Chap 7 - Laws of Motion & Momentum
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is Newton’s 1st law?
An object will remain at rest or continue to travel at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a resultant force.
If the speed or direction of an object in motion changes, you know a … acting on it.
Resultant force must be acting on it.
The sum of forces actin on object/body undergoing Newton’s 1st law is…
The forces are balanced, so the sum of forces must be zero (when object stationary or at constant velocity)
What is Newton’s 3rd law?
When 2 objects interact, they exert equal and opposite forces on each other.
Newtonian pairs only occur when …
The forces are the same magnitude/size
The forces are opposite in direction (acting along a straight line)
The forces are the same type
The forces are acting on different objects.
What are the four fundamental forces?
Gravitational, electromagnetic, strong nuclear & weak nuclear,
Define linear momentum
The product of an object’s mass and it’s velocity.
Momentum is a _____ quantity so we must ___
Momentum is a vector quantity so we must assign positive and negative directions.
What is the defining equation for momentum
p = mv
momentum = mass x velocity
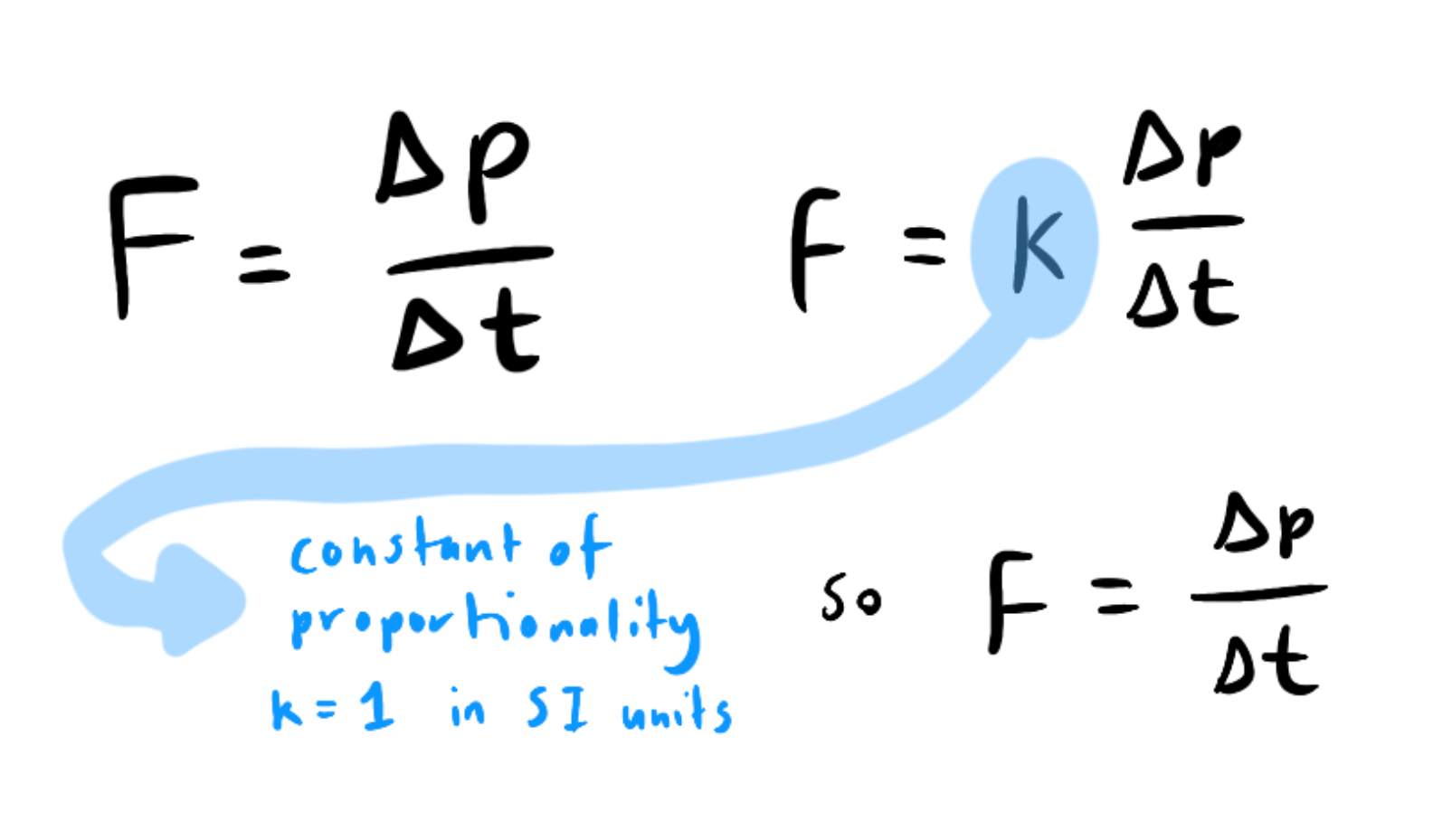
When does f = ma occur?
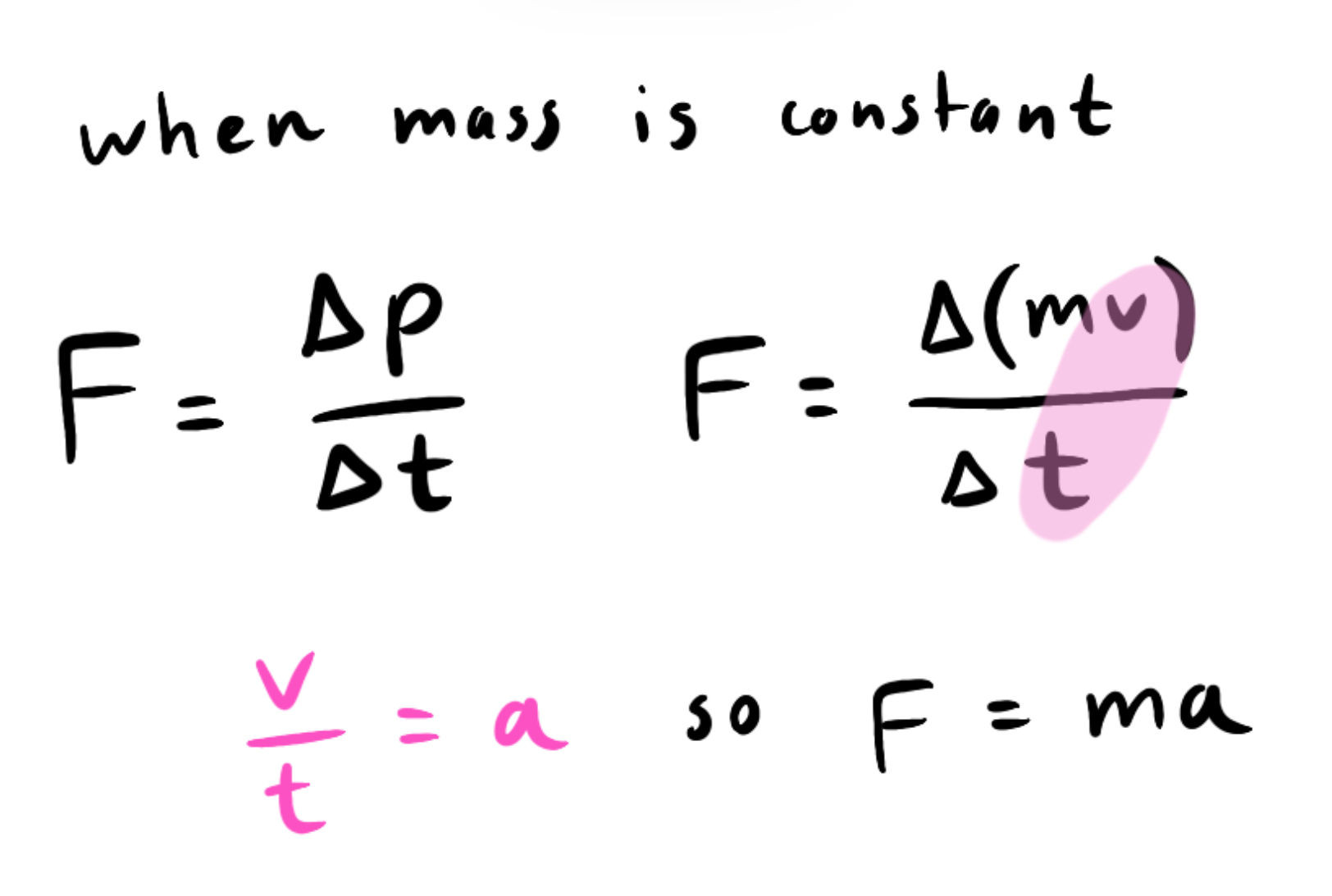
Form an equation from newton’s second law.
What is the principle of the conservation of momentum?
For a system of interacting objects, total momentum in a specified direction remains constant - as long as no external forces act on the system (closed system).
In an inelastic collision …. is conserved
In an inelastic collision, total energy and momentum are conserved
In a perfectly elastic collision …. is conserved
In a perfectly elastic collision, total kinetic energy and momentum are conserved
In perfectly elastic collisions objects typically …
In inelastic collisions objects typically….
In perfectly elastic collisions objects typically bounce off each other (eg. molecular motion)
In inelastic collisions objects typically stick together and move at common velocity.
Define impulse
The product of the average net force acting on an object and the time it acts on it for.
Defining equation of impulse
Δv = FΔt
Impulse = force x change in time
What does the area under a force - time graph equal?
Impulse (change in momentum)
SI base units for impulse & momentum
kgms-1 (Ns-1)
Base units for Force
kgms-2 (newtons)