Microbiology Lab exam
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:05 AM on 6/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
1
New cards
what is aseptic technique
a way to handle microbes and limit contamination of media and self
2
New cards
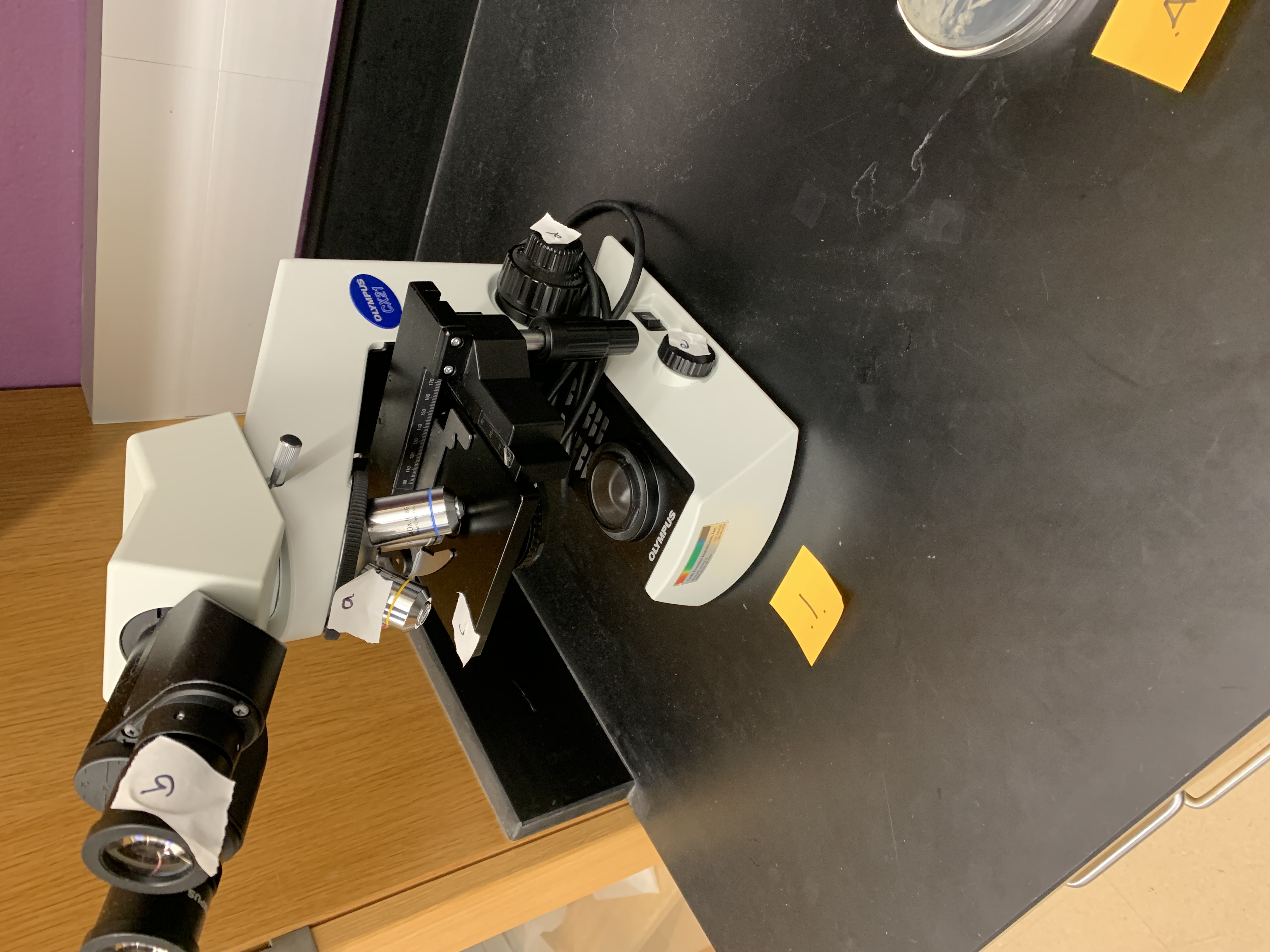

what is A
nose piece
3
New cards
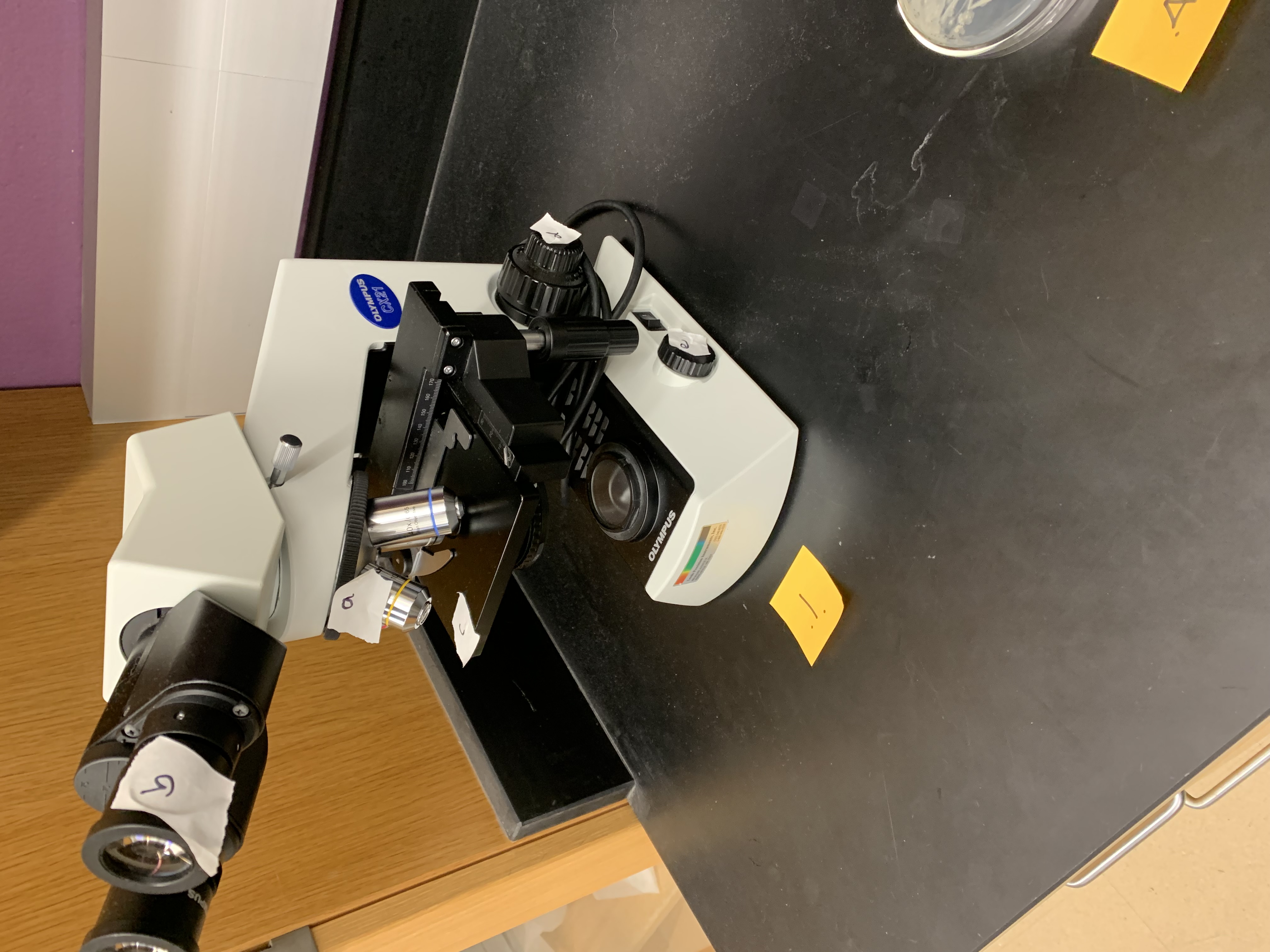

what is B
ocular lense
4
New cards
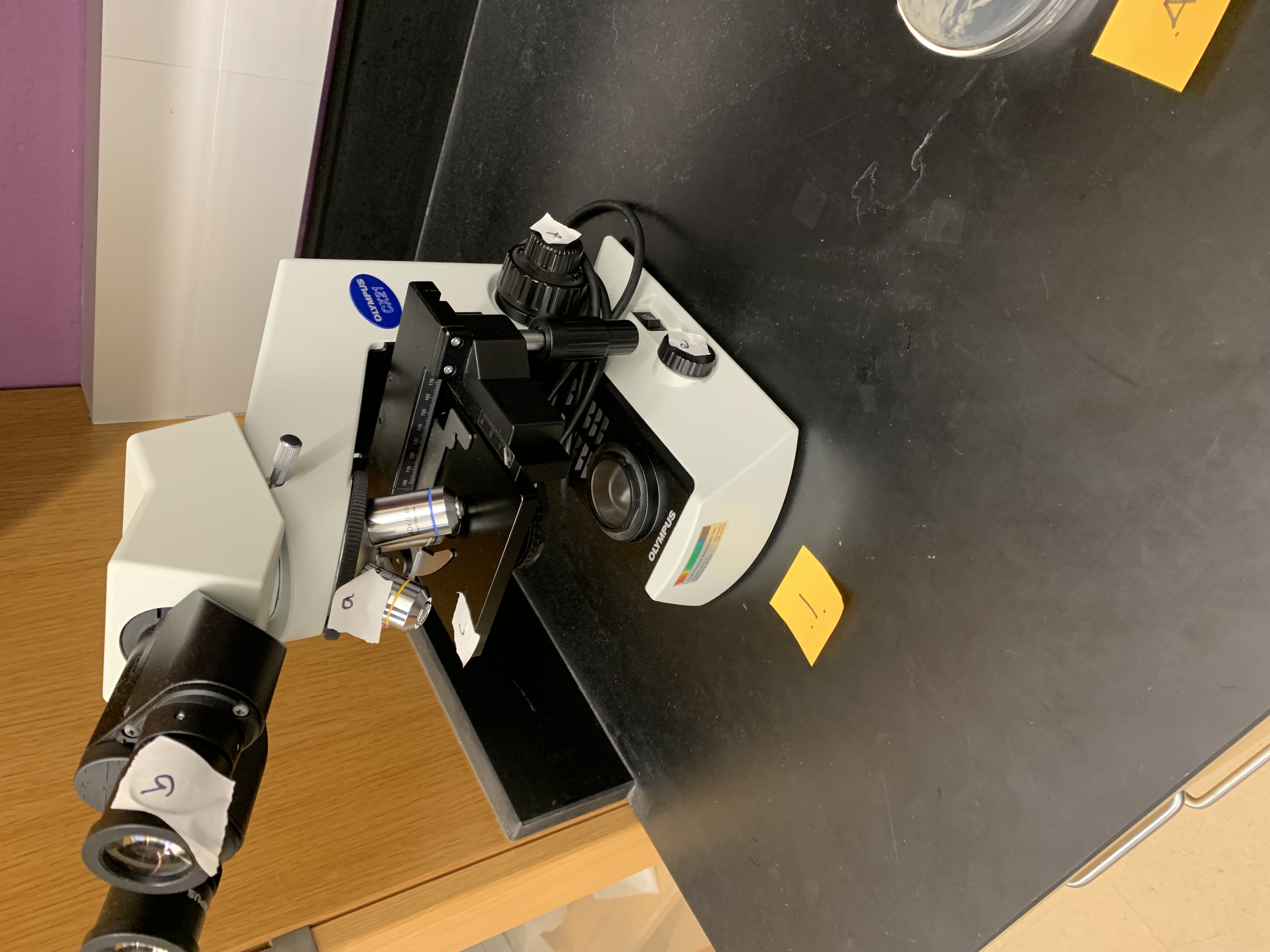

what is C
stage
5
New cards
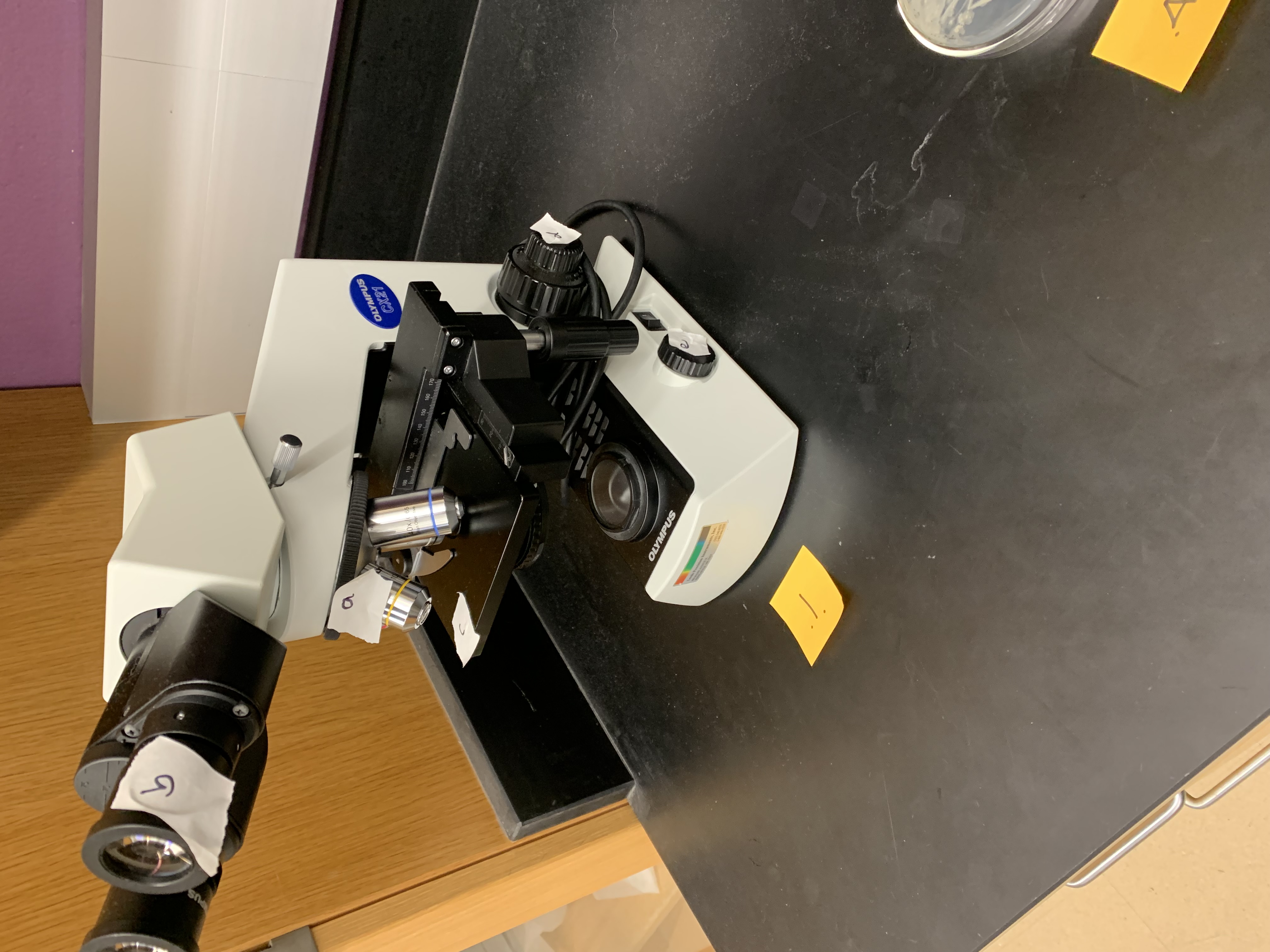

what is D
fine adjustment
6
New cards
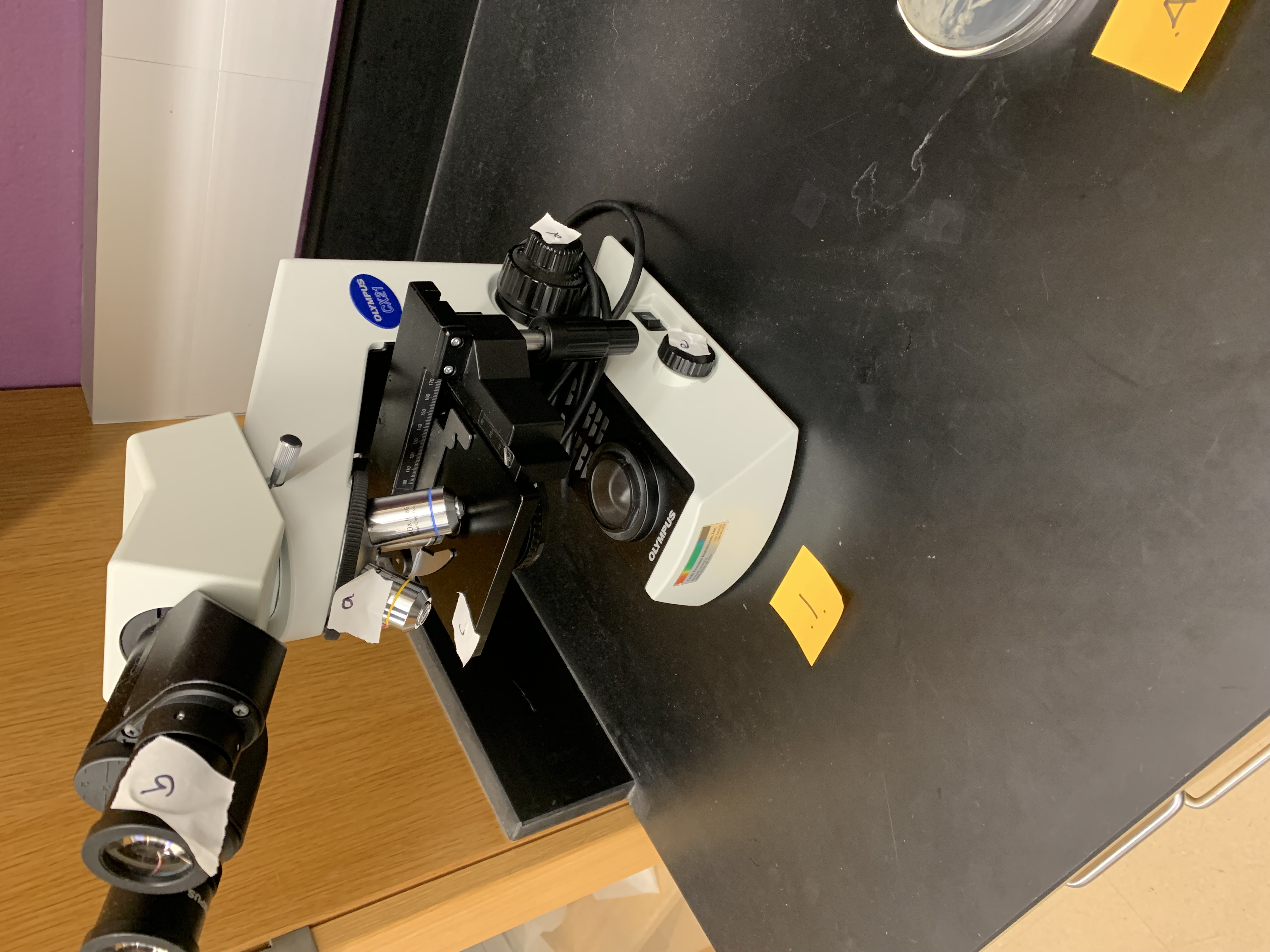

what is E
illumination dial/ light adjustment
7
New cards
what is the purpose of a streak plate
to get isolated colonies
8
New cards
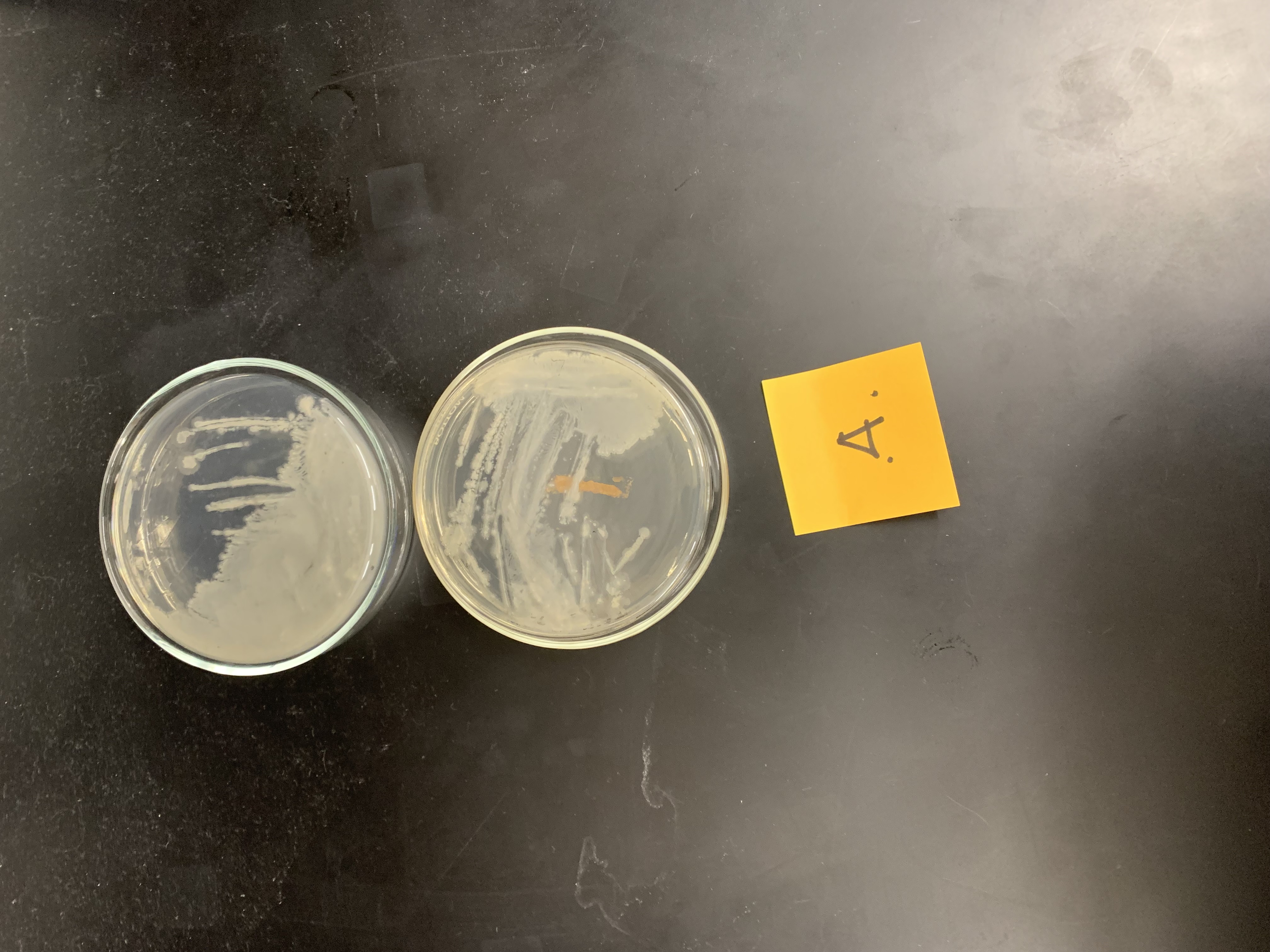
what mistakes were made with these plates
the needle was not sterilized in the flame in-between each section
9
New cards
Nutrient agar is what type of media
general purpose (neither selective or differential)
10
New cards
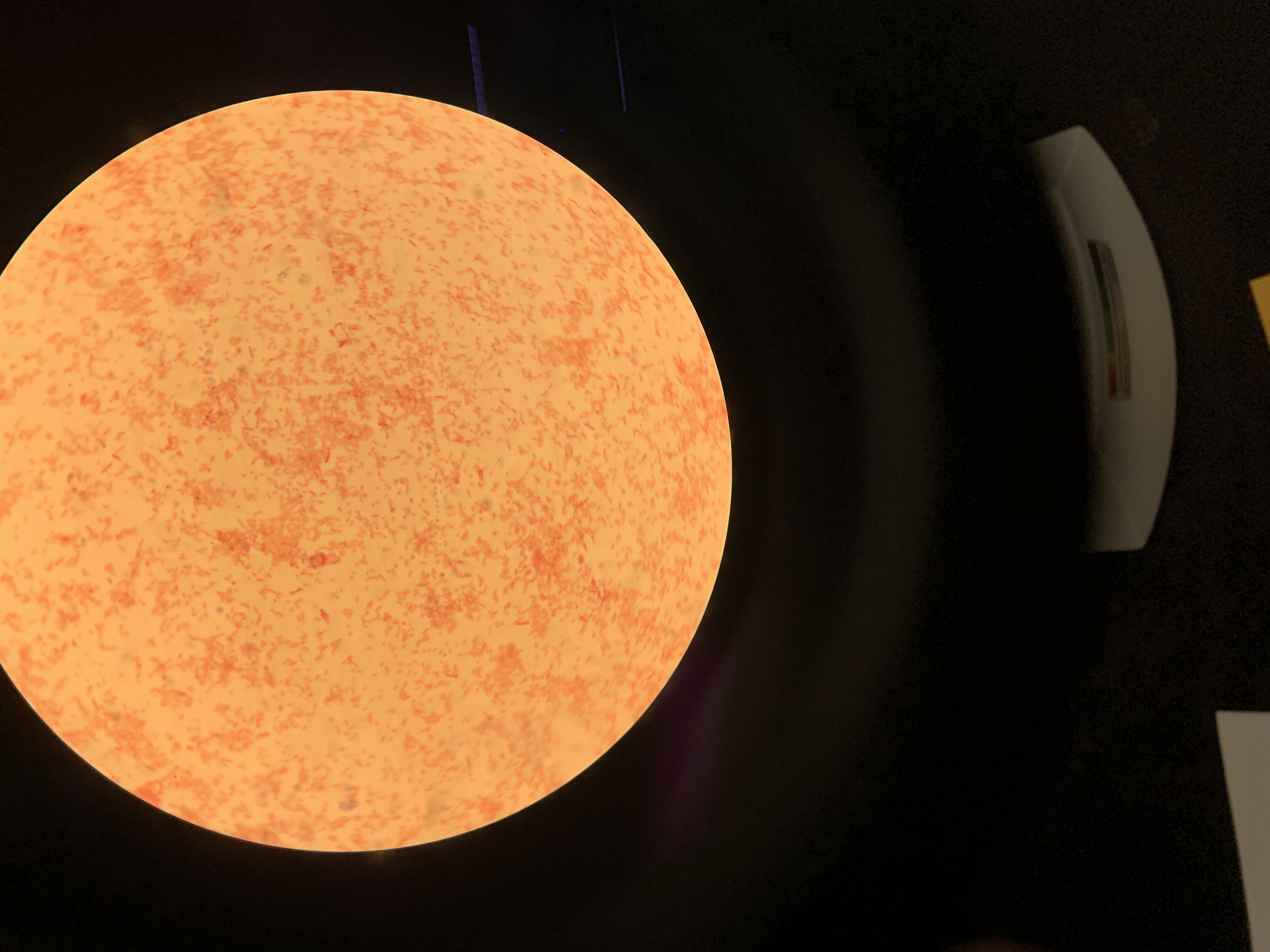
is this a gram positive or negative stain
negative
11
New cards
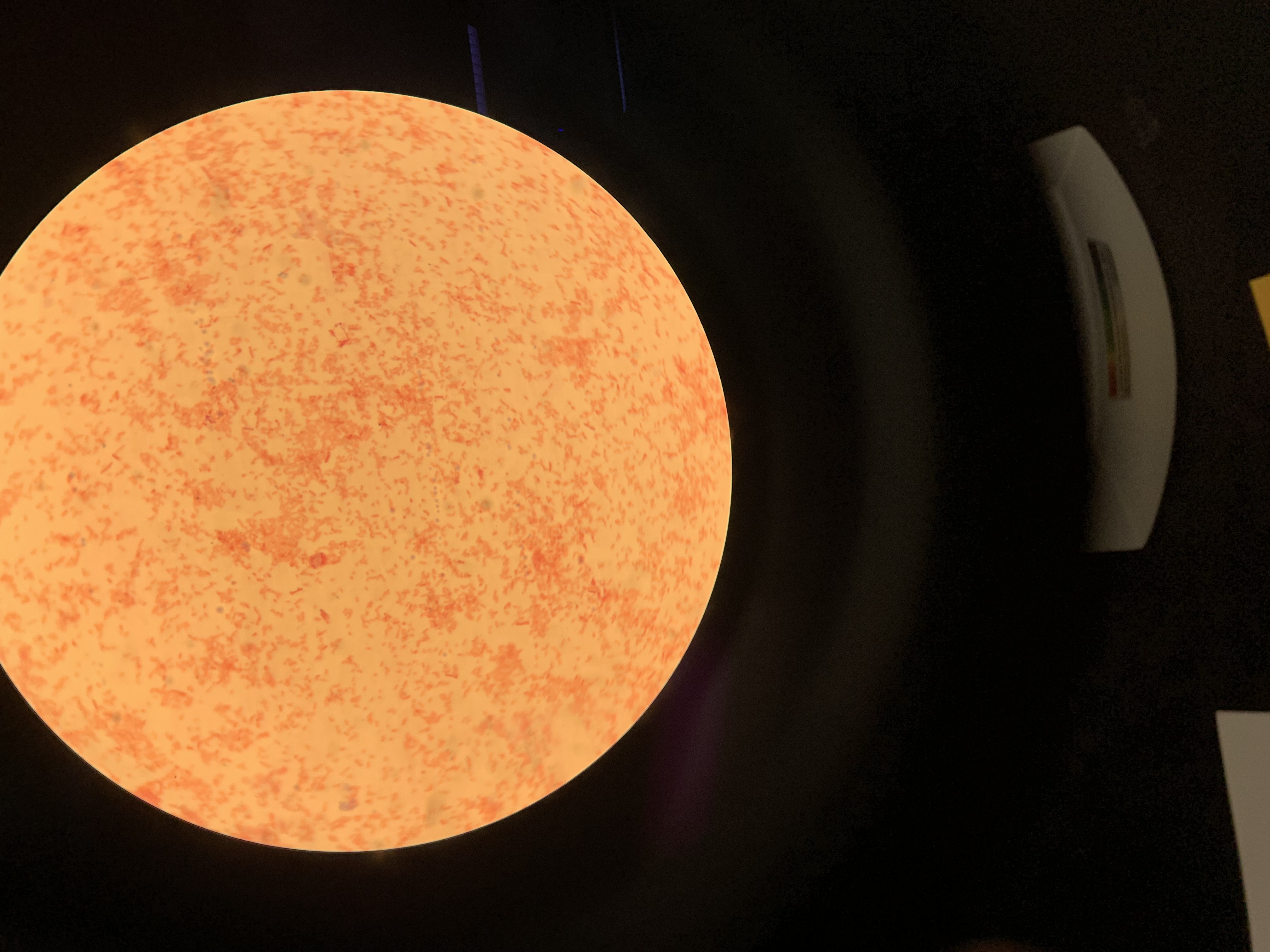
what shape is the bacteria
bacillus
12
New cards
first step of a gram stain
crystal violet
13
New cards
second step of a gram stain
iodine
14
New cards
third step of a gram stain
ethanol
15
New cards
fourth step of a gram stain
safranin
16
New cards
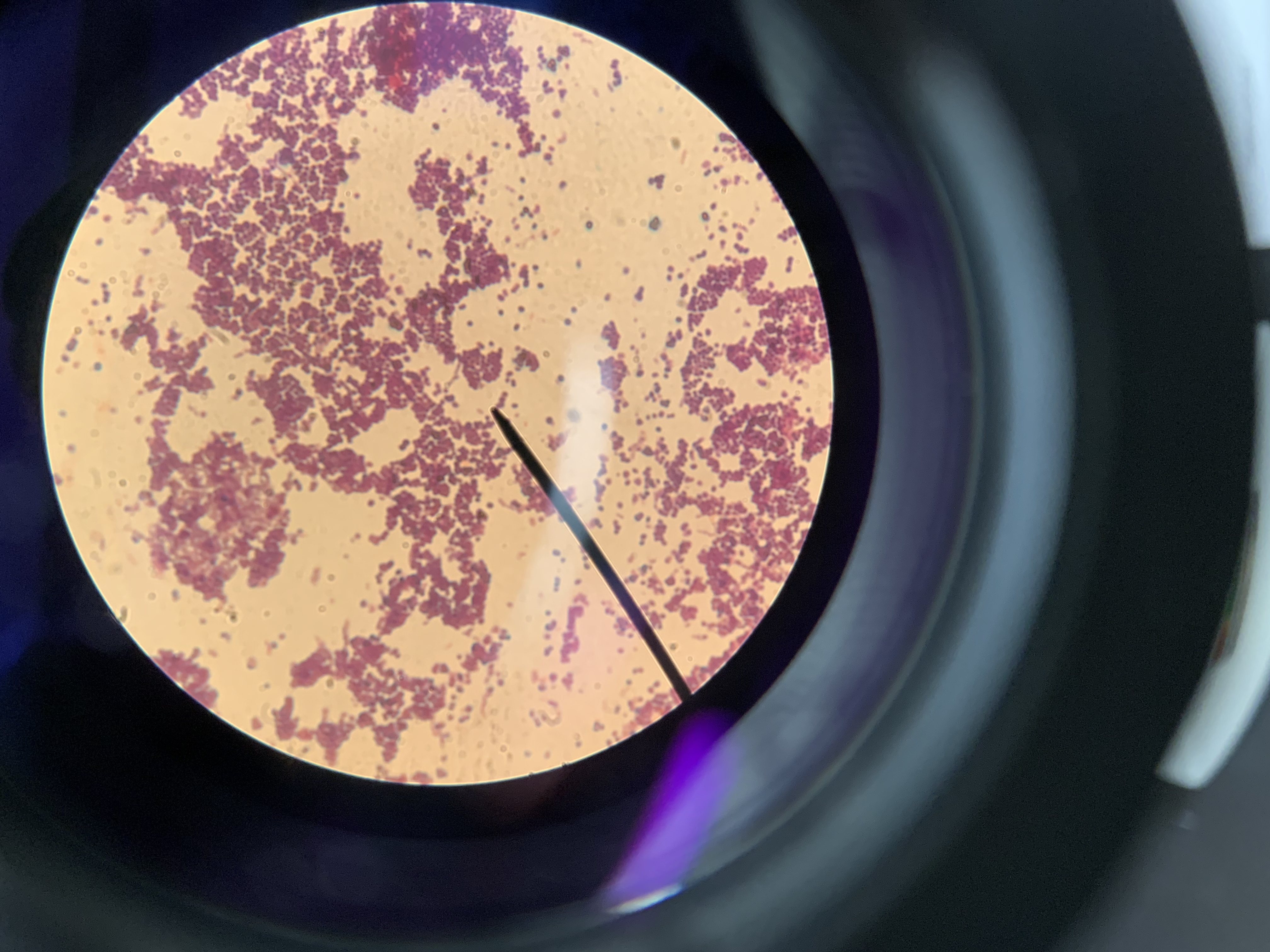
is this a gram positive or negative bacteria
postive
17
New cards
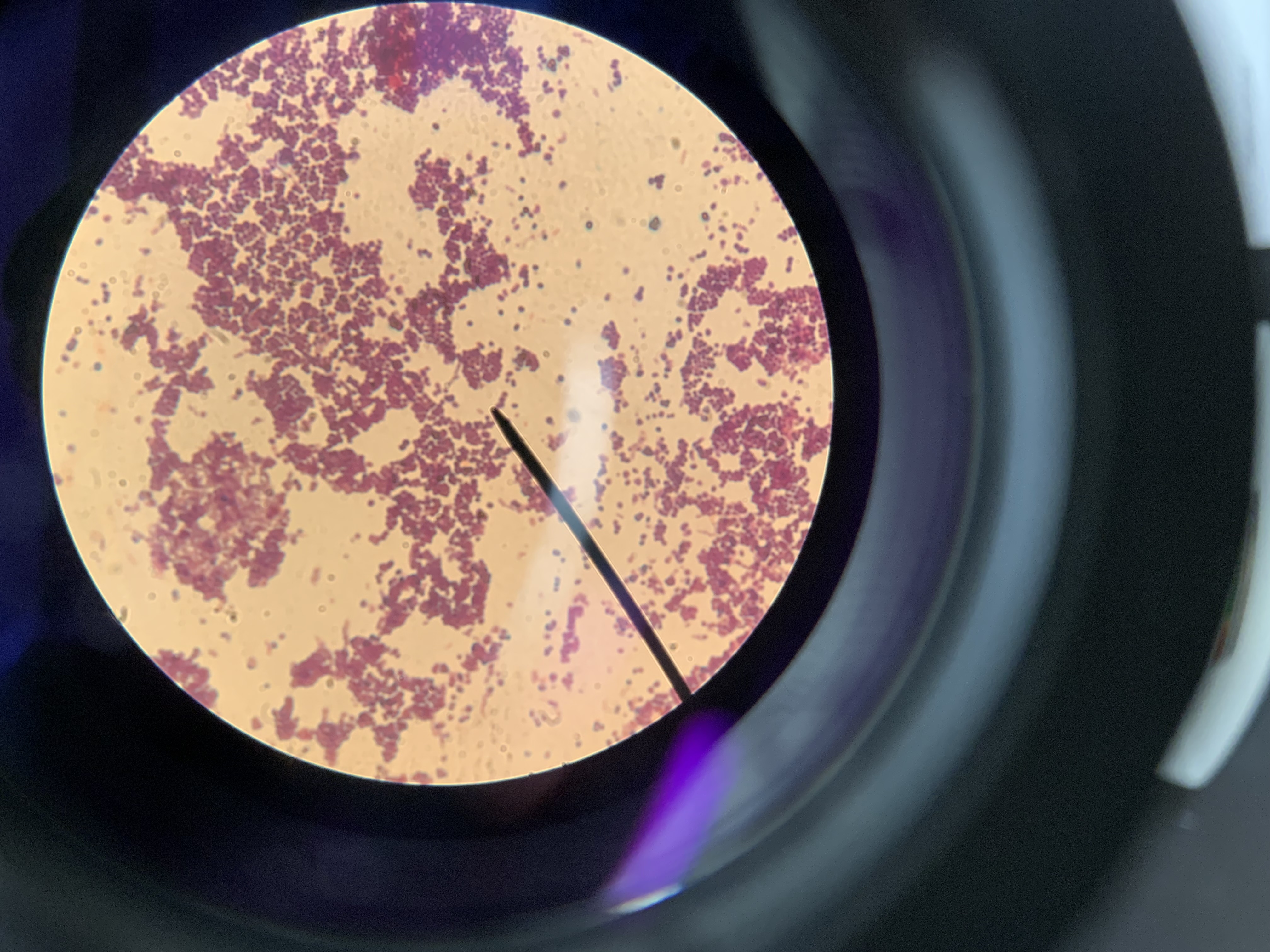
what shape is the bacteria
cocci
18
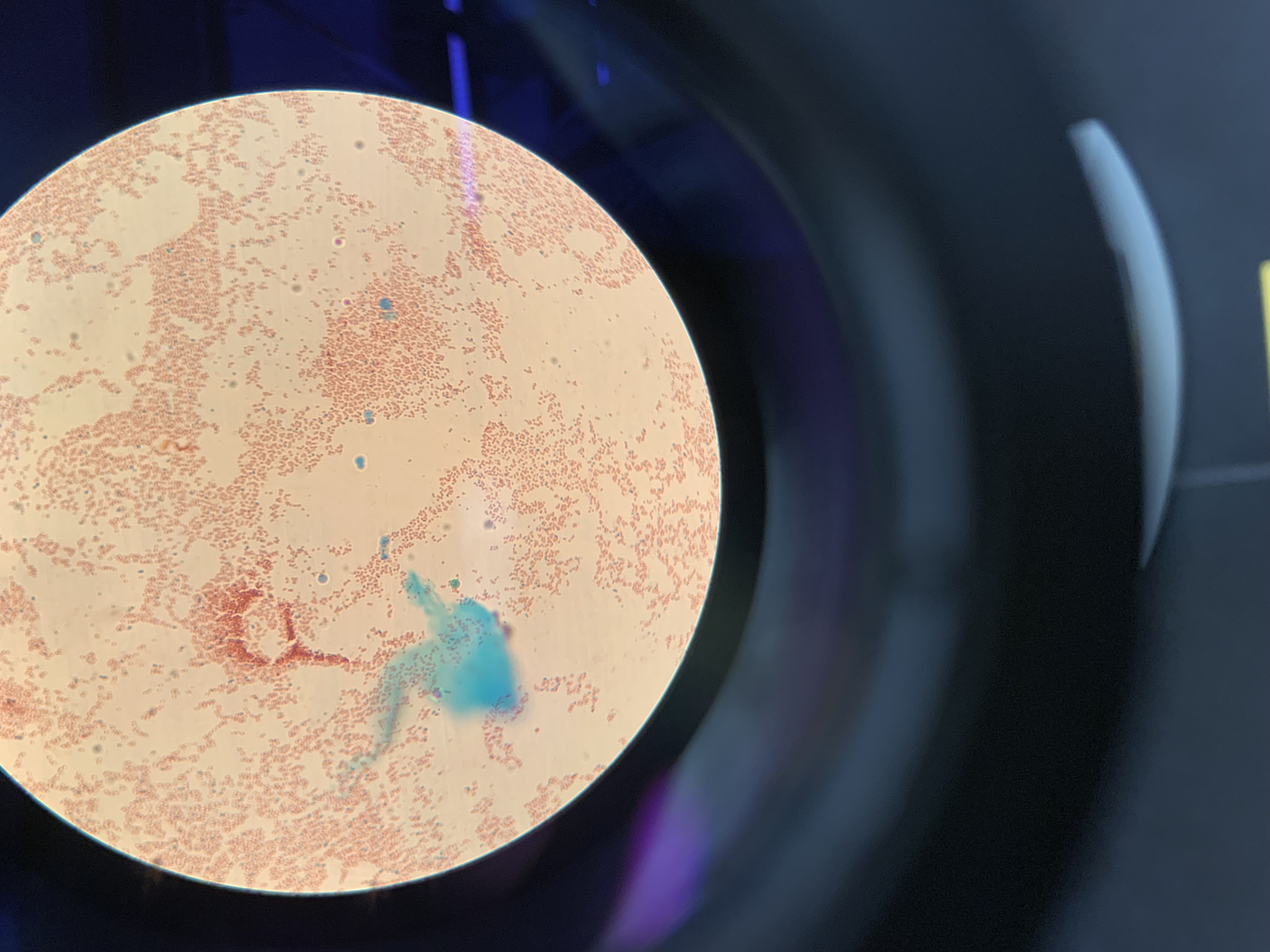
New cards
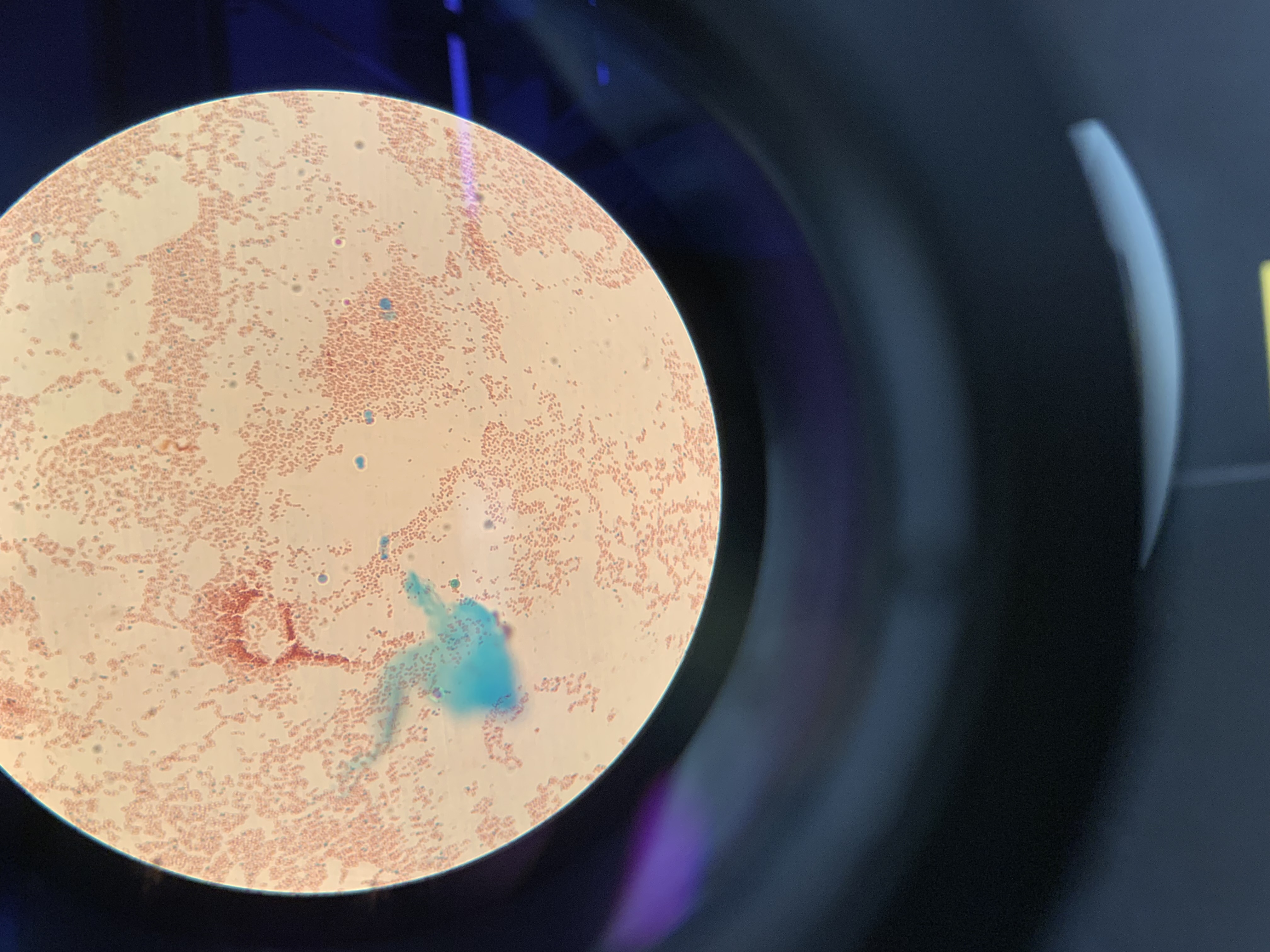
what is the green structure
endospore
19
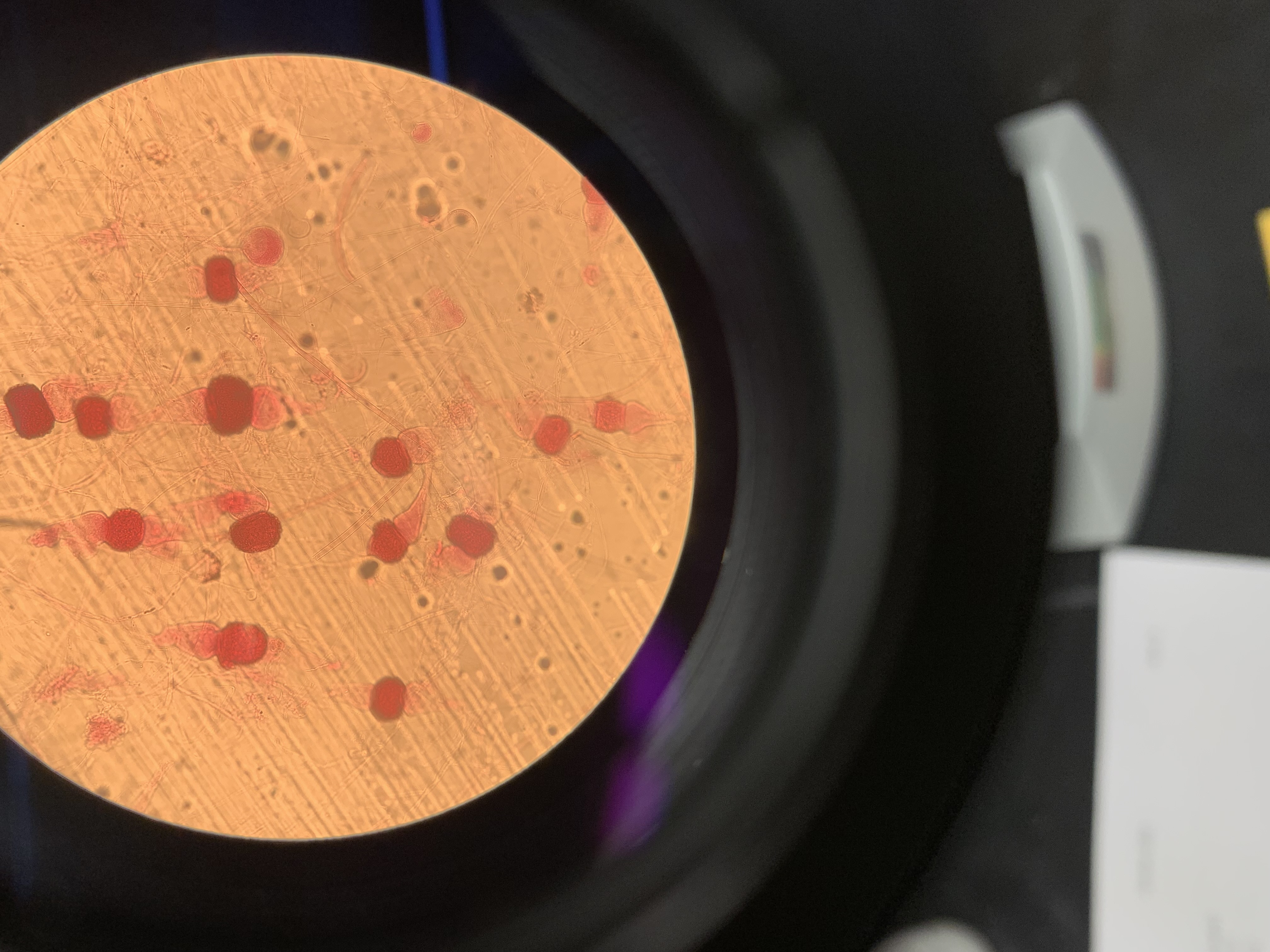
New cards
what genera of bacteria could this be
Bacillus
20
New cards
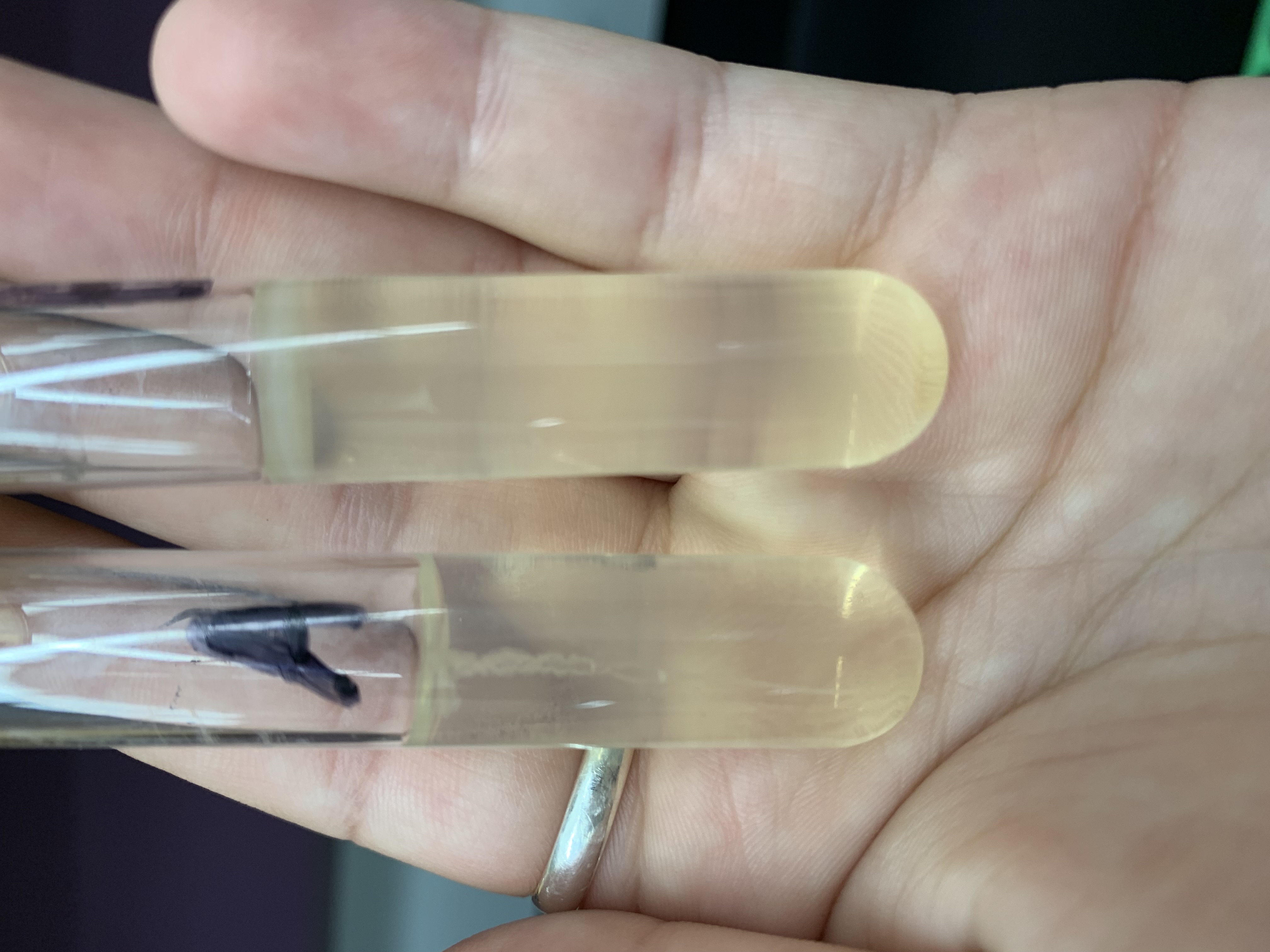

what tube is a motile bacteria
Tube B
21
New cards
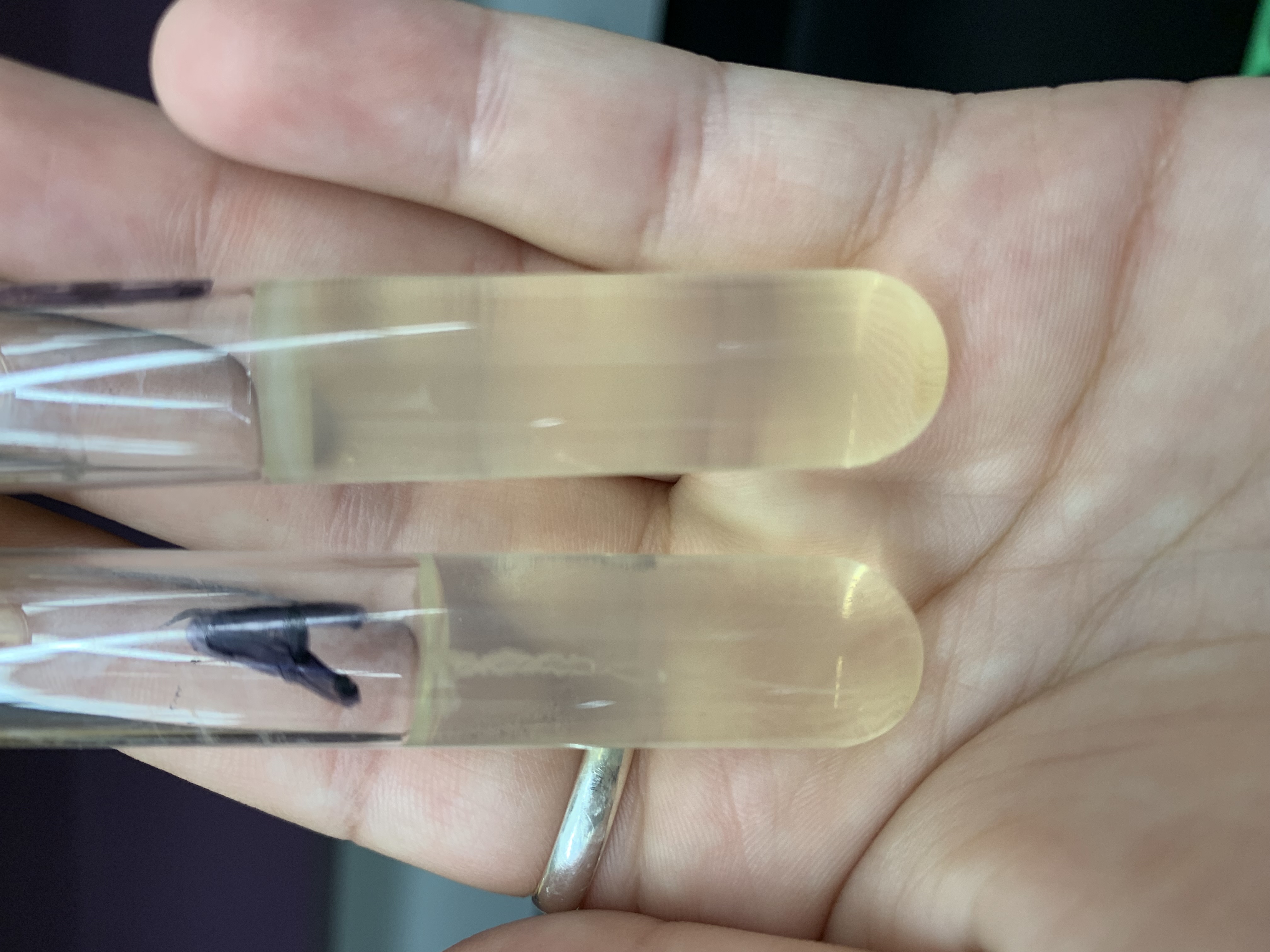

what tube is a nonmotile bacteria
Tube A
22
New cards
what structure confers motility
flagella
23
New cards
What type of media is used to culture fungi
potato dextrose agar
24
New cards
Is this an asexual or sexual spore
Sexual
25
New cards
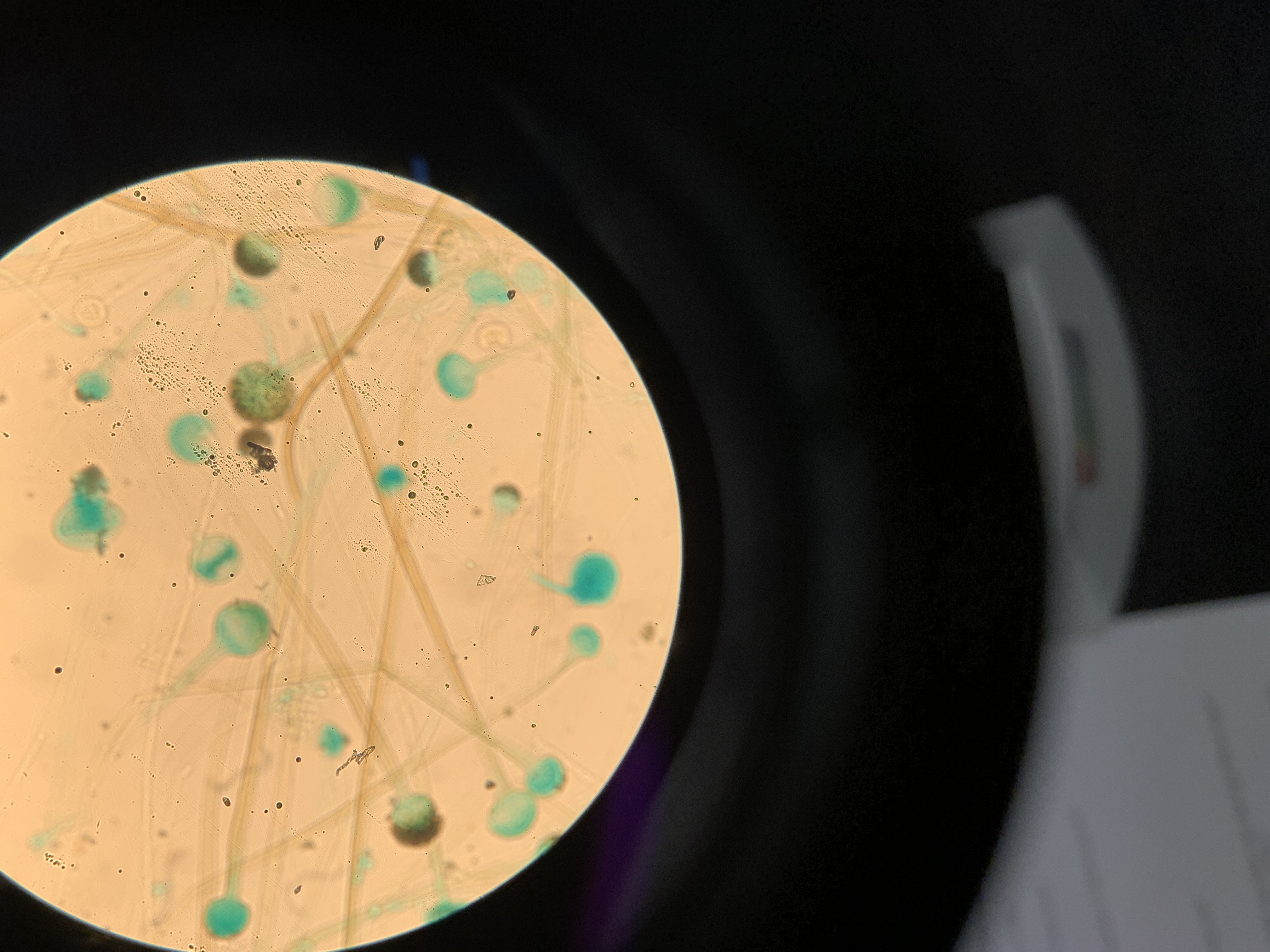
is this an asexual or sexual spore
asexual
26
New cards
what are unicellular fungi called
yeasts
27
New cards
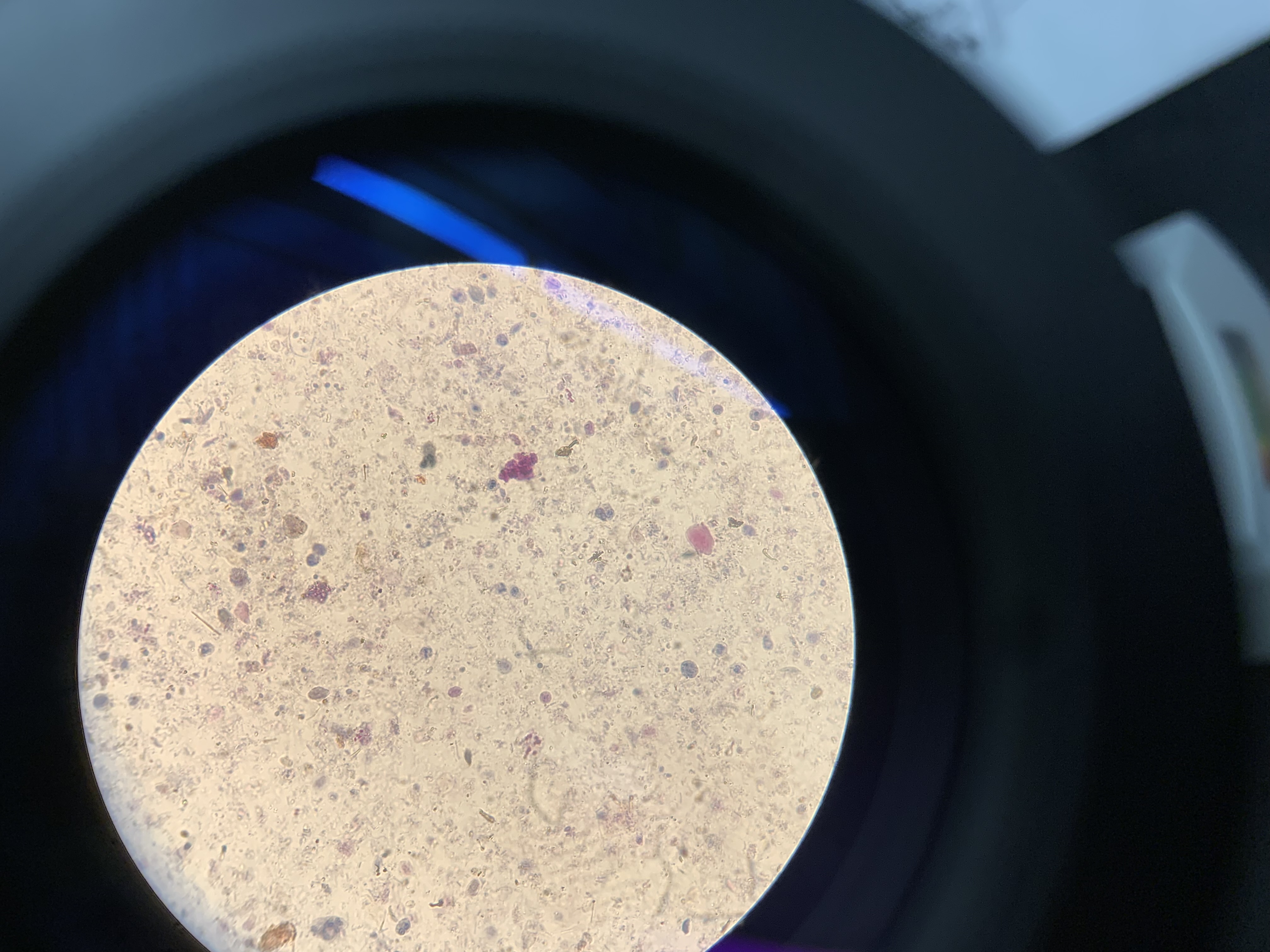
This is Giardia; is it prokaryote or Eukaryote
eukaryote
28
New cards
High salt agar is
selective media
29
New cards
EMB is
both selective and differential media
30
New cards
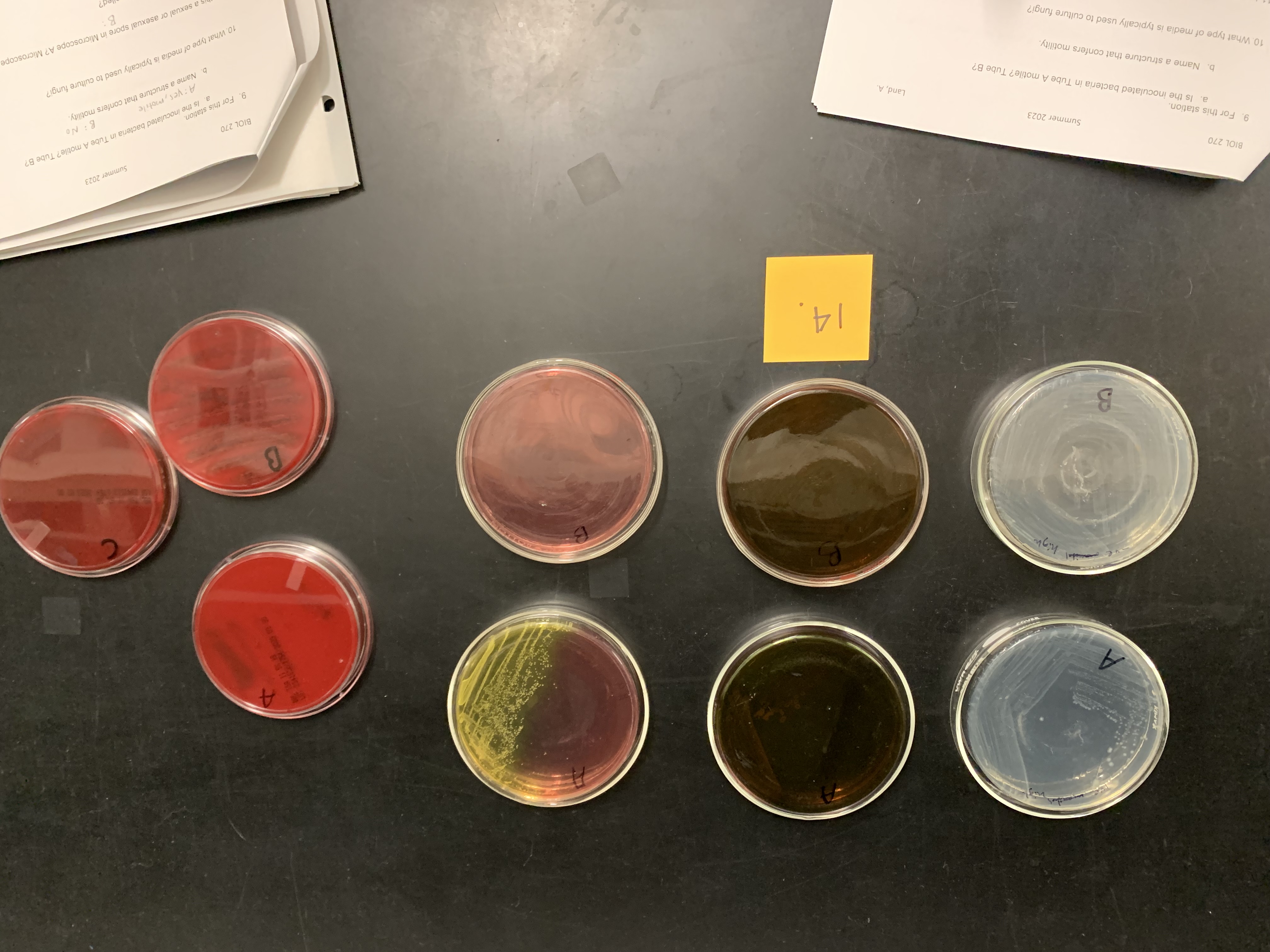
Mannitol salt agar is
selective and differential media
31
New cards
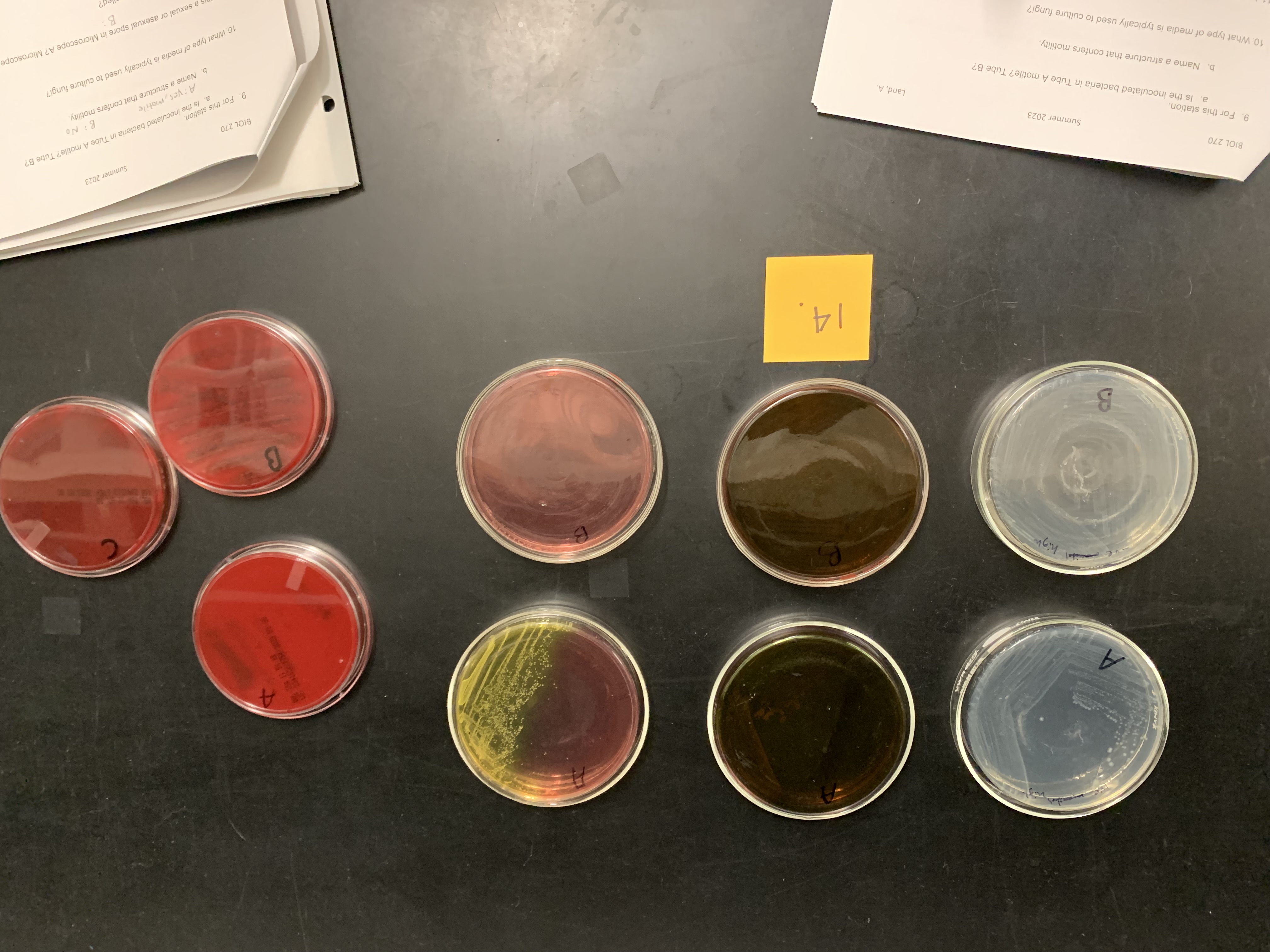
blood agar is
enriched media
32
New cards
High salt agar shows
salt tolerance if bacteria grows
33
New cards
EMB shows
purple/ metallic green growth is it is a lactose fermenter
34
New cards
Mannitol salt agar shows
salt tolerance
35
New cards
blood agar shows
type of hemolysis (alpha, beta, gamma)
36
New cards
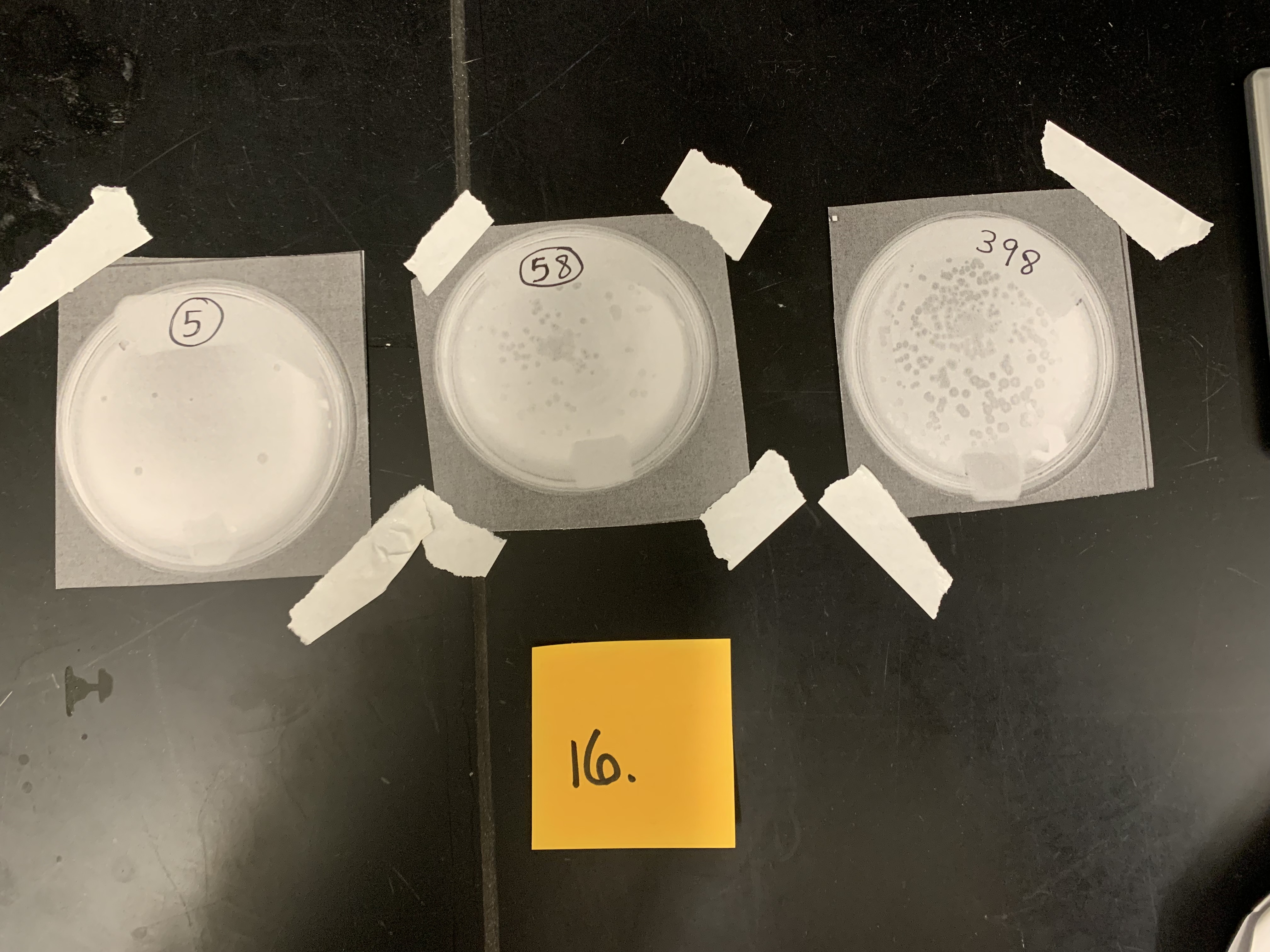

what are the cleanings called
plaques
37
New cards
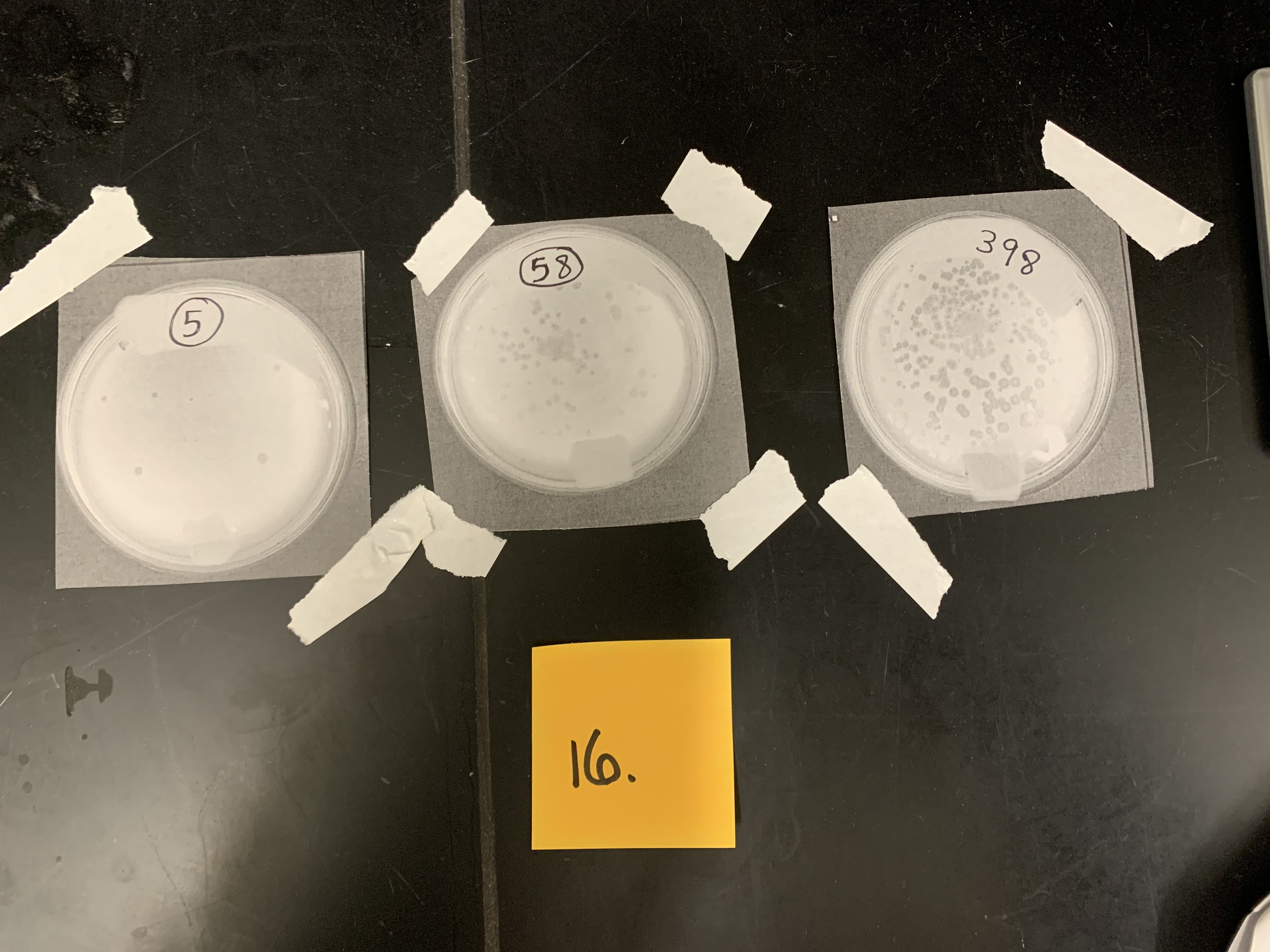

Dilution factor is 10 to the -6 o.1ml of phage was used; what is the original concentration of the phage
5\.8 x 10 to the 8 PFU/mL
38
New cards
what is the purpose of top agar
even coverage; allows bacteria to occupy completely
39
New cards
what is the purpose of a control plate
to compare to other plates
40
New cards
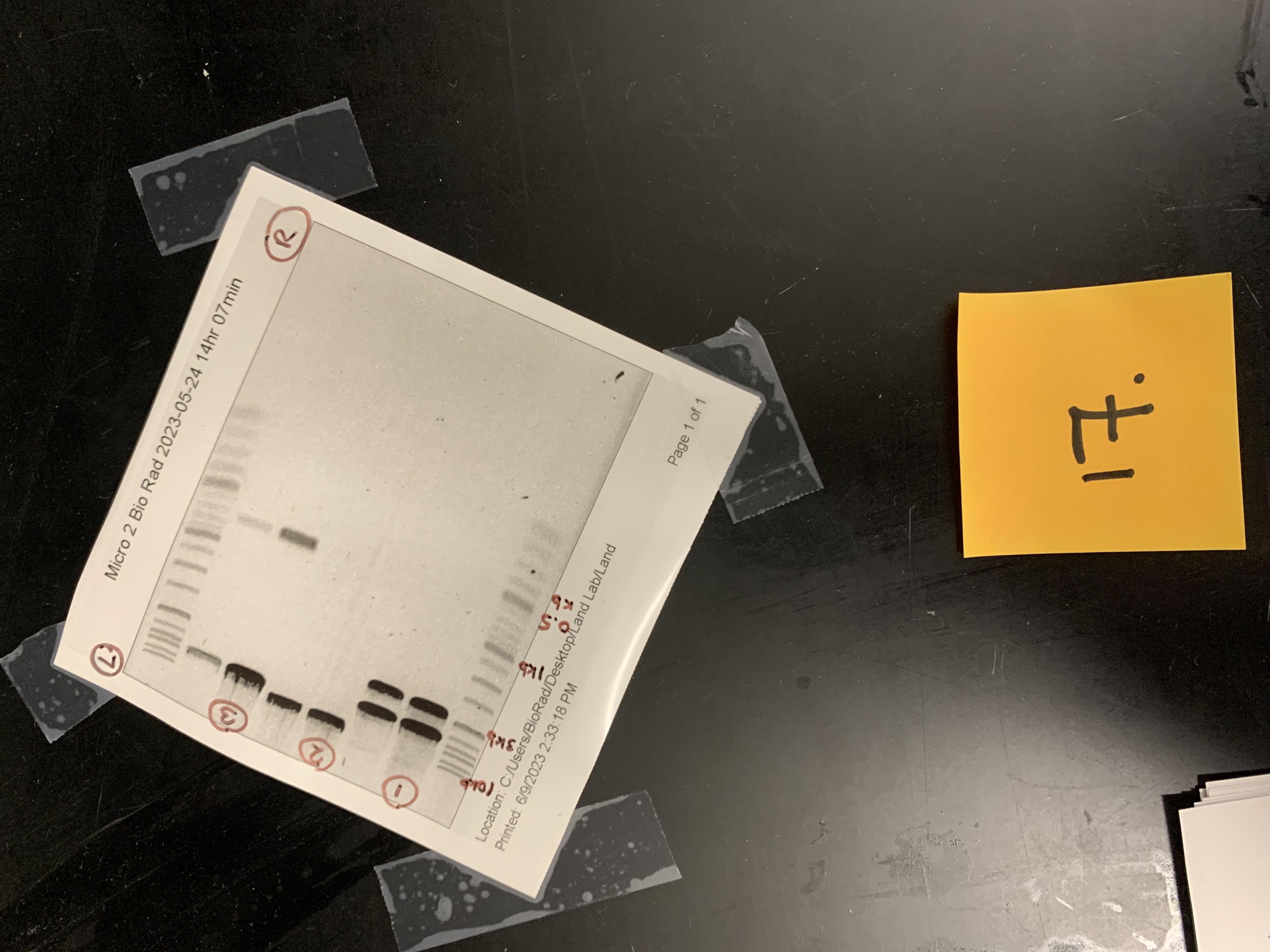
where the wells loaded on the L or R
left
41
New cards
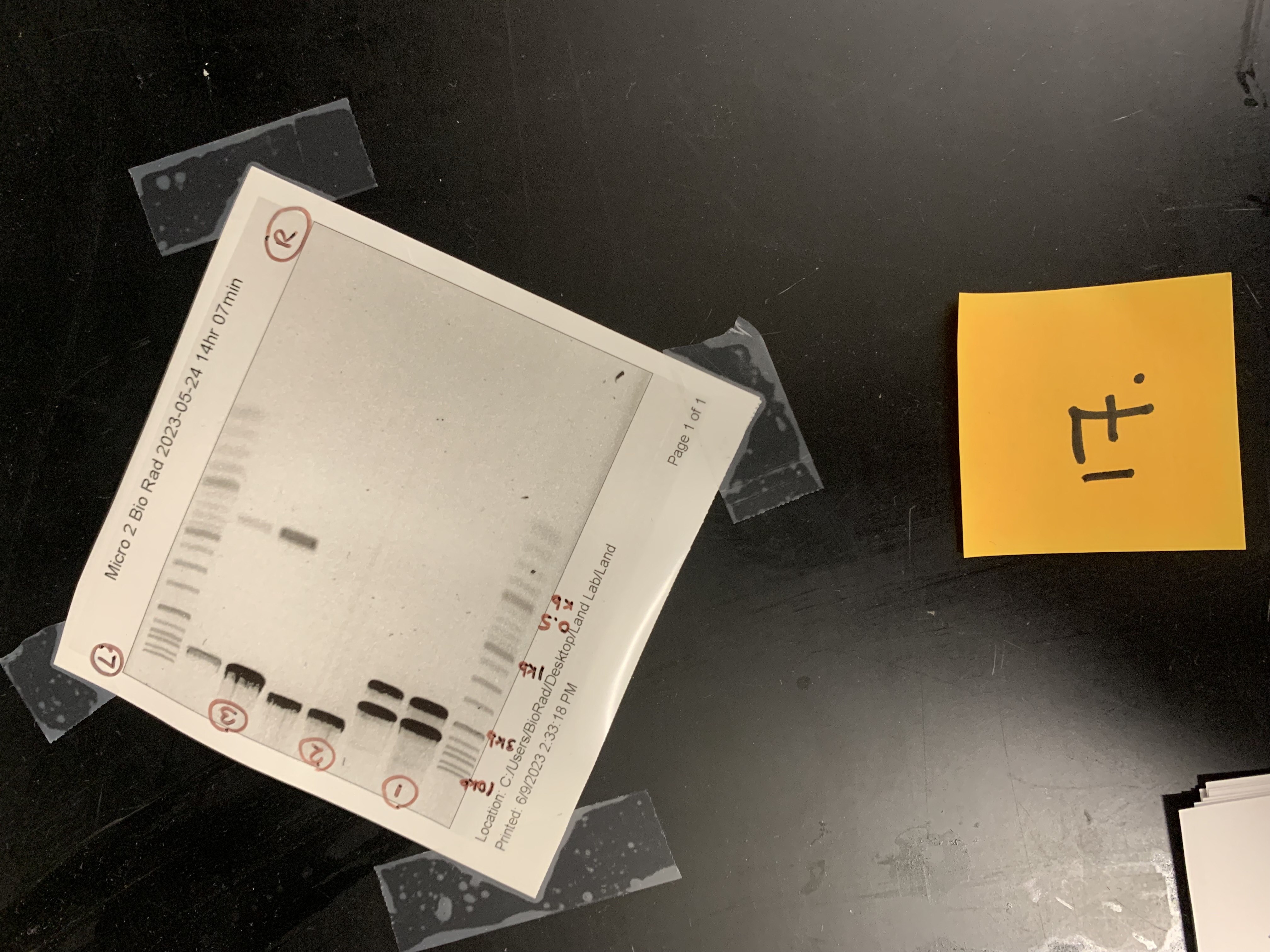
what lane would EcoRl (6.2 kb) split into .7kb and 5.5kb
lane 3
42
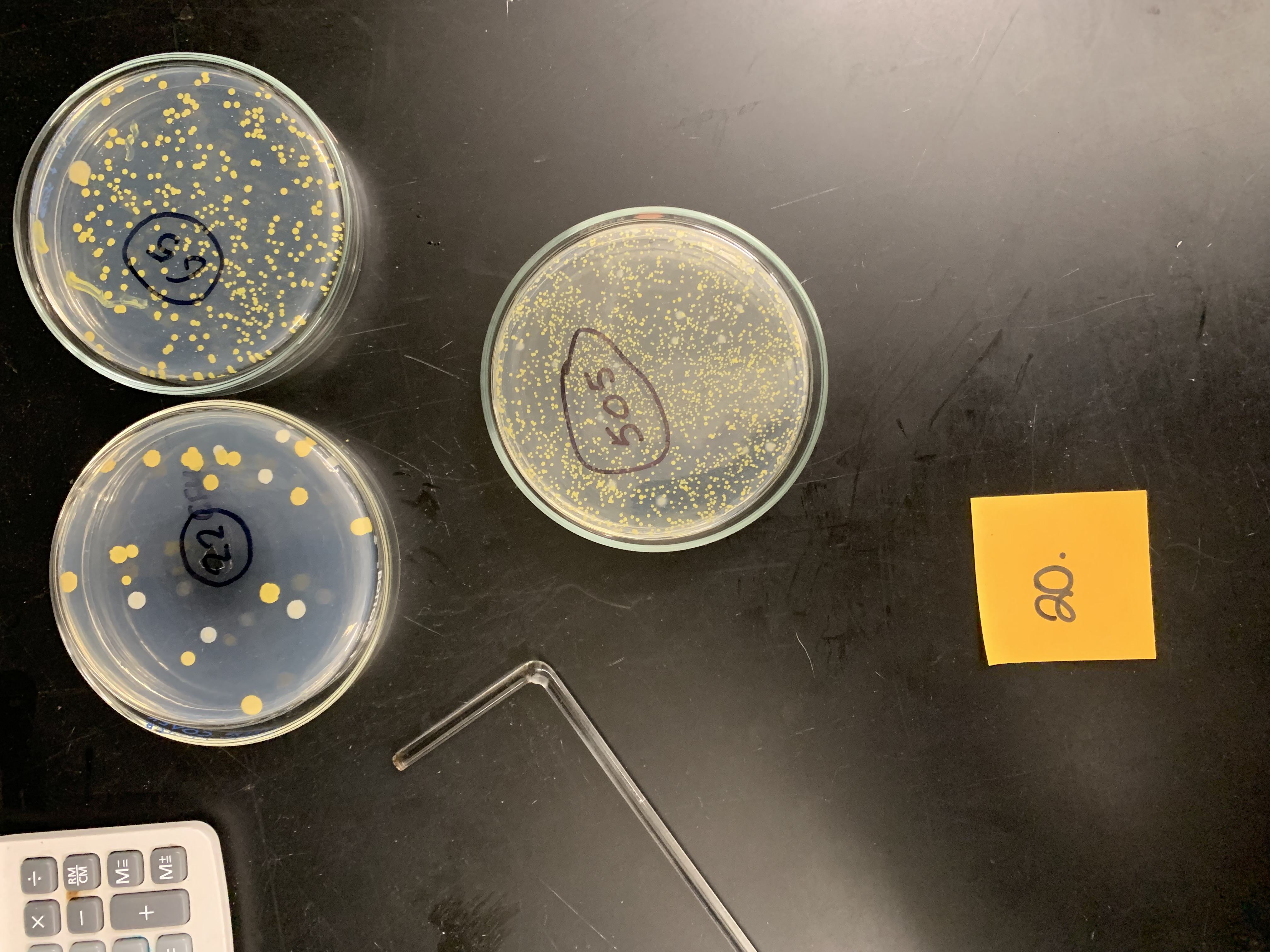
New cards
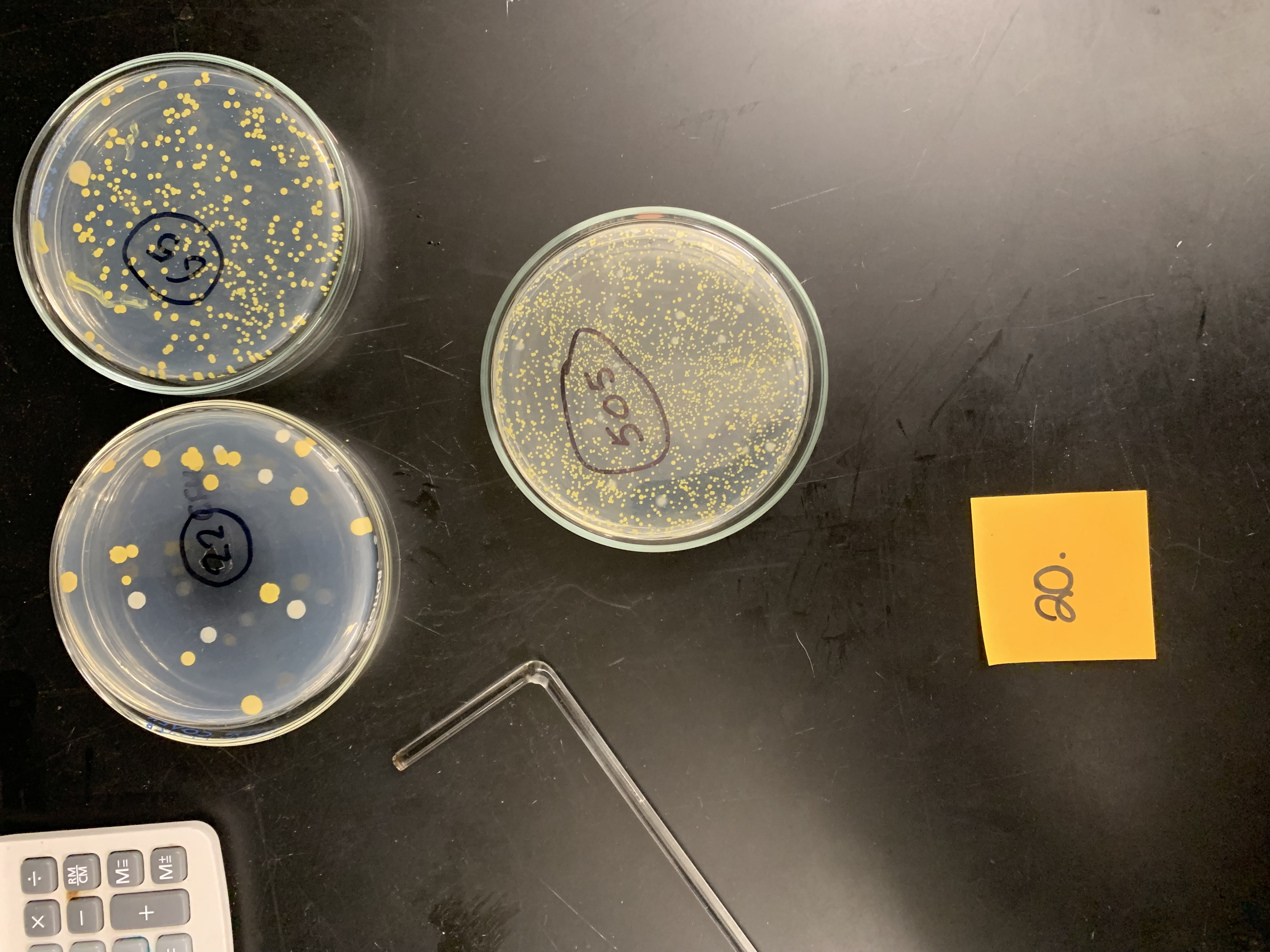
Dilution factor is 10 to the -7 and 0.1 of culture was plated, what is the original concentration of the culture
6\.5 x 10 to the 9 CFU/mL
43
New cards
what is the stick called
hockey stick
44
New cards
what is the technique that uses the hockey stick
spread plate
45
New cards

(Phenol red sucrose tube) interpret the tube
acidic; no gas; which is a fermenter with acid production only
46
New cards

(Phenol red sucrose tube) interpret the tube
acidic; gas; which is a fermenter with acid and gas production
47
New cards

(Phenol red sucrose tube) interpret the tube
alkaline; no gas; non fermenter
48
New cards
what carbohydrate is fermented in a Phenol red test
sucrose
49
New cards
what is the purpose of a Durham tube
gas trap
50
New cards

what is this testing for
catalase
51
New cards

what does a positive reaction look like
immediate bubbling
52
New cards
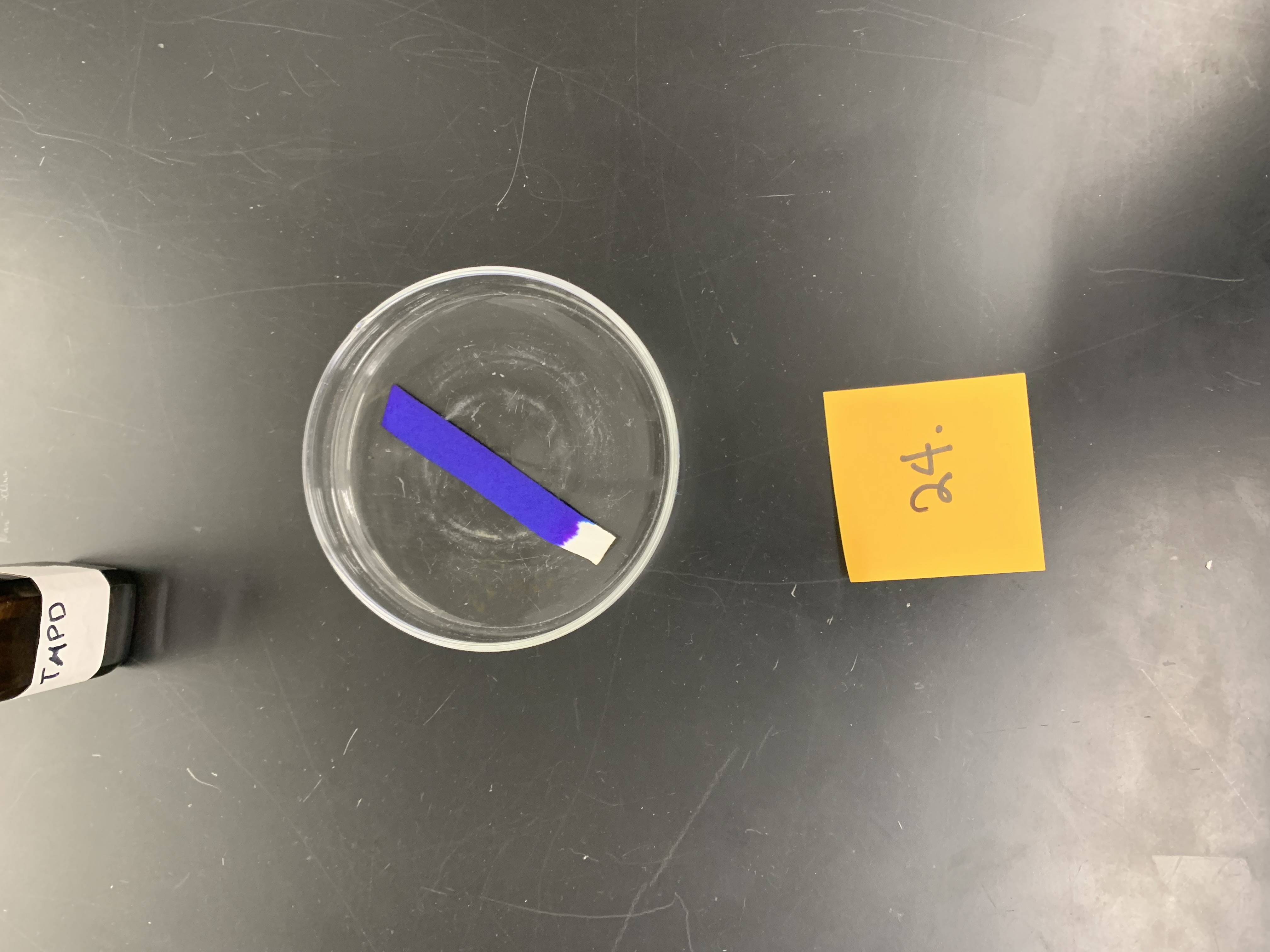

what is this testing for
oxidase
53
New cards
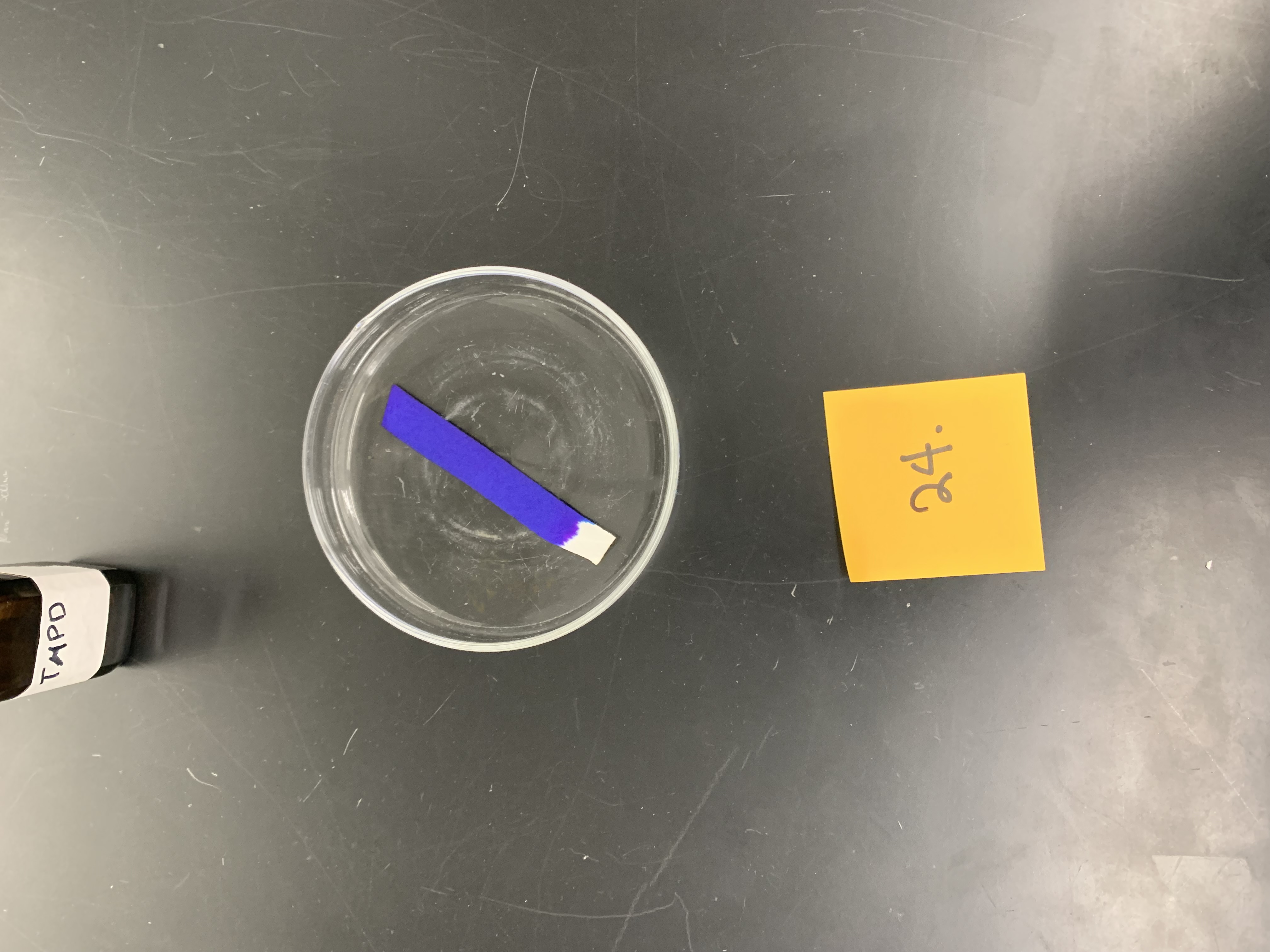

is this a positive or negative result
positive oxidase
54
New cards
what does MIC stand for
minimum inhibitory concentration
55
New cards
what does MBC stand for
minimum bactericidal concentration
56
New cards
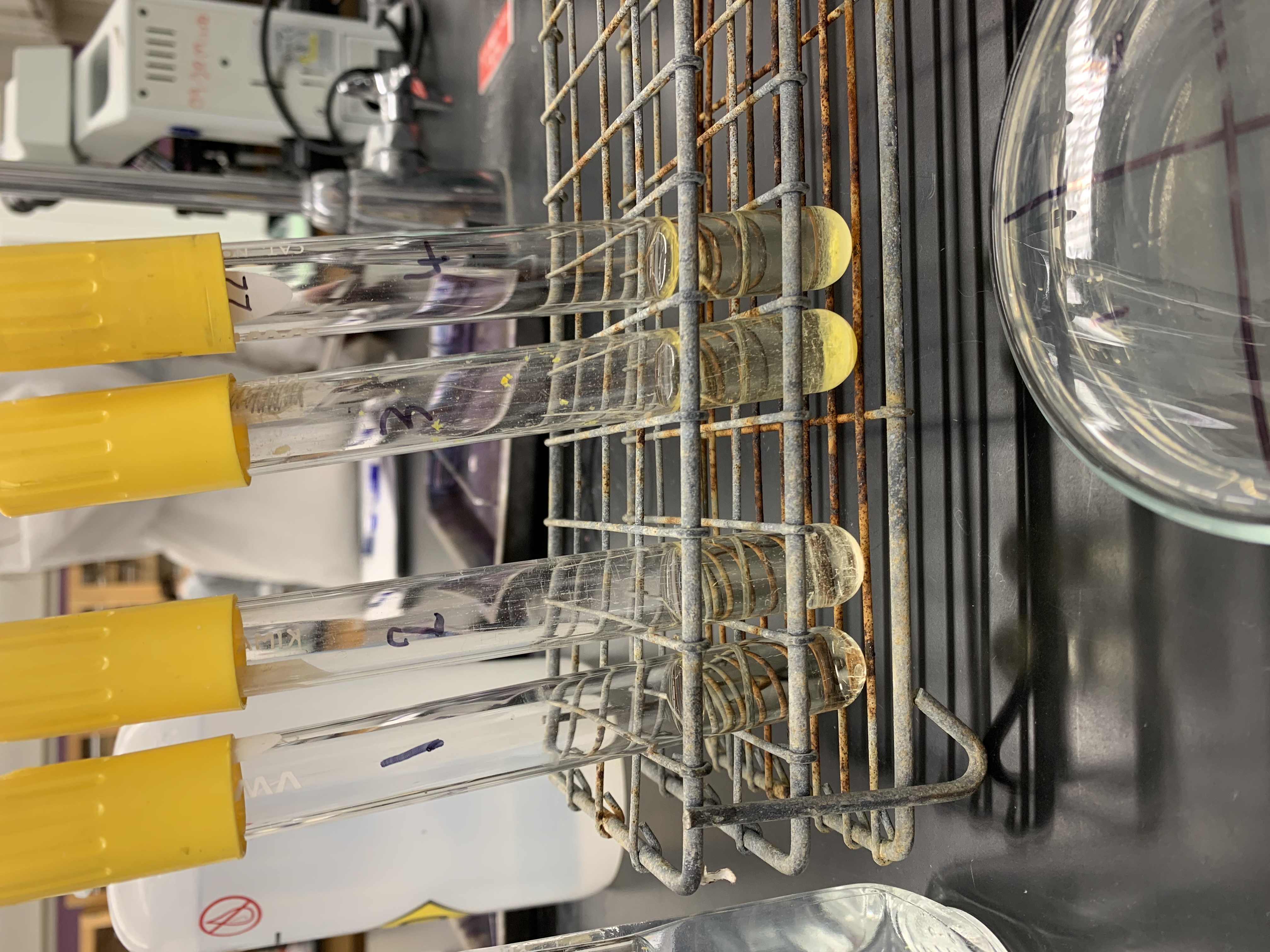

What do you interpret MIC from
tubes
57
New cards

what do you interpret MBC from
plates
58
New cards
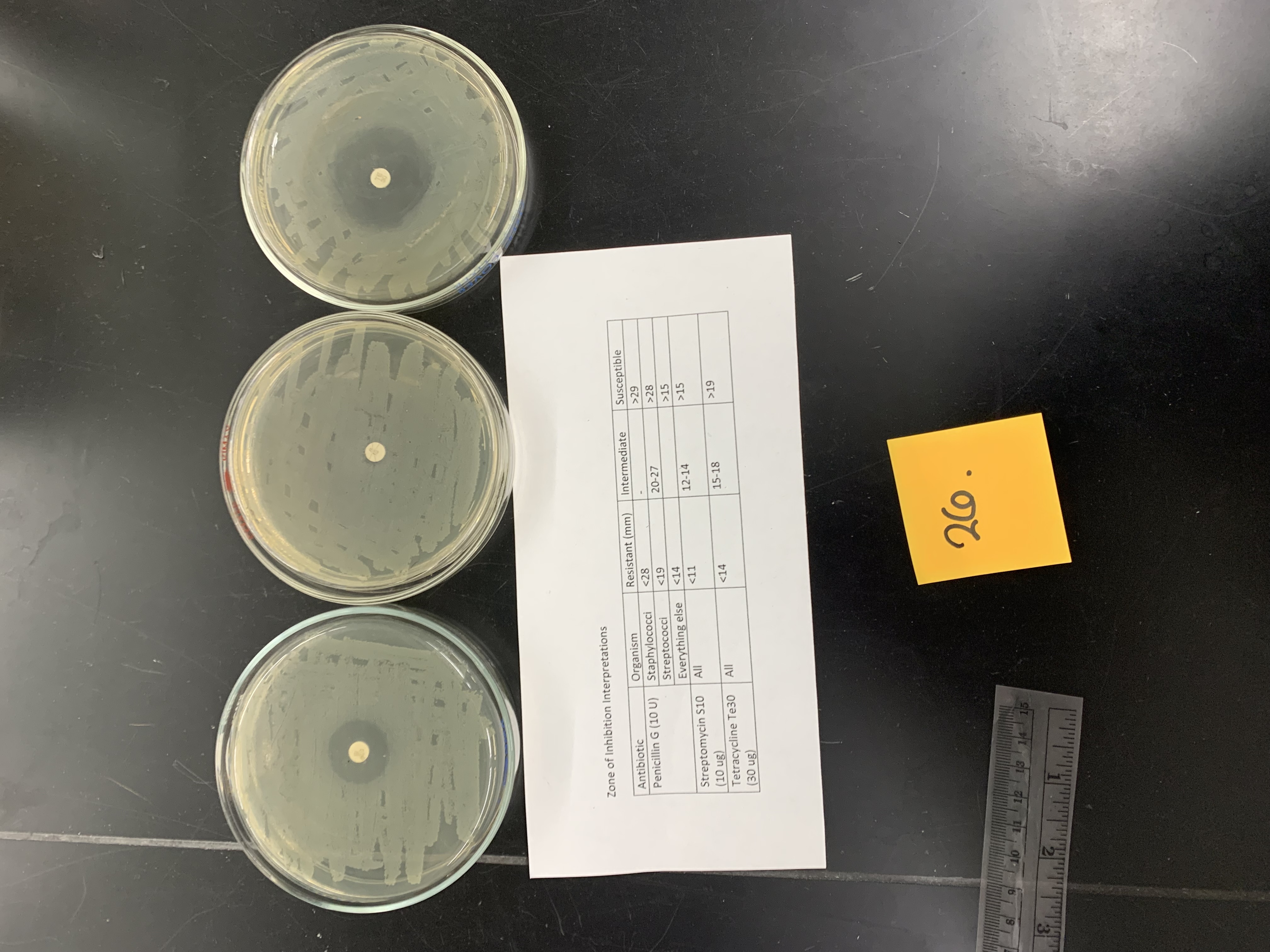
what is the name of this test
Kirby Bauer/ zone of inhibition
59
New cards
why are there precise rules for the Kirby Bauer test
so it can be used internationally; bacteria resistance can also be compared internationally
60
New cards
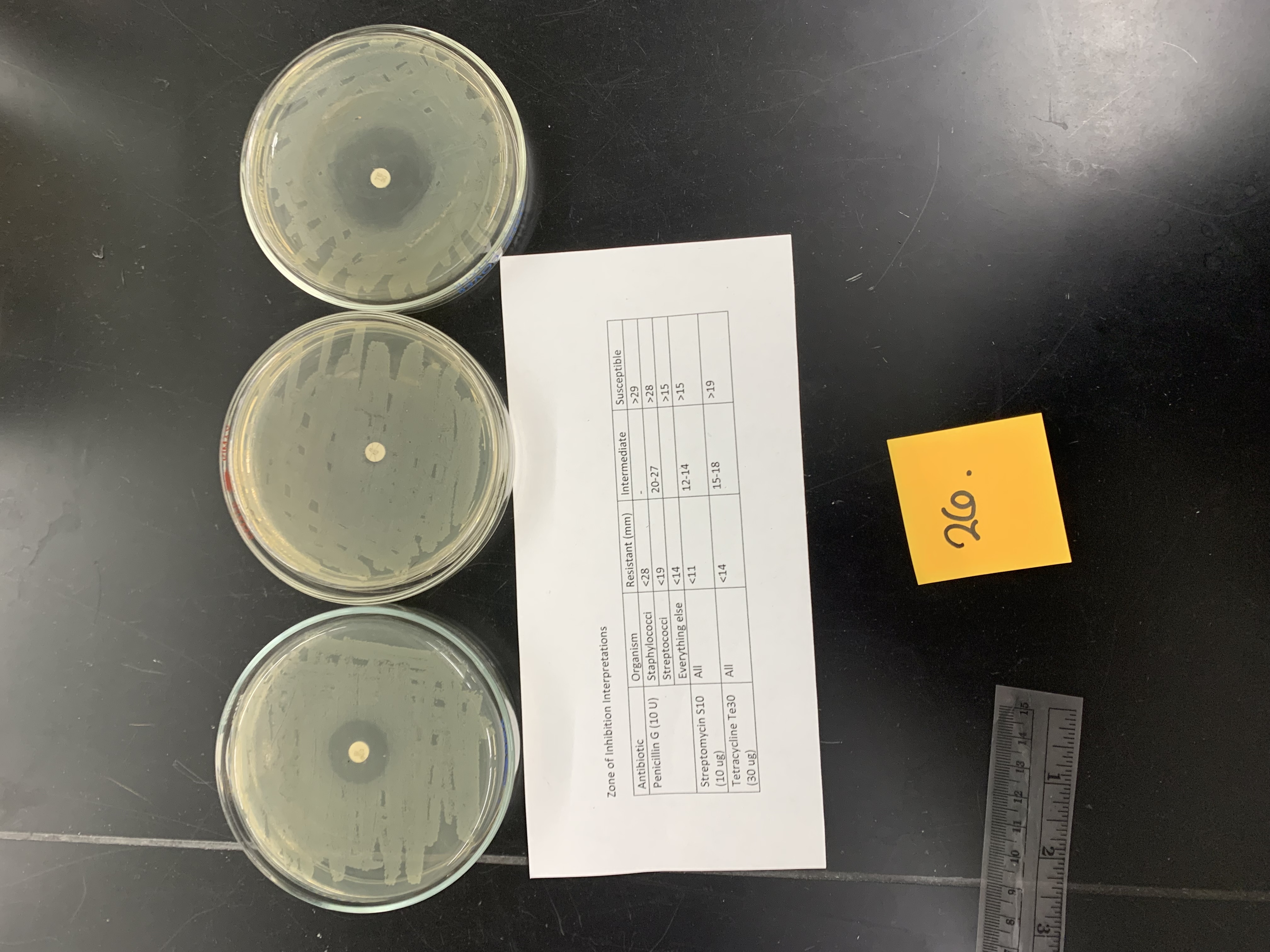
if this is staphylococcus epidermis how would the results be interpreted; Penicillin G (10 U)
resistant
61
New cards
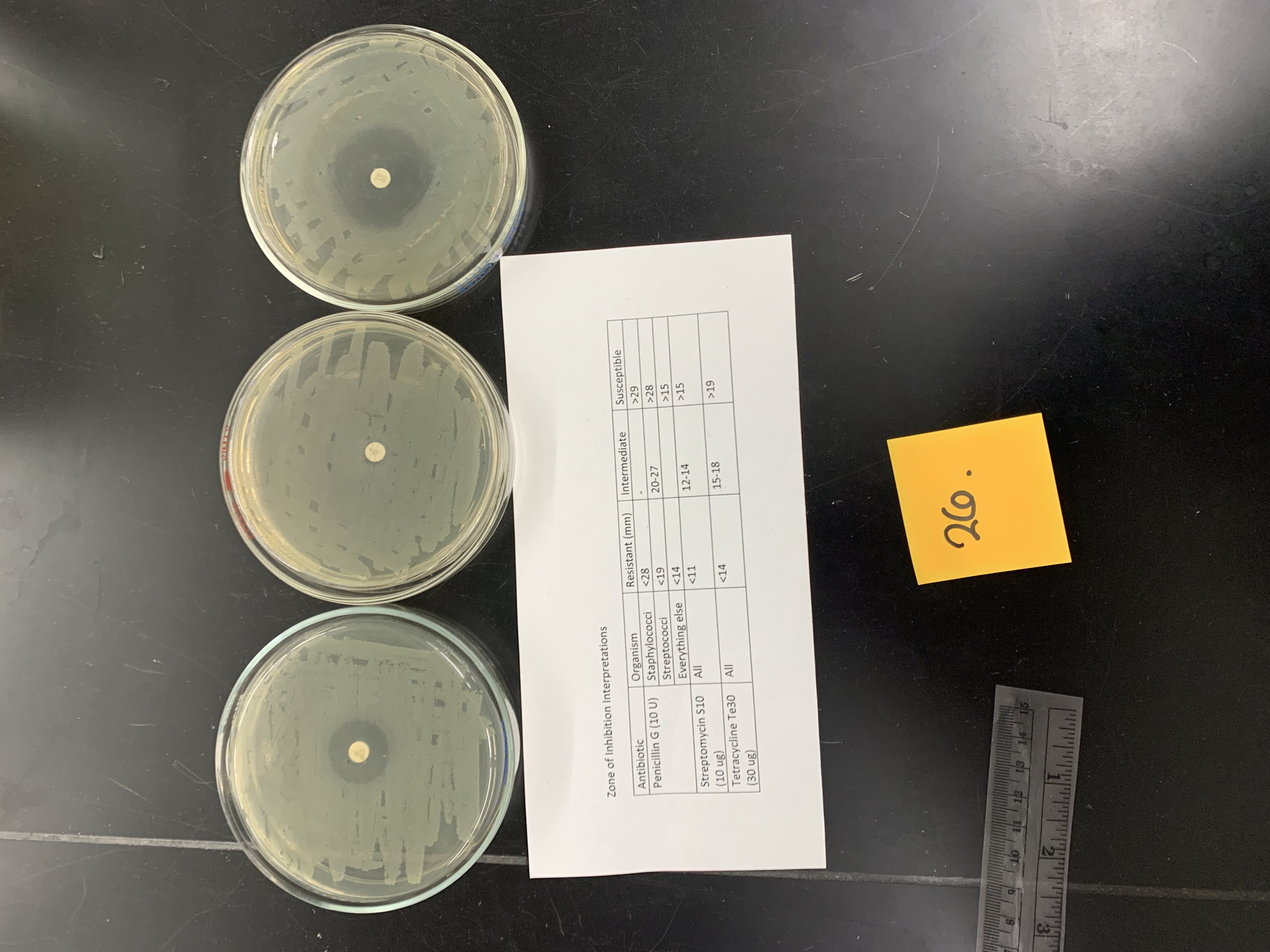
if this is staphylococcus epidermis how would the results be interpreted; Streptomycin s10 (10ug)
resistant
62
New cards
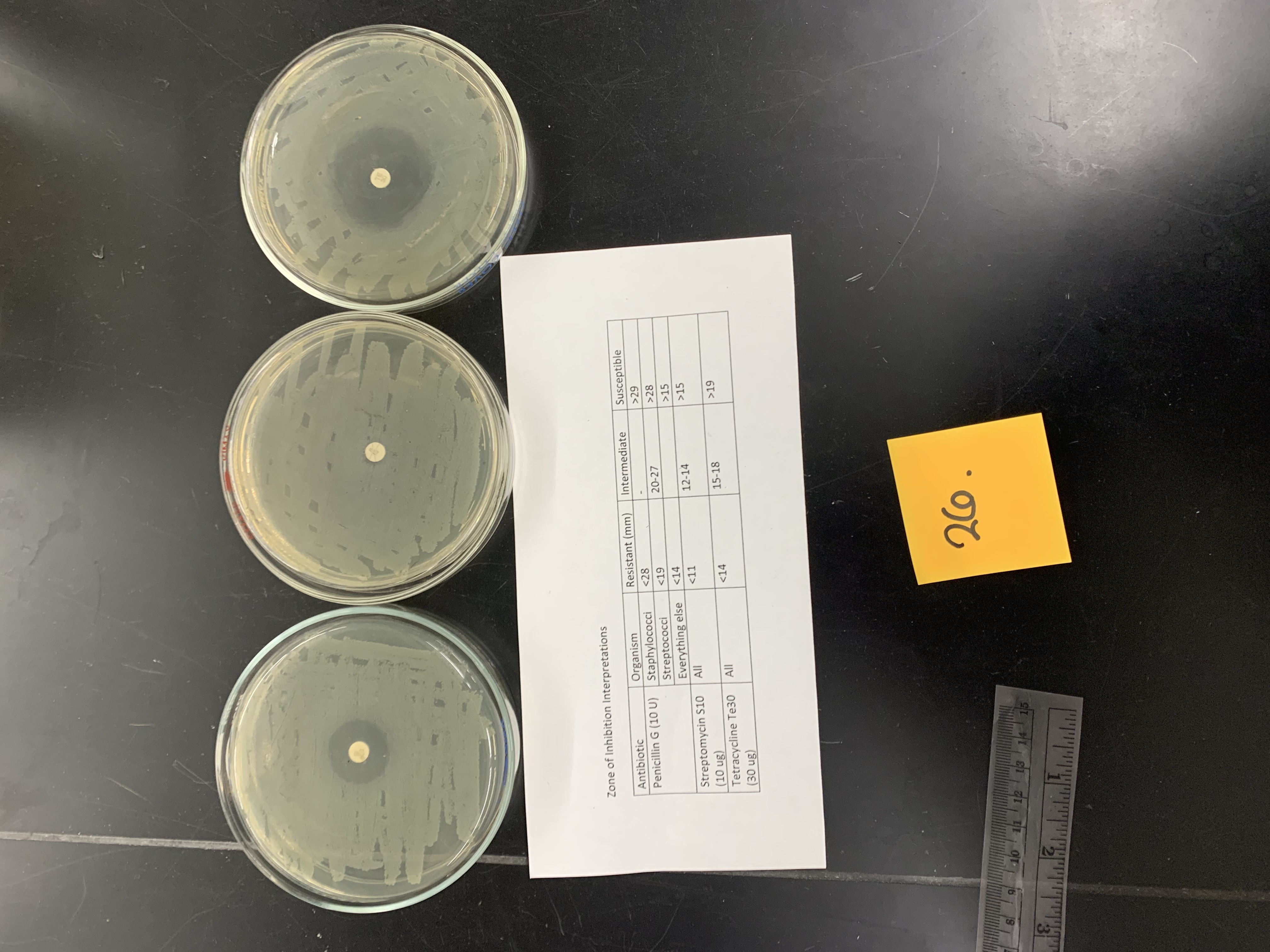
if this is staphylococcus epidermis how would the results be interpreted; tetracycline Te30 (30 ug)
susceptible
63
New cards
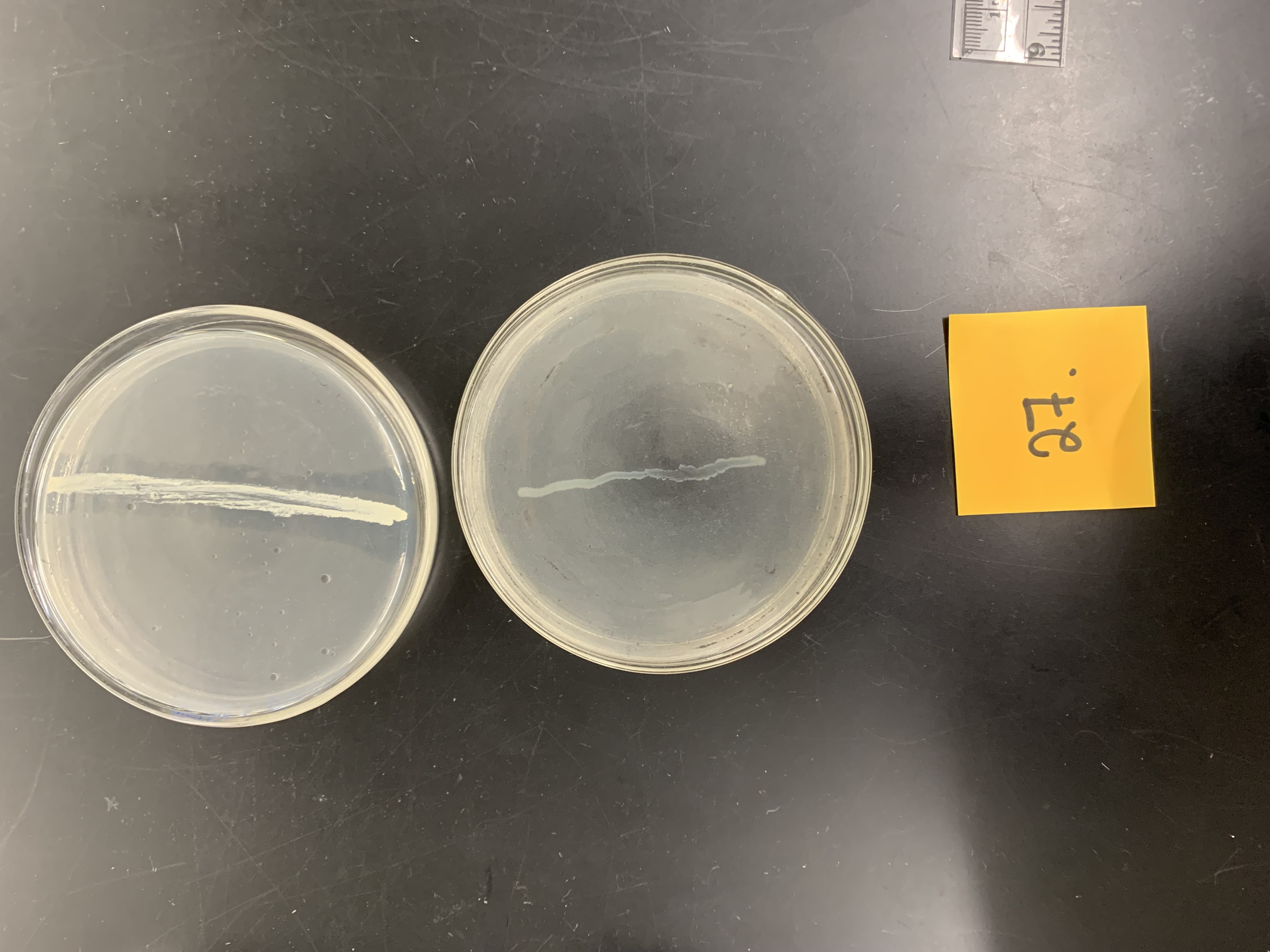
what type of substate is tirbutyrin
lipid
64
New cards
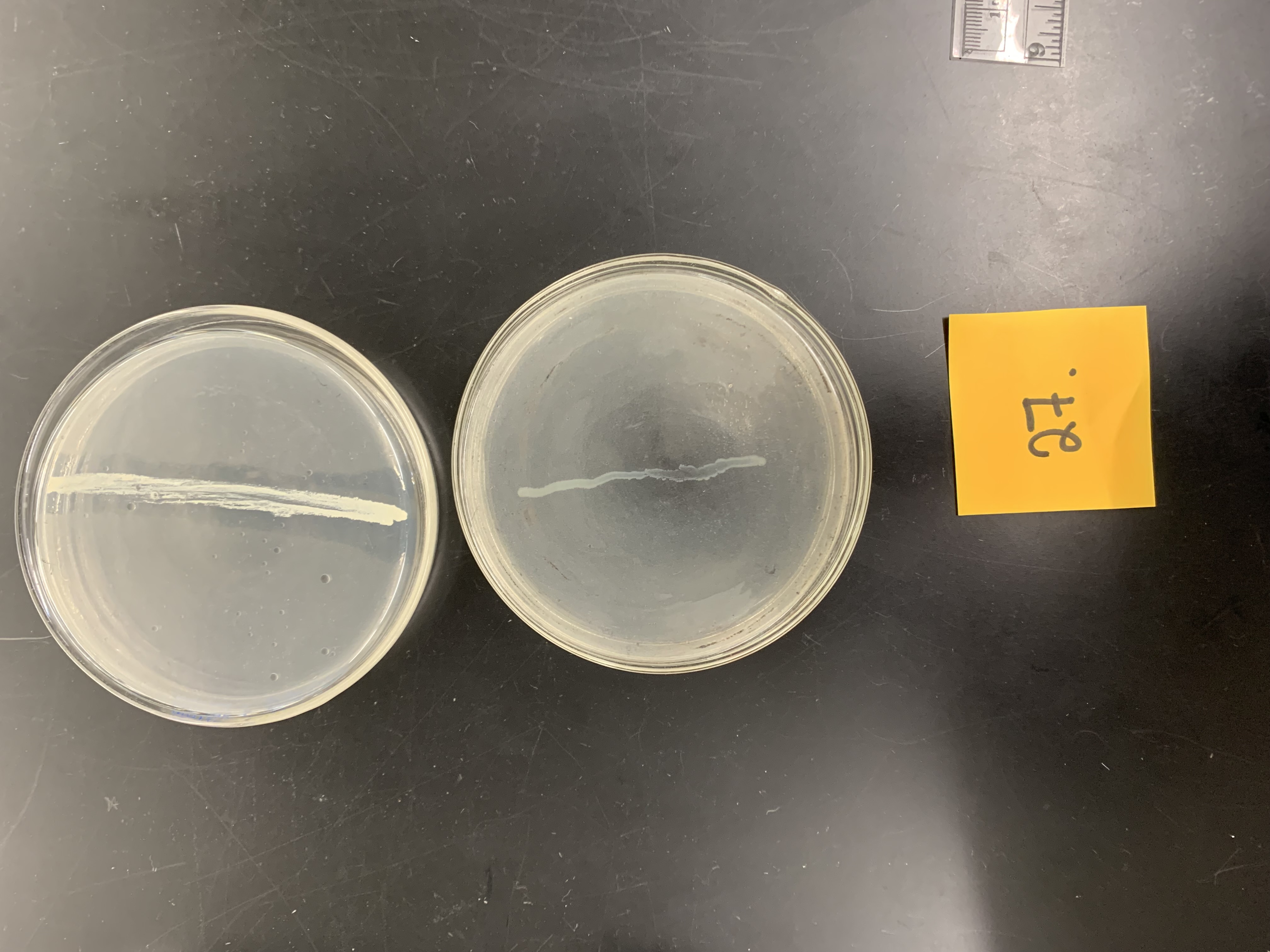
what enzyme is it testing for
lipase production
65
New cards
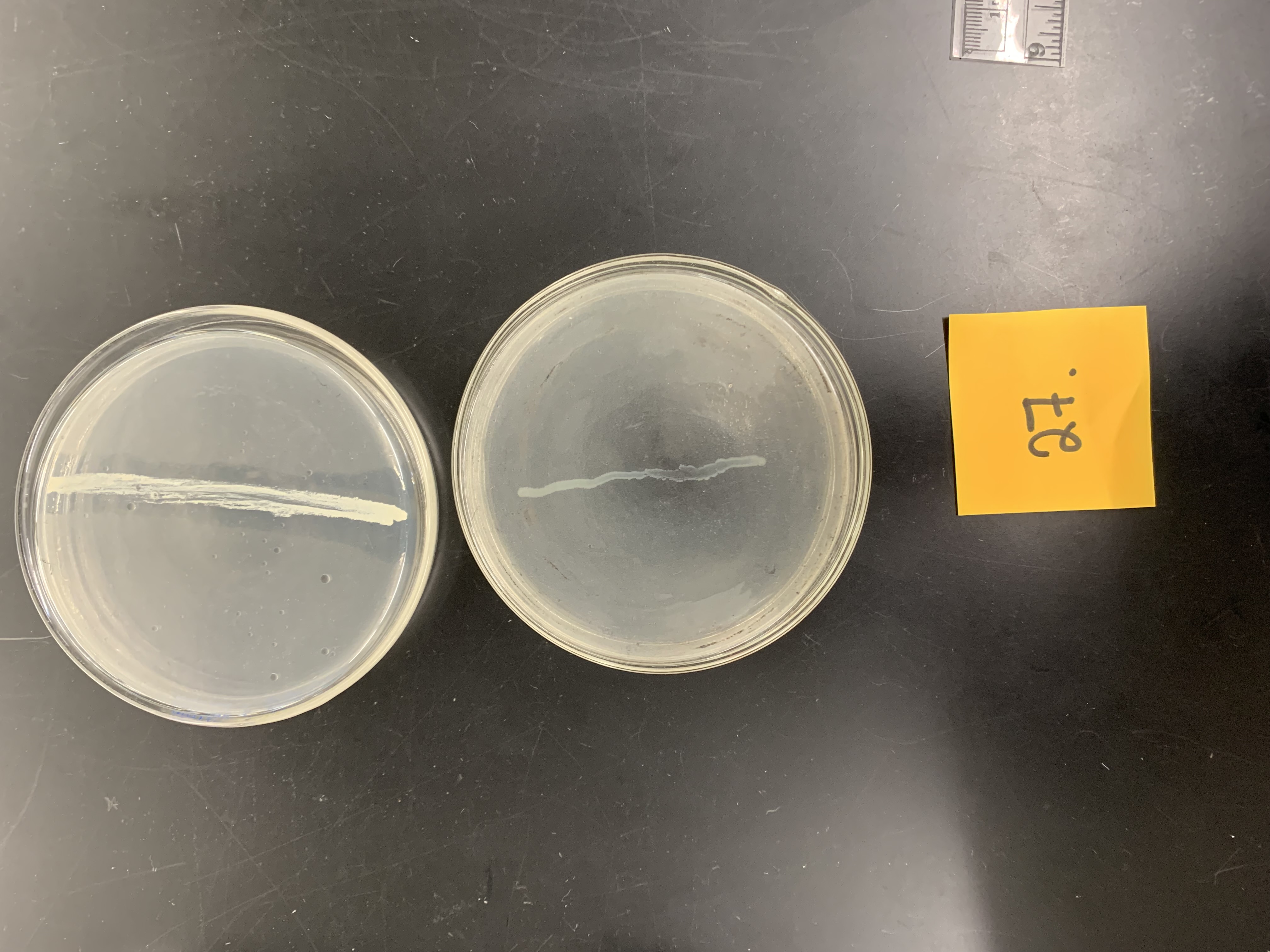
How would the top plate be interpreted
positive for lipase production
66
New cards
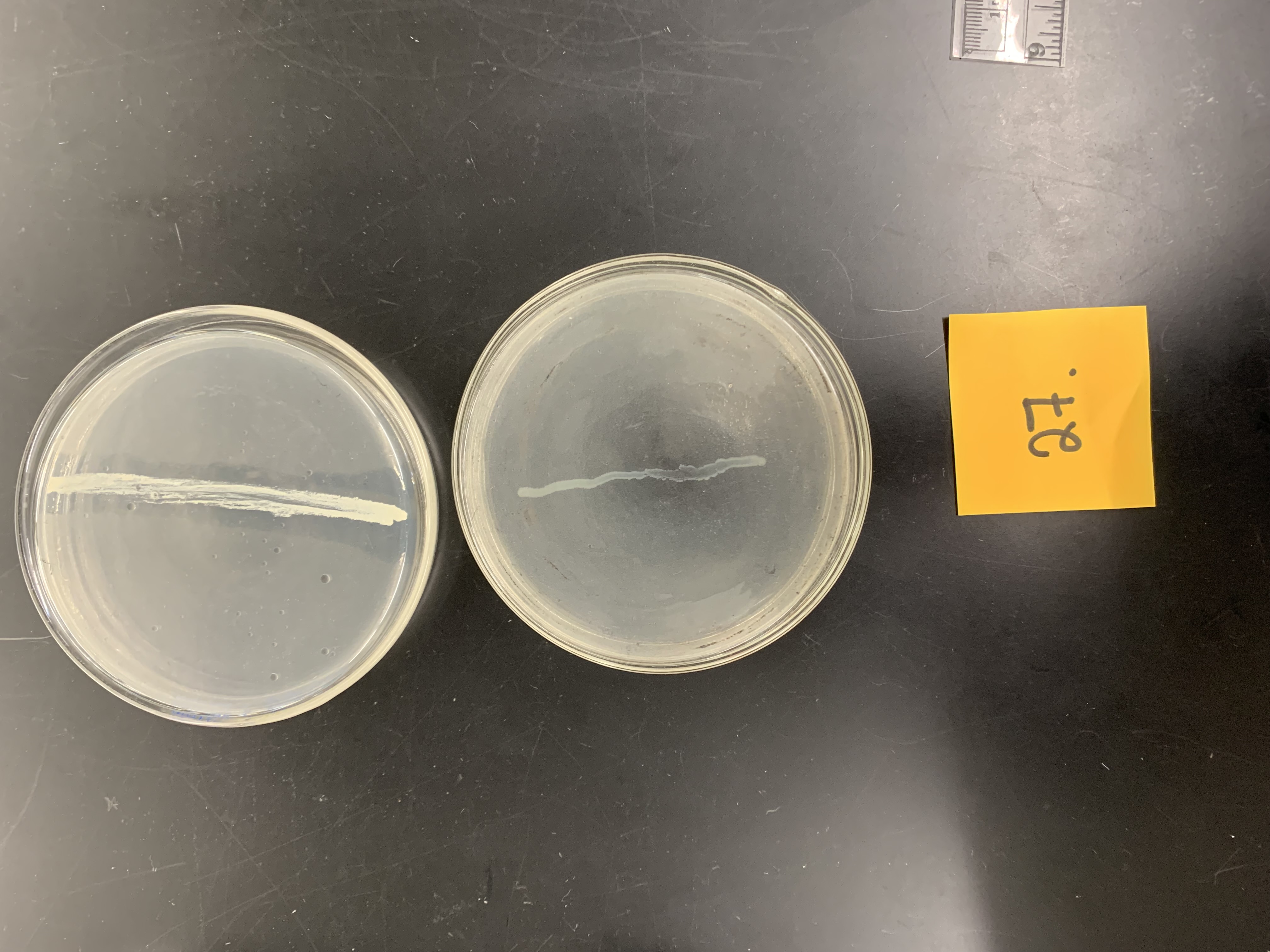
how would the bottom plate be interpreted
negative; no lipase production
67
New cards
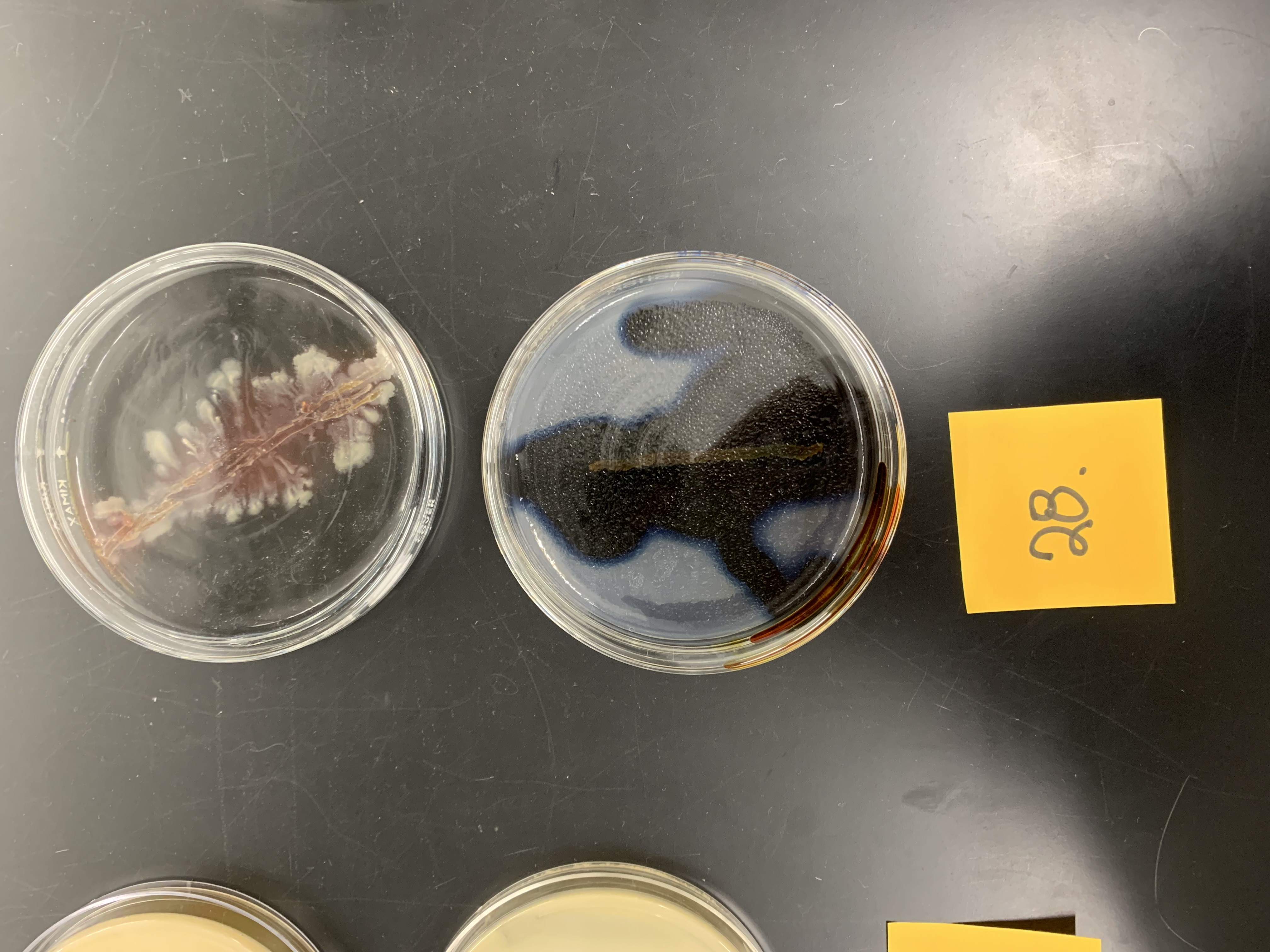

what was added to the plates to allow interpretation
iodine
68
New cards
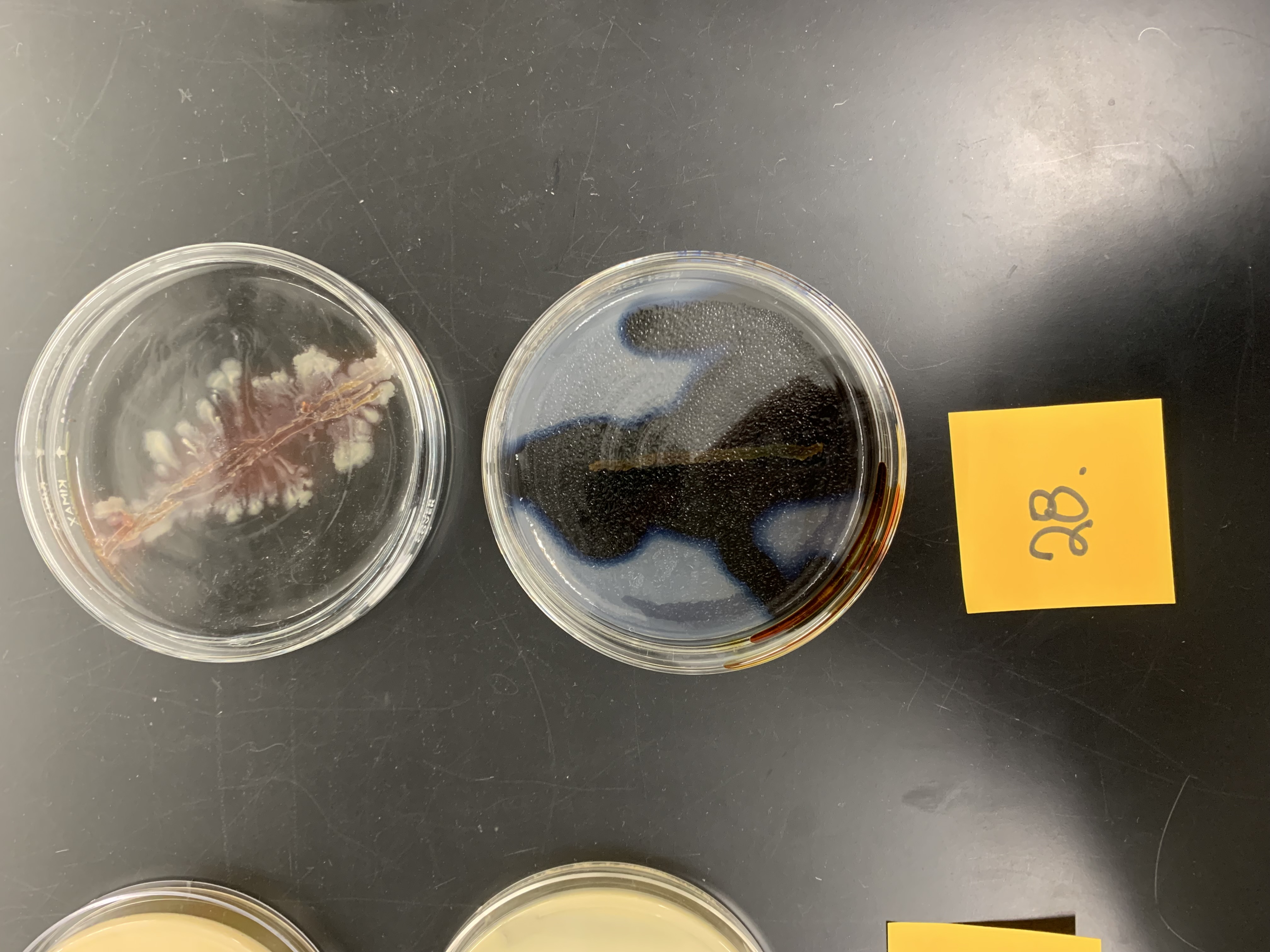

starch agar plates; what enzyme is being tested
amylase production
69
New cards
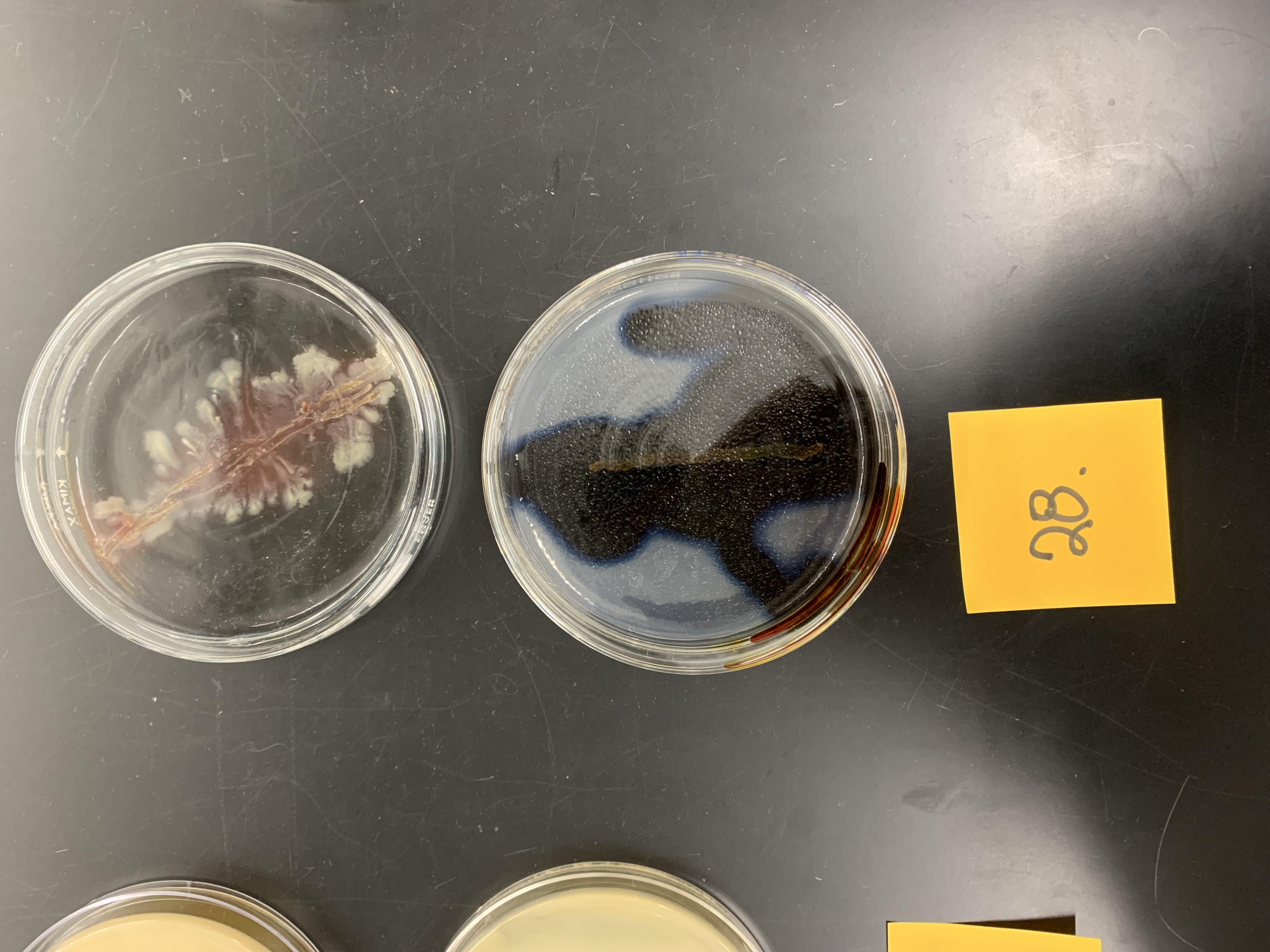

how would you interpret the top plate
postive for amylase production
70
New cards
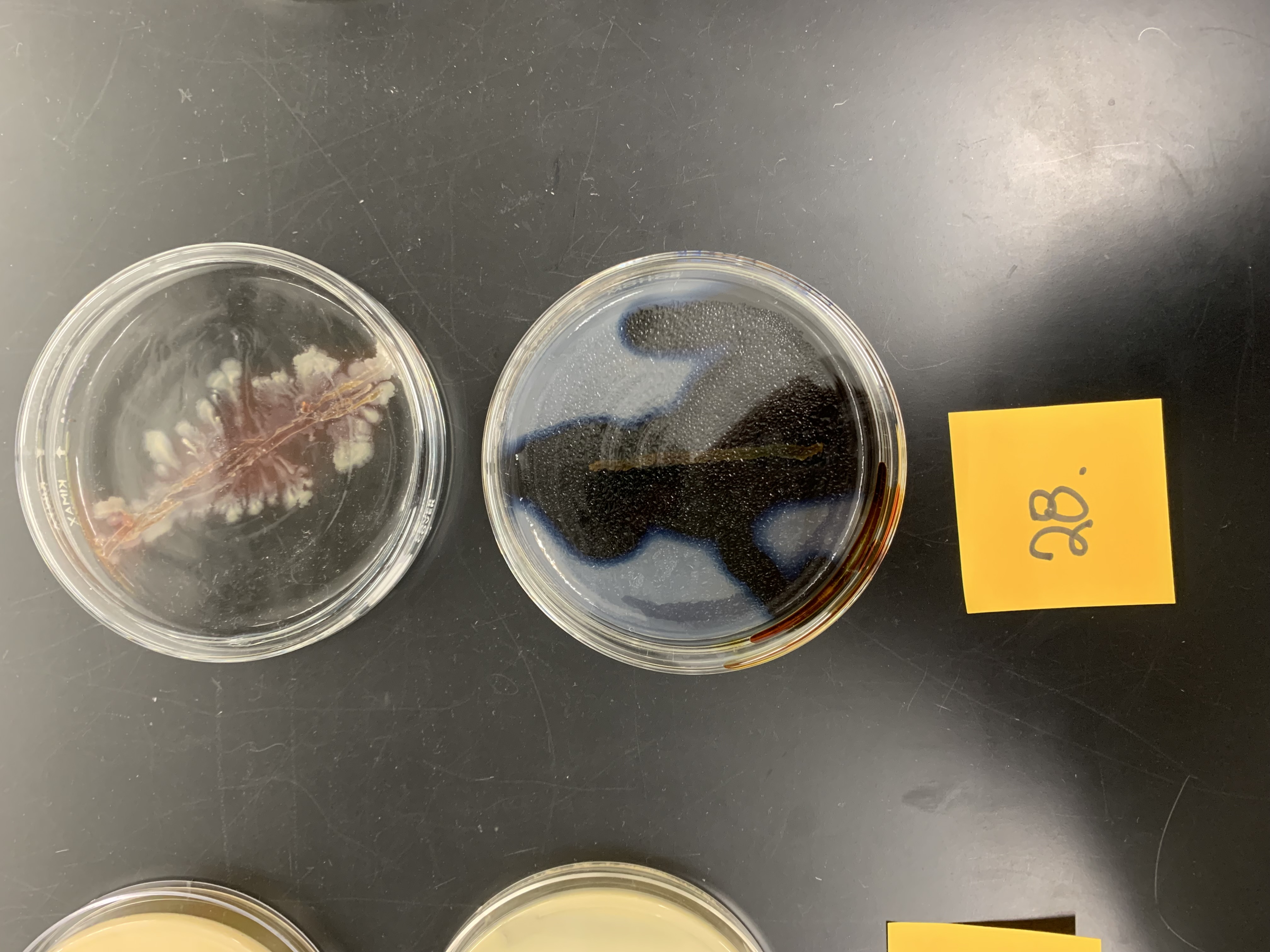

how would you interpret the bottom plate
negative for amylase production
71
New cards
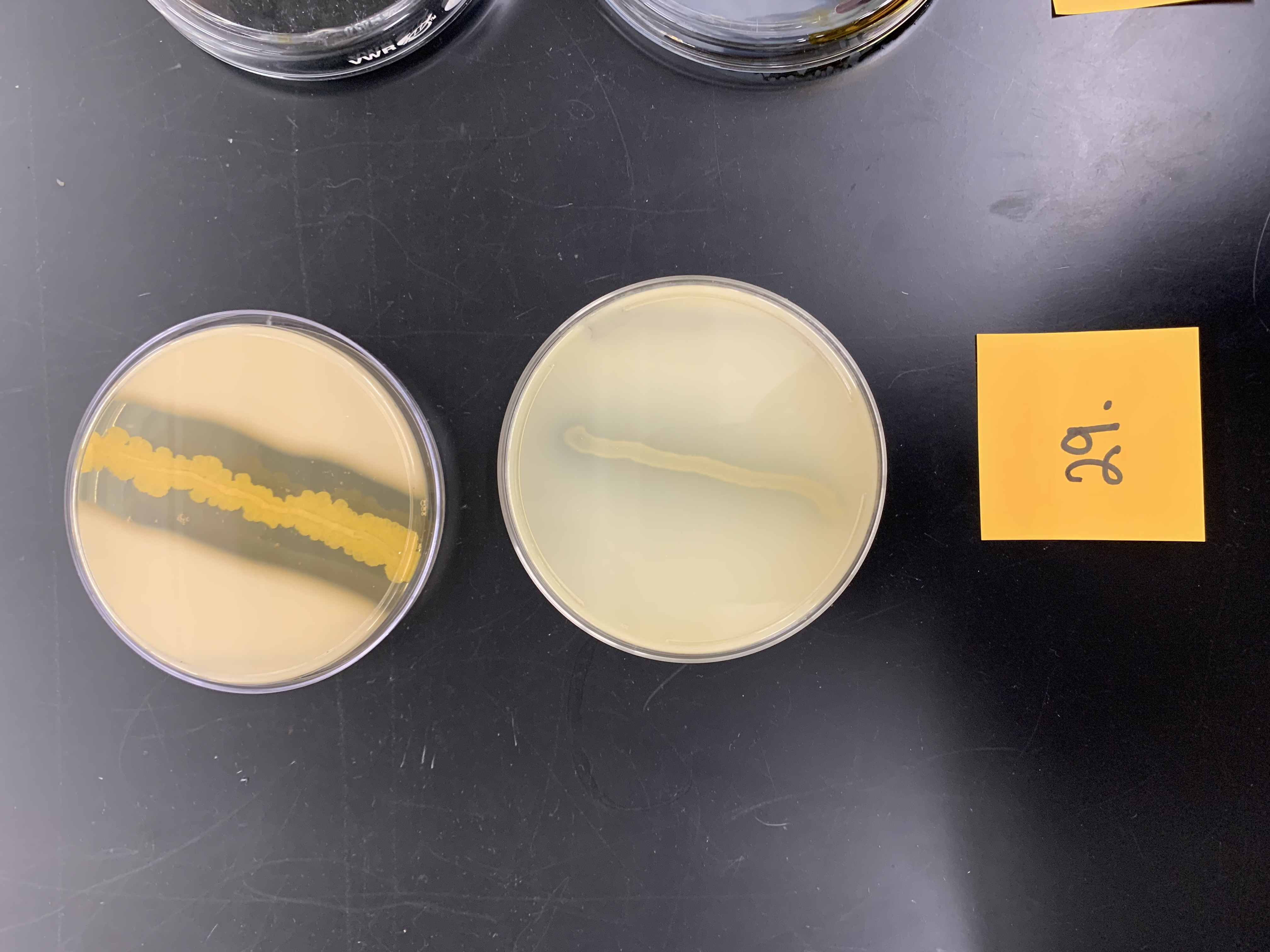
skim milk agar; what enzyme is being tested
caseinase production
72
New cards
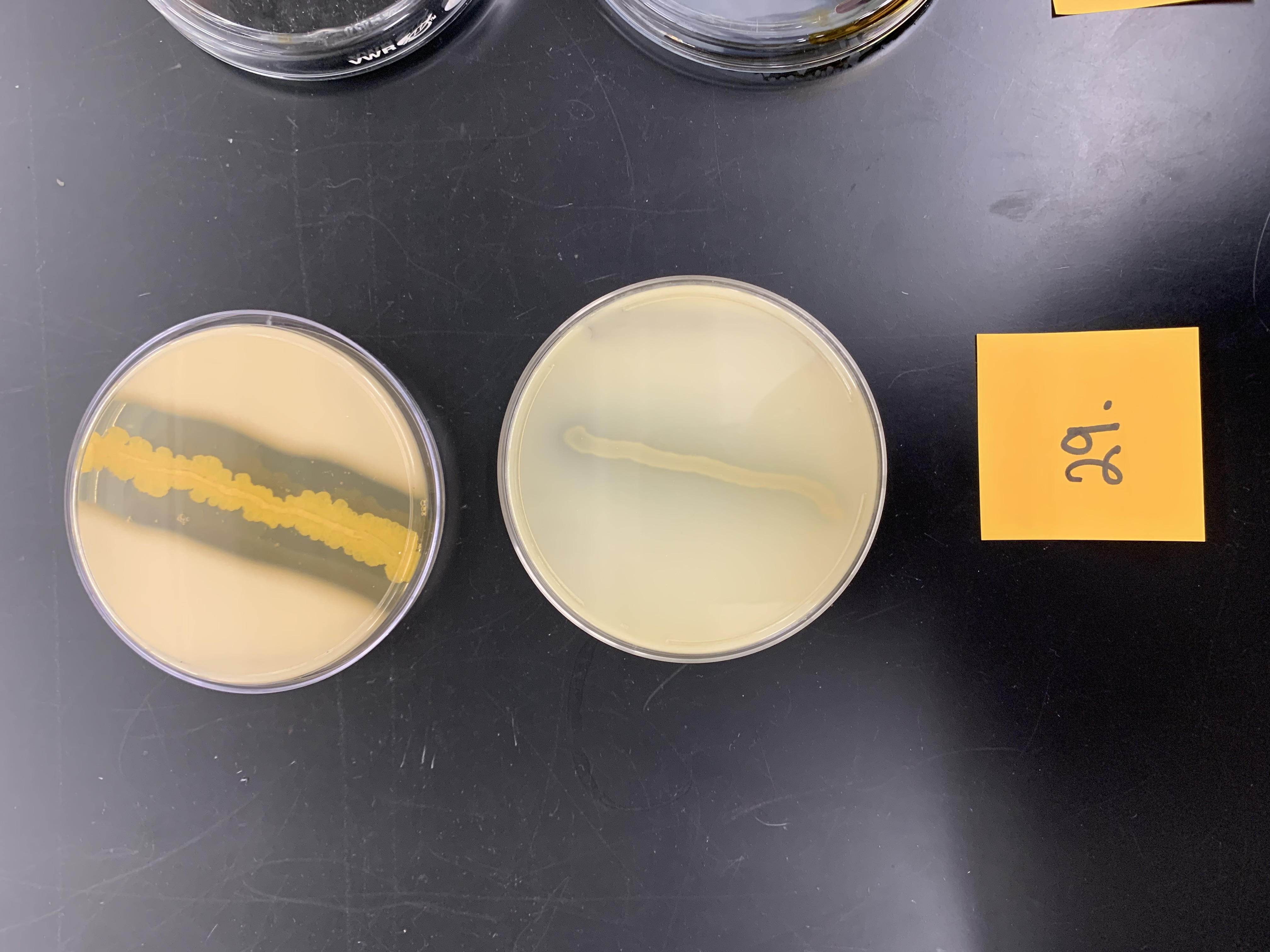
how would you interpret the top plate
positive for caseinase production; clearing around line of bacteria
73
New cards
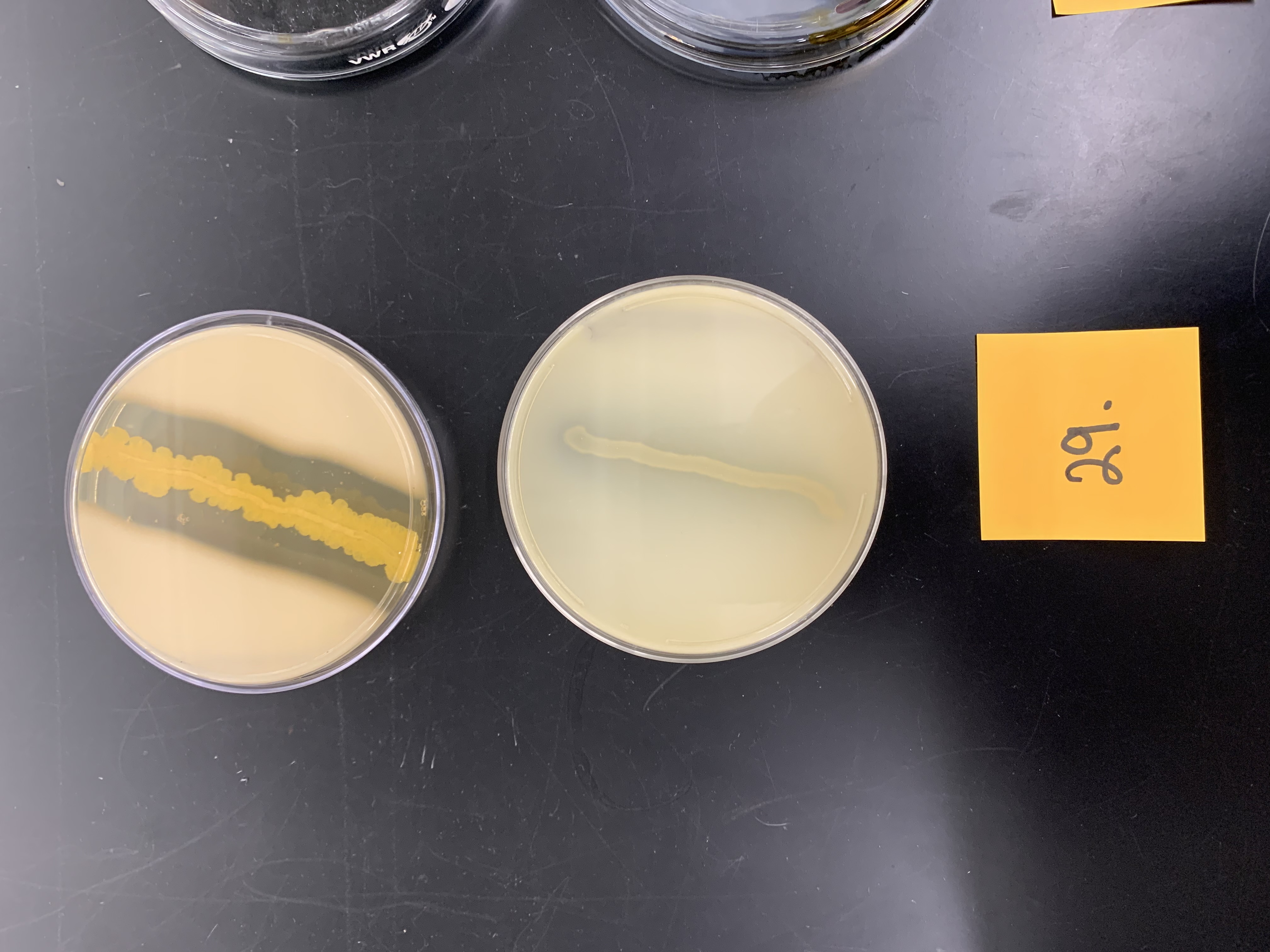
how would you interpret the bottom plate
negative for caseinase production; no clearing
74
New cards

gelatin tubes; what enzyme is being tested
gelatinase
75
New cards

how would you interpret tube A
solid; negative for gelatinase production
76
New cards
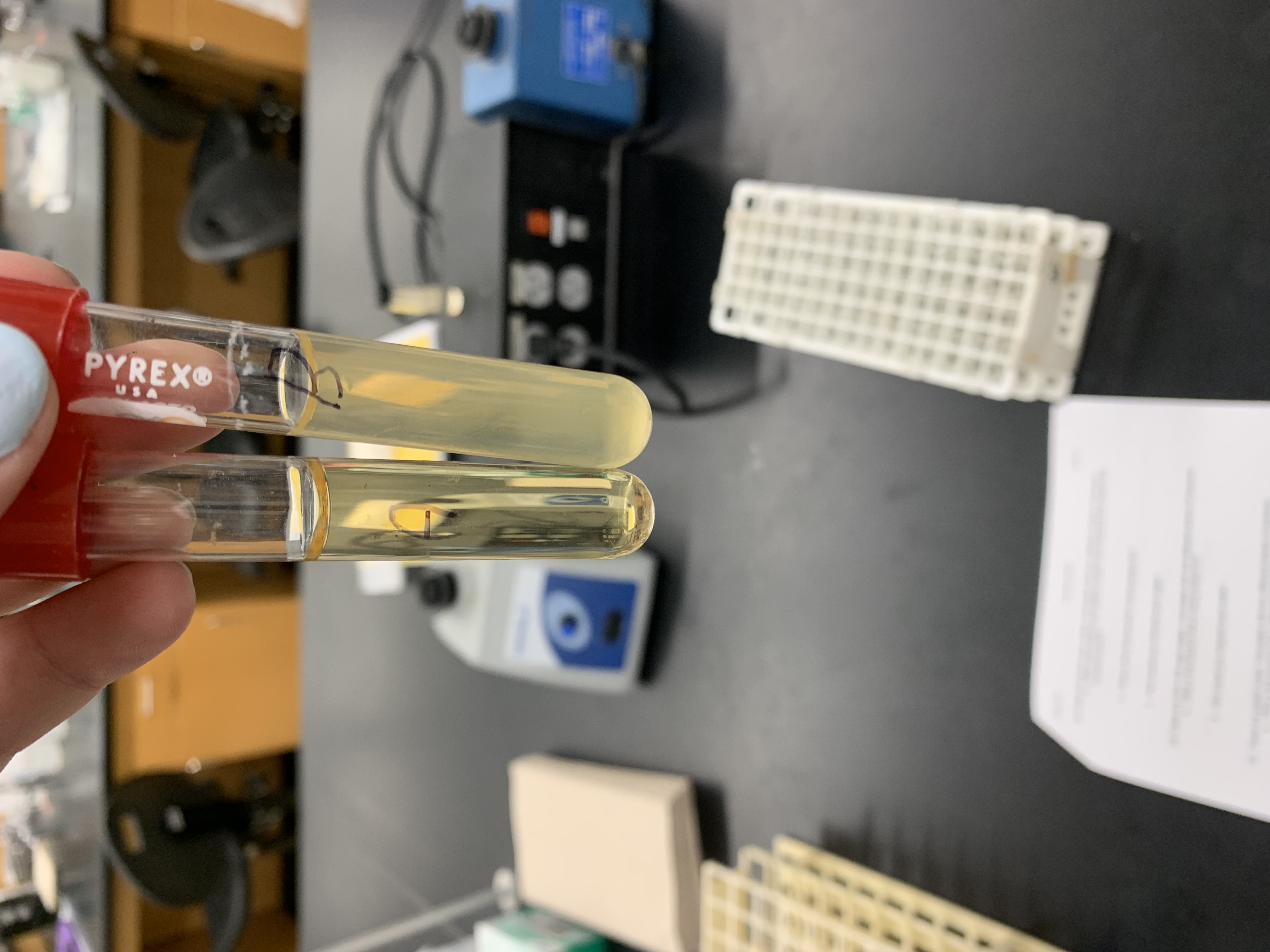

how would you interpret tube B
liquid; positive for gelatinase production
77
New cards

citrate slants; what is being tested
citrate production
78
New cards

how would you interpret tube A
negative for citrate production
79
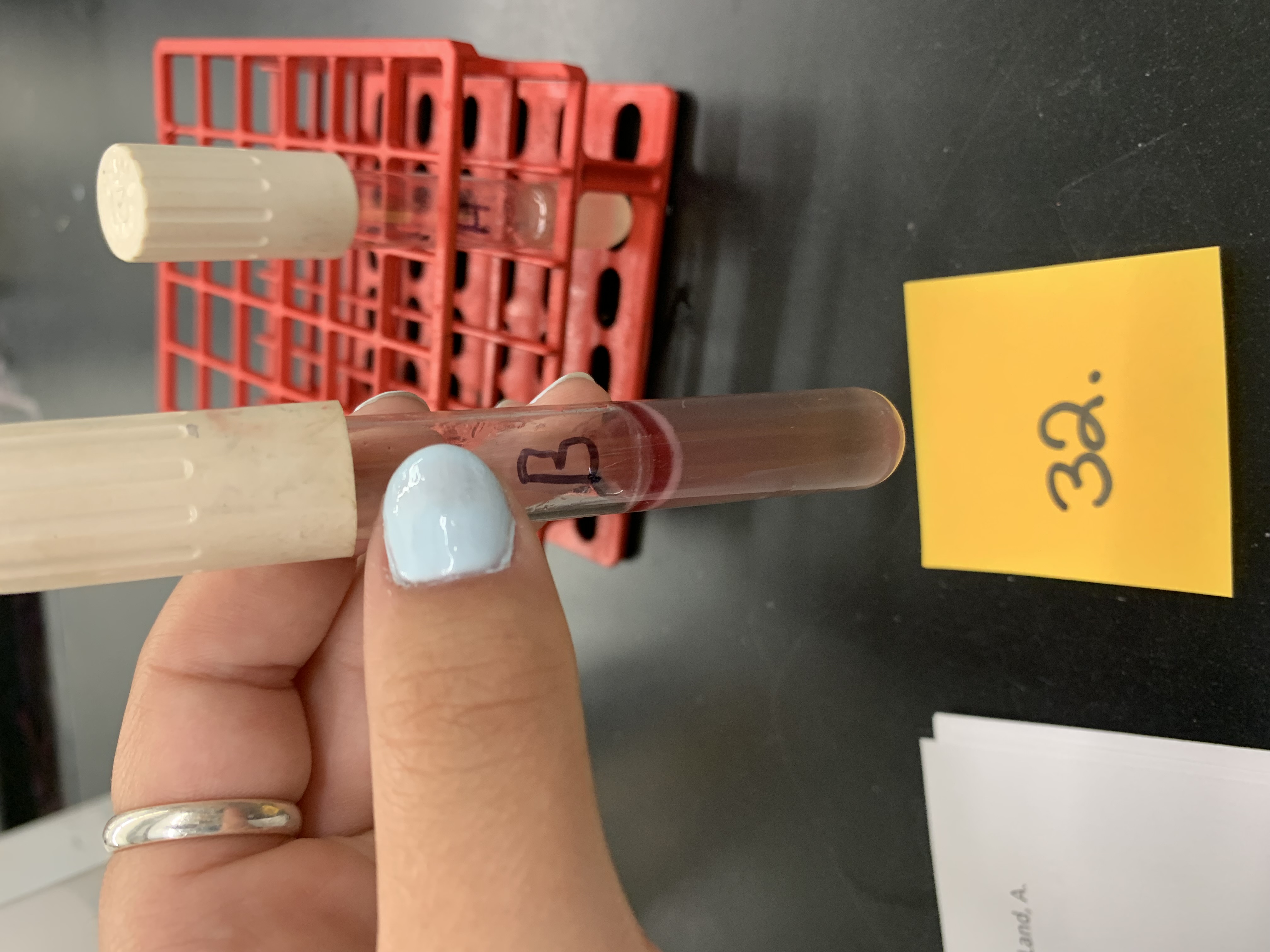
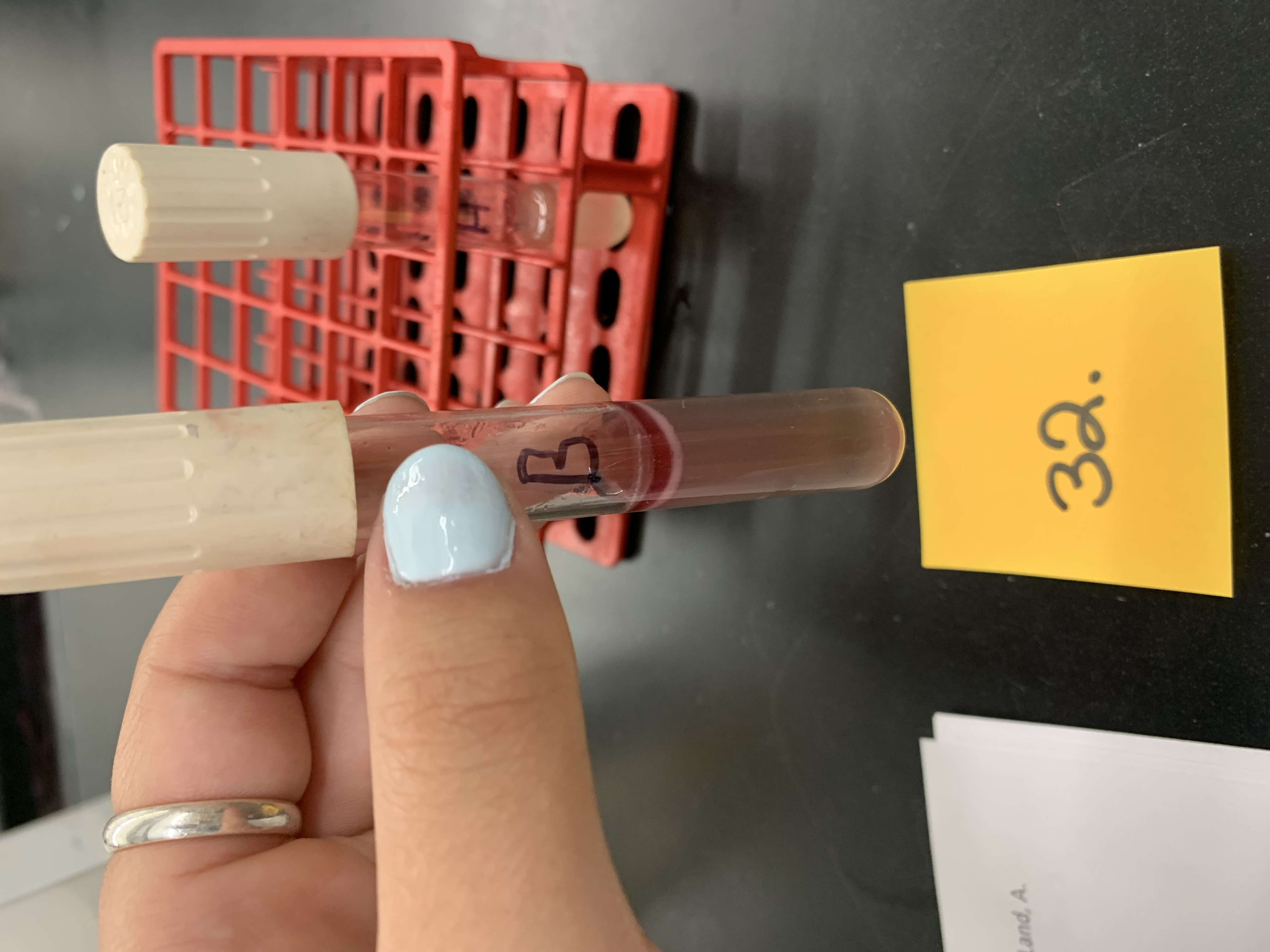
New cards

how would you interpret tube B
postive for citrate production
80
New cards

tryptone tubes; what is this testing for
ability to degrade amino acids
81
New cards

how would you interpret tube A
positive for indole production (a)
82
New cards

how would you interpret tube B
positive for indole production (b)
83
New cards
what does a negative indole test look like
stays the same color/ yellowish
84
New cards
what is coliform
gram negative non spore forming rods that ferment lactose to acid and gas
85
New cards
what does MPN stand for
most probable number
86
New cards
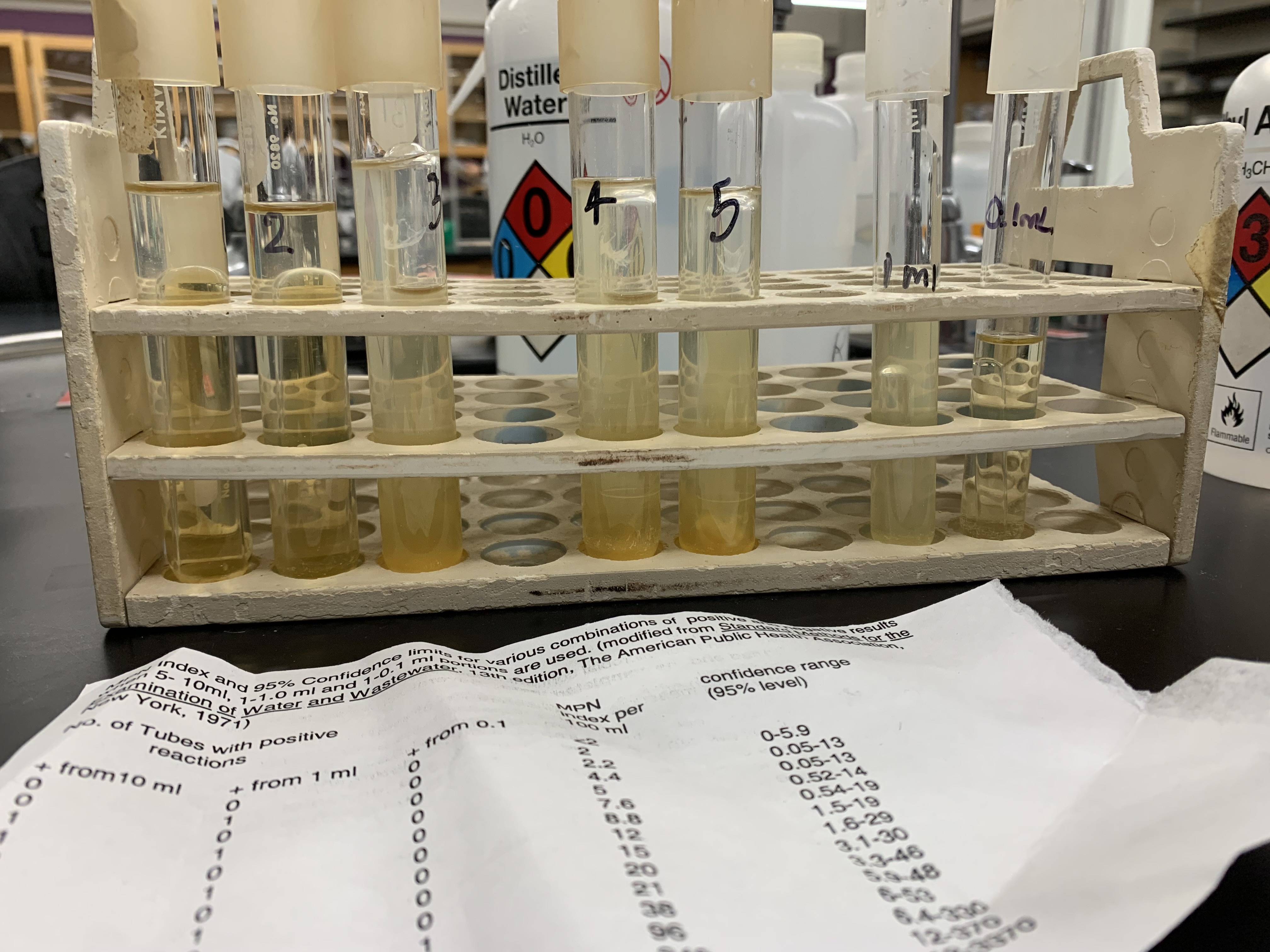

What tubes are positive for coliforms
3,4,5, and 1mL
87
New cards
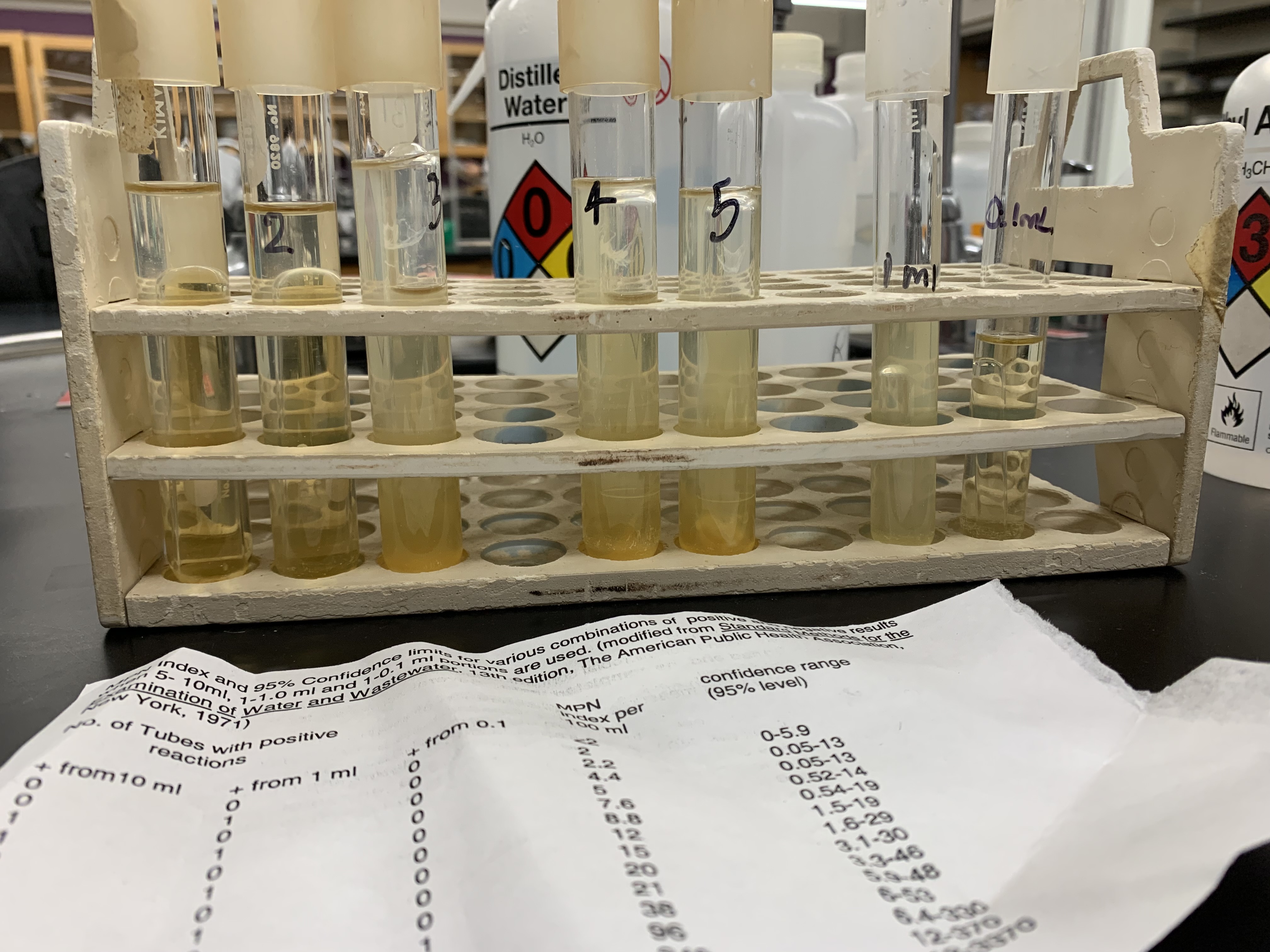

what is the result of this assay
12 MPN
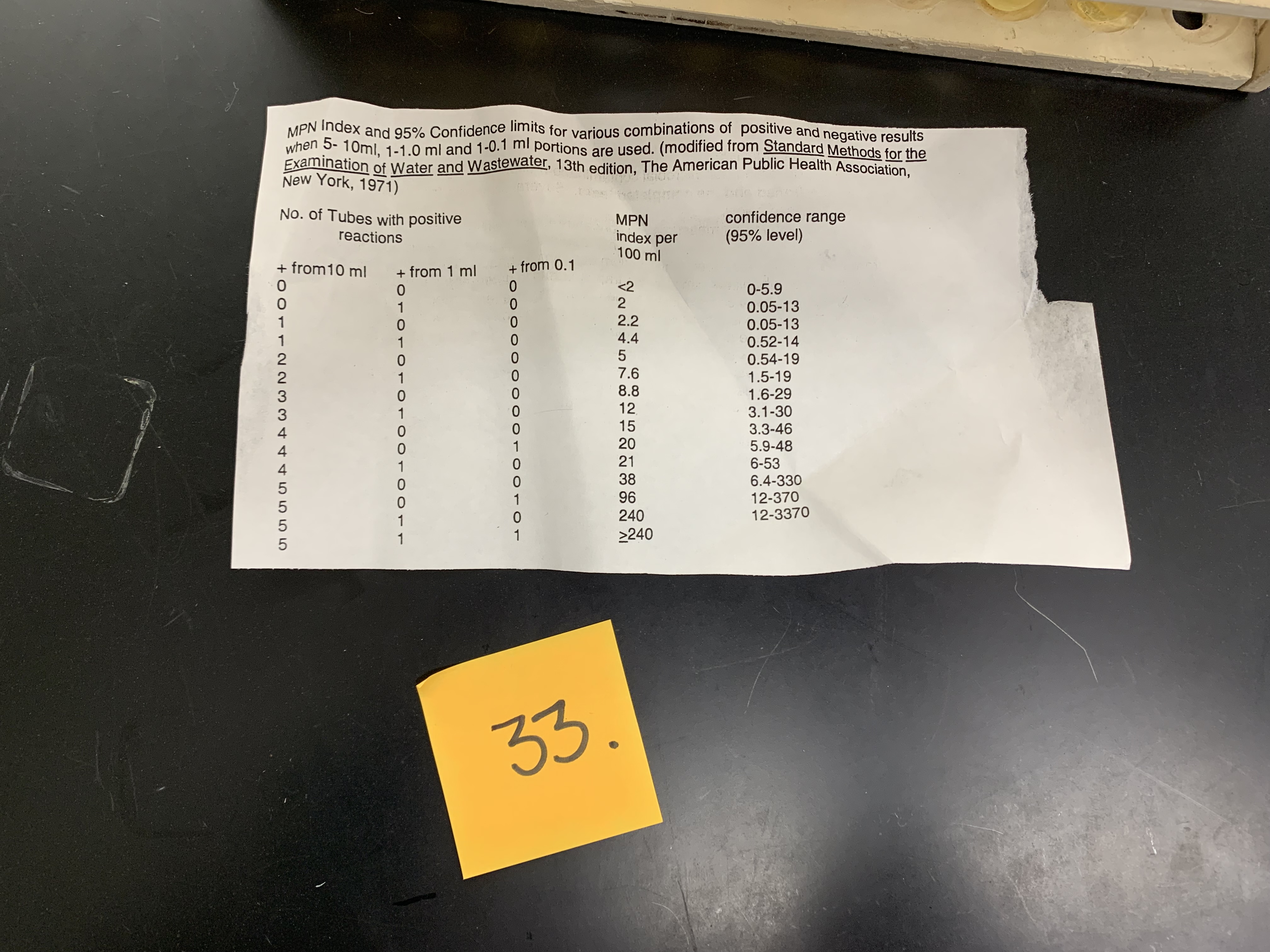
88
New cards
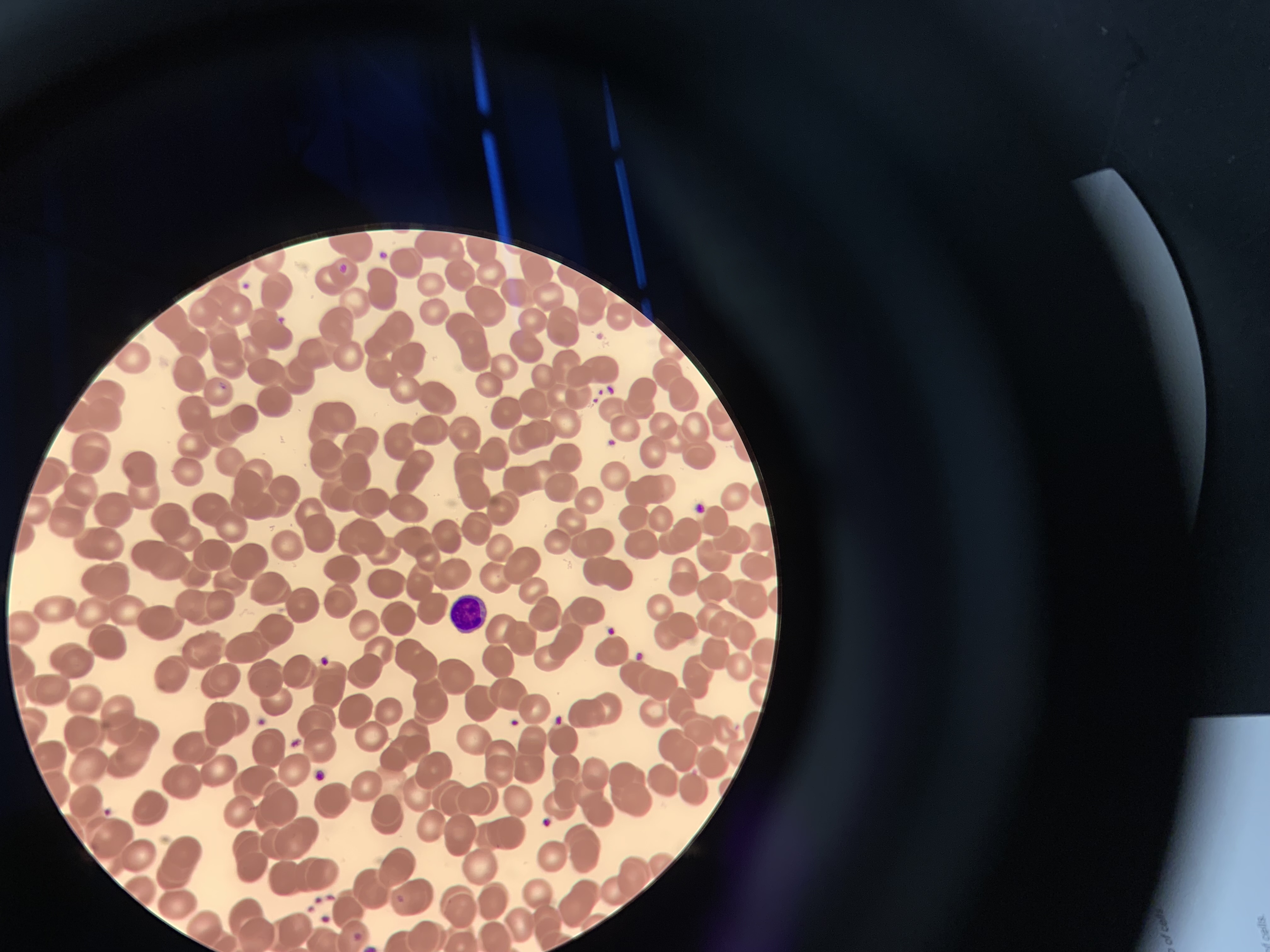
what immune cell is this
lymphocyte
89
New cards
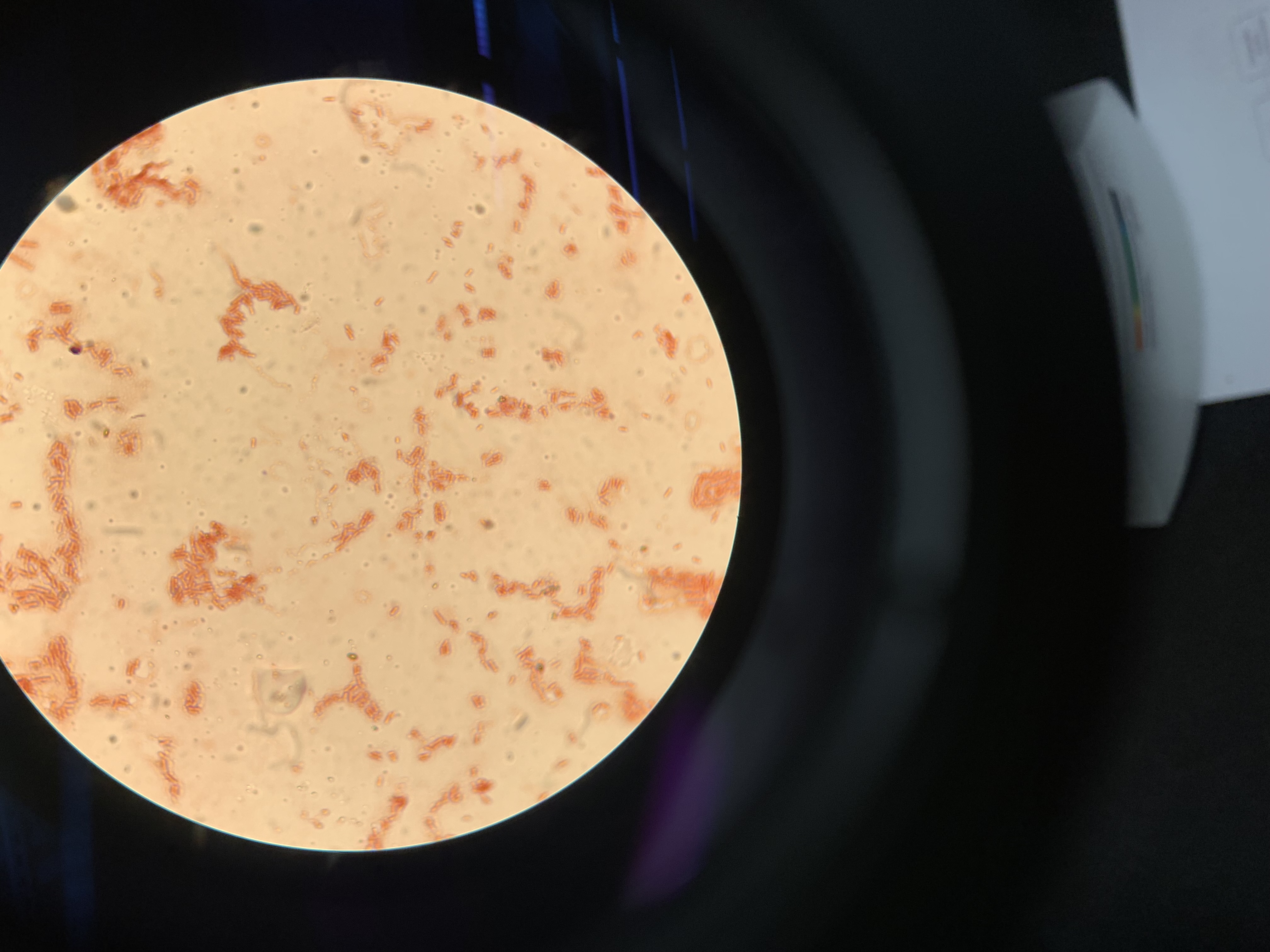
what are the results of this gram stain
gram negative bacilli
90
New cards

what are the results of this oxidase test
postive
91
New cards
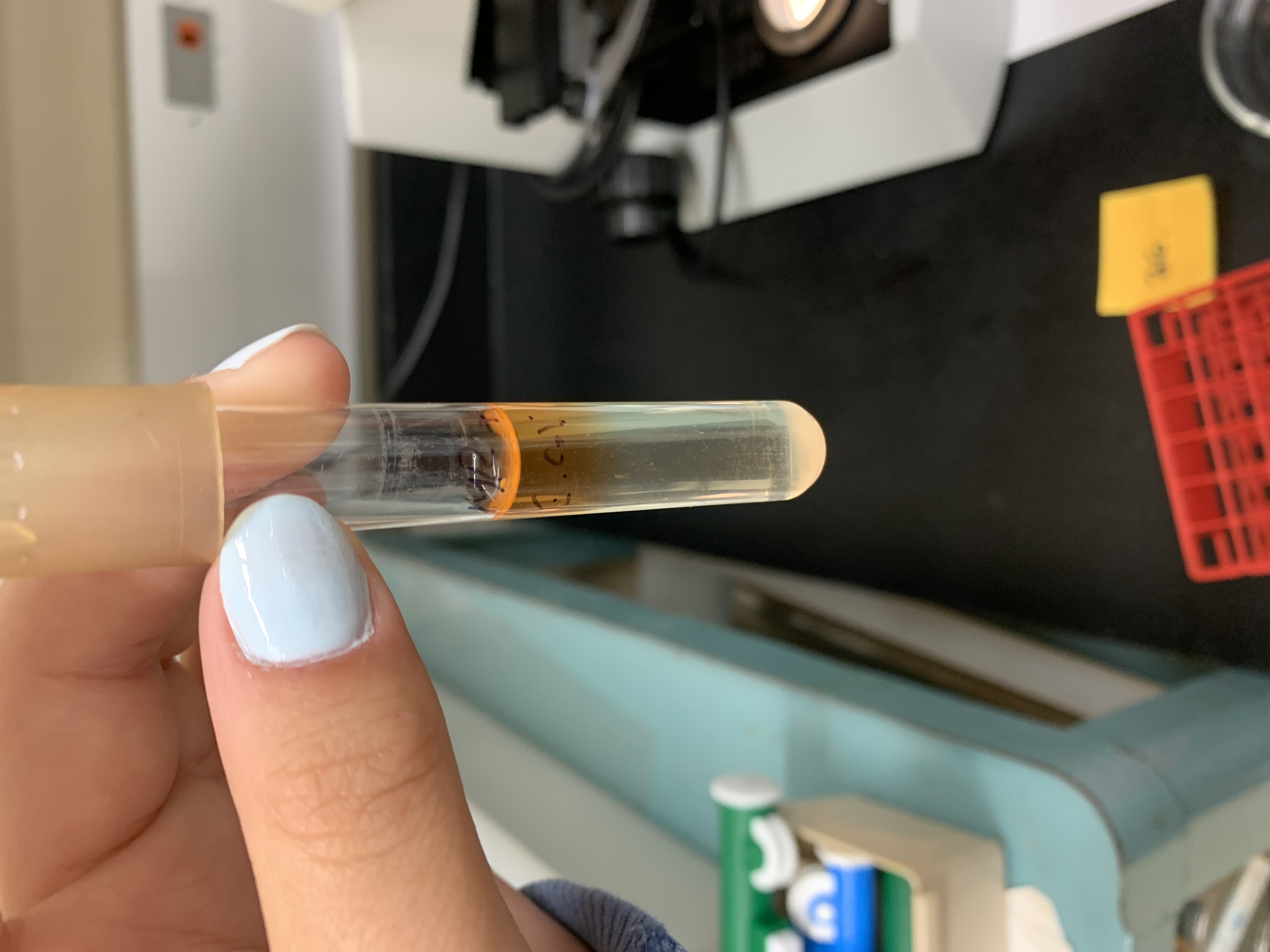

what are the results of this MR test
postive
92
New cards
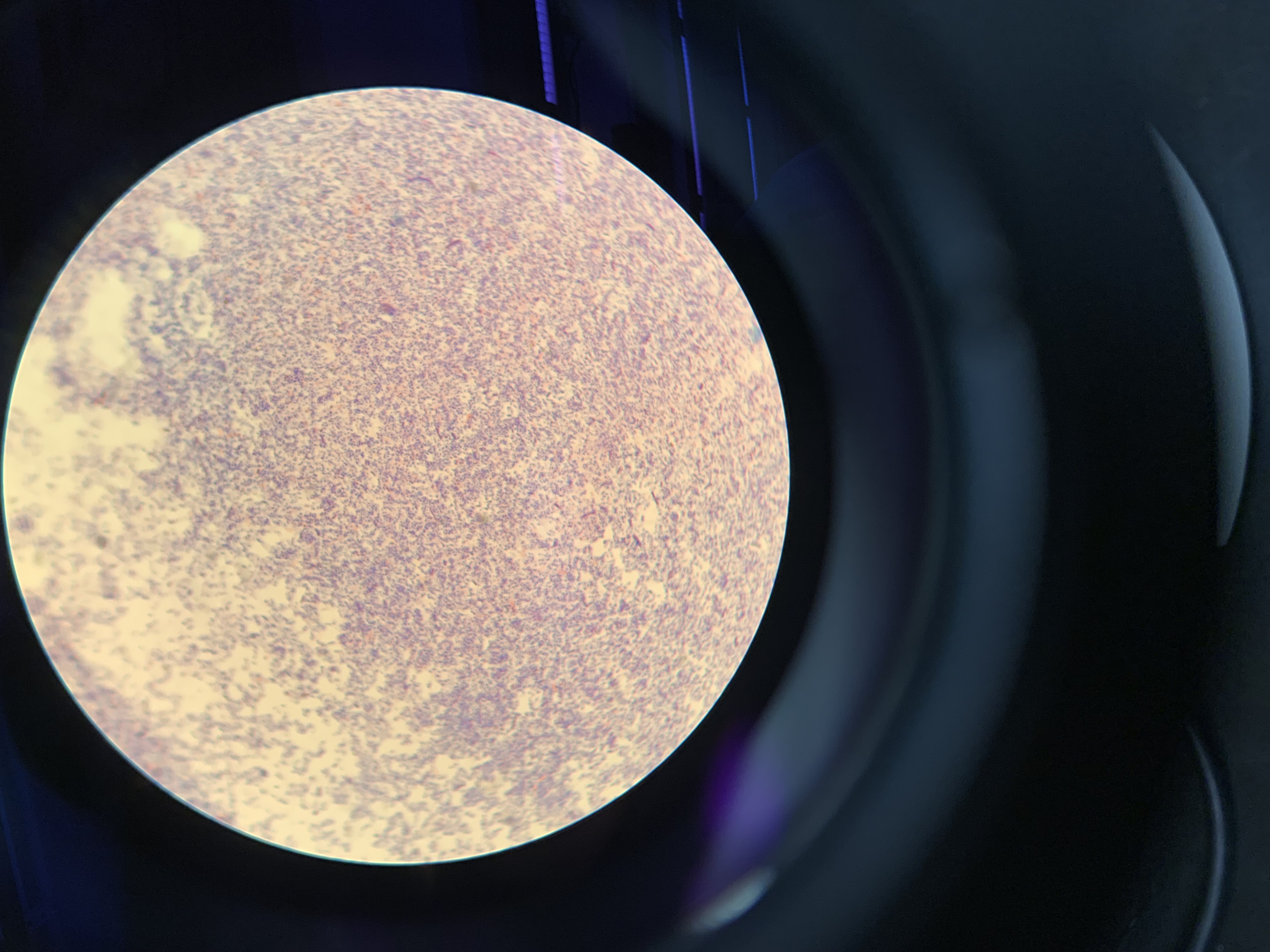
what are the results of this gram stain
gram postive bacilli
93
New cards
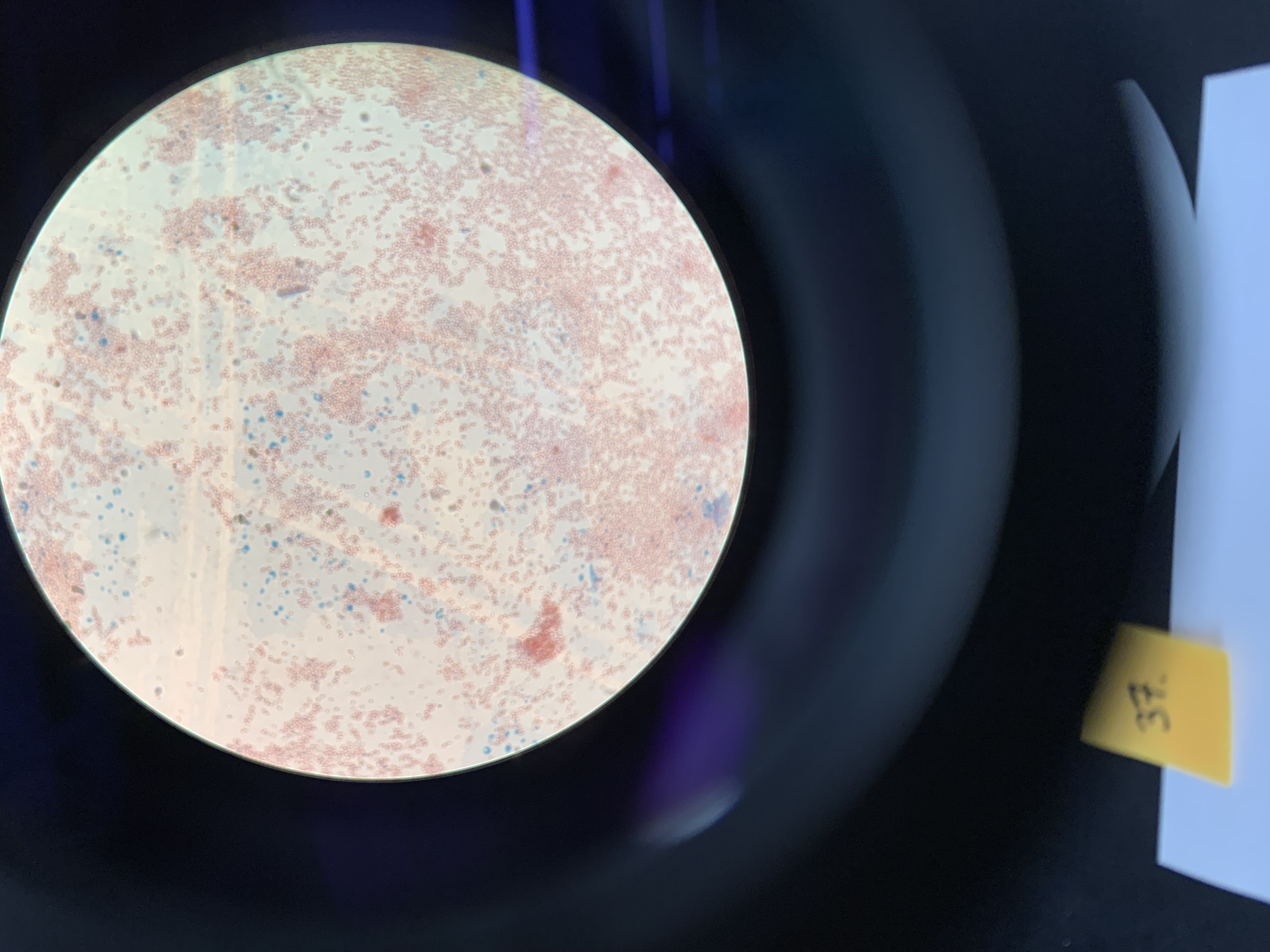
what are the results of this spore test
postive endospore forming
94
New cards
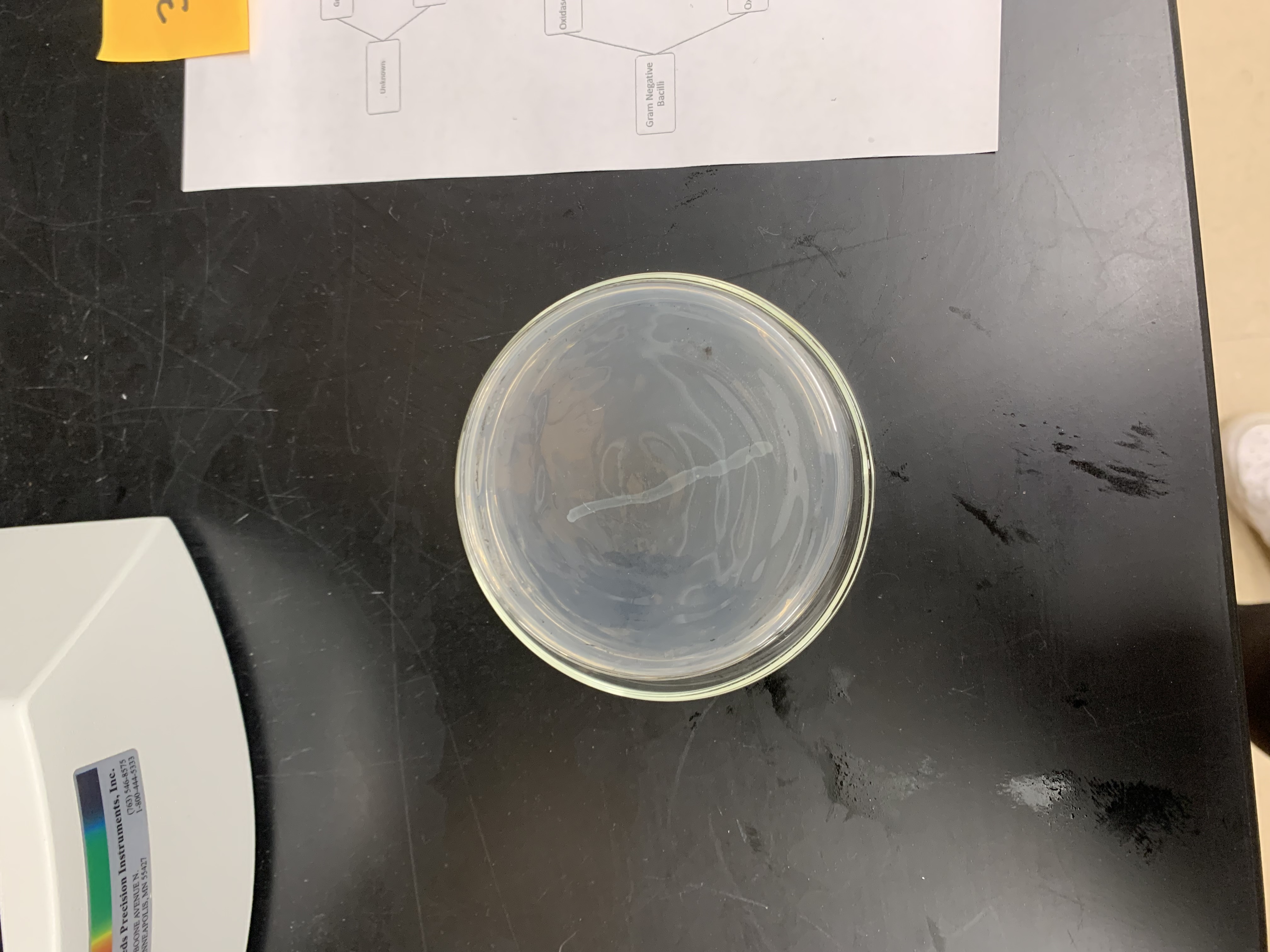

what are the results for this amylase test
negative for amylase production; no clearing
95
New cards

what are the results of this MR test
positive for glucose fermentation
96
New cards
what are the results of this MR test
negative for glucose fermentation
97
New cards
what are the results of this VP test
positive for the presence of acetoin
98
New cards
what are the results of this VP test
negative for the presence of acetoin
99
New cards

what plate section is used to determine the MBC
section 1
100
New cards
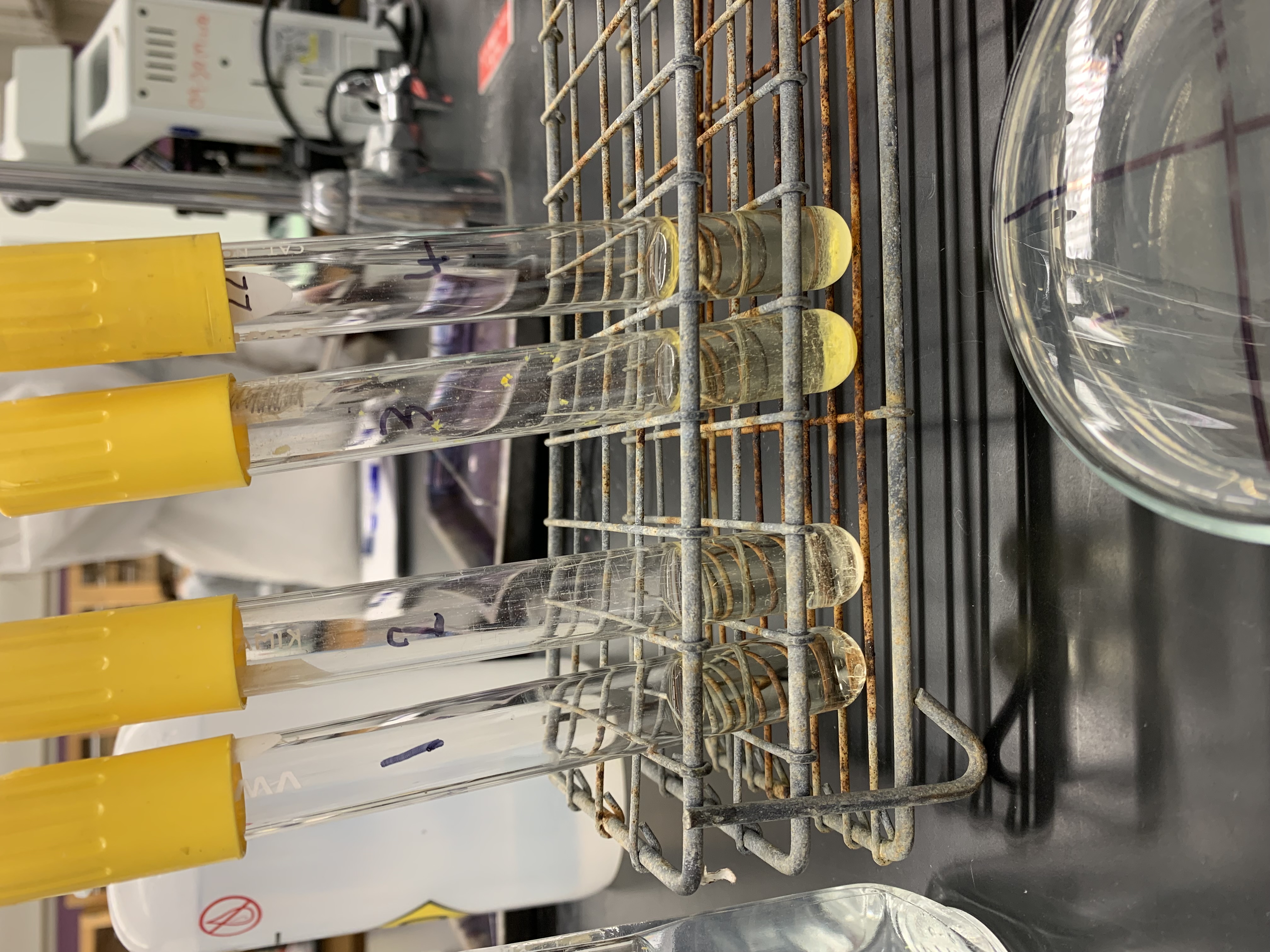

what tube is used to determine the MIC
tube 2