Bone pathology
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
osteogenesis imperfecta
brittle bone disease, type 1 collagen maturation
opalescent teeth, blue sclera, and maxillary hypoplasia associated with
osteogenesis imperfecta
cleidocranial dysplasia
hypoplastic/absent clavicles, supernumerary teeth
focal osteoporotic bone marrow defect is not pathology and does not need treatment
both statements are true
focal osteoporotic bone marrow defect is not a variation of normal and is asymptomatic
first statement is false second statement is true
idiopathic osteosclerosis radiolucency with no association with inflammation and is associated with teeth
both statements are false
age demographic for patients with paget disease
older patients
paget disease
abnormal/deposition of bone
weakened distorted bones
paget disease clinical/radiographic features
M>F, maxilla, usually asymptomatic, xray- cotton wool appearance
polyostotic
multiple bones affected
monostotic
one bone affected
paget’s disease radiographic appearance
cotton wool
central giant cell granuloma
common in kids and young adults, mandible, F>M, 1st molar or anterior, uni or multilocular
we see aggressive CGCG more often than we non-aggressive
false
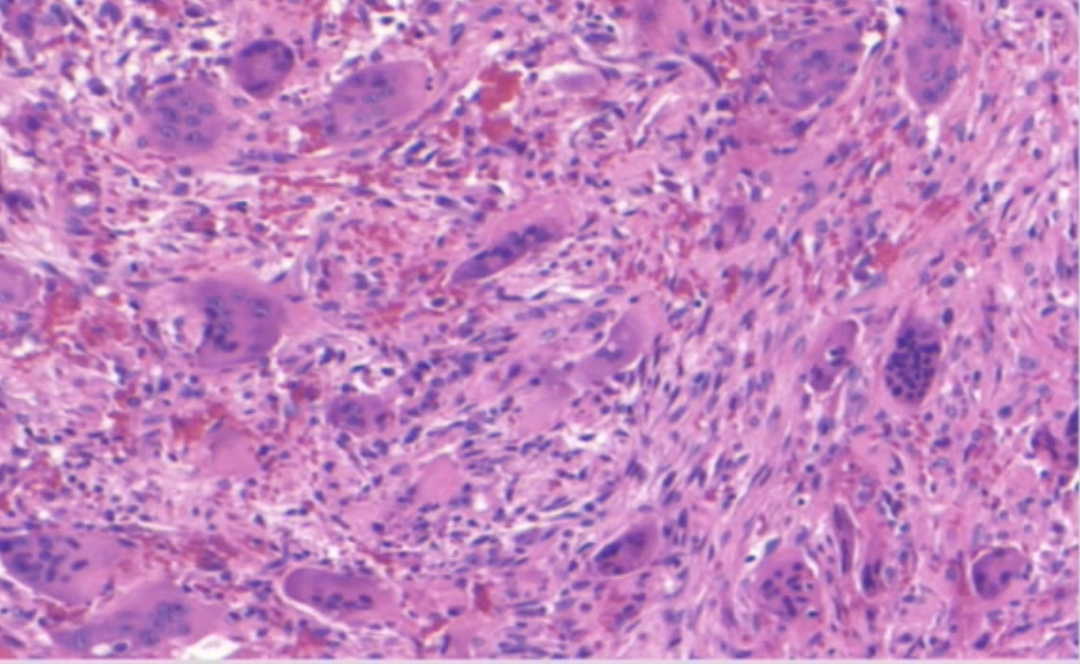
what are the areas with numerous purple circles
multinucleated giant cells
multinucleated giant cells histology is associated with
CGCG
cherubism associated with
CGCG
histology looks the same
CGCG, brown tumor of hyperparathyroidism, cherubism
fibro-osseous lesions require clinical and radiographic info along with histology for a specific diagnosis
true
GNAS1 gene associated with
fibrous dysplasia
fibrous dysplasia most commonly affects the mandible and is M>F
both statements are false
characteristics of fibrous dysplasia
cafè-au-lait pigmentation (coast line of Maine), ground/frosted glass and radiopaque radiograph
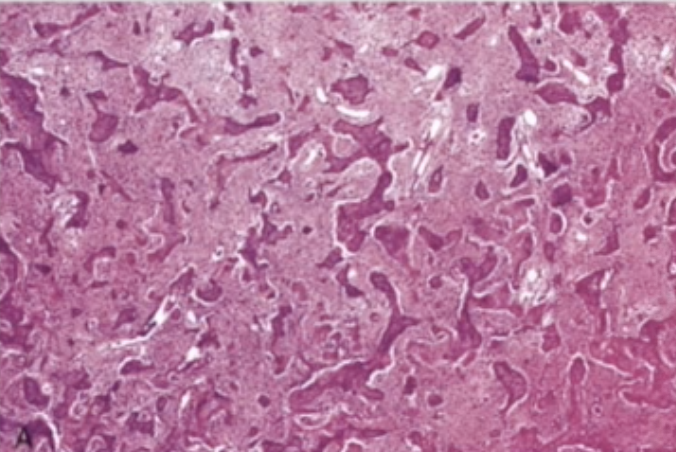
irregular bony trabeculae
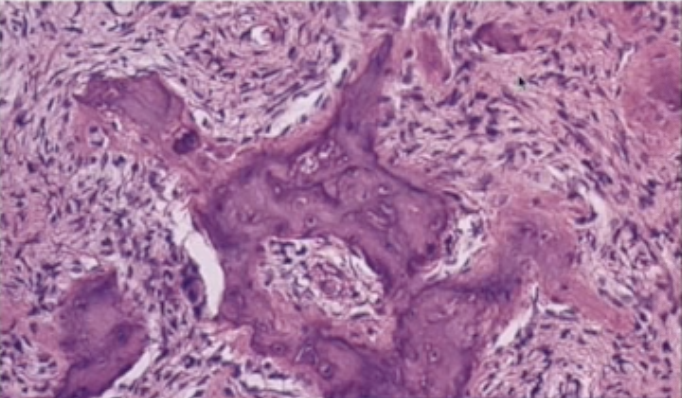
irregular bony trabeculae
most common benign fibro-osseous lesion
cemento-osseous dysplasia
focal cemento-osseous dysplasia gender predilection
F>M
focal cemento-osseous dysplasia asymptomatic/symptomatic
asymptomatic
focal cemento-osseous dysplasia radiographic appearance
mixed
periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia location
anterior MD
focal cemento-osseous dysplasia demographic predilection
african women
in periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia teeth are
vital
florid cemento-osseous dysplasia symptomatic/asymptomatic
asymptomatic
florid cemento-osseous dysplasia demographic predilection
middle aged african/asian women
bony trabeculae are associated with
fibrous dysplasia
cemento-osseous dysplasia gender predilection
F>M
cemento-osseous dysplasia radiographic appearance
progressive RL —> RO
osteoma radiographic appearance
RO
how do you diagnose paget disease
increased alkaline phosphatase
paget disease tx
bisphosphonates
frosted/ground glass appearance aside from fibrous dysplasia
psammomatoid - juvenile ossifying fibroma
most common primary malignant tumor of bone
osteosarcoma
radiographic sunburst appearance
osteosarcoma
garrington’s sign
widening of PDL space
what is garrington’s disease seen in
osteosarcoma
first sign of cancer
metastatic lesions
moth eaten radiographic appearance
metastatic lesions