CORNEAL TOPOGRAPHY
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
HVID RANGE AND AVERAGE
10 - 14 mm average: 11.7 mm
VVID RANGE AND AVERAGE
average: 10.6 mm <HVID by 0.5 - 1.0 mm
CORNEAL THICKNESS Clinical studies and Gullstrands eye
Clinical Studies: 0.50 – 0.65 mm
Gullstrand’s Eye No. 1: 0.50 mm
Used to measure corneal thickness
pachometer
2 types of pachometers
ultrasonic
optical
Epithelium refractive index
1.401
Corneal Substance Refractive index
1.376
Anterior stroma RI
1.380
Posterior Stroma RI
1.373
During early life what kind of astigmatism does a person have
WTR
Limbal topography influences SCL fitting
TRUE
What is used to assess for limbal topography
Slit lamp
Placido disc
What is the deviation of peripheral curvature from the apical curvature
asphericity
The point of maximum curvature or shortest radius
CORNEAL APEX
Revolution of a conic about an axis of symmetry
CONICOID
Degree of peripheral asphericity
ECCENTRICITY
ECCENTRICITY VALUE OF THE HUMAN CORNEA Give the range and average
range: 4.41 - 0.58
average: 0.47
What are the regions of corneal asphericity
central region or corneal cap
mid-peripheral region
peripheral region
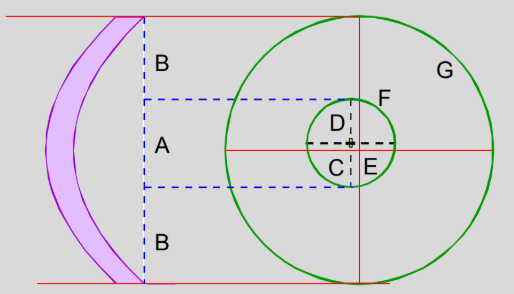
identify the following letters
A. Apical zone
B. Transitional zone
C. Visual centre
D. Apical centre
E. Geometric centre
G. Keratometric limbus
F. Limiting margin
Region of greater flattening
Evidence of negative asphericity
Mid-peripheral region
Diameter of corneal cap
4mm approx
90% of semi-meridians had positive asphericity
• Remainder - zero or negative
• Nasal and superior-nasal asphericities were greater than the other semi- meridians
Peripheral regions
Give the method of measurement for corneal topography in optical
reflection
optical profiling
interferometry/Mo
Give the method of measurement for corneal topography in contact methods
casting and molding
ultrasound
trial contact lenses
This method of corneal topography measurement is
Non-contact/non-invasive
Rapid data collection
Most convenient
Output in readily used form
OPTICAL REFLECTION
Give example for optical reflection
keratometer
This method of corneal topography measurement is
Non-contact/non-invasive
Can be rapid data collection
High accuracy possible
Only one meridian per scan
Still a technical challenge but could surpass keratometry
Optical profiling 2D
Give example for Optical Profiling
Laser tomographers
This method of corneal topography measurement is
• Some are non-contact
• Can be rapid data collection
• Very high accuracy possible
• 3D scan (single scan only)
• Some technical difficulties
OPTICAL PROFILING (3D)
Give example of optical profiling 3d
Laser interferometers
This method of measurement is:
• Contact may distort topography
• Time consuming
• On some methods only qualitative result possible
• Data can be difficult to interpret
contact method
Give example for contact method
casting/moulding
ultrasound
trial contact lens
give instruments to measure corneal topography
• Placido disc
• Photokeratoscope
• Keratometer
• Computer-assisted Topographic analysis
This instrument has:
• Wide field of view
• More complete mire locus
• Qualitative
PHOTOKERATOSCOPE/ PLACIDO DISK
This instrument has the main function of measuring radius of curvature of the optic cap giving the information about front surface corneal radii and total corneal power
keratometer
Give the 4 types of doubling systems
• Fixed doubling
• Variable doubling
• Divided doubling
• Full doubling
In this doubling system there is image size and mire seperation as well as a fixed object height and doubling device distance
Fixed Doubling
In this doubling system there is a distance in doubling device, there is also a fixed mire seperation and image size
variable doubling
This doubling system has:
Full-aperture:
beam-splitting device
Full doubling
Types of keratometer
• 2-position
• 1-position
This type of keratometer specifies in rotation about the axis to measure second meridian
2-POSITION KERATOMETERS
This type of keratometer specifies in simultaneous measurements of
both meridians
1-POSITION KERATOMETERS
Give the parametric descriptors for topographic analysis systems
hint: Sim K, SAI, SRI
Simulated keratometry value (Sim K)
Surface asymmetry index (SAI)
Surface regularity index (SRI)
GIVE THE OCULAR PARAMETER MEASUREMENTS IN CONTACT LENS FITTING
• Corneal diameter
• Pupil diameter
• Palpebral aperture and lid position
• Keratometry
• Photokeratoscopy
This abnormal corneal topography has non-inflammatory thinning and
protrusion and cause disruption of mires
Keratoconus
This abnormal corneal topography is generalized enlargement of the cornea
KERATOGLOBUS
What changes can contact lens wear cause
• curvature/power
• refractive index
• thickness
PRINCIPAL RADII OF CURVATURE
What are the types of CONIC SURFACES hint* theres 2
• Sagittal radius
• Tangential radius
The normal perpendicular to the tangential radius extending from point P on the conic surface to its intersection with the optic axis
SAGITTAL RADIUS
The normal perpendicular to the sagittal radius extending from point P on the conic surface to the tangential point on the evolute
TANGENTIAL RADIUS