A 1.2 Nucleic Acids
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
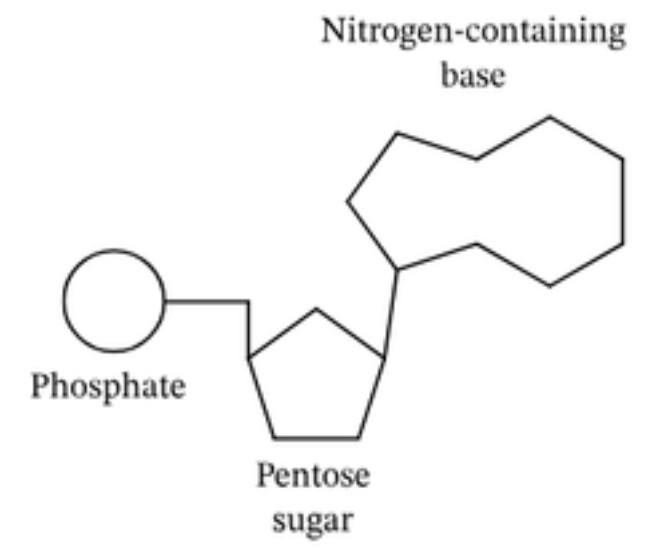
what are the building blocks of nucleic acids? whats its structure?
nucleotides
its structure:
phosphate group (acidic because ti is negatively charged)
pentose sugar ( 5 carbon sugar)
nitrogenous base (A,T,U,G,C)
nucleic acids can be:
DNA or RNA
where is the DNA located in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells? and what type? do viruses have DNA?
eukaryotic:
location: DNA is in a membrane bound nucleus
type: linear DNA in the form of chromosomes. (it has 2 ends, starting point and ending point)
prokaryotic:
location: no nucleus, so the DNA is in the cytoplasm in an area called nucleoid. DNA is not membrane bound
type: circular DNA (no ends, because the ends are connected)
viruses are NOT living but they also have DNA, but they use DNA (or RNA) as genetic material
what are the 2 primary functions of nucleic acids?
gene expression: transcription (DNA → mRNA) and translation (mRNA [with the help of tRNA] → protein)
DNA replication: DNA replicates itself so when mitosis occurs no DNA is lost and both daughter cells are identical(to each other and to the parent)
whats the difference between DNA and RNA ?
DNA:
found in nucleus in eukaryotic cells
deoxyribose sugar
thymine as nitrogenous base
RNA:
found in the nucleus and cytoplasm
ribose sugar
uracil as nitrogenous base
what are the 2 types of nitrogenous bases? explain them
purines (bigger):
guanine
adeninepyrimidines (smaller):
cytosine
uracil (in RNA)
thymine (in DNA)
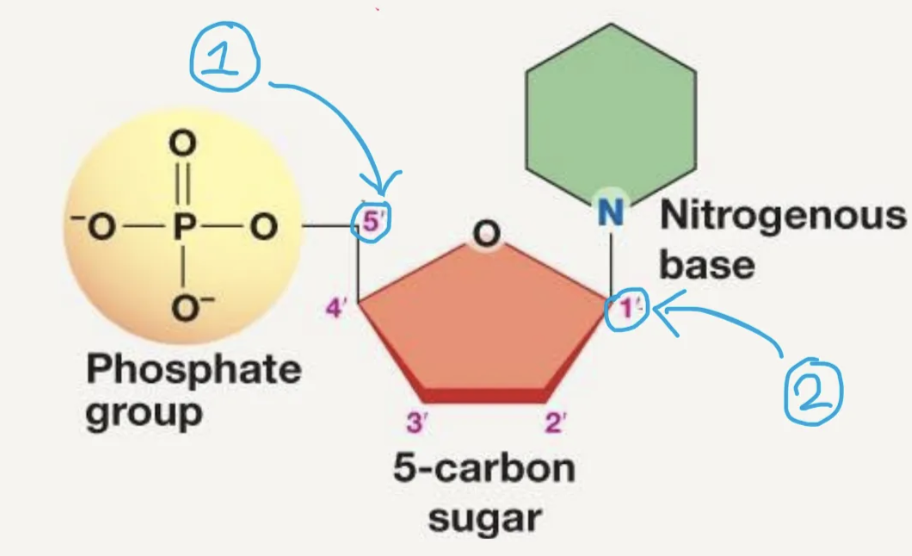
where is the phosphate group and nitrogenous base bonded to? (what carbon are they bonded to on the sugar)
the phosphate is bonded to 5’ carbon (① in the picture)
nitrogenous base is bonded to 1’ carbon ( ② in the picture)
what is a condensation reaction?
a type of chemical reaction where two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, with the loss of a water molecule
what is a phosphodiester linkage? how does it happen? what does it create?
it’s the bond between the sugar and the phosphate group (of different nucleotides)
the 2 nucleotides go through a condensation reaction, releasing water. this creates the Sugar–phosphate backbone of rna and dna
adenine and thymine are held together by how many bonds?
2 hydrogen bonds
guanine and cytosine are held together by how many bonds?
3 hydrogen bonds
what do you know about the major and minor groves?
DNA has major and minor groves:
major grove → mostly has the DNA that needs to be transcribed because the base pairs are more expanded
minor grove → less likely to get transcribed because its base pairs are less exposed.
DNA is a _____ ____ and is made of 2 _____ strands
double helix
antiparallel