Skeletal Muscles
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
4 Main functions of Skeletal Muscles
Causes movement of the skeleton
Maintains posture
Stabilises bones & joints
Generate heat in the body
Unique Characteristics of Muscle Tissue:
Excitability
Excitability - Able to receive and respond to a stimulus (can be electrically stimulated)
Contractility - Able to contract/shorten when stimulated
Extensibility - Able to be stretched a little
Elasticity - Able to return to original shape/recoil after being stretched, resuming resting length
Unique Characteristics of Muscle Tissue:
Contractility
Contractility - Able to contract/shorten when stimulated
Unique Characteristics of Muscle Tissue:
Extensibility
Extensibility - Able to be stretched a little
Unique Characteristics of Muscle Tissue:
Elasticity
Elasticity - Able to return to original shape/recoil after being stretched, resuming resting length
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Structure:
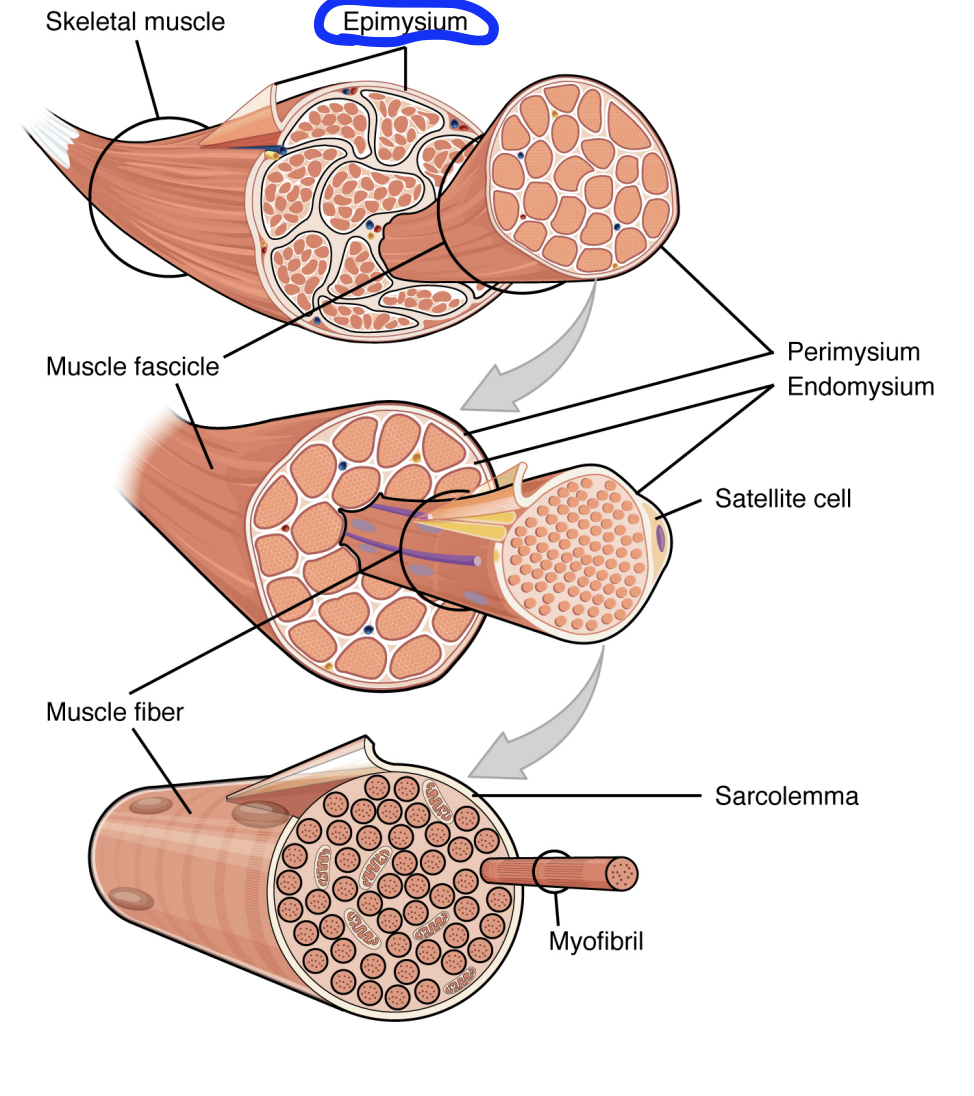
Epimysium
A covering of connective tissue around the entire muscle.
Epi- meaning upon
Outermost covering of muscle.
Not muscle tissue, but a dense fibrous connective tissue
Provide the muscle structural integrity
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Structure:
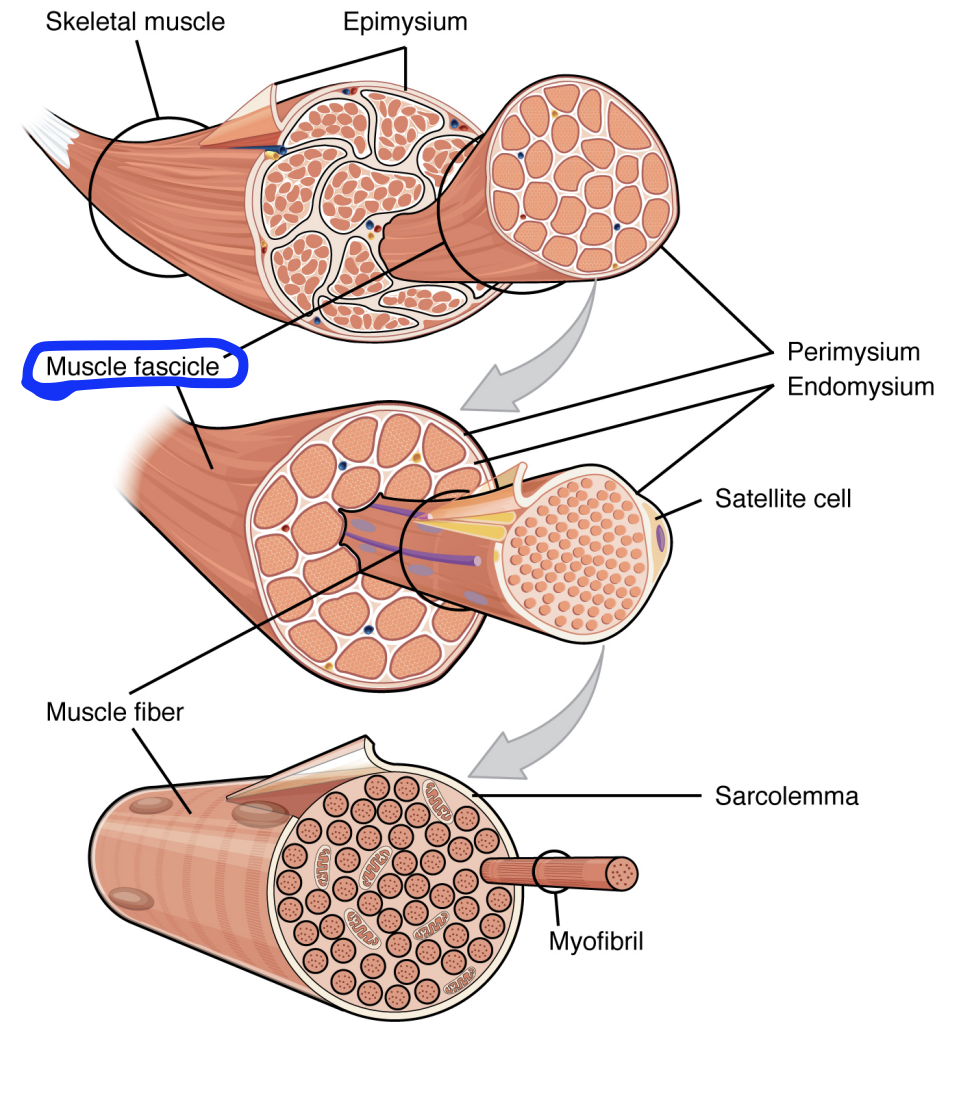
Muscle Fascicles
Bunched together muscle fibres
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Structure:
Perimysium
A covering of connective tissue around the muscle fascicles.
Peri- meaning around
Wraps around each muscle fascicle
Not muscle tissue, but a dense fibrous connective tissue
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Structure:
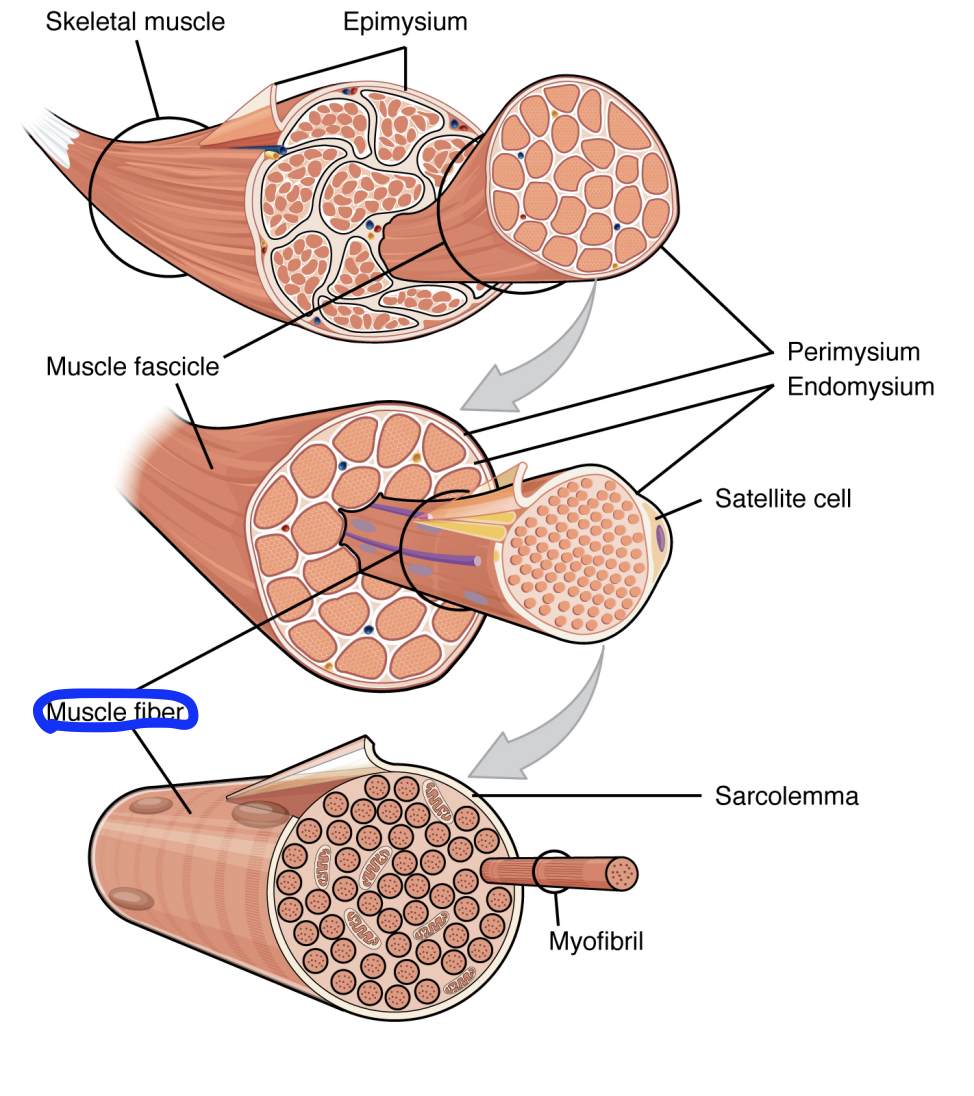
Muscle Fibre/Muscle cell
A single muscle cell running the entire length of the muscle, from one end to the other
Multinucleated
Abundance of mitochondria
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Structure:
Endomysium
A covering of connective tissue around a muscle fibre.
Endo- meaning within
Wraps around each muscle fibre
Not muscle tissue, but a dense fibrous connective tissue
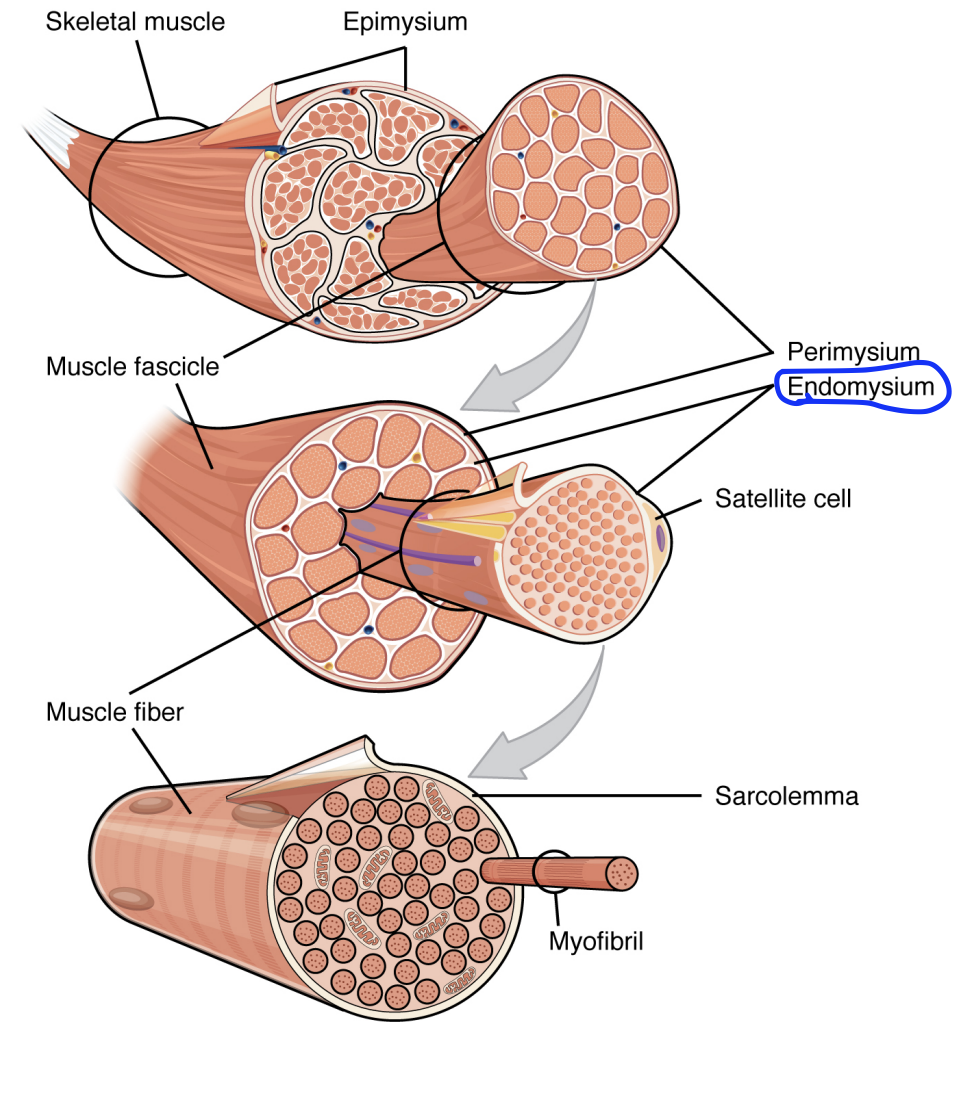
Epimysium, perimysium & endomysium
All three layers of connective tissue combine at the end of the muscle body with the tendon’s connective tissue.
Contribute to the elasticity and flexibility of the muscle
Origin (muscle attachment site)
Proximal attachment site
Located closer to the attachment to the body’s trunk
Insertion (muscle attachment site)
Distal attachment site
Located further from the attachment to the body’s trunk
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Structure:
Blood vessels & Nerves
Run through the connective tissues of muscles
Good blood supply, good ability to repair
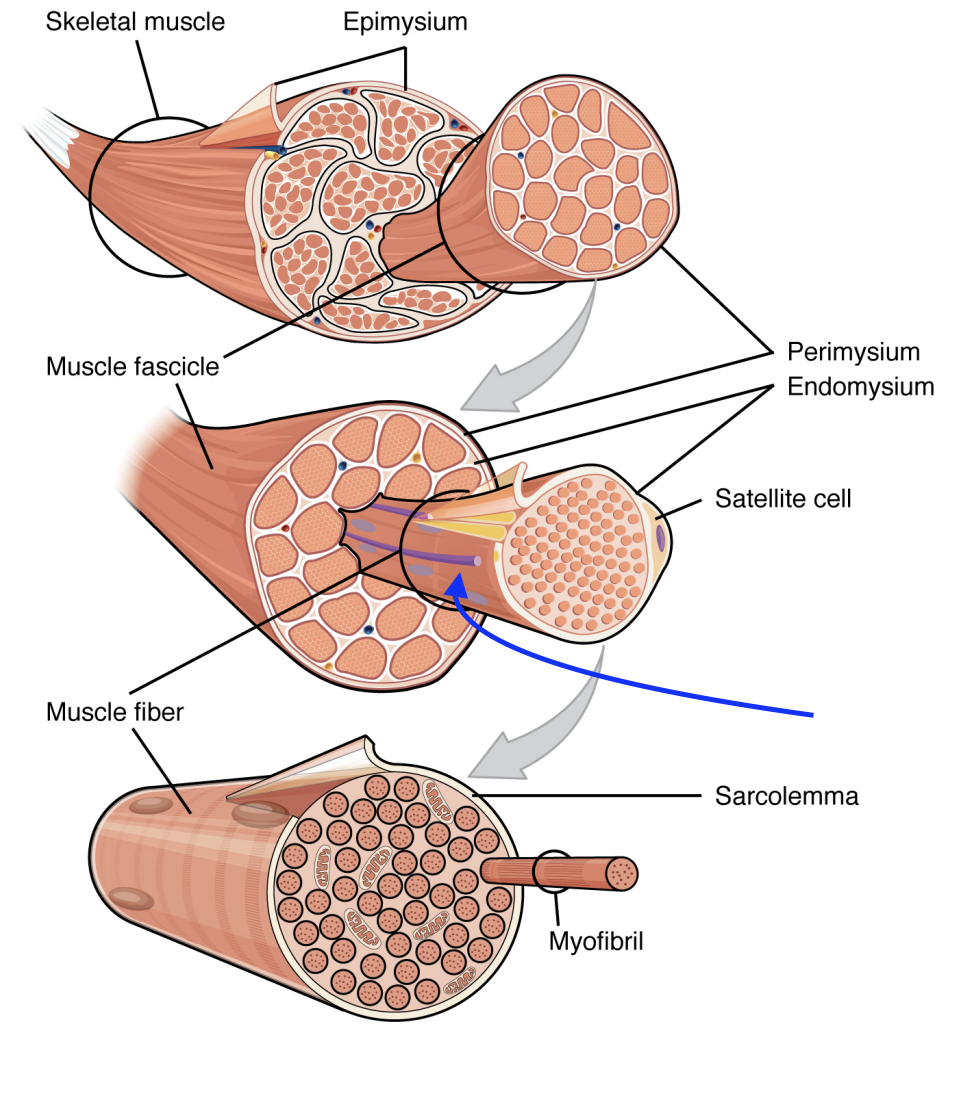
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Structure:
Sarcolemma
The cell membrane of the muscle cell/fibre. Located directly under the endomysium
Part of the muscle cell, unlike the endomysium
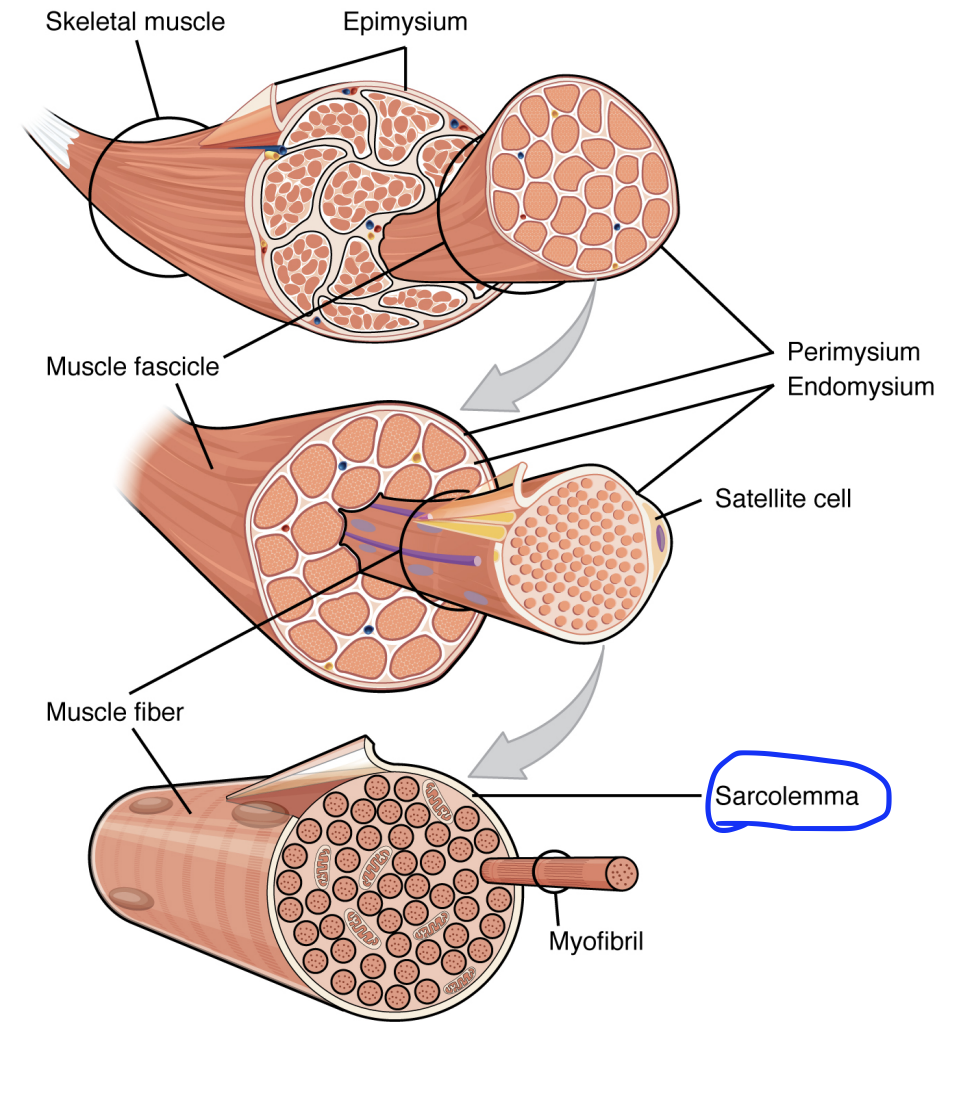
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Structure:
Myofibril
The functional unit of the muscle cell. Packed within the muscle fibre.
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Structure:
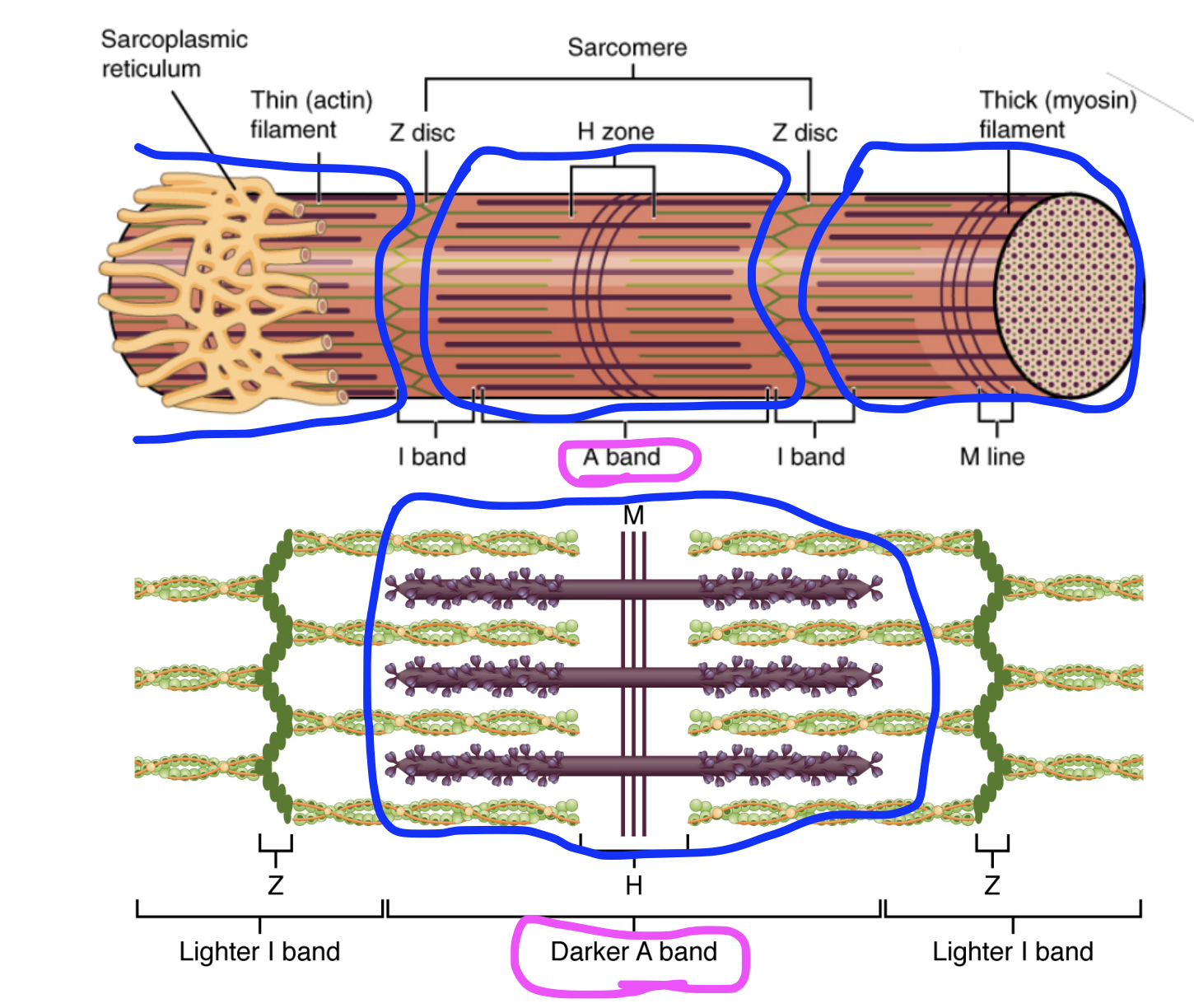
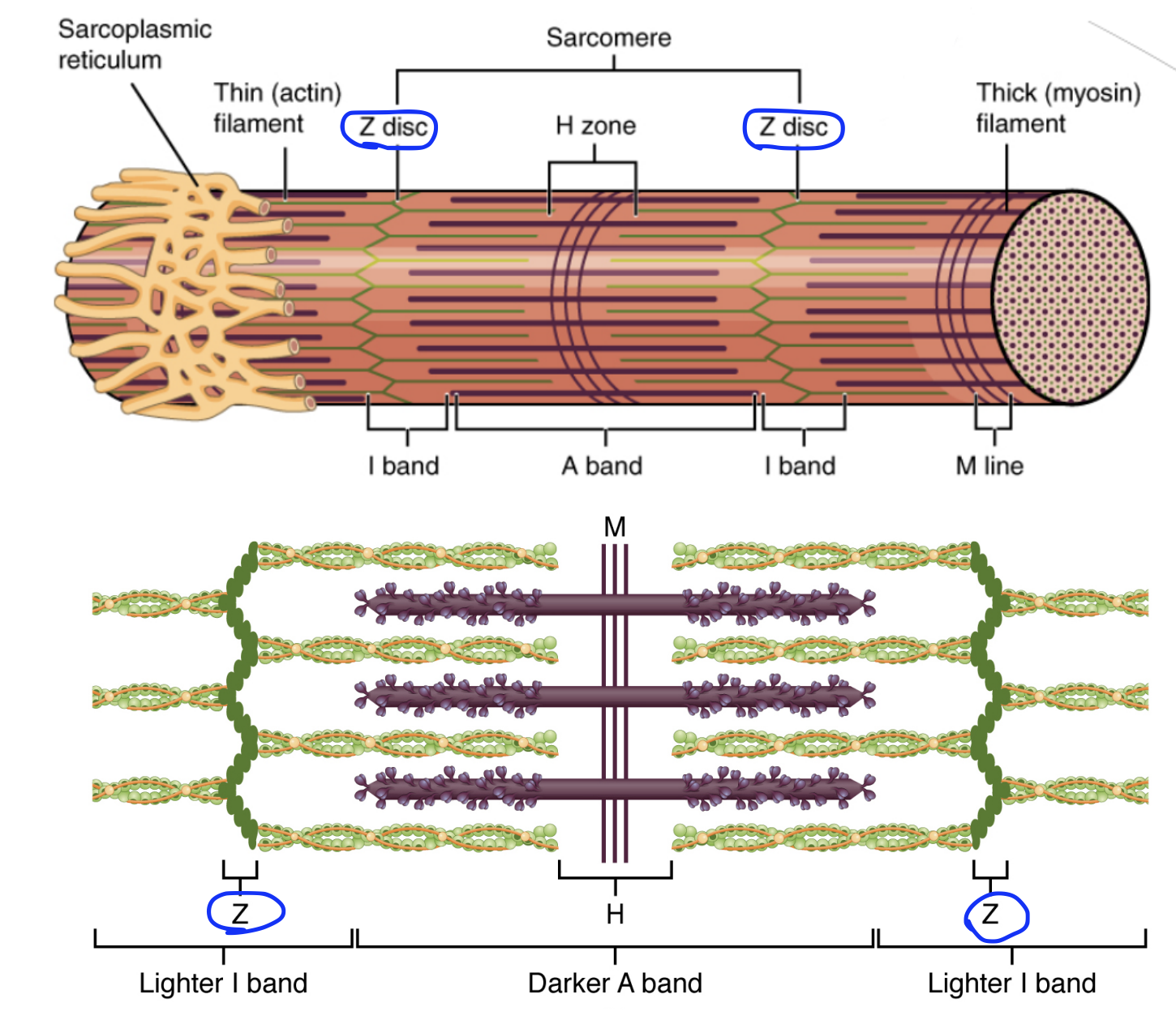
Sarcomere
Repeating units from end to ends of a myofibril. There are many sarcomeres inside a single myofibril.
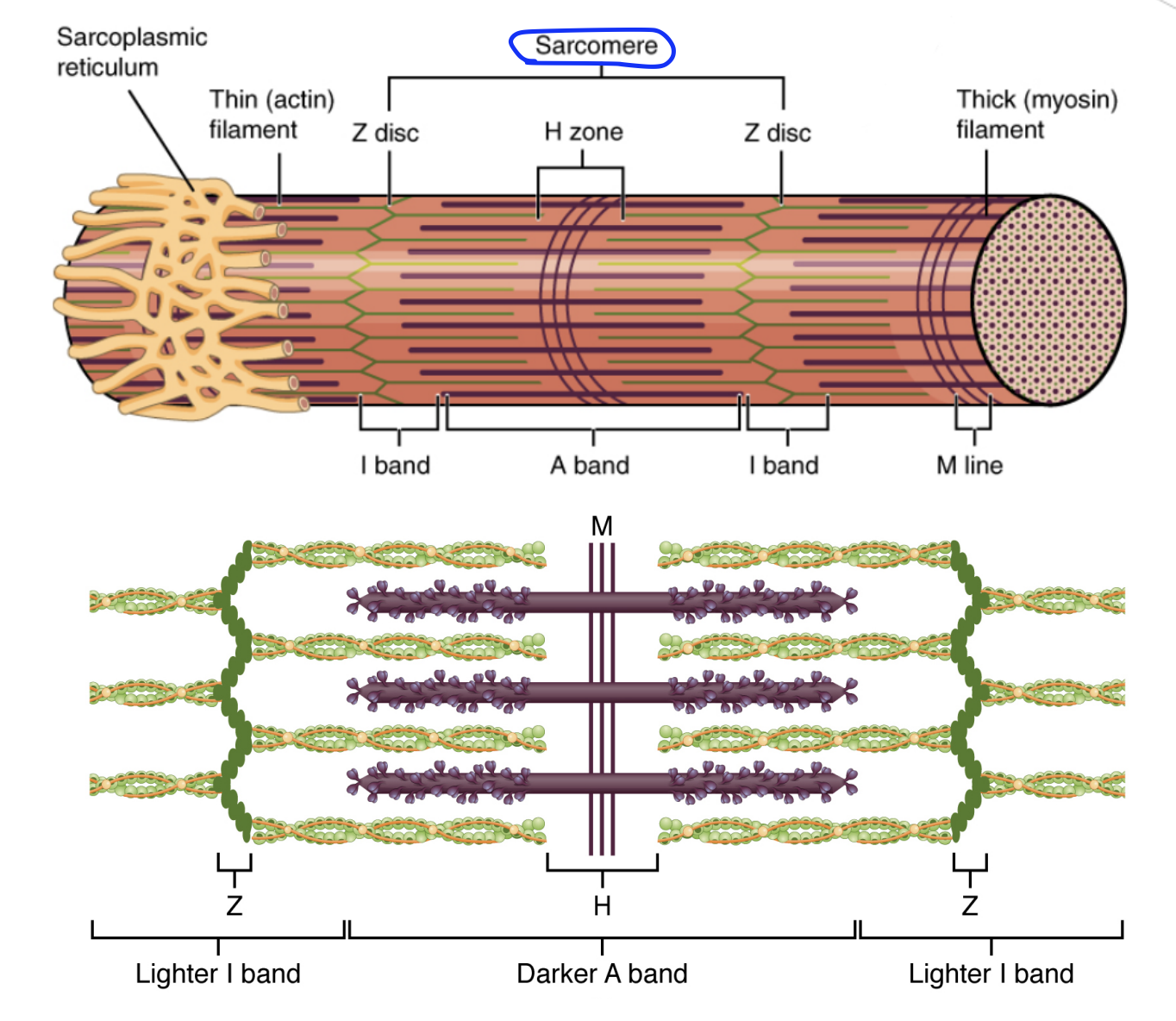
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Structure:
Z-discs
Regions flanking each end of the sarcomere. Used to isolate each sarcomere.
z-discs are proteins
From one z-disc to another, is a sarcomere, the functional unit of a myofibril
Located in the I-band
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Structure:
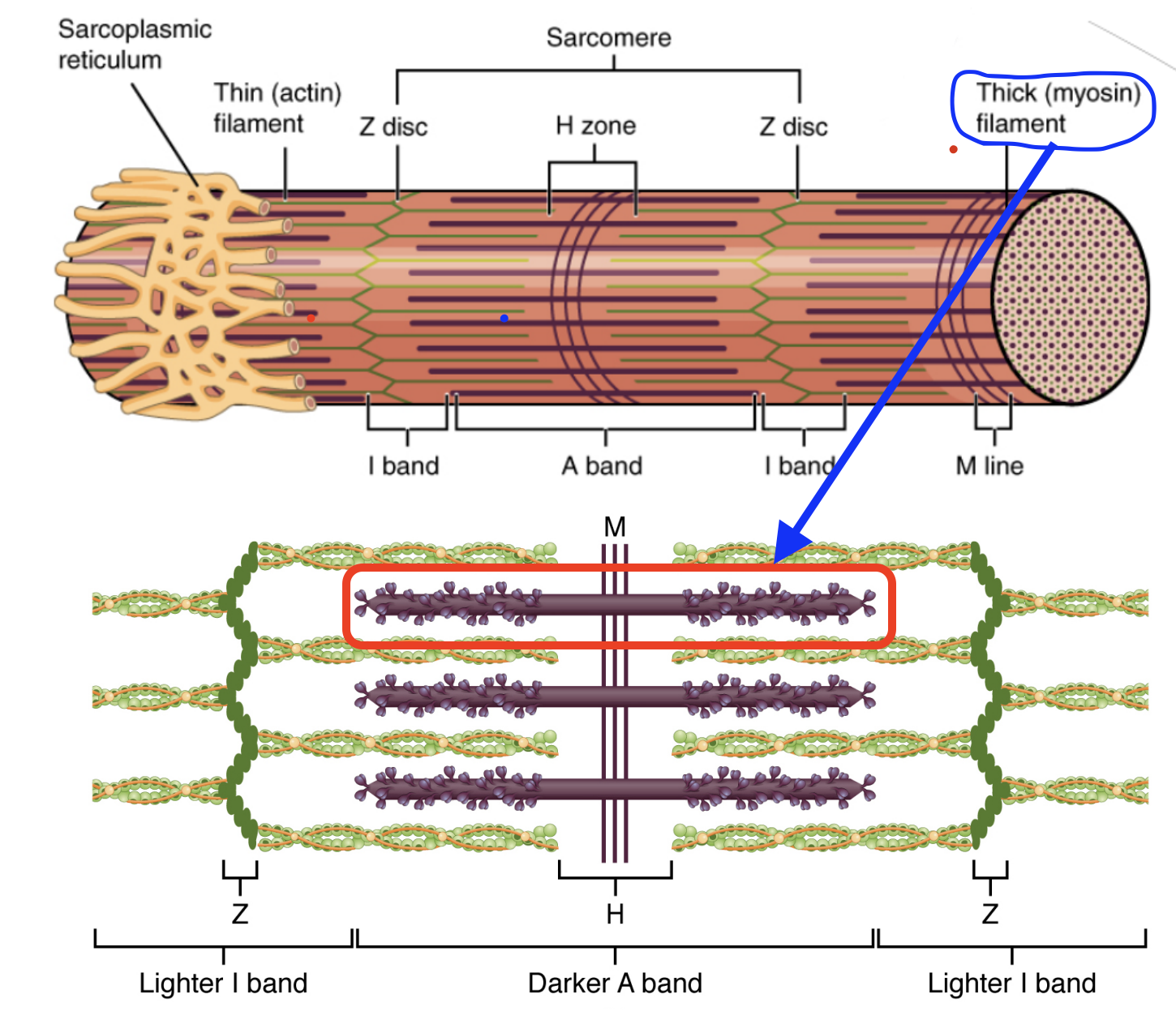
Myofilament: Myosin
Thick filaments.
Myosin is a protein
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Structure:
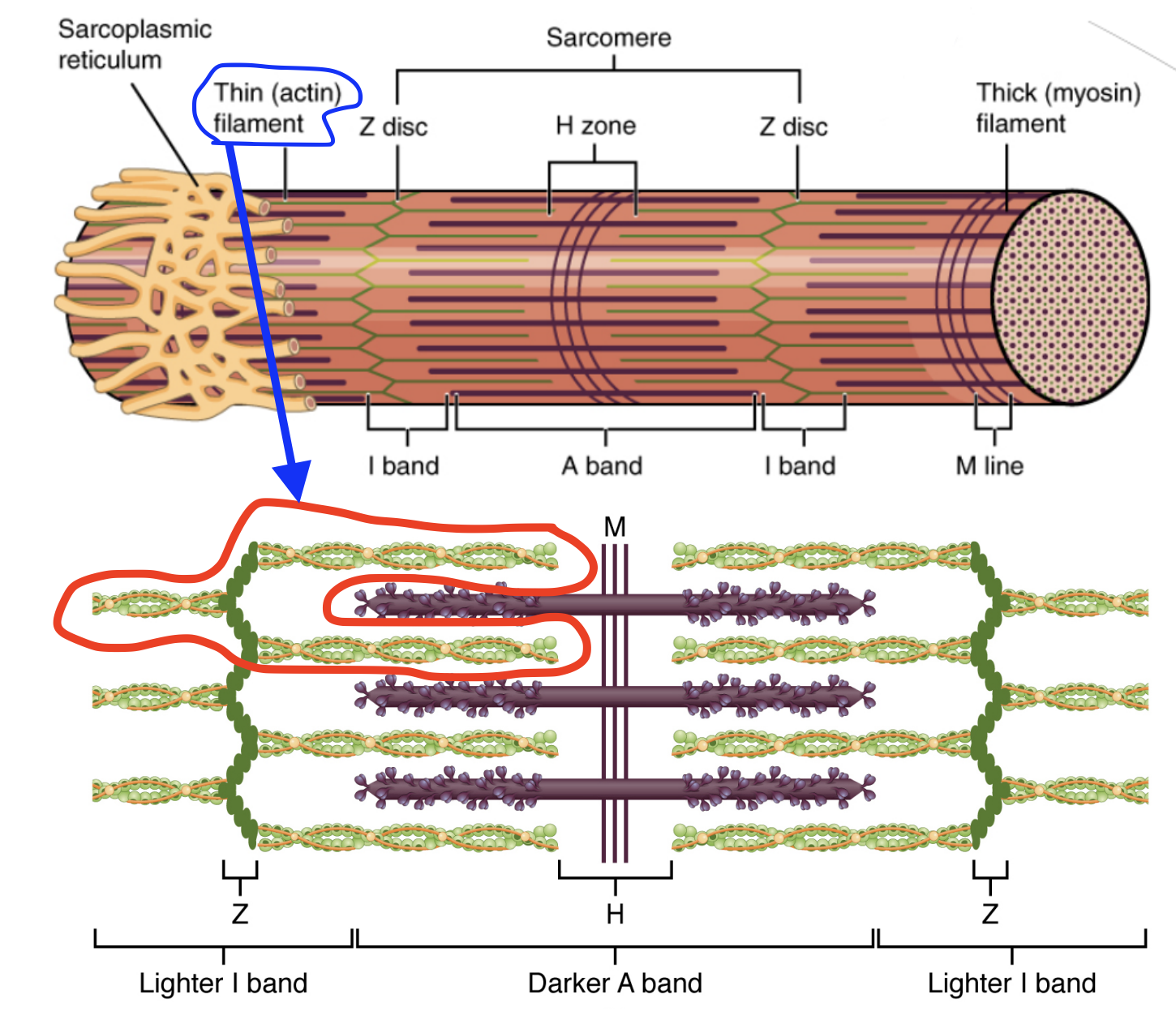
Myofilament: Actin
Thin filaments.
Actin is a protein twisted upon itself.
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Structure:
Striated Pattern
Unique banding pattern of skeletal muscles
The arrangement of myofilaments (actin & myosin) is what differs between smooth, cardiac & skeletal muscle
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Structure:
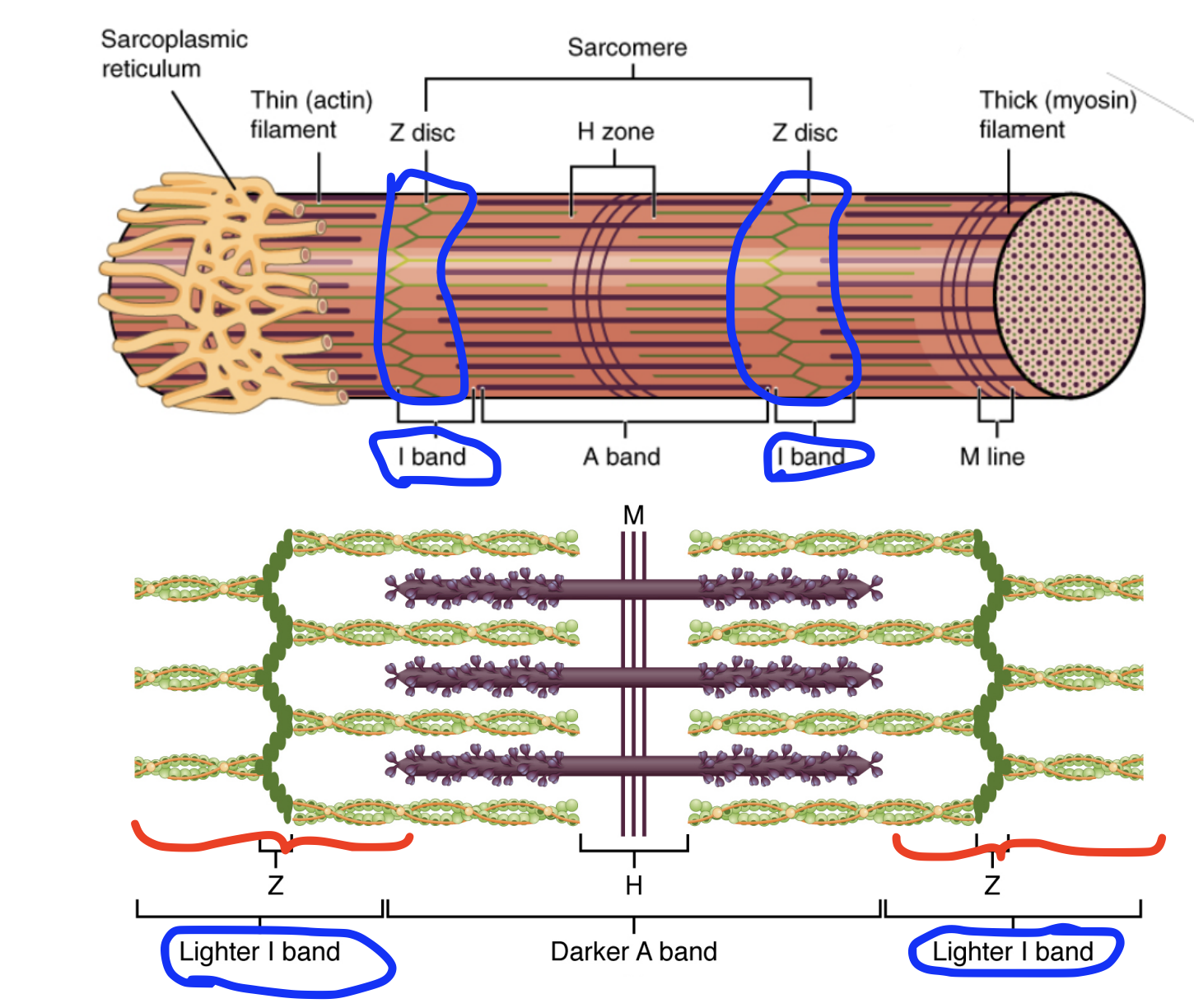
I-band
Region of the sarcomere sans thick filaments (myosin), where the z-discs are found.
Only actin (thin filaments) are in the I-band
‘Lighter‘ areas when looking at sarcomeres under the microscope
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Structure:
A-band
Region of the sarcomere with myosin present as well as actin, region between the z-discs.
Both actin and myosin filaments are in the A-band
‘Darker‘ areas when looking at sarcomeres under the microscope
Due to myosin, the thicker filament being present, giving a striped, striated banding pattern