Medical Imaging Exam 1
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
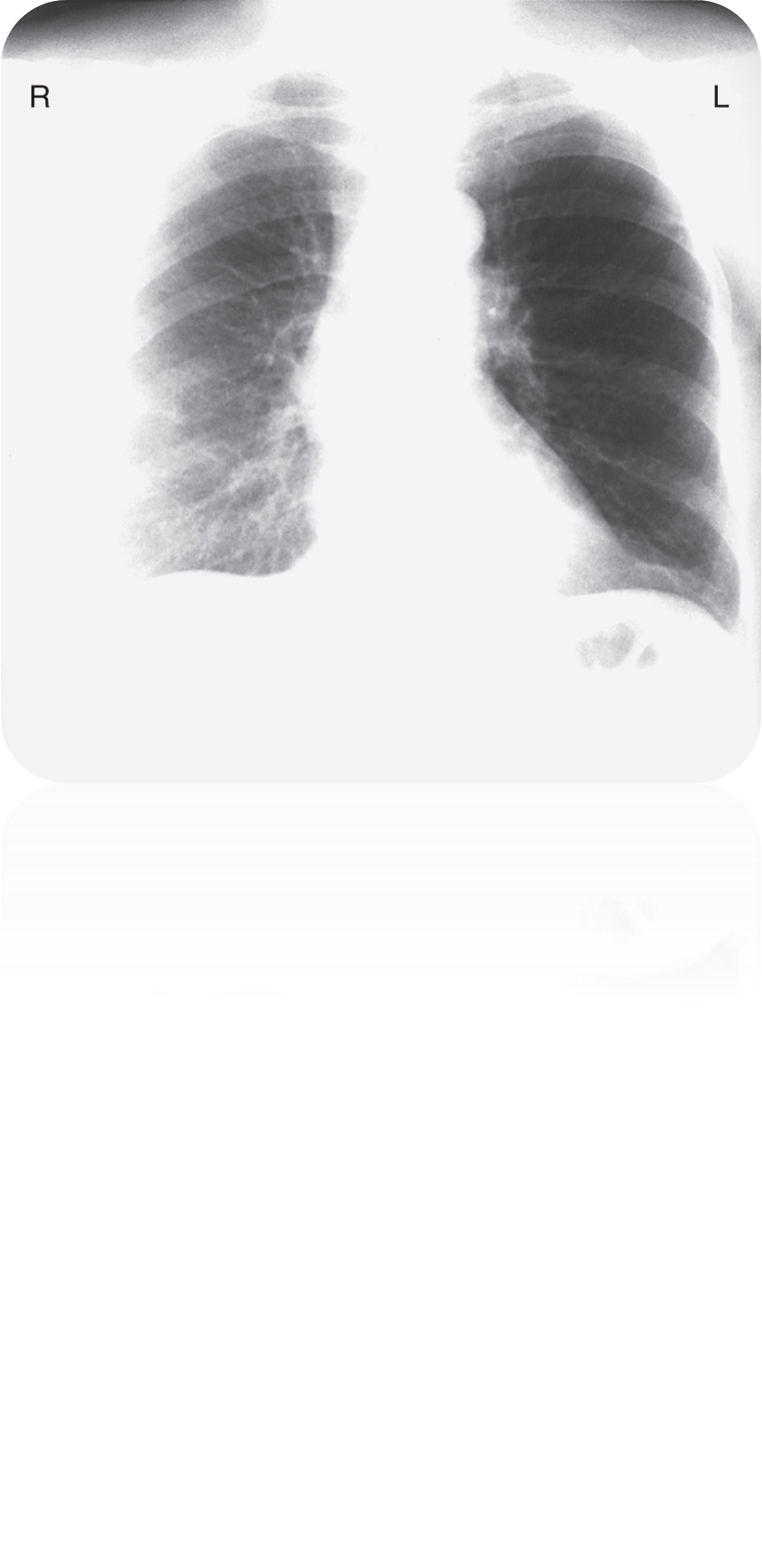
This patient has a history of left mastectomy; what should you be cautious about when interpreting this CXR?
R breast accentuates pulmonary vessels at base of R lung — with mastectomy history, these accentuations can be mistaken for RLL infiltrates & the darker left lung can be misinterpreted as hyperinflation.
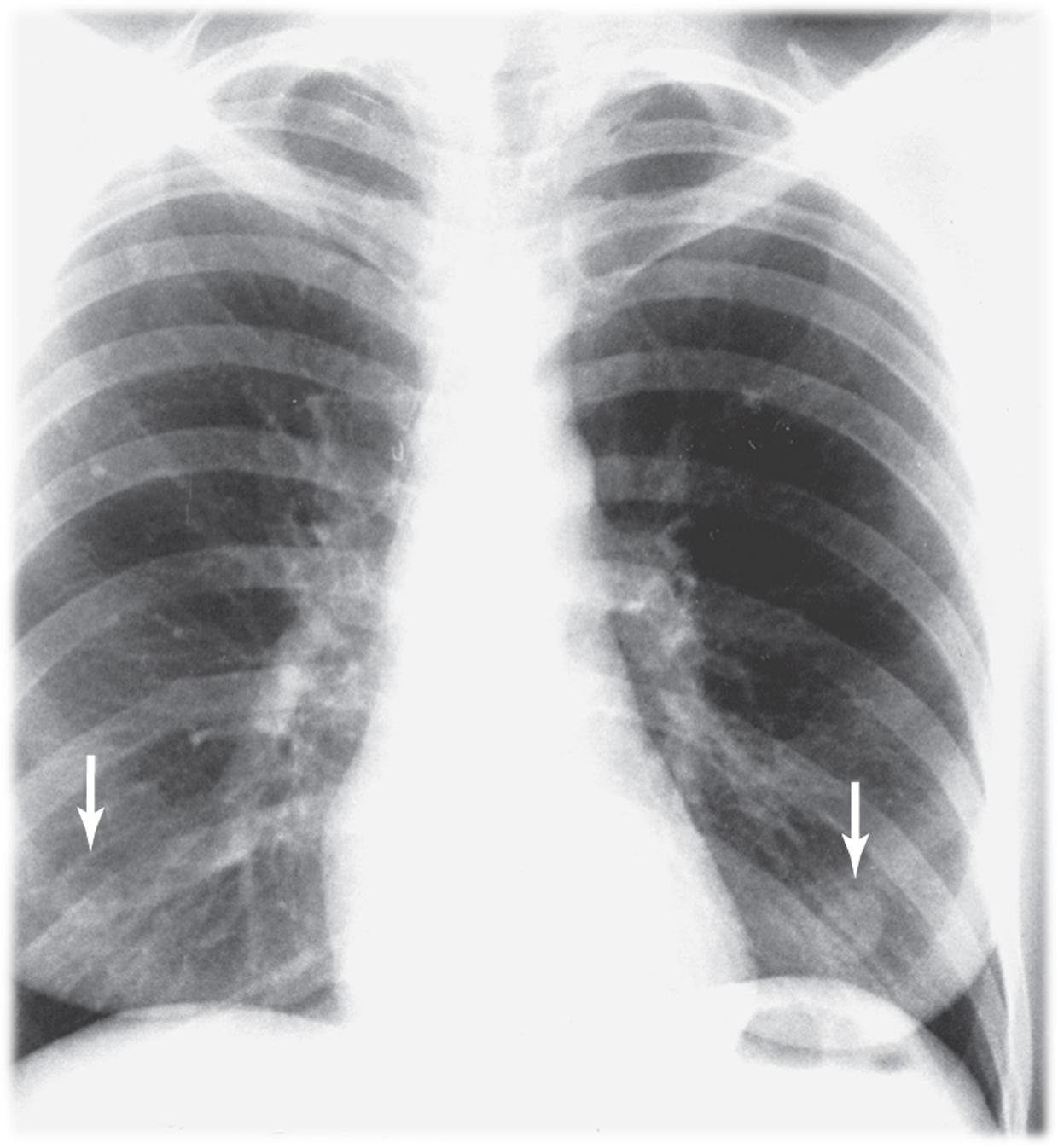
Nipple shadows
seen in mid-clavicular line over lower half of R & L lungs
if single nodule, refer to lateral CXR to confirm in the nodule projects within the lung
NOTE: IF nodule only seen in PA view, tape metallic BB marker and repeat PA view. If nodule aligns with BB = nipple shadow confirmed
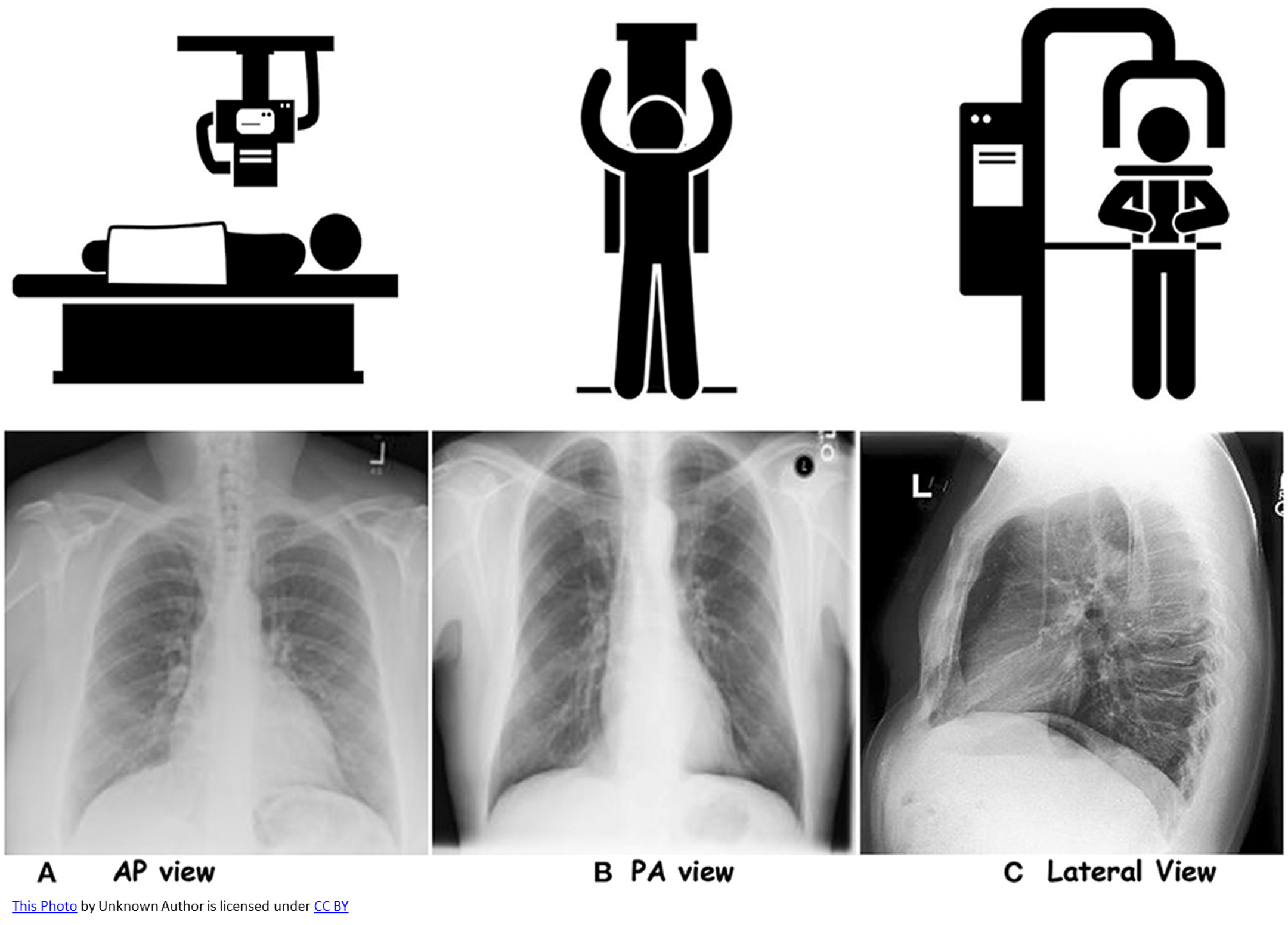
Patient stands upright with chest against detector and beam entering from the back. What projection technique is this?
Posteroanterior (PA) projection
Patient lies supine, with beam entering from front with the detector behind them. What projection technique is this?
Anteroposterior (AP) projection
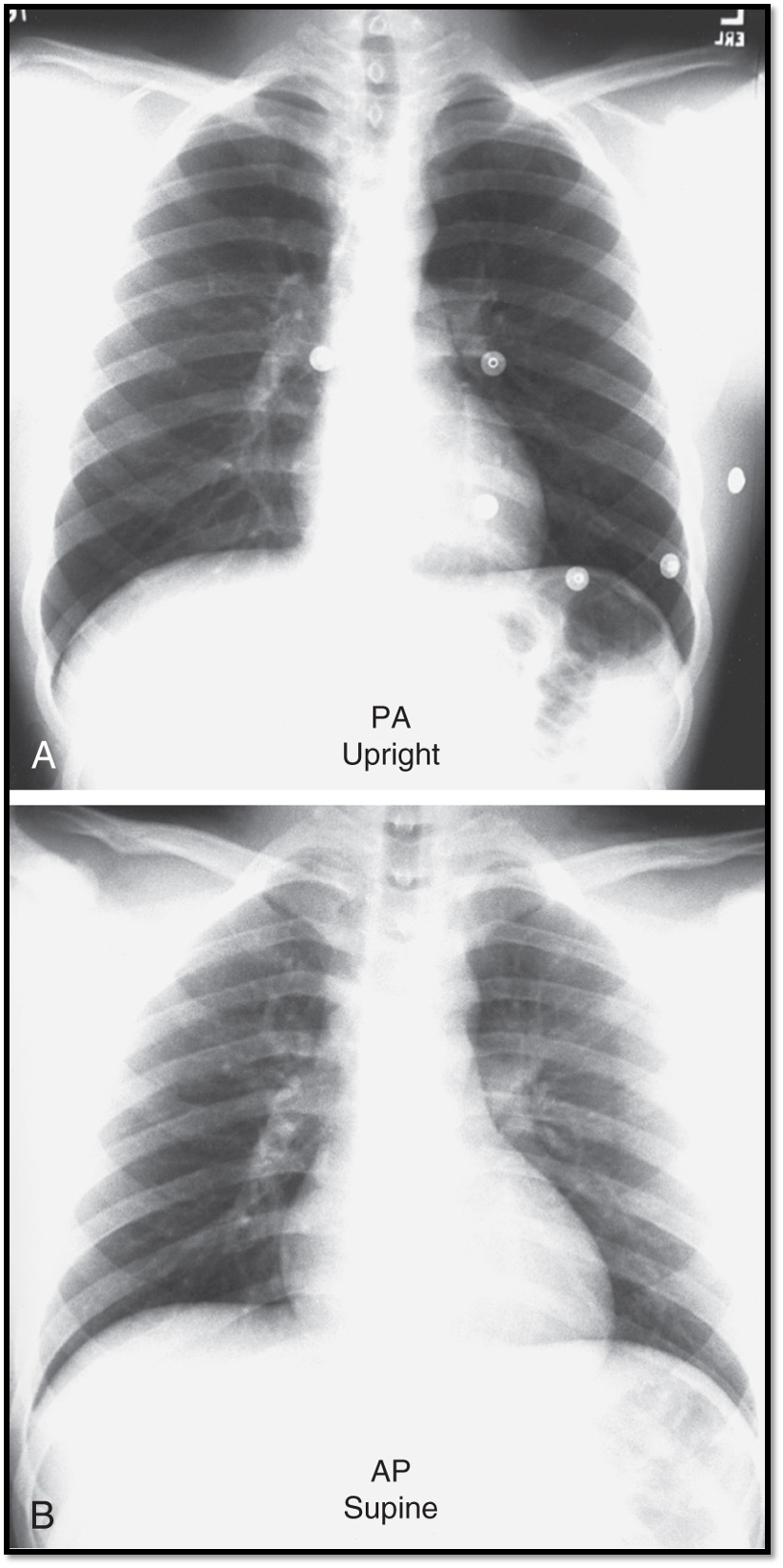
Main difference between PA vs. AP views?
patient positioning
beam direction
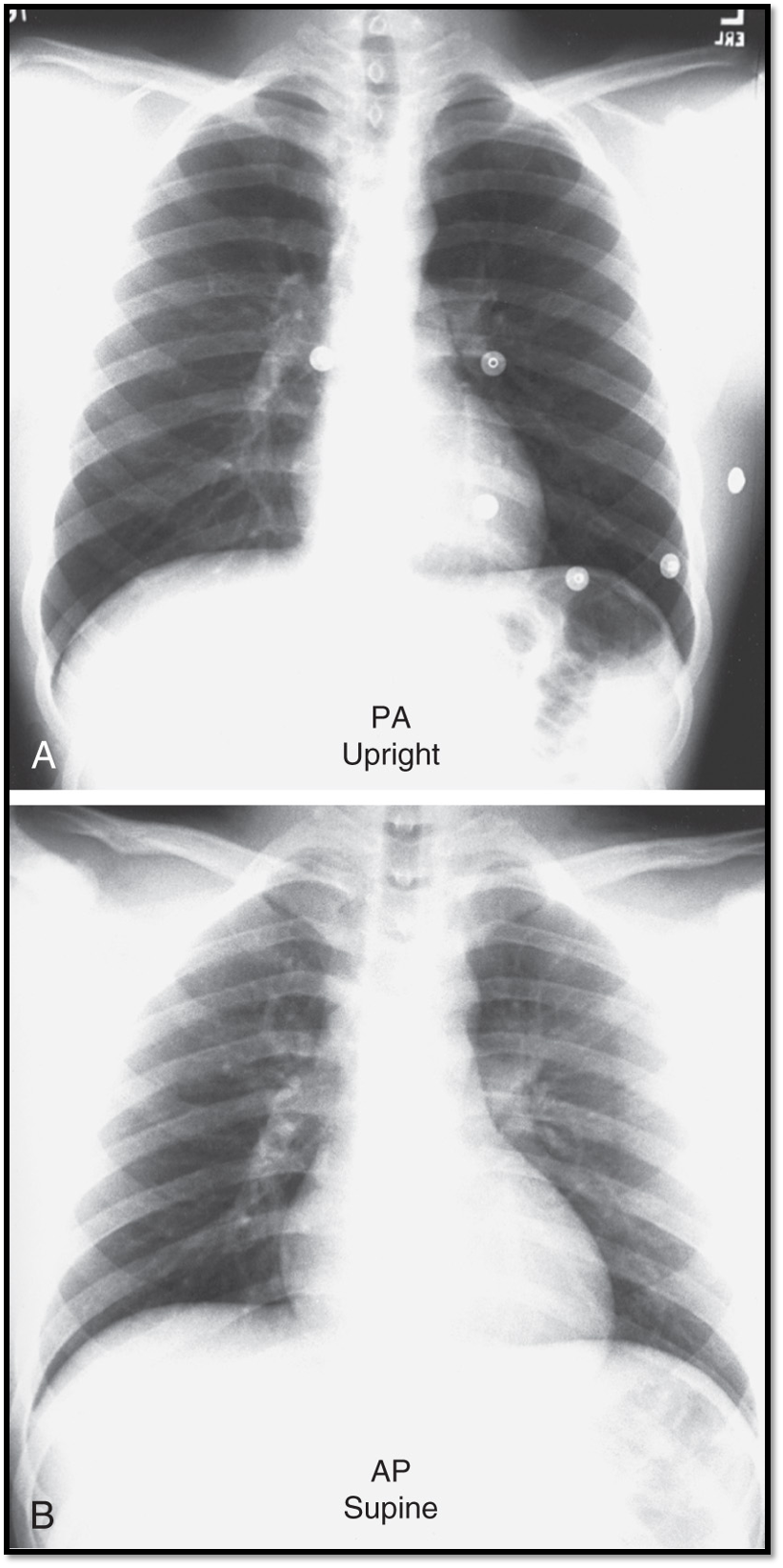
How is heart size affected in AP CXRs?
Heart size may appear larger due to magnification effects
Which CXR projection provide a more accurate depiction of heart size?
Posteroanterior (PA) projection
Benefits of upright PA view?
Allows for deeper breaths, producing better lung expansion and clarity of lung fields & provides a more accurate depiction of heart size.
Limitations of supine AP view?
Lungs may appear hypoinflated, lower lung fields may appear hazy, obscuring costophrenic angles and the heart may appear enlarged.
What CXR view minimizes distortion and allows for more accurate assessment of the heart and lungs?
Posteroanterior (PA) view
Diagnostic advantages of upright position CXR?
enhanced lung visualization
easier detection of pleural effusions
improved visibility of pneumothoraces
reduced anatomical distortion
Diagnostic limitations of supine CXR?
limited lung inflation
apparent heart enlargement
difficulty detecting smaller pleural effusions and pneumothoraces
When would expiration view on CXR be beneficial?
In highlighting small pneumothoraces
Benefit of combined inspiration and expiration imaging?
Helps in detecting air trapping and mediastinal shifts caused by foreign body obstructions.
Suspicion of pneumothorax: inspiration or expiration imaging?
Expiration imaging
Flattened diaphragm on lateral CXR is a key sign of _________.
hyperinflation
CXR maging with ____ level voltage improves visualization of soft tissues, pulmonary vessels and the heart.
High voltage
CXR maging with ____ level voltage improves visualization of bones but lowers visualization of pulmonary vessels.
Low voltage
What CXR voltage level would be best to visualize a rib fracture?
Low voltage
What CXR voltage level would be best to visualize suspected injury of soft tissues, pulmonary vessels and the heart?
High voltage
Normal CXRs are taken at a relatively ____ voltage.
High
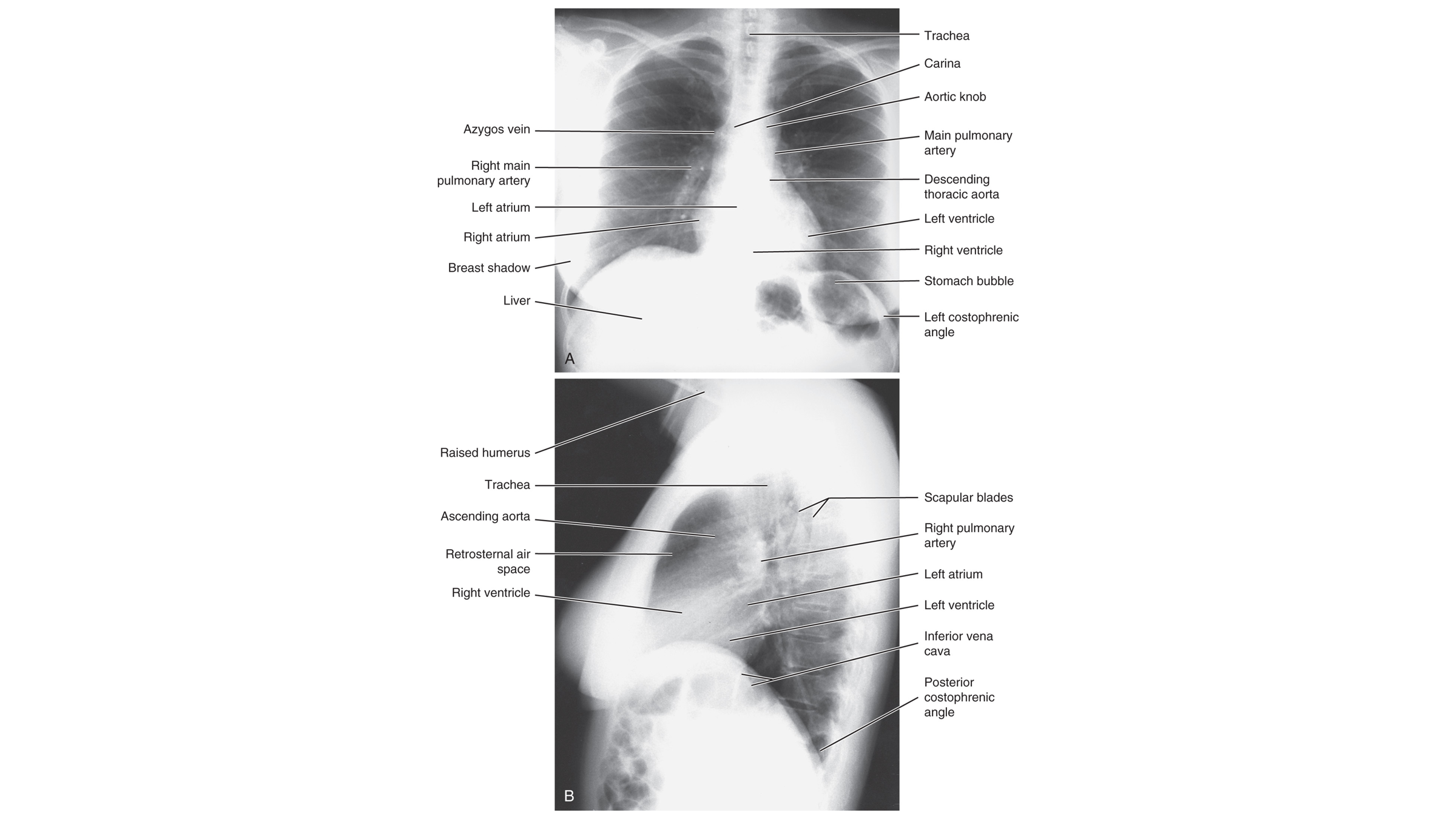
Prior to interpreting a CXR what should you do?
confirm patient details (name, DOB, ID number)
date and time the film was taken
evaluate any previous imaging
RIPE is used to assess image quality- what does it stand for?
Rotation
Inspiration
Projection
Exposure
To carry out a structured interpretation of a CXR, the mneumonic ABCDE is often used. What does it stand for?
Airway (trachea, carina, bronchi, hilar structures)
Breathing (lungs, pleura)
Cardiac (heart size, borders)
Diaphragm (& costophrenic angles)
Everything else (mediastinal contours, bones, soft tissues, tubes, valves, pacemakers, wires)
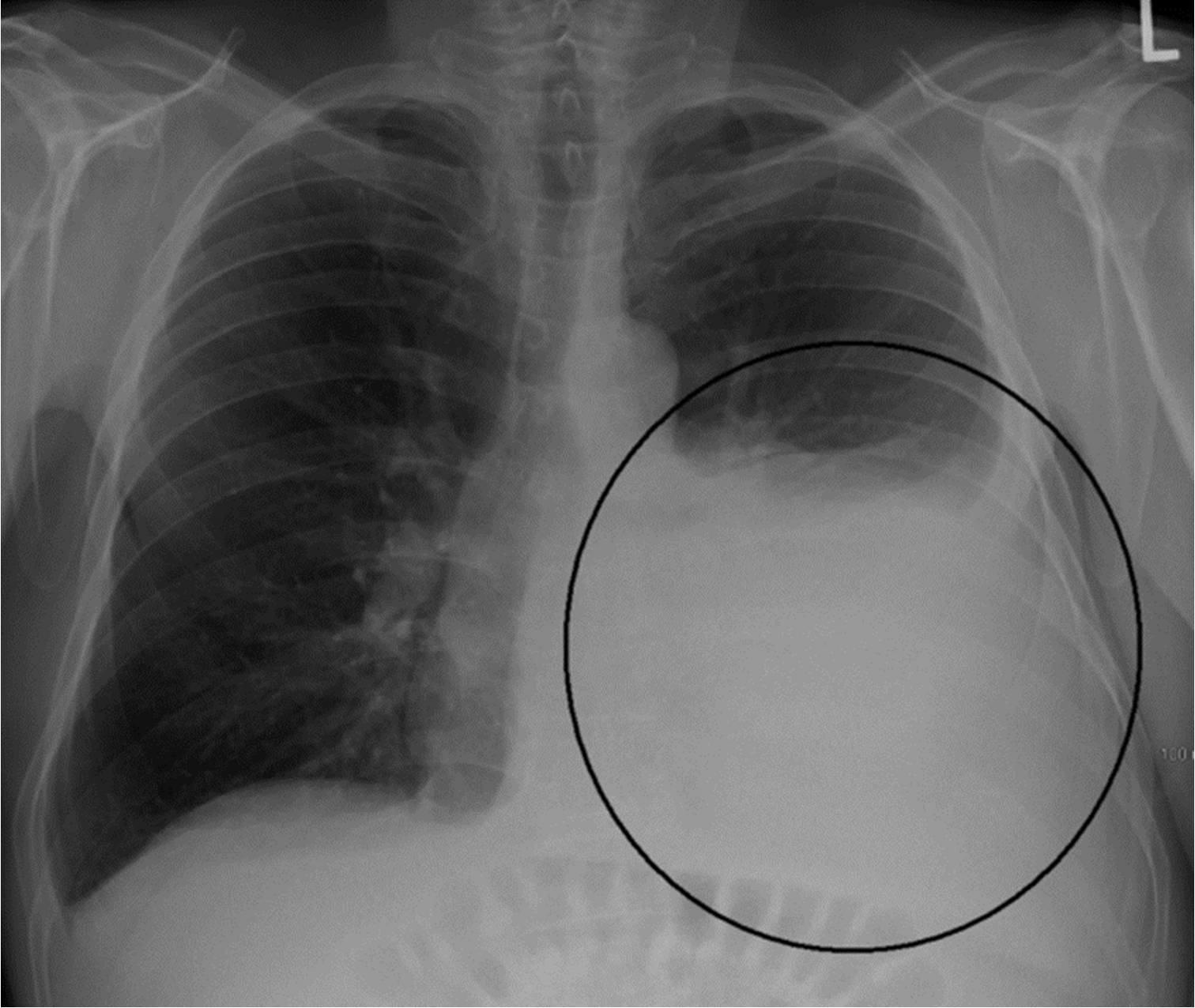
Pleural effusion with tracheal deviation
Important landmark on CXR when assessing NG tube placement
Carina
NOTE: a correctly placed NG tube will bisect the carina
The ____ main bronchus is wider, shorter and more vertical than the ____ main bronchus.
right; left
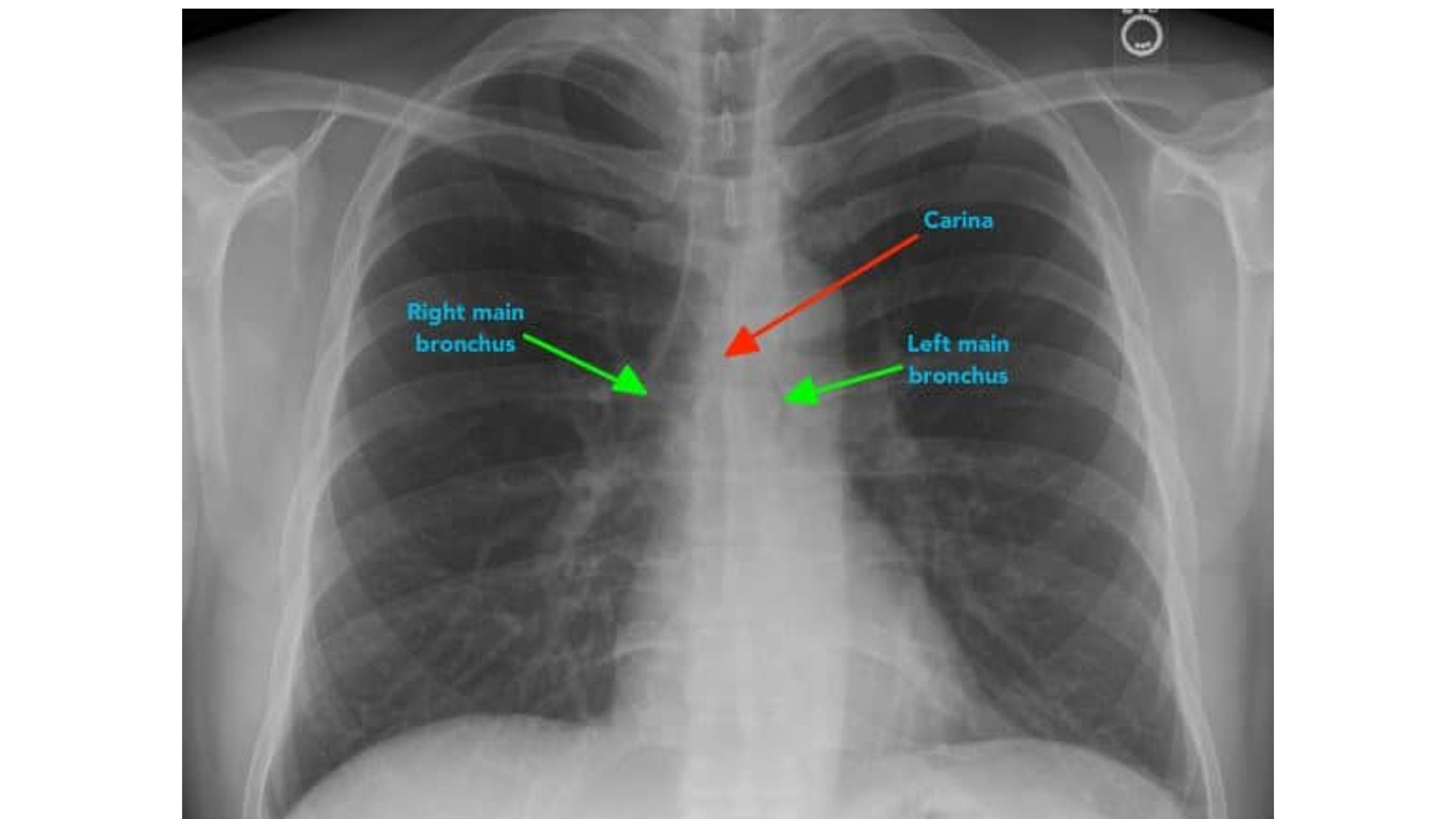
It is more common for inhaled foreign objects to become lodged in the ____ main bronchus.
right
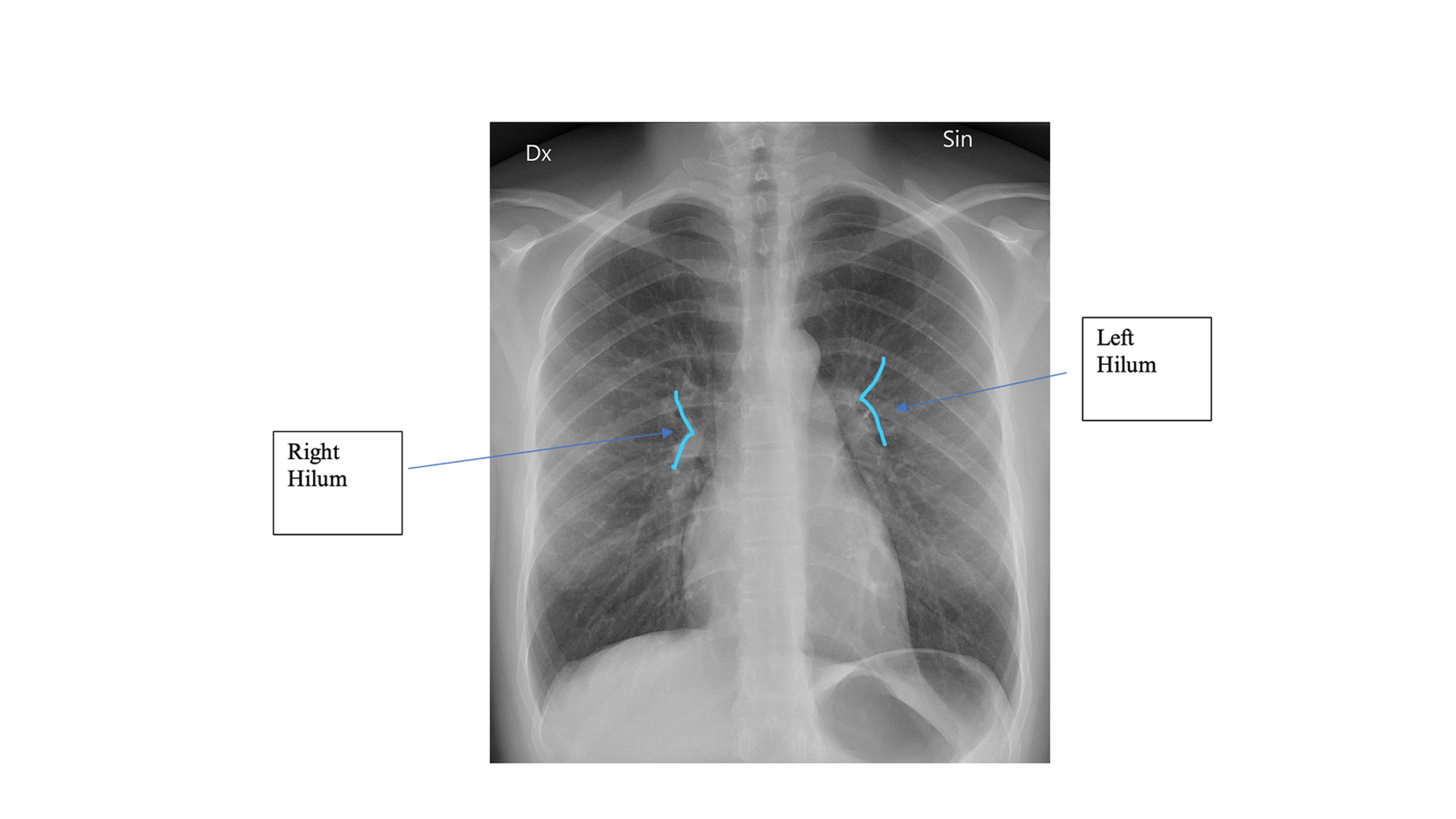
On CXR, the ___ hila should appear lower than the ___ hila
right hila appears lower than the left
On CXR, blurred vessels near hila may suggest infiltrates or fluid accumulation in what disease?
CHF
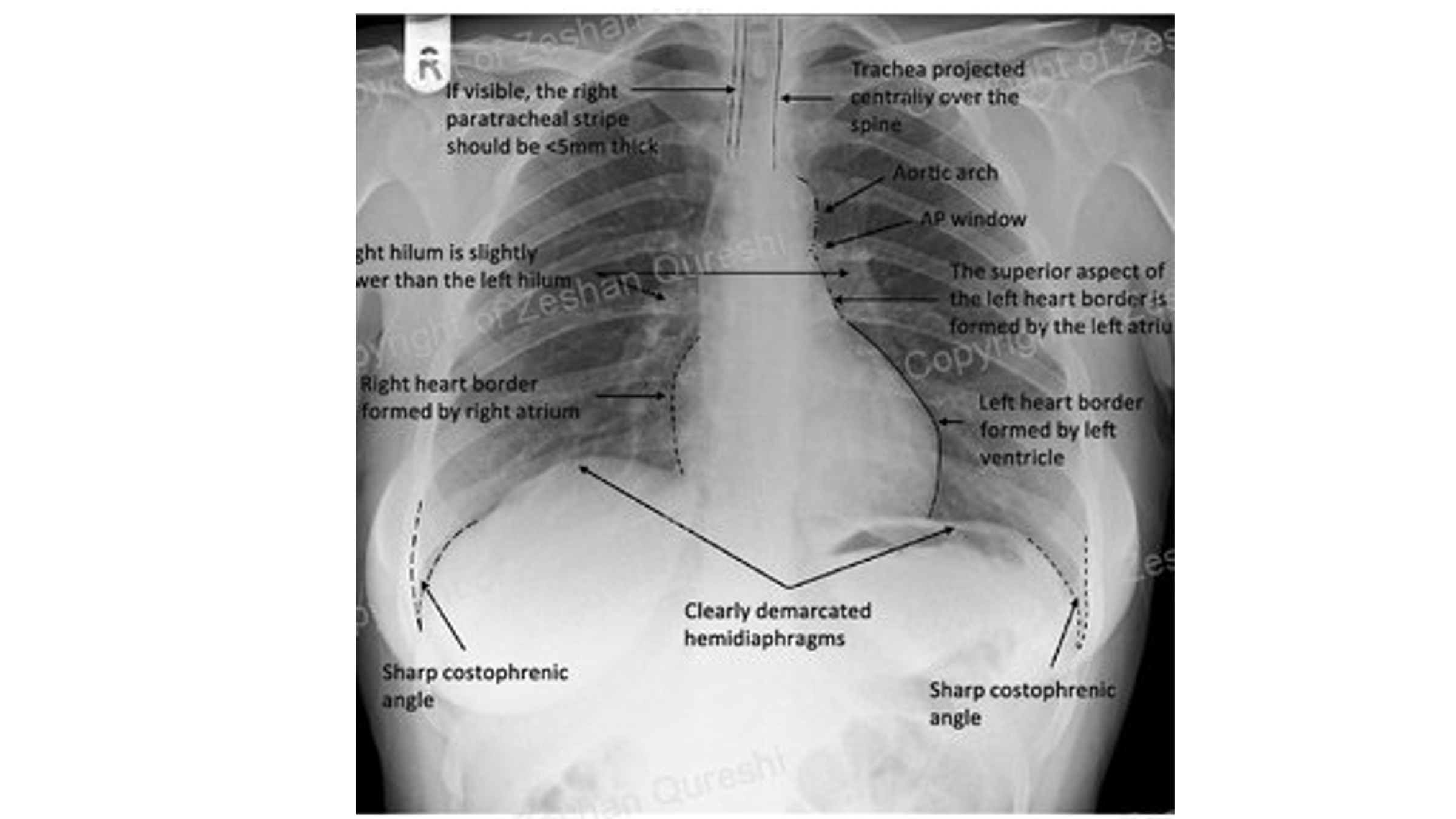
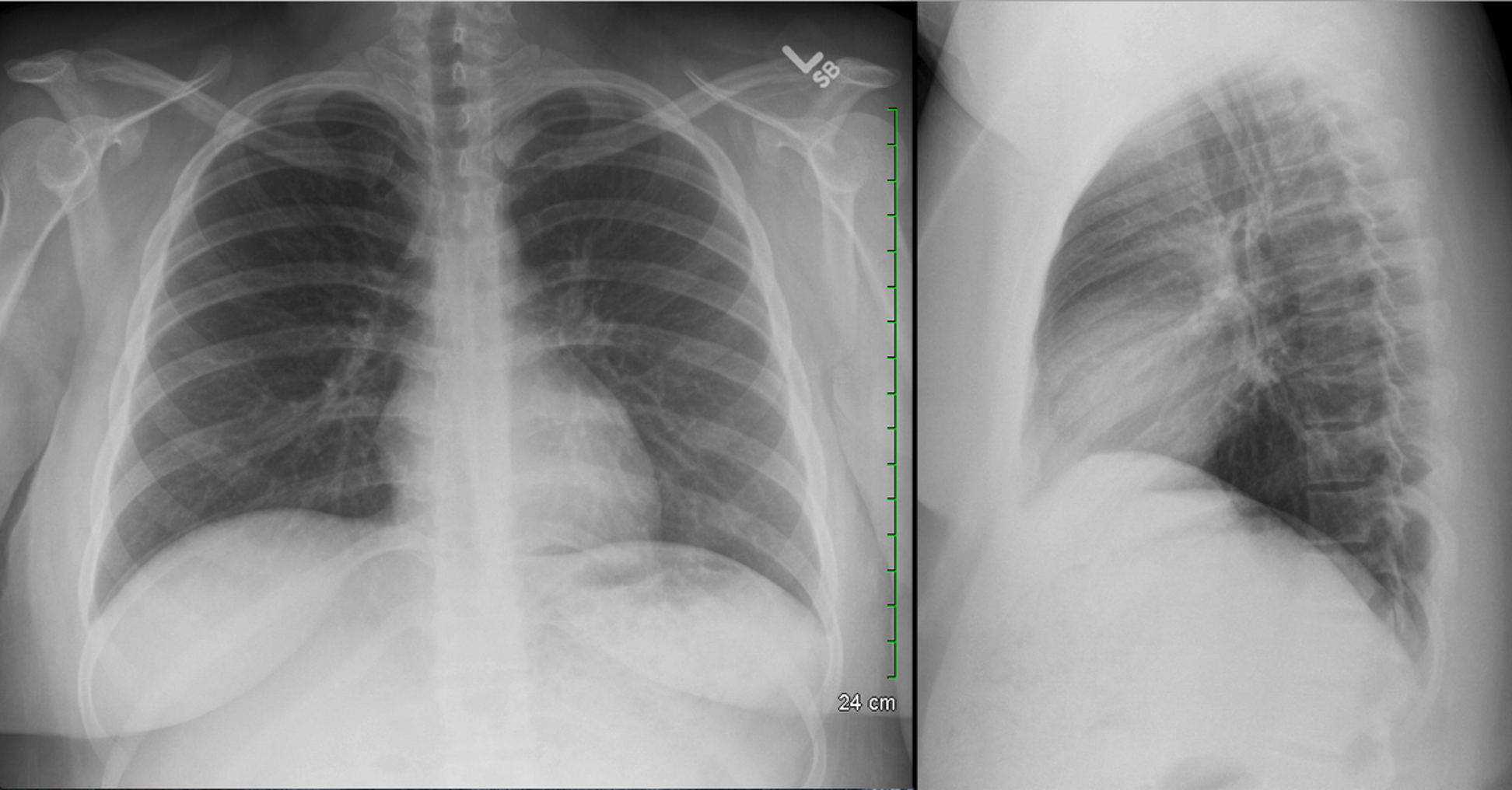
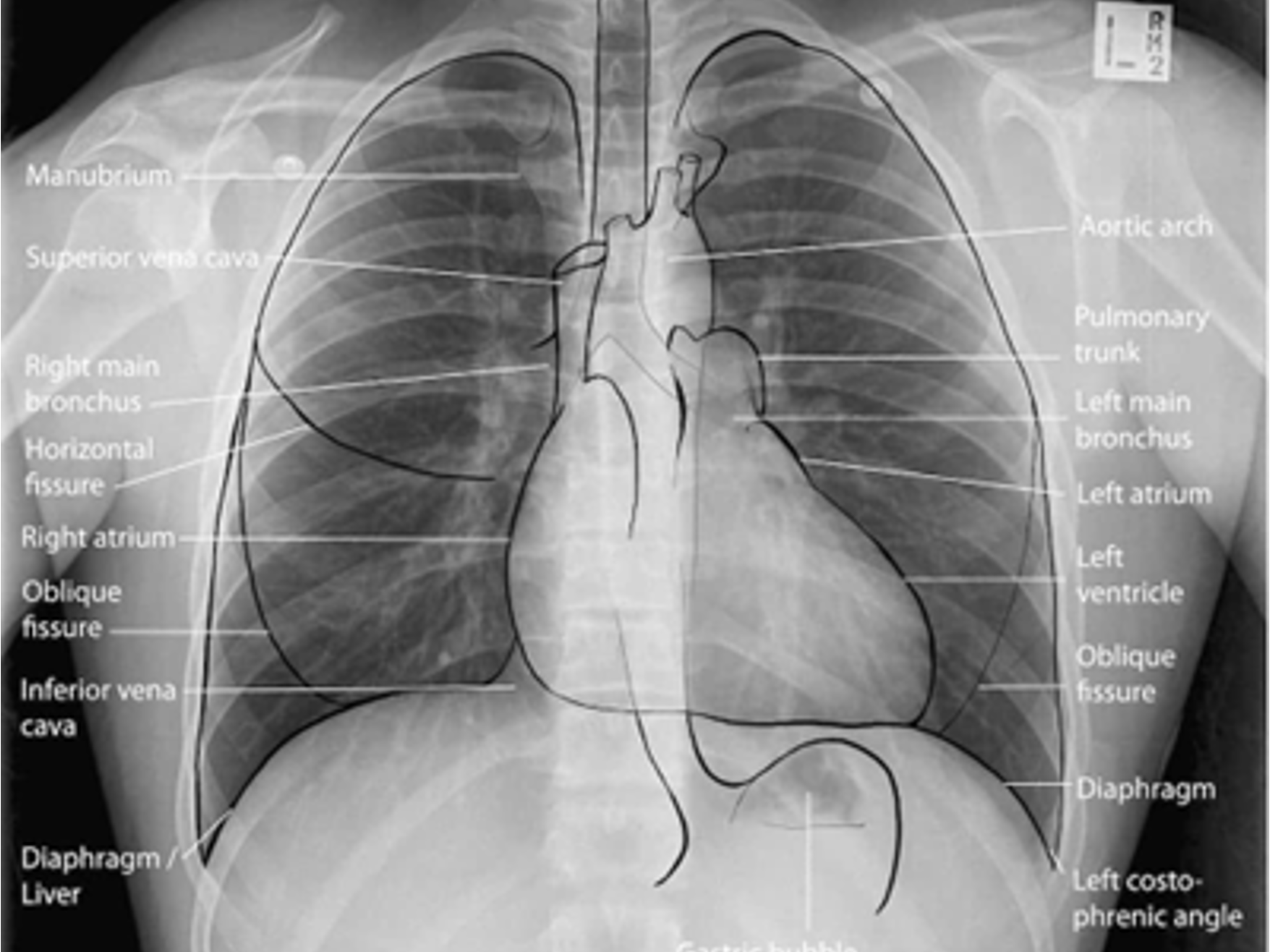
Normal CXR (PA & Lateral)
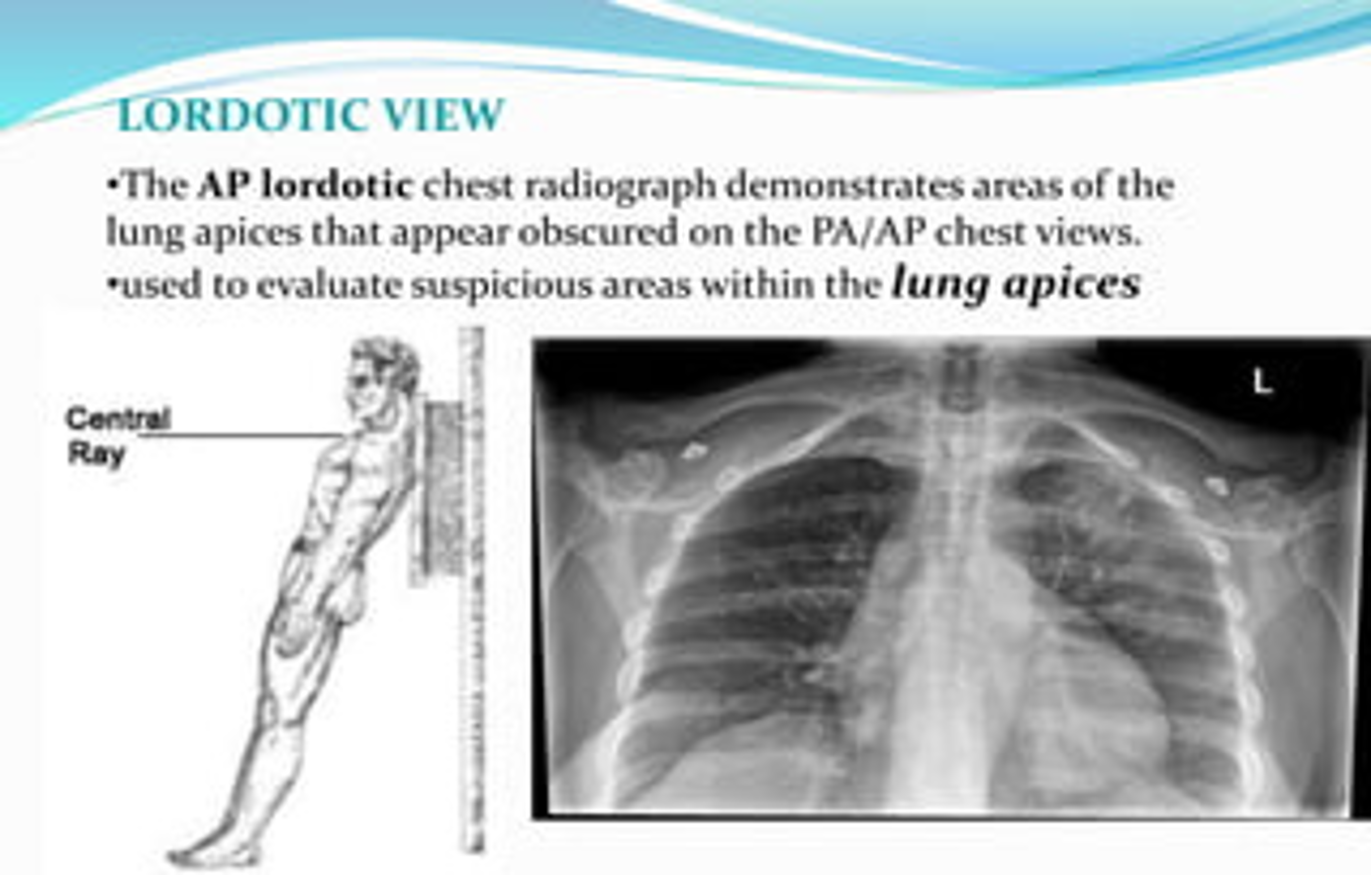
CXR view used to evaluate suspicious areas within the lung apices
Lordotic view
Visualization of more than __ ribs on CXR indicates adequate inspiratory effort.
More than 7
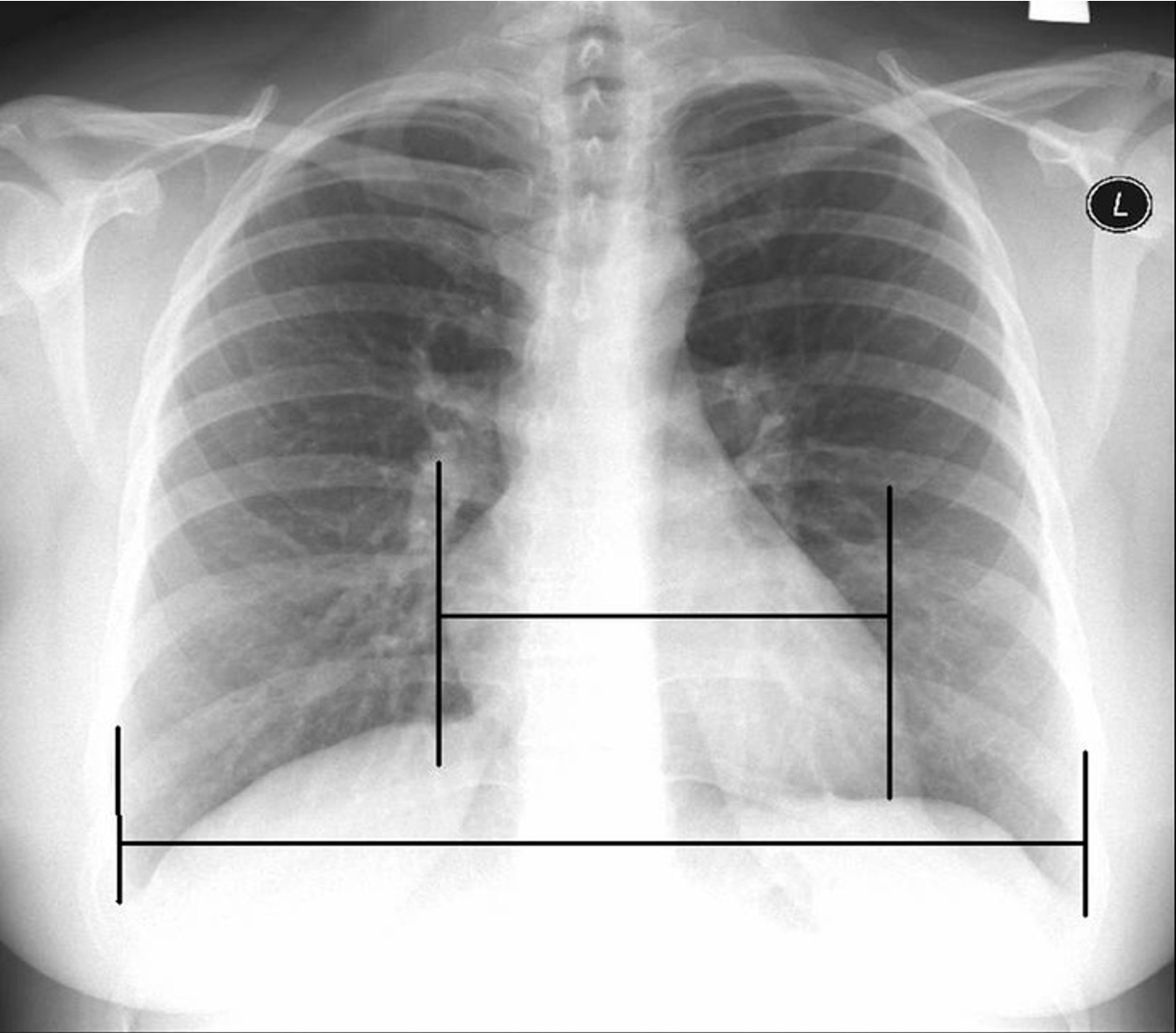
A cardiothoracic ratio above __ may indicate cardiomegaly.
0.5
The width of the heart should not be less than ___ the width of the thoracic cavity.
½
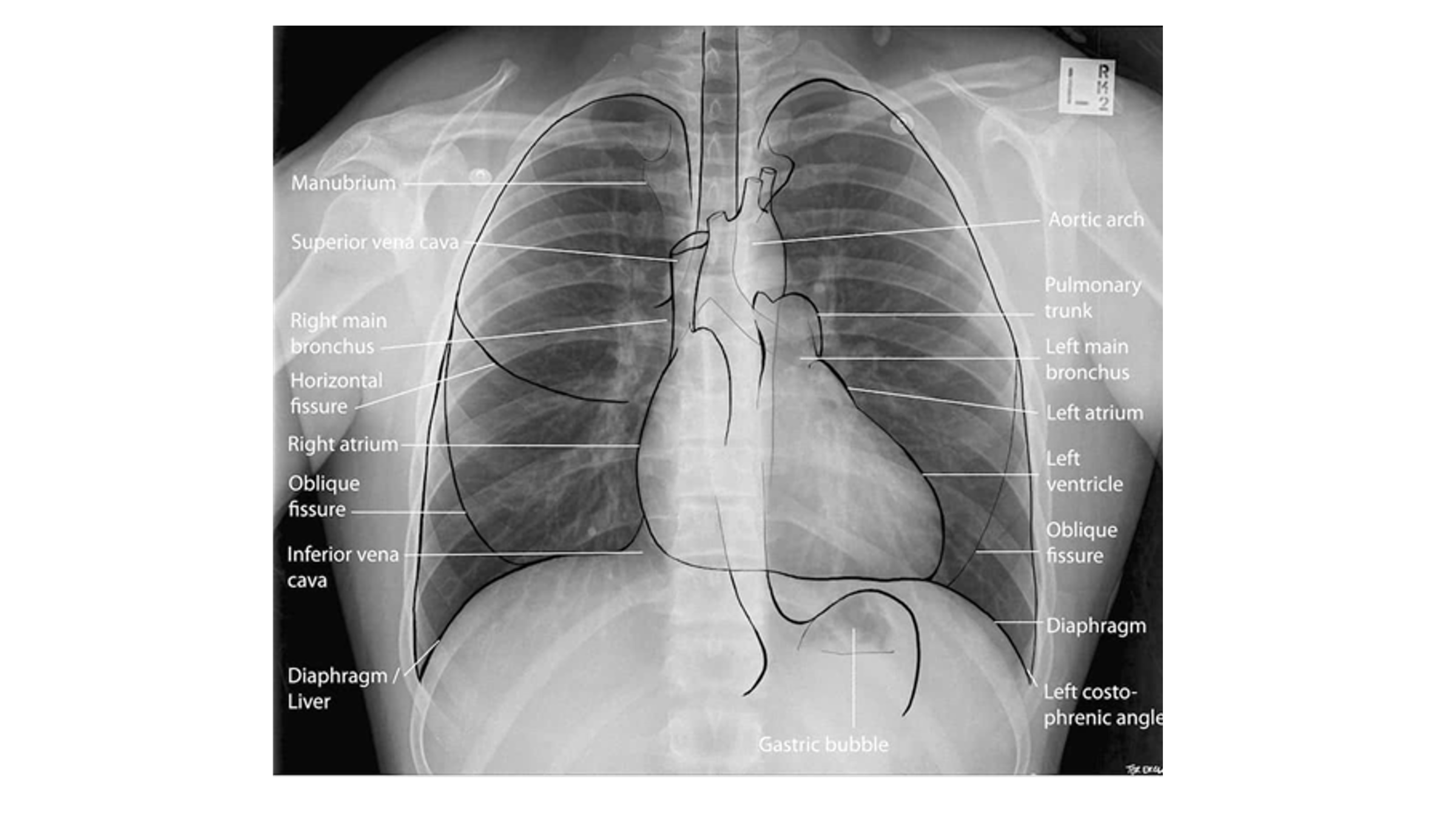
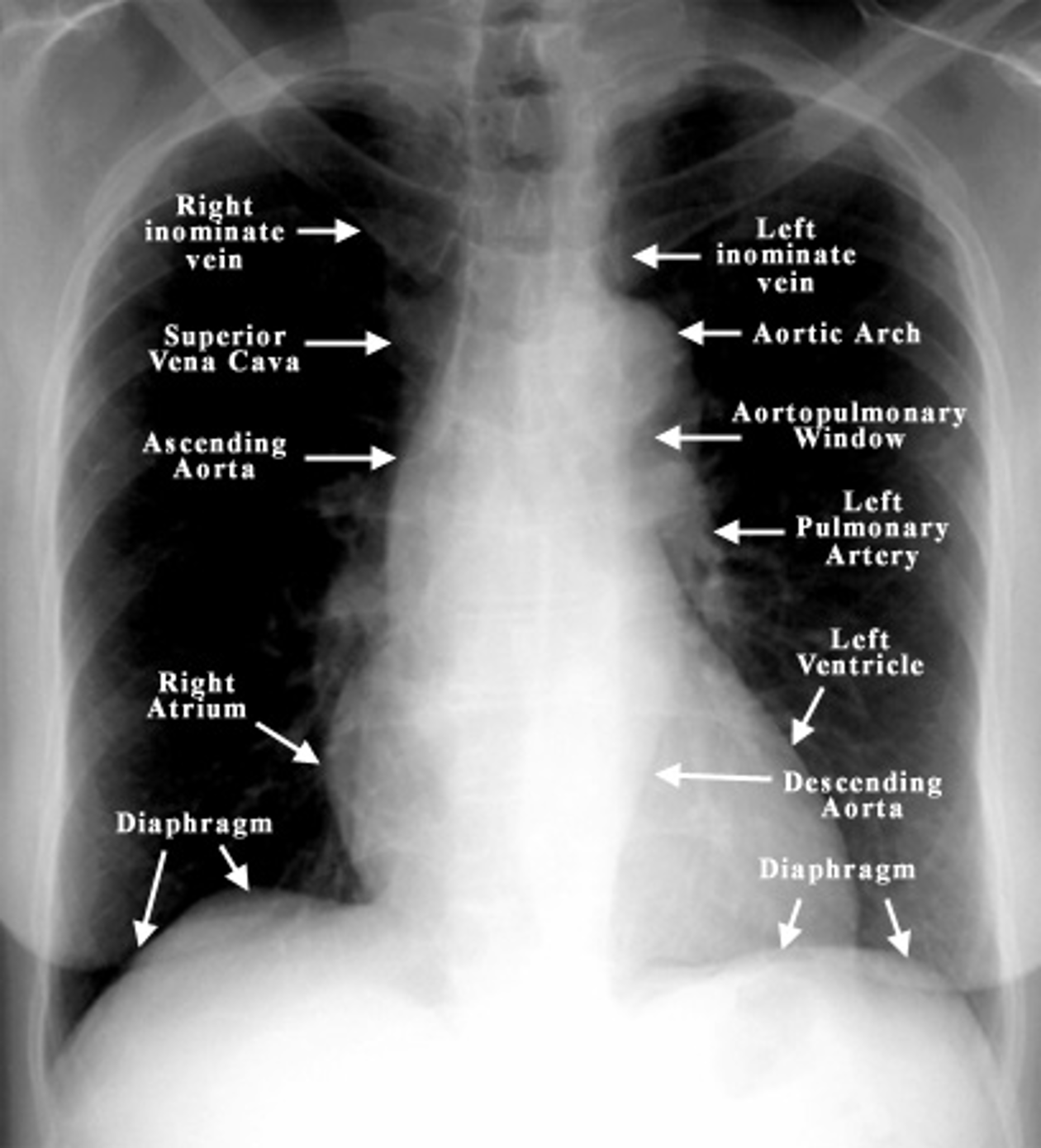
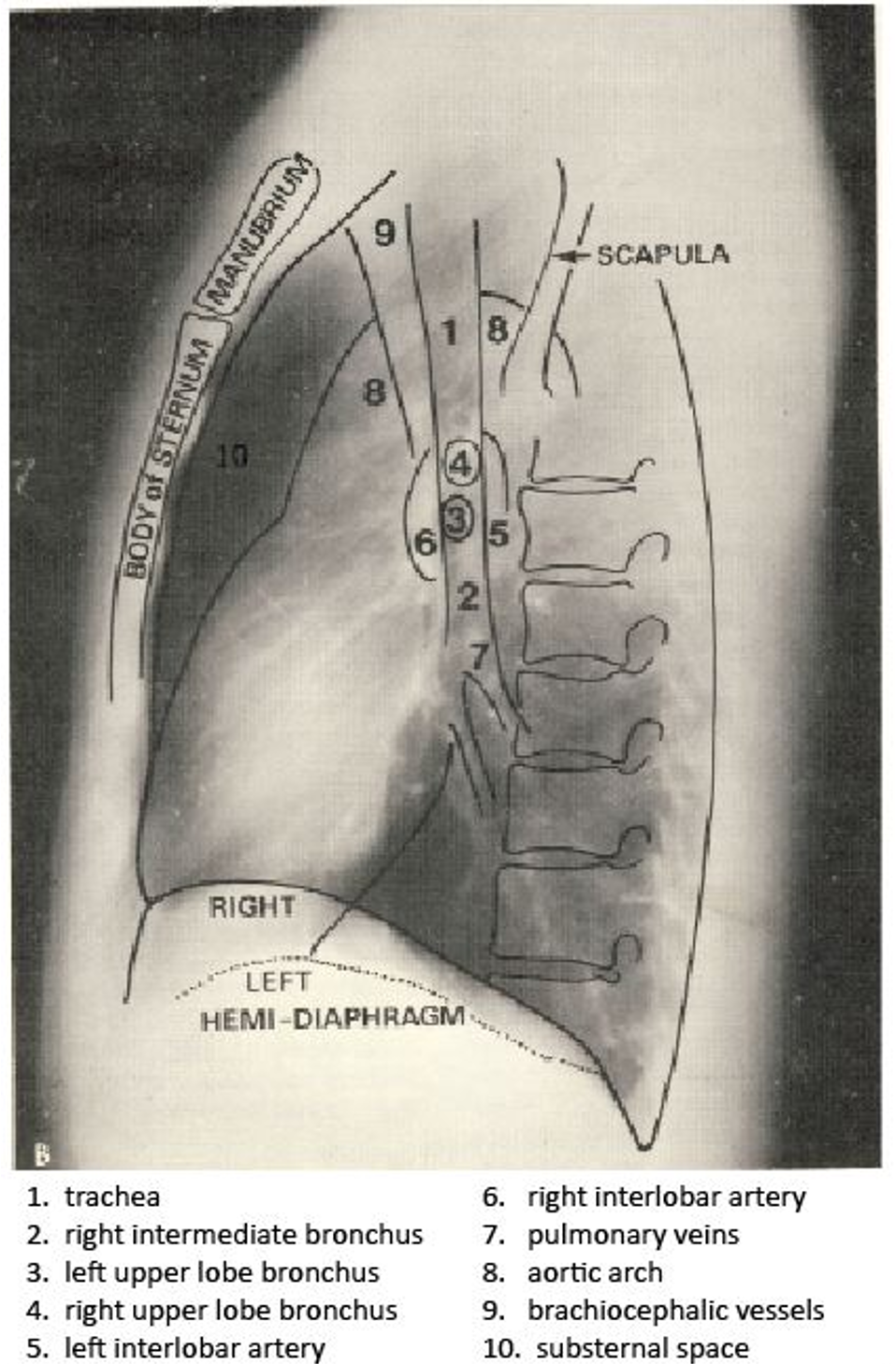
Which 3 mediastinal vessels are visible on the right side in mediastinal imaging?
brachiocephalic vessels
azygos vein
ascending aorta
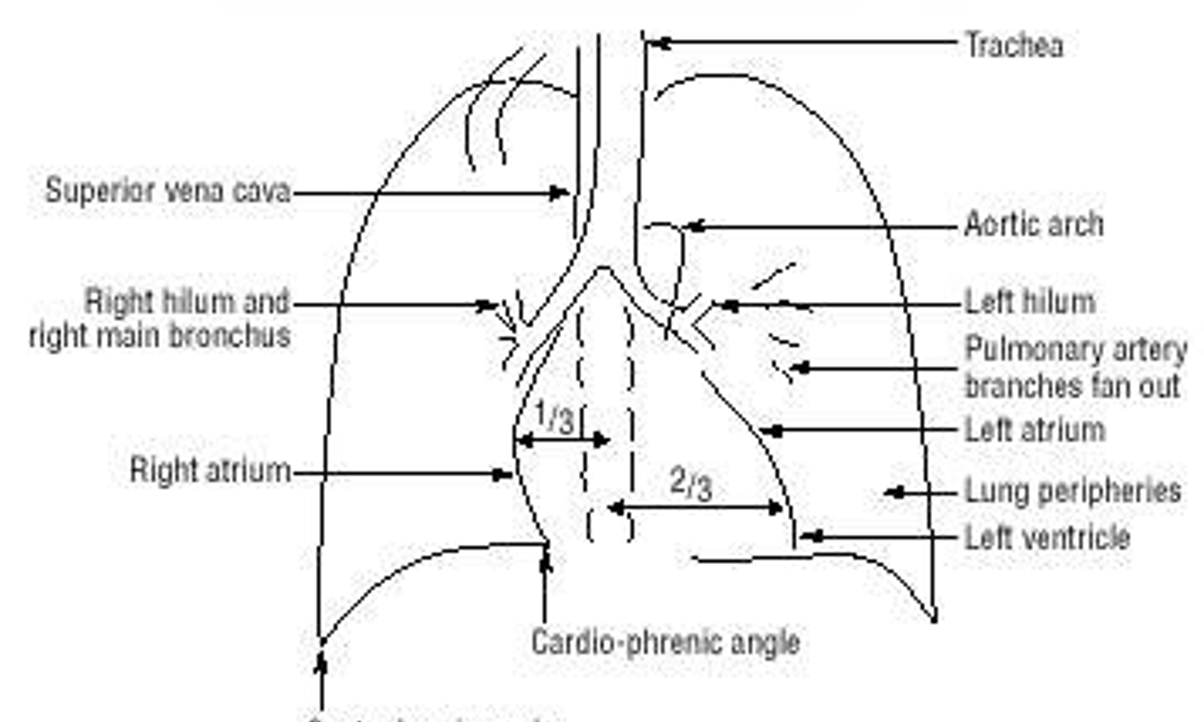
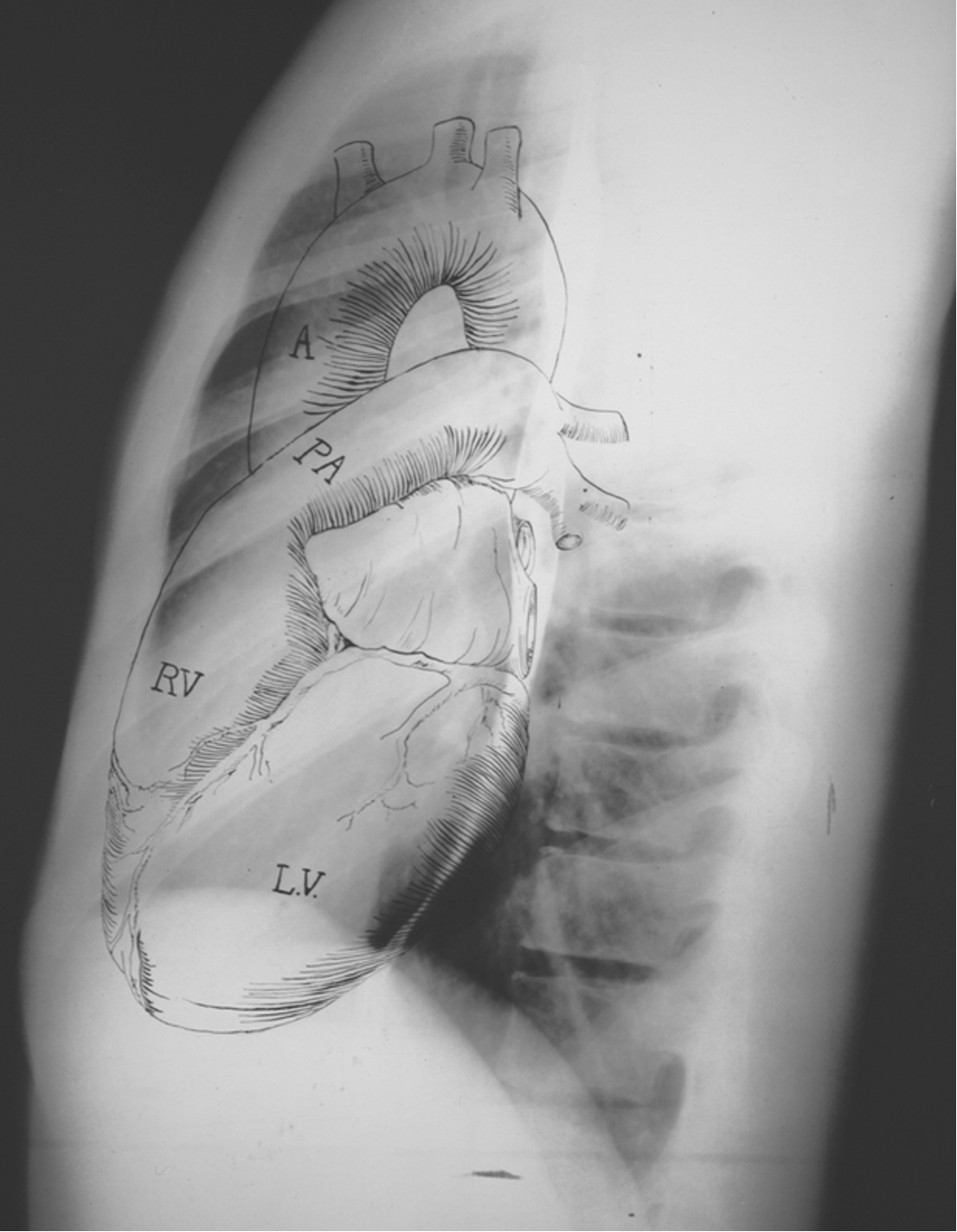
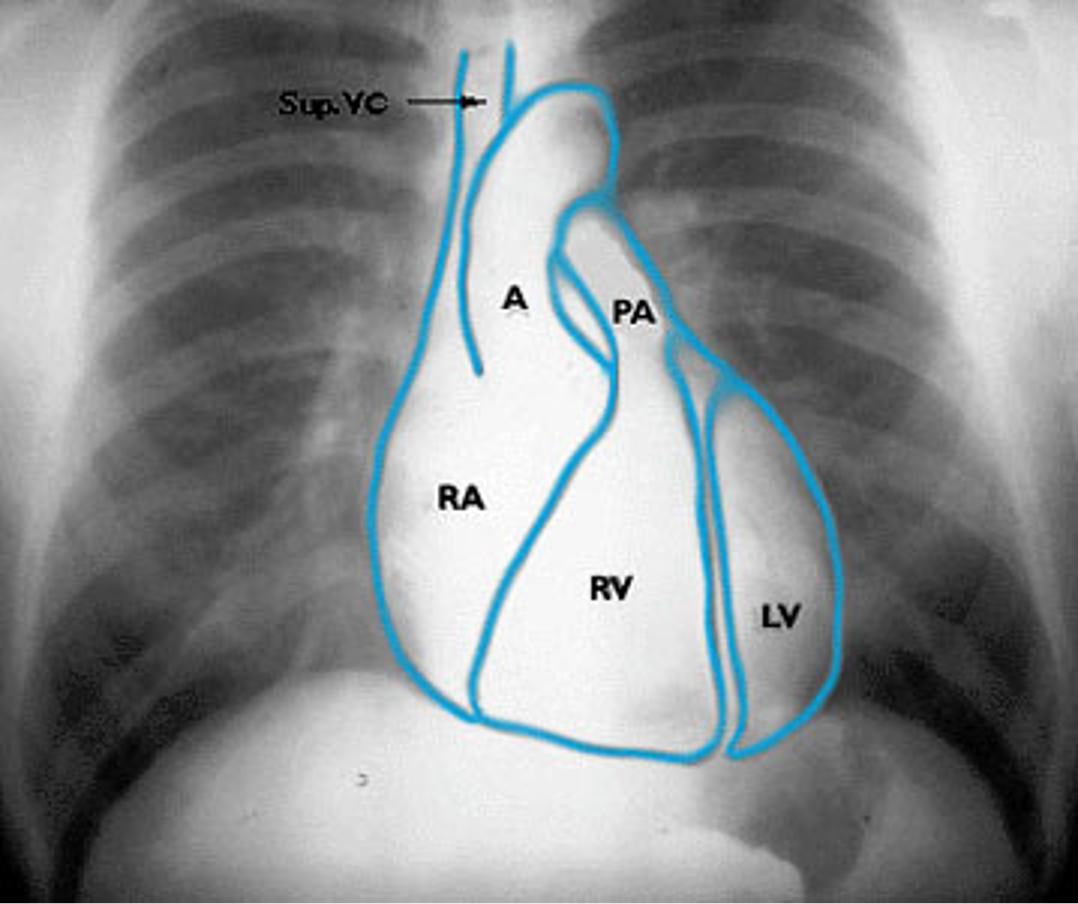
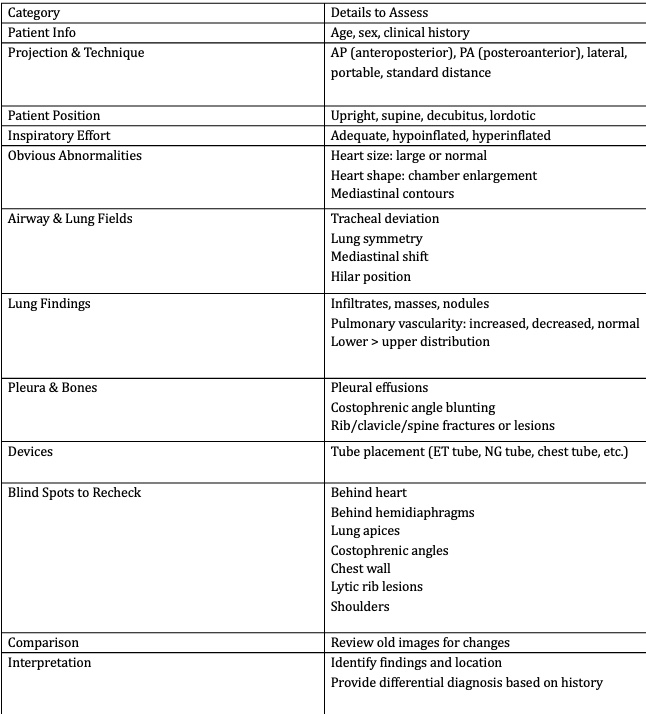
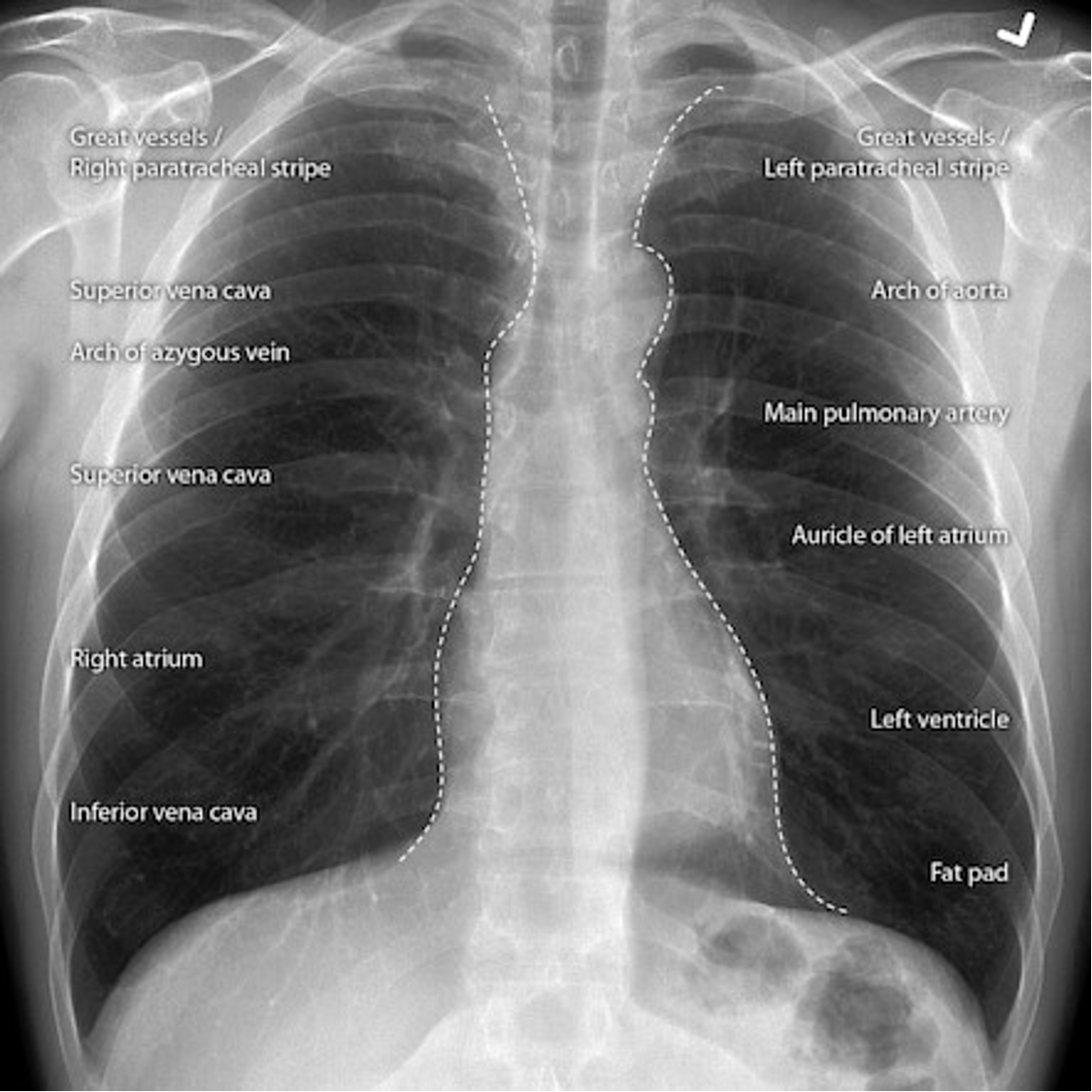
Name the mediastinal contours according to the numbers
1- superior vena cava
2- right atrium
3- inferior vena cava
4- aortic arch or knob
5- left pulmonary trunk
6- left pulmonary artery
7- left atrium
8- left ventricle
9- left cardiophrenic angle
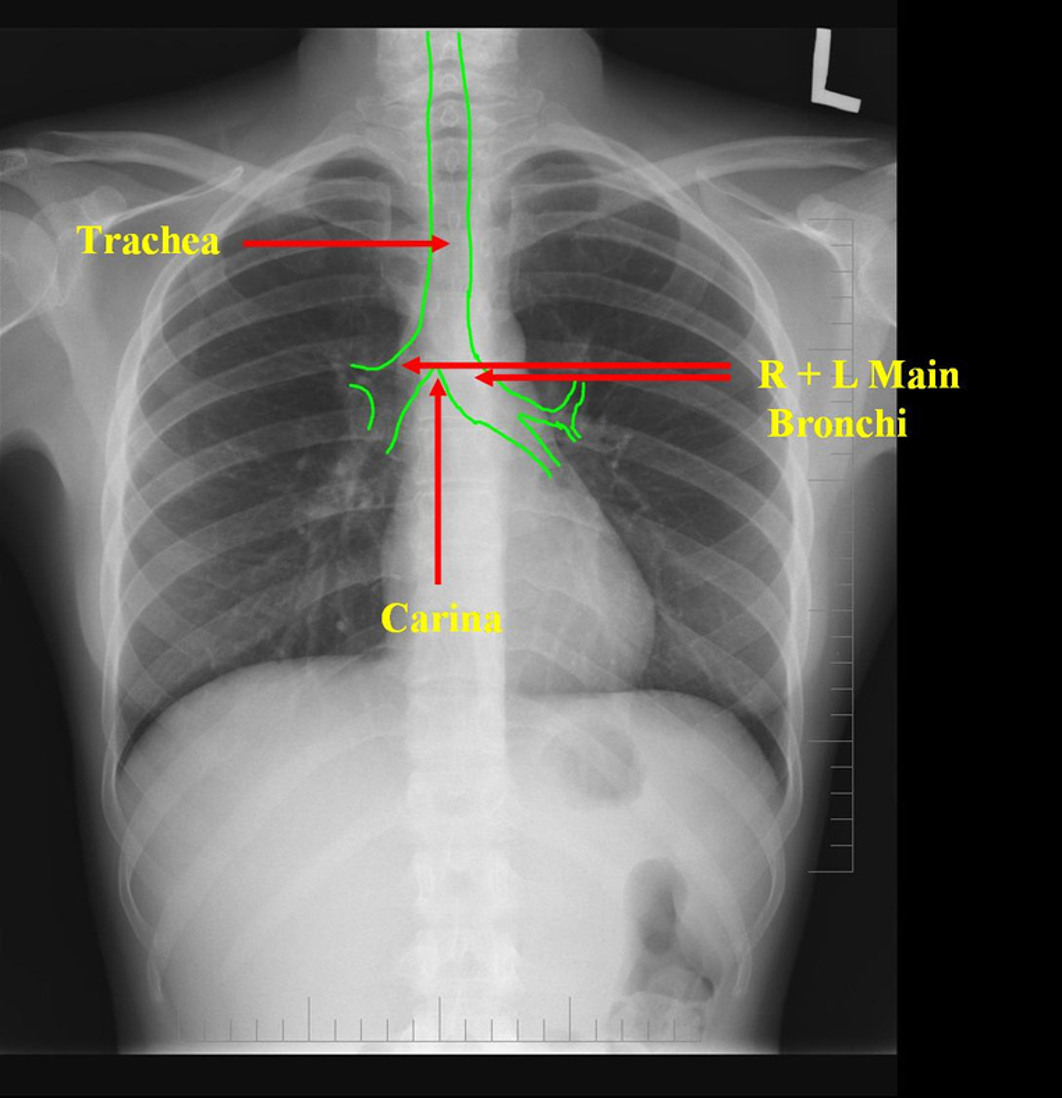
Airway Structures on CXR
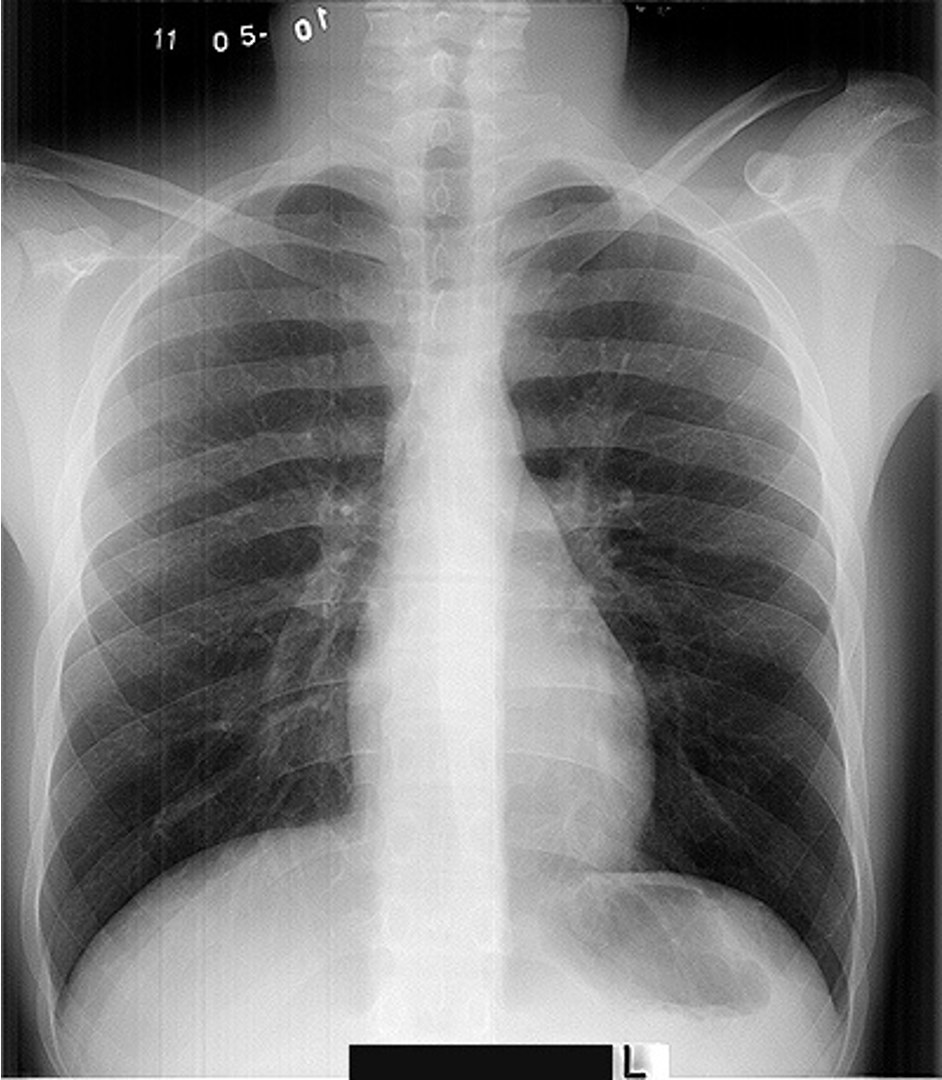
Which lung hilum should appear higher on CXR?
Left hilum
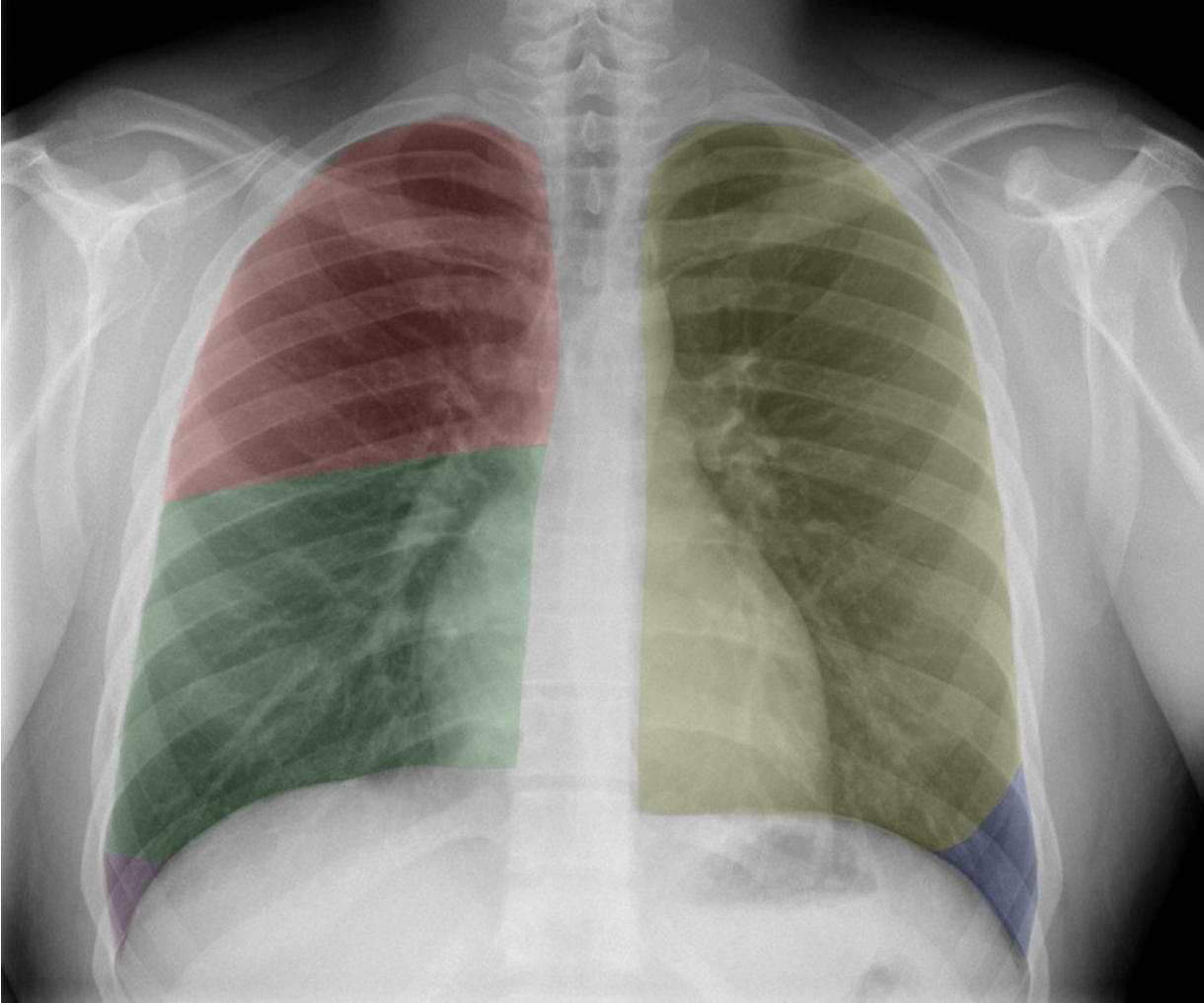
Name the lung lobes according to color
Red = RUL
Green = RML
Purple = RLL (not seen in picture)
Yellow = LUL
Blue = LLL
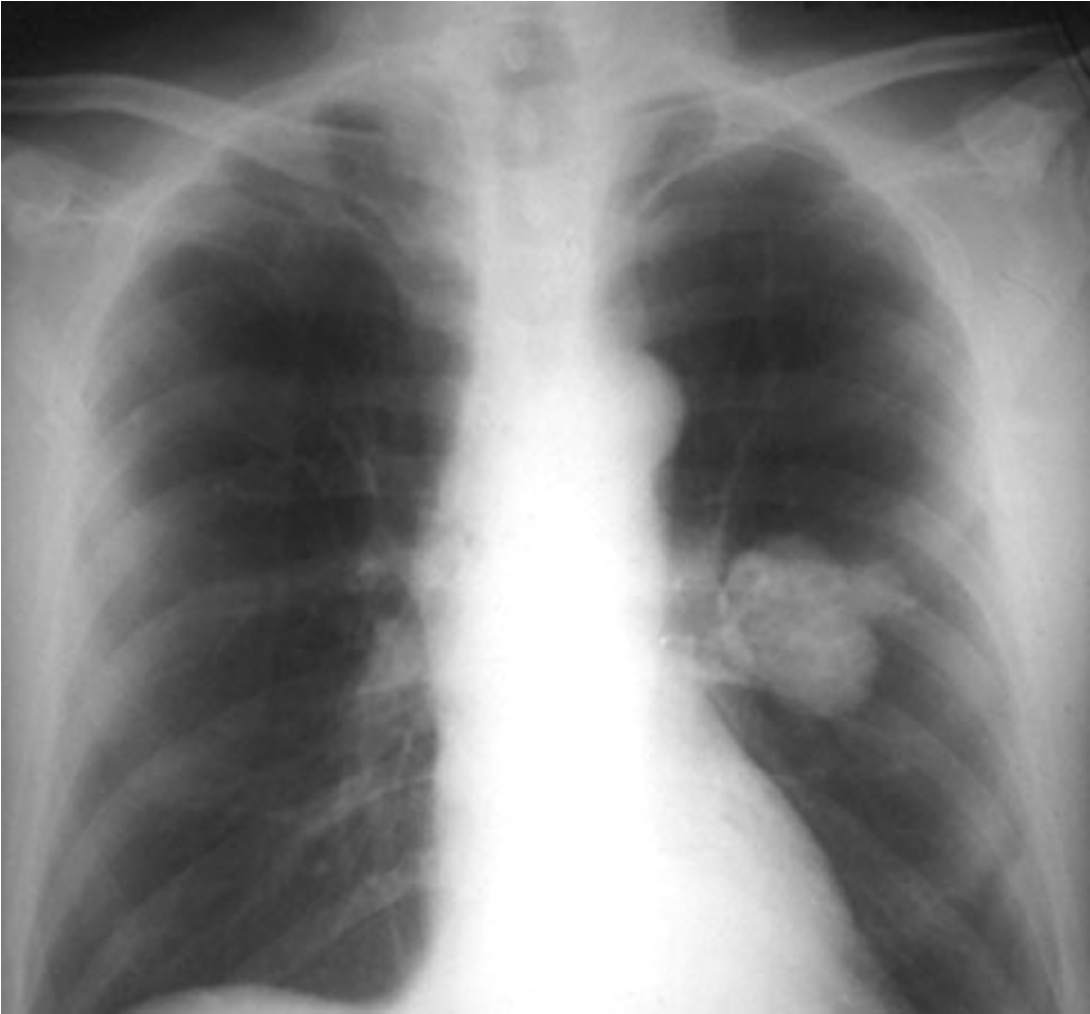
Lung Mass:
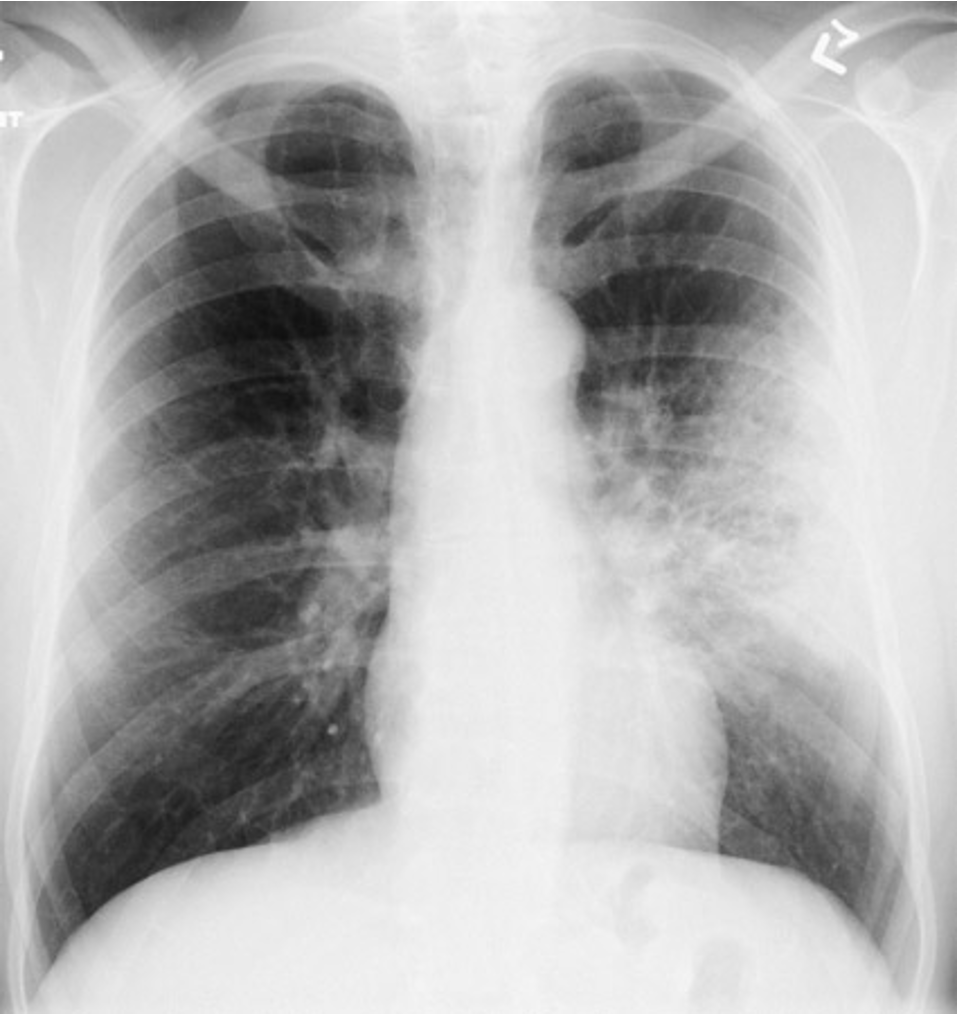
Lung Infitrate:
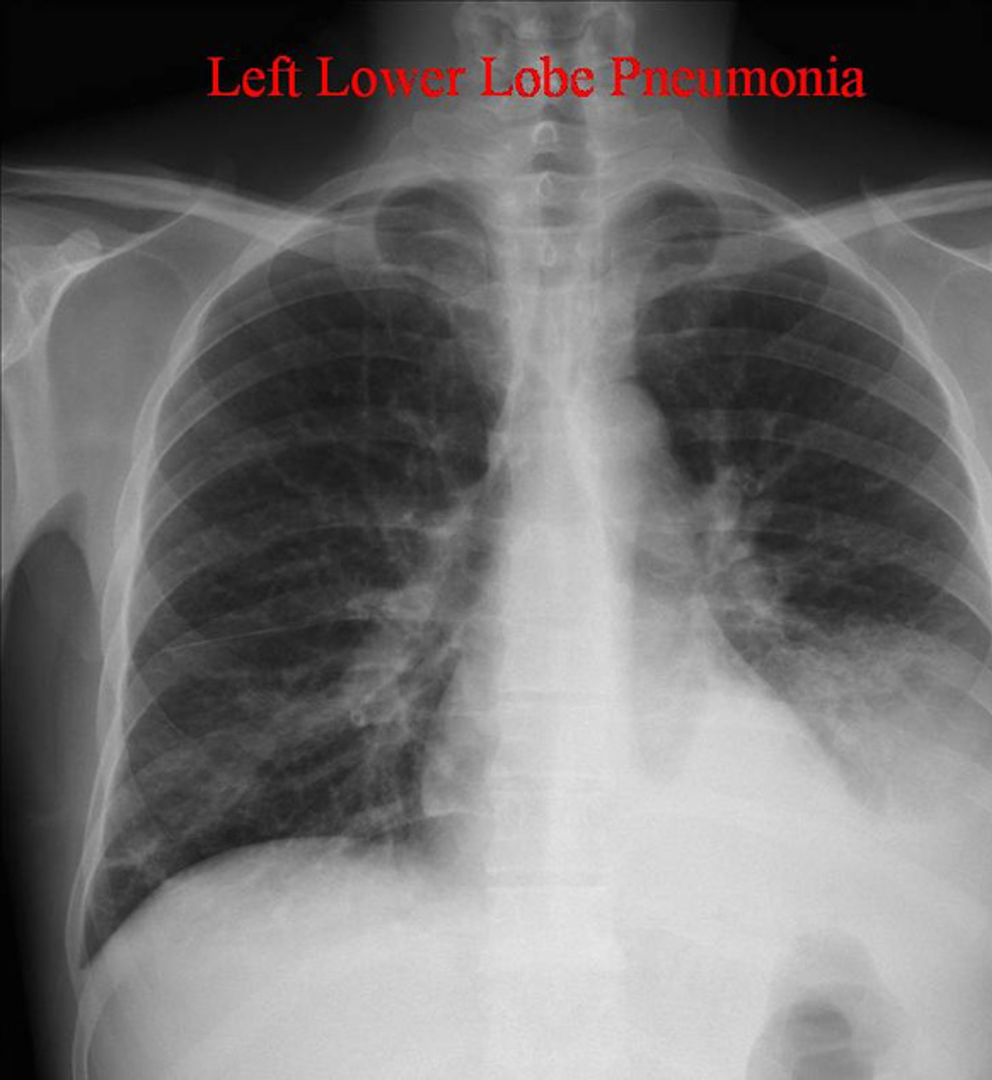
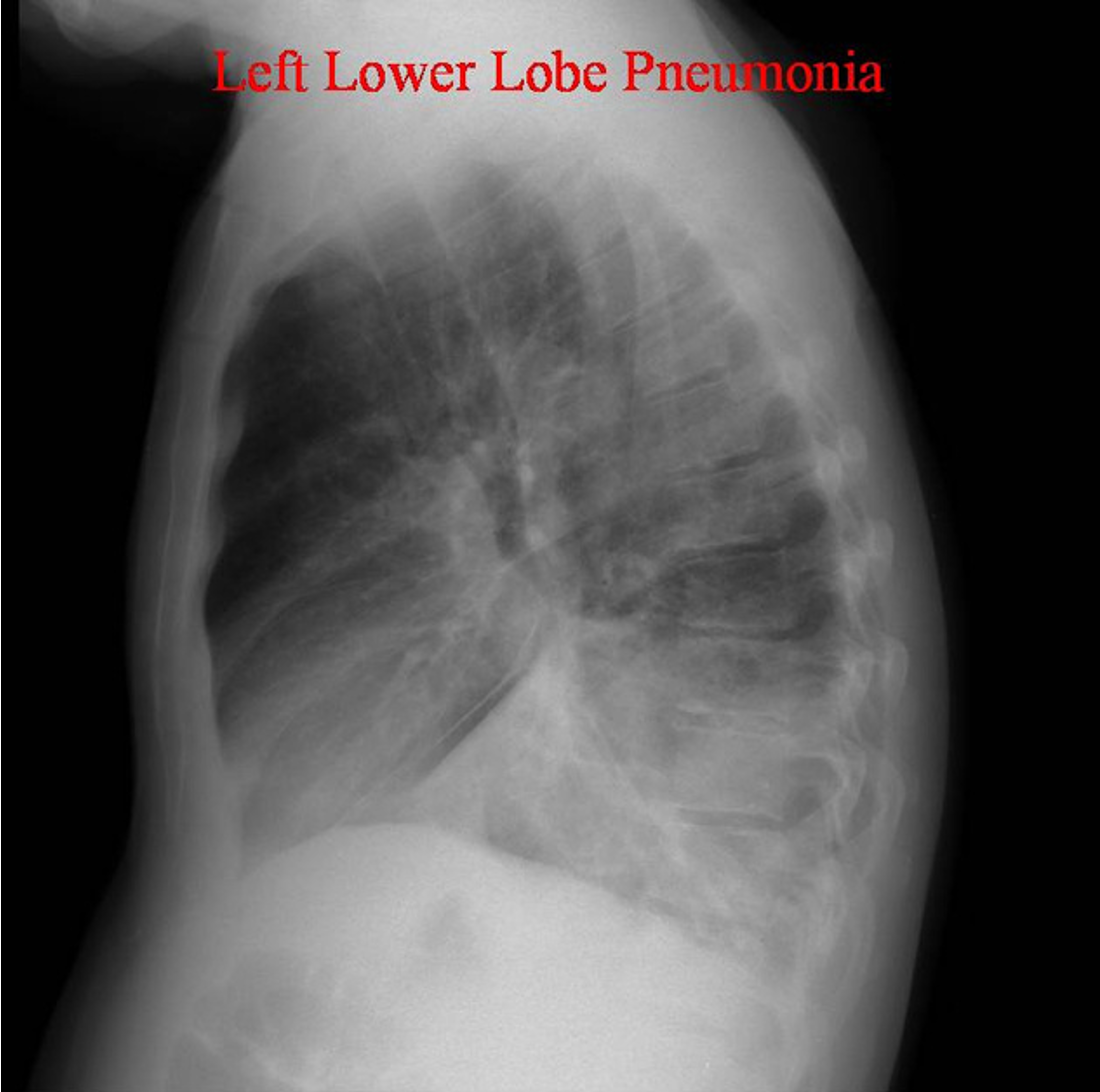
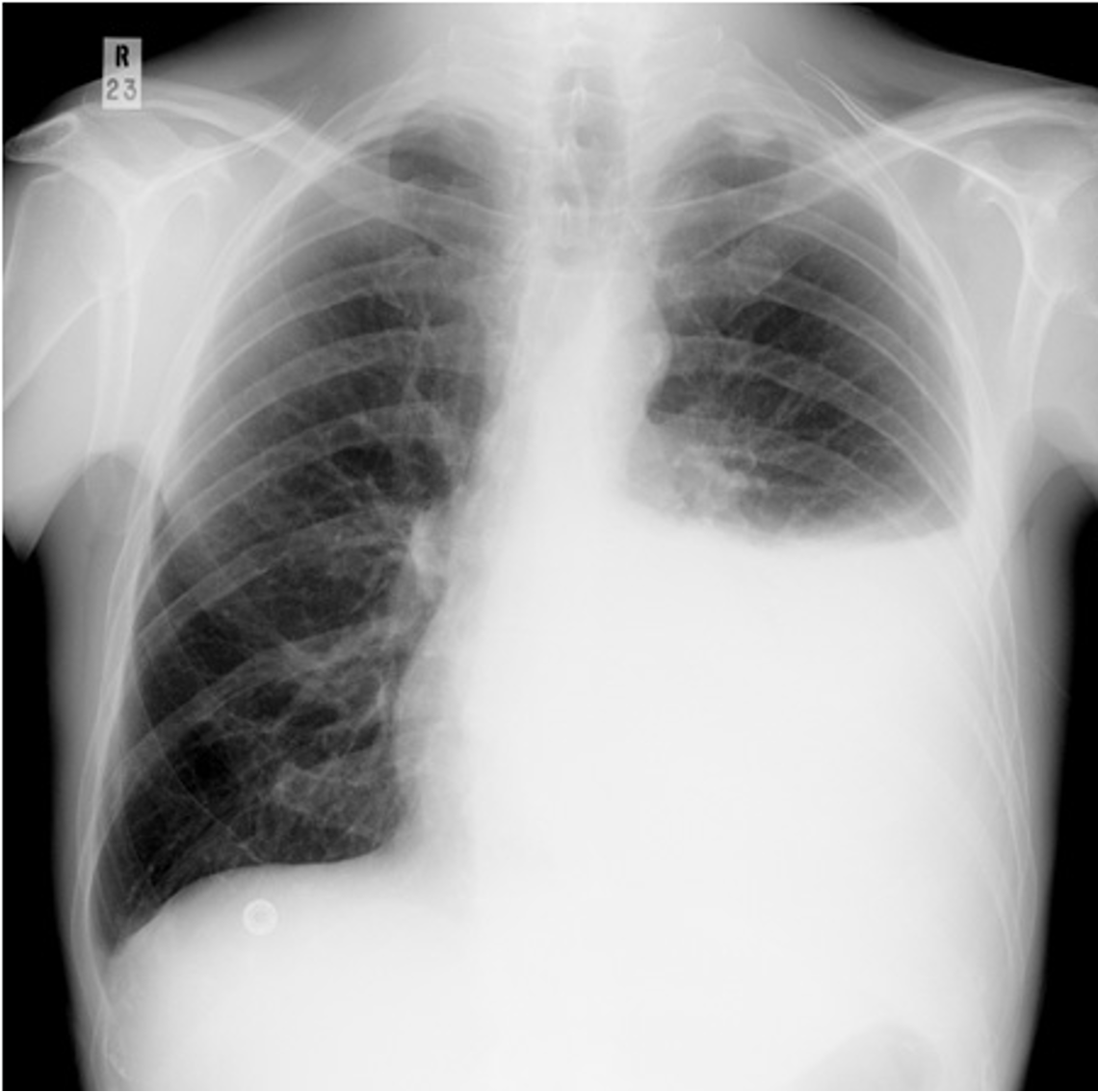
What is this?
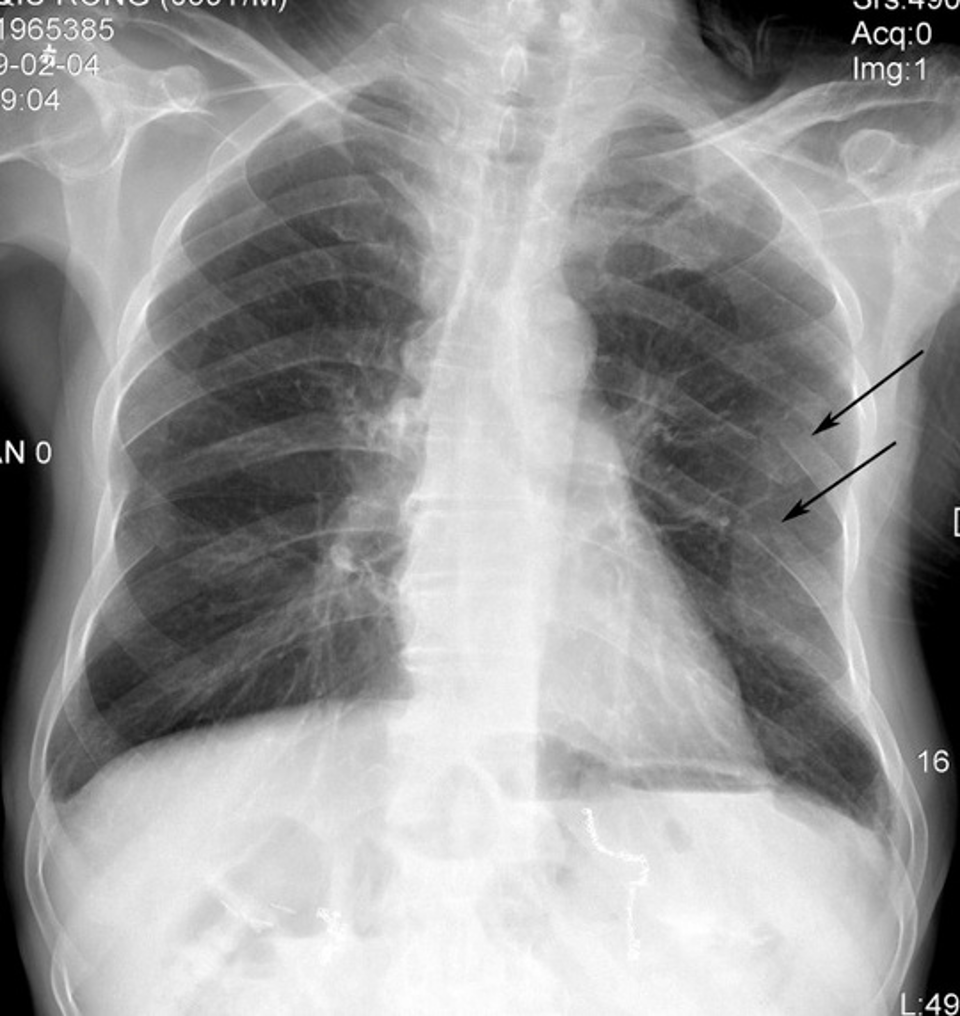
What is this?
Broken rib
An endotracheal tube should be placed at least 1 cm above the carina. If improperly placed, what is a potential complication?
Improper placement of an endotracheal tube can lead to atelectasis (collapse) of a lung.
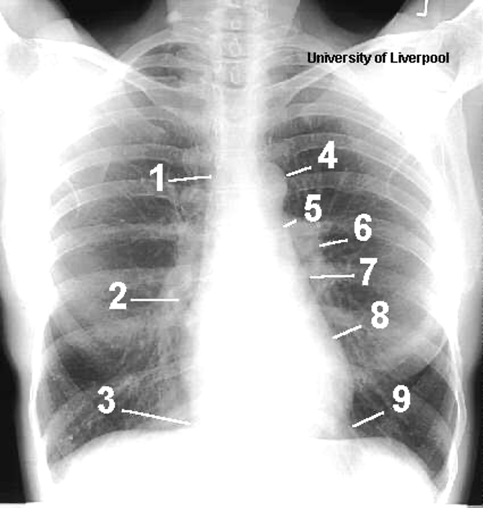
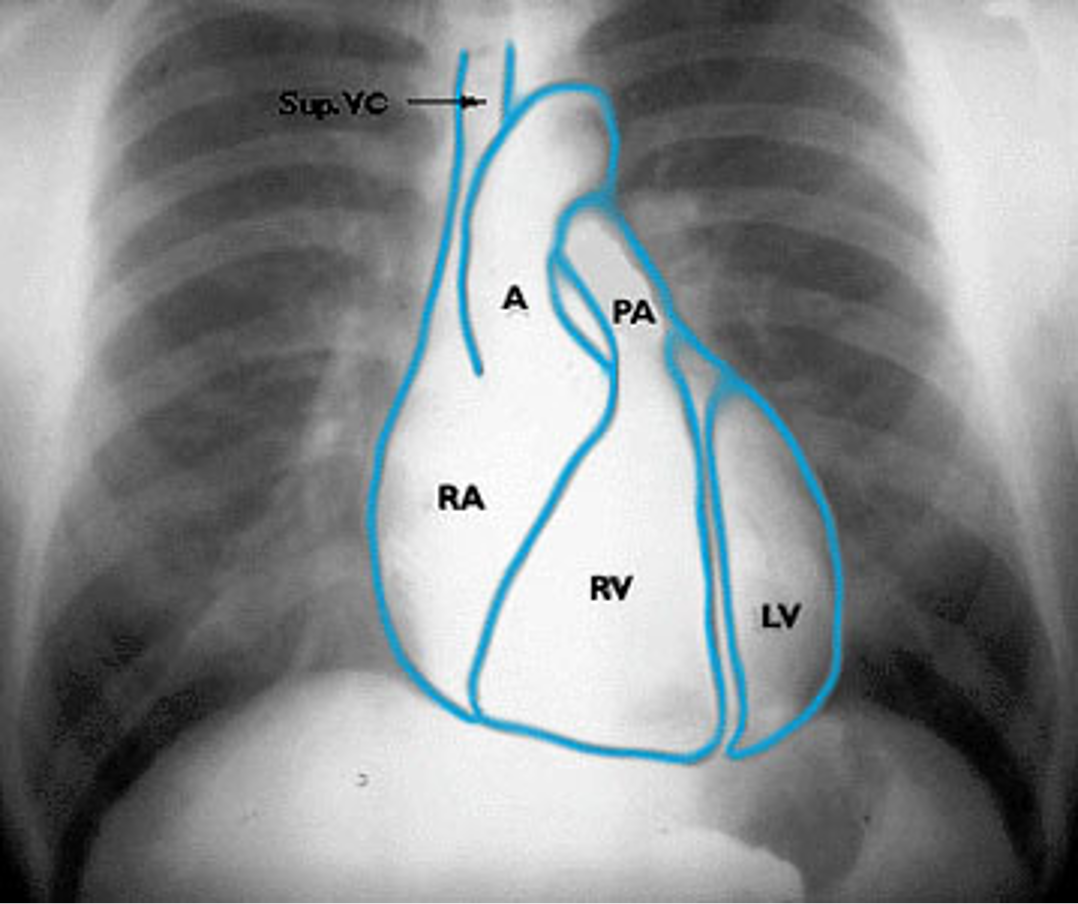
Name the structures according to number
1- superior vena cava
2- right atrium
3- inferior vena cava
4- aortic arch or knob
5- left pulmonary trunk
6- left pulmonary artery
7- left atrium
8- left ventricle
9- left cardiophrenic angle
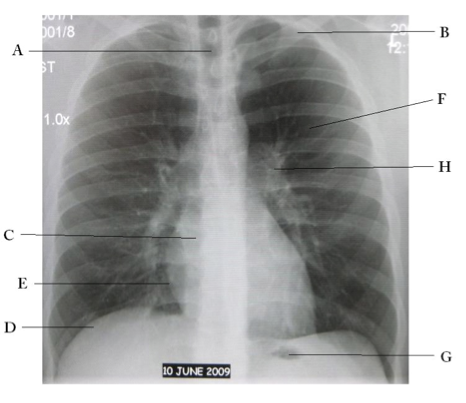
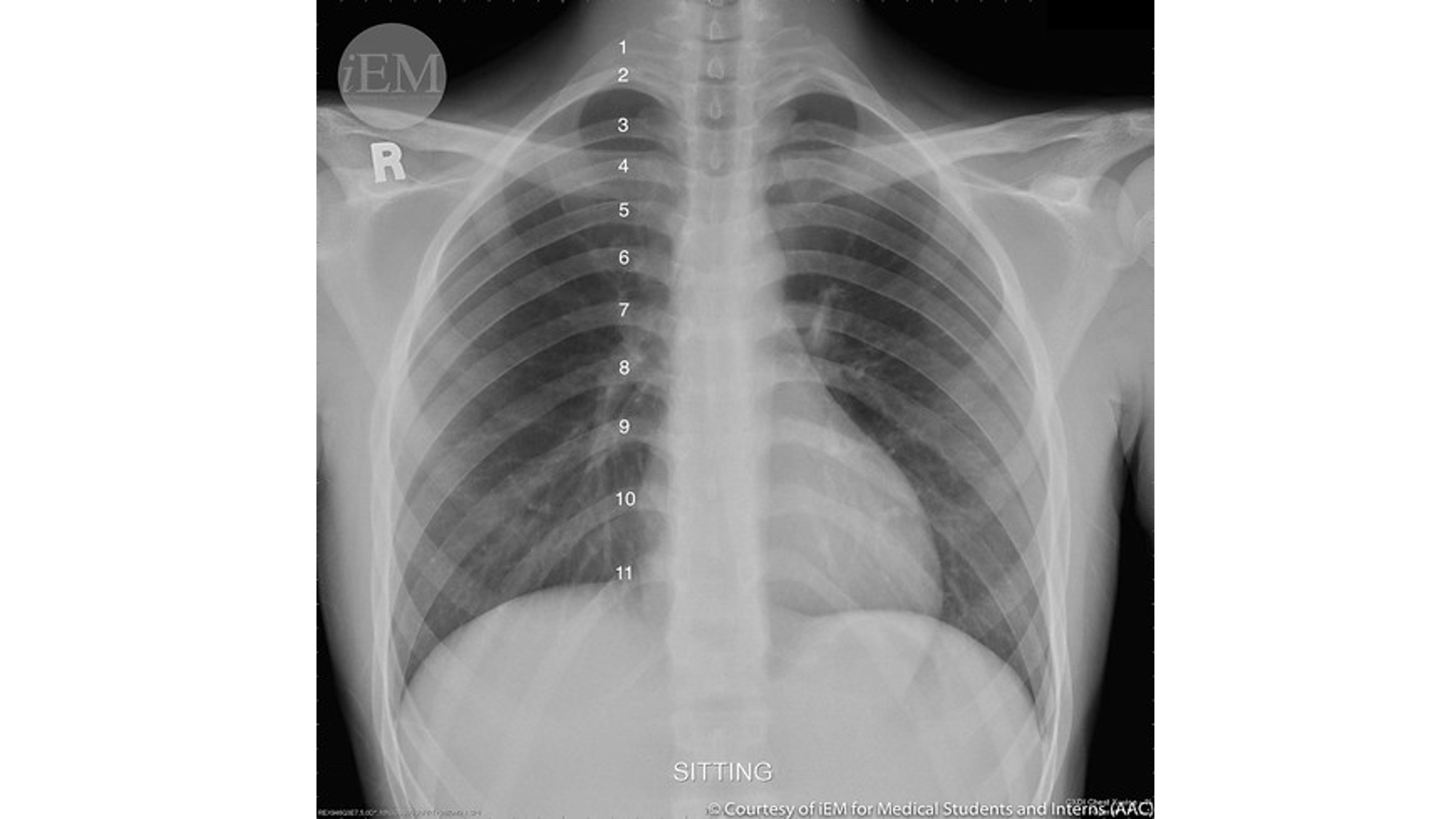
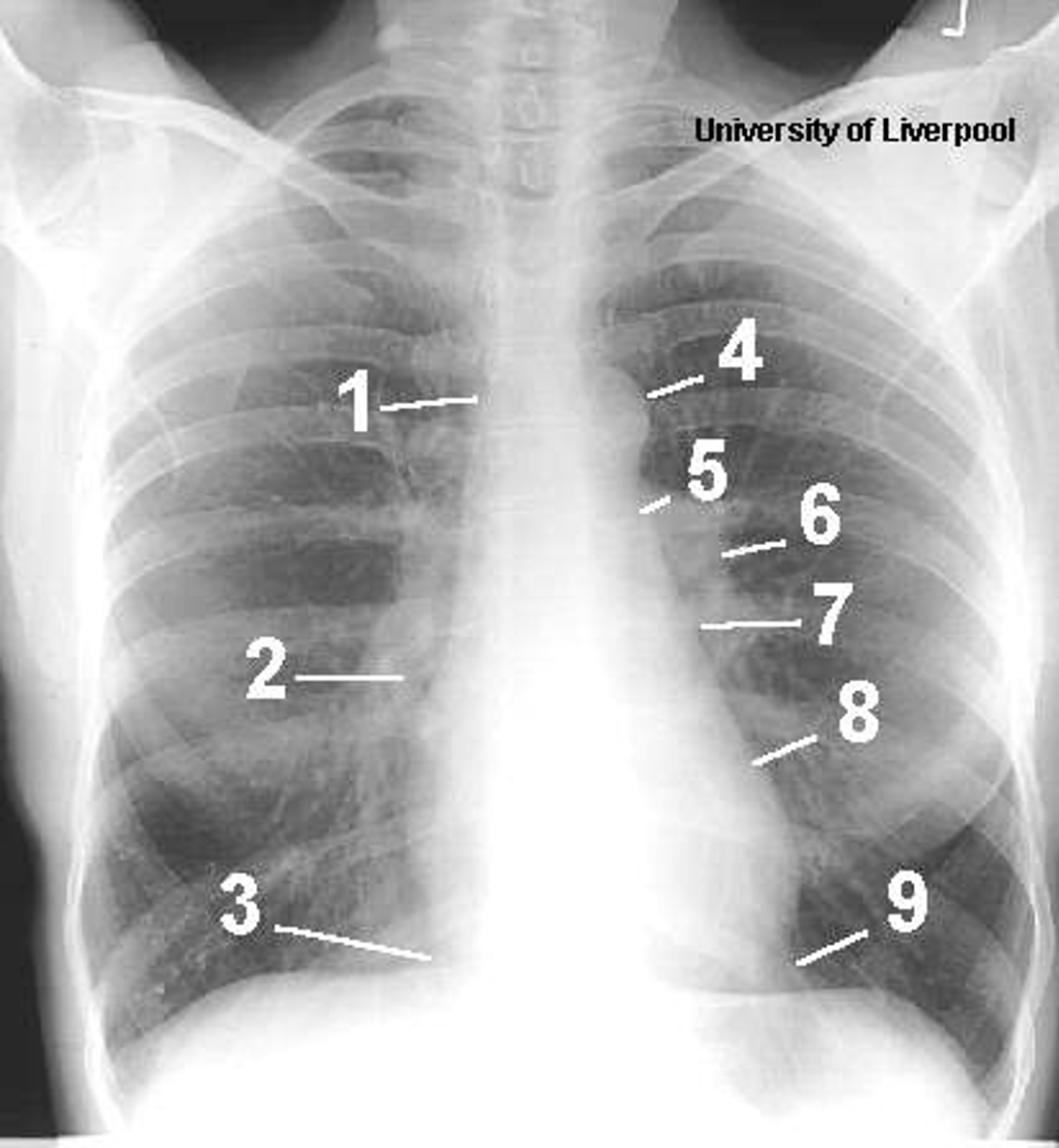
Name the structures according to letter
A – Trachea
B – Clavicle
C – Right Atrium
D – Diaphragm
E – Cardiophrenic angle (Costocardio)
F – Left upper lobe
G – Gastric Bubble
H – Left Hilum
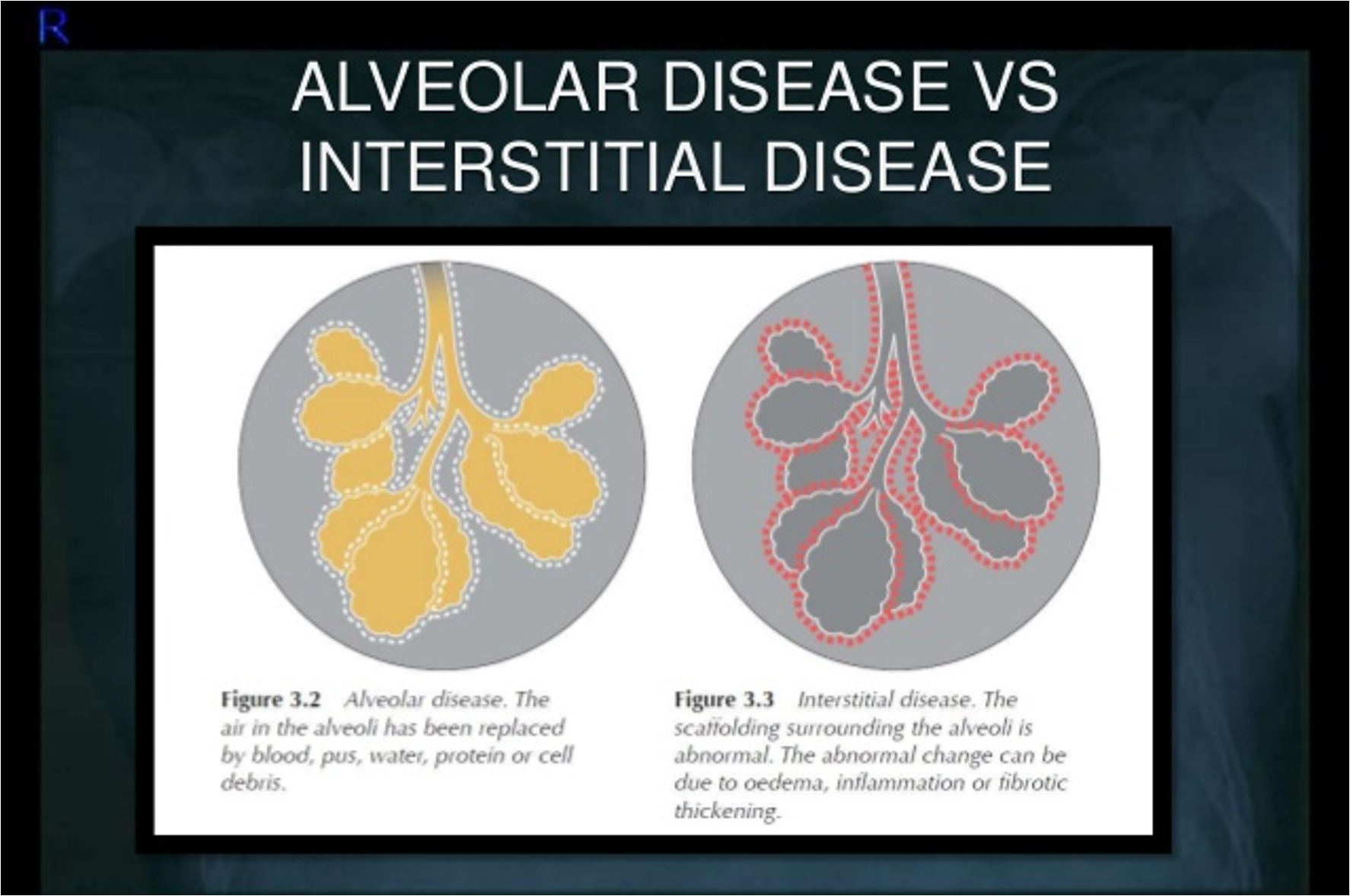
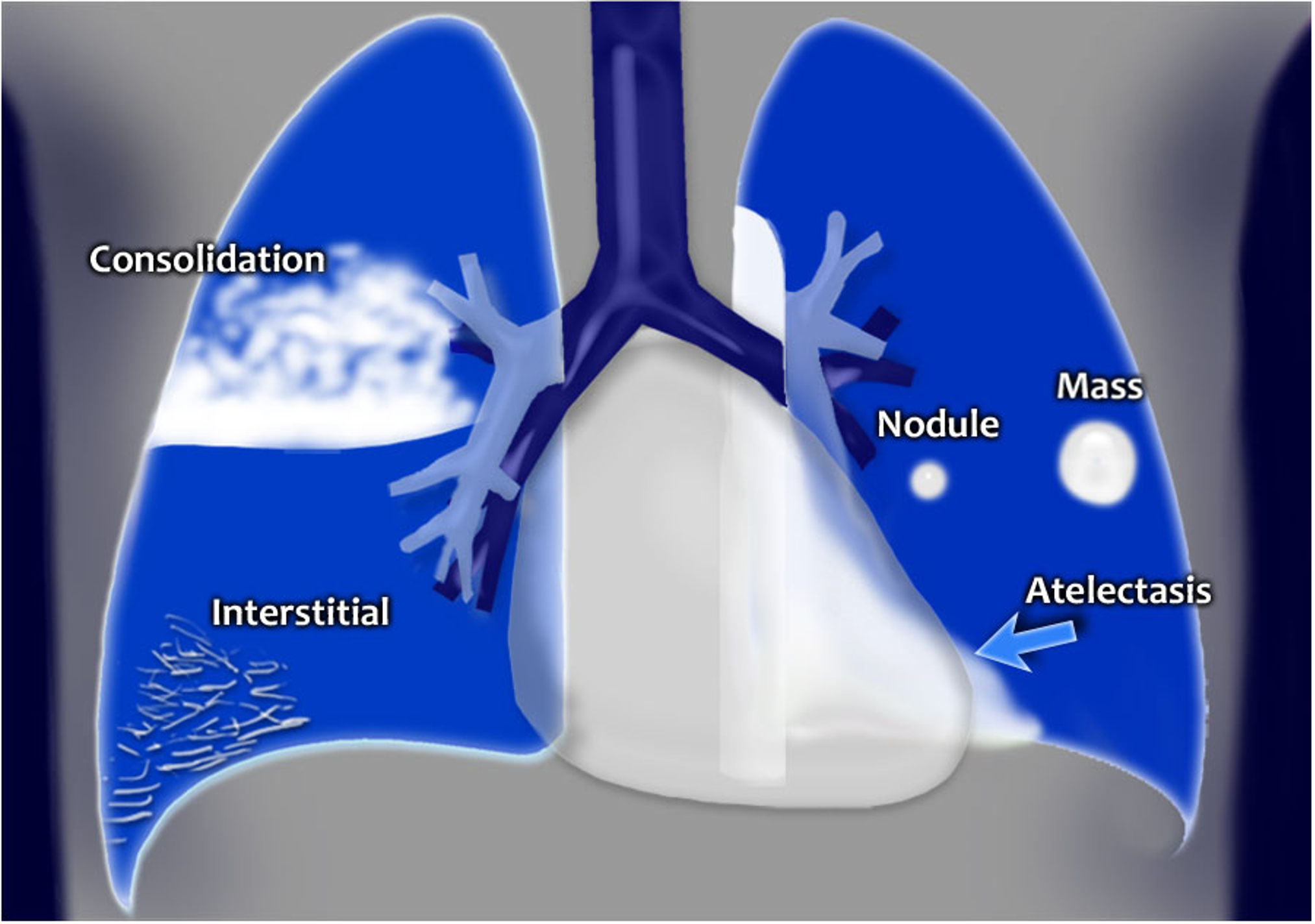
Air space pathology infiltrates: ______ & ______
alveolar & interstitial
Which type of infiltrate tends to be localized
alveolar
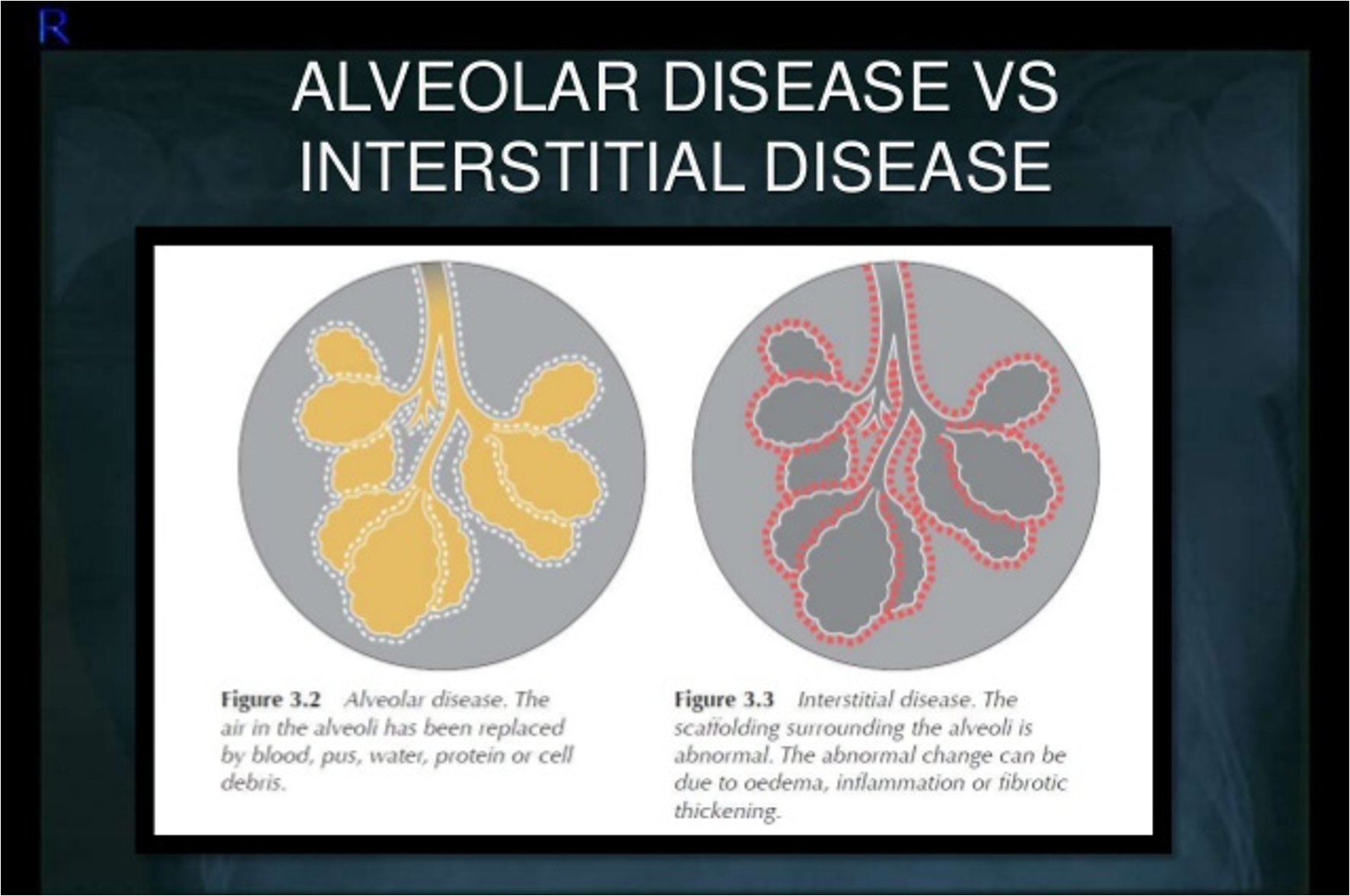
Which type of infiltrate is diffuse?
interstitial
______ happens when the alveoli can’t inflate properly. It can be caused by pressure outside of the lung, blockages, low airflow or scarring. The most common cause is surgery with anesthesia. It typically resolves after treating the underlying cause.
Atelectasis
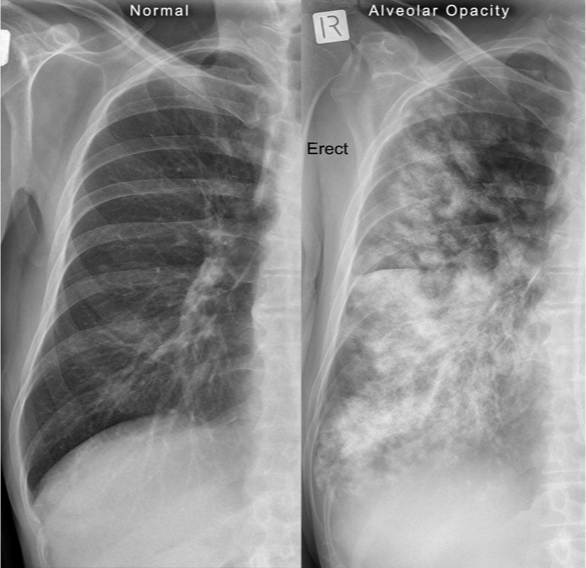
Radiographic finding described as poorly marginated density or “fluffy”
alveolar infilatrate
NOTE: alveolar infiltrates can appear as fluffy or as complete consolidations
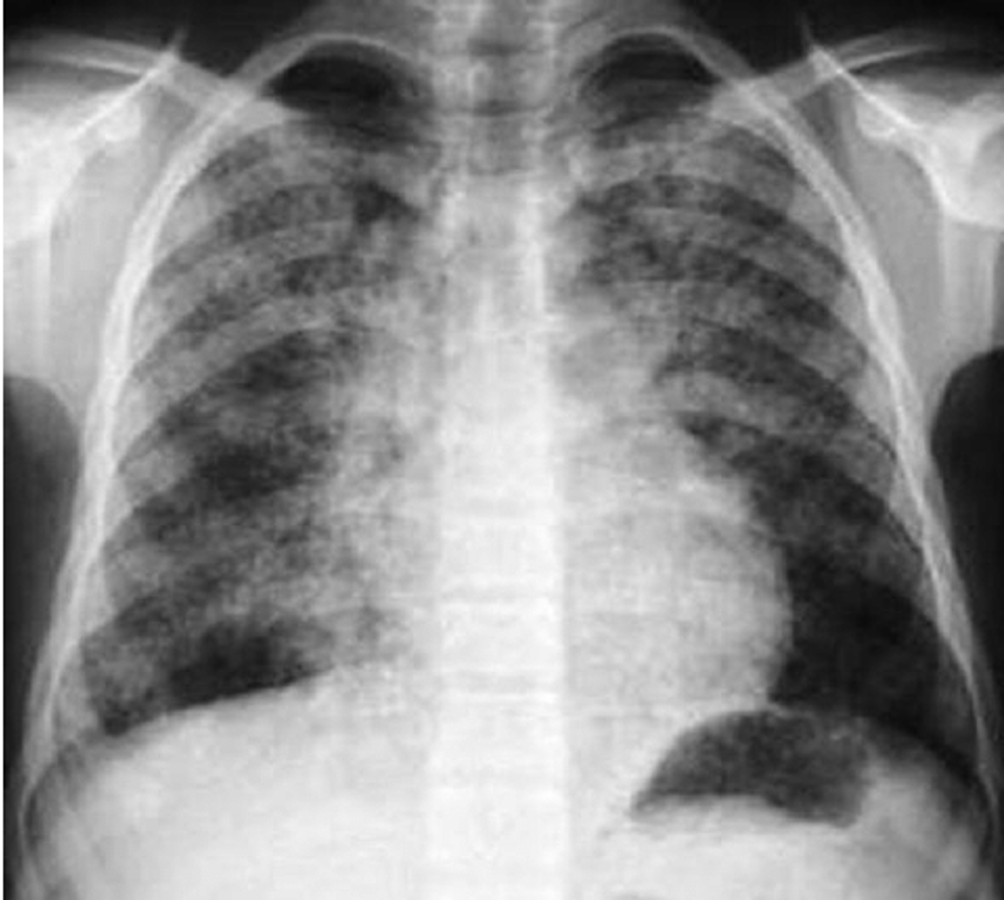
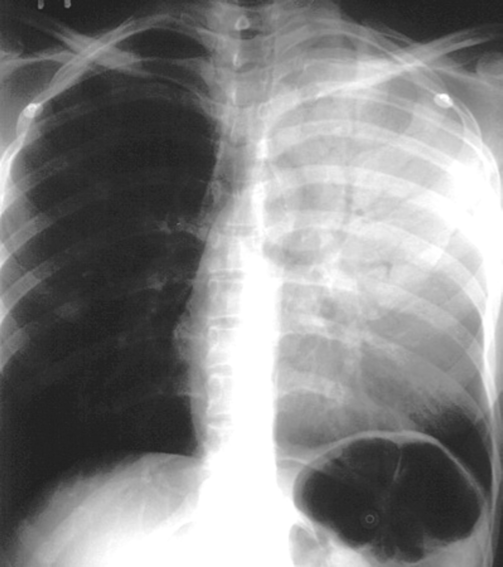
Pattern seen on CXR or CT scans when air-filled bronchi become visible against a background of dense lung tissue.
Air bronchogram sign
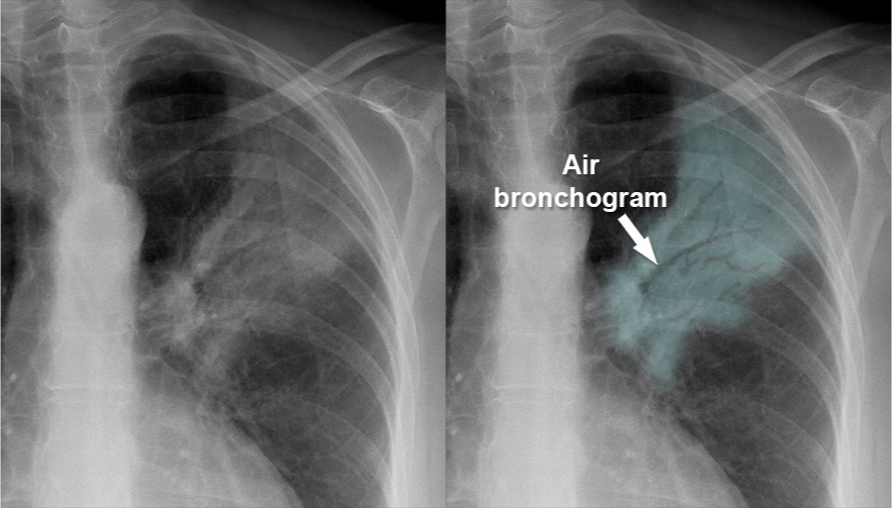
Which air space pathology is usually diffuse, seen as thin white lines and sometimes may present with a honeycomb appearance?
interstitial infiltrates
Are interstitial infiltrates specific or non-specific?
non-specific
NOTE: can be caused by many processes such as CHF, pulmonary fibrosis, collagen vascular diseases etc.
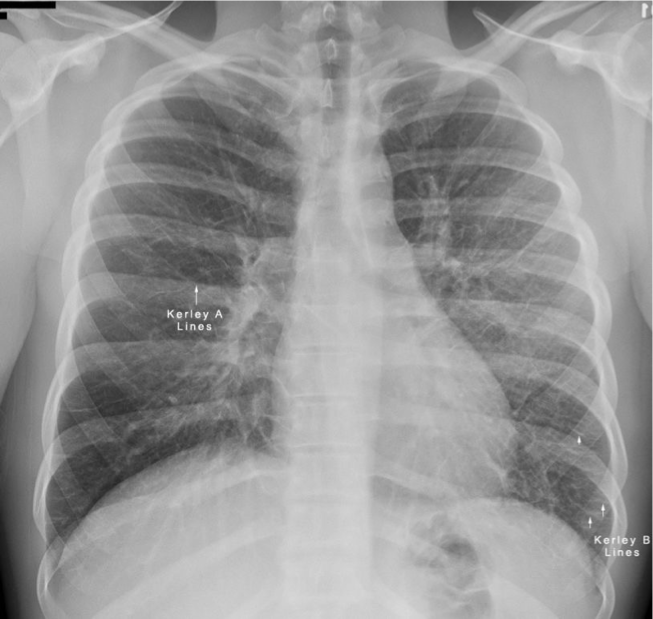
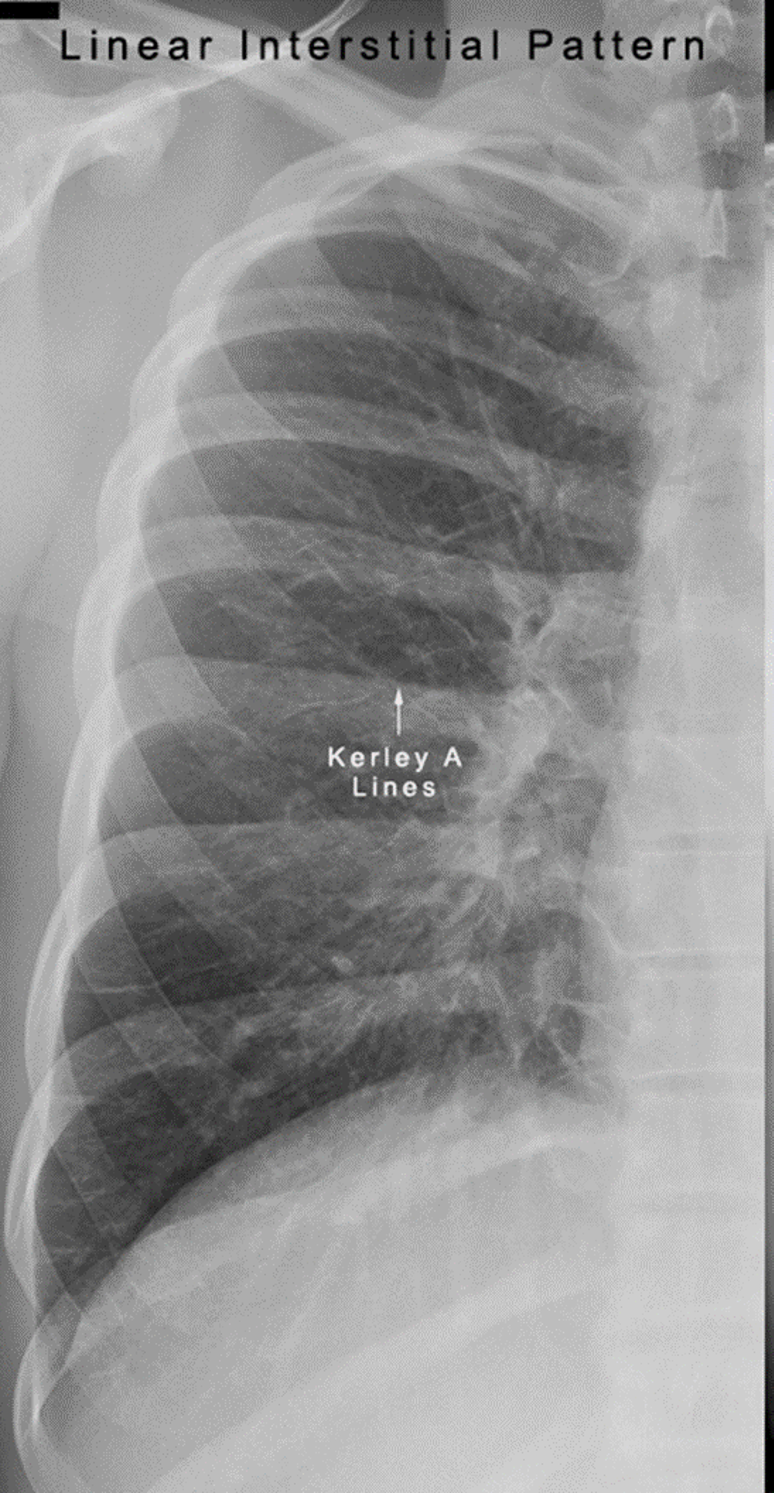
Differentiate between Kerley A vs Kerley B lines.
Kerley A: linear opacities extending from periphery to hila
Kerley B: small, horizontal, peripheral lines seen at the lung bases (represent thickened interlobular septa on CXR)
Interstitial infiltrate pattern on CXR found in patients with interstitial pulmonary edema?
Kerley lines
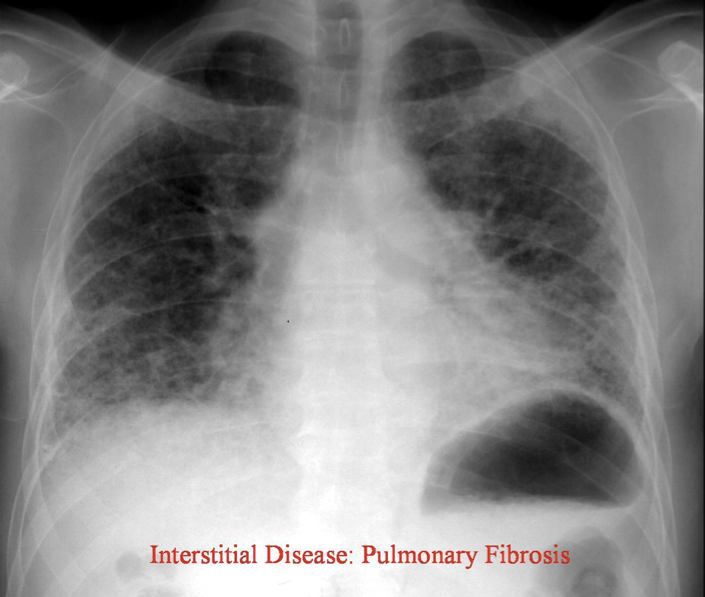
How would you describe the interstitial pattern on CXR in pulmonary fibrosis?
Reticulonodular
On a CXR, what is a spine sign?
A radiographic sign indicating pleural effusion, where the appearance of the spine becomes more visible due to the overlying fluid.
What microorganism is the most likely cause of interstitial pneumonia in normal adults?
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
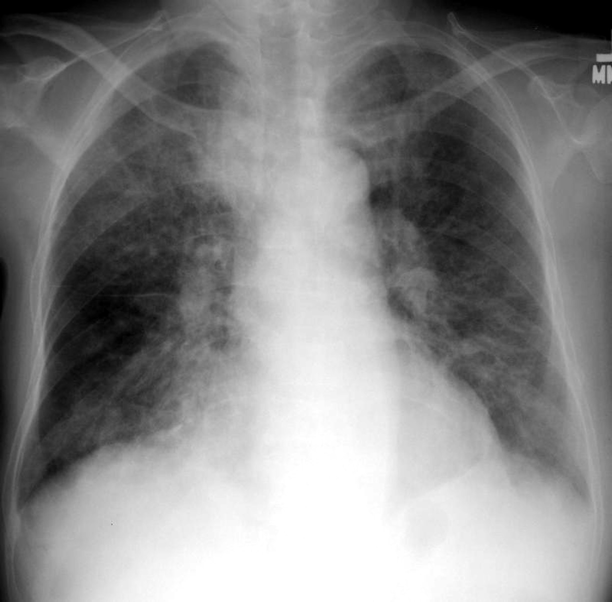
PJP
is a type of pneumonia caused by the fungus Pneumocystis jirovecii, primarily affecting immunocompromised individuals. Evolves from a normal CXR to an interstitial pattern to an alveolar pattern.
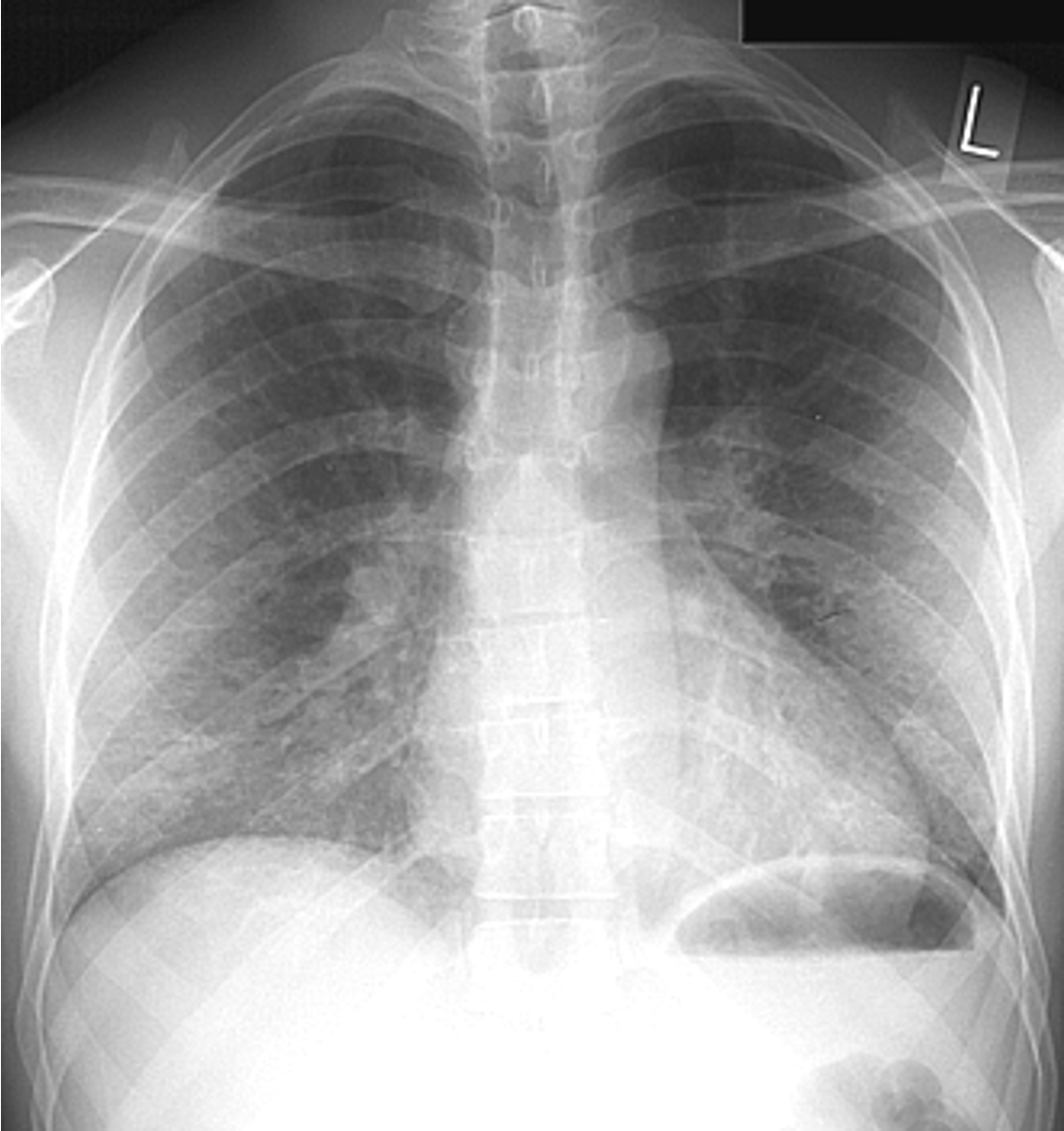
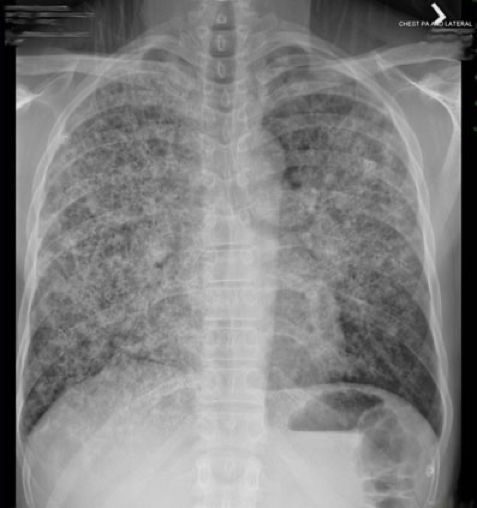
CXR showing diffuse bilateral reticulonodular interstitial infiltrates. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Cystic PJP
What population does PJP most commonly affect?
Primarily immunocompromised individuals, such as those with HIV/AIDS, cancer, or those on immunosuppressive therapy.
Most common imaging feature of ARDS
bilateral airspace opacities and consolidations
What is the most common benign tumor of the lung?
hamartomas
When would a CT scan be indicated for a pulmonary nodule?
> 3 cm in patients younger than 35
any size in patients older than 35
Definitive diagnosing and staging of lung cancer?
Diagnosis = bronchoscopy
Staging = CT scan with contrast
Most common type of lung cancer; usually occurring peripherally.
adenocarcinoma
Lung cancer typically occurring centrally and with cavitation
squamous cell carcinoma
Type of lung cancer that often presents as an indistinct hilar or perihilar mass
small cell carcinoma
Type of lung cancer that can occur either peripherally or centrally and grows rapidly with early metastasis.
non-small cell carcinoma
What are common sites of metastasis with lung cancer
liver, adrenal glands, bones and brain
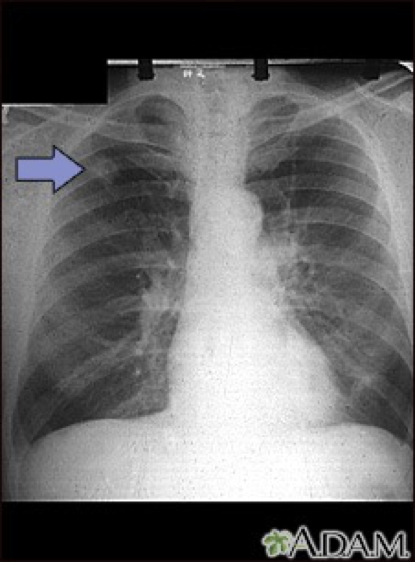
Type of lung cancer commonly occurring peripherally
adenocarcinoma
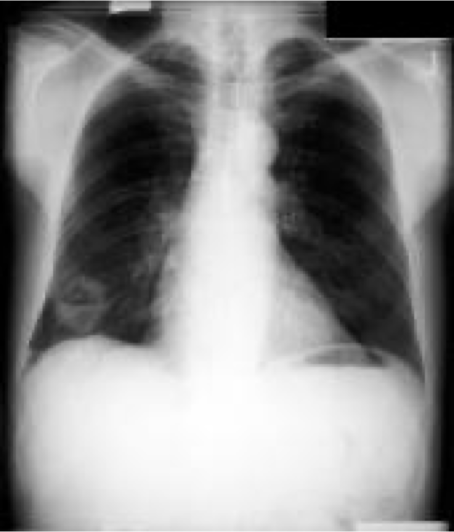
What type of lung cancer is this?
squamous cell carcinoma
Type of lung cancer that commonly exhibits mediastinal lymphadenopathy
small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC)
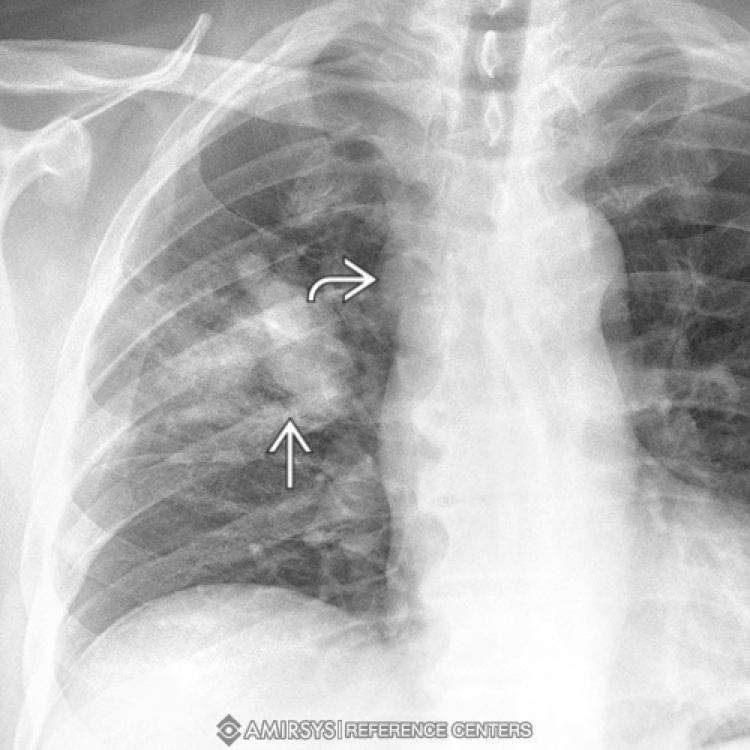
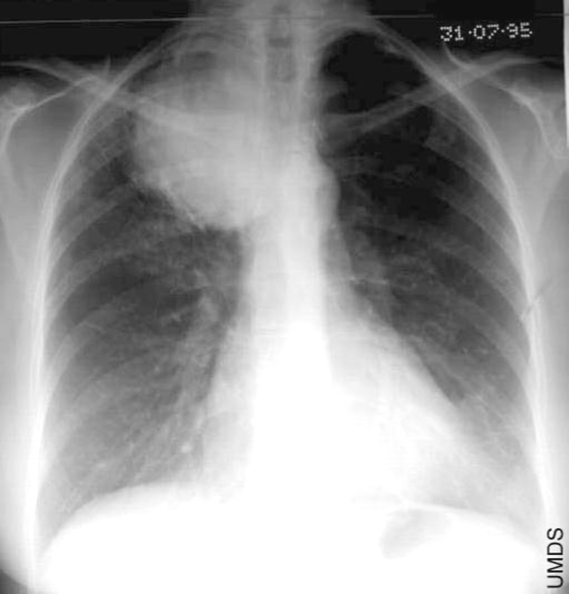
What is a pancoast tumor?
Type of lung cancer located at the lung apices
Silhouette sign?
Loss of normal contour between adjacent structures on imaging
Spine sign?
Radiological finding indicating a lung mass adjacent to the spine
What does spine sign look like on lateral CXR?
Localized opacity of the spine; due to a lung mass in the posterior mediastinum obscuring the normal appearance of the vertebral bodies