lab techniques
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MCAT lab techniques
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
what do boiling chips do in distillation?
provide a site for gas bubbles to form (nucleation site), preventing the liquid or solution from superheating by ensuring smooth boiling and preventing bumping.
what is a vacuum’s use in distillation?
It lowers pressure inside flask, lowering the boiling point of liquids, allowing for distillation at reduced temperatures and minimizing thermal decomposition.
If gibbs free energy is negative, Keq is (less than or greater than) 1?
Keq is greater than 1
Means that at equilibrium, the products of the reaction predominate over the reactants
Keq > 1 according to dG=-RTln(Keq)
how do you know if an atom can have an expanded octet?
if they are at period 3 or beyond of the periodic table
Ex: phosphorus, sulfur, or chlorine, xenon, bromine, iodine
accommodate more than eight electrons in their valence shell due to having a d-orbital
count total number of valence electrons
subtract bonds
subtract the remaining lone pairs for substituents
remaining electrons/2 are the number of lone pairs
explain hydrophobi molecules in water vs hydrophilic molecules in terms of entropy and energetic favorability
Type | Water Behavior | Entropy (ΔS) | Energy Favorability |
|---|---|---|---|
Hydrophobic | Water forms ordered shell | ↓ (decreases) | Unfavorable |
Hydrophilic | Water bonds freely, stays fluid | ↑ (increases) | Favorable |
hydrophobic effect
Locally around each individual nonpolar molecule → entropy ↓ (because of the ordered shell)
When nonpolar molecules aggregate (hydrophobic effect) → overall system entropy ↑ (because water molecules are freed up and become more disordered)
The phenomenon where nonpolar molecules cluster together in aqueous environments, leading to an increase in overall entropy as water molecules are released from their ordered state around individual nonpolar molecules.
what is the relationship between Keq, Ka, and Kd?
Keq: equilibrium constant, which is Ka or Kd based on the direction.
Ka: association constant; 1/Kd
Kd: dissociation constant; 1/Ka
electrolytic cells vs. galvanic cells vs. capacitors
Feature | Electrolytic Cells | Galvanic Cells | Capacitors |
|---|---|---|---|
Function | Convert electrical energy into chemical energy consume electrical energy to drive chemical rxns | Generate electrical energy from spontaneous chemical reactions chemical rxn generates electrical energy | Store electrical energy as charge |
Reaction | Chemical reactions (oxidation/reduction) driven by an external power source | Spontaneous redox reactions generating electricity | No chemical reactions, just charge accumulation |
Energy Source | Requires external power to drive reaction | No external power needed; energy is generated spontaneously | Does not need external power once charged |
Energy Flow | Electrical energy is consumed to drive chemical reactions | Electrical energy is produced by spontaneous reactions | Energy is stored and released when needed |
Uses | Electroplating, electrolysis, chemical synthesis | Batteries, fuel cells, galvanic batteries | Smoothing circuits, power backup, storing energy for flashes |
Example | Electrolysis of water into hydrogen and oxygen | Zinc-copper galvanic cell (e.g., battery) | Storing energy for a flash in a camera |
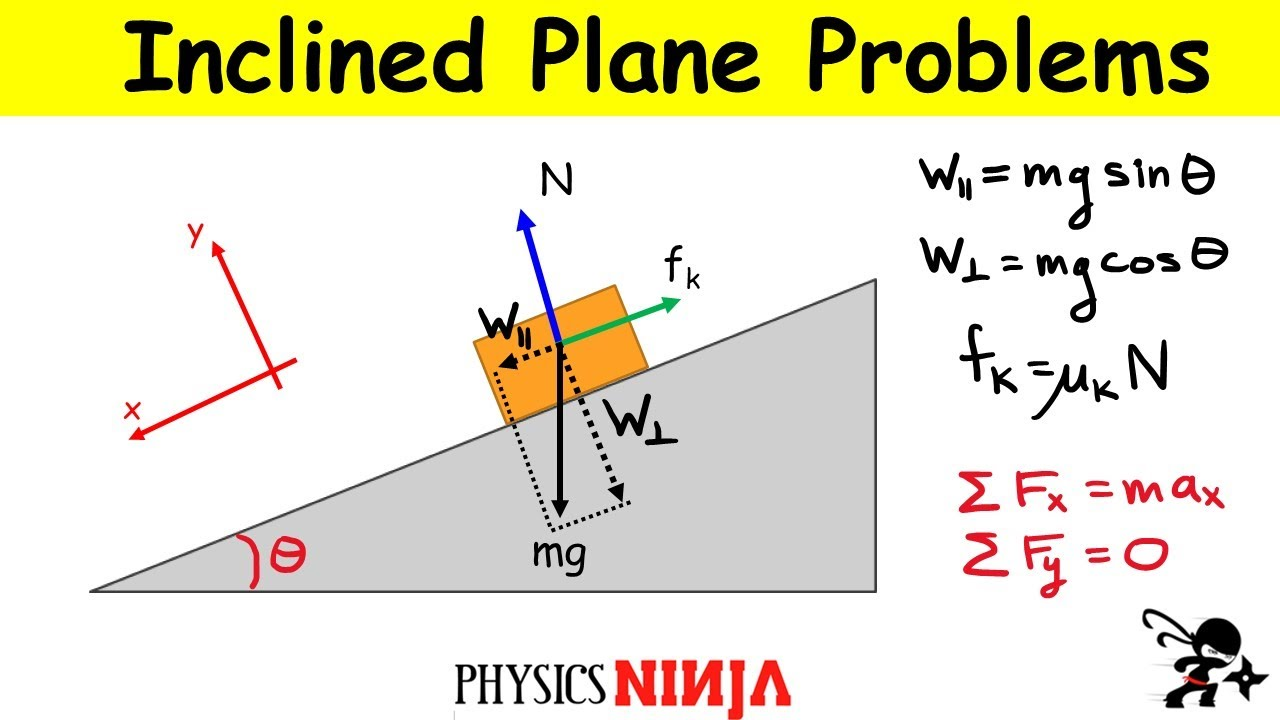
forces on ramp physics questions
mgcosθ: crushing force; perpendicular to plane
mgsinθ : sliding force; parallel to plane
what does heating the distillation flask at a slower rate do during fractional distillation?
the temperature raises more slowly. A slower heating rate ensures that heat is transferred effectively to the mixture, allowing the more volatile components to vaporize at their respective boiling points. This prevents the less volatile components from prematurely vaporizing, which can contaminate the distillate.
what does creating a lower pressure inside the distilling apparatus do in fractional distillation
lowers the boiling points of both liquids and NARROWS their difference in boiling point making it necessary to increase the length of the fractionating column to achieve the same degree of separation
what are the IR values for OH, C=O, C=C, sp3, and aromatics?
3300 (OH)
1700 (C=O)
1600 (C=C)
2800-3000 (SP3)
below 1600 (aromatics)
Gel filtration chromatography
Size exclusion chromatography
Smaller cells are trapped by pores and elute last
Bigger cells elute first (faster)