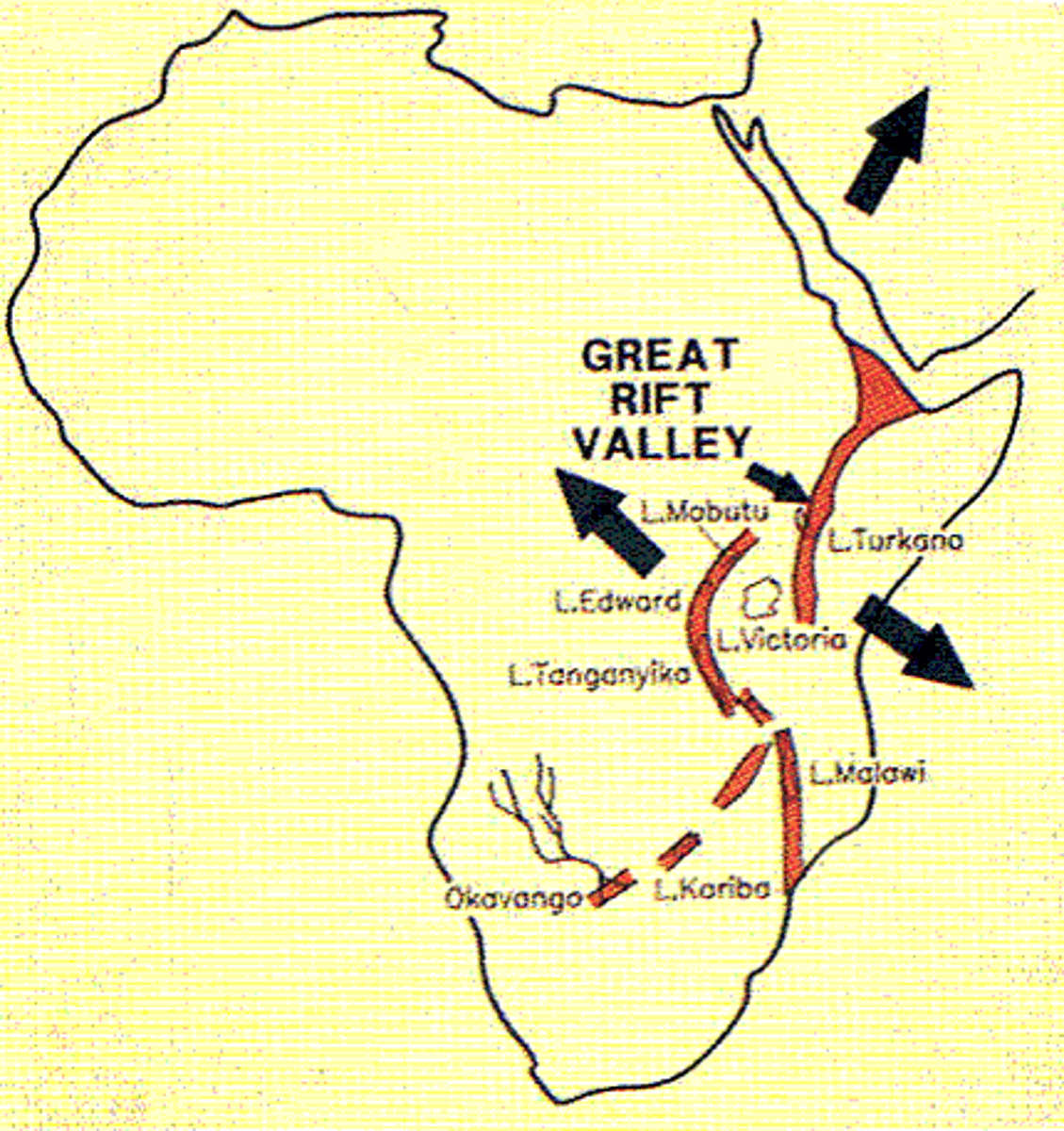
convergent boundaries
Occur where two plates slide TOWARD each other, commonly forming either a subduction zone or orogonic belt.
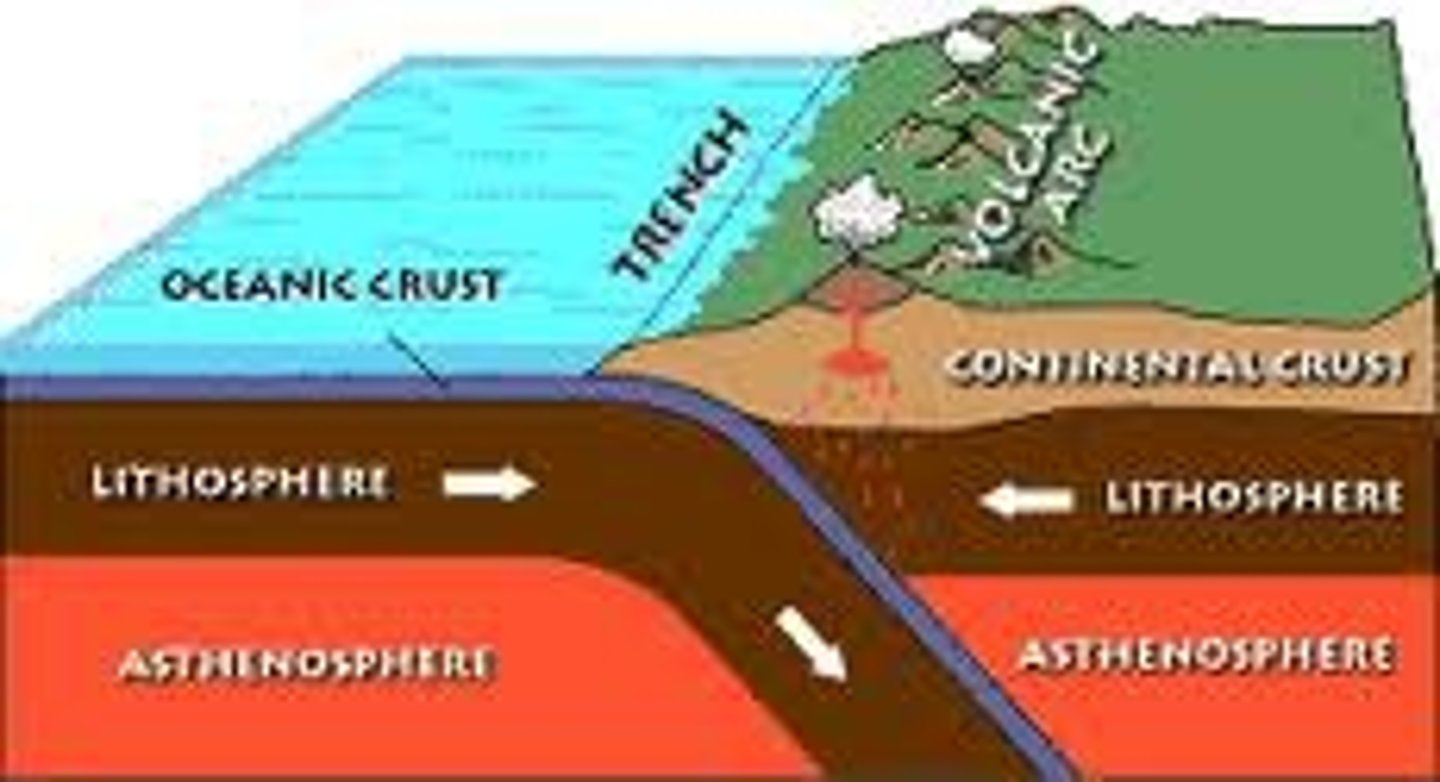
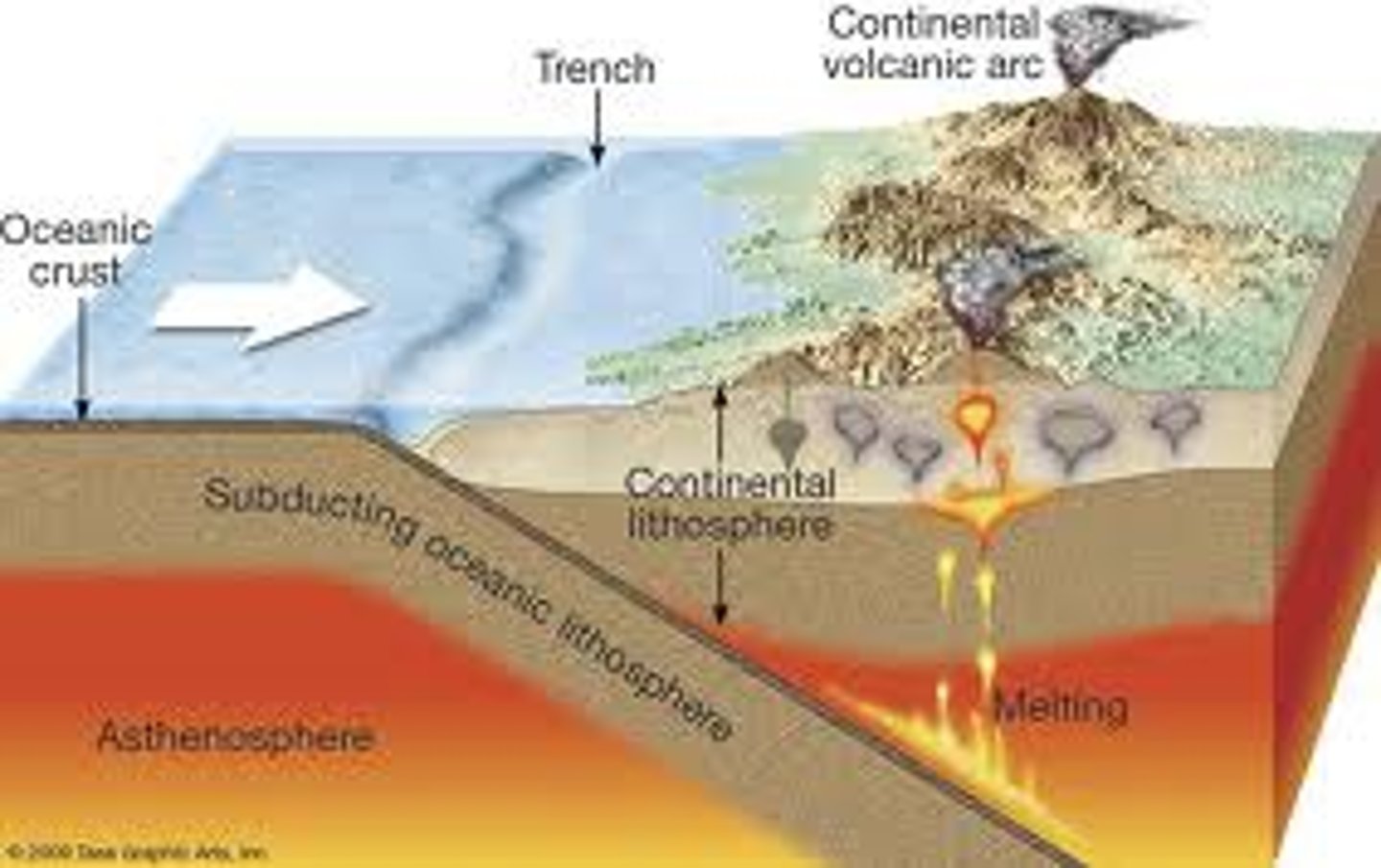
subduction zone
Occurs when a denser oceanic plate moves underneath (subducts) a less-dense continental plate.
e.g. Cascade Mountain range (includes Mount Saint Helens)
island arc
A curved chain of volcanic islands created when two oceanic plates converge.
e.g. Japan and the Aleutian Islands in Alaska
mountain range
Created when two continental plates collide.
e.g. Himalayas (Nepal and China)

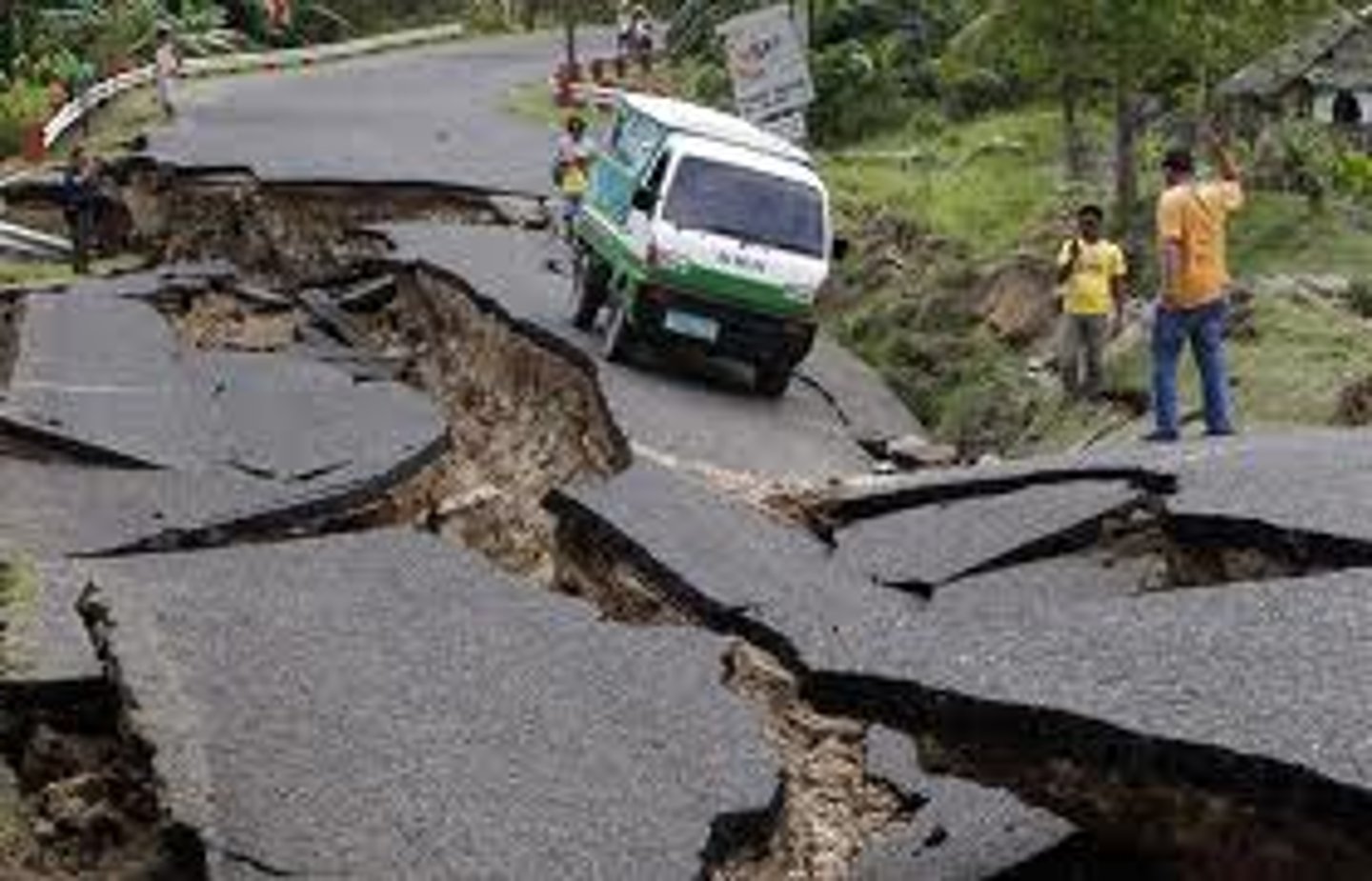
earthquakes
Caused by friction and stress buildup from the sliding plates, a common feature along transform boundaries.
e.g. Haiti Earthquake 2010

seismic waves
energy released in the form of vibrations when there is abrupt movement on an existing fault; they move in all directions through the surround rock
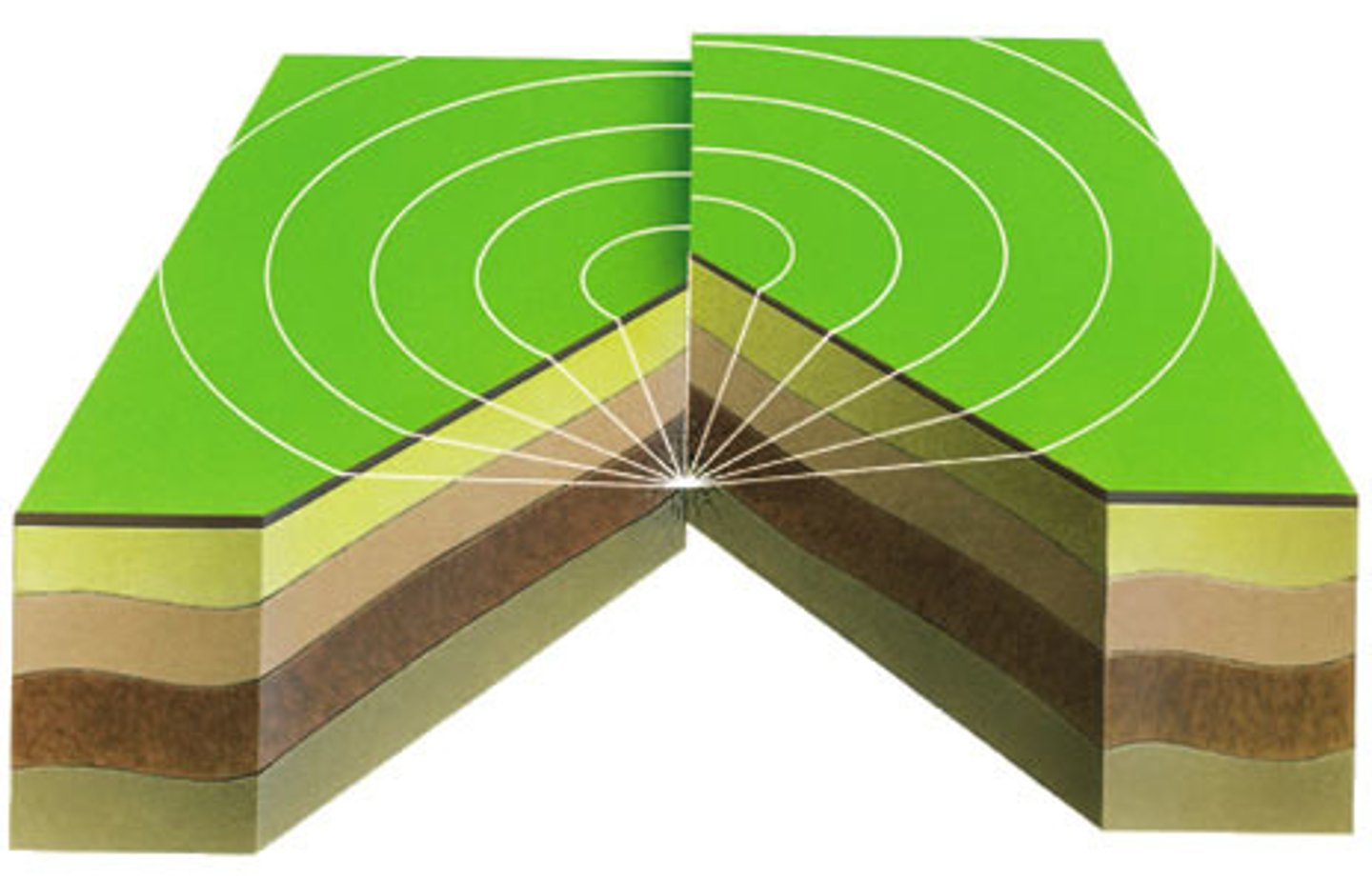
The severity of an earthquake depends on:
-The amount of potential energy that had been stored
-The distance the rock mass moved when the energy was released
-How far below the surface the movement occured
-The makeup of the rock material

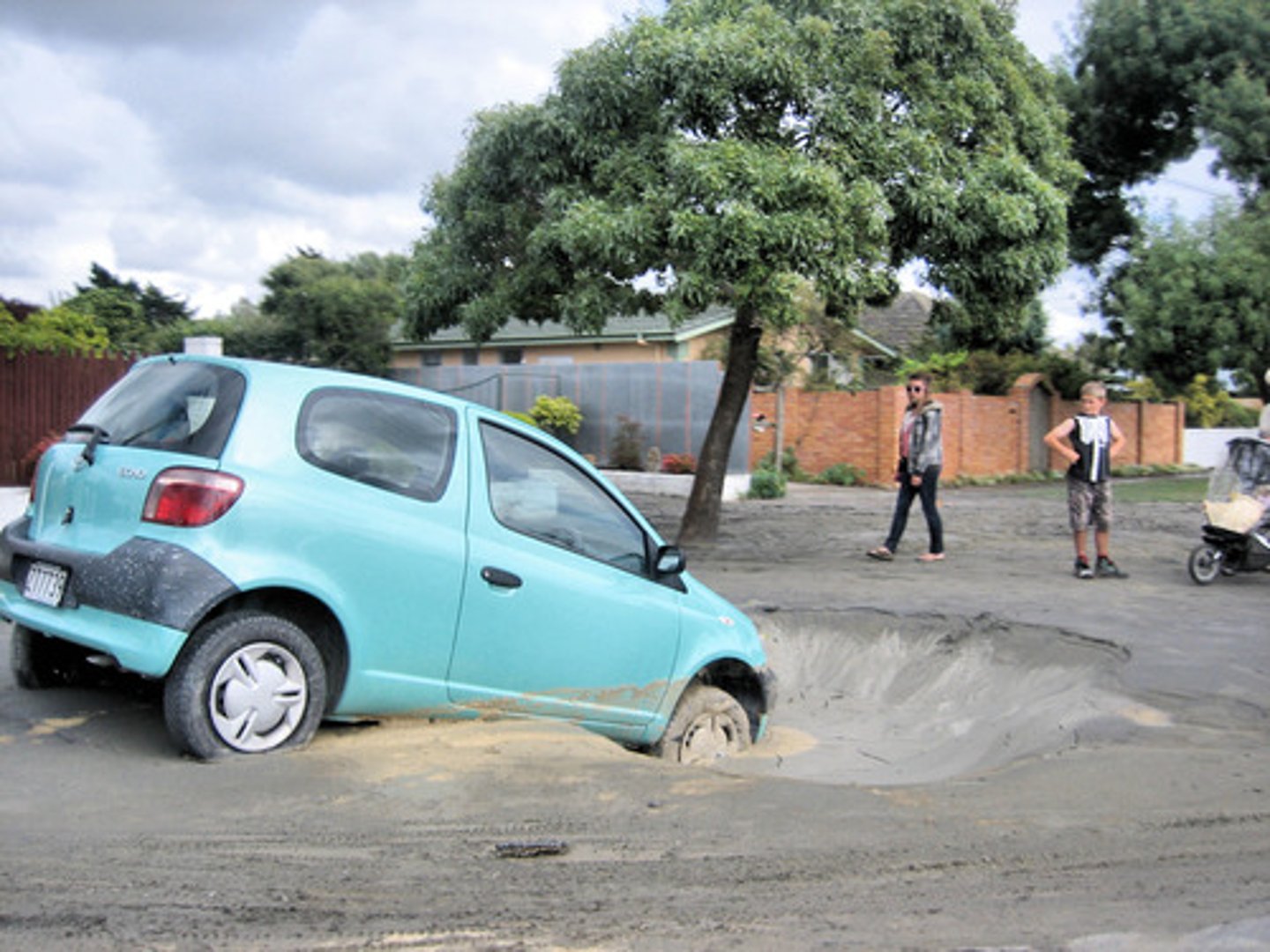
liquefaction
The process by which an earthquake's violent movement suddenly turns loose soil into liquid mud.

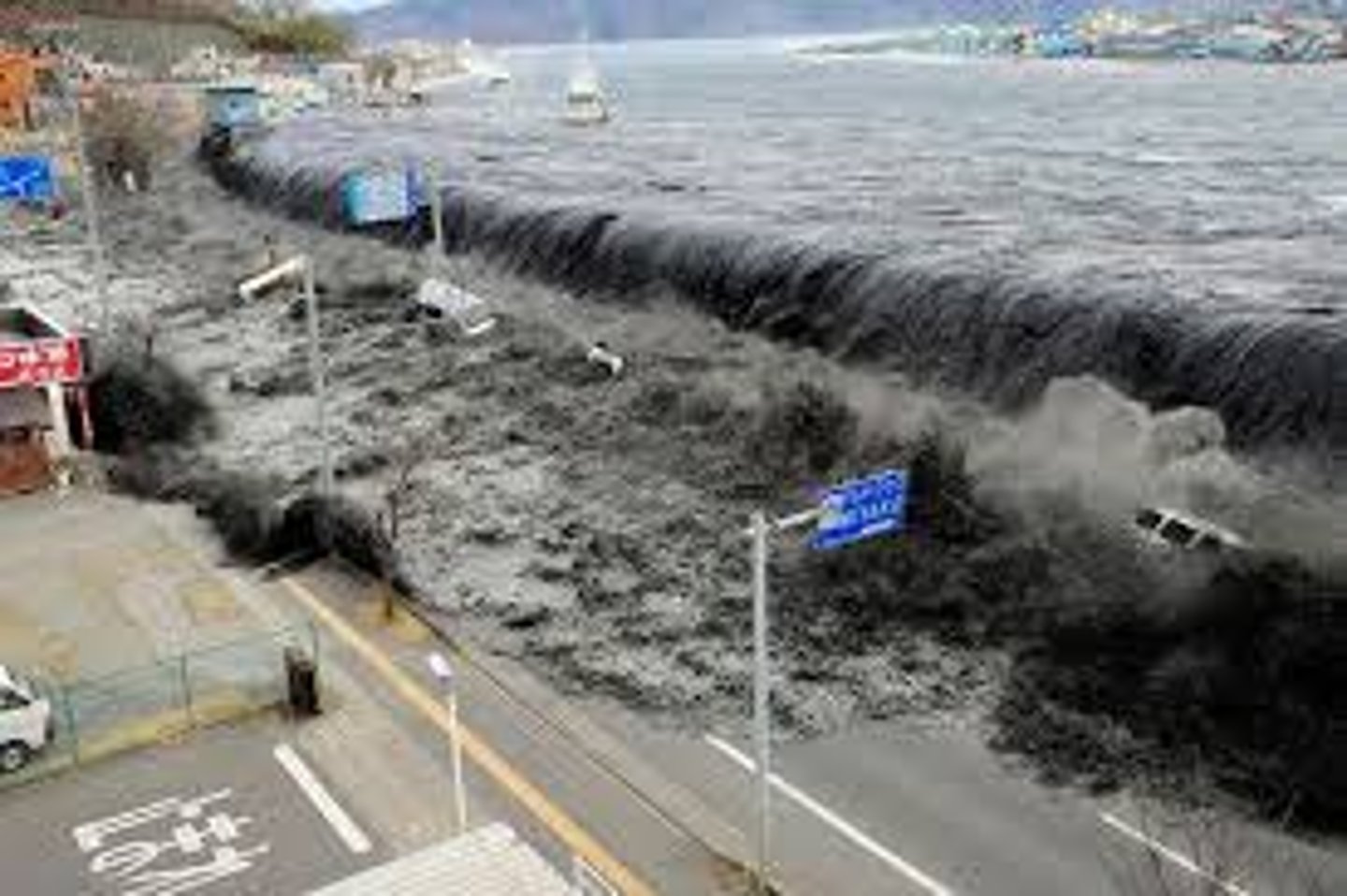
tsunami
A series of waves created when a body of water is rapidly displaced usually be an earthquake.
e.g. Tōhoku, Japan Earthquake and Tsunami 2011 (also led to nuclear meltdown at Fukushima)

volcano
A mountain or hill having a crater or vent through which lava, rock fragments, hot vapor, and gas are being or have been erupted from the earth's crust
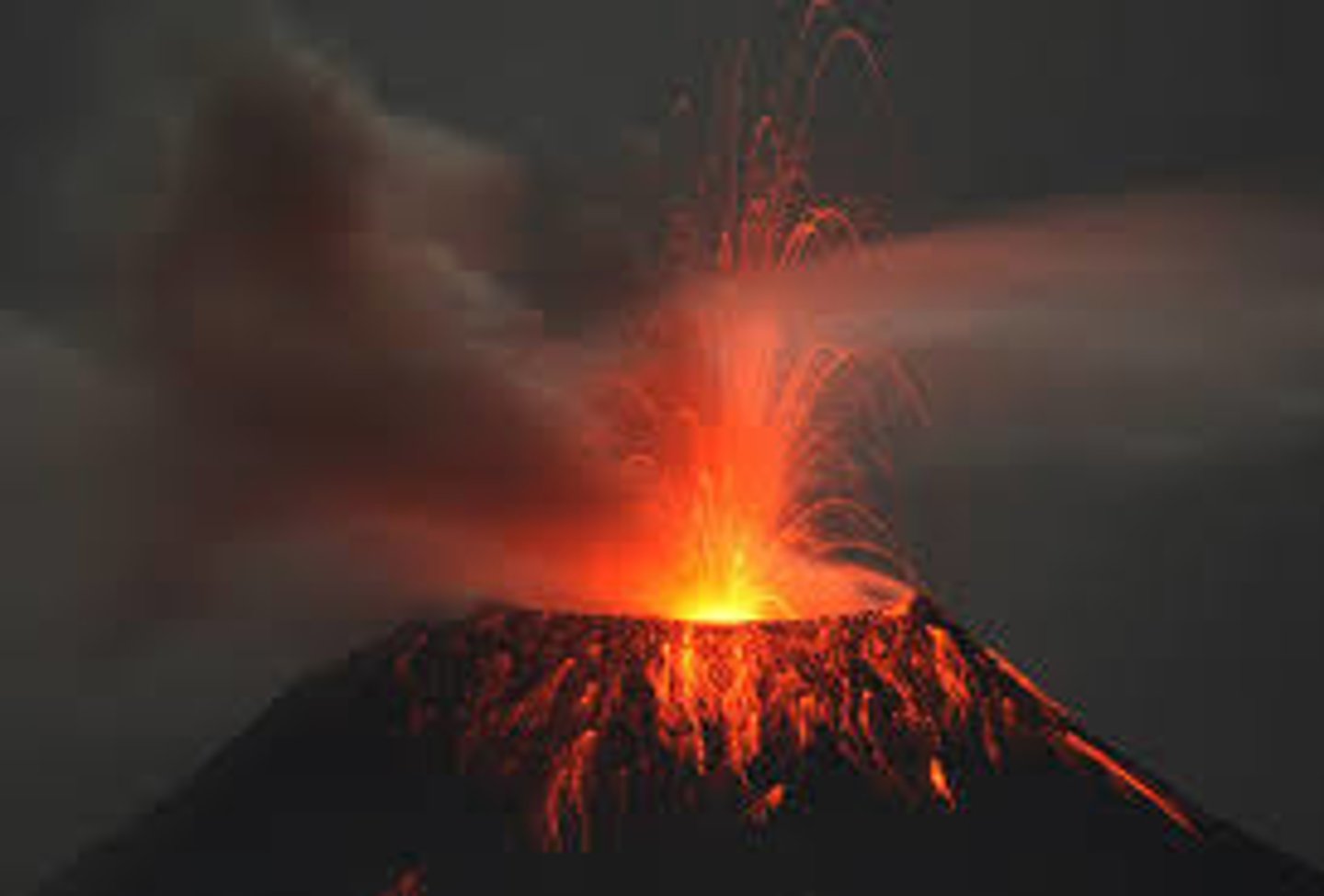

What do volcano eruptions do to our atmosphere?
-Release CO2, SO2, HCl
-debris and particulates can block sunlight, making a cooler climate

Factors that affect the amount of solar energy at the surface of the Earth:
-Earth's rotation (once every 24 hours)
-tilt of Earth's axis (23.5 degrees)
-revolution around the sun (once per year)
-closest to sun in winter, furthest in summer
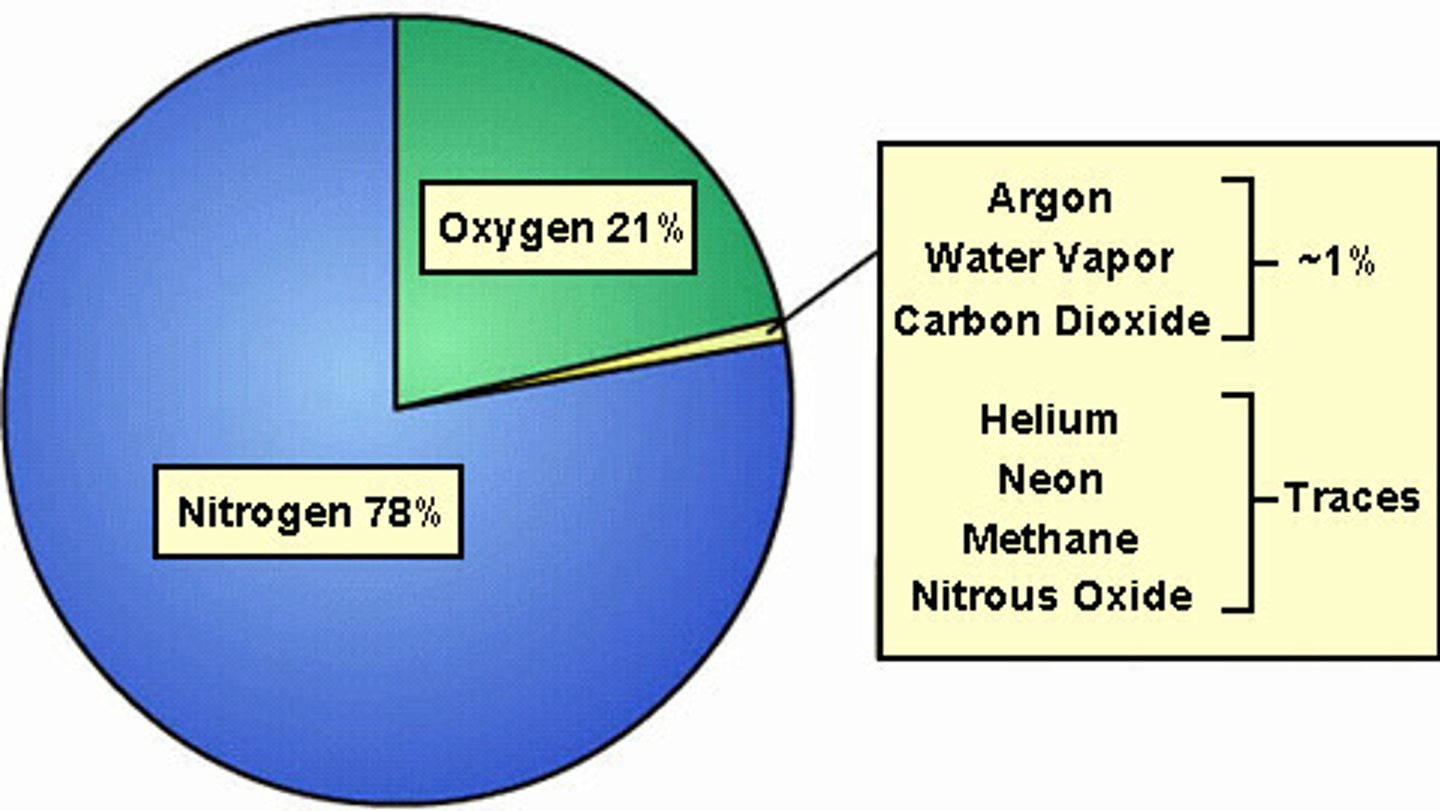
What seven primary compounds is the Earth's atmosphere composed of?
-nitrogen (78%)
-oxygen (21%)
-water vapor (0-4%)
-carbon dioxide (<<1%)
-methane (<<<1%)
-nitrous oxide (<<<1%)
-ozone (<<<1%)
Nitrogen (N2)
Fundamental nutrient for living organisms. Deposits on Earth through nitrogen fixation and reactions involving lightning and subsequent precipitation. Returns to the atmosphere through combustion of biomass and denitrification.
Oxygen (O2)
Oxygen molecules are produced through photosynthesis and are utilized in cellular respiration.

Water vapor (H2O)
Largest amounts occur near equator, over oceans, and in tropical regions. Areas where atmospheric water vapor can be low are polar areas and deserts.
-most voluminous greenhouse gas, cannot be added or reduced

Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Volume of CO2 has increased about 25% in the last 300 years due to the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation. CO2 is produced during cellular respiration and the decay of organic matter. It is a reactant in photosynthesis. CO2 is also a major greenhouse gas.
-stays in atmosphere 100 years

Methane (CH4)
Methane contributes to the greenhouse effect. Since 1750, methane has increased about 150% due to use of fossil fuels, coal mining, landfills, grazers, etc.
-stays in atmosphere 12 years

Nitrous oxide (NO2)
Concentration increasing about 0.3% per year. Sources include burning of fossil fuels, use of fertilizers, burning biomass, deforestation, etc. Can come from livestock farts.
-stays in atmosphere 120 years

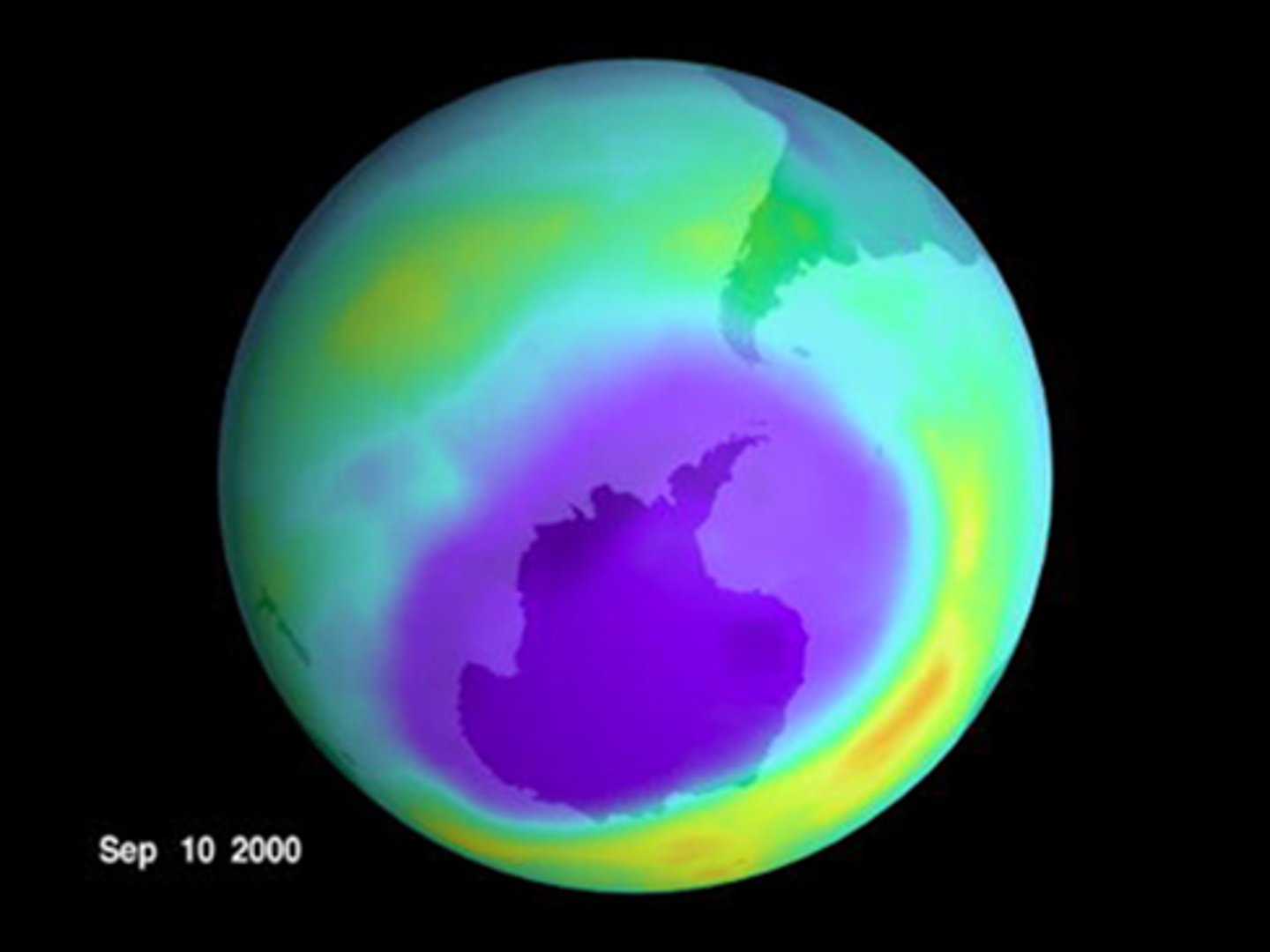
Ozone (O3)
97% of ozone is found in the stratosphere (ozone layer). Ozone absorbs UV radiation. Ozone is produced in the production of photochemical smog. CFC's have contributed to ozone layer depletion. Ozone is a pollutant in the troposphere.
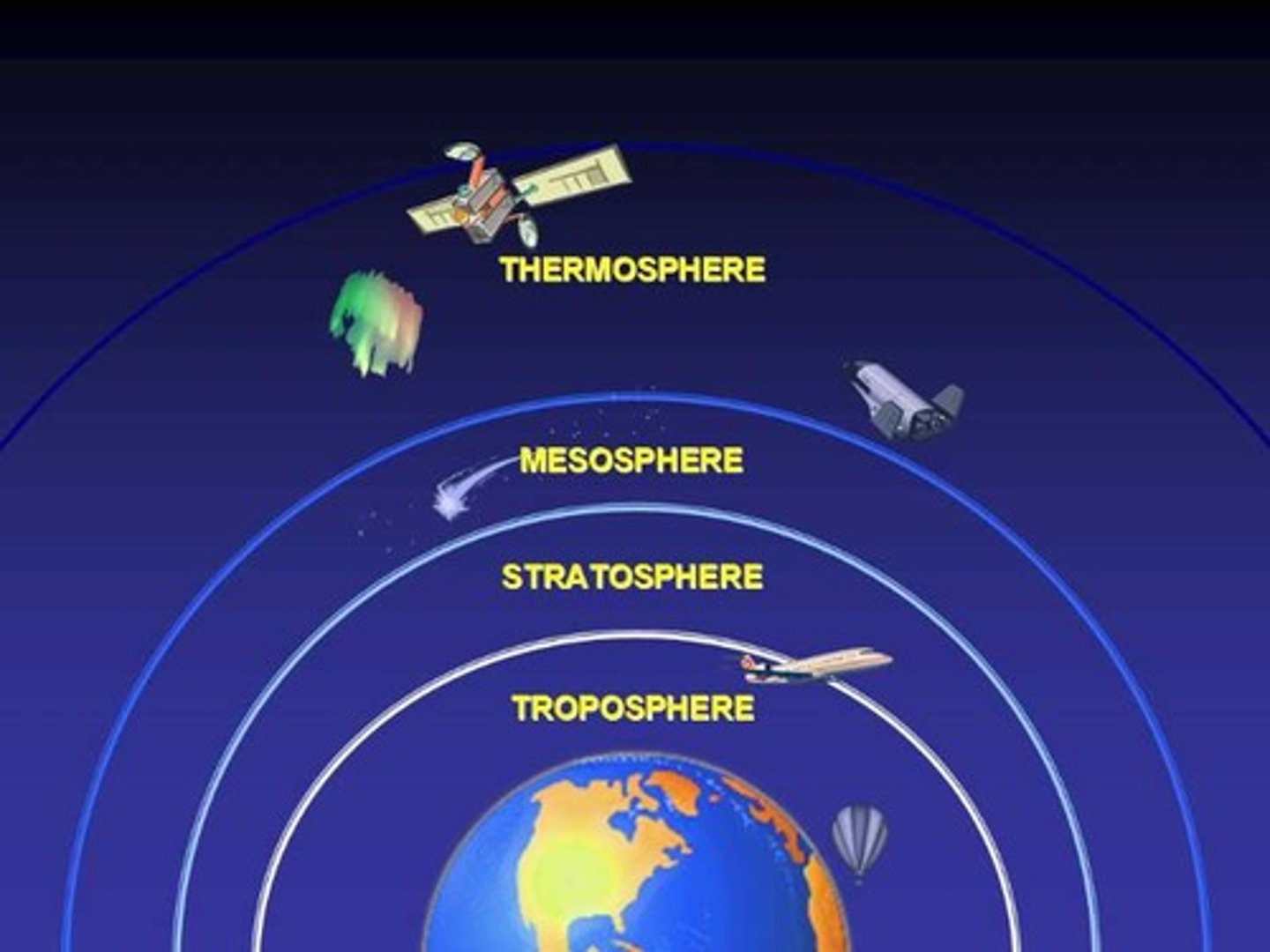
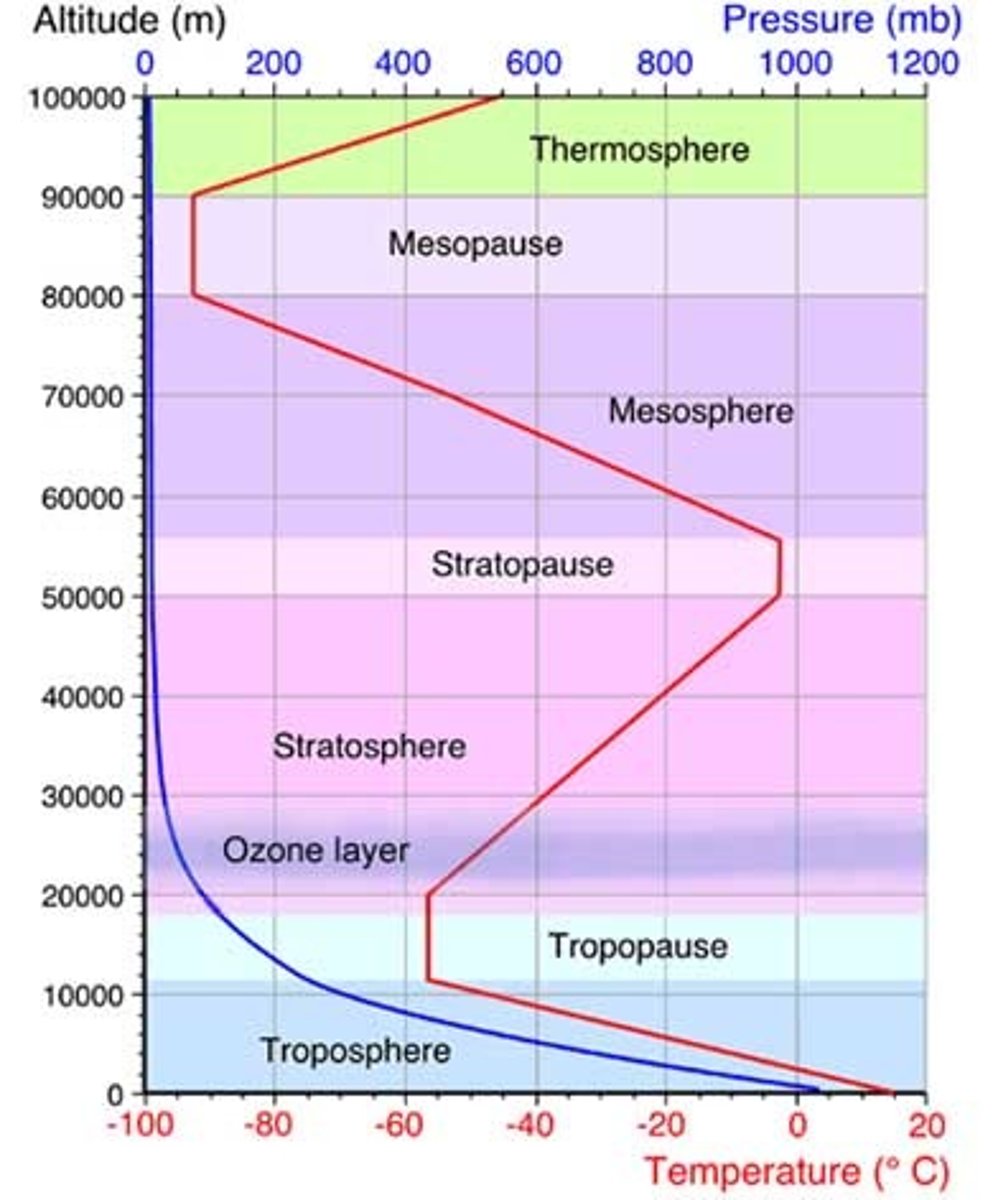
stratosphere
-temperature increases with altitude due to absorption of heat by ozone
-ozone is produced by UV radiation and lightning
-contains the ozone layer
mesosphere
-temperature decreases with altitude
-coldest layer
-ice clouds occur here
-meteors (shooting stars) burn up in this layer
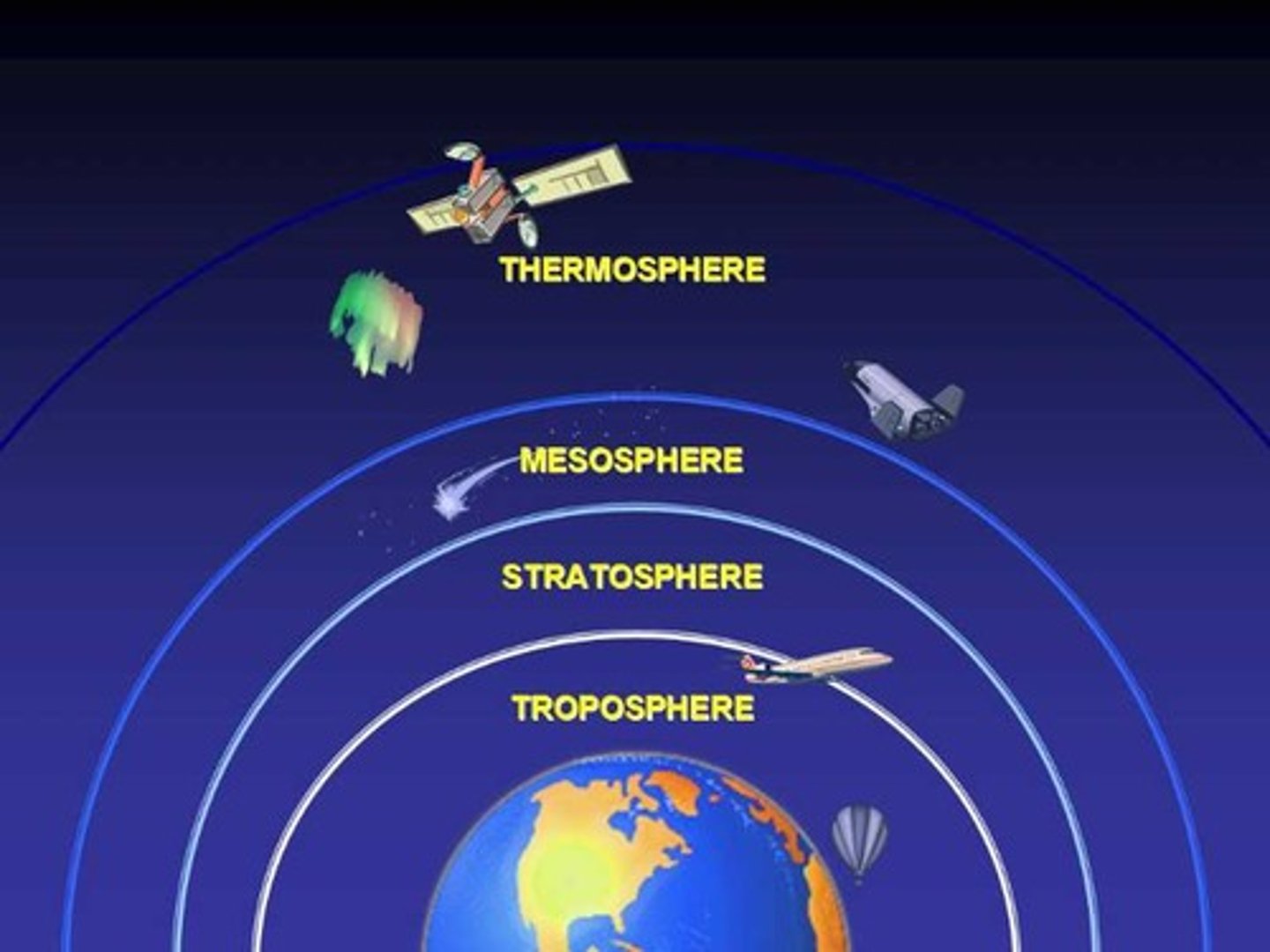
thermosphere (ionosphere)
-temperature increase with height due to gamma rays, X rays, and UV radiation
-molecules are converted into ions
-causes Northern lights
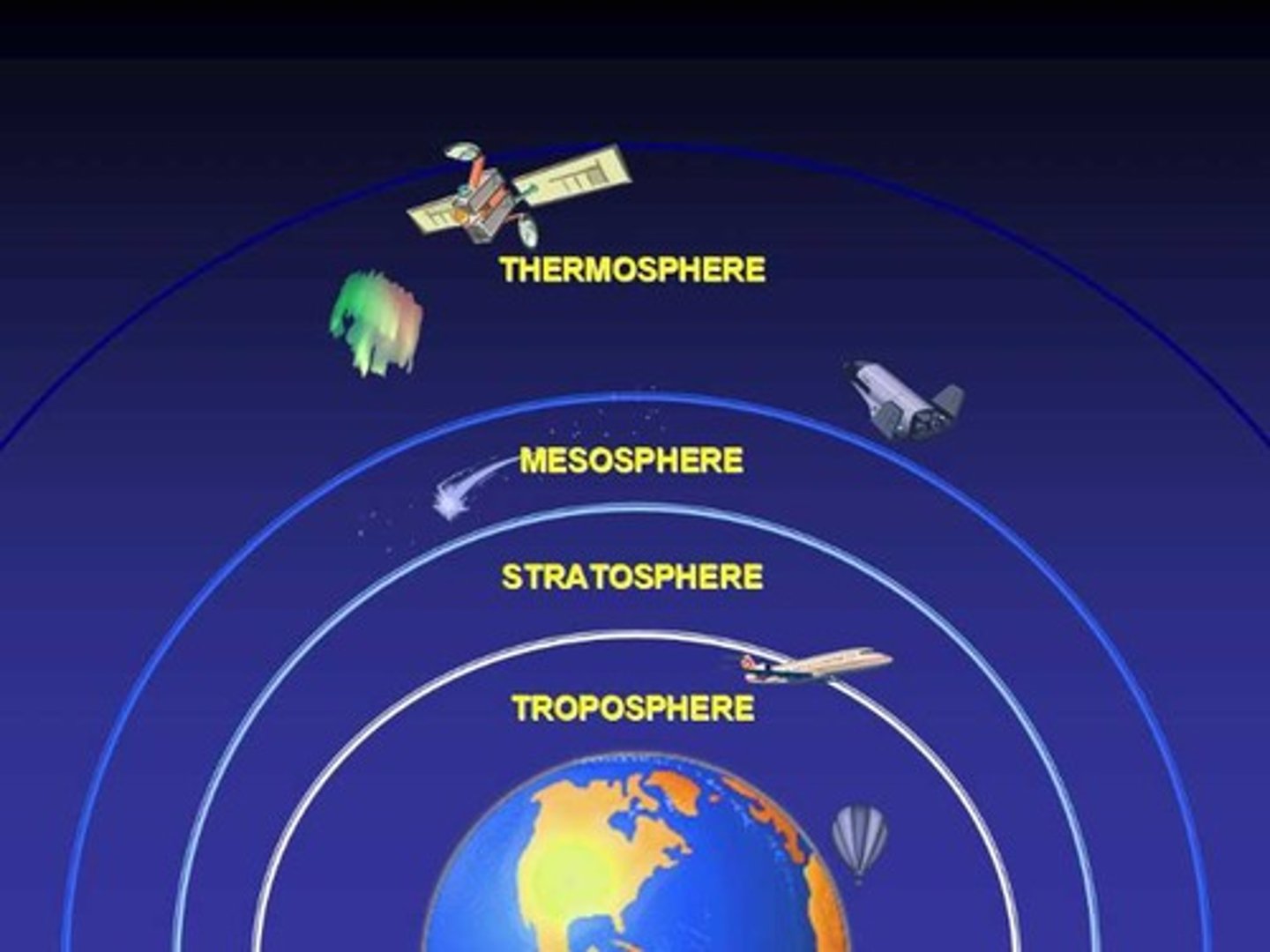
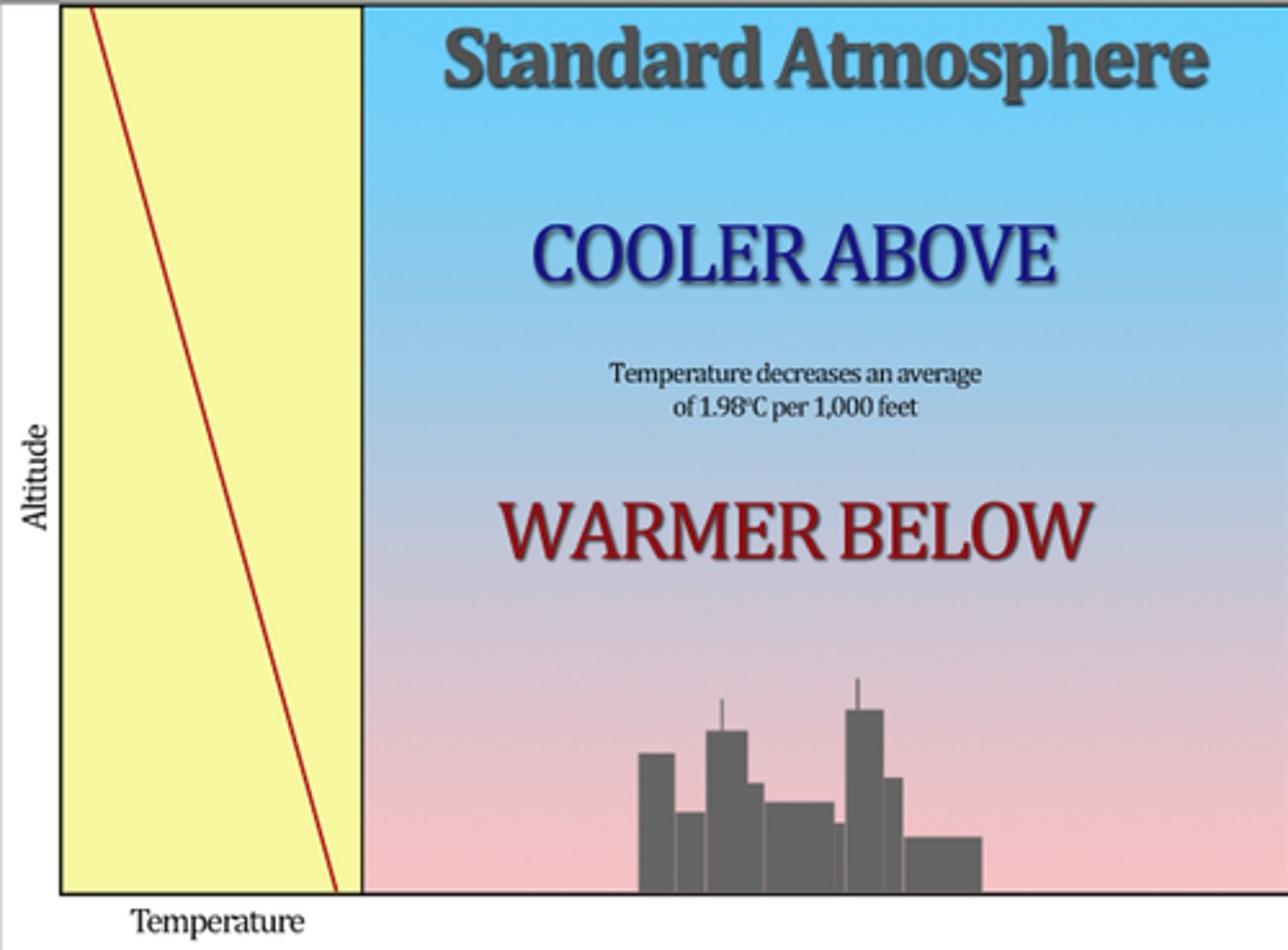
Relationship between altitude, pressure, and temperature within the zones
weather
is a LOCAL area's short-term temperature, precipitation, humidity, wind speed, cloud cover, and other physical conditions of the lower atmosphere as measured over hours or days
-caused by movement of heat energy

radiation
the flow of electromagnetic radiation. Method by which Earth receives solar energy.
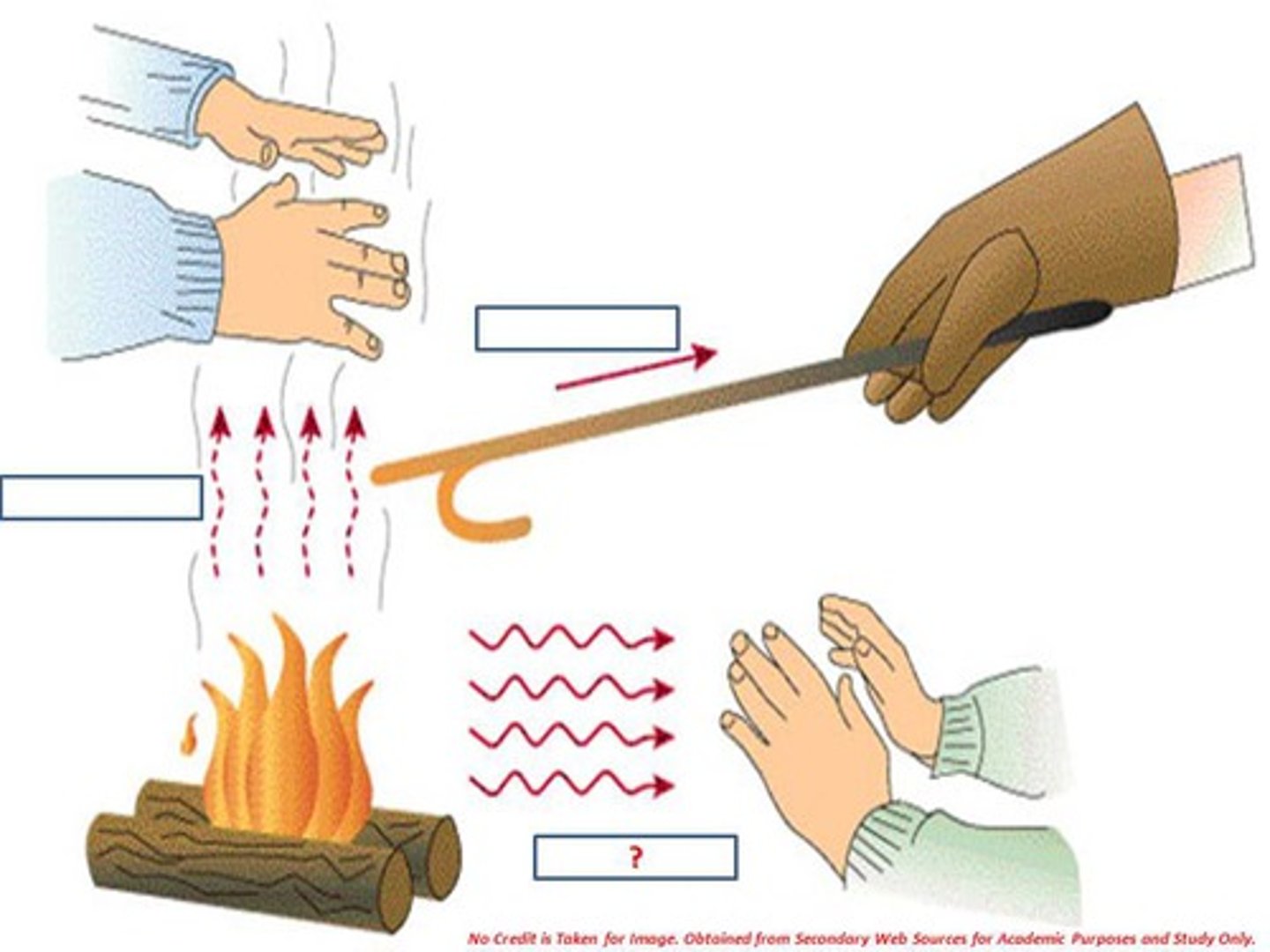
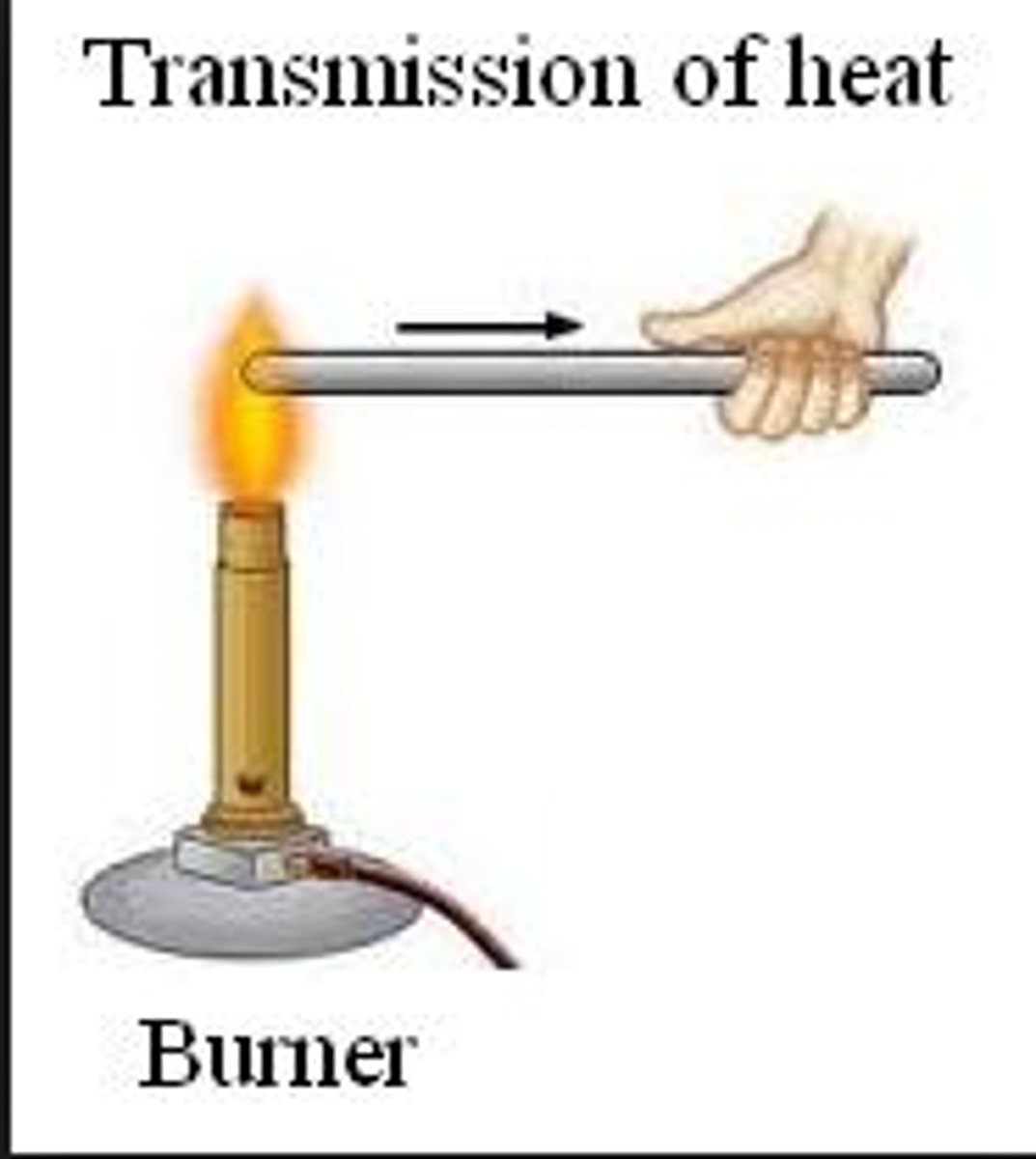
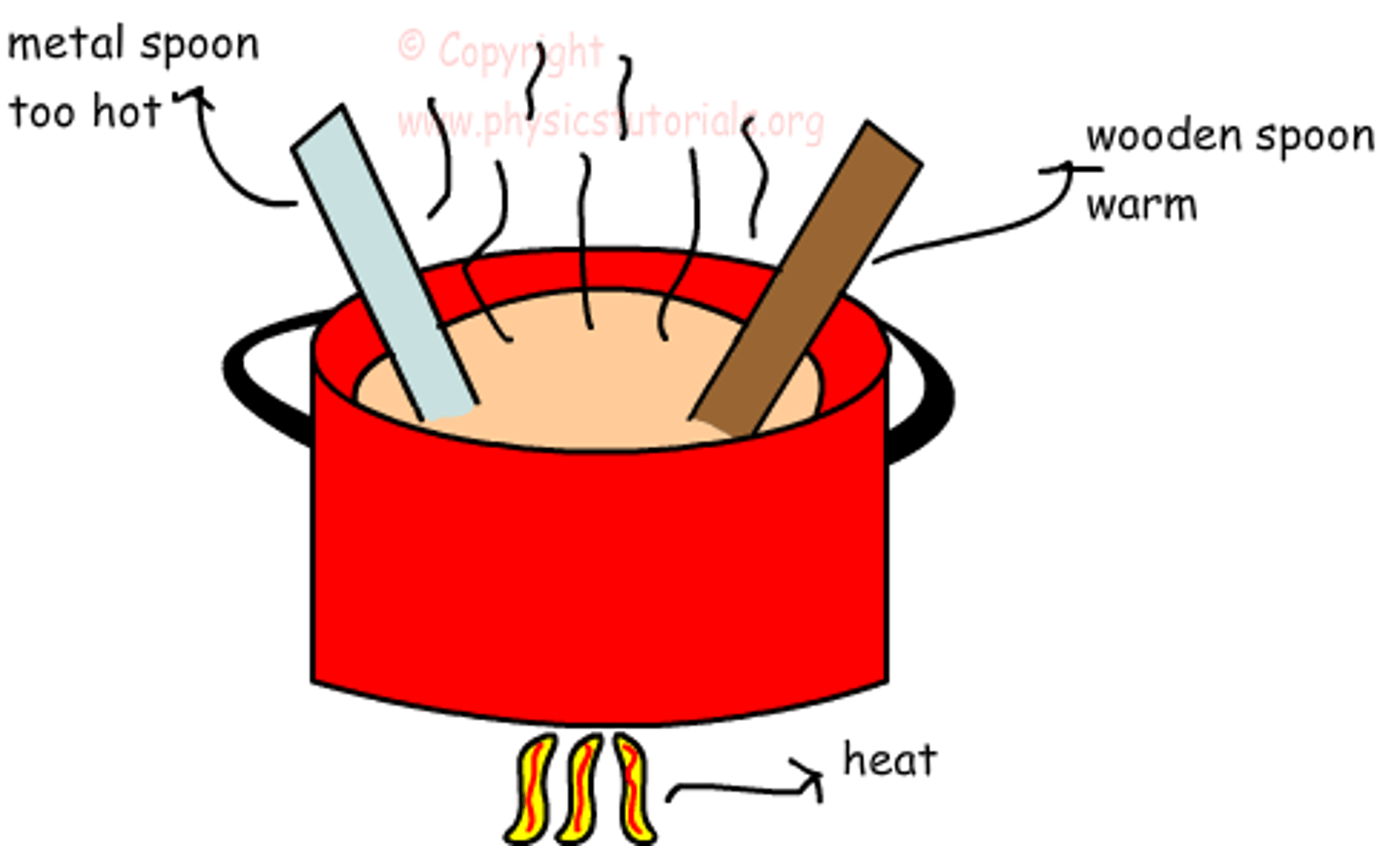
conduction
involves transfer of heat through a substance that results from a difference in temperature
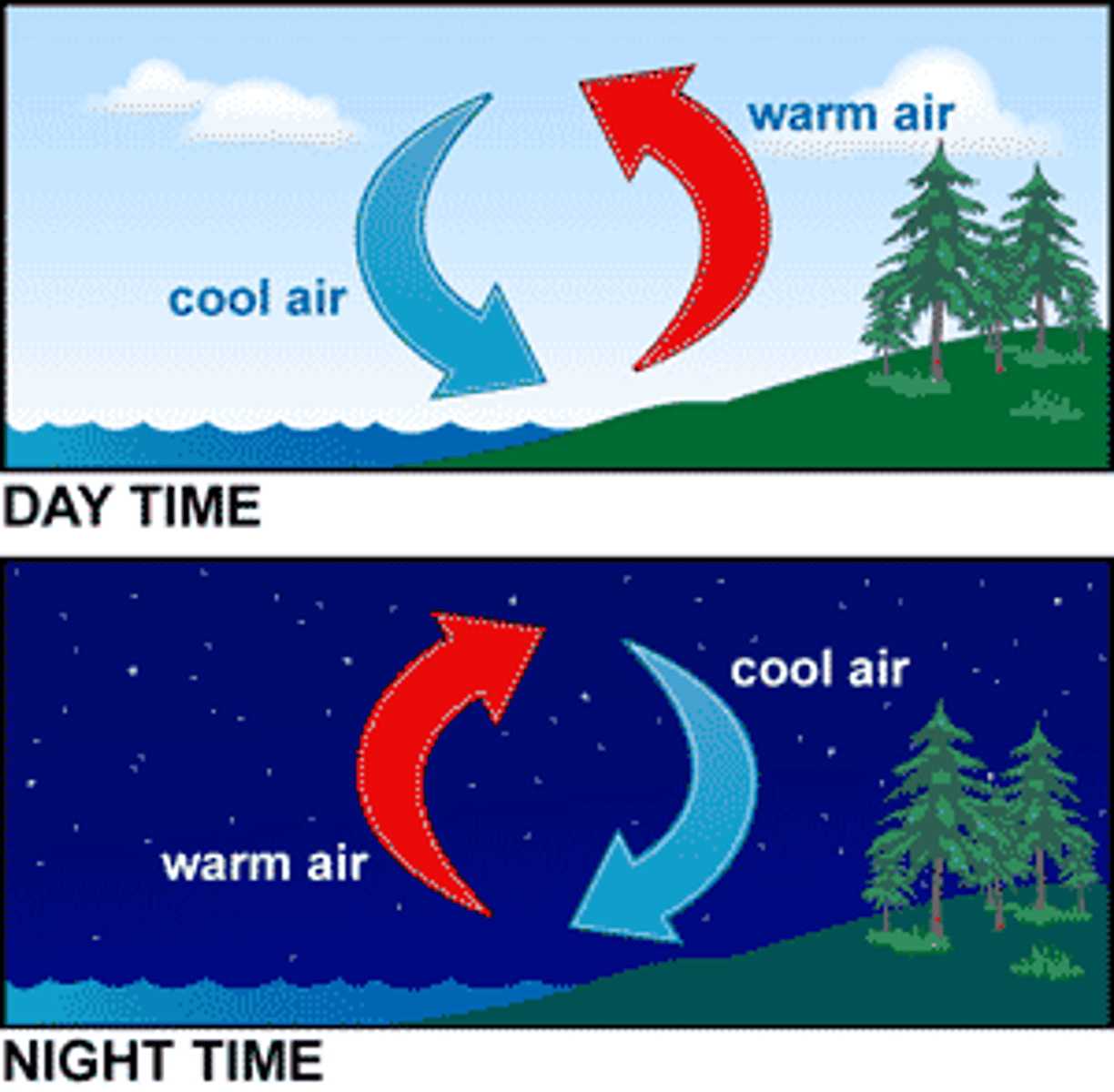
convection
is the primary way energy is transferred from hotter to colder regions in the Earth's atmosphere and determines weather patterns
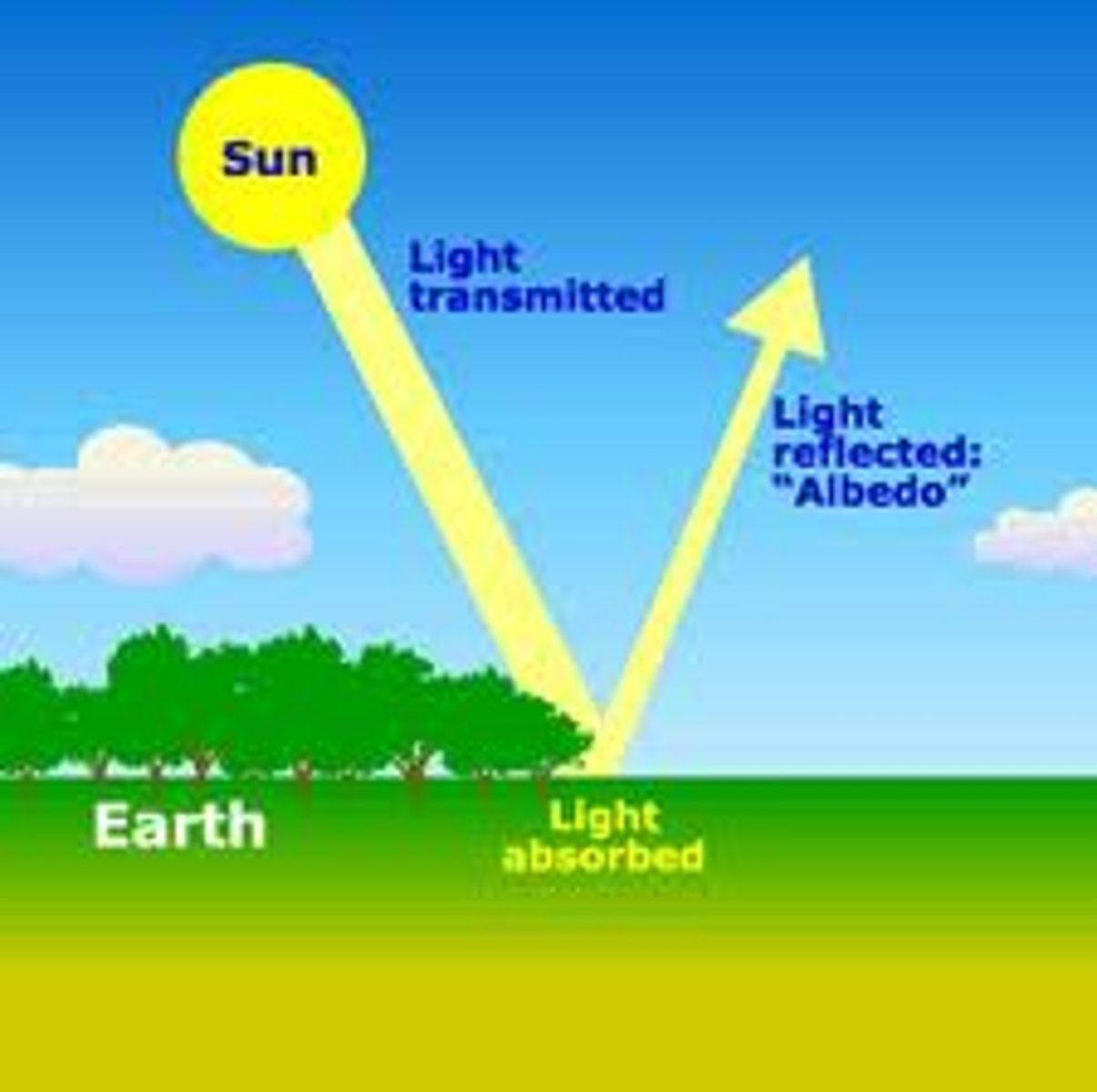
albedo
is the diffuse reflectivity or reflecting power of a surface
specific heat
is the amount of heat per unit mass required to raise the temperature by one degree Celsius (water has a high specific heat)
temperature inversion
stops atmospheric convection (which is normally present) from happening in the affected area and can lead to the air becoming stiller and murky from the collection of dust and pollutants that are no longer able to be lifted from the surface. Worsens pollution.
(COLD air) OVER (WARM air)
formation of clouds
when rising air, through expansion, cools to the point where some of the water vapor molecules "clump together" faster than they are torn apart by their thermal energy. Some of that (invisible) water vapor condenses to form (visible) cloud droplets or ice crystals.

dew point
is the temperature below which the water vapor in a volume of humid air condense into liquid water

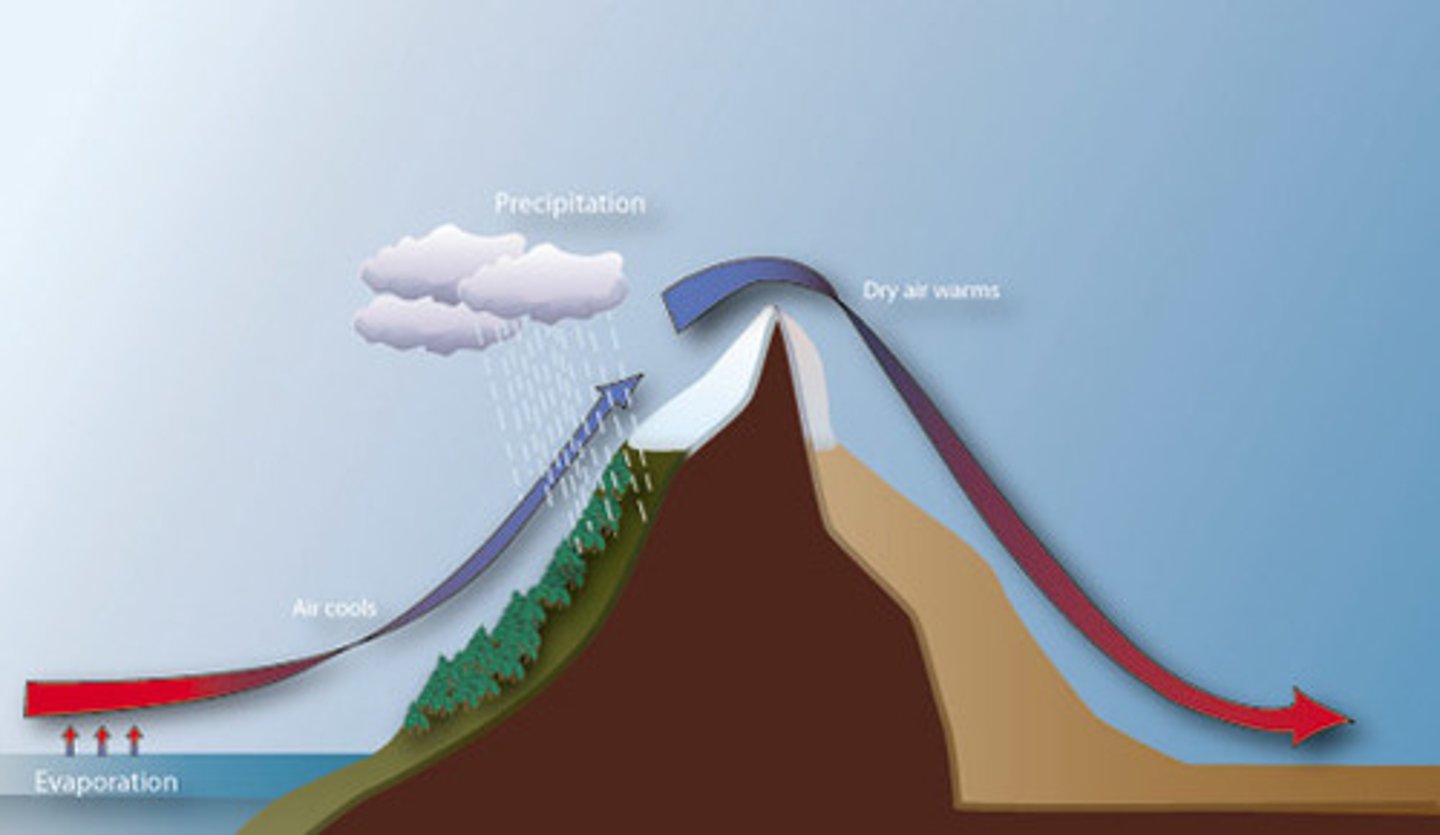
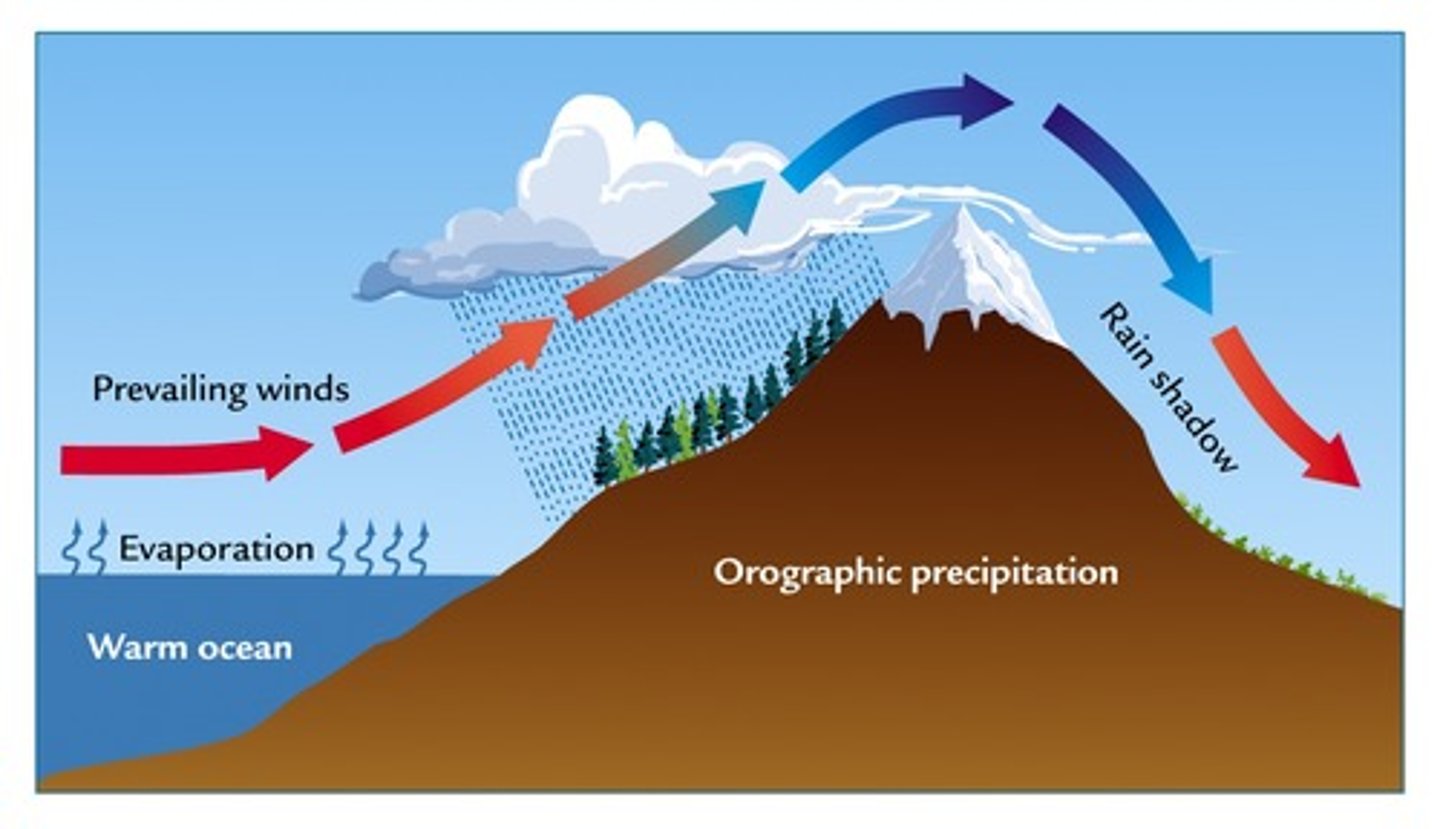
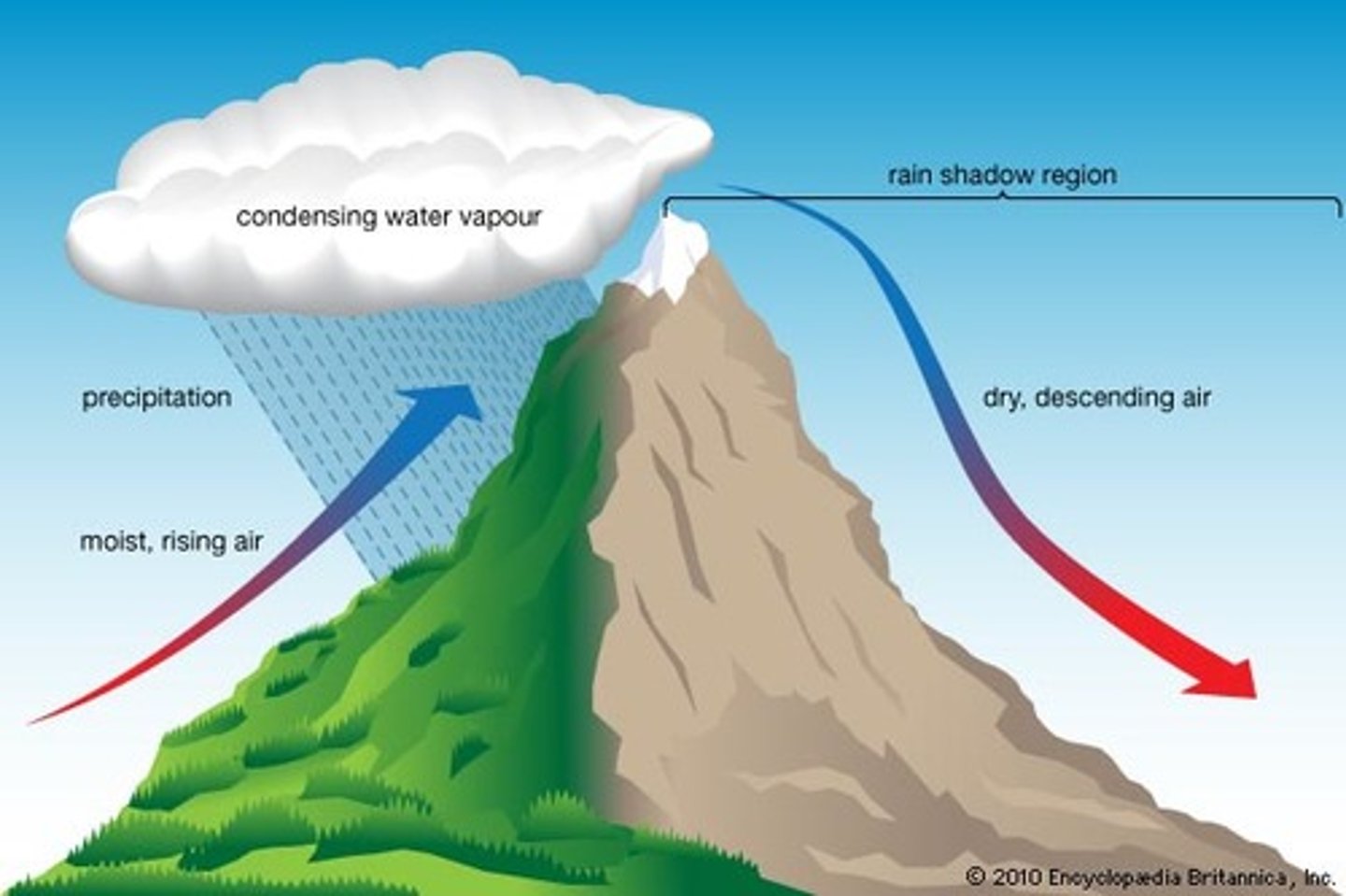
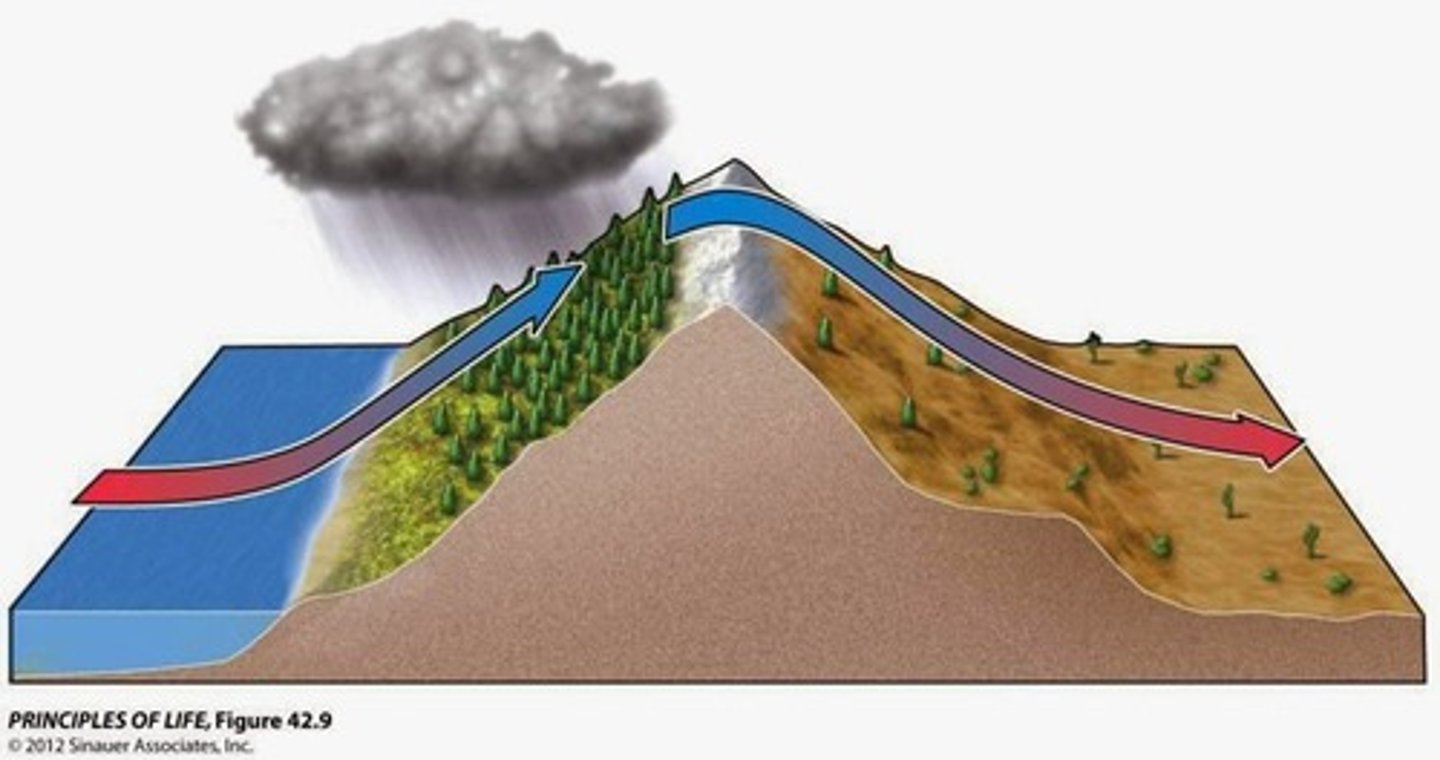
Rain shadow (orographic) effect
the loss of moisture from the landscape and the resulting semiarid or arid conditions on the leeward side of high mountains
-Windward= lush, green, clouds, precipitation, ocean...leedward= deserts, sinking air, dry
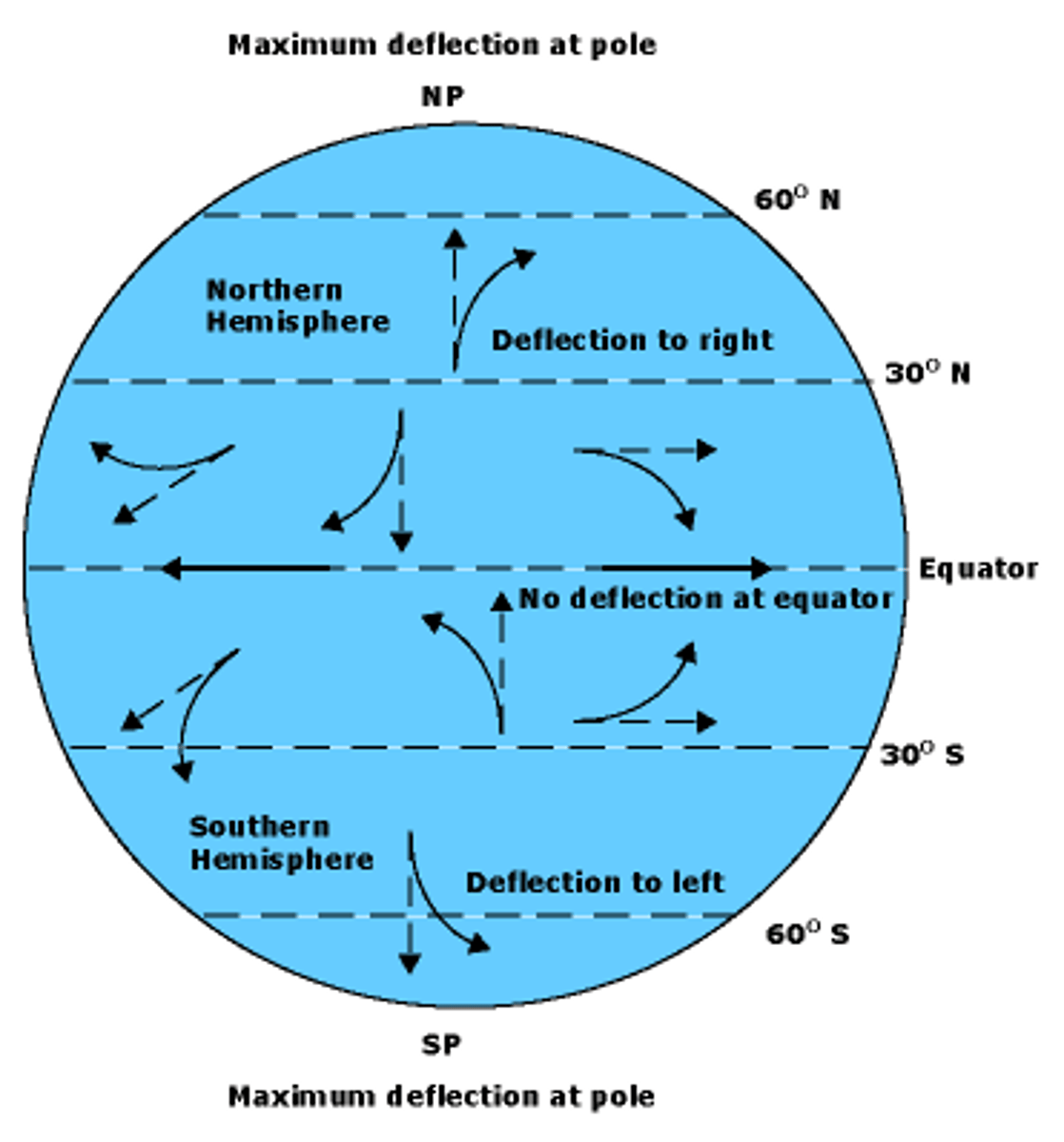
Coriolis Effect
an effect whereby a mass moving in a rotating system experiences a force (the Coriolis force) acting perpendicular to the direction of motion and to the axis of rotation.
monsoons
a seasonal prevailing wind in the region of South and Southeast Asia, blowing from the southwest between May and September and bringing rain (the wet monsoon), or from the northeast between October and April (the dry monsoon)

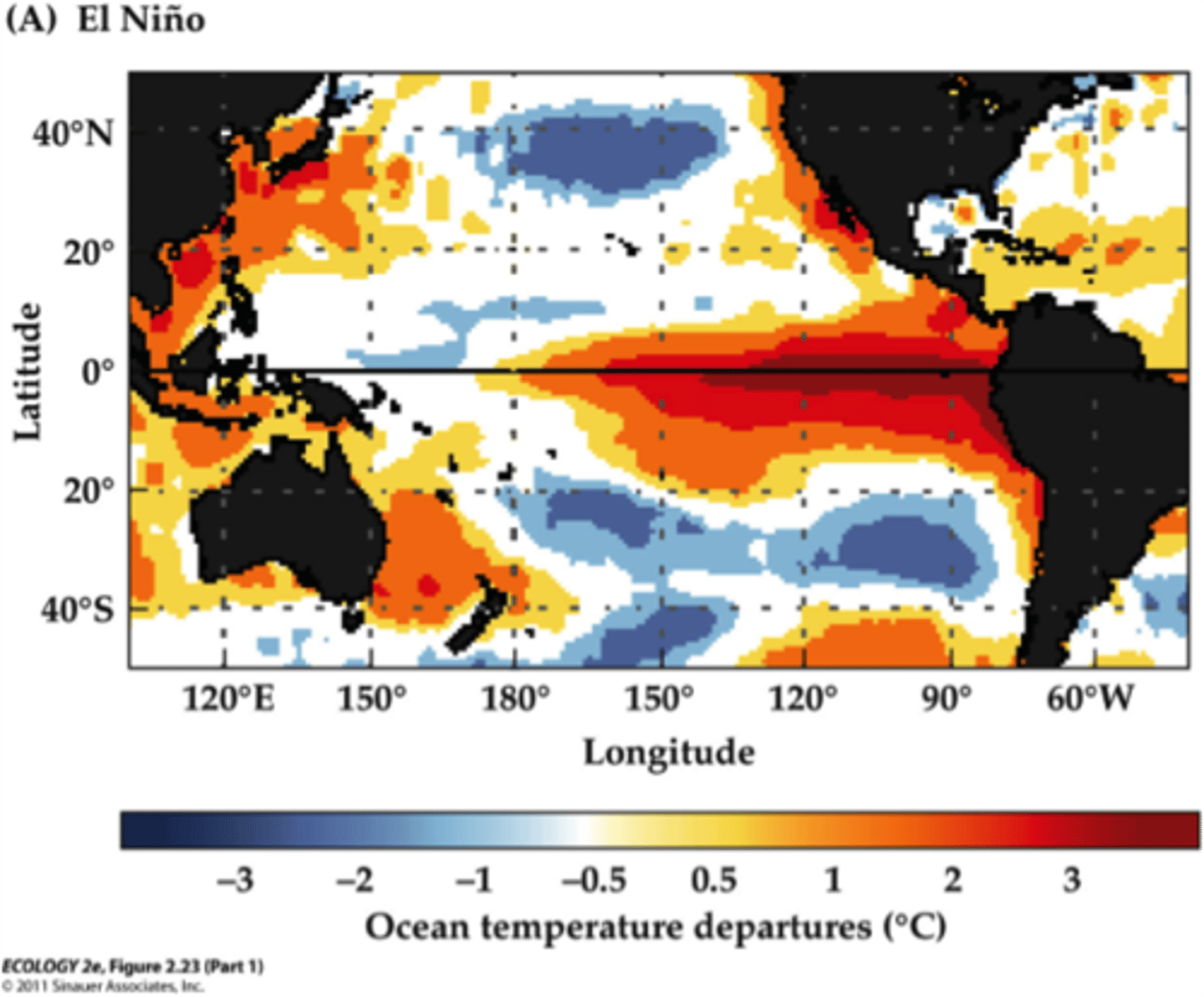
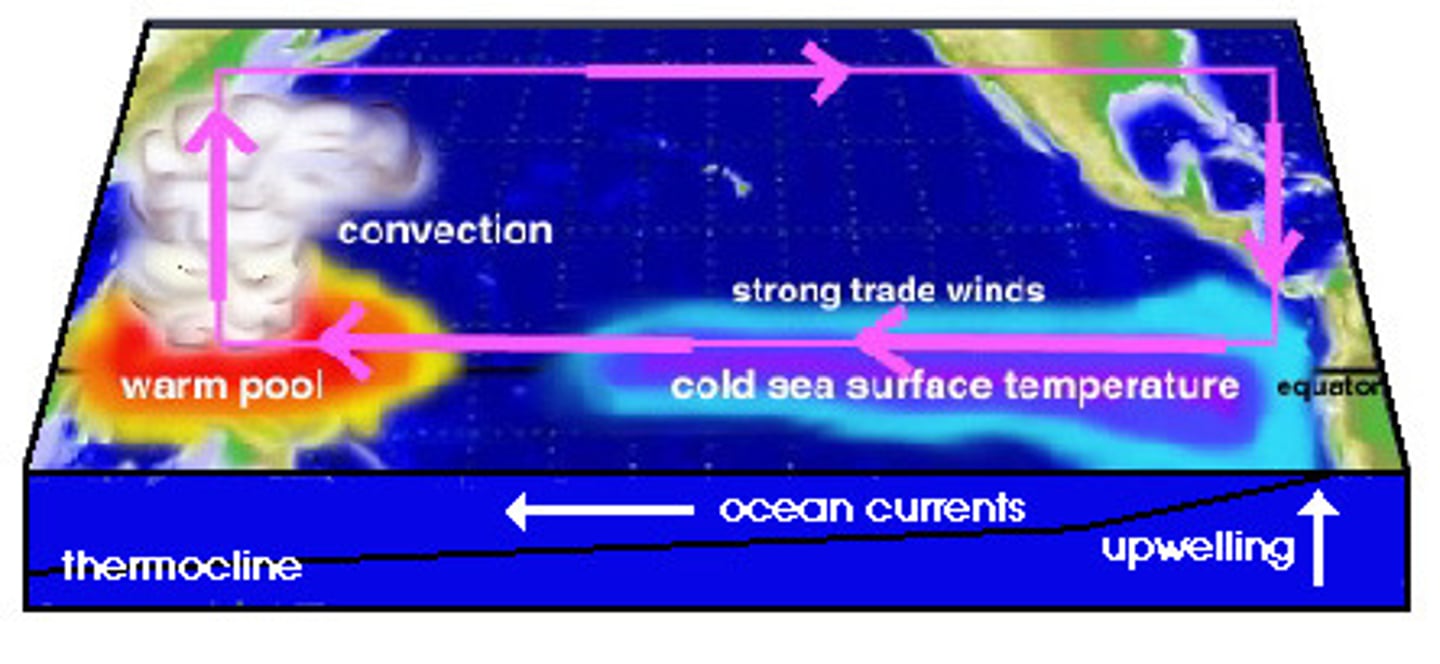
El Niño and La Niña (Southern Oscillation (ENSO))
large-scale weather phenomenon occurs every few years when prevailing winds in the tropical Pacific Ocean weaken and change direction
o Above-average warming of Pacific waters affects populations of marine species by changing the distribution of plant nutrients, hurting fishing industry
o Low nutrients, low dissolved oxygen (in South America, but in Australia during La Niña)
o Severe flooding, storms, drought, mudslides, $ damage, human health hazards (dehydration, diarrhea, zoonotic diseases [lyme, Hanta])
![<p>large-scale weather phenomenon occurs every few years when prevailing winds in the tropical Pacific Ocean weaken and change direction</p><p>o Above-average warming of Pacific waters affects populations of marine species by changing the distribution of plant nutrients, hurting fishing industry</p><p>o Low nutrients, low dissolved oxygen (in South America, but in Australia during La Niña)</p><p>o Severe flooding, storms, drought, mudslides, $ damage, human health hazards (dehydration, diarrhea, zoonotic diseases [lyme, Hanta])</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fd5828e9-e98a-47b2-87df-aa99beeed08a.jpg)
Climate
Average weather that occurs in a region over a long period.
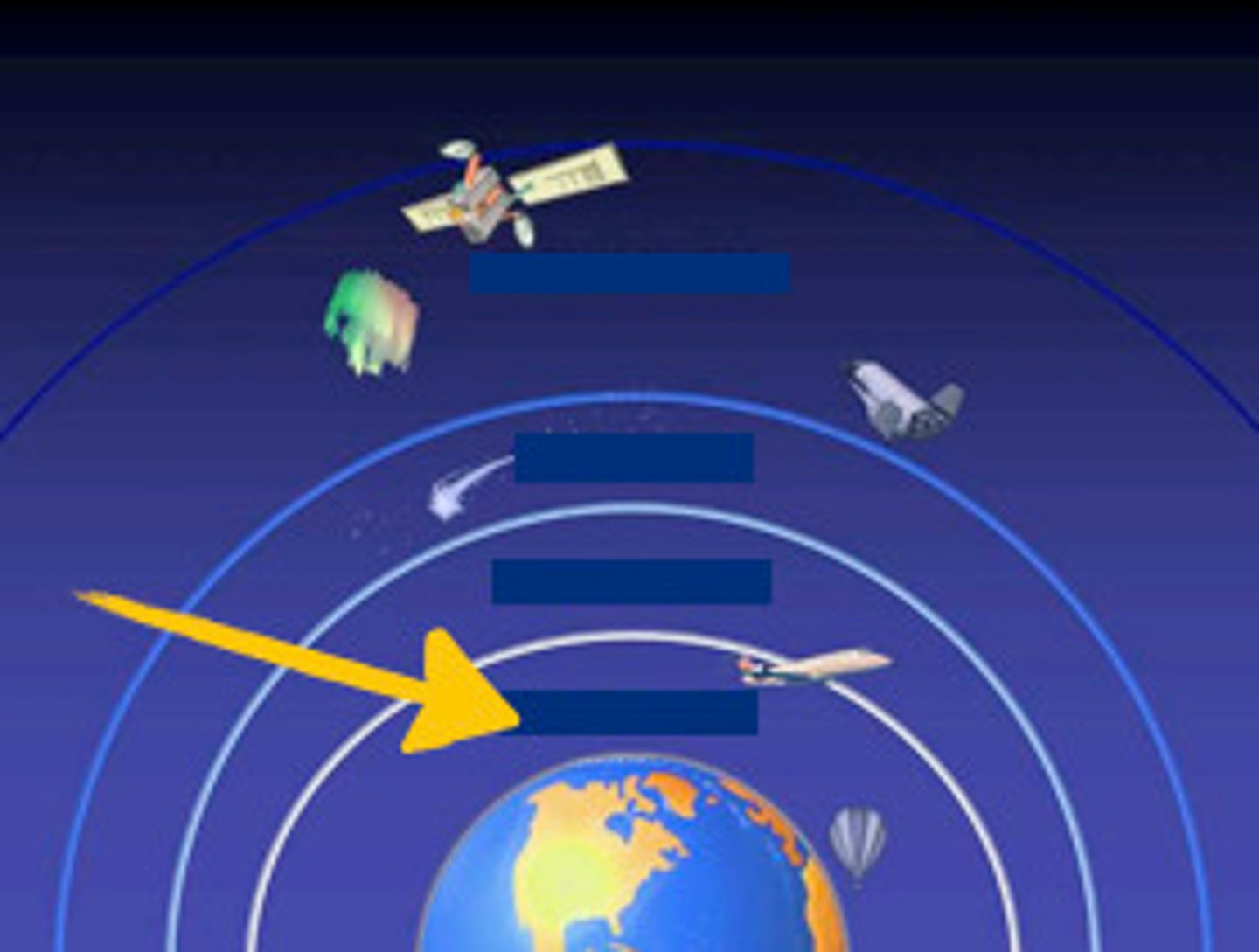
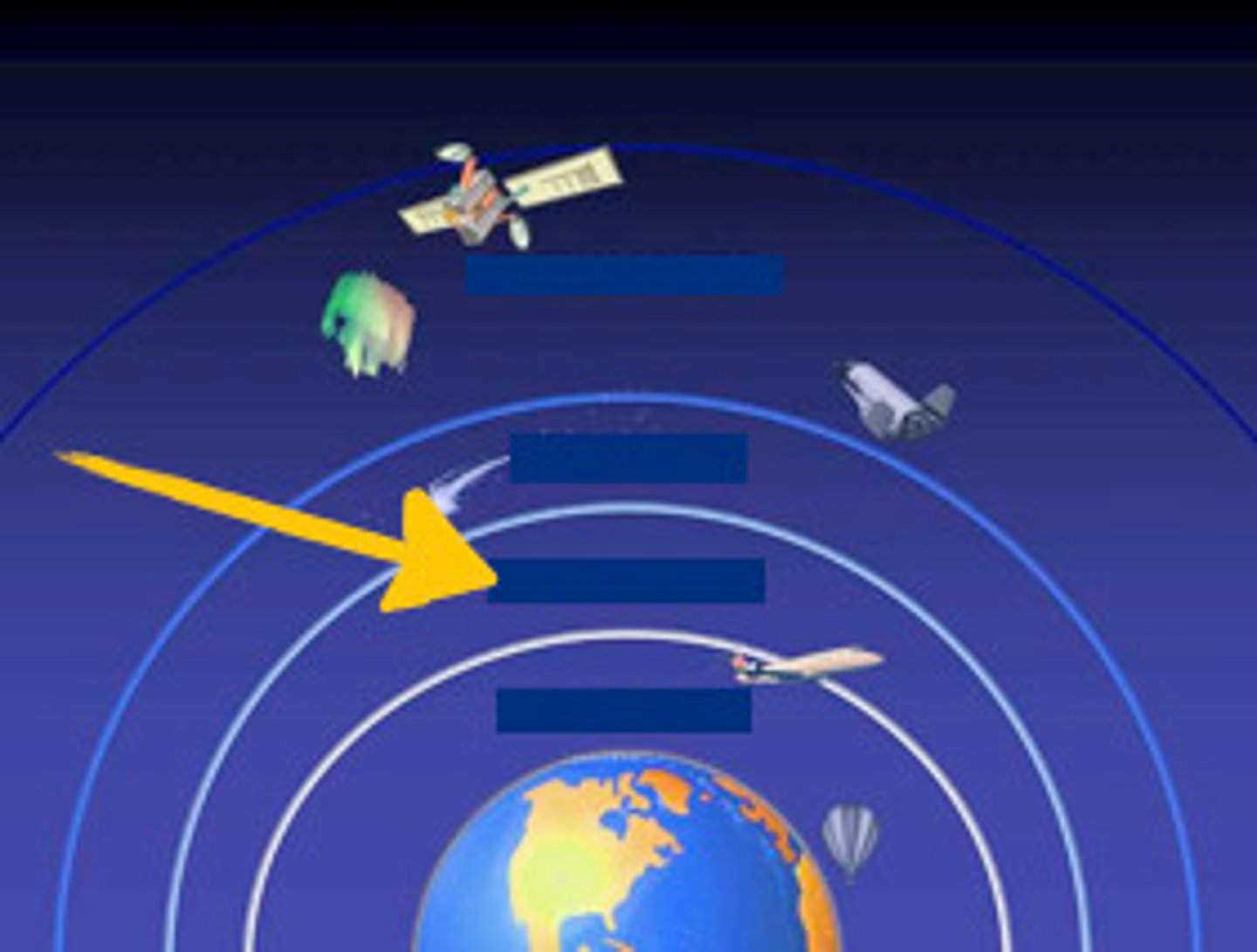
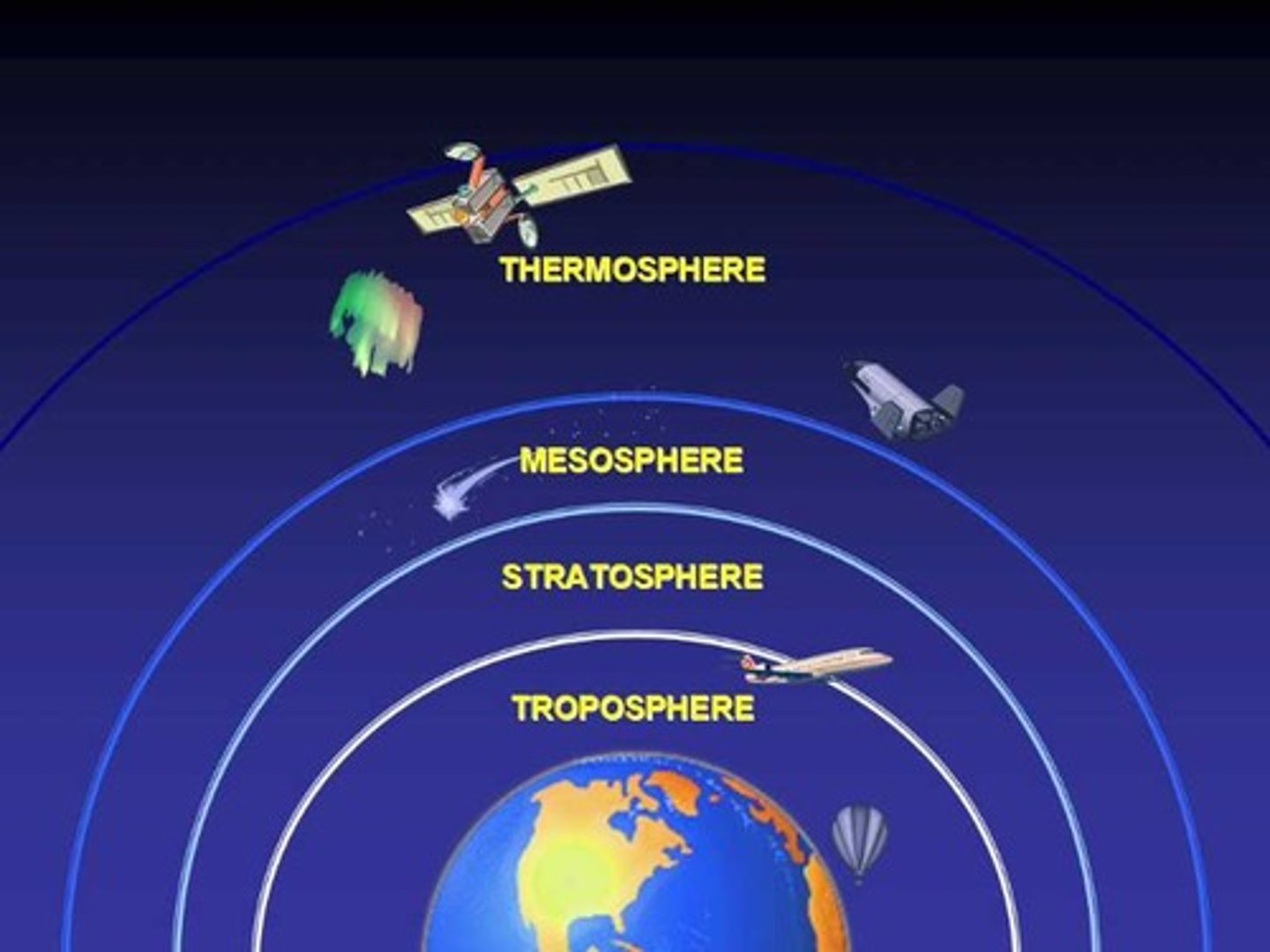
Layers of Atmosphere
exosphere, thermosphere, mesosphere, stratosphere, troposphere
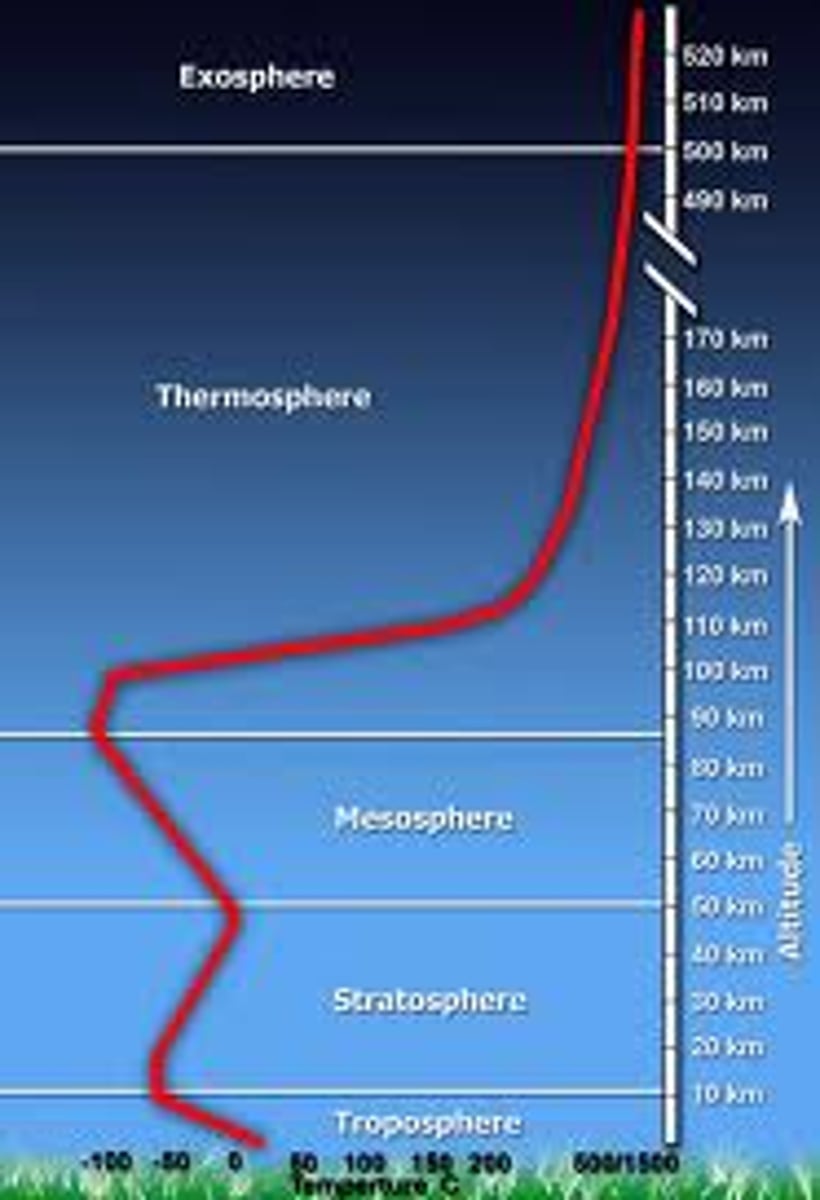
Troposphere
Most of the N2, O2 and H2O vapor is here. Densest Layer of Atmosphere. Where weather occurs.
Stratosphere
Less dense. Ozone is formed here. Blocks UV radiation
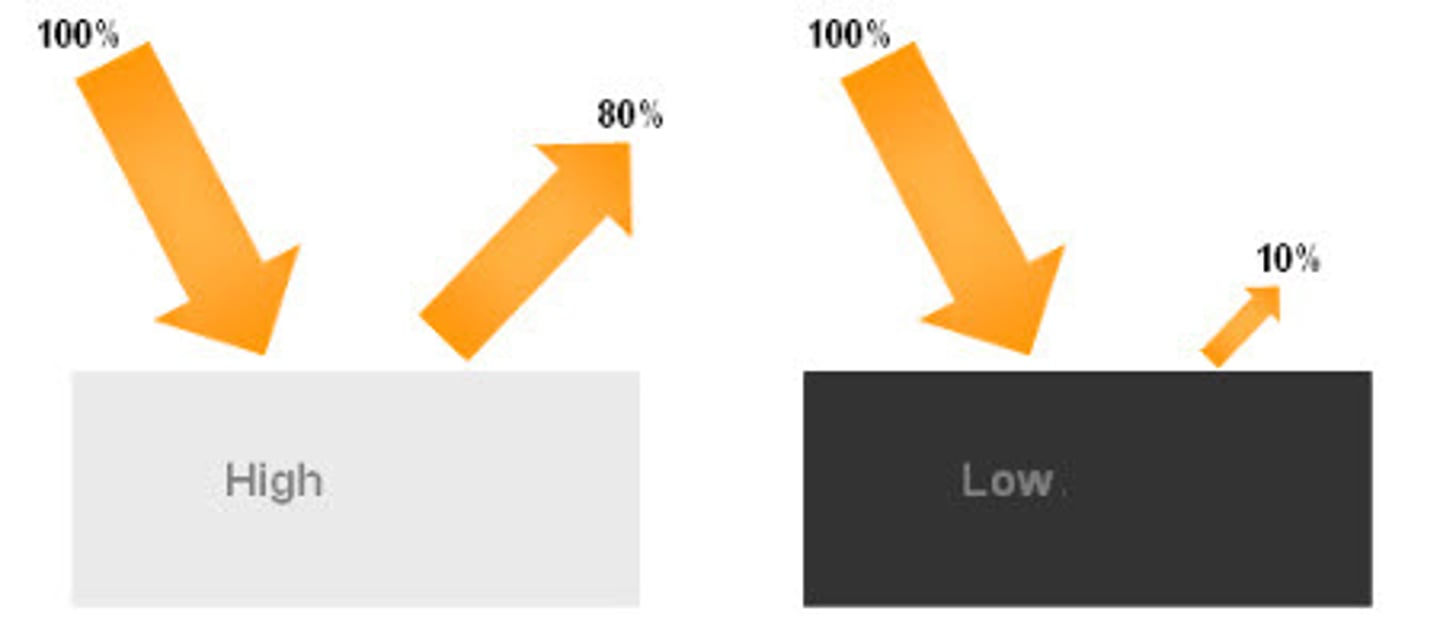
Albedo
% of incoming sunlight that is reflected from a surface, the ability of an object to reflect light
Saturation Point
Max amount of H2O vapor that can be in the air

Adiabatic Cooling
Lower pressure lowers the temp of air and expands its volume
Adiabatic Heating
Higher pressure decreases the volume and raises the air temp
Latent heat release
Water vapor in the atmosphere condenses into liquid and energy is released
Hadley Cell
Convection Currents that cycle between the equator, 30 degrees North and South.
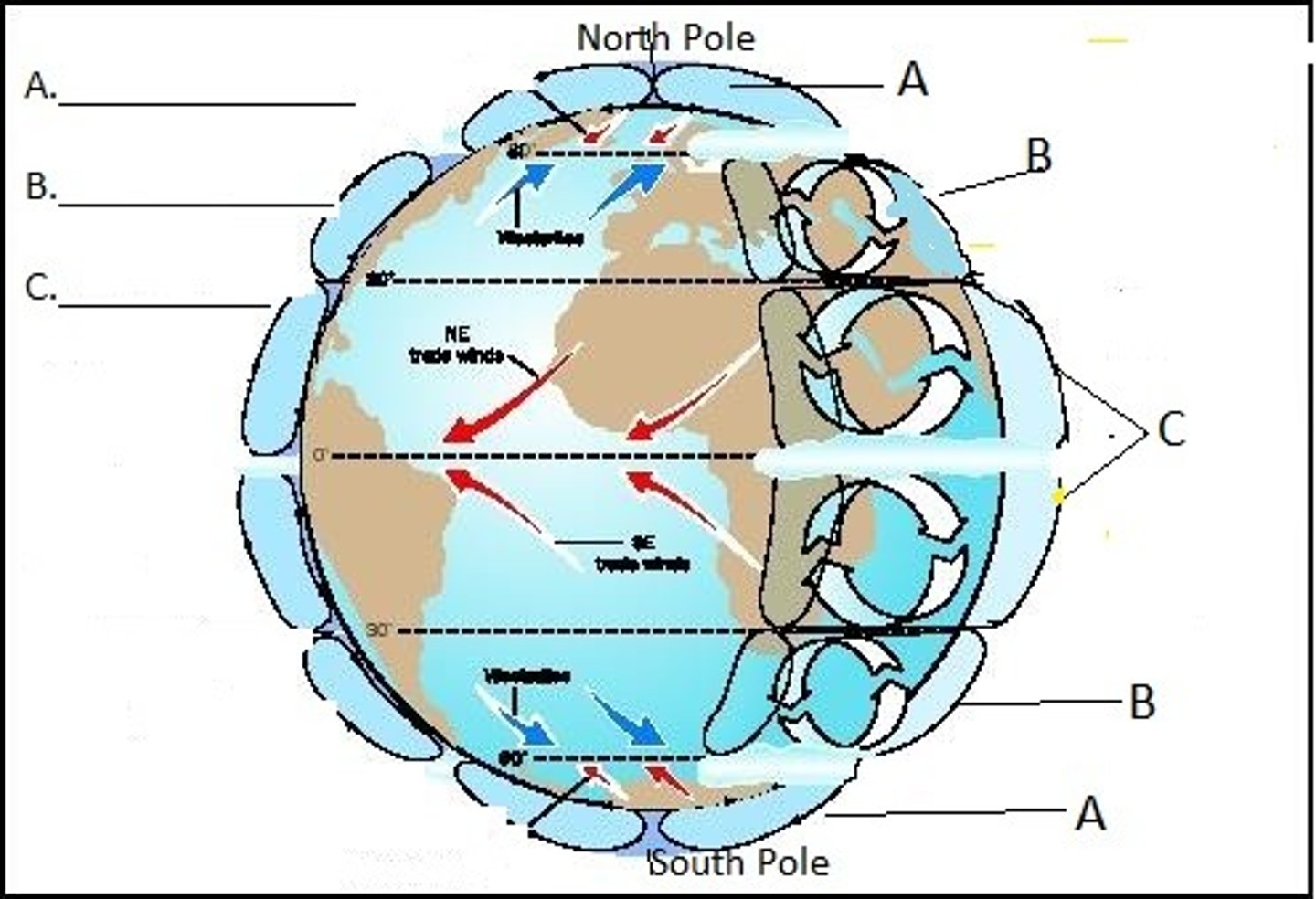
Intertropical Convergence Zone
Area of Earth that receives the most intense sunlight
Polar Cells
Air currents above 60 degrees North and South
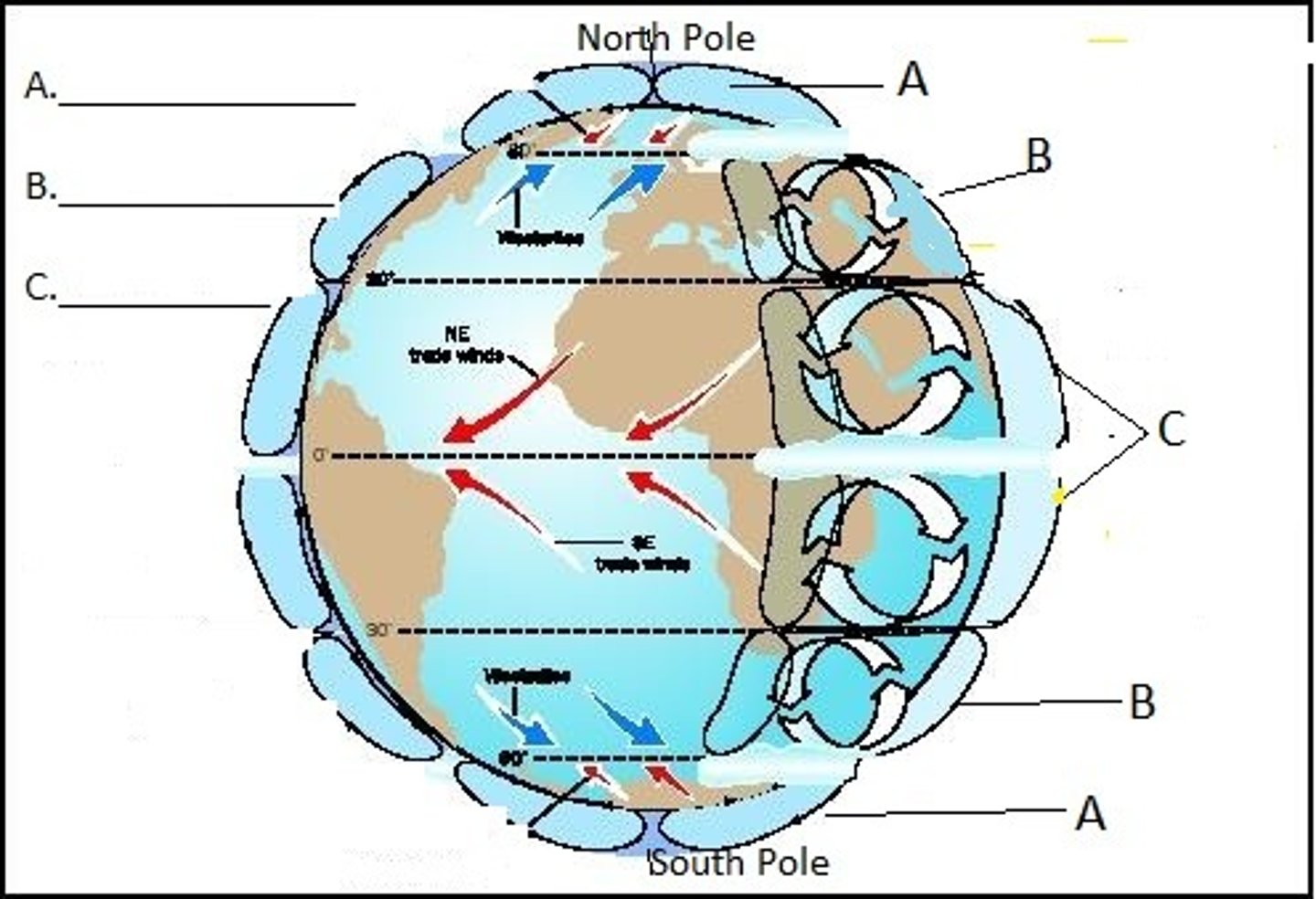
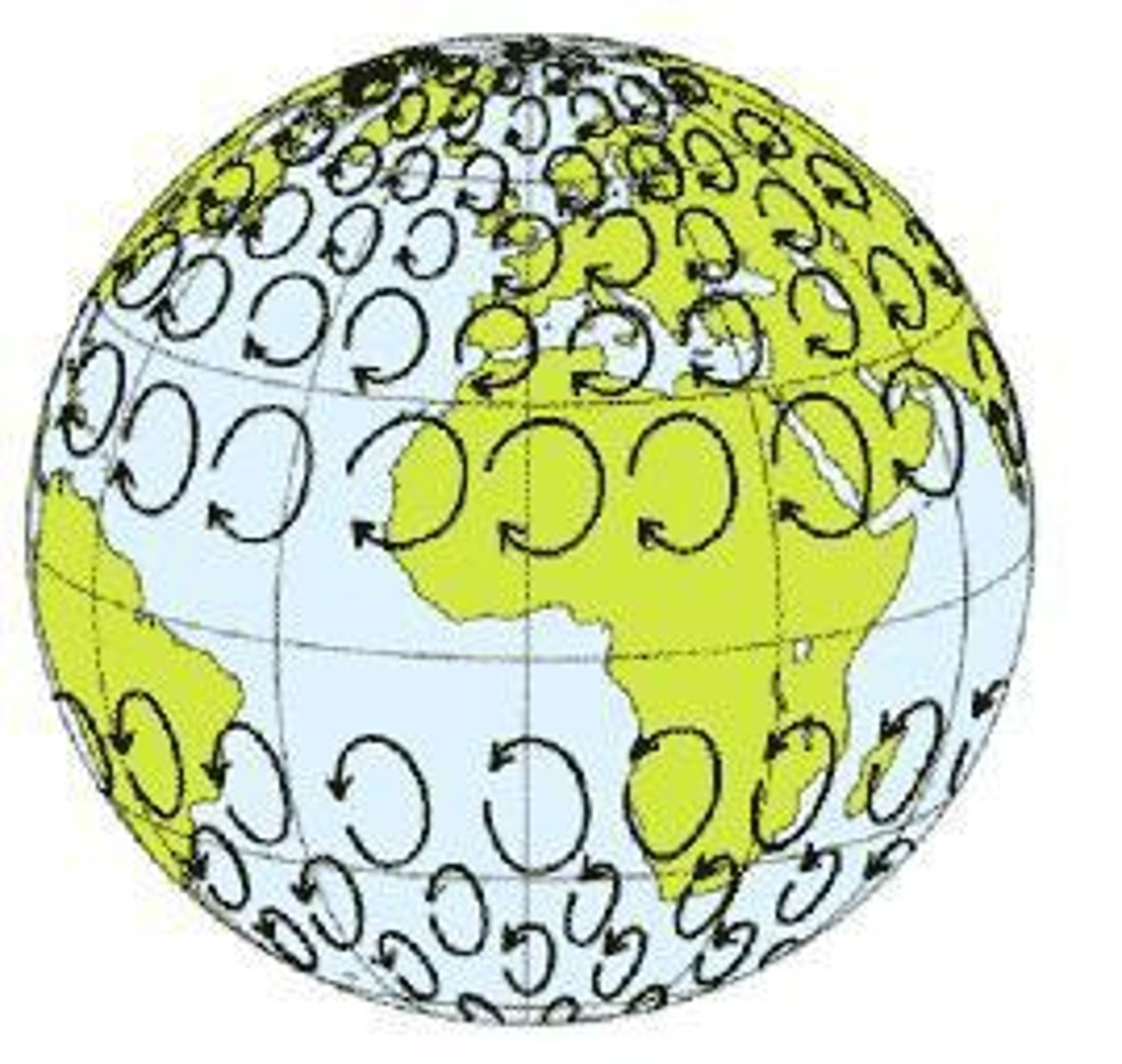
Coriolis Effect
The deflection of an objects path due to Earth's rotation
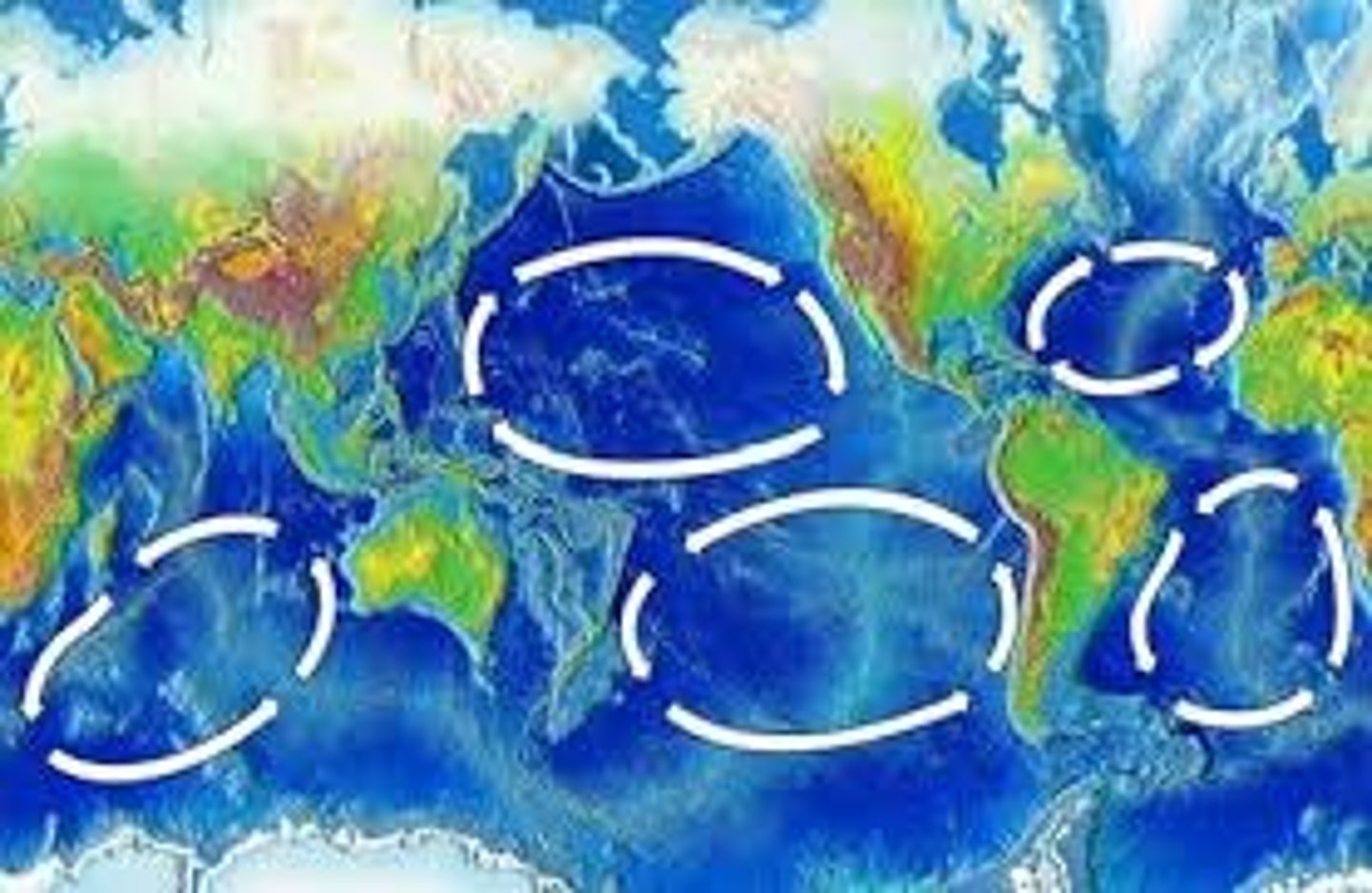
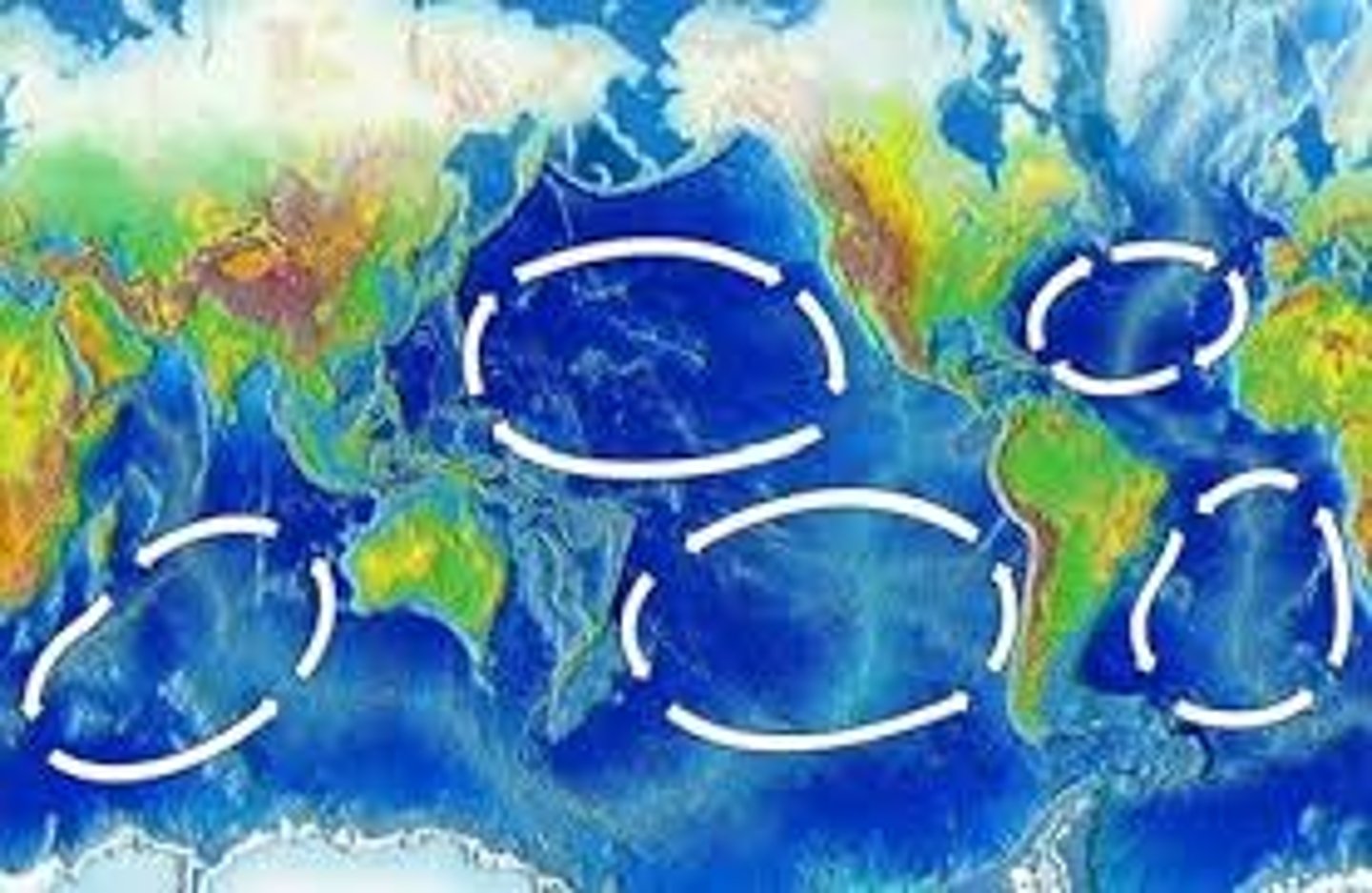
Gyres
Large scale patterns of Water circulation. Ocean surface currents rotate in a clockwise direction in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
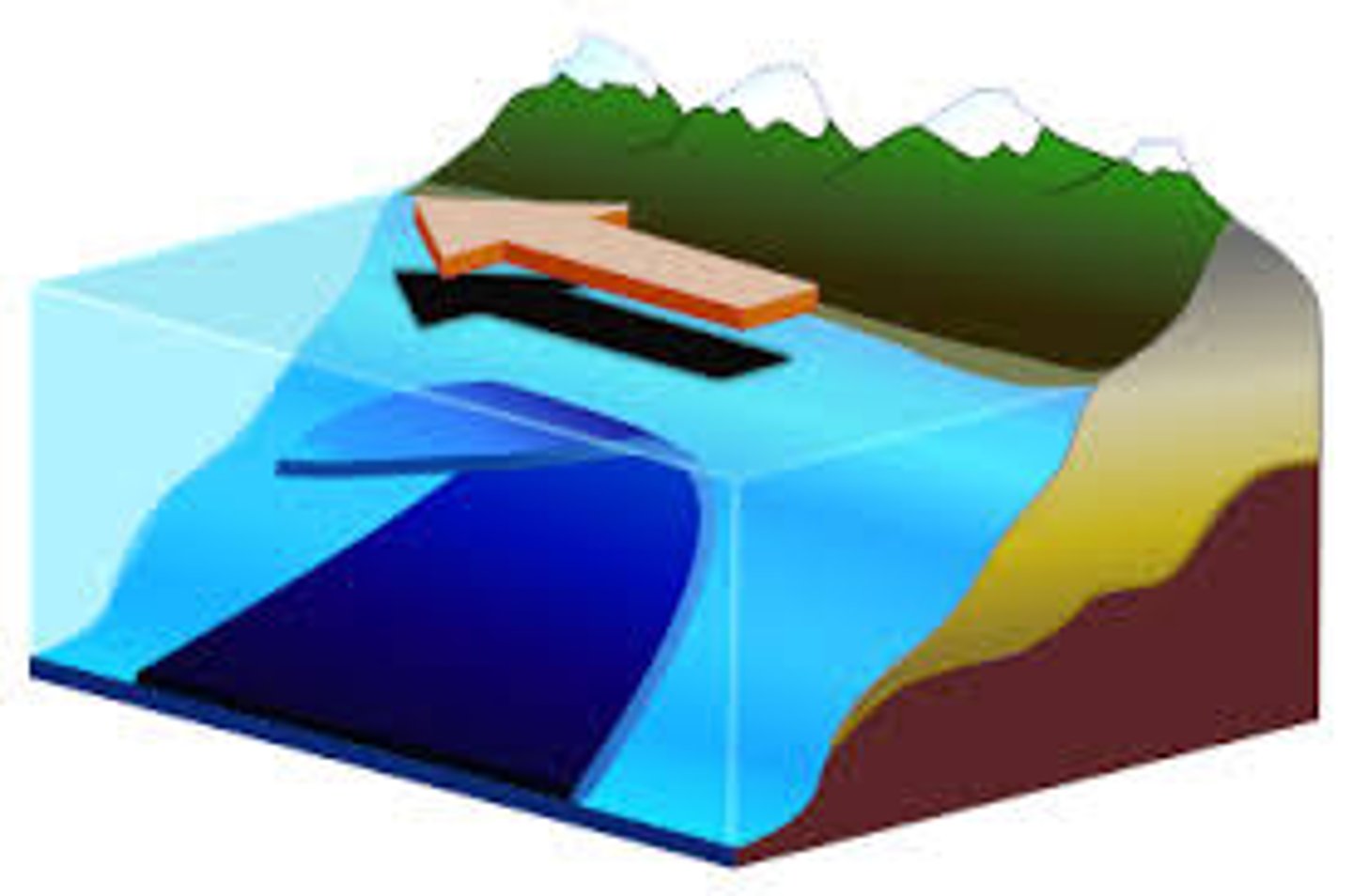
Upwelling
Deeper water rising and replacing the previous water. (The upward movement) brings in nutrients
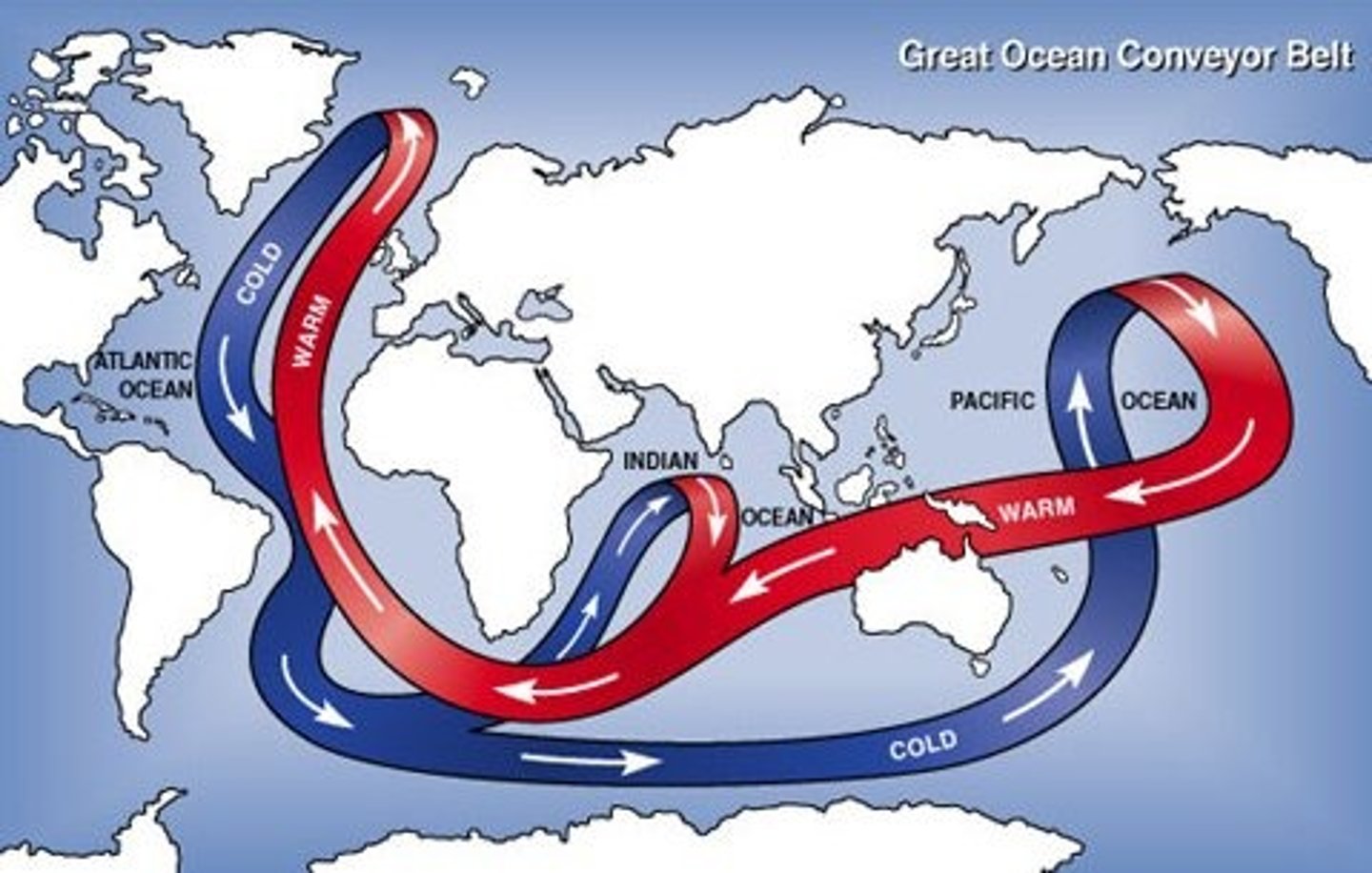
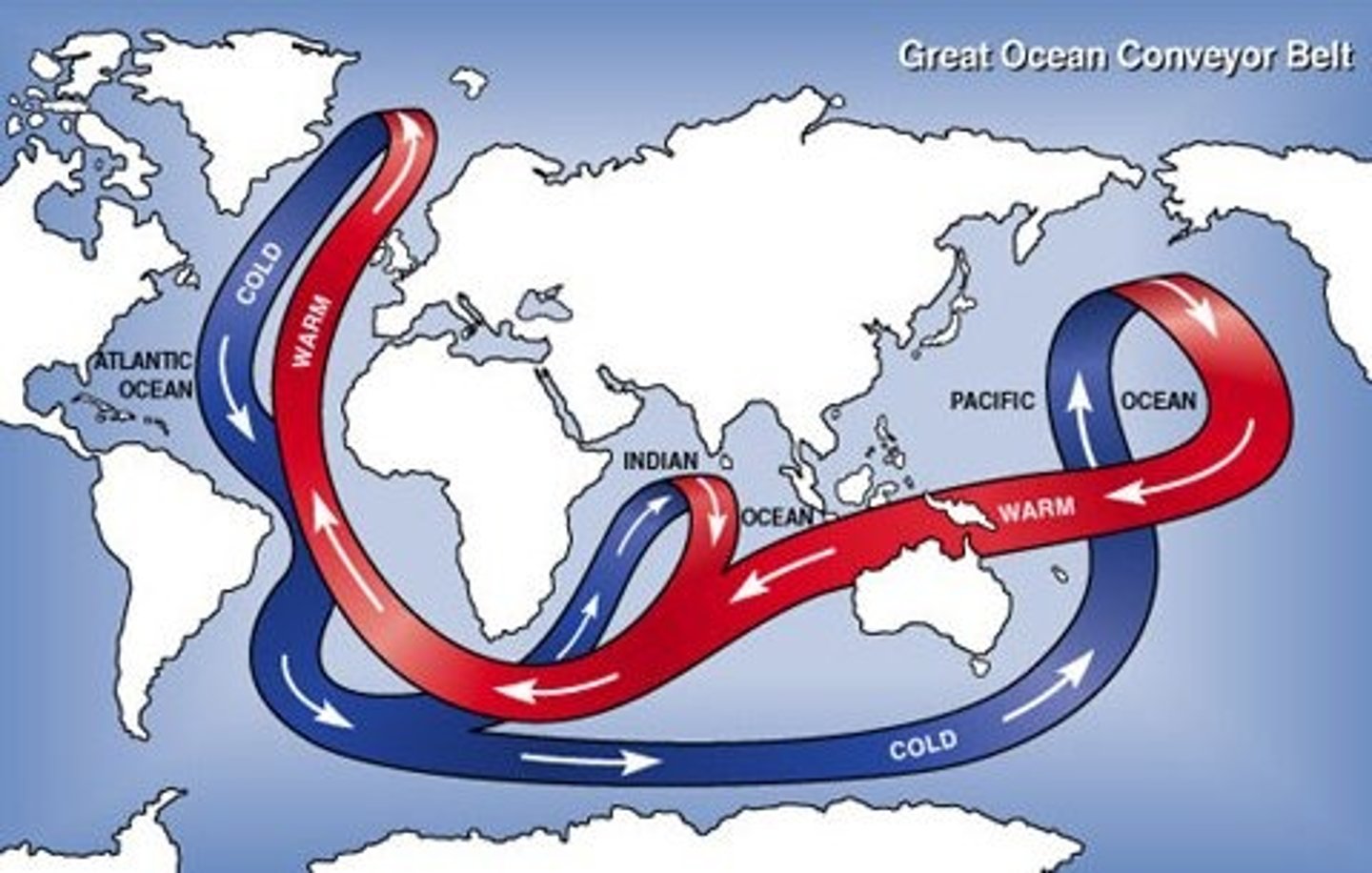
Thermohaline Circulation
Drives the mixing of surface water and deeper water. Critical for moving heat and nutrients around the globe.
El Nino-Southern Oscillation
Periodic changes in winds and ocean currents.
Rain Shadows
one side of a mountain receives all the rain while another does not due to moisture falling on the windward side of the mountain
stratosphere
which layer of the atmosphere contains the ozone?
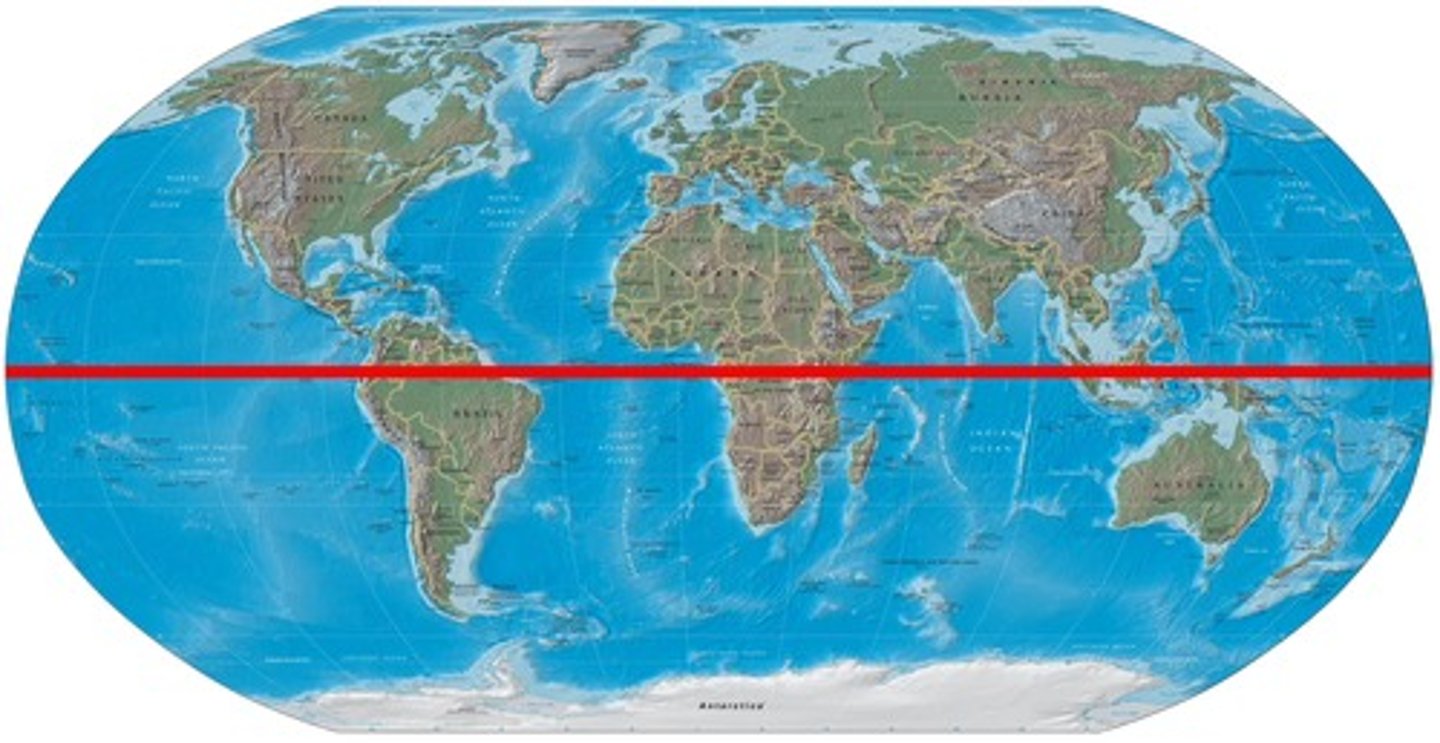
equator
at this location air rises and large amounts of precipitation fall
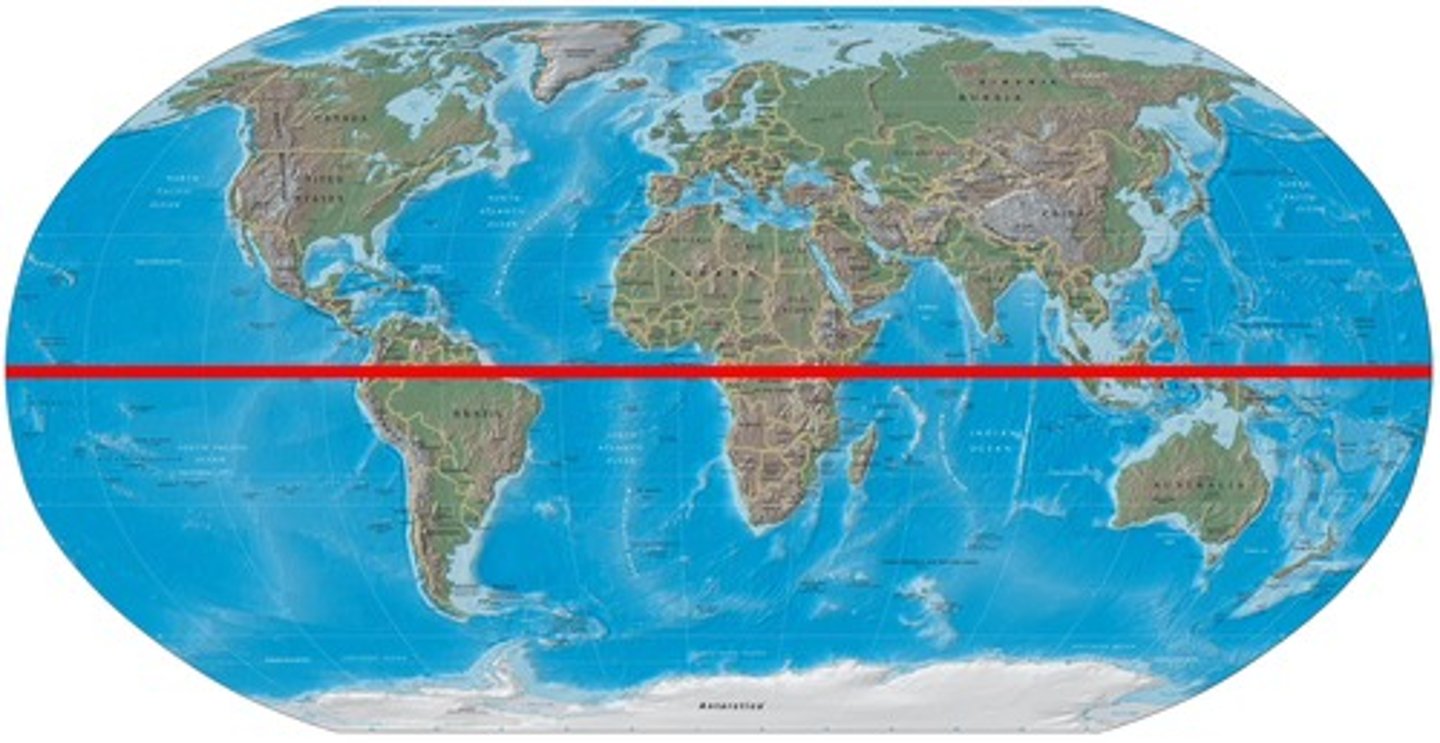
equator or 0 degrees
at what position on earth does the earth move at the highest velocity?
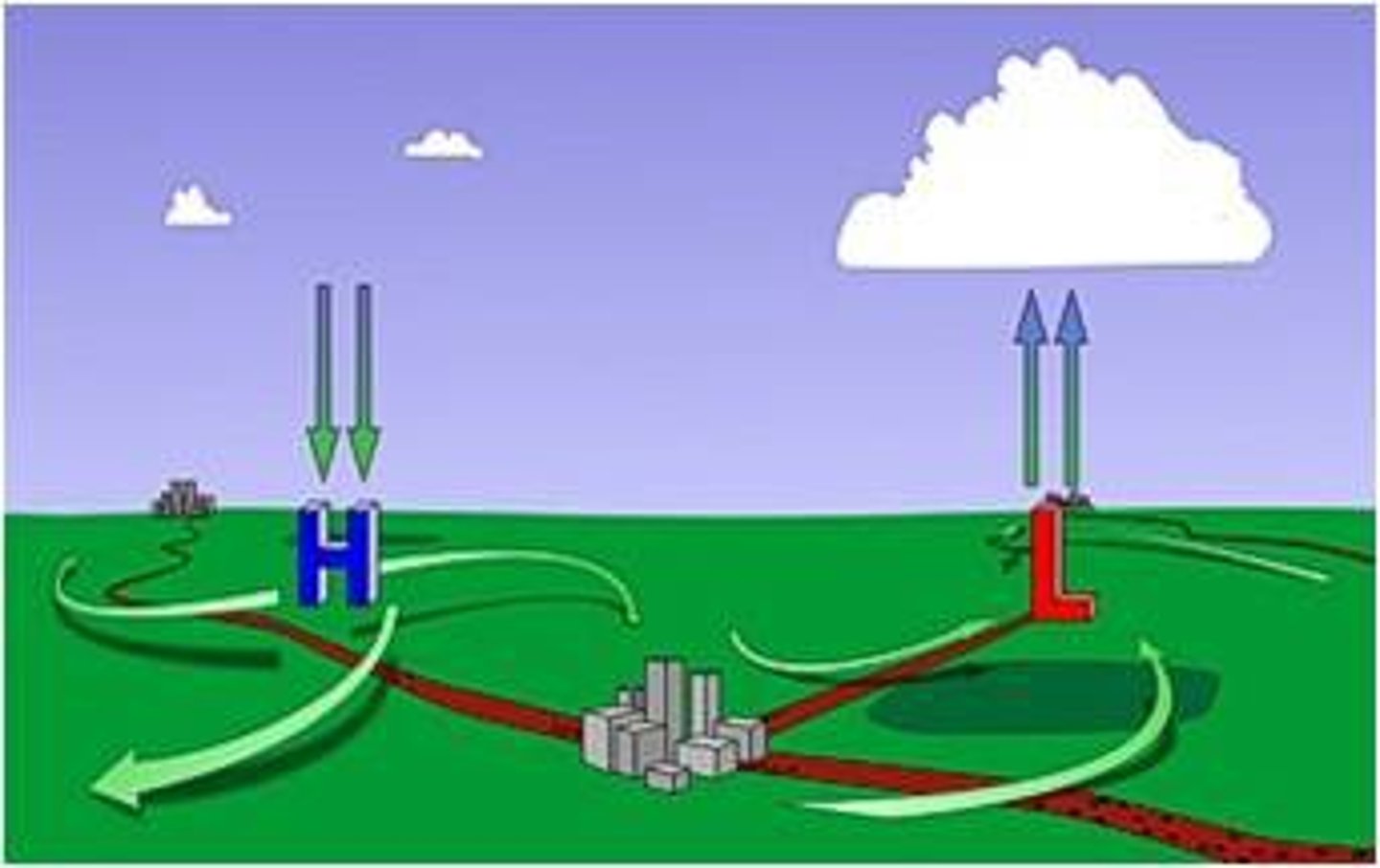
High Pressure
what type of pressure would we expect do see in desert biomes?
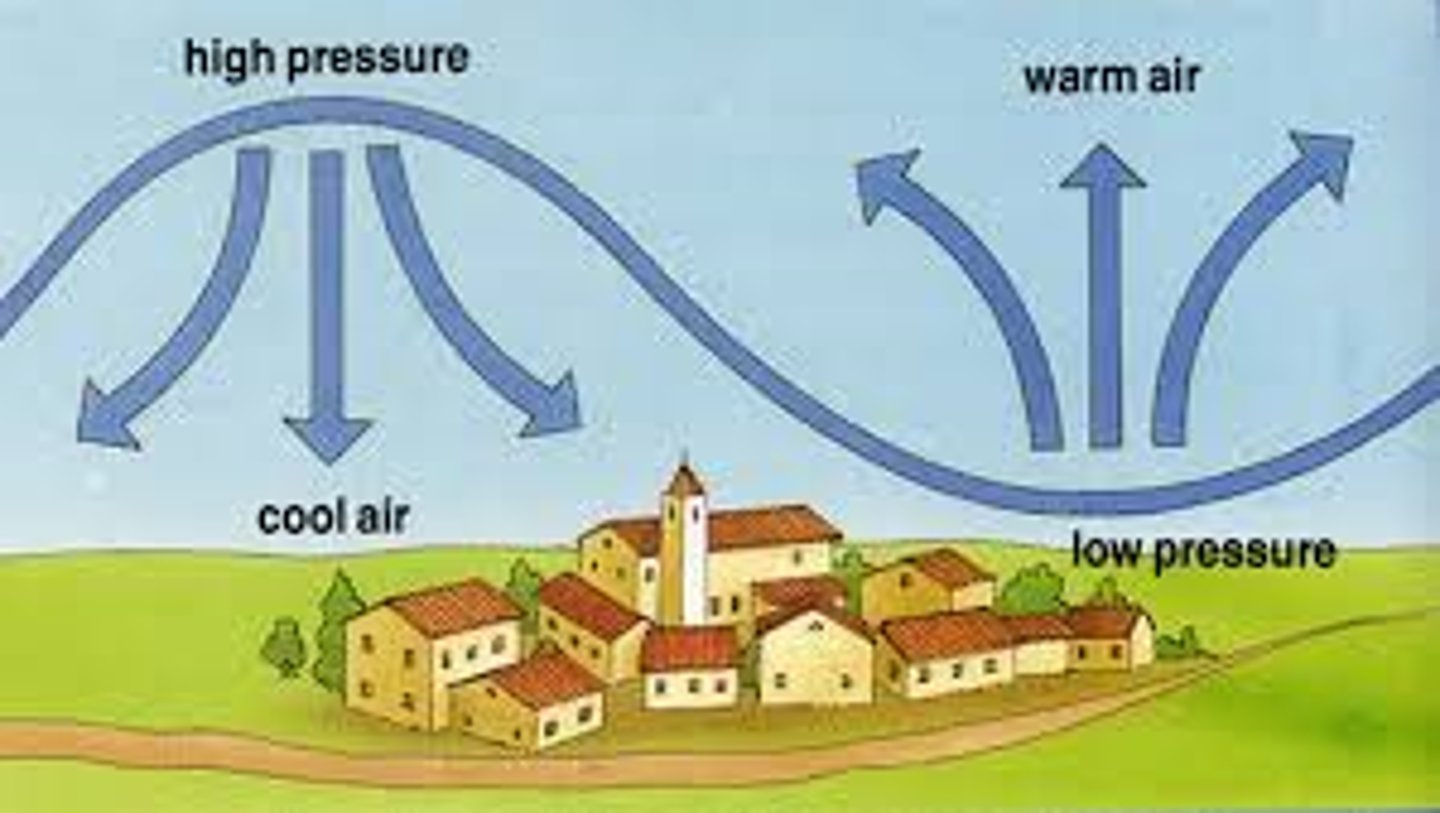
Low Pressure
what type of pressure would we expect to see at the equator and around 50-60 degrees north latitude?
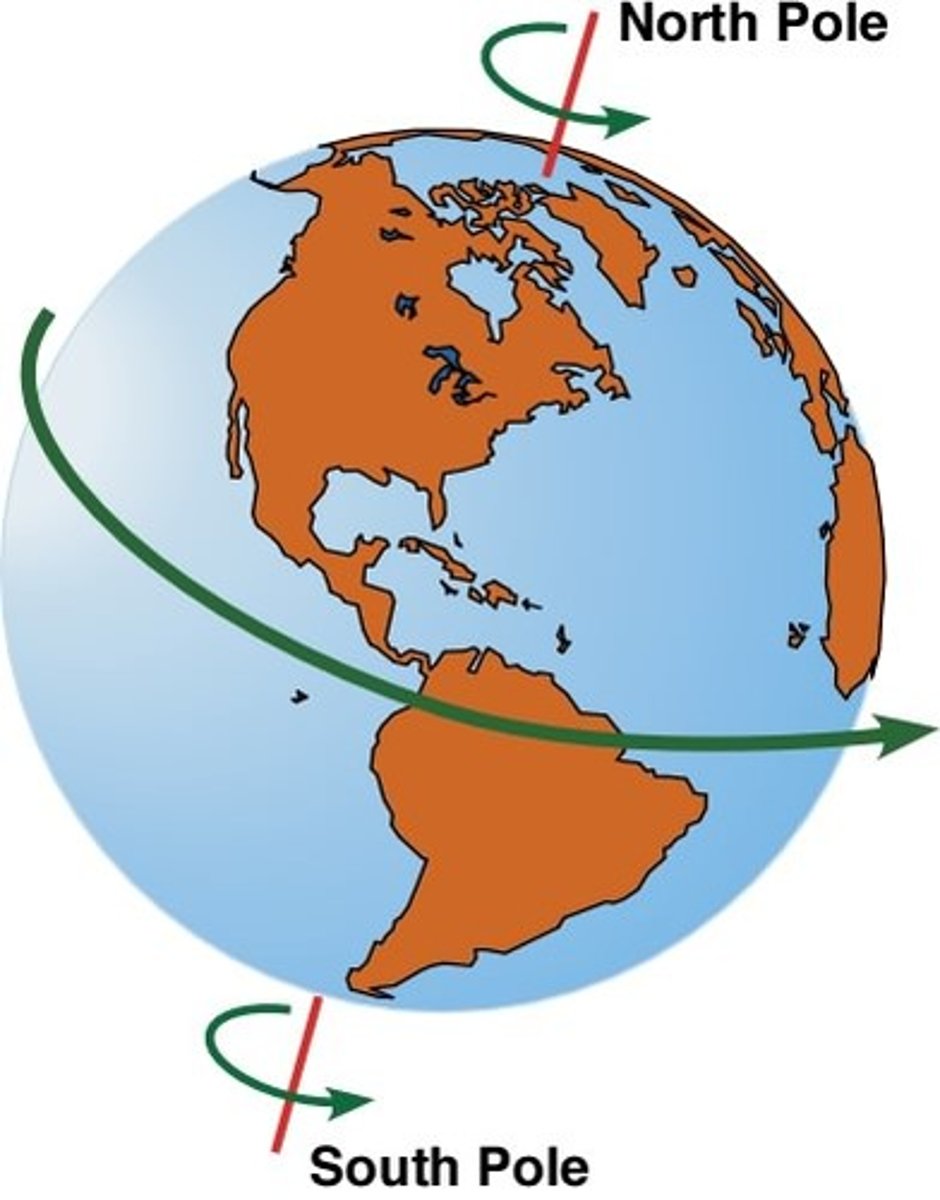
clockwise
which direction do gyres flow in the northern hemisphere?
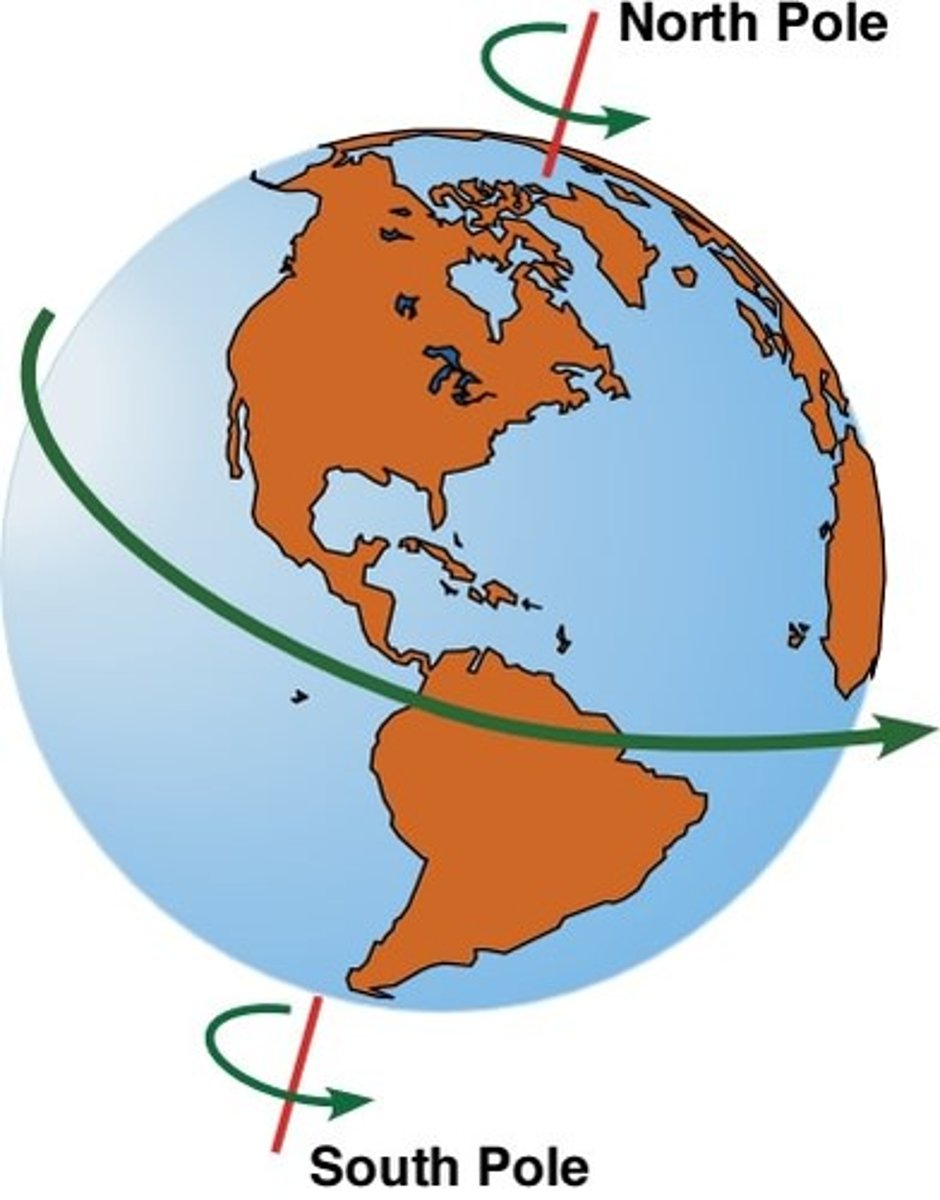
counterclockwise
which direction to gyres flow in the southern hemisphere?
global conveyor belt
what term describes the deep water circulation of the ocean?
Left side
which side is the windward and wet side?
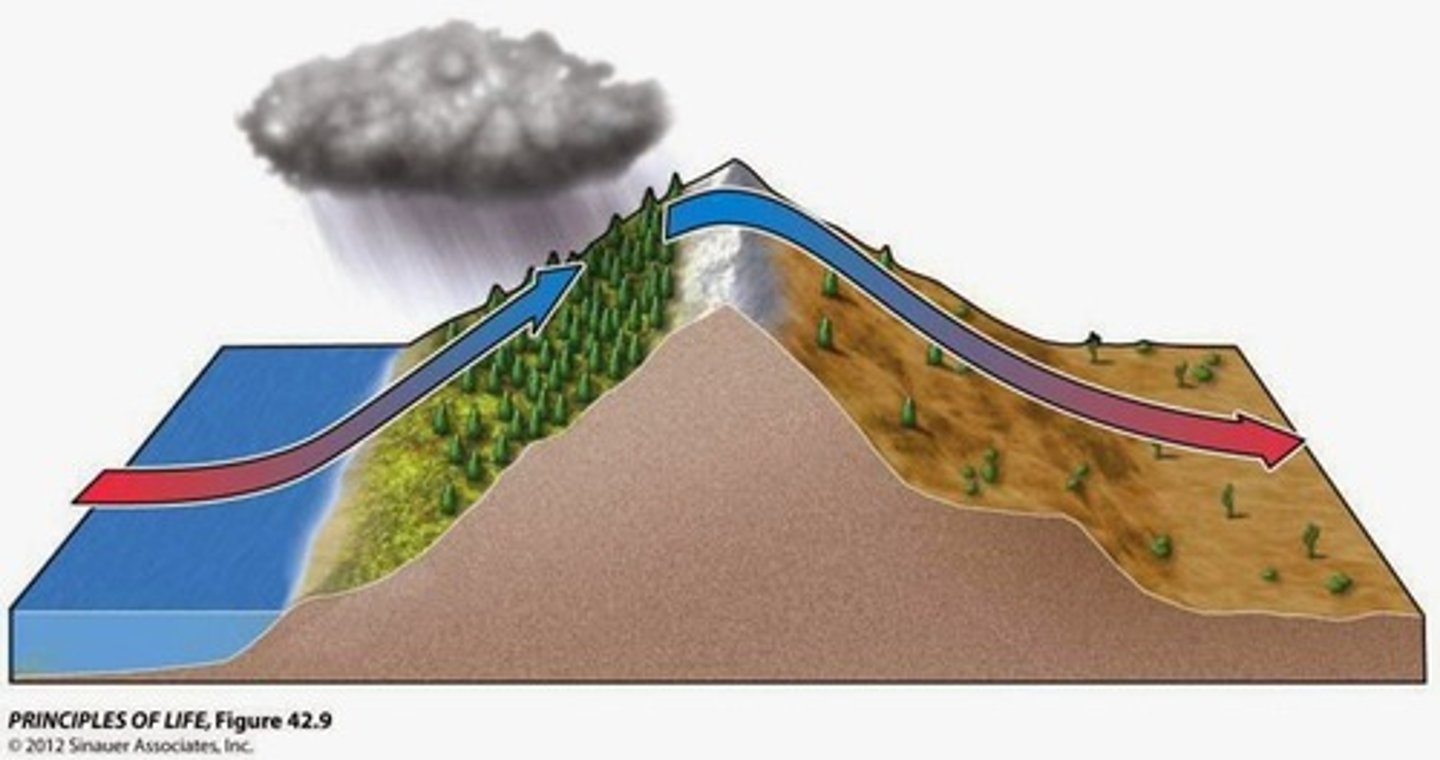
right side
which side is the leeward and dry side?
it decreases
what happens to temperature as you move upward through the troposphere?
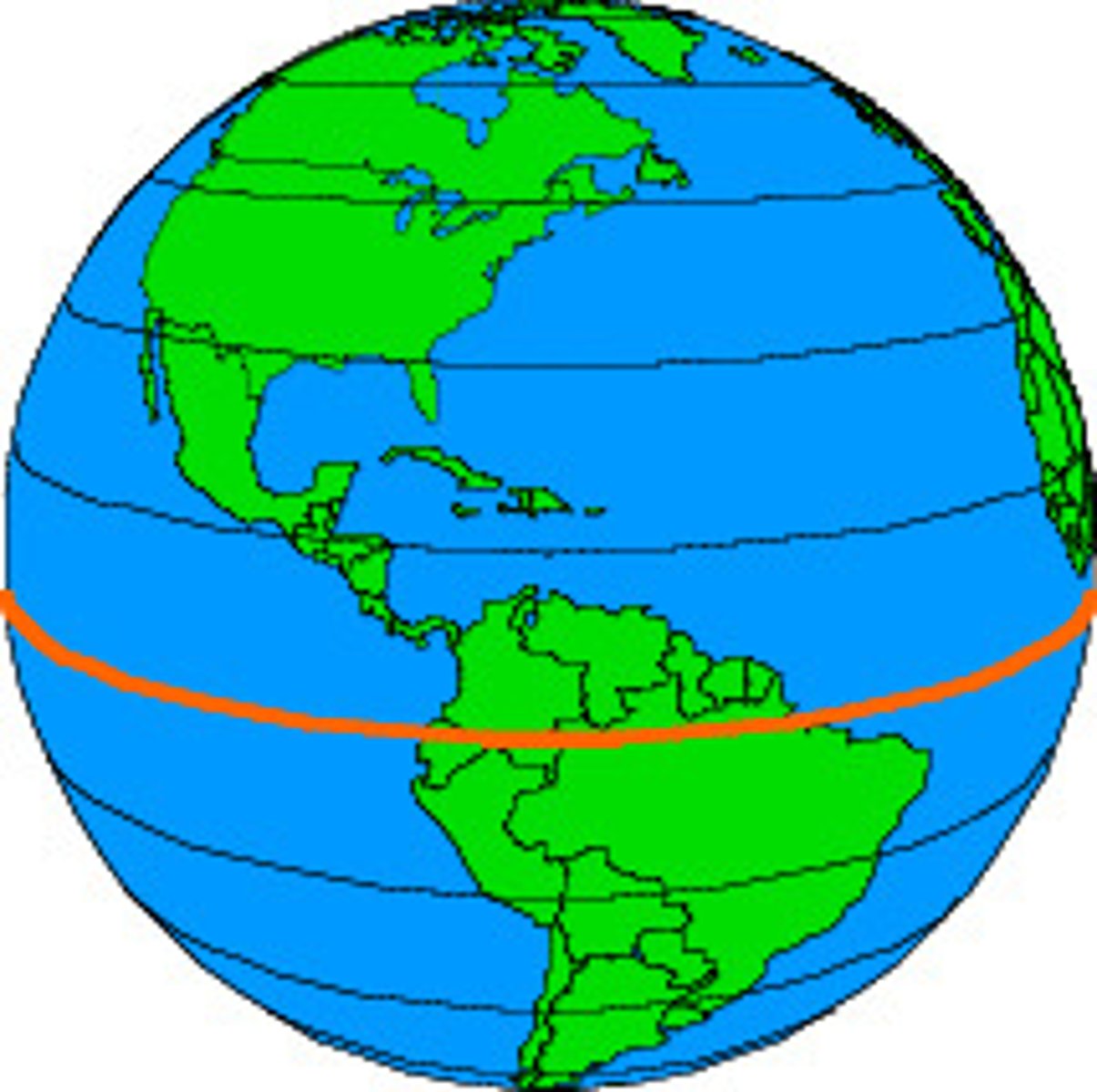
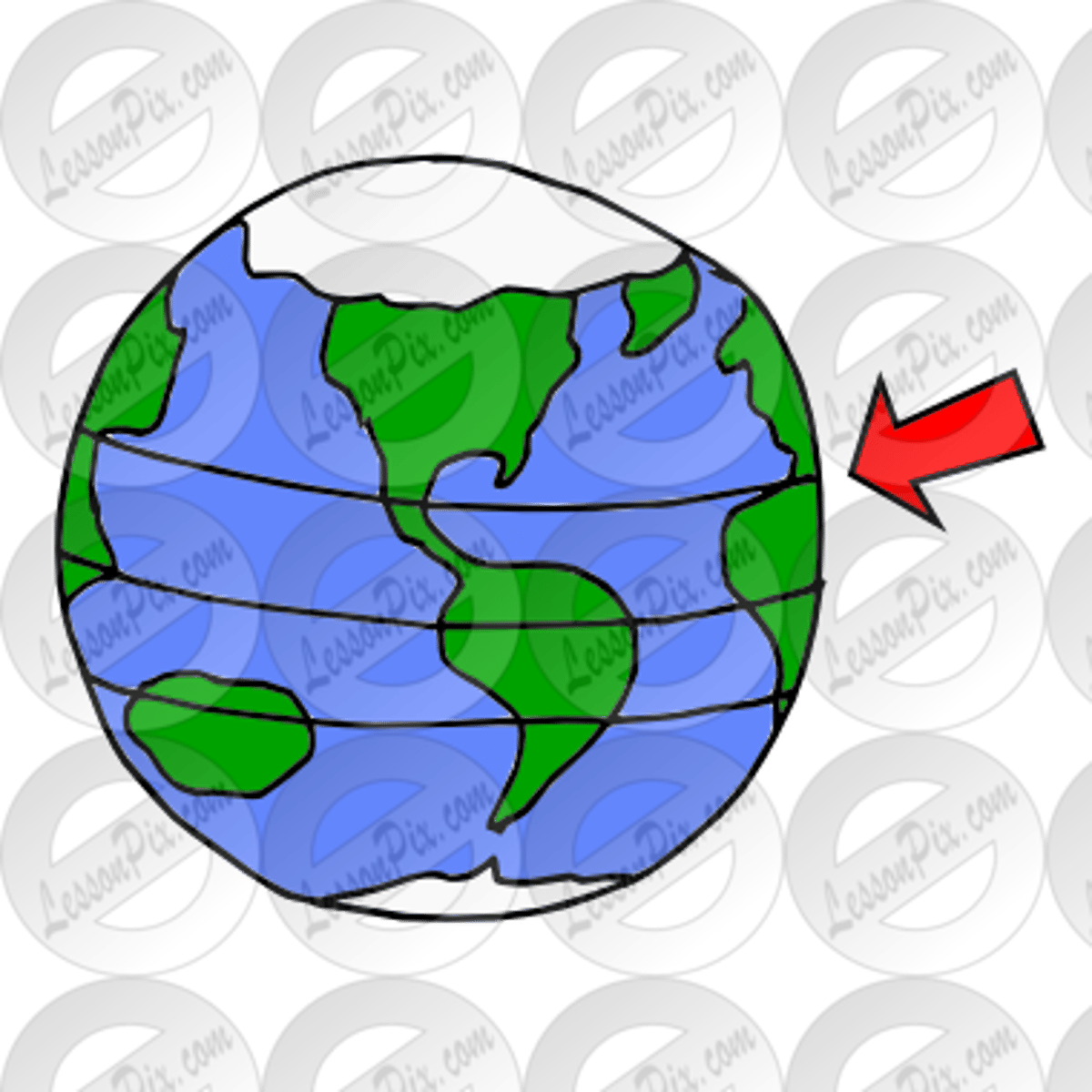
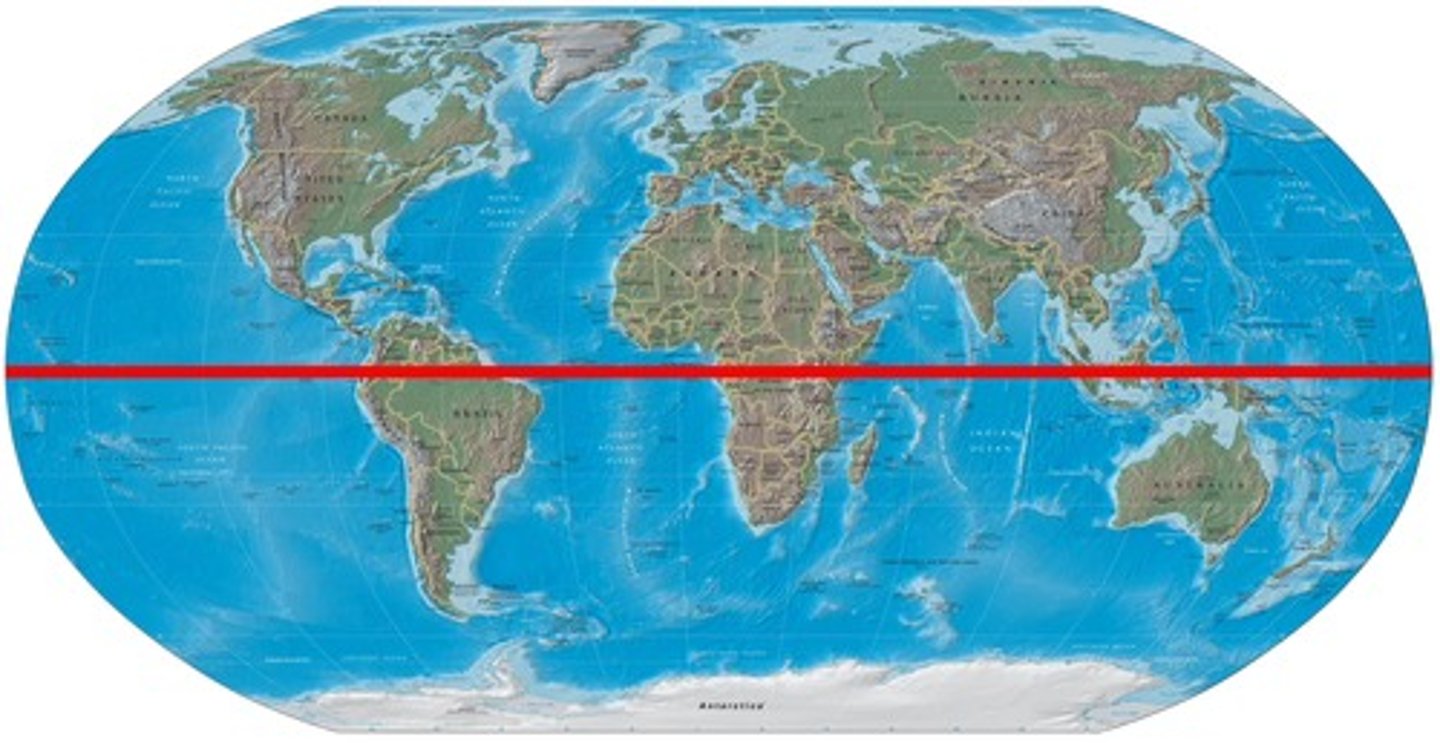
Tropic of Cancer
what line is the arrow pointing to?
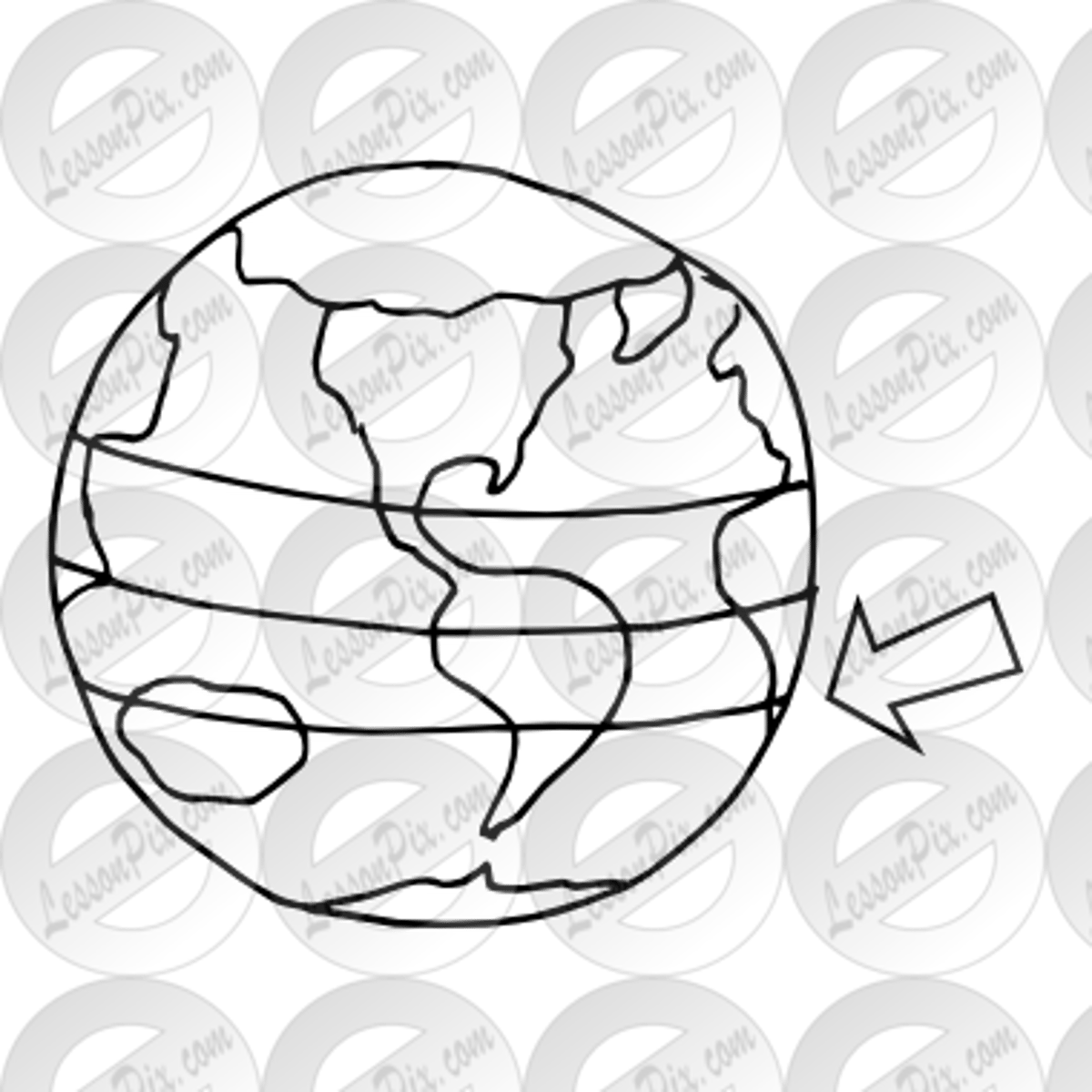
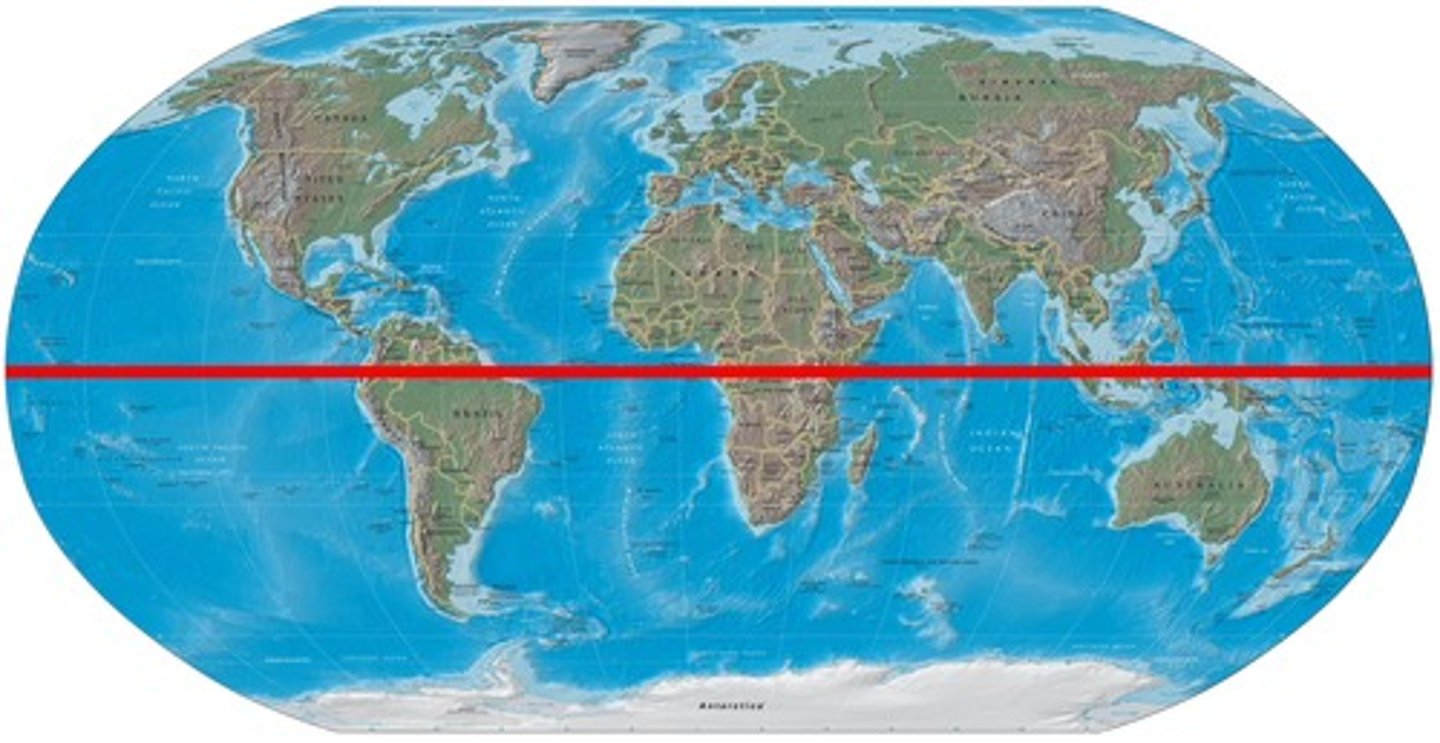
Tropic of Capricorn
what line is the arrow point to?
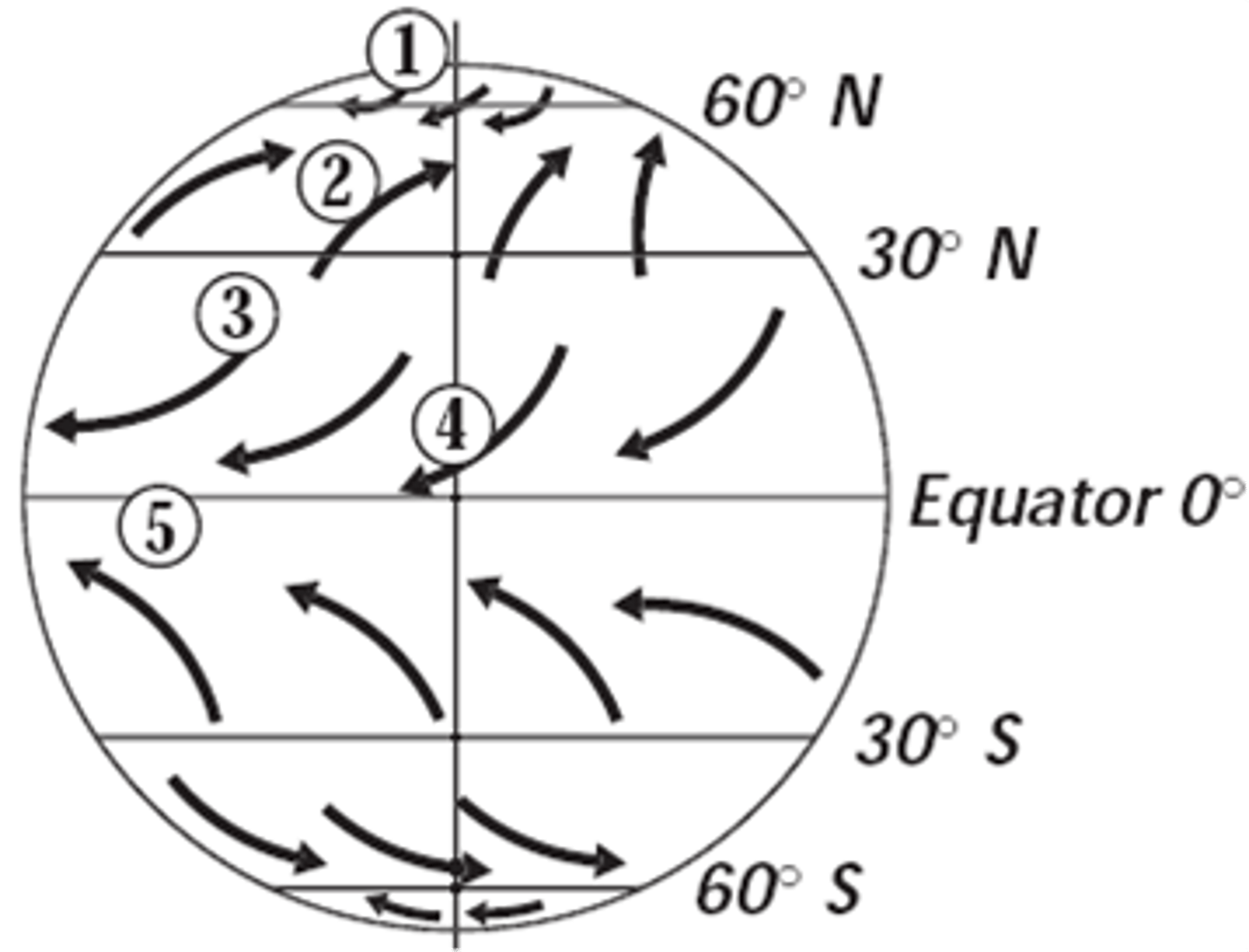
1. polar easterlies
2. westerlies
3. Northeast Trade Winds
4. ITCZ (Intertropical convergence zone)
5. Southeast Trade WInds
label 1-5
Equinox
This happens twice a year in the spring and fall when there is approximately equal lengths of day and night all over the earth.
troposphere
The densest layer of the atmosphere is the _________
Upward
In what direction does the air generally move at the equator?
3 multiple choice options
Downward
In what direction does the air generally move at the poles?
3 multiple choice options
High, since the air is falling
Generally what type of pressure system is found at the poles?
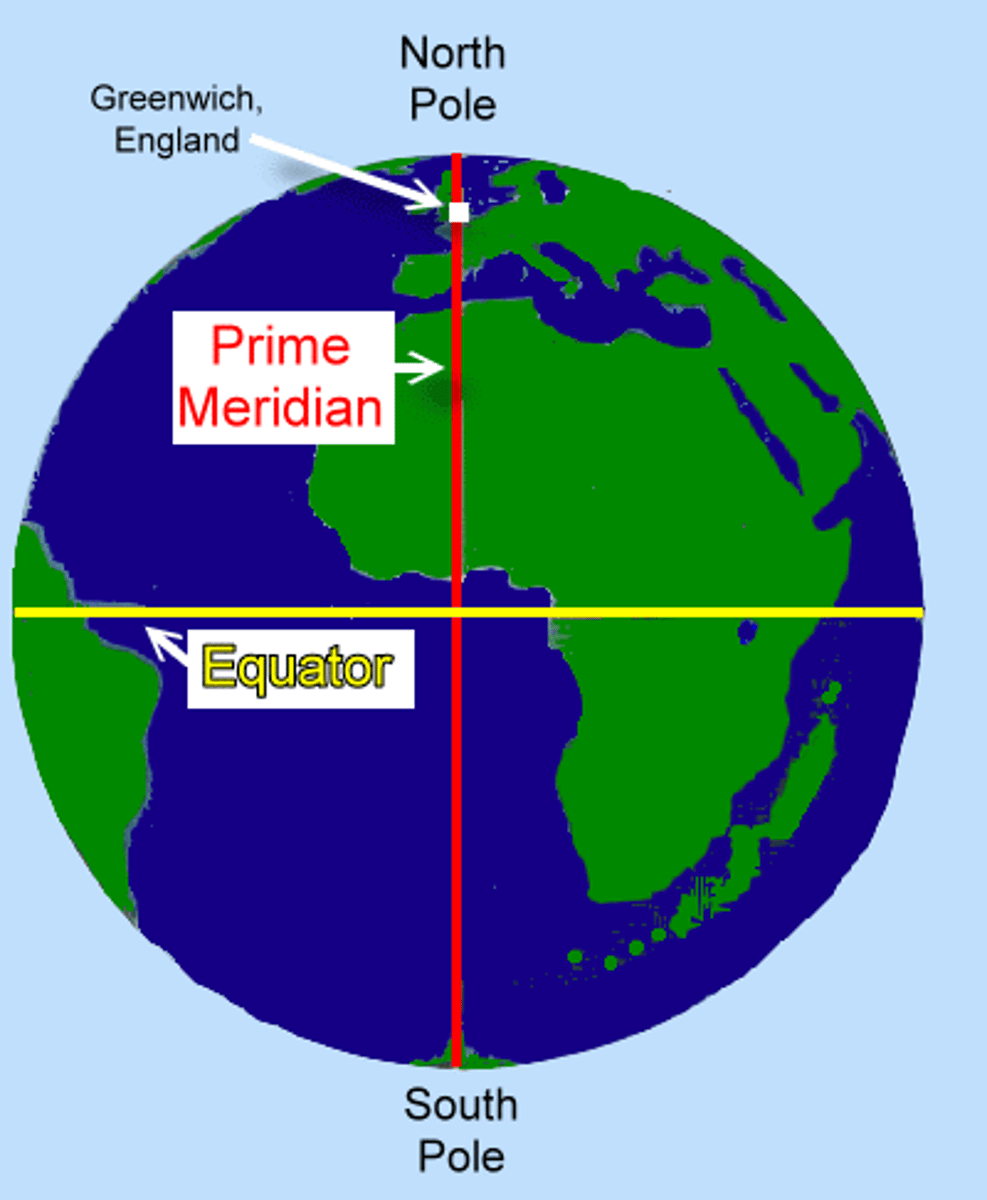
Low, since the air is rising
Generally what type of pressure system is found at the equator?
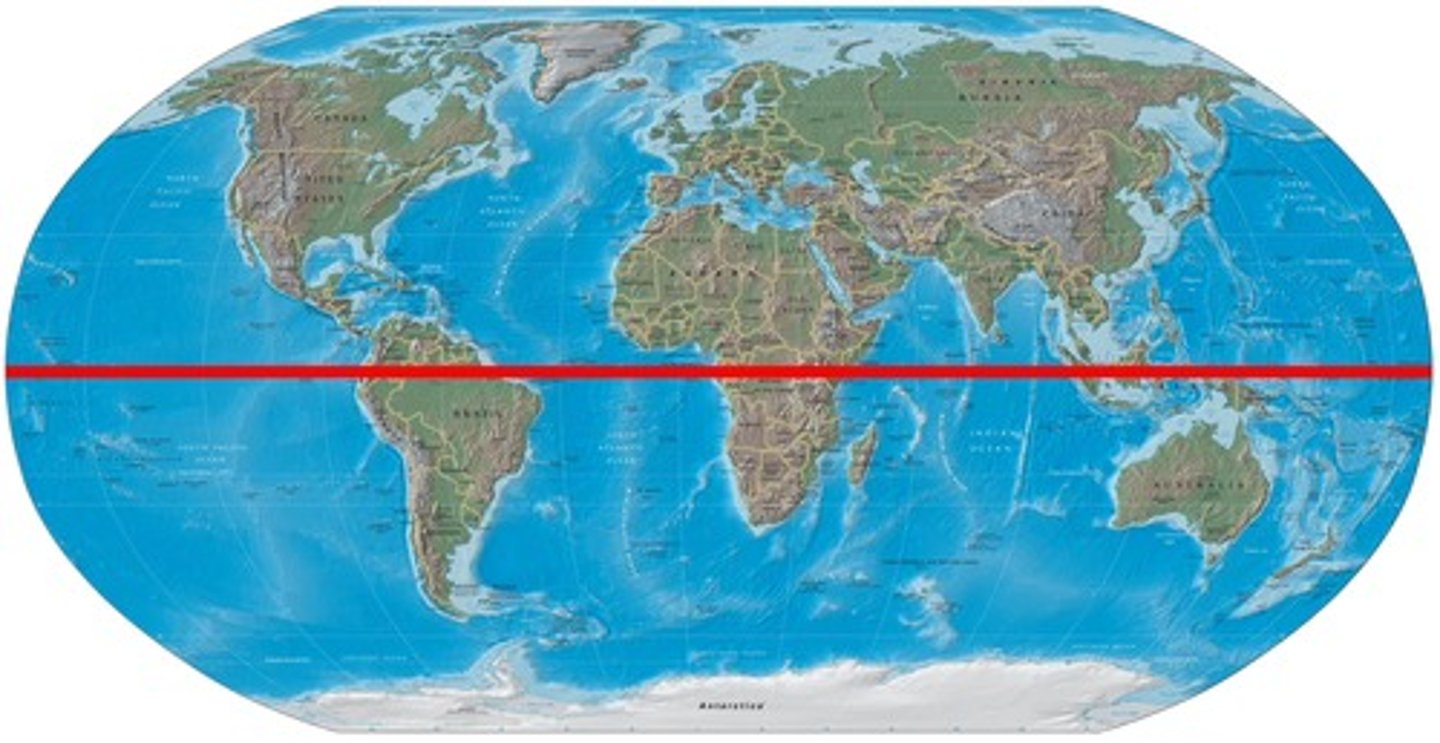
gyres
the major role of these is that they distribute heat from the Equator to Northern latitudes (and to southern latitudes)
Tropical Pacific Ocean
where does El Nino occur?
leeward
what side of the mountain receives the least rain in the rain shadow effect?
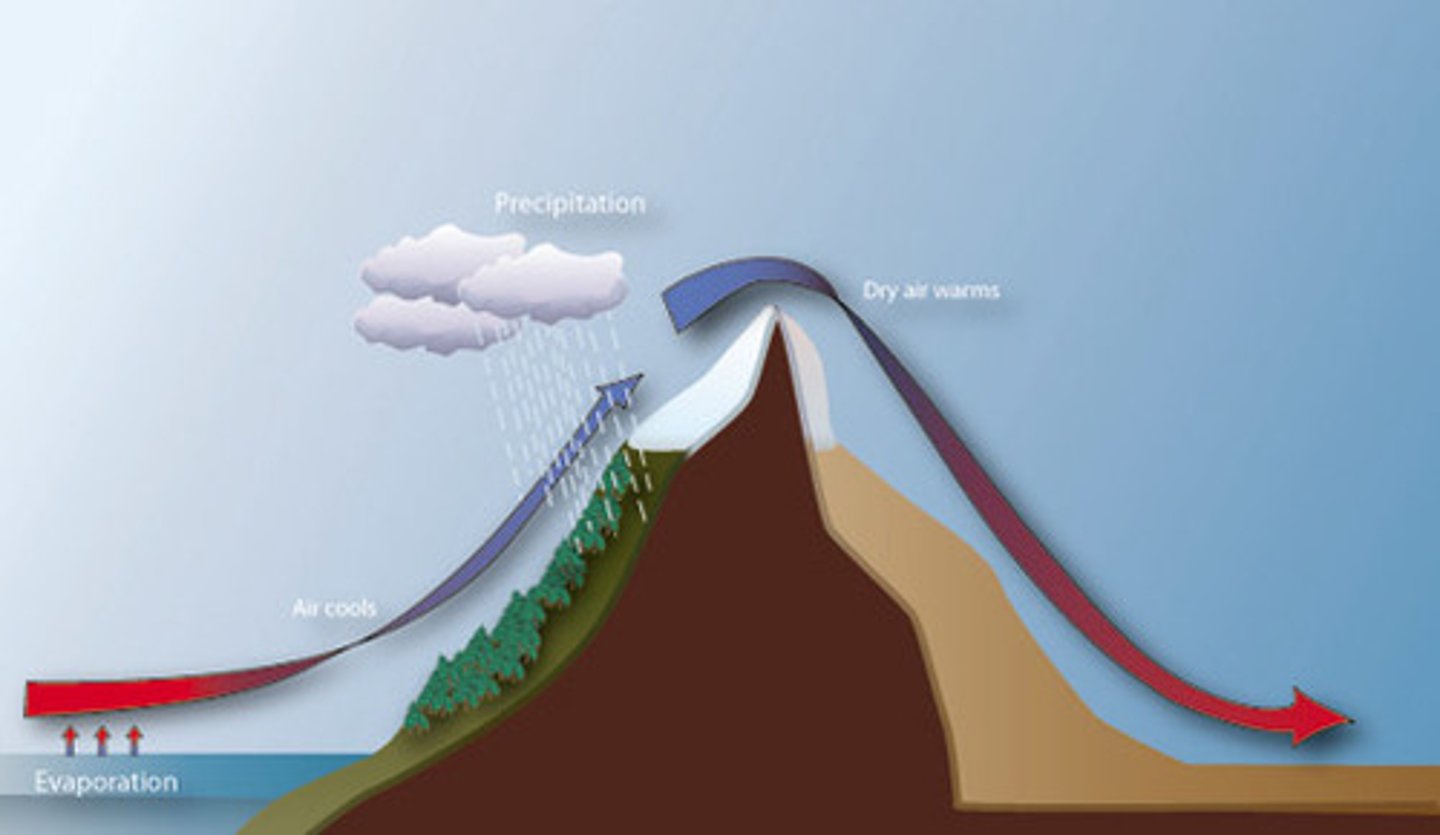
windward
What side of the mountain receives the most rain in the rain shadow effect?