SCSC 105 Test #2
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Define ecosystem. What are the five components of an ecosystem?
Collective function of organisms and their environment.
Food Chains
Diversity
Competitive Exclusion
Plant Succession
Nutrient cycles
Name important functions that ecosystems provide.
Carbon Sequestration
Climate Regulation
Erosion Control
Wildlife
Define agroecosystem
Ecosystems modified to produce food, fiber, and/or shelter
Compare nutrient cycling in agroecosystems
Nutrient cycles are altered, and inputs are required
What are two plant available forms of nitrogen?
Nitrate
NO_3^-
Ammonium
NH_4^+
Describe the differences and/or similarities of natural ecosystems compared to agroecosystems in terms to diversity, inputs, management, breeding, and nutrient loss.
Agroecosystems have low diversity, high input (Fertilizers, pesticides, labor), High management, high breeding, high nutrient loss.
Natural ecosystems have high diversity, no inputs, no management, no breeding, and no nutrient loss.
What are TWO risks associated with simplified agroecosystems? Give an example of a simplified agroecosystem from history.
Limited plant diversity
Problems become magnified
Ex = Wheat and Dust Bowl in the 30s
What are three important functions served by soils?
Anchor plants
Storage of water and nutrients for plant uptake
Habitat for soil organisms (bacteria, fungi, insects, and invertebrates)
Name the five soil forming factors
Climate
Organisms
Relief (topography)
Parent Material
Time
Name the 7 predominant soil orders in Texas
Mollisols
Vertisols
Ardiosols
Ultisol
Alfisols
Entisols
Inceptisols
What is soil organic matter (SOM)?
Portion of the soil that includes animal and plant residues in various stages of decomposition.
What are the five different functions of soil organic matter (SOM)?
Carbon sequestration
Nutrient Source
Soil aggregation and structure
Water storage
Chemical sequestration
As C:N ratio increases, what happens to decomposition rates of plant material?
The rate of decomposition decreases.
What are the three soil particle sizes?
Sand
Silt
Clay
Know how to use the soil textural triangle to classify soil by texture.
How to read:
Start on % sand and go up and left
% silt down and left
% clay strait across to the right
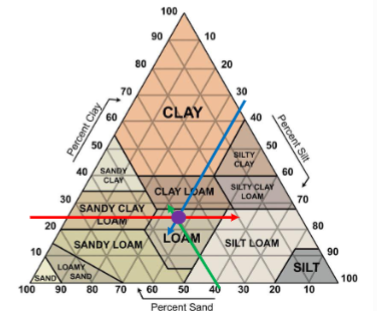
Define gravitational water, field capacity, and permanent wilting point.
Water drains readily through the soil
Water is held in the pore spaces and is readily available to plants
Water is held tightly by soil particles and is not available to plants
What is soil tilth and what does it determine?
Physical condition of the soil as related to plant growth.
ease of tillage
root penetration
aeration
water infiltration/drainage
Define shrink-swell potential in soil. Why is it important?
A measurement of the amount of volume change that can occur when a soil wets and dries. It must be considered in structural or engineering project plans.
Compare and contrast soil particle size (sand, silt, clay) for water holding capacity, drainage, CEC, ability to store plant nutrients, shrink-swell potential, and ease of cultivation.
Sand
Low total water holding capacity
High (fast) Drainage
Low Cation exchange capacity
Very low shrink swell-potential
High (Easy) ease of cultivation
Silt
Moderate total water holding capacity
Slow - moderate drainage
Low - moderate cation exchange capacity
low shrink swell capacity
Moderate ease of cultivation
Clay
high total water holding capacity
High cation exchange capacity
Mod. - very high shrink-swell potential
Low (Difficult) ease of cultivation
What is CEC? What does it measure?
Cation Exchange Capacity, the amount of exchangeable cations a soil can sustain
How does pH affect nutrient availability and soil organisms?
Plants vary in the required pH range for best growth and yields
pH of 6 - 7 is best
pH of 5.5 - 7 is optimal
Where do saline soils typically occur and what is the cause?
Dry regions and is a result from the accumulation of soluble salts (Na, Ca, Mg, K) that dissolve in water
List the 17 essential elements needed for plant growth and their symbol.
C = Carbon
H = Hydrogen
O = Oxygen
N = Nitrogen
P = Phosphorus
K = Potassium
Ca = Calcium
Mg = Magnesium
S = Sulfur
Fe = Iron
Mn = Manganese
Cu = Copper
Zn = Zinc
B = Boron
Mo = Molybdenum
Cl = Chlorine
Ni = Nickel
What is the best way to determine nutrient availability in a specific soil? Briefly describe how to collect a soil sample.
Soil testing
Know the phrase, “Don’t guess, ____ ____.”
Soil test
What are the differences between organic and inorganic fertilizers?
Organic = derived from living matter and contains carbon
Inorganic = Synthetic or mined elements, no carbon
List and describe the 3 types of organic fertilizers.
Animal manures
Compost
Green manures
What is fertilizer analysis or grade?
Where is it displayed? Why is it displayed? How is it displayed? (hint - ratio)
Amount of nutrients contained in a commercial fertilizer
Must be displayed on label
For consumer protection
Must include N-P-K (20-10-5)
List and briefly describe the six different fertilization methods.
Broadcast = Applied evenly across the entire area
Injection = Water soluble liquids (or gases) placed under soil surface near roots
Banding = applied at planting within 2” of the row
Popup fertilizers = placed IN the seedbed with the seed
Side-dressing = placed alongside the row (mid-season)
Fertigation = injecting the fertilizer in the irrigation water
List 6 best nutrient management practices
Test soil regularly
Test manure before application
Time fertilizer and manure application to crop needs
Use the most efficient method for fertilizer application
Combine nutrient management with the soil conservation
management
Incorporate green manures, cover crops, and perennials into rotations
What is soil erosion and what are four ways to reduce its effects?
Accelerated loss of soil through the action of wind or water
Crop rotations
Contour Stripping
Conservation tillage
Conservation Reserve Program (CRP)
What is a weed?
A plant growing where it is not wanted
What are the five methods of weed control?
Prevention
Cultural practices
Biological control
Mechanical or manual control
Chemical control
What are the five characteristics of weeds that allows them to thrive?
Large seed production
Long seed dormancy
Seed dispersal
Vegetative reproduction
They can grow anywhere
Define Critical Weed Free Period. When does it occur in the growing season?
Window of time in the growing season that weeds cause the largest reduction in yield, and must be controlled.
Occurs 4-6 weeks after crop emergence