HL Biology 8.1 Metabolism
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/6
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
1
New cards
Metabolic Pathways
Metabolism describes the sum total of all chemical reactions that occur within an organism in order to maintain life
* metabolic processes are controlled and coordinated by a series of enzyme-catalysed reactions
* metabolic pathways are typically organized into chains (glycolysis) or cycles (Krebs cycle, Calvin cycle)
* metabolic processes are controlled and coordinated by a series of enzyme-catalysed reactions
* metabolic pathways are typically organized into chains (glycolysis) or cycles (Krebs cycle, Calvin cycle)
2
New cards
Enzyme Action
Every chemical reaction requires a certain level of energy in order to proceed - this is called activation energy (EA)
\
Enzymes speed up reaction rates by lowering the activation energy threshold (destabilise substrate bonds = increases product conversion)
* If reactants contain more energy than the products, the reaction is **exergonic** as energy is released (catabolic reactions)
* If reactants contain less energy than the products, the reaction is **endergonic** as energy is absorbed (anabolic reactions)
\
Enzymes speed up reaction rates by lowering the activation energy threshold (destabilise substrate bonds = increases product conversion)
* If reactants contain more energy than the products, the reaction is **exergonic** as energy is released (catabolic reactions)
* If reactants contain less energy than the products, the reaction is **endergonic** as energy is absorbed (anabolic reactions)
3
New cards
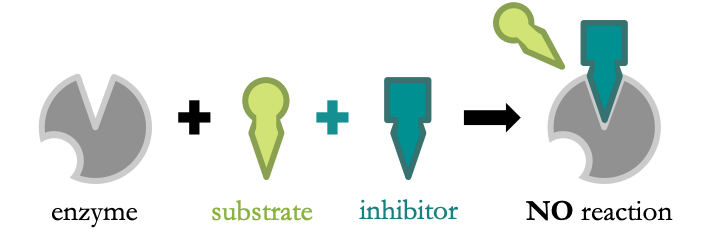
Competitive Inhibition
* inhibitor is structurally similar to the substrate
* it directly blocks the active site of the enzyme
* increasing substrate concentration will reduce inhibition
* it directly blocks the active site of the enzyme
* increasing substrate concentration will reduce inhibition
4
New cards
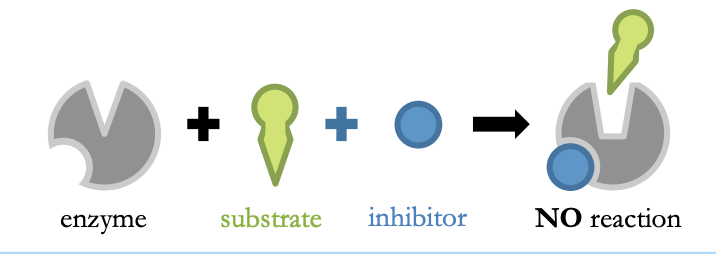
Non-competitive Inhibition
* inhibitor is not structurally similar to the substrate
* it binds to an allosteric site (not the active site)
* it induces a conformational change in the active site
* it binds to an allosteric site (not the active site)
* it induces a conformational change in the active site
5
New cards
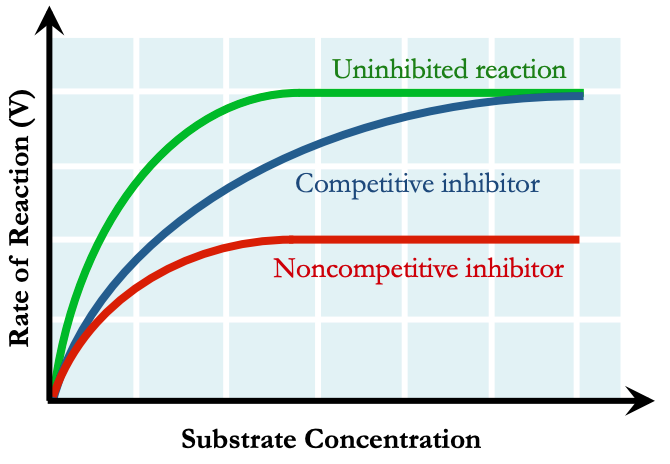
Enzyme Kinetics
Enzyme inhibitors lower reaction rates by reducing levels of uninhibited enzymes
6
New cards
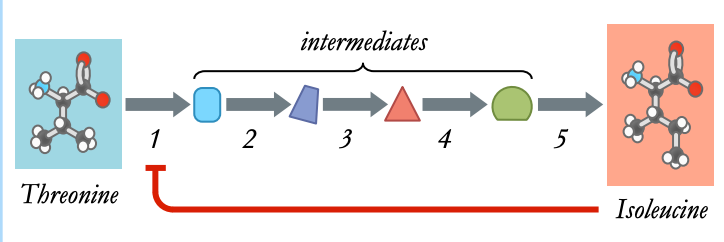
Feedback Inhibition
Metabolic pathways can be controlled by feedback inhibition (end product inhibition), where a product inhibits an earlier step
* this ensures product levels are always tightly regulated
\
Example: Isoleucine Synthesis
* threonine deaminase convert threonine into isoleucine
* isoleucine inhibits the enzyme’s activity (non-competitive)
* thus, isoleucine synthesis inhibits further formation
* this ensures product levels are always tightly regulated
\
Example: Isoleucine Synthesis
* threonine deaminase convert threonine into isoleucine
* isoleucine inhibits the enzyme’s activity (non-competitive)
* thus, isoleucine synthesis inhibits further formation
7
New cards
Rational Drug Design
Inhibitors can be used to treat infectious diseases by targeting the enzymes involved in pathogenesis (anti-malaria drugs)
* inhibitors can be identified by database mining (bioinformatics) or constructed via combinatorial chemistry techniques
* inhibitors can be identified by database mining (bioinformatics) or constructed via combinatorial chemistry techniques