A.5.2 special relativity
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
the two postulates of special relativity
the laws of physics are the same in all inertial frames of reference
The speed of light in a vacuum is the same as measured by all inertial observers.
velocities don’t add up
with objects moving close to the speed of light time slows down
time relative to the motion in reference frames, and motion still relative
time dilation
when we can’t add velocities, as max is c
if the object has to travel more and object has a velocity of almost the speed of light, the time slows down,
seen from s = d/t
proper time
The proper time is the time measured by a clock in a rest frame
eg, a gilr in a rocket from earth to moon has proper time rather than girl measuring time on earth. The girl can measure both takeoff and landing with same clock, clock stays in the same position.
length contraction
if rocket has velocity clsoe to speed of light the clock slows down, which causes the length (distance to travel) to contract, due to the equation d=vt
velocity close to the speed of light
time slows down, increases
distance/length decreases, contracts
at the speed of light no time or distance, can be anywhere anytime
proper length
the distance measured by an observer at rest relative to the length
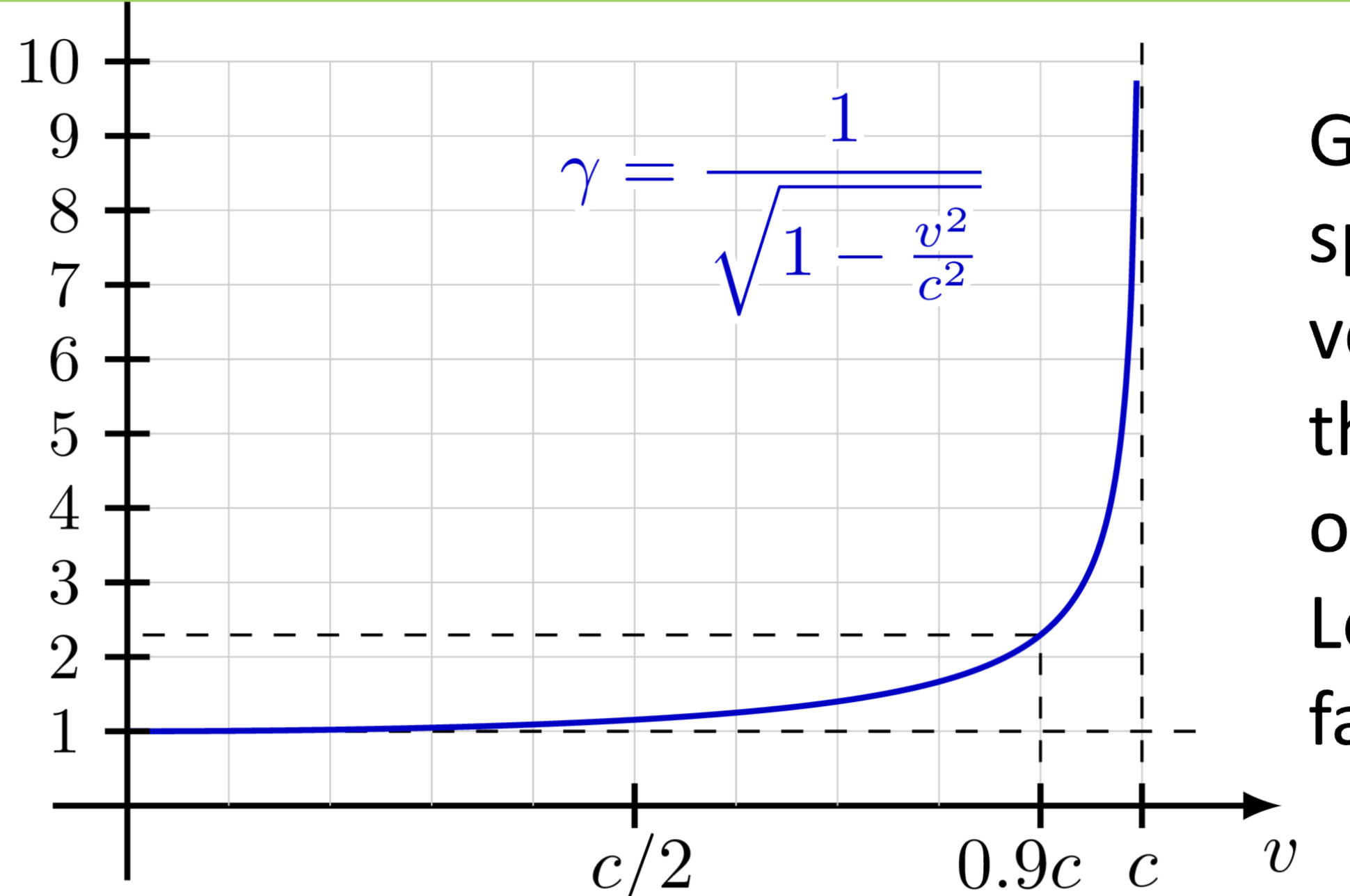
Lorentz transformations
to relate the measurements in one frame to another, when the velocity of light is the same in all inertial frames of reference
how to proof that speed of light is the same for both frame of references
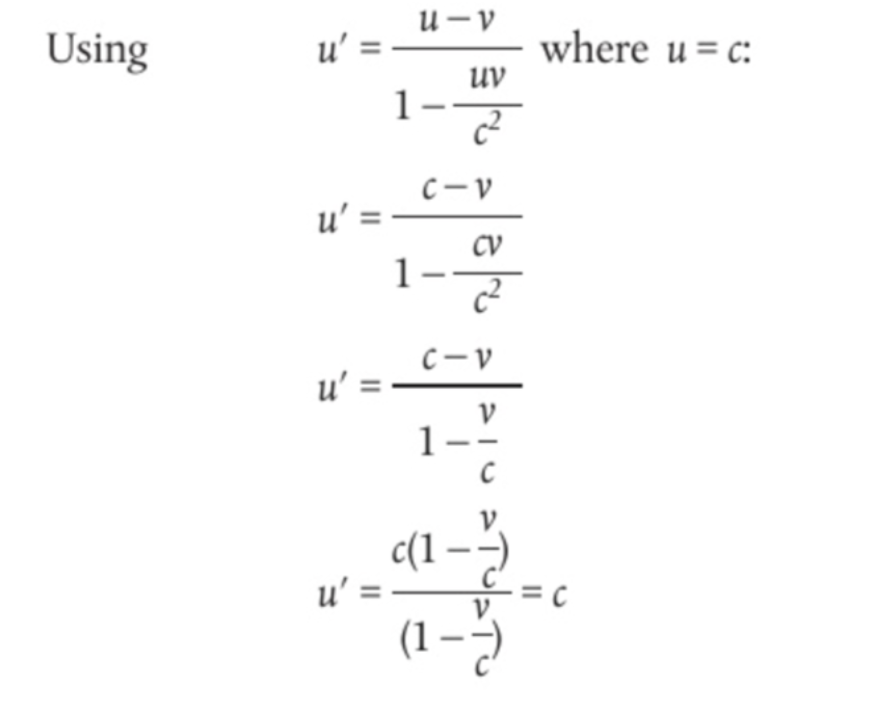
graph for speed vs lorentz factor
lower the Lorentz factor, the slower speed is