Oral Health & Prevention Midterm
1/312
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
313 Terms
Reserve space
space reserved for adult teeth by primary teeth
anatomic crown
the part of the tooth covered with enamel
clinical crown
the part of the tooth visible in the mouth
parts of the root
cementum- dentin - root canal
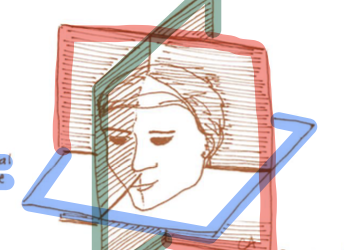
Red zone
frontal plane
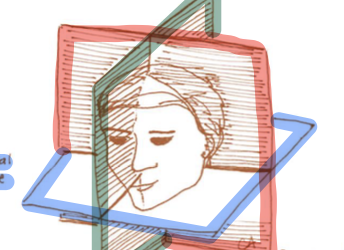
Green zone
sagittal plane
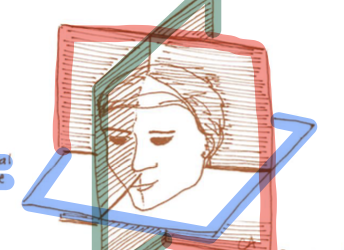
Blue Zone
Horizontal plane
mixed dentition
primary and permanent teeth mixed in the mouth - starts at 6 yrs
Canine numbers
6, 11, 22, 27
first molar numbers
3, 14, 19, 30
when does the permanent first molar erupt?
6 years - mixed dentition - mandibular molar first
when does the exfolliation of the primary second molar occur?
12 years - maxillary molar last - all permanent dentition now
number of primary teeth
20 - incisors 8, canine 4, molars 8
what permanent tooth is first to errupt?
primary mandibular molar
Succedaneous teeth
teeth that follow after deciduous teeth in the same pockets (so not permanent molars)
longest teeth
canines
teeth with longest root
canines
last primary teeth to typically be lost
canines
labial side of tooth
front of anterior teeth
facial side of tooth
front of anterior teeth
incisal side of tooth
the top of the anterior teeth - sharpe cutting edge
interproximal
space between two teeth
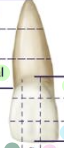
name the divisions top to bottom
root tip - apical
middle of root - middle
root connecting to tooth - cervical
tooth connecting to the root - cervical
middle of tooth - middle
tip of tooth - incisal
height of contour
the most elevated part on the buccal/lingual surface (like a bulge)
fossa
the close area of the incline leading to a pit or groove
sulcus
the broad depression/valley on posterior teeth
embrasures
v shaped spaces that are formed by the curvature of the teeth (gum line between teeth/ triangles at bottom of teeth) - gingival, occlusal, buccal, lingual
ADA naming system
US system 1-32
Palmer-Zigmondy naming system
1-8 with upper and lower indications
FDI Naming System
Canadian naming system
(Adult - 11,21,31,41)
(Child - 51, 61, 71, 81)
when do maxillary 1st molars errupt
6 yrs
when do maxillary 2nd molars erupt
12-13 yrs
when do maxillary 3rd erupt
18 - 25 yrs
when do mandibular 1st molars erupt
6-7 yrs
when do mandibular 2nd molars errupt
11-13 yrs
when do mandibular 3rd molars errupt
17-21 yrs
when do maxillary 1st premolars errupt
10-11 year
when do maxillary 2nd premolars errupt
12-13 yrs
mandibular 1st premolar eruption
10-12 years
mandibular 2nd premolars
11-12 yrs
occlusion
the relationship between the masticating surfaces
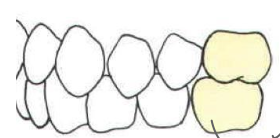
type of occlusion
normal occlusion
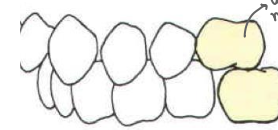
Type of occlusion
class 2 malocclusion - upper molar is shifted forward of the mandibular molar
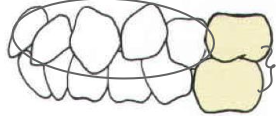
type of occlusion
class 1 malocclusion- crowding of front teeth
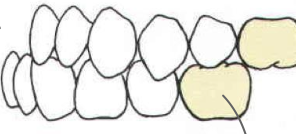
type of occlusion
class 3 malocclusion - maxillary molar is shifted way back, not even with the mandibular molar
Angles classification of malocclusion
normal - maxillary molar pretty even/slightly behind mandibular molar
class 1 - maxillary molar pretty even/slightly behind mandibular molar but incisal teeth are crowded
class 2 - maxillary molar is shifted in front of mandibular molar
class 3 - maxillary molar is shifted behind the mandibular molar so they barely contact
gnathology
the concept of the importance of the bumps/grooves in the teeth
centric relation
Centric Relation is the jaw position where the lower jaw joints sit securely and stably in their sockets, regardless of how the teeth touch.
Centric Occlusion
The very first spot your teeth touch when your jaw joints are in their stable position.
Maximal Intercuspation position
The position where your teeth fit together as tightly and completely as possible, like a puzzle locking in.
TMJ joint works how?
unusual synovial joint
first 10% is rotation of condyle
transverse movement along glenoid fossa
what type of tissue covers the TMJ
fibrocartilage (NOT hyaline cartilage)
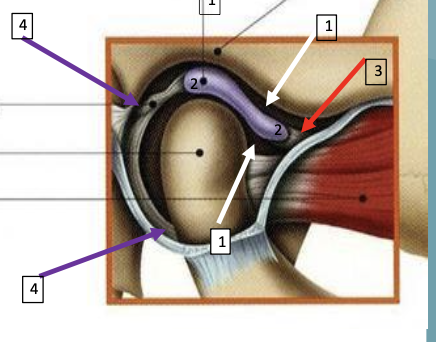
what does each line correspond to
articular disc
articular disc in articular fossa
grey = ligament
middle dot = condyle
red = muscle
Anterior Coupling
describes how the teeth fit into eachother in bioesthetics
Pankey & Dawson Schools
build occlusion from centric relation, differ in managing front teeth, and allow Long Centric—a smooth slide from CO to MIP
Long Centric
flattening the lower incisors and broadening the upper cingulum—we can allow the jaw to slide smoothly from CO to MIP (about 1.5–2 mm) without changing the bite height.
Conformational
Occlusion
works with the patient’s current bite, letting them function as is; it’s common in practice, unless the bite has problems
How to find most relaxed state of jaw and what does it tell us
use electronic stimulation of muscles to locate the jaw muscles’ most relaxed state, and in this position, the resting muscle length sets the condyle’s position
Joint-based occlusion
sets the bite based on the position of the condyle and disk in the joint during maximum tooth contact
articulating eminence
the bony ridge in the jaw that guides the opening and closing of the jaw, specifically the articulating disc
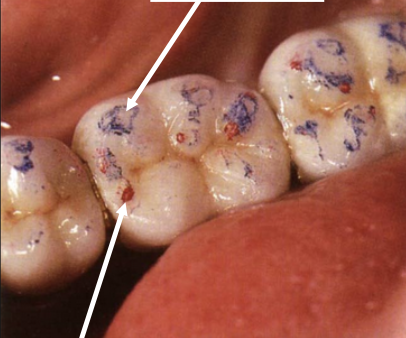
Arrows point at?
top arrow - functional contacts
bottom arrow - static contacts
mutually protected occlusion
Back teeth protect the front teeth when biting, and front teeth guide the jaw to protect the back teeth during movement.
canine guidance
he canines lead the jaw’s side movements, preventing the back teeth from touching. - just canines touch
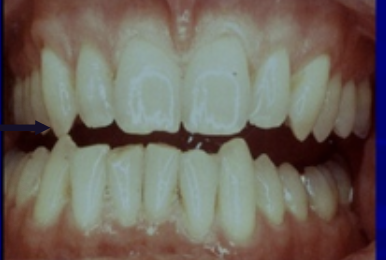
What is happening
canine guidance
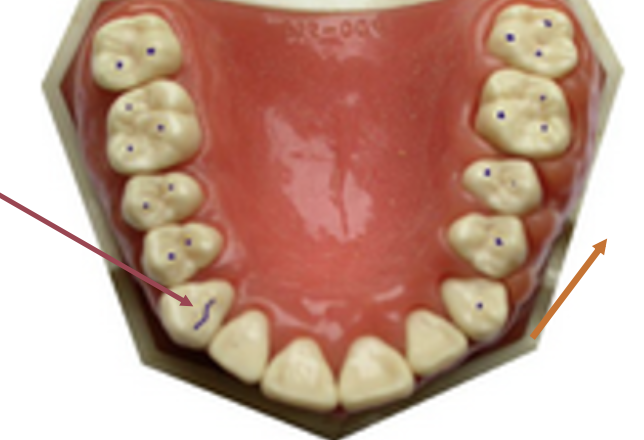
What is the lef arrow pointing at
Canine Guidance Occlusion
anterior guidance
The front teeth lead jaw movements, protecting the back teeth from contact.
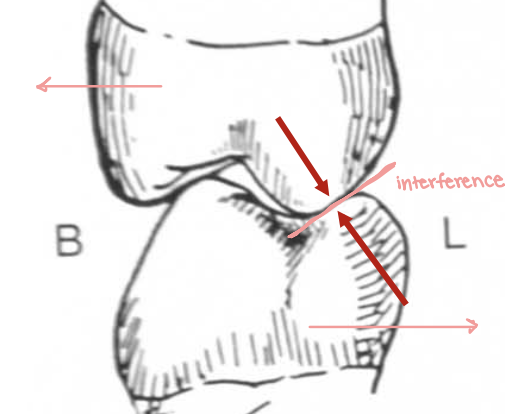
what is happening?
anterior guidance
group function
Teeth on the moving side work together to handle the load, and teeth on the opposite side don’t touch.
one side touches the other doesn’t
posterior
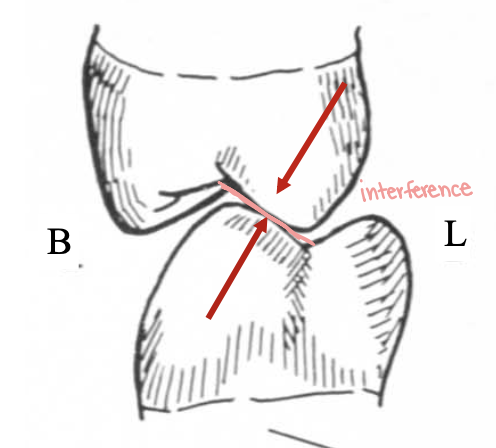
What is the red arrow pointing at
working side during group function
Bilateral Balanced Occlusion
For dentures so working and non working side contact at the same time to not tip the dentures.
disclusion
when some teeth touch, preventing other teeth from touching
eccentric movements
jaw motions away from full bite, like moving forward, backward, or side-to-side.
Laterotrusive contacts
working contacts that touch on the Lingual inclines of maxillary lingual cusps interacts with buccal Inclines of mandibular lingual cusps.
mediotrusive contacts
non-working contacts where The buccal inclines of the maxillary lingual cusps interacts with the lingual inclines of the mandibular buccal cusps.
Type of contact
laterotrusive (working)
Type of contact
mediotrusive (non-working)
Posselt’s Envelope of Motion
The limits (range) of mandibular
movement in three planes of space
along the three axes of “rotation”.
first 10-20mm of jaw opening
rotation
50-60mm of jaw opening
translation
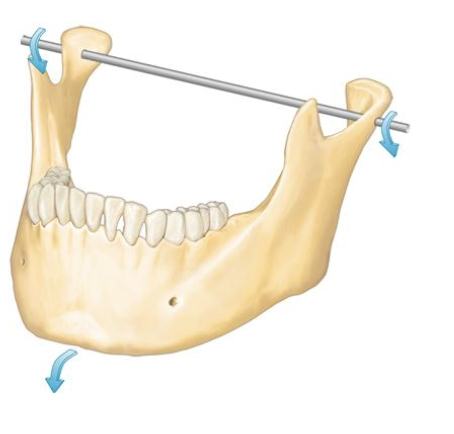
Axis of rotation
horizontal
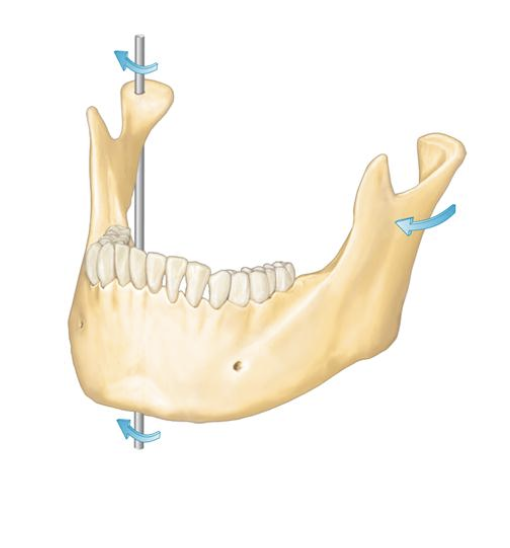
Axis of rotation
frontal
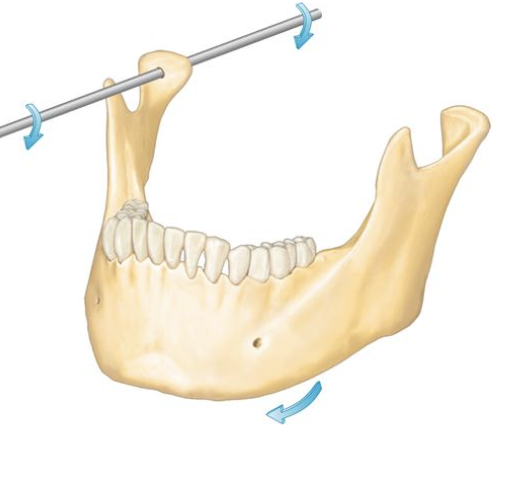
Axis of rotation
sagittal
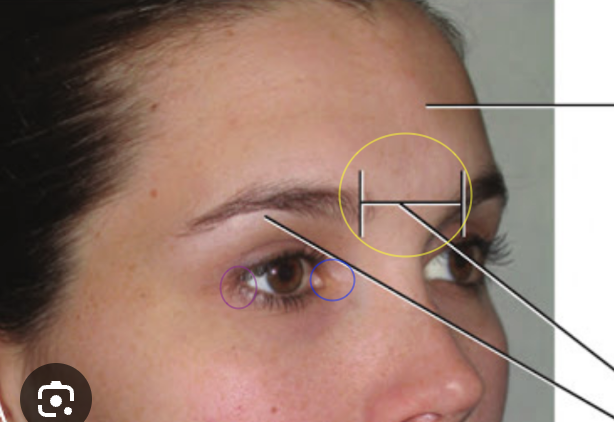
What are the circles
Yellow - glabella
blue - medial canthus
purple - lateral canthus
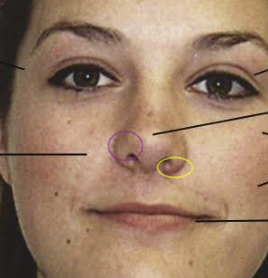
What are the circles
yellow - naris (opening of nasal cavity)
purple - ala (wing of nose)
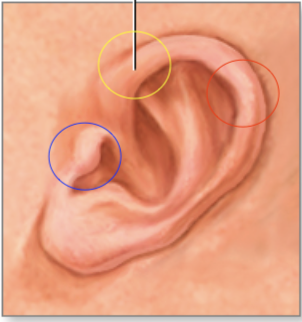
what are the circles
yellow - pinna (auricle)
blue - tragus
red - helix
landmarks for facebow
glabella, tragus
nasolabial folds
laugh lines
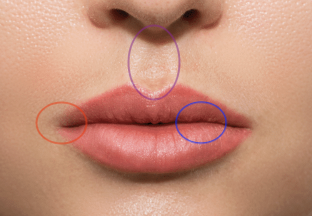
what are the circles
Red - comisures
Blue - vermillion border
Purple - philtrum
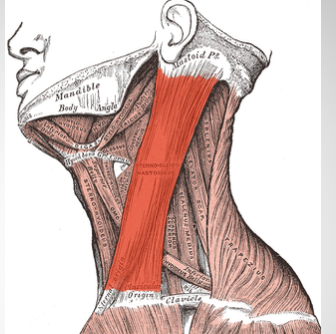
red muscle
sternocleomastoid muscle
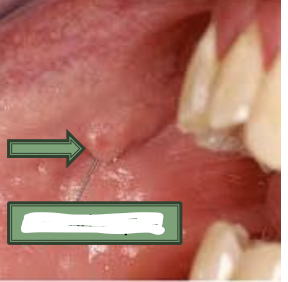
What is the arrow pointing to?
parotid papilla - covers stenson’s duct
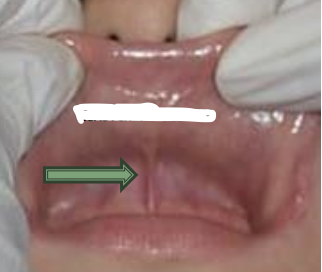
What is the arrow pointing to? what is the area next to it
labial frenum
vestibule is the space between teeth/lips/cheeks
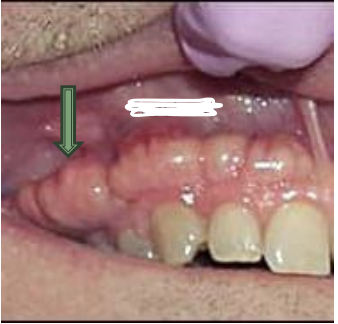
What is the arrow pointing to?
exostosis
the bony ridge or raised thickened border of the upper or lower jaw that contains the sockets of the teeth
Alveolar Process
Stensons duct location
parotid duct - by maxillary secondary molar
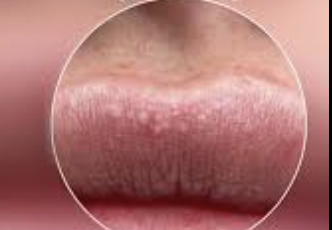
What is on the lip
fordyce granules - etopic sebaceous glands
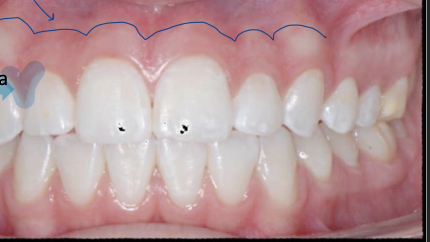
Blue line and blue hilighetd regions
blue line - Mucogingival line
blue hilighter - interdental papilla
black triangle
place of missing interdental papilla
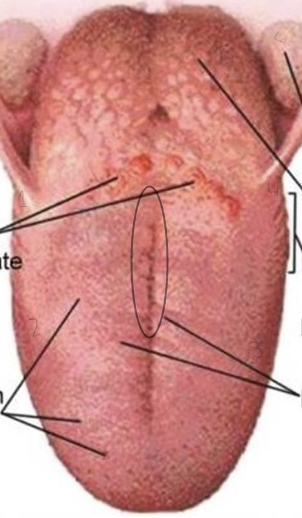
What is at each number and in the circle
circumvate papillae
fungiform papillae
filiform papillae
foliate papillae
lingual tonsil
palatal tonsil
circle = medial sulcus
Lateral border of tongue contains
foliate papillae
dorsal surface of tongue
top of tongue