Biology MCAS
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
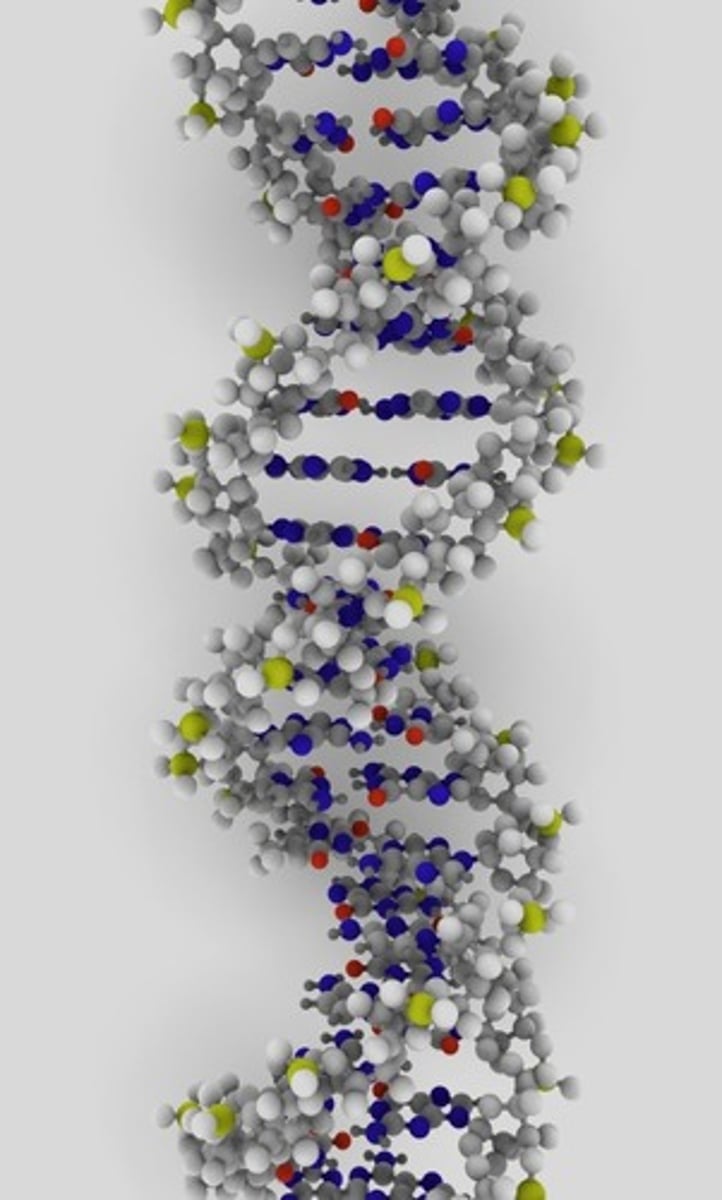
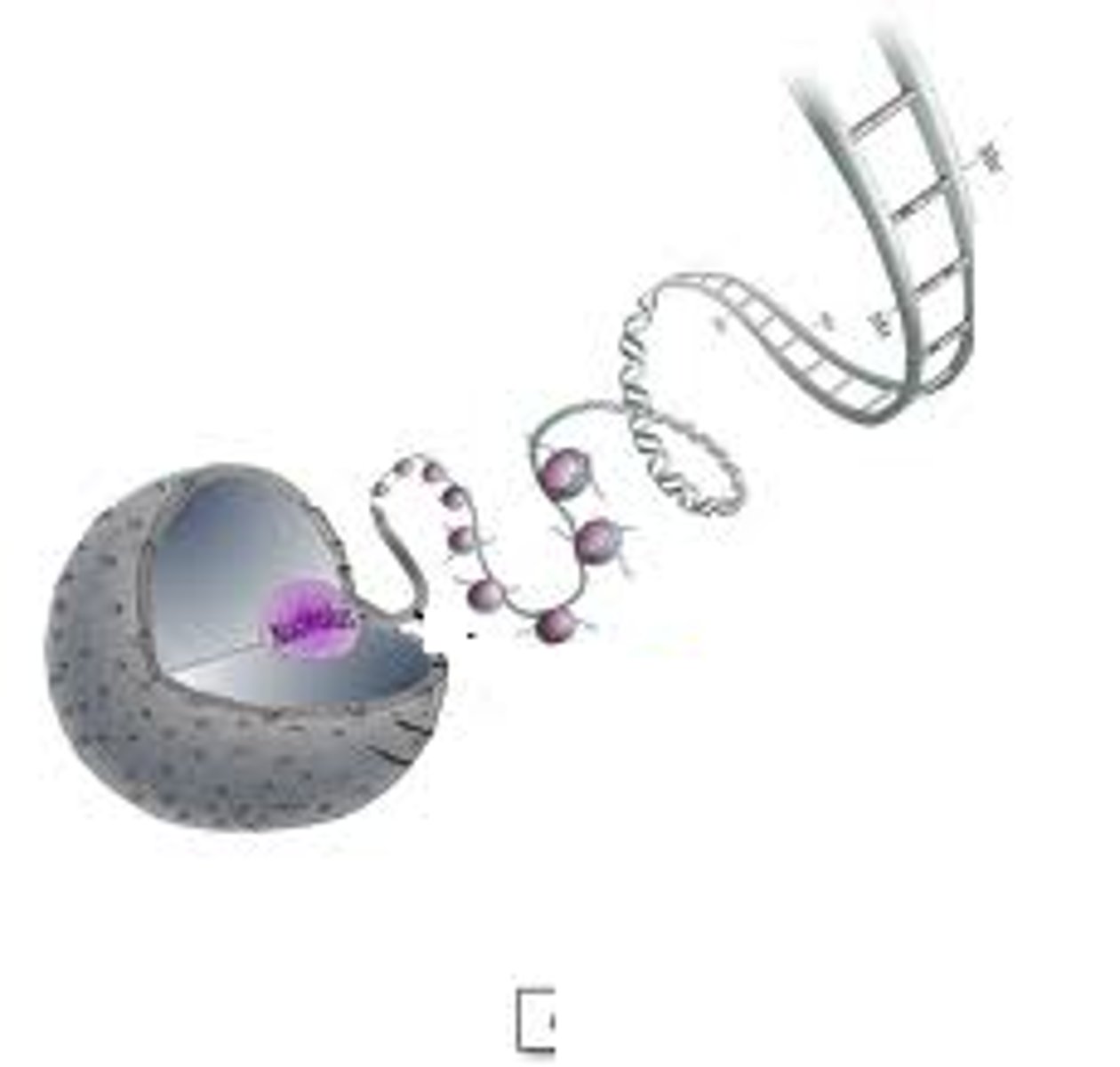
DNA
>Contains hereditary information in the Nucleus in each of the genes
>Genes code for everything in our bodies
>is too big to leave the cell
>Deoxyribonucleic Acid
>Double stranded molecule
RNA
>Classified as a Nucleotide
>is the messenger between DNA and Ribosomes
>Contains Uricil
mRNA
>Copies DNA in the Nucleus and carries info to ribosomes into cytoplasm
rRNA
>Ribosomal DNA
>Makes up a large part of the ribosomes
>Reads and decodes mRNA
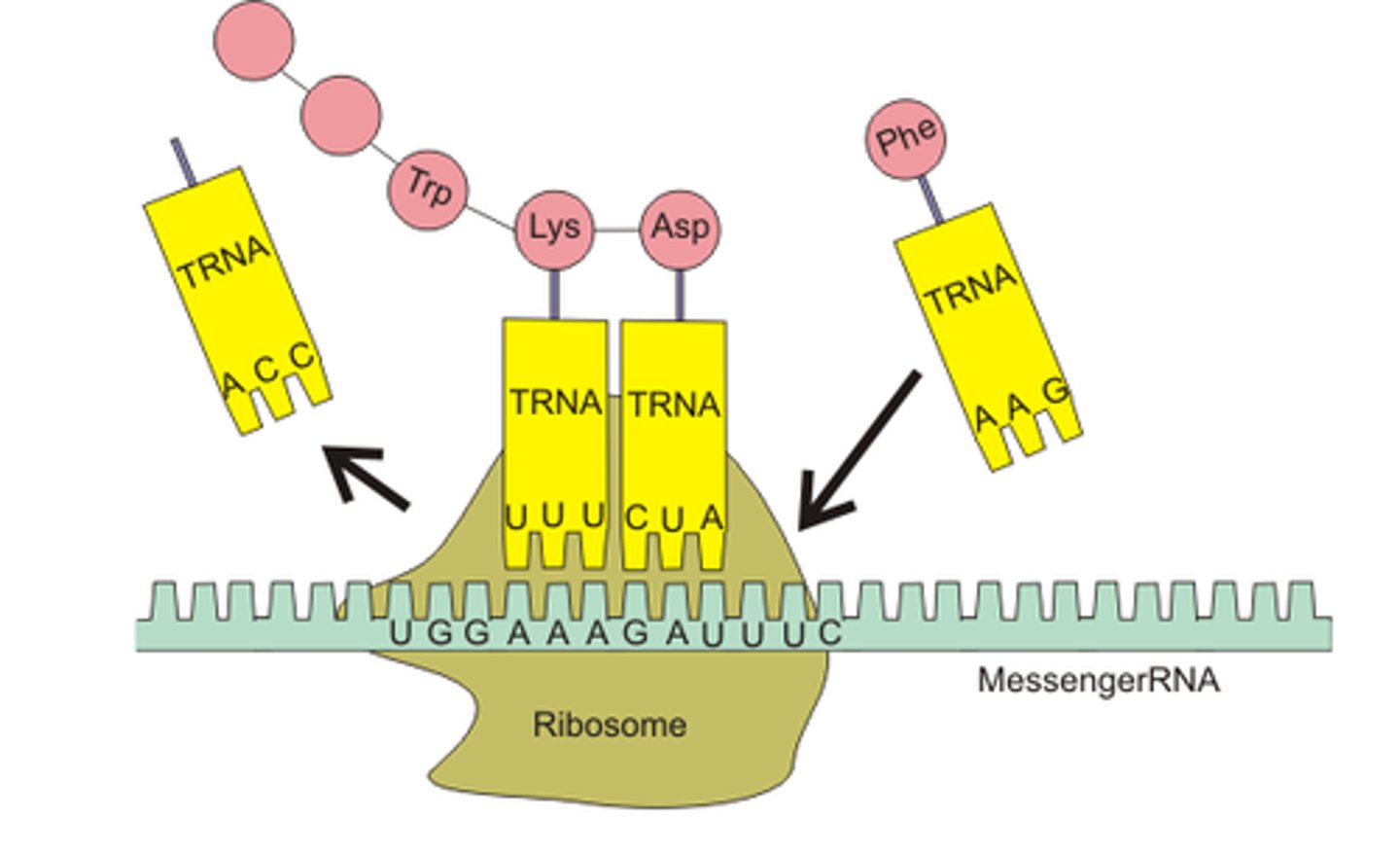
tRNA
>Transport RNA
>Carries Amino Acids to the Ribosomes
Translation
>Reading the mana code and assemblying amino acids into ploypeptides
Transcriptoin
>Copying DNA code into mRNA
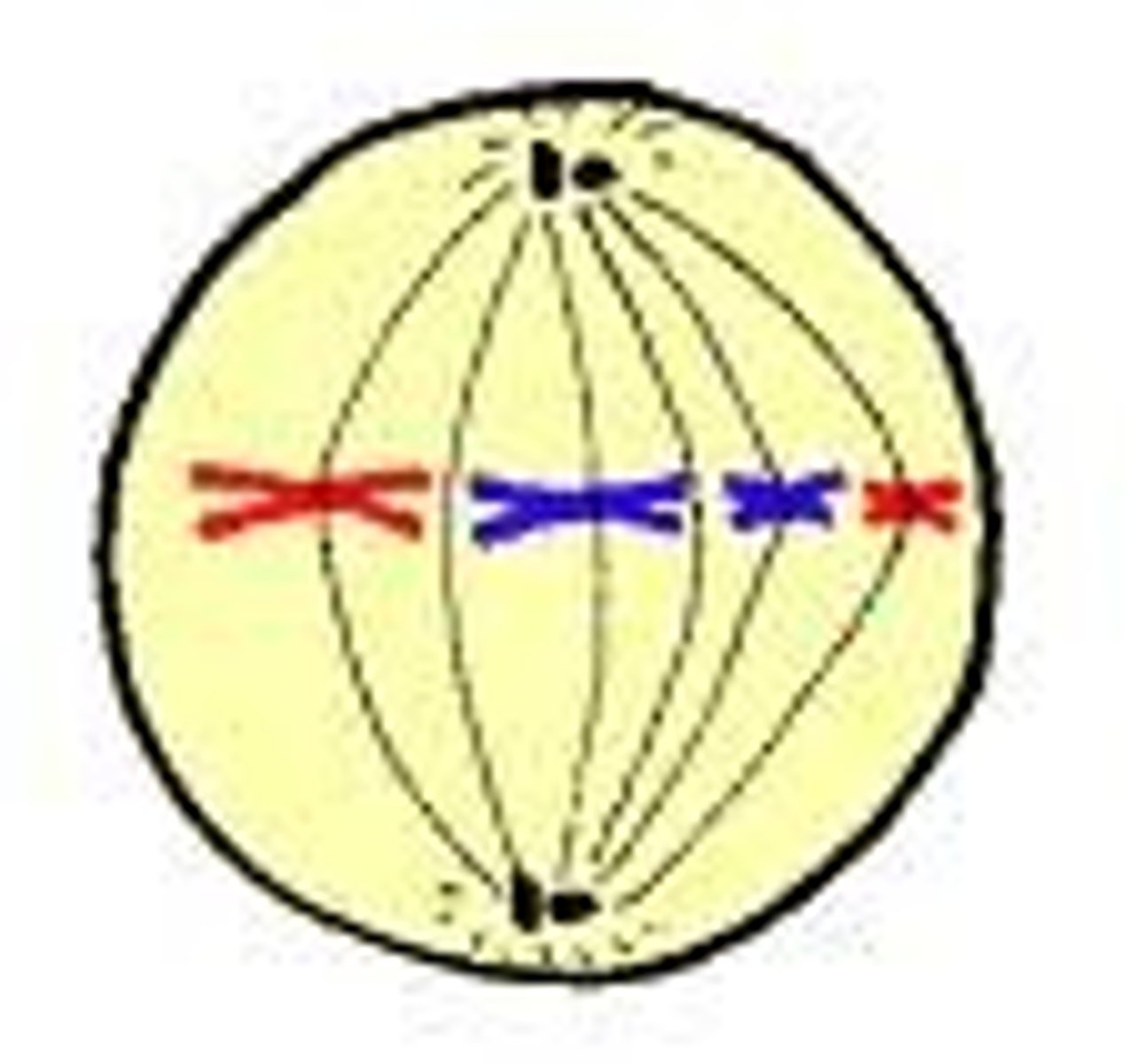
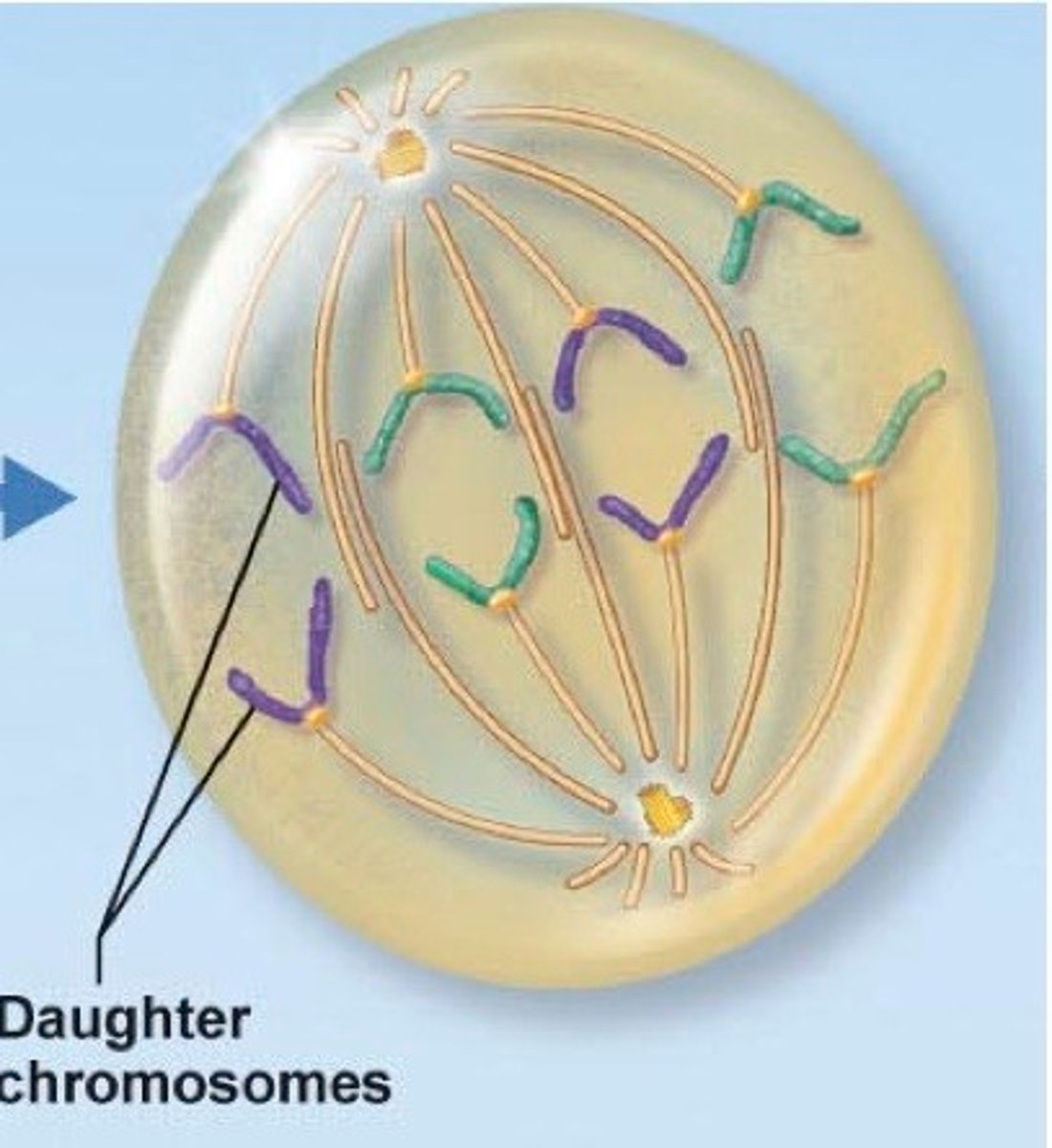
Metaphase
>Chromosomes line up at the middle of the cell
>Spindle fibers attach to each sister chromatin at the centriomire
Telophase
>Chromosomes return to chromatin form
>Nuclear membranes and nucleus reform spindel fibers disapaer
>Nucles divison is complete
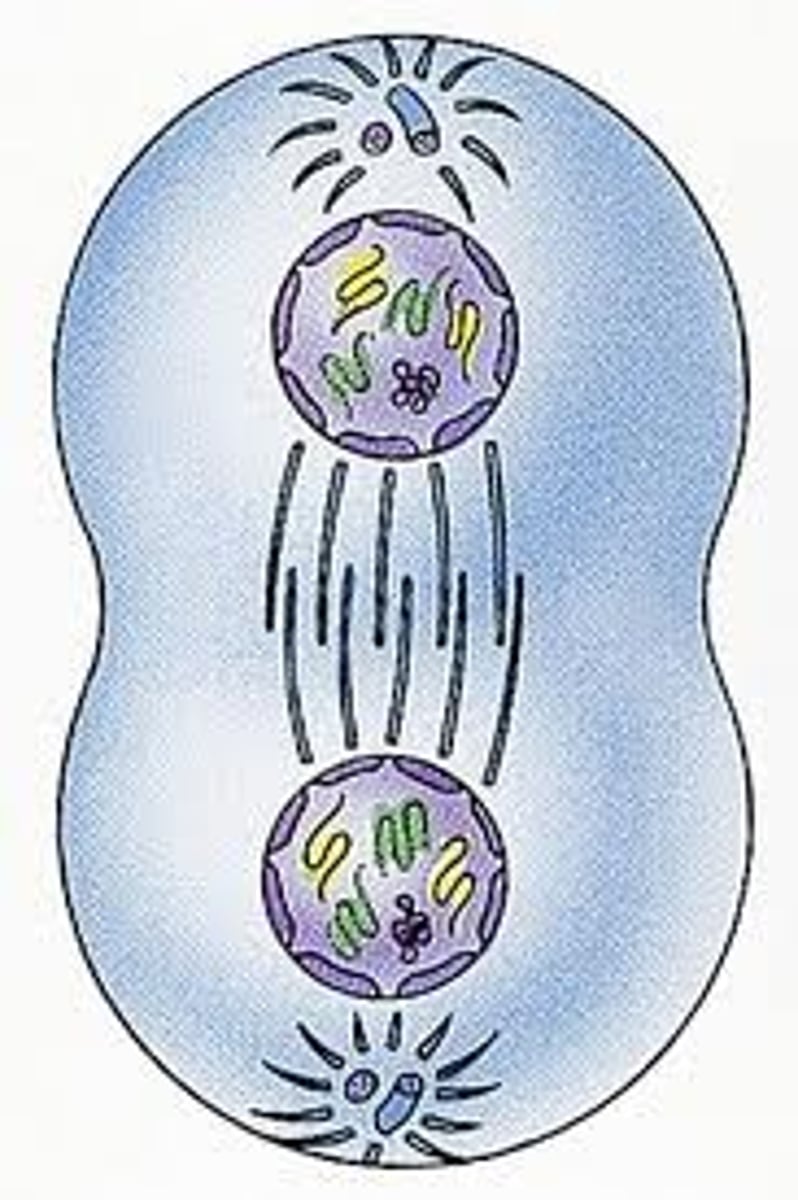
Anaphase
>Spindle Fibers contract and pull apart the chromosomes to opposite ends of the cell
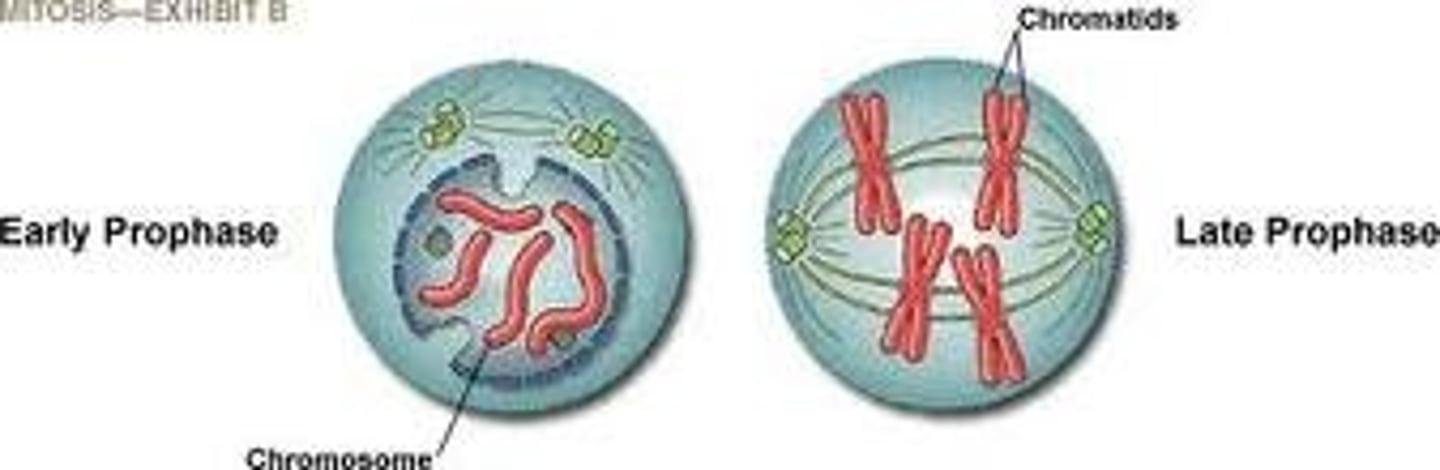
Early/Late Prophase
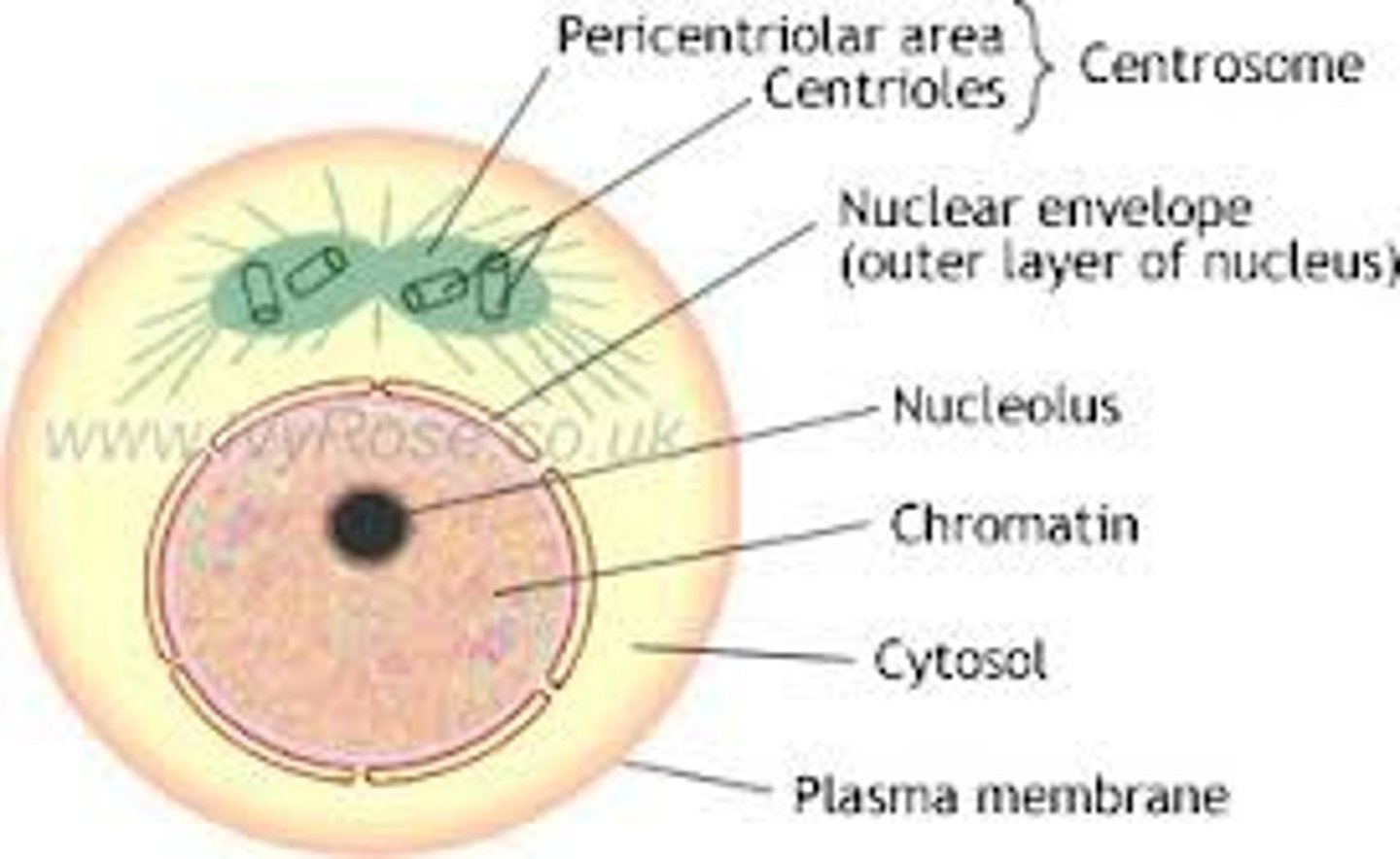
Interphase
>Nucleus is still intact
>Nucleous is still visible
>DNA is in chromatin form
Nucleotide
>Monomer name for DNA
>Basic building block
>Contains phospate
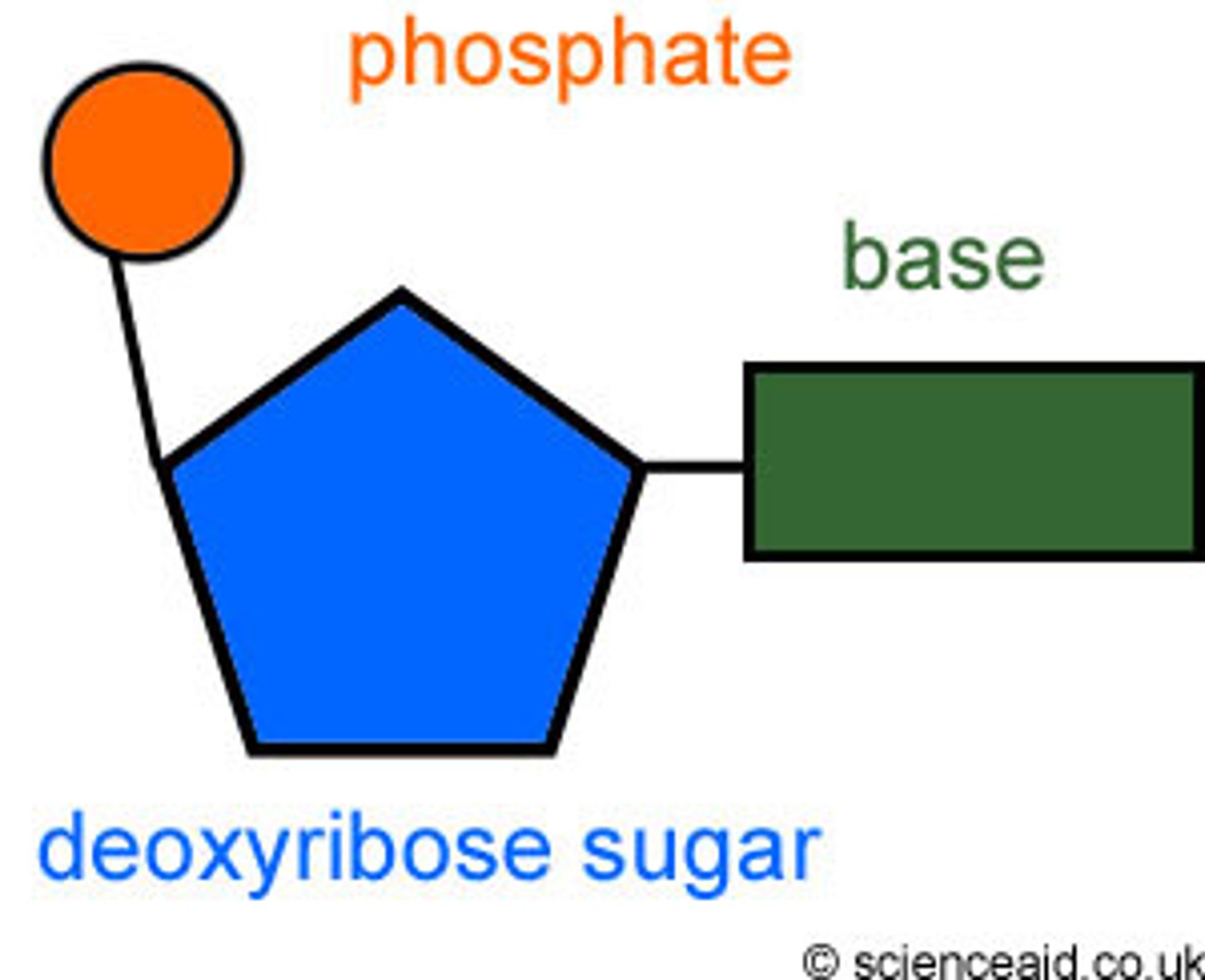
Nucleic Acid
>Organic Compound
>Two chains of nucleotides carry genetic information
N Base
>Subunit of Nucleotide, A T C G
Deoxyribose
>5 Carbon sugar that is a submit of a nucleotide
Phosphate Group
>Subunit of a nuclotide
Base Pairing Rules
A-T C-G
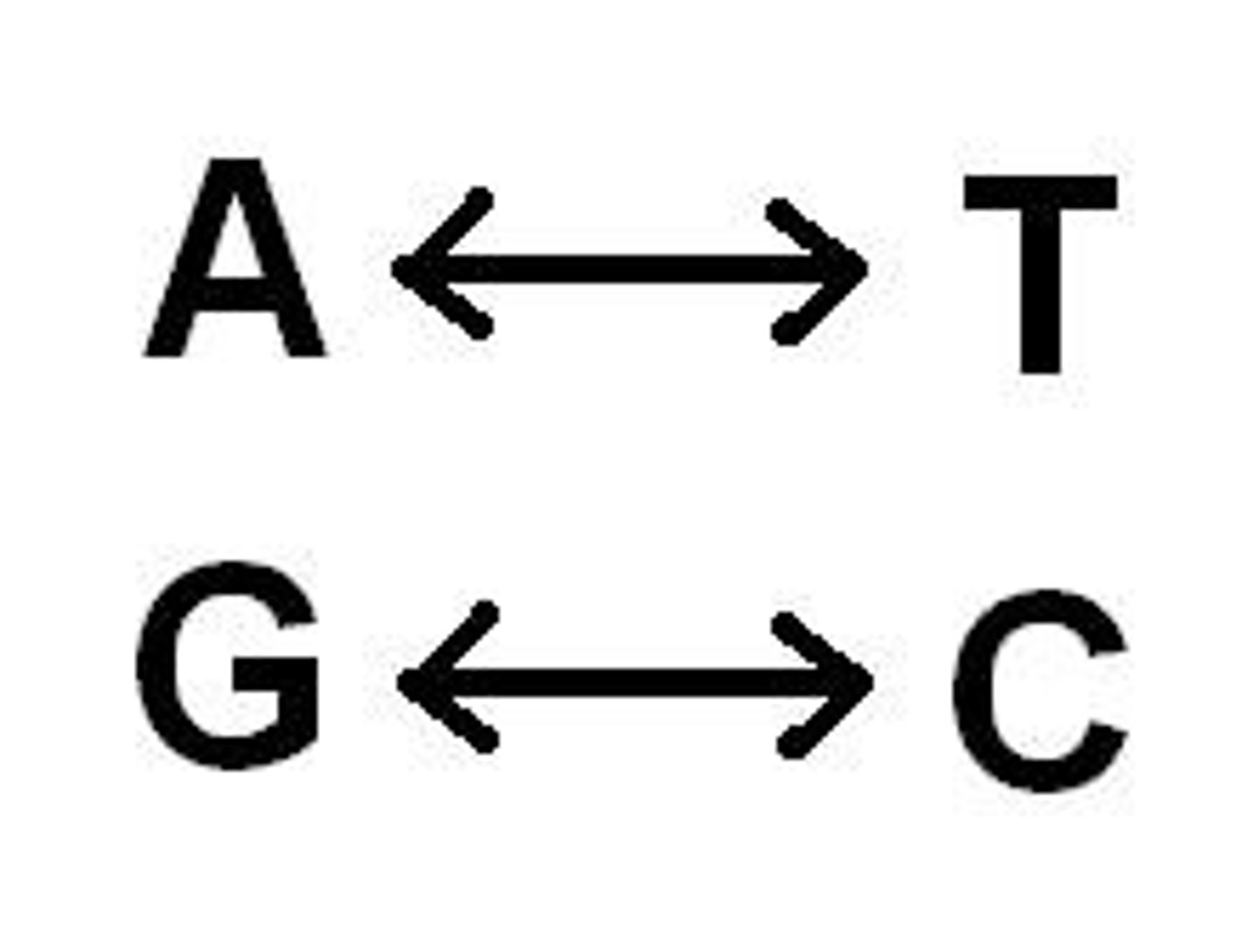
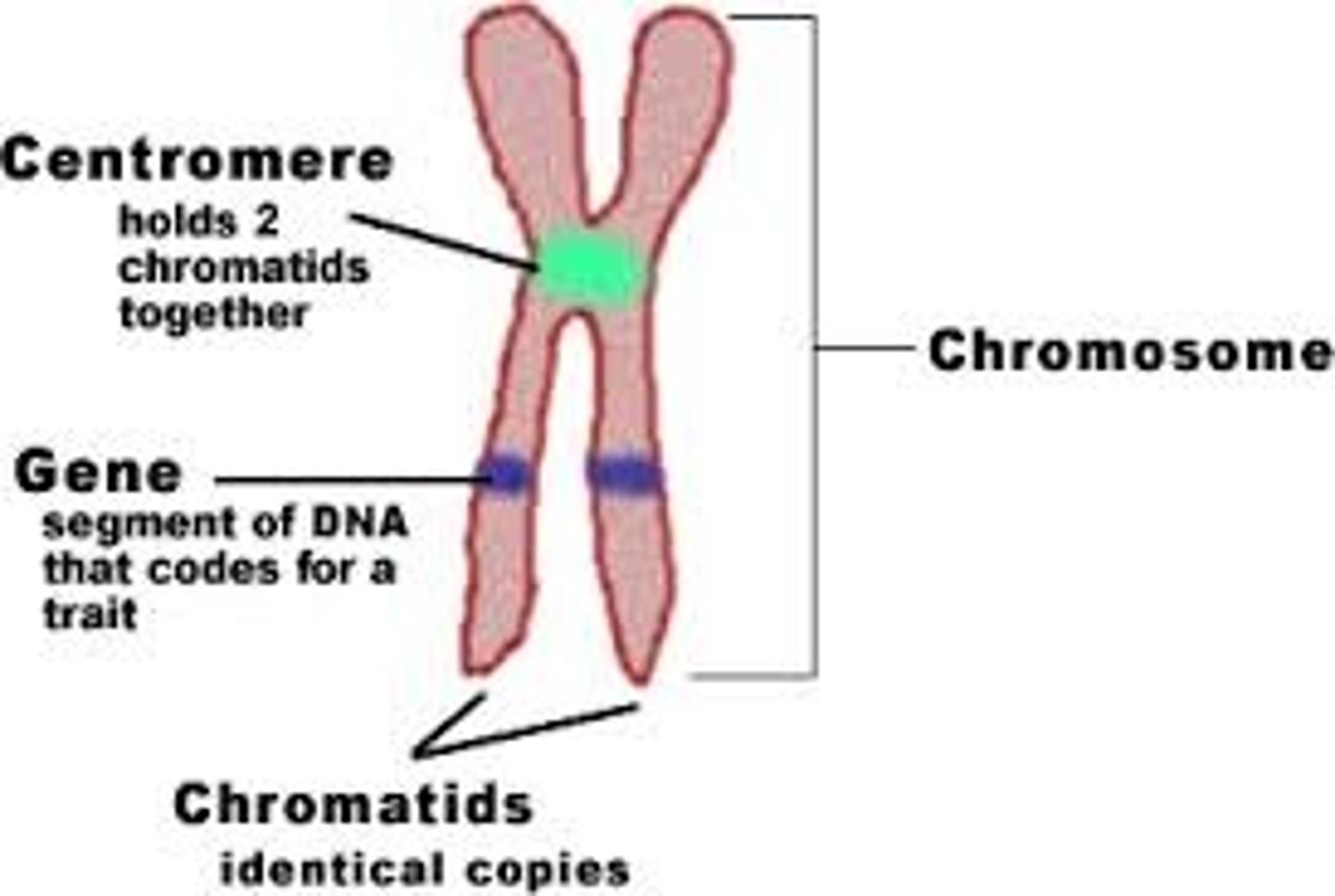
Chromosomes
>Tightly coiled strands of DNA that carries genetic information
Respitory System
>System of the body where the blood picks up O2 and drops off extra CO2
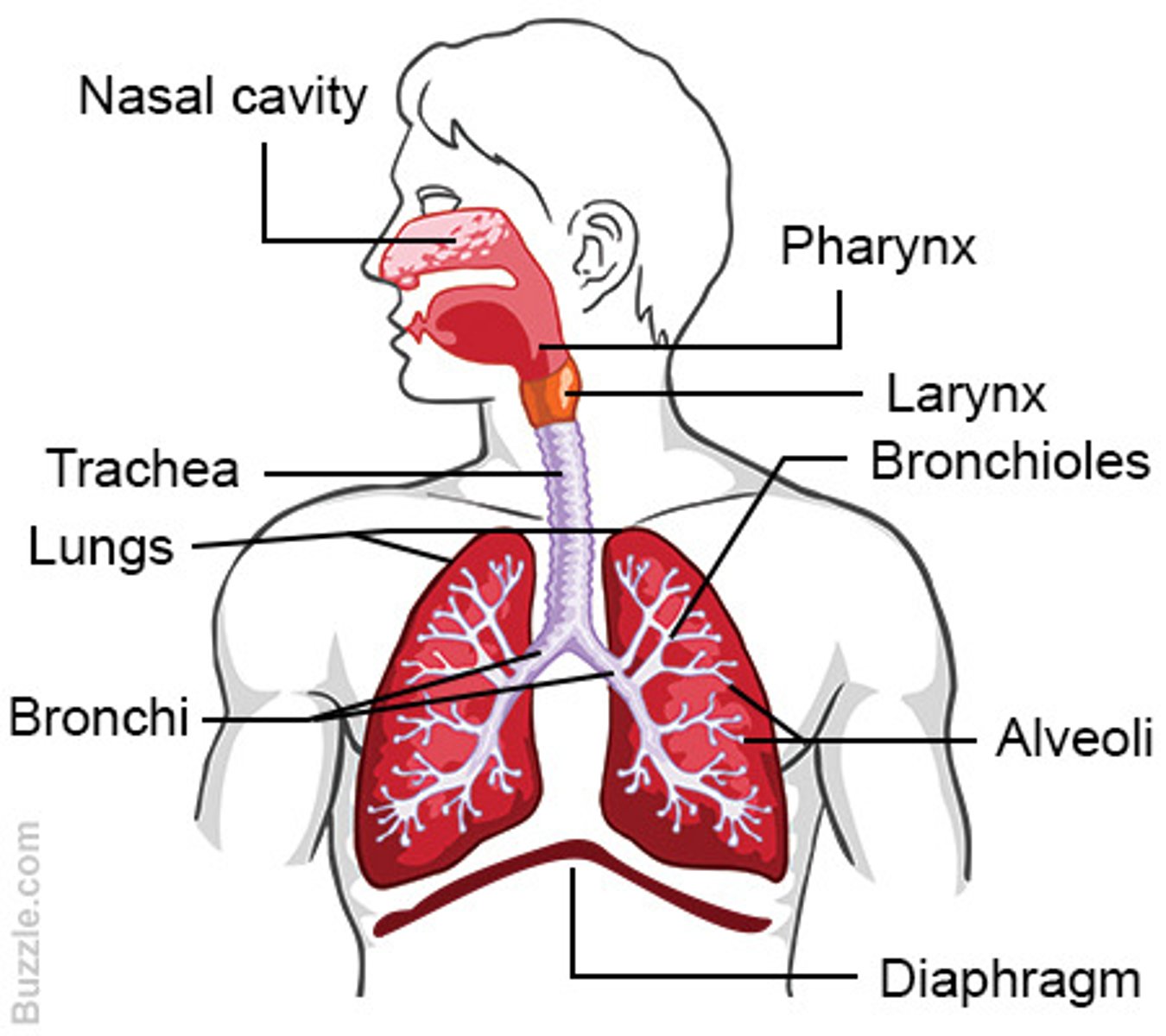
Diaphragm
>Dome shaped muscle that contracts and relaxes to change air pressure in the lungs
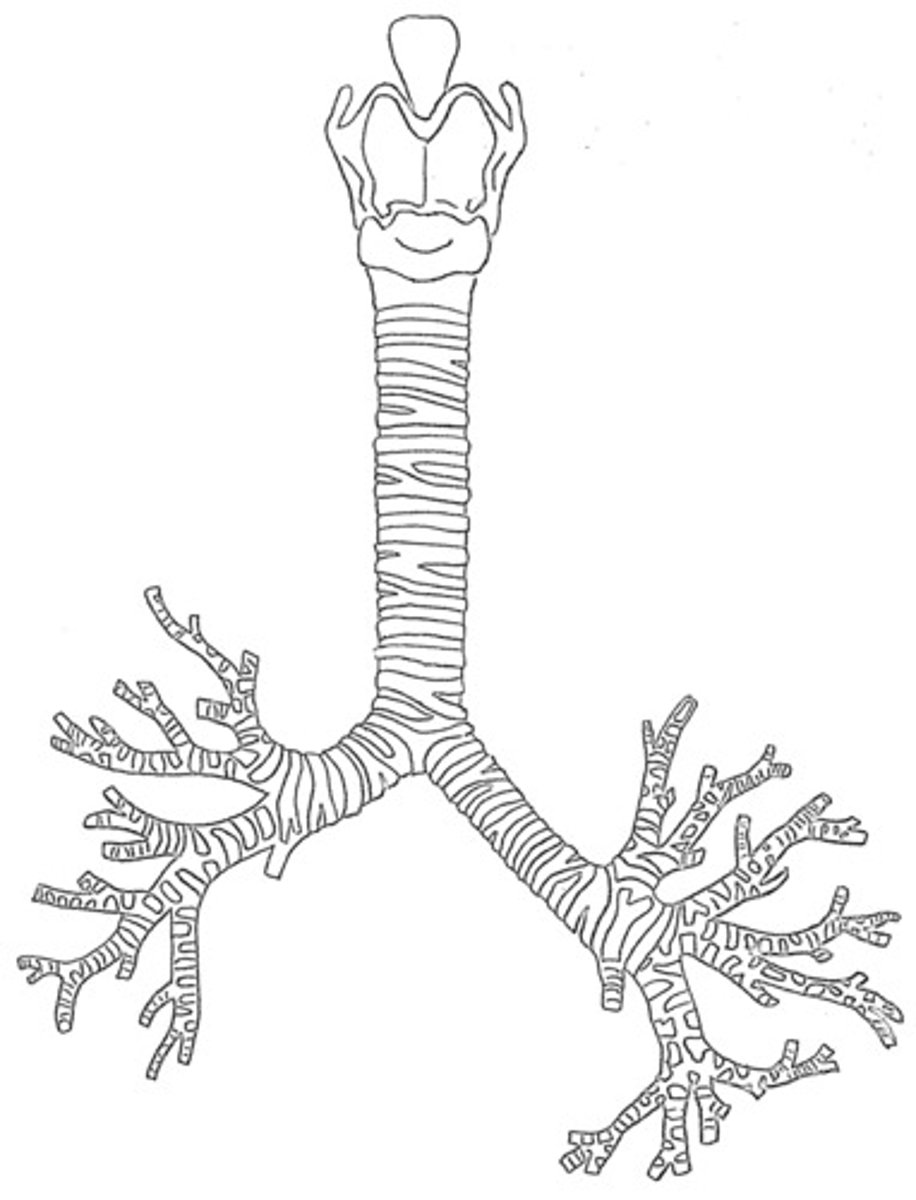
Trachea
>Windpipe tube that connects the Larynx, Pharynx and Lungs
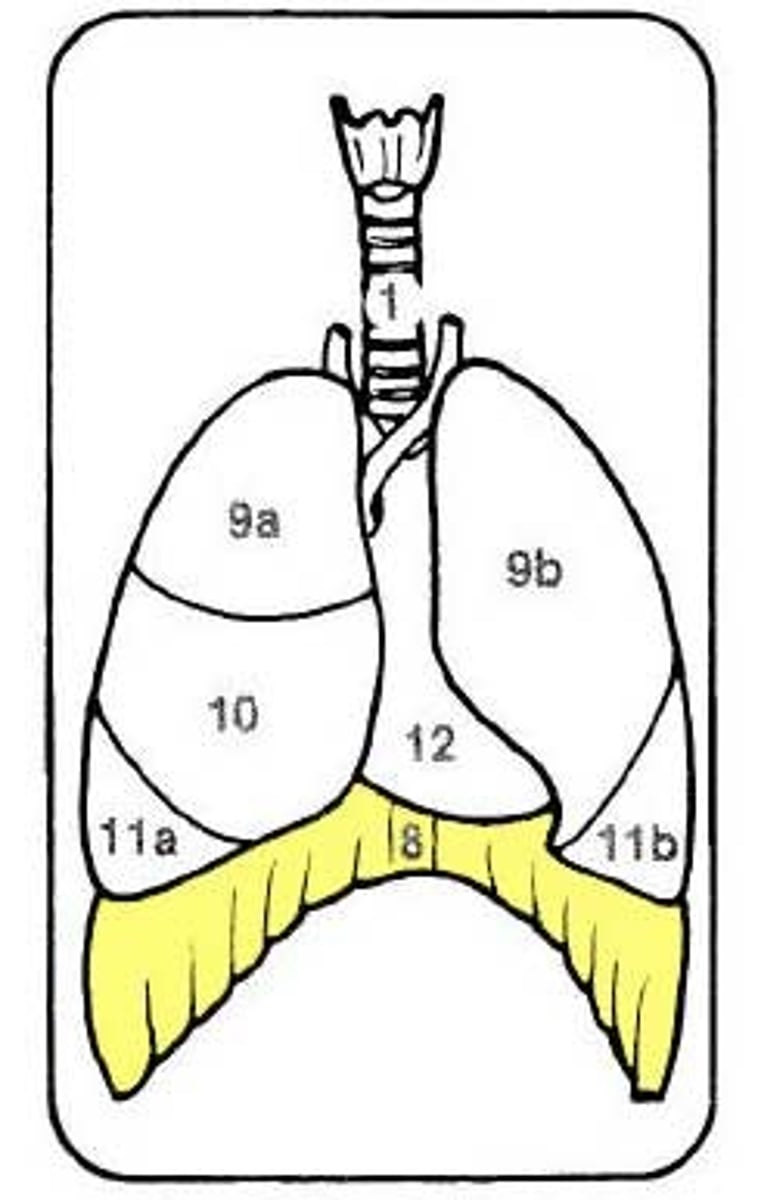
Lungs
>Two large ballon shaped muscles that contract to bring O2 into the body and exhale CO2
Alviol
>Bronchioles end here in clusters of tiny sacks (look like grapes)
Gene
>Section of DNA on a chromosome
Allele
>Different form of a trait
>One allele from each parent
Homozygous
>Having the same 2 alleles for genetic trait
Heterozygous
>Having two different alleles for the same trait
Dominant
>the trait that expresses itself over another
Recessive
>The trait that is masked or hidden by the dominant trait
Genotype
>The gene make up of a trait expressed as a set of capital and lower case letters
Phenotype
>The physical presentation of the genetic presentation
Law of Independent Assortment
>The law that states the genes separate independently of one another in meiosis
Law of Segregation
>Mendel's law that the pairs of homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis so that only one chromosome from each pair is present in each gamete
Monosacharide
>One unit of sugar
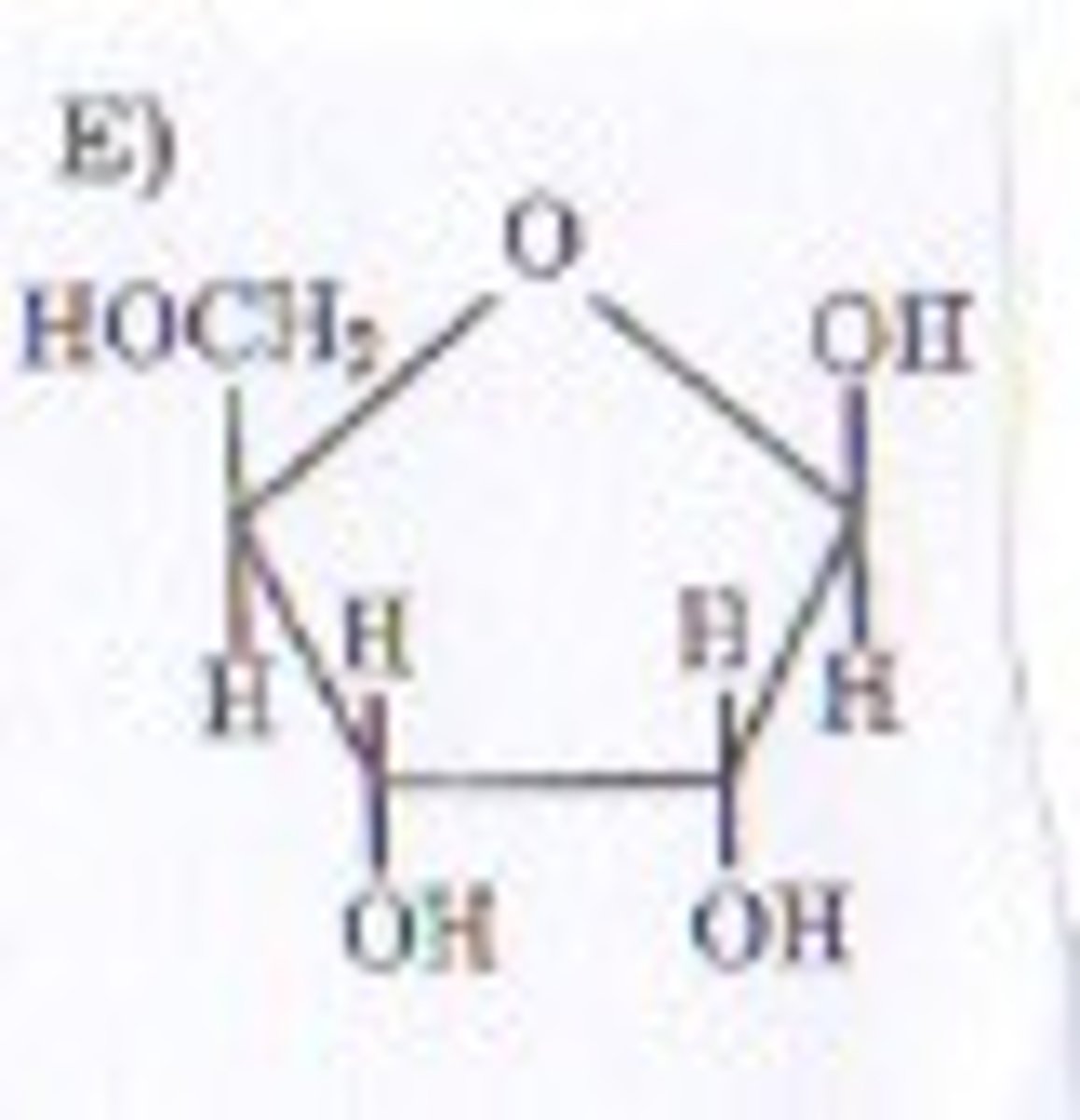
Polysaccharide
>Two or more sugar units
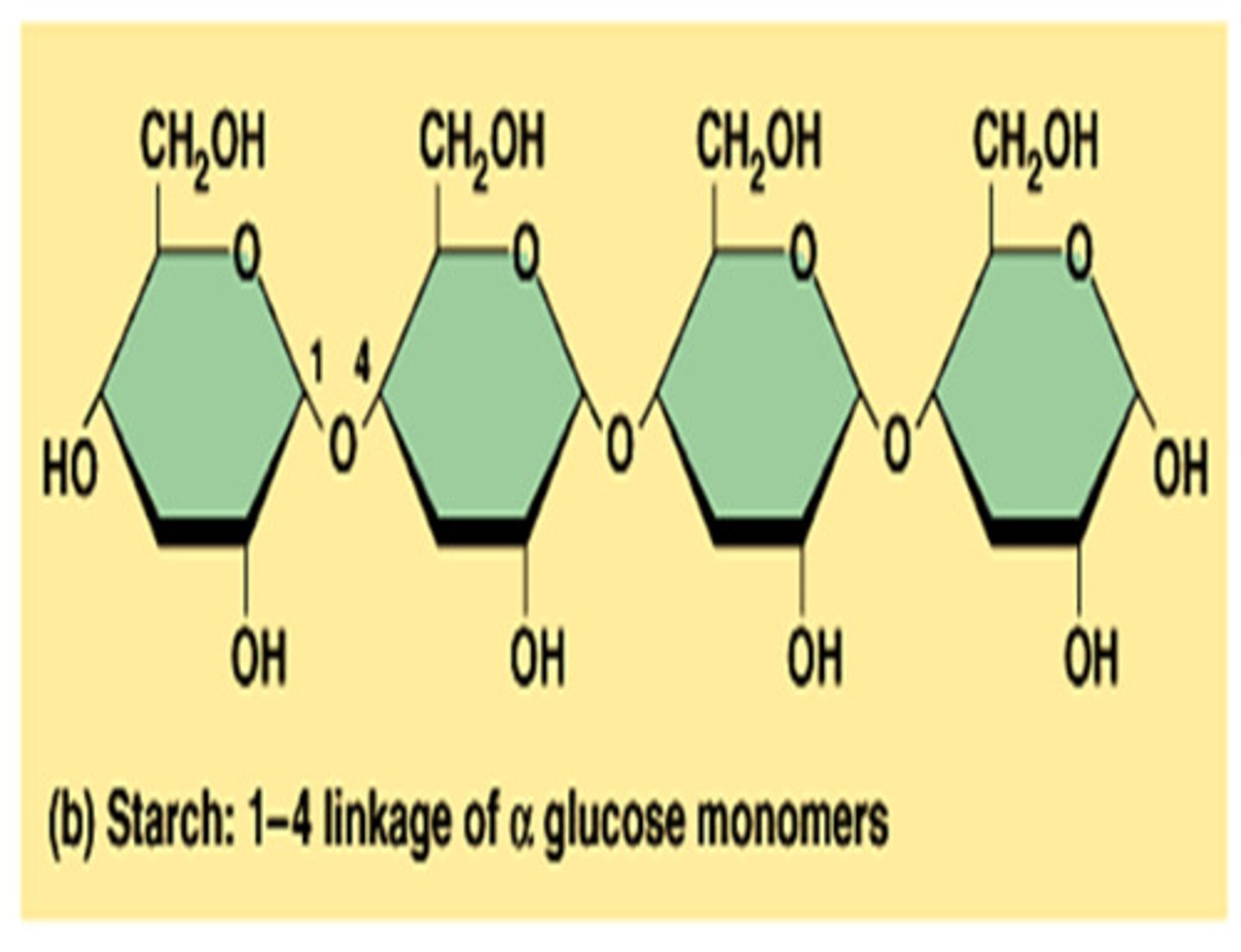
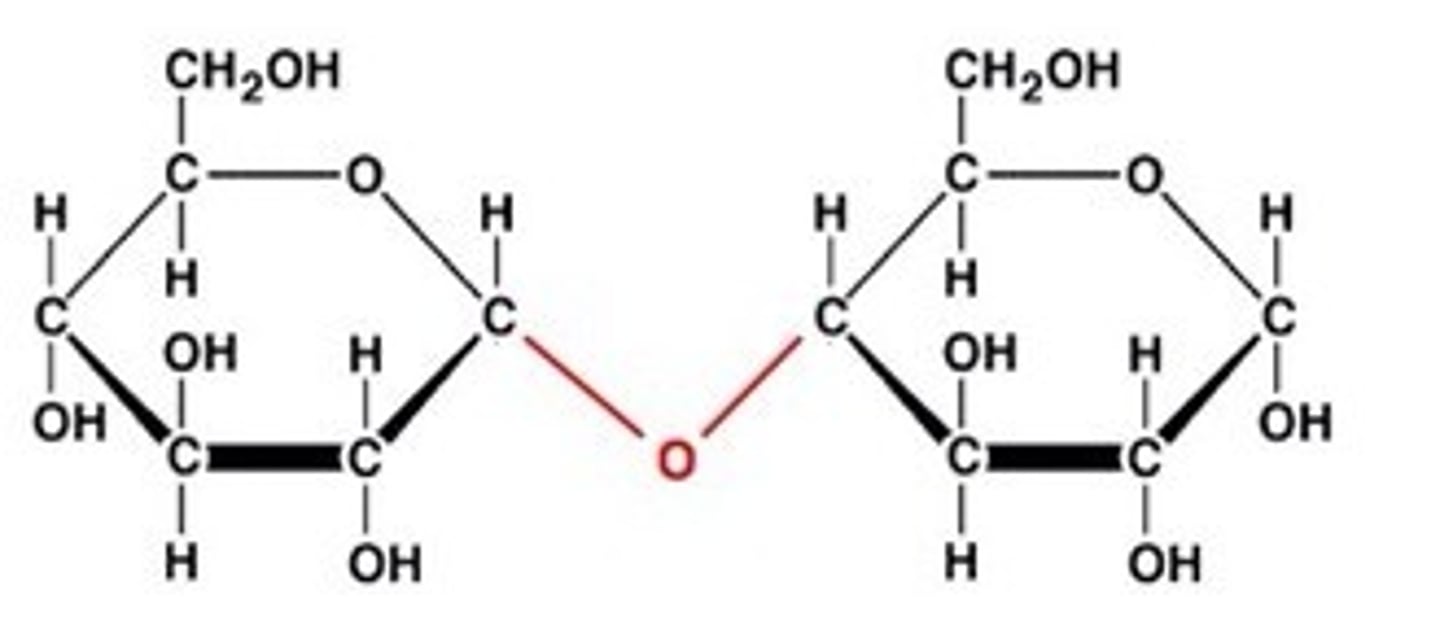
Disaccharide
>Two sugar units
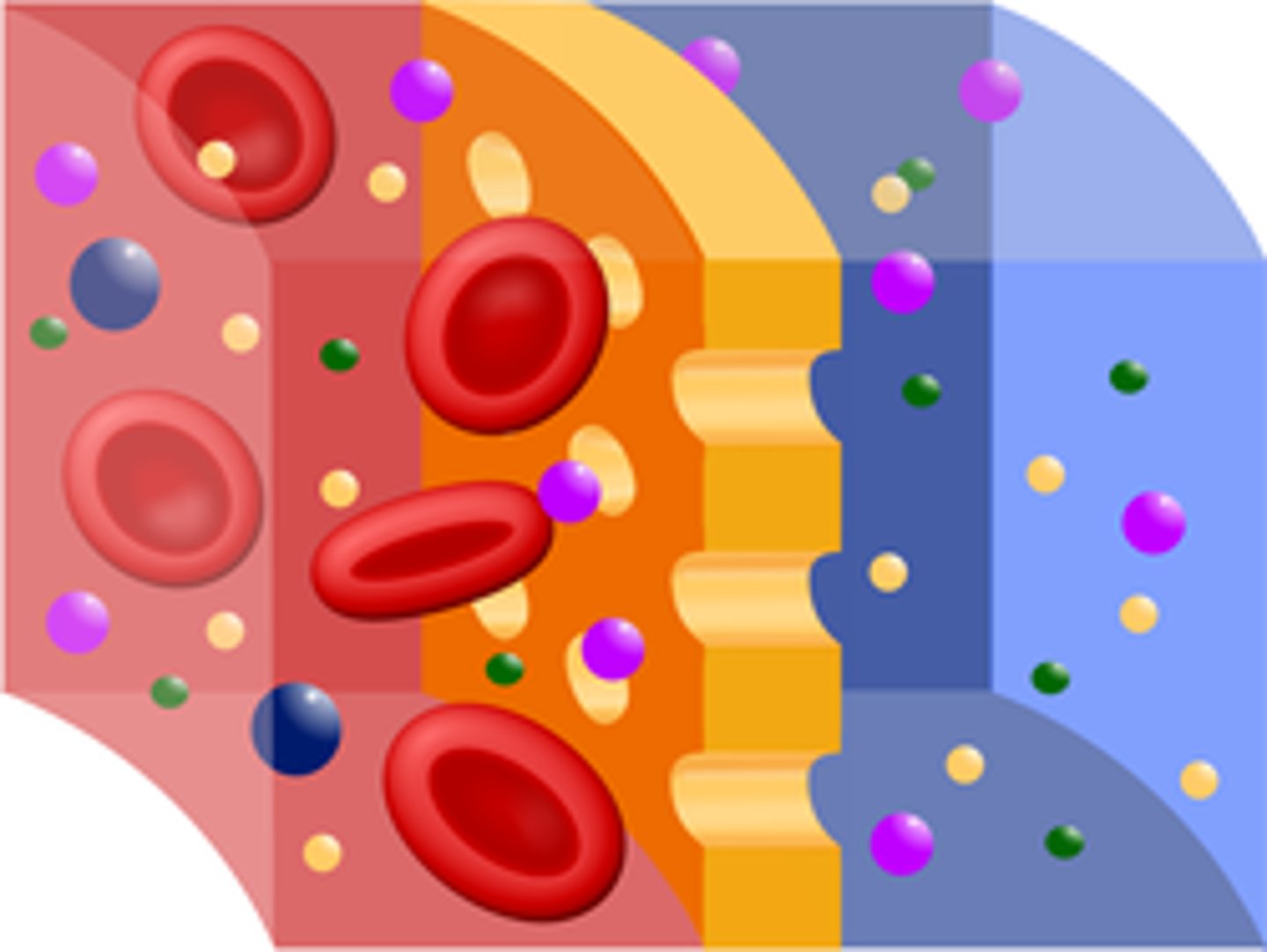
Capillary
>Network of small vessels that connect arteries and veins throughout the body
>Are the smallest and reach every part of the body
>Brings blood from the heart to the body
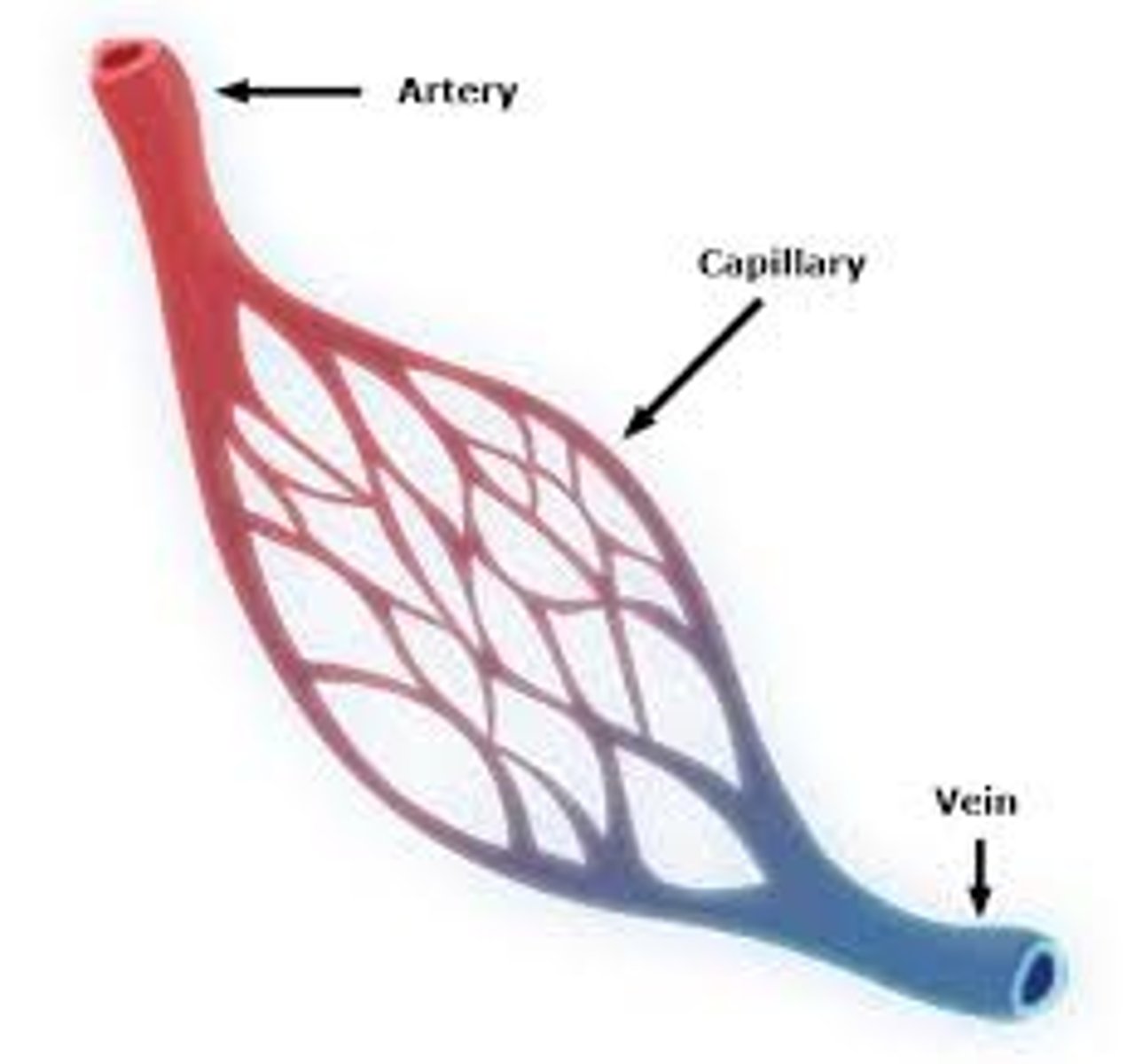
Vein
>Vessel that carries blood back to the heart
>Second largest
Artery
>Vessel that carries the blood from your heart to the rest of your body
>Largest of the three
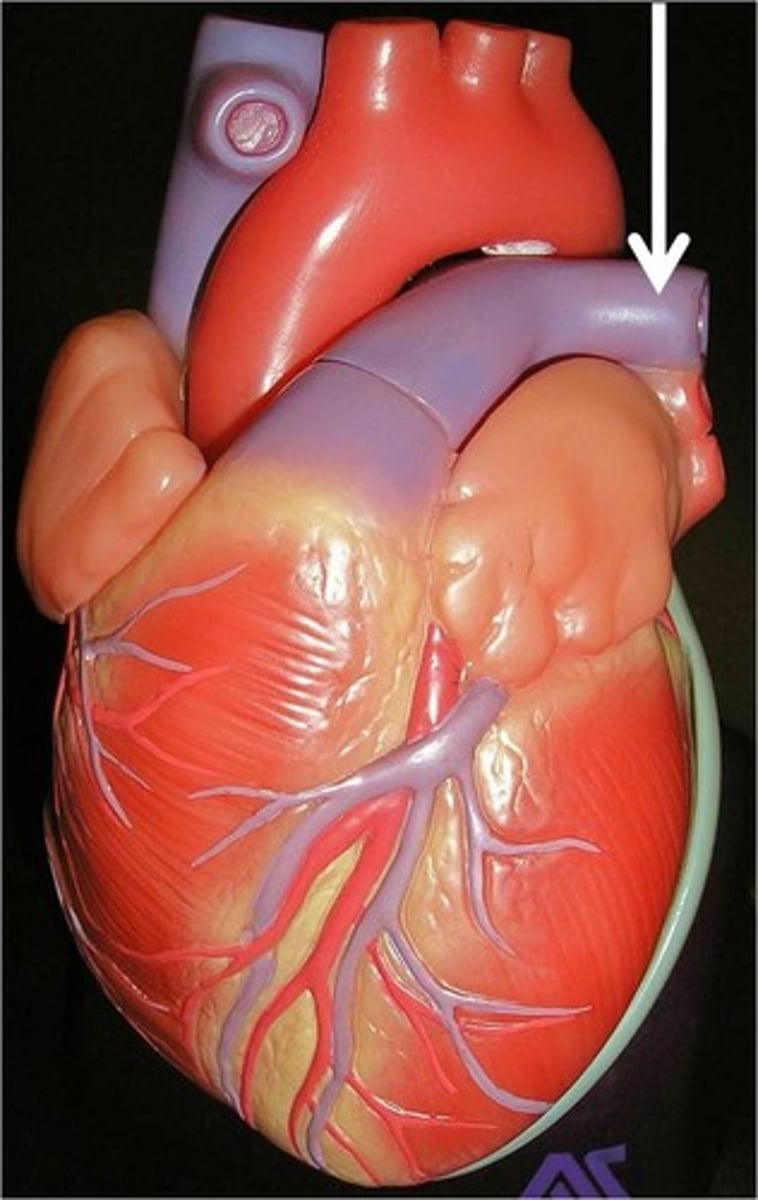
Heart
> 4 chambered muscle that pumps oxygenated blood throughout the body
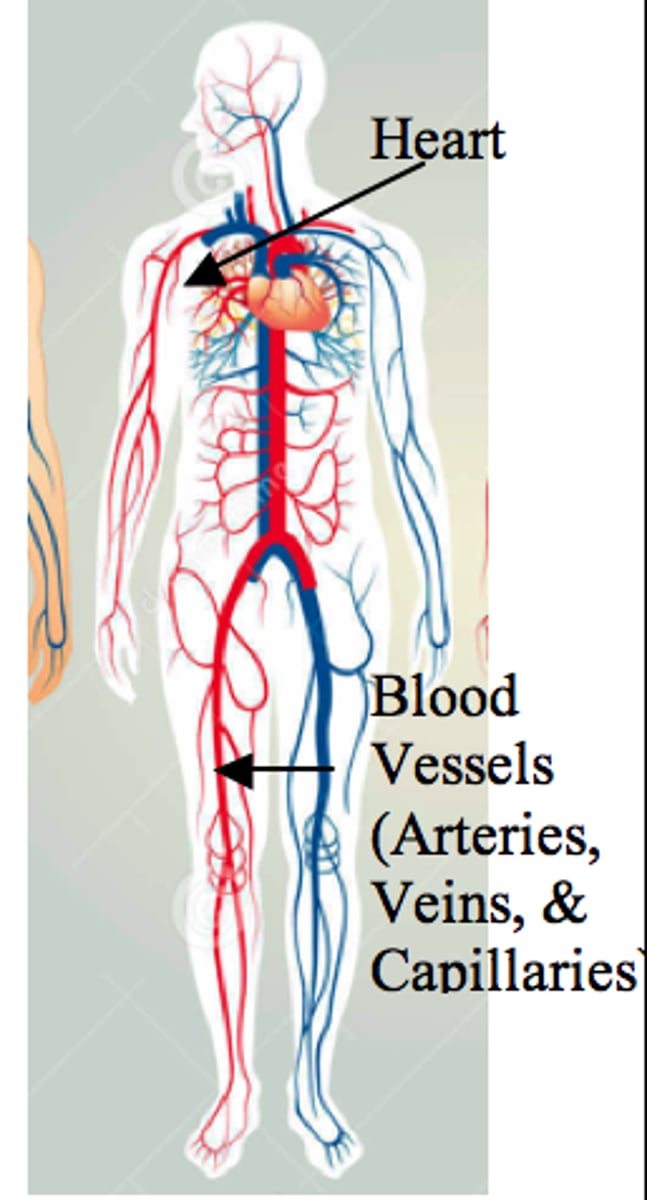
Circulatory System
>Carries blood to all parts of the body through a network of arteries, veins and capillaries
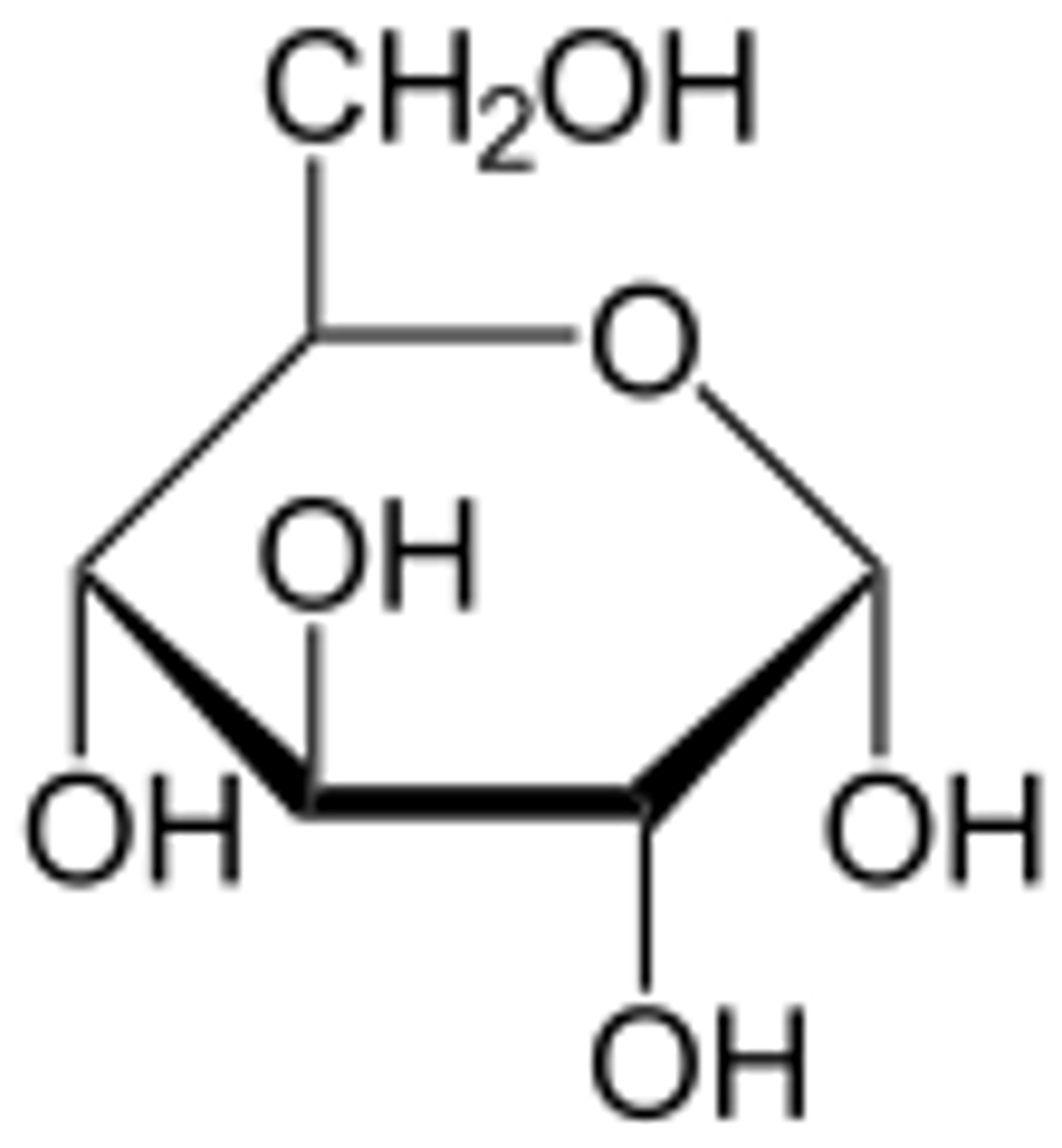
Carbohydrate Characteristics
>Makes sugars and starches
>C H O
>Short term energy
>Dissolves in water
Hypertonic
>High concentrate of solute
>If a cell is submerged in this it shrinks
Hypotonic
>Low concentration of solute
>If cell is submerged in this it explodes
Isotonic
>The same/even concentration
>Keeps cells at homeostasis
Glycerol
>Building block for lipids
Red Blood Cells
>Carries oxygen and CO2
>Contains platelets
White Blood Cells
>Breaks down illnesses
>Contains plasma

Platelets
>Stops bleeding in a cut
Cardiac Conduction
>Beating of the heart through electrical impulses
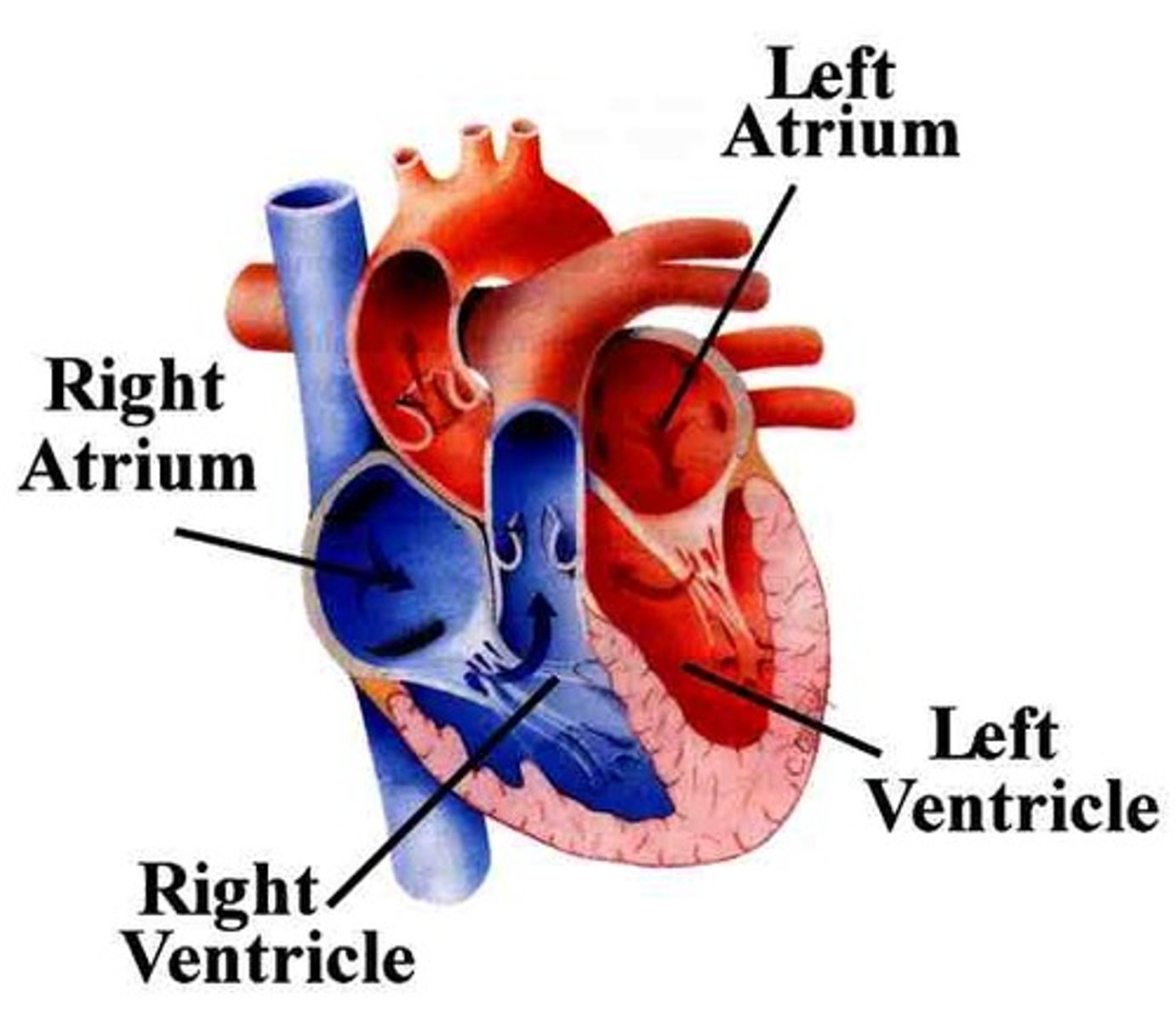
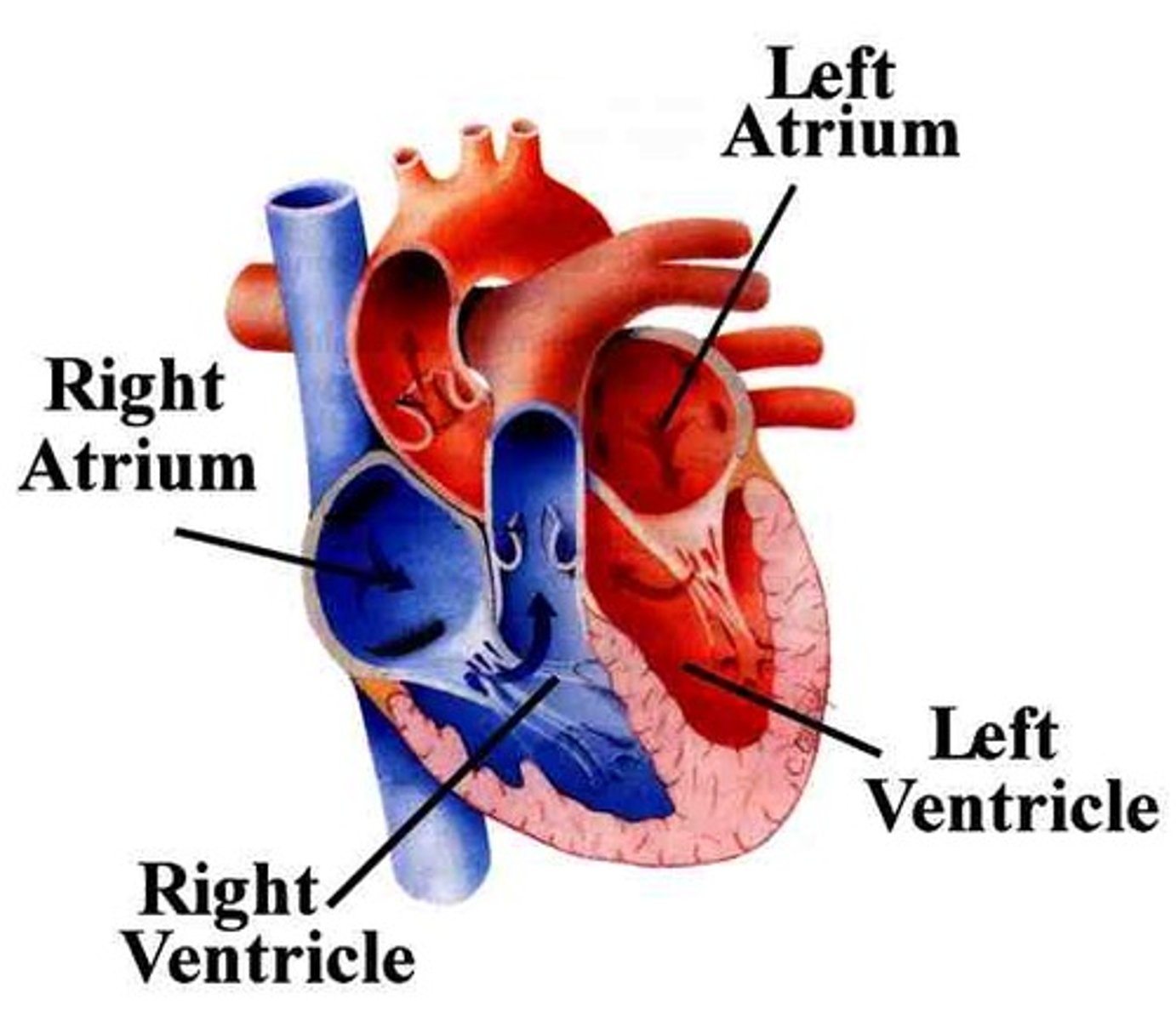
4 Heart Chambers
Right Atrium
Left Atrium
Right Ventricle
Left Ventricle
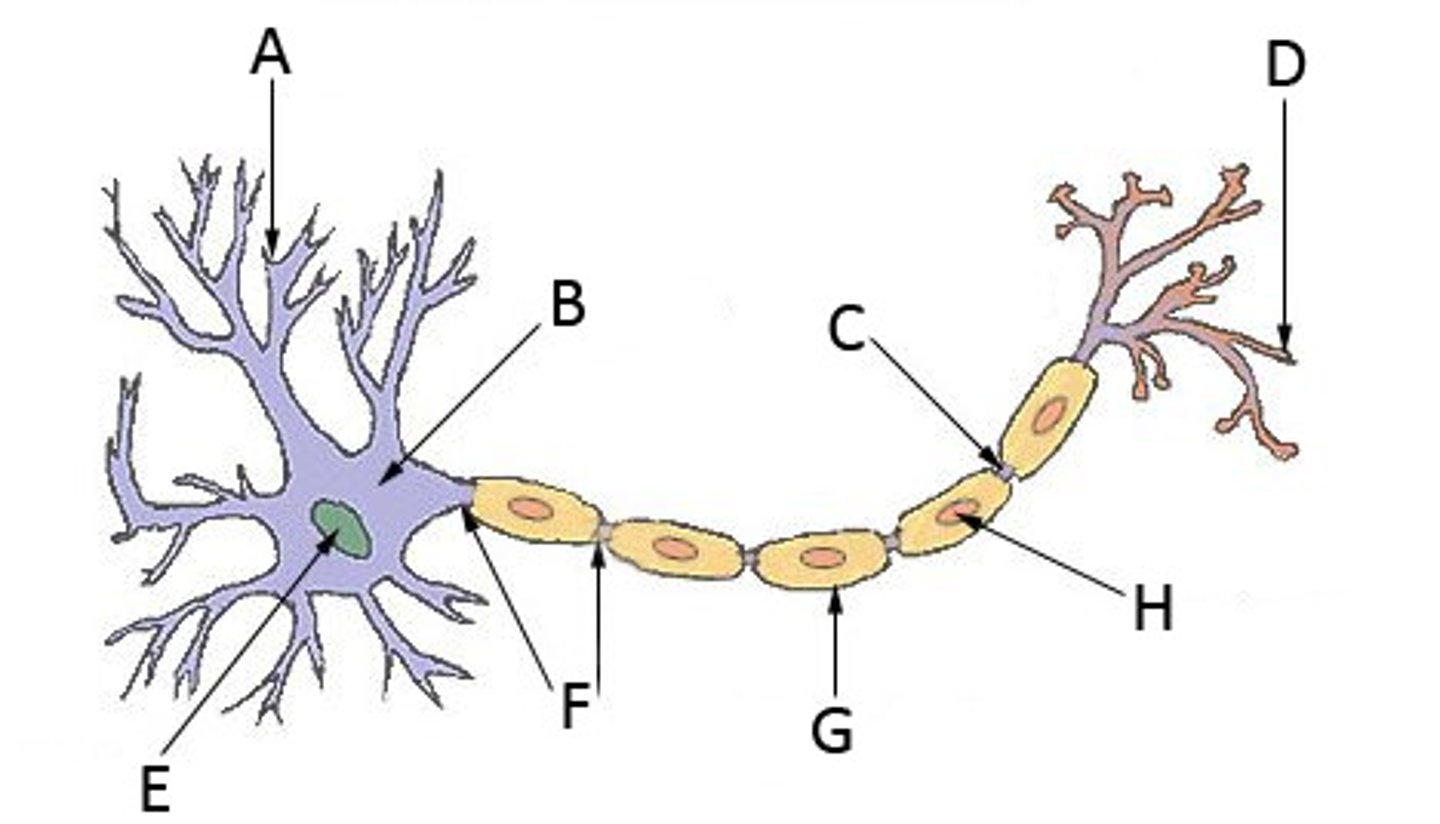
Neuron
>The basic functioning unit of the nervous system
>Over 100 Billion of these specialized cells in the brain alone
Sensory Neurons
>Type of neuron responsible for sending impulses towards the CNS
Central Nervous System
>CNS
>Responsible for processing all incoming information to determine a proper bodily response.
>Consists of the brain and spinal cord
Motor Neurons
>Type of neuron responsible for sending impulse from the CNS to different organs throughout the body to react to different tasks
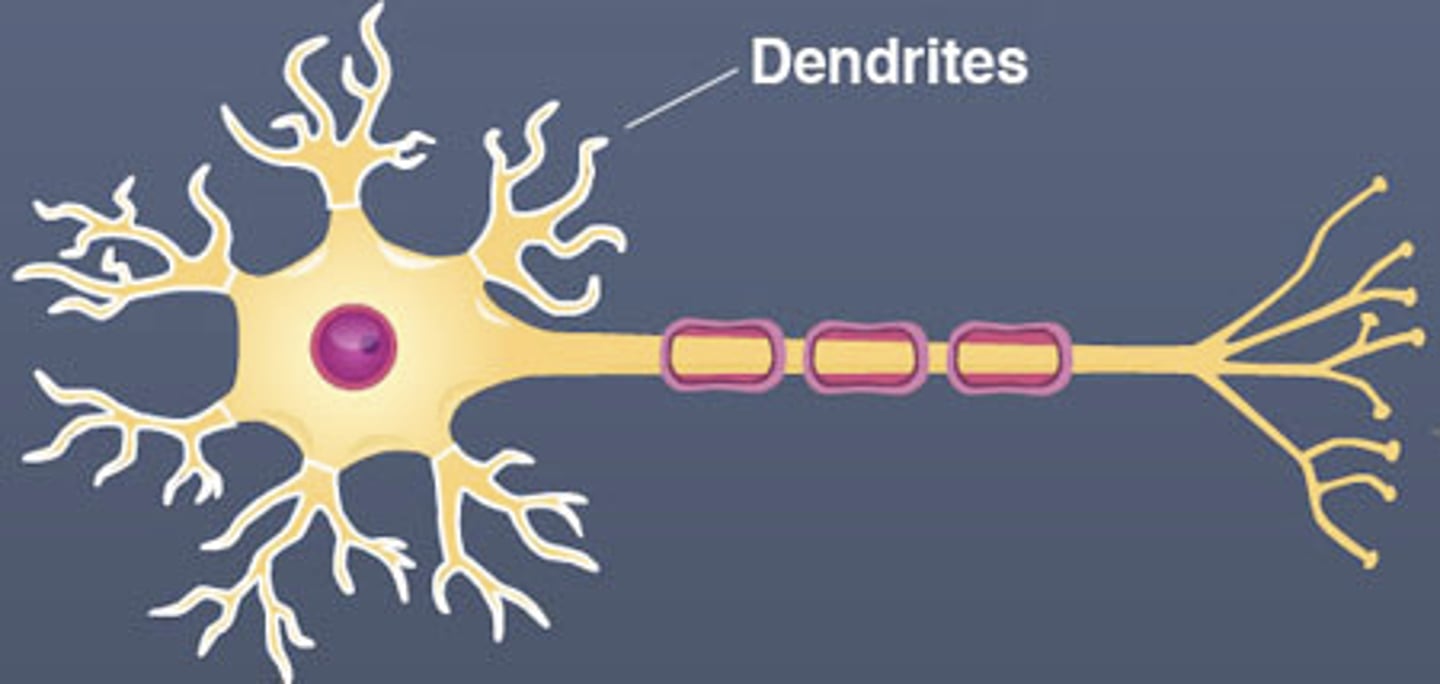
Dendrite
>Receives electrical impulses from neighboring neurons
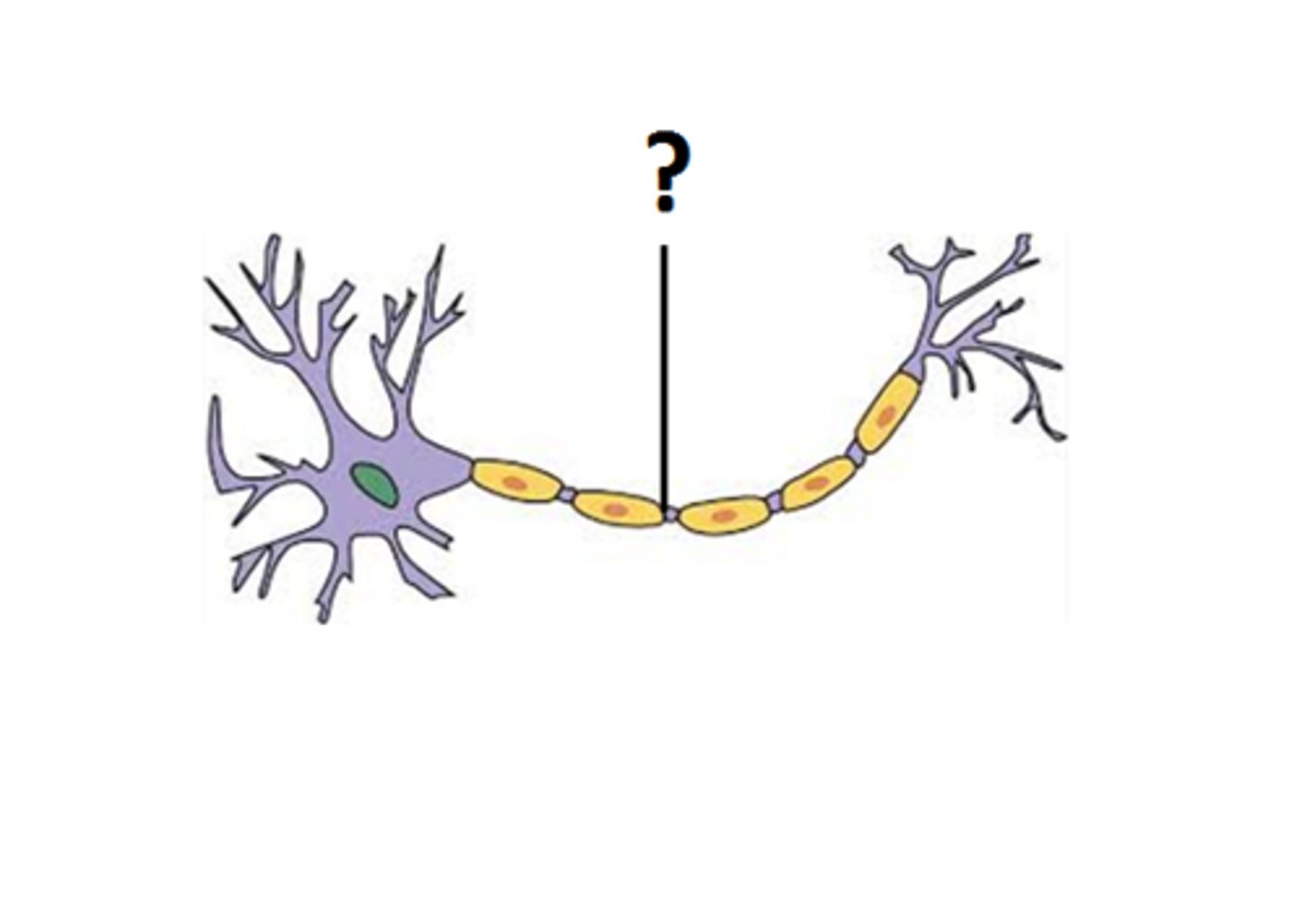
Axon
>Transfers electrical impulses signals from the cell body to the synapse
Impulse
>Fast moving electrical signals passed from neurons to neurons that can travel throughout the body at speeds of 150 m/s
Peripheral Nervous System
>PNS
>Made of many nerves that connect all areas of the body to the
CNS
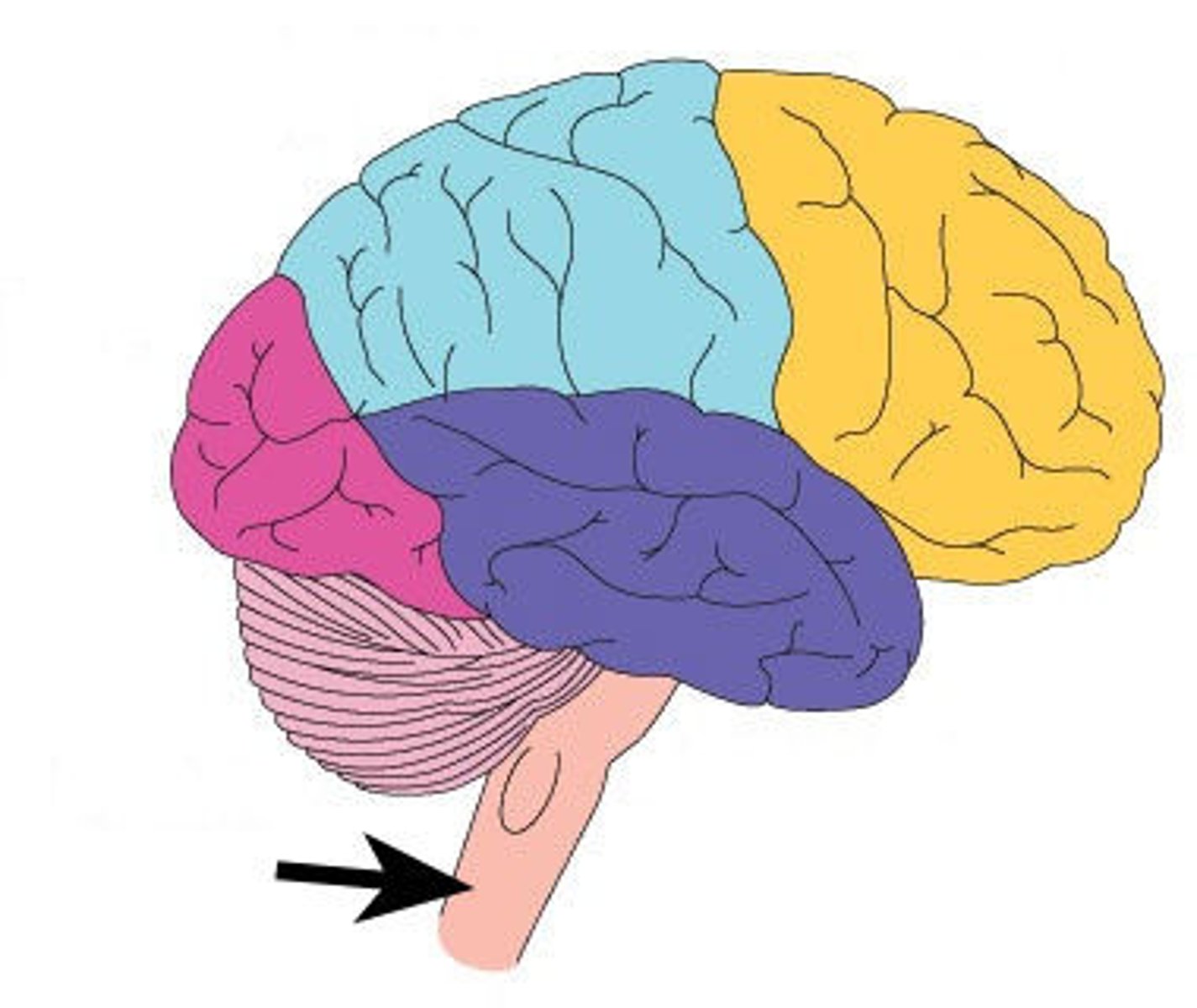
Brain
>It is also one of the largest and most complex organs in the body
>Main parts include, Cerebrum, Cerebellum, Brain Stem, Pititutary Gland, Hypothalathamus
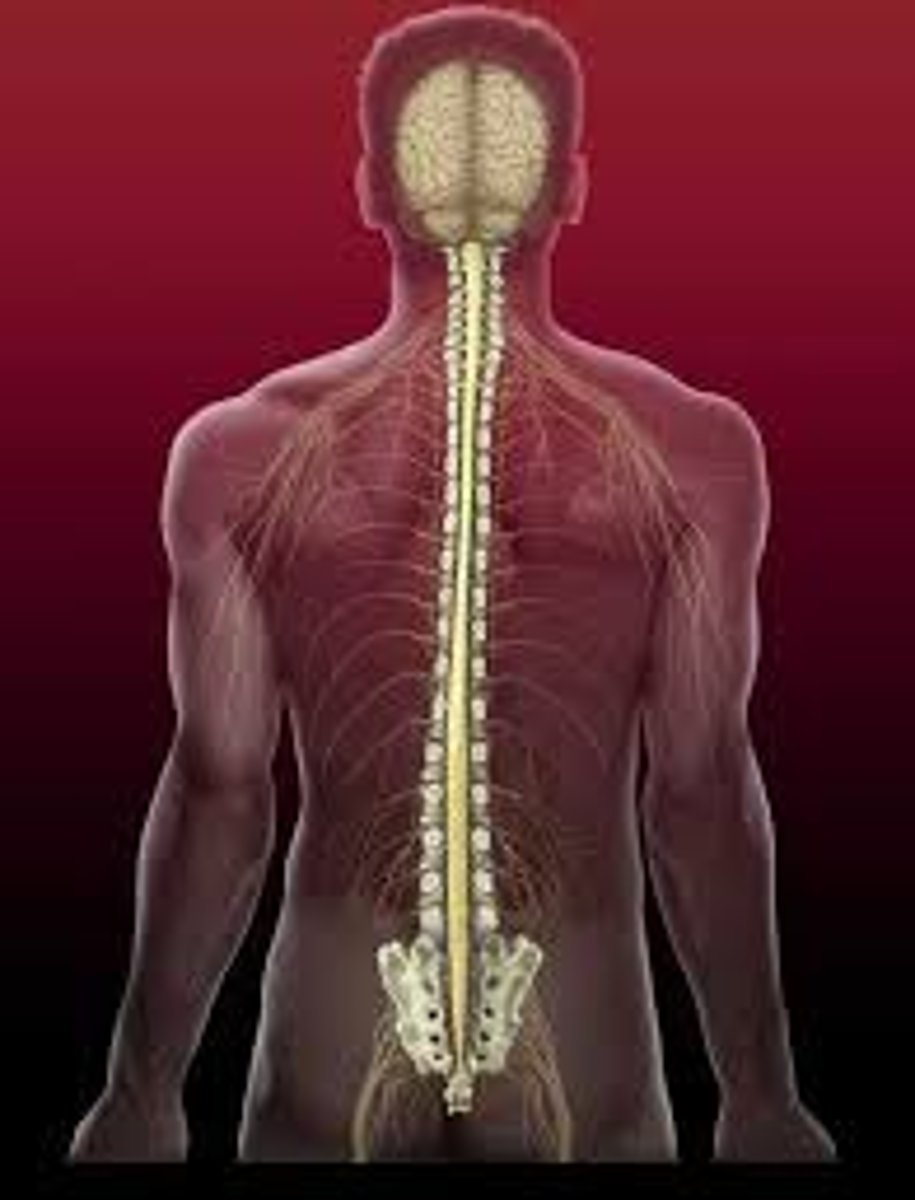
Spinal Cord
>The main pathway for information connecting the brain and the PNS
>It is protected by bones called vertebrae
Stimulus
>A change in an environment that triggers the reaction of a neuron.
>Ex: physical movements or stress chemicals, light, temp, etc
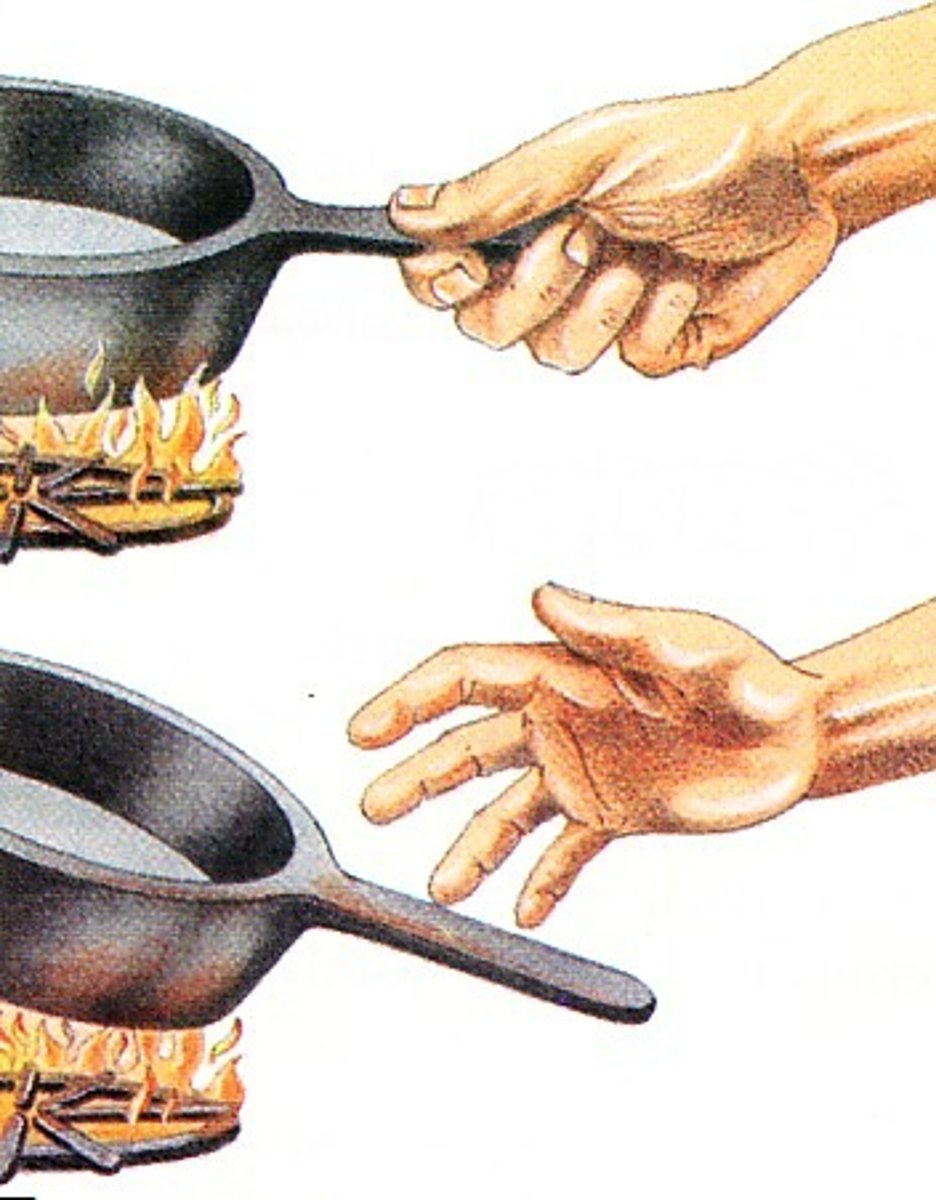

Reflex
Involuntary and nearly instaneous movement in response to a stimulus
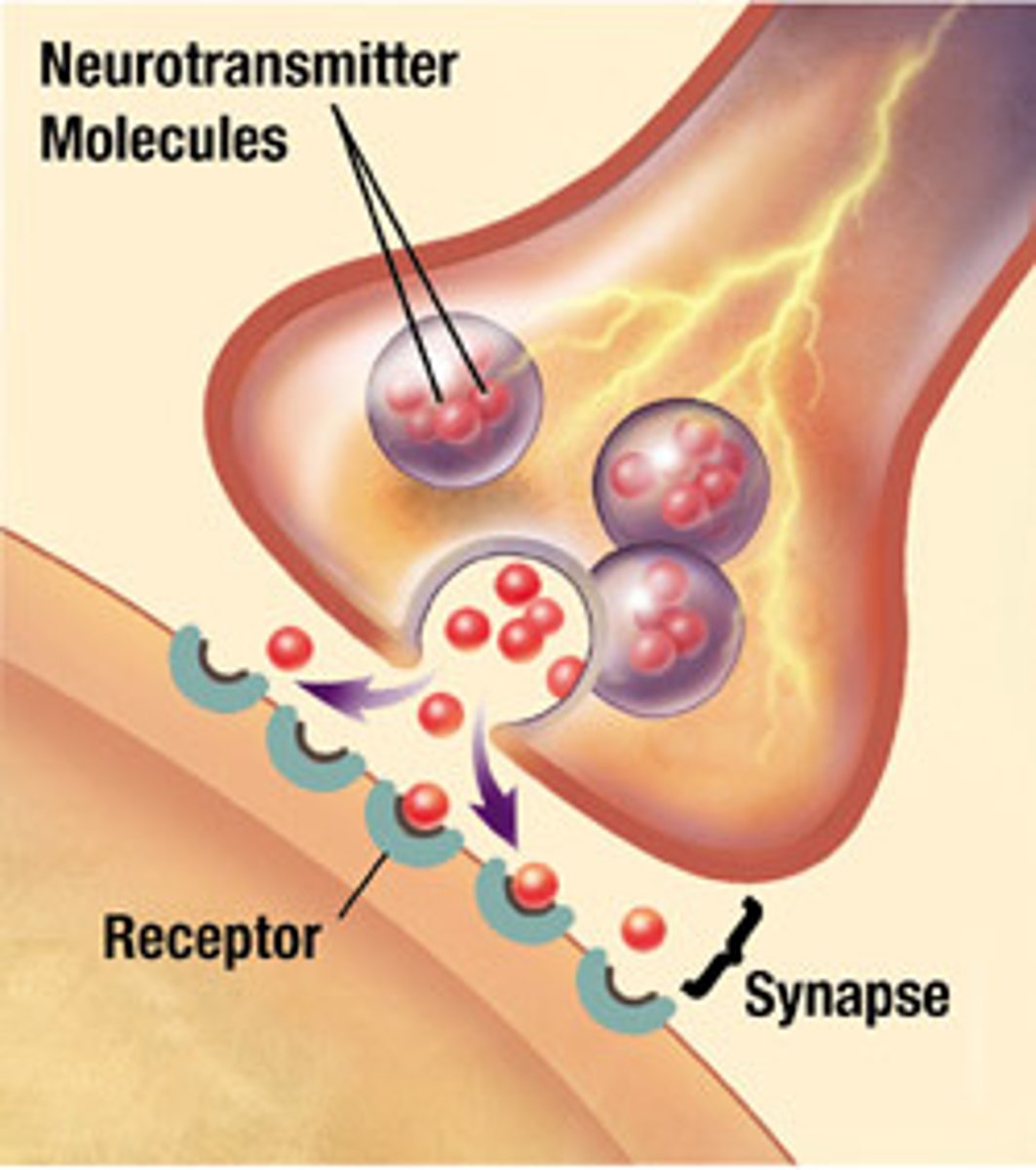
Synapse
>Sends electrical impulses to neighboring neurons
>Has too jump over an empty space to get to the next neuron
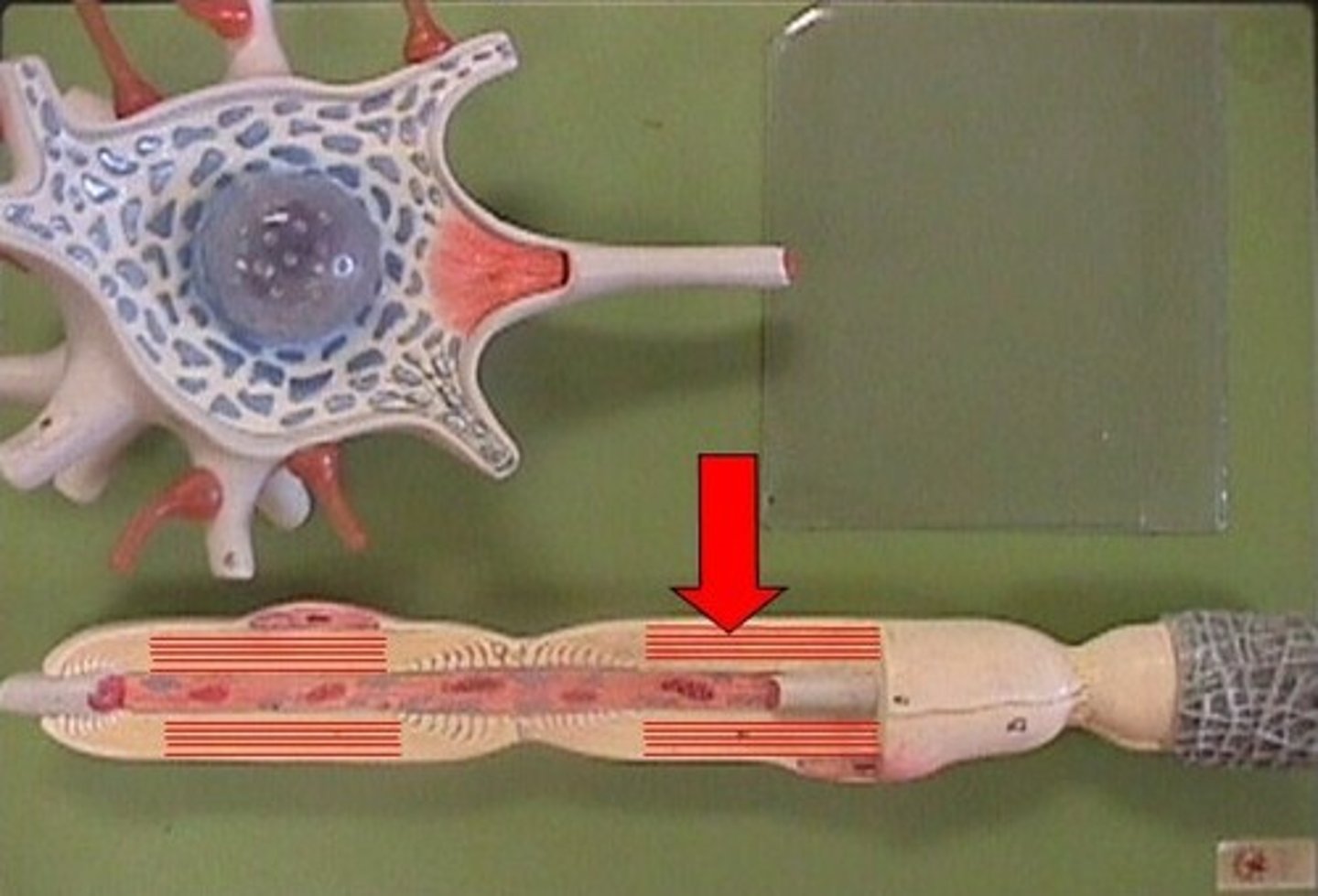
Myelin Sheaths
>Covers the axon and works like insulation to help keep electrical signals inside the cell, which allows them to move more quickly
Soma
>The cell body which contains most of the cells organelles
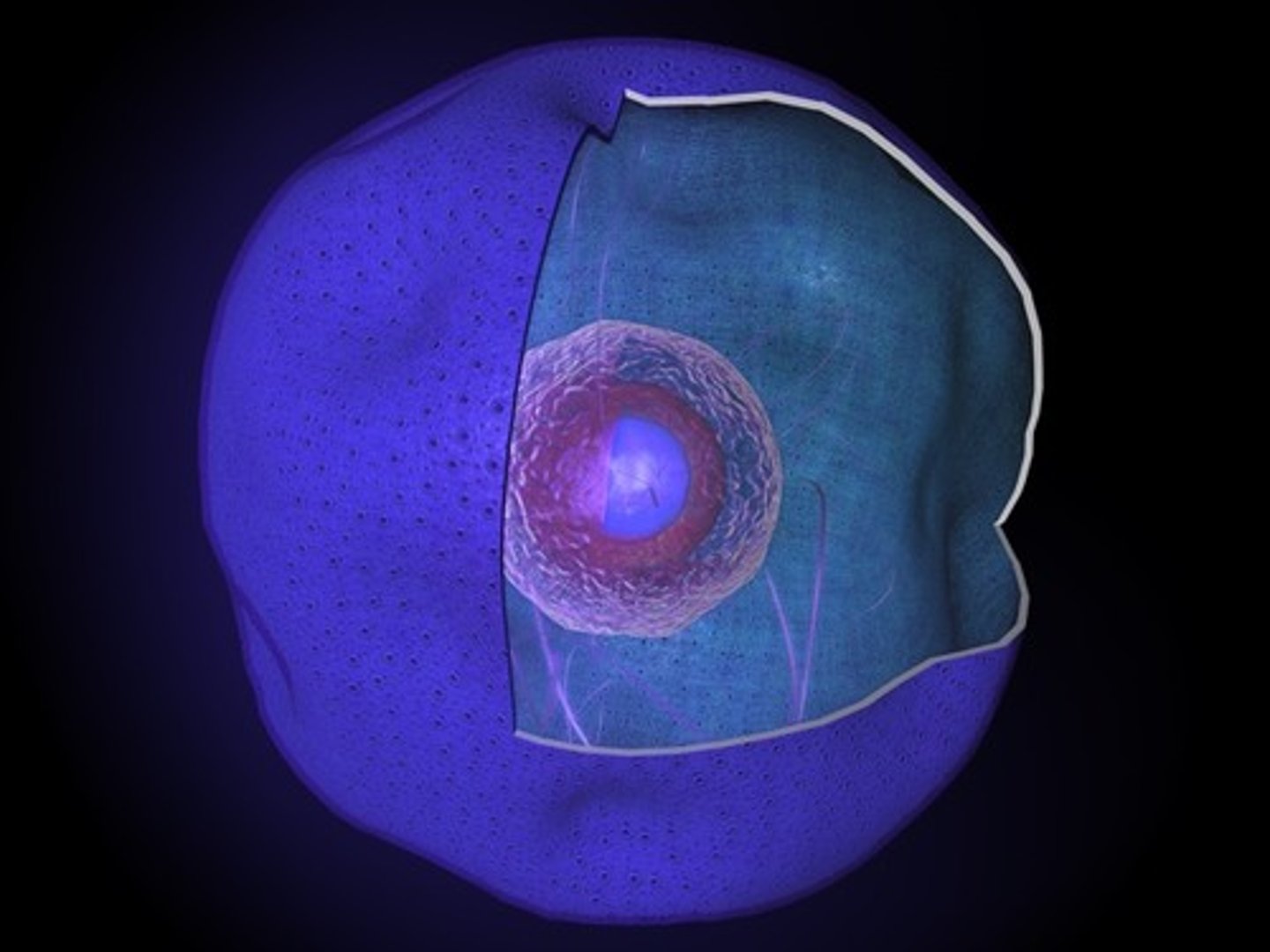
Nucleus
>Main control of the cell
>Contains DNA
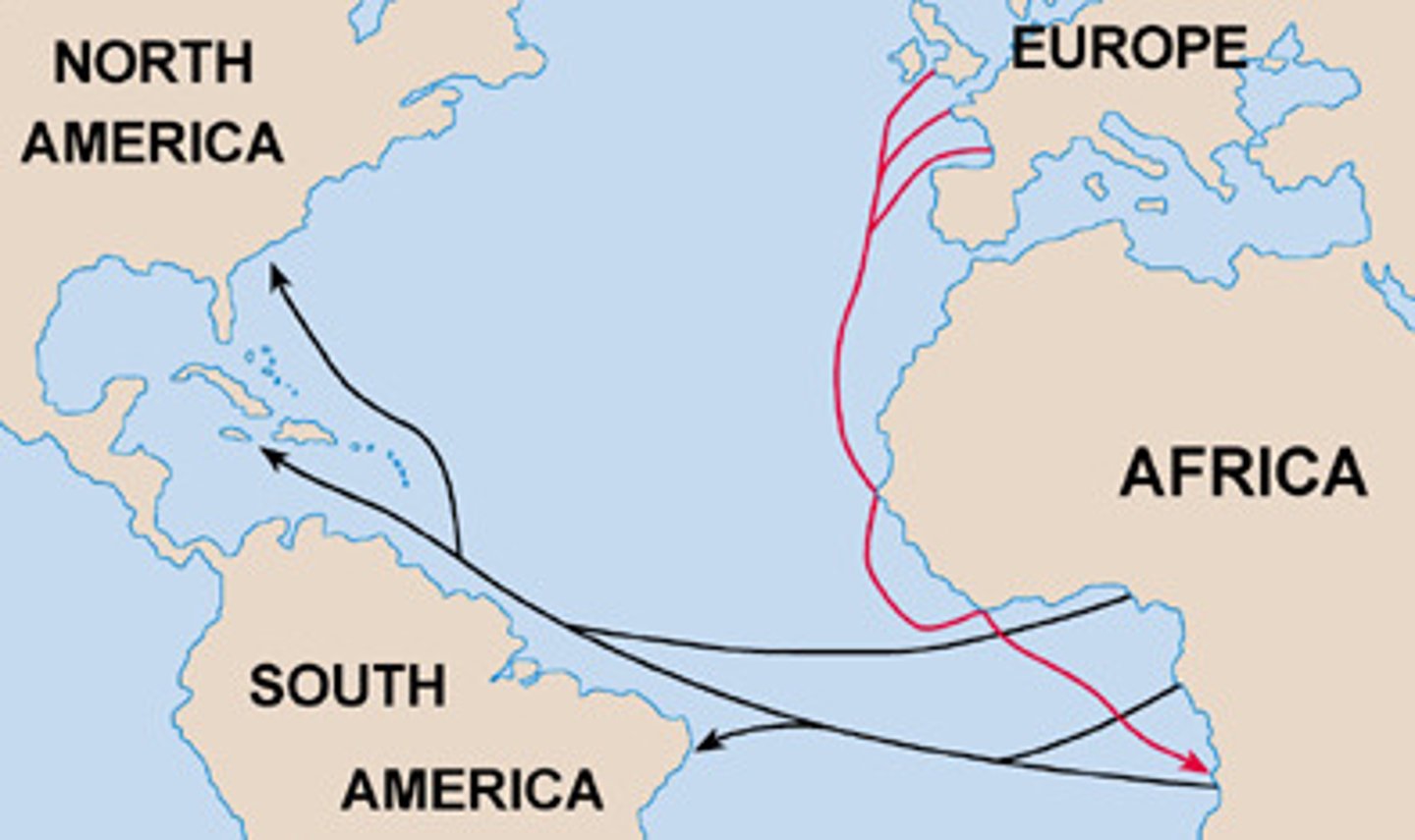
Immigration
>Movement of individuals into a population

Births
>Amount of individuals born into a population
Emigration
>Amount of individuals that are leaving somewhere

Deaths
>Size of population decreasing when people die
Geographic Dispersion
>of a population shows how individuals are spread out
Population Density
>The number of people that live in one defined area

Experimental Growth
>Occurs when population size increases dramatically over a period of time
Logistical Growth
>Begins with periods of slow growth followed by brief exponential growth before leveling off
Density Dependent
>Affected by the number of people in a given area
Density Independent
>Aspects of environmental that limits population growth regardless of density
Selectively Permeable
>Choose what can come in and what can go out
>EX: cell membrane
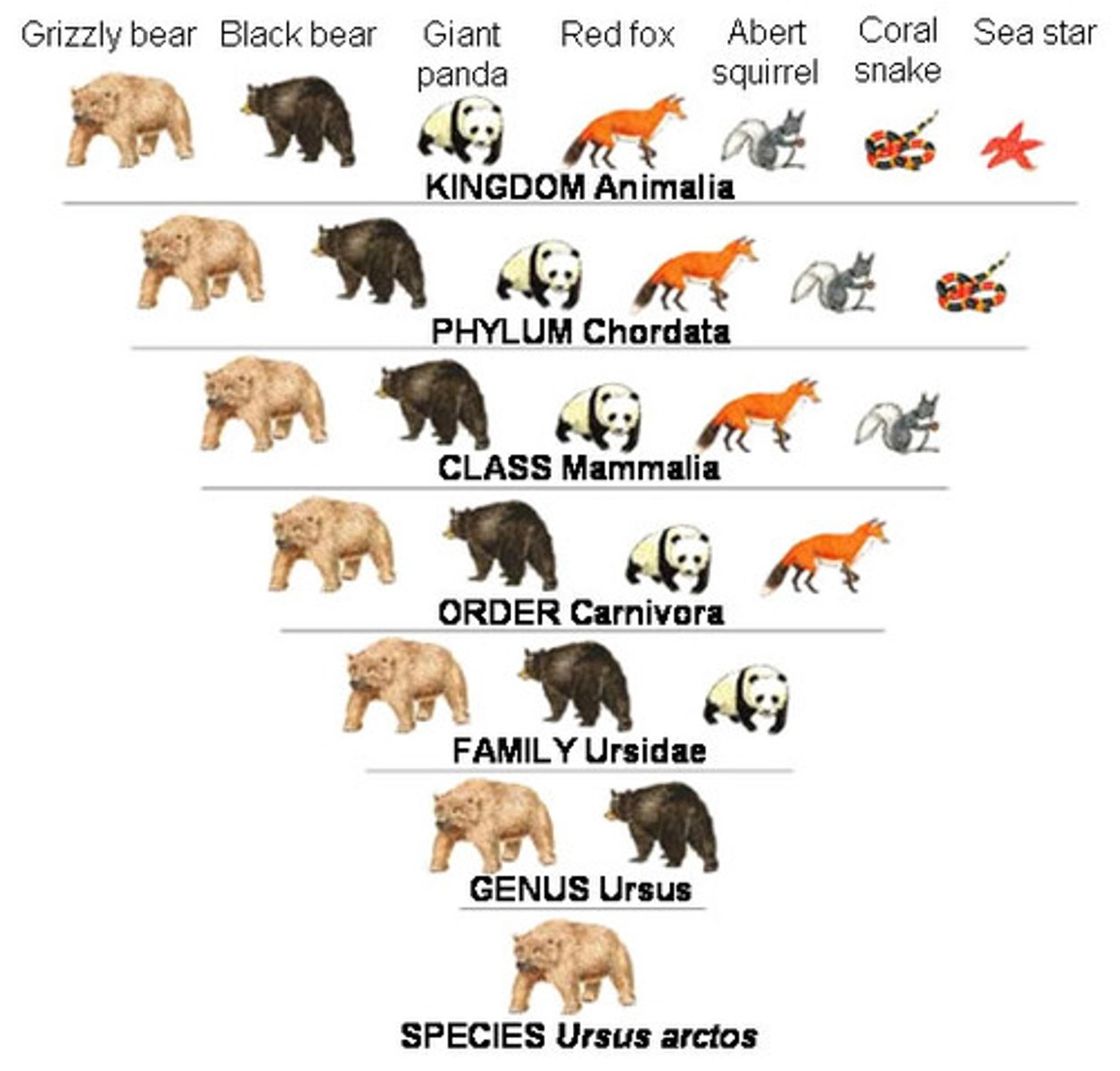
Order of Classification
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Organization of Life
Biosphere---Earth
Ecosystem---Forest
Community---All living things in a marsh
Population---Herd of Bison
Organism---Squid
Organ System---Digestive System
Organs---Kidney
Tissue---Nerve
Cells---Epidermis
Organelles---Nucleus
Molecules---
Elements---Oxygen
Subatomic Particles---Electron
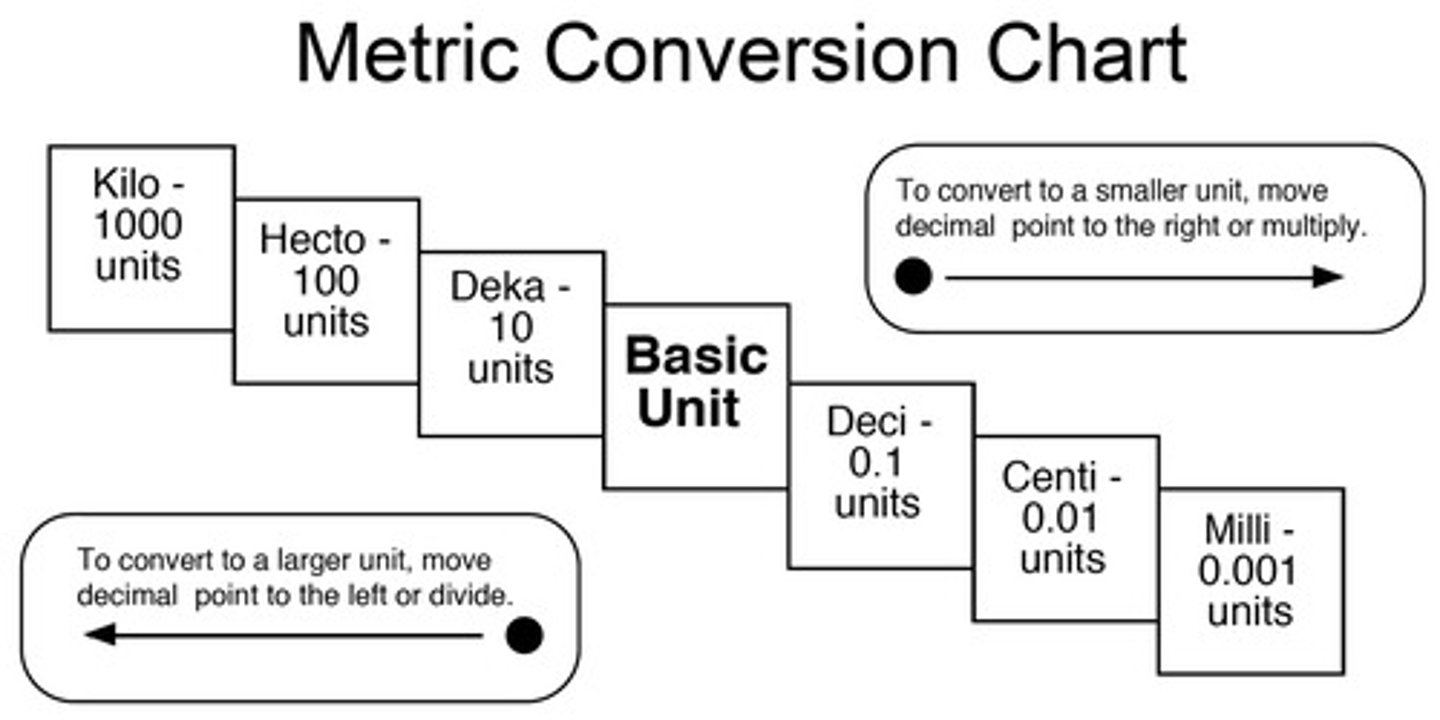
Metric Conversation
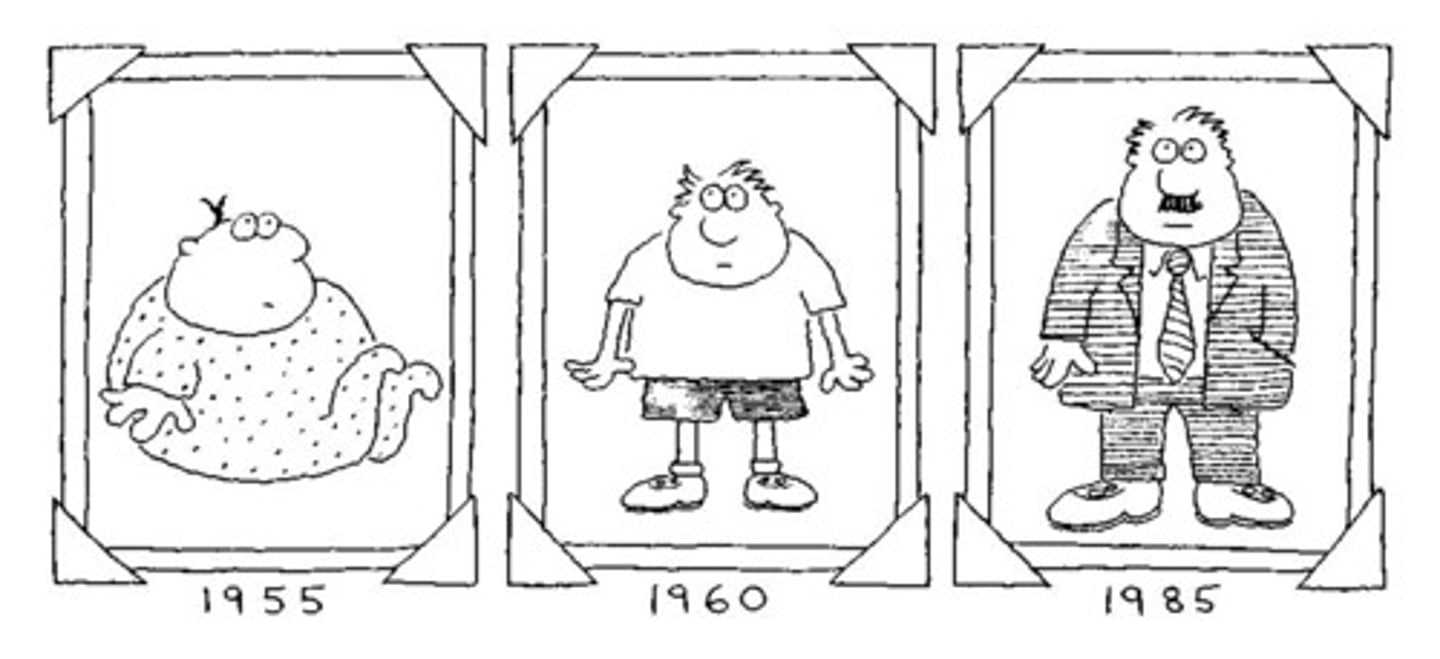
Growth and Development
>The series of changes that an organism undergoes during its lifetime
Autotroph
>An organism that obtains energy through the process of photosynthesis

Homeostasis
>An organisms ability to maintain a stable internal environment
Metabolism
>The process by which an organism takes in material from the environment and transforms them into useable energy
Heterotroph
>An organism that obtains energy by eating other animals

Kingdom
>Taxonomic system with six groups of organisms falling into it
Eukaryote
>An organism made up of cells containing membrane bound organelles and can be found in plantae, animalia, fungi and protista.
Domain
>Taxonomic System with three groups that fall into it
Sexual Reproduction
Form of reproduction that needs two parents, a male and female, to produce and offspring
Evolution
>Gradual change over time
Asexual Reproduction
>Form of reproduction done by using one parent that copies the DNA into two different copies
Organism
>Anything that carries out life process
>A living thing

Prokaryote
>Single celled organism congaing no membrane bound organelles (Studio Apartment)
Response to Stimuli
>A response to a physical or chemical change in an environment
Biosphere
>The part of the Earth where life exists in all the living components
Metric System
>System that uses grams, liter and meters

Gram
>Measurement of mass
Meter
>Measurement of distance or length