#9: AAs as Biosynthetic Precursors & AA Metabolic Diseases
1/134
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
When the degradation of Tyrosine is inhibited, Homogentisate accumulates and is excreted as urine where, upon oxidation, turns black
Alkaptonuria (“Black Urine Disease”)
Patients with Alkaptonuria are prone to developing _______
arthritis
Name the term coined by Sir Achibald Garrod (1902) who recognized the link between metabolic disease and genetics
Inborn Errors of Metabolism
Which disease did Sir Achibald Garrod (1902) first describe?
Alkaptonuria (“Black Urine Disease”)
Alkaptonuria (“Black Urine Disease”) is due to a __________ in the ________ responsible for breaking down _______________ (________________ _________________).
deficiency, enzyme, Homogentisate, Homogentisate 1,2-Dioxygenase
Tyrosine Synthesis:
Reactants: _____________, _____
Enzyme: _______________ _____________
Products: __________, _____, ______
phenylalanine, NADH, Phenylalanine Hydroxylase, tyrosine, H2O, NAD+
Tyrosine Breakdown:
Reactant: ___________
Intermediate: ______________
Products: __________, __________
tyrosine, homogentisate, fumarate, acetoacetate
Name the 2 processes that make up “Phenylalanine breakdown”
Tyrosine synthesis, Tyrosine breakdown
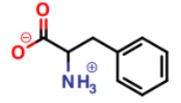
What is this a picture of?
phenylalanine
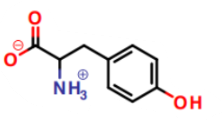
What is this a picture of?
tyrosine
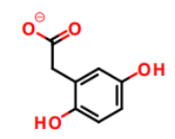
What is this a picture of?
homogentisate
Genetic defect in Phenylalanine Hydroxylase (liver) causing phenylalanine to accumulate, which activates an alternative pathway; produces buildup of phenylalanine, phenylpyruvate, and phenyllactate in the blood, tissues, and urine.
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
A genetic defect in which enzyme causes Phenylketonuria (PKU)?
Phenylalanine Hydroxylase
Phenylketonuria (PKU) Alternative Pathway
Reactants: ________________, __________
Enzyme: _______________ _____________
Cofactor: ______
First Products: _________, ________________
Second Product: _________________
phenylalanine, pyruvate, Phenylalanine Transaminase, PLP, alanine, phenylpyruvate, phenyllactate
Which disease is very easy to detect by testing the urine?
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Which disease leads to severely impaired brain development, which is why newborns are frequently screened for it?
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
What is the treatment for newborns with Phenylketonuria (PKU)?
low-protein diet
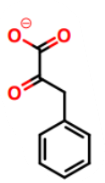
What is this a picture of?
phenylpyruvate
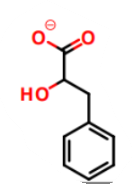
What is this a picture of?
phenyllactate
Where does Tyrosine Synthesis & Phenylalanine/Tyrosine Breakdown occur?
liver, kidneys
What is the amino acid precursor for the bioactive amine Dopamine?
tyrosine
What is the amino acid precursor for the bioactive amine Norepinephrine?
tyrosine
What is the amino acid precursor for the bioactive amine Epinephrine?
tyrosine
Tyrosine — Bioactive Amine Synthesis
Reactant: ___________
Enzyme: ____________ _______________
Intermediates: __________, ______
Enzyme: ___________ ____ _____________
Cofactor: _______
First Product: _______________
Enzyme: ______________ _____-_____________
Second Product: ___________________
Enzyme: ______________________ ___________ _________________
Cofactor: ________
Final Product: _____________________
tyrosine, Tyrosine Hydroxylase, L-Dopa, CO2, Aromatic AA Decarboxylase, PLP, dopamine, Dopamine beta-Hydroxylase, norepinephrine, Phenylethanolamine N-methyl Transferase, SAM, epinephrine
________________ = increase heart rate, blood pressure, stimulate an increase in blood glucose, neuromodulators
Catecholamines
What are 3 examples of Catecholamines?
dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine
Which bioactive amine is responsible for triggering our “fight or flight” response?
Which amino acid is its precursor?
epinephrine, tyrosine
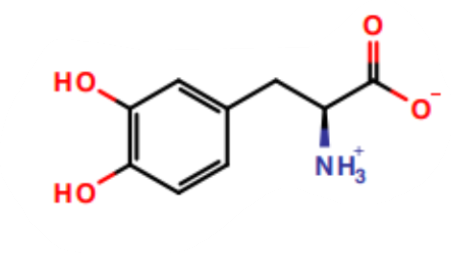
What is this a picture of?
L-Dopa
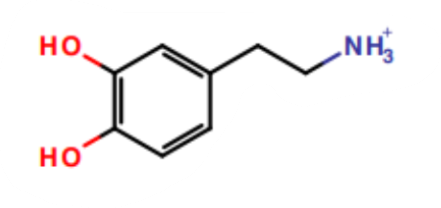
What is this a picture of?
dopamine
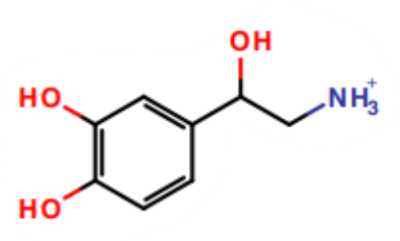
What is this a picture of?
norepinephrine
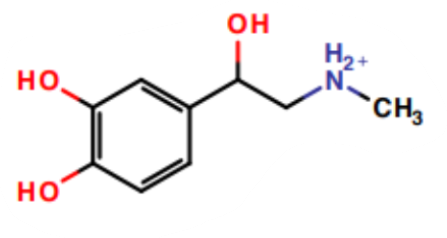
What is this a picture of?
epinephrine
In the central nervous system (CNS): dopamine is a _______________
neurotransmitter
Outside the CNS: dopamine functions as a ________ __________
chemical messenger
Name the bioactive amine that inside the CNS is associated with motor control, reward-motivated behavior, and hormone release
dopamine
Name the bioactive amine that outside the CNS is associated with blood pressure, kidney function, intestinal motility, and insulin release
dopamine
When the neurons responsible for producing neurotransmitters like dopamine in the substantia nigra are dying, leading to a dopamine deficiency in the brain (CNS)
Parkinson’s disease
Parkinson’s Disease is associated with a deficiency of _____________
dopamine
In order to treat Parkinson’s Disease, we need to increase ____________ levels in the _______. To do this we give 2 things: _________ and _____________.
dopamine, brain, L-Dopa, carbidopa
drug that inhibits the Aromatic Amino Acid Decarboxylase that produces dopamine
carbidopa
Which enzyme involved in dopamine synthesis does carbidopa inhibit?
Aromatic AA Decarboxylase
Can dopamine cross the blood/brain barrier?
no
Can L-Dopa cross the blood/brain barrier?
yes
Can carbidopa cross the blood/brain barrier?
no
True or False: dopamine is easily degraded in circulation
true
Why inhibit the Aromatic AA Decarboxylase with Carbidopa? → L-Dopa is rapidly decarboxylated by Aromatic AA Decarboxylase in the ________ and other sites to form _________. High levels of circulating __________ have bad side effects (______). CarbiDOPA cannot _____ the _____/_____ ________ so it only inhibits ________ production _________ the CNS leading to fewer side effects and more L-Dopa reaching the _____ since it isn’t being used to make _________ outside the brain.
intestine, dopamine, dopamine, nausea, cross, blood/brain barrier, dopamine, outside, brain, dopamine
Why L-Dopa instead of Dopamine for Parkinson’s Disease? → L-Dopa can _____ the _____/____ _______ in order to reach the _____ while dopamine cannot and is __________ in the circulation
cross, blood/brain barrier, brain, degraded
What is it about carbidopa’s structure that prevents the synthesis of dopamine?
Hydrazine group forms Schiff’s Base with PLP and gets stuck because the extra nitrogen prevents the resonance-stabilized carbanion from forming
___________ ___________ = a drug that inhibits a biological process by becoming covalently bonded to an enzyme
Example: __________
suicide inhibitor, carbidopa
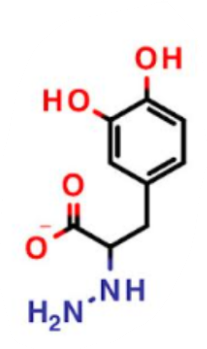
What is this a picture of?
carbidopa
What is the amino acid precursor for the bioactive amine Gamma-Aminobutyrate (GABA)?
glutamate
_________ = most common neurotransmitter; excites neurons
glutamate
_______ = inhibitory neurotransmitter
GABA
Glutamate — Bioactive Amine Synthesis
Reactant: ___________
Enzyme: ____________ _____________
Products: ________, ______
glutamate, Glutamate Decarboxylase, GABA, Co2
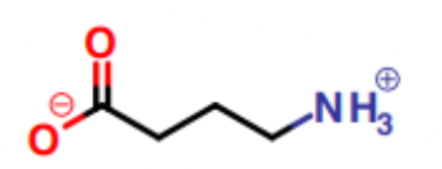
What is this a picture of?
GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyrate)
What is the amino acid precursor for the bioactive amine Histamine?
histidine
_________ = vasodilator; allergic response
histamine
_________ (______________) = inhibits histamine response by binding to histamine receptor
Benadryl, Diphenhydramine
Histidine — Bioactive Amine Synthesis
Reactant: ___________
Enzyme: ____________ _____________
Products: ____________, ______
histidine, Histidine Decarboxylase, histamine, CO2
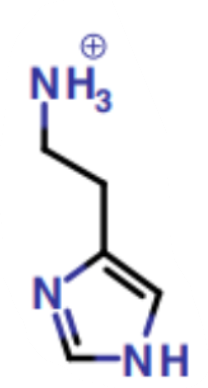
What is this a picture of?
histamine
What is the amino acid precursor for the bioactive amine Serotonin?
tryptophan
Where is Serotonin found? (3)
intestine, platelets, CNS
When released into the intestine, _________ helps regulate gut movements
serotonin
When released by platelets at the site of blood clots, __________ acts as a vasoconstrictor and helps stop bleeding
serotonin
When released in the CNS by serotonergic neurons, _________ can affect mood, appetite, and sleep
serotonin
Modulation of ________ action at nerve synapses thought to be target of antidepressants called SSRIs
serotonin
Tryptophan — Bioactive Amine Synthesis
Reactant: ____________
Enzyme: ____________ _____________
Intermediate: ___-_________ ____________
Enzyme: ___________ ____ _______________
Cofactor: ______
Products: ____________, ______
tryptophan, Tryptophan Hydroxylase, 5-hydroxy tryptophan, Aromatic AA Decarboxylase, PLP, serotonin, CO2
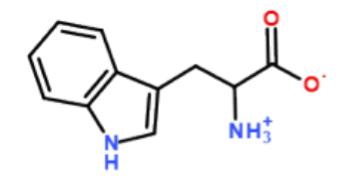
What is this a picture of?
tryptophan
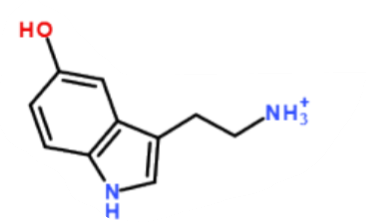
What is this a picture of?
serotonin
Glycine — Bioactive Amine Synthesis
Reactants: ________, _____________
Enzyme: ______-___________________ _____________
Cofactor: ______
Minor products: _____, ______
Intermediate: 2x _____-__________________
+ 2x H2O
Intermediate: 4x _________________
Minor products: 4x ______, ______
Intermediate: _____________________
Minor products: 6x _____
+ Fe2+
Final Product: _______
glycine, succinyl-CoA, delta-Aminolevulinate Synthase, PLP, CoA, CO2, delta-Aminolevulinate, Porphobilinogen, NH4-, H2O, Uroporphyrinogen III, CO2, Heme
Where is heme synthesized?
liver, RBCs (erythroid cells)
______ = key component of hemoglobin, myoglobin, and cytochromes
heme
Which bioactive amine is important for transporting oxygen and carbon monoxide?
What amino acid is its precursor?
heme, glycine
What is the amino acid precursor for the bioactive amine heme?
glycine
What is found in feces that gives it its red-brown color?
stercobilin
Degradation of _________ = Bruising process and development
heme
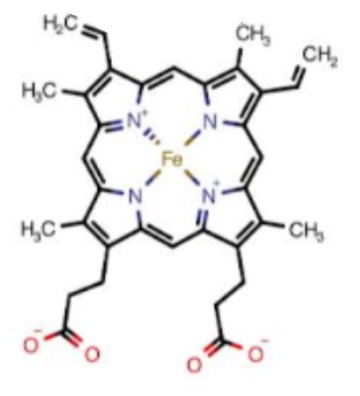
What is this a picture of?
heme
Degradation of Heme: A Colorful Process
Reactant: ______ (color = _______)
Minor products: _____, ____
Intermediate: ___________ (color = _______)
Intermediate: ___________ (color = _______)
Transported to _____ via _______ _______
Excreted in ______
Digested via __________ microbes
Intermediate: ______________
If reabsorbed: _________ (excreted in ______) (color = ________)
If NOT reabsorbed: ____________ (color = ________)
heme, purple, Fe2+, CO, Biliverdin, green, Bilirubin, yellow-orange, liver, serum albumin, bile, intestinal, Urobilinogen, Urobilin, yellow, urine, Stercobilin, red-brown
What are the amino acid precursors for the bioactive amine phosphocreatine? (2)
glycine, arginine
Arginine — Bioactive Amine Synthesis (PCr)
Reactants: _______, __________
Minor product: ___________
Intermediate: _________ _________
Cofactor: _____
Intermediate: __________
Travel from _______ to ______ in the circulation
Enzyme: ________ ________
+ ATP
Products: ________________, ____
glycine, arginine, ornithine, guanidine acetate, SAM, creatine, kidneys, muscle, Creatine Kinase, phosphocreatine, ADP
Where does creatine synthesis occur?
kidneys
Where does phosphocreatine synthesis occur?
muscle
Acts as energy buffer in muscle
phosphocreatine
Serum Creatine-Kinase levels = marker for ______ _______
heart attacks
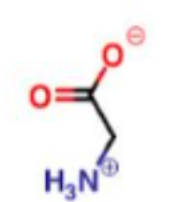
What is this a picture of?
glycine
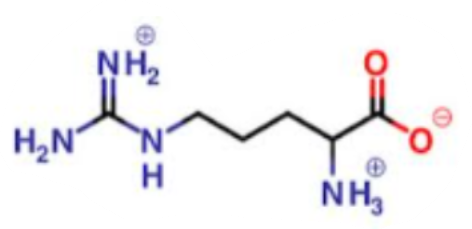
What is this a picture of?
arginine
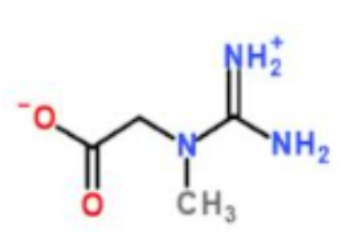
What is this a picture of?
creatine
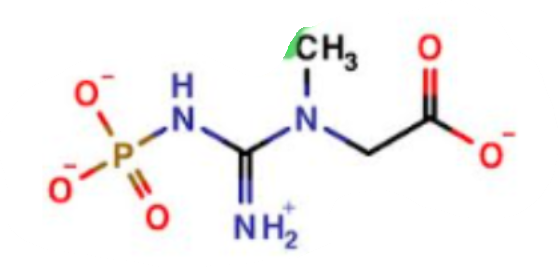
What is this a picture of?
phosphocreatine
What is the amino acid precursor for the bioactive amine nitric oxide?
arginine
Arginine — Bioactive Amine Synthesis (NO)
Reactants: __________, _______
Enzyme: ______ ______ _________ (____)
Products: ______ ______, ___________
arginine, NADPH, Nitric Oxide Synthase, NOS, nitric oxide, citrulline
Which bioactive amine is a free radical gas?
nitric oxide
Which bioactive amine is used for short-distance signaling because it is a hormone that acts locally as it readily diffuses across membranes and breaks down rapidly?
nitric oxide
What are the 3 main functions of nitric oxide?
neurotransmission, blood clotting, vasodilation
Which bioactive amine’s signaling pathway is an important target for pharmaceutical companies?
nitric oxide
Nitric Oxide Signaling Pathway
In ___________ cells (_____ ______ wall), ___________ binds to Muscarinic GPCR; stimulates ____ production via GALPHA and phospholipase C activity
IP3 stimulates _____ release from ___ by activating ER membrane channel
Ca2+ binds to _________ which activates ______ ______ __________ (_____)
______ ______ travels to _______ _______ cell; binds to Guanylate Cyclase; catalyzes production of cGMP from GTP
cGMP activates _________ ________ ___ (______); induces _____________
endothelial, blood vessel, acetylcholine, IP3, Ca2+, ER, Calmodulin, Nitric Oxide Synthase, NOS, nitric oxide, smooth muscle, Protein Kinase G, PKG, vasodilation
___________ helps in immune response by relaxing blood vessels, allowing white blood cells to get to inflammatory site
vasodilation
Nitric Oxide Signaling Pathway Inhibition
cGMP ________________ converts cGMP to GMP to turn off signaling pathway, thus _________ blood flow
Drugs like ________ (aka ______) block this enzyme to _______ blood flow
Phosphodiesterase, reducing, Sildenafil, Viagra, increase
drugs that provide nitric oxide to relieve Angina Pain (chest pain) by relieving pressure (2)
nitroglycerin, amylnitrate
Heart
Primary fuels = _____ _____, _______ _______, uses some _______
Constant __________ (~100,000 beats/day)
Highly ________; lots of ______________ → need to generate lots of ATP bc it’s constantly moving
Lack of ___ will cause damage
fatty acids, ketone bodies, glucose, exertion, aerobic, mitochondria, O2
Skeletal Muscle
Fuel = _______, _____ _____, or ______ _______
Fuel used depends on level of ______ and _______
_______ and ________ respiration
Doesn’t have FAS or Glucose-6-phosphatase (cannot _____ fatty acids or ______ glucose)
Under normal conditions, muscles use all fuel it _______ to make ____
Can’t ______ fuels (except during _________ by breaking down proteins)
_________ __________ → 1-2% of mass, but much more skeletal muscle so overall this is the major site of _________ storage
Energy Hierarchy = ____ pool, _________________, ___________ (depleted within 1hr of activity), _____ ______
glucose, fatty acids, ketone bodies, activity, exertion, aerobic, anaerobic, make, export, imports, ATP, export, starvation, glycogen reserves, glycogen, ATP, phosphocreatine, glycogen, fatty acids
During rest/light activity, what are the main fuels used in skeletal muscle to make ATP? (3)
glucose, fatty acids, ketone bodies