Embryology and pregnancy
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Gestation period
The entire pregnancy period starting at fertilization to birth (38 week)
Prenatal period
Period before birth where the embryo is developing
All principal adult organs are present
foetal development
Entire fetal development
Placenta is fully functional
Neonatal period
First 42 days after birth takes place
Physiology of lactation
is the production and release of milk
Prolactin from anterior pituitary increases during pregnancy
Progesterone inhibits effect of prolactin until delivery
After delivery, progesterone levels drop
Suckling increases the release of prolactin & oxytocin (milk ejection reflex)
Nursing causes neural feedback to the hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary gland
Which stimulates the production of PRF and prolactin
Helps mammary glands prepare for the next nursing period
When suckling stops, milk secretion stops
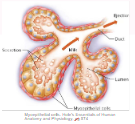
Milk ejection reflux
Oxytocin cause milk to become released into the mammary ducts
Stimulation of touching nipple causes hypothalamus to release oxytocin
Oxytocin causes a contraction of myoepethelial cells
Milk is moved from the alveoli into mammary ducts
Oxytocin release by other stimuli (Hearing a babys cry)
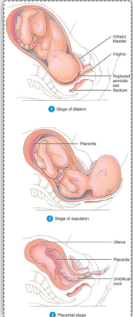
Stages of labour
Dilation
6-12 hours
Regular contractions of the uterus
Rupture of amniotic sac & dilation of cervix (10cm)
Expulsion
10 minutes to several hours
Baby moves through birth canal
Placental
30 minutes
Afterbirth is expelled by uterine contractions
Constrict blood vessels that were torn
Reduce the possibility of haemorrhage
True vs false labour
True labour begins when uterine contractions occur at regular intervals, usually producing pain
Other signs of true labour may be localization of pain in the back, which is affected by walking
Dilation of the cervix
“Show” signs (discharge of blood-containing mucus from the cervical canal)
False labour produces pain at irregular intervals but there is no cervical dilation
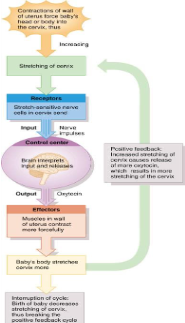
Positive feedback during labour
Uterine contraction forces foetal head into cervix (stretch)
Nerve impulses reach hypothalamus causing release of oxytocin
Oxytocin causes more contractions producing more stretch of cervix and more nerve impulses
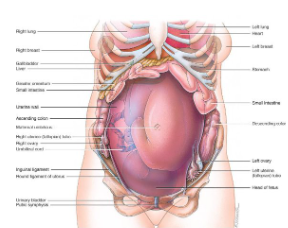
Anatomical and physiological changes during pregnancy
Weight gain
Increased protein, fat & mineral storage
Marked breast enlargement
Lower back pain
Increase in heart rate by 10-15%
Pulmonary function alterations
GI tract compressed
Heartburn & constipation
Pressure on bladder
Glomerular filtration rate rises
Compression of vena cava
Varicose veins & oedema in the legs
Skin may display increased pigmentation
Lactation
Production and release of milk