Pulmonary Assessment Terms & Definitions for Medicine Study
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is dyspnea?
- A common presenting symptom of pulmonary disorders
- This is air hunger/suffocation vs increased effort/WOB vs chest tightness
- It can be positional: orthopnea, platypuses, or trepopnea
What causes dyspnea?
- Respiratory diseases: airway, parenchymal lung, pulmonary vascular, pleural issues, neuromuscular issues, chest wall issues
- CV: increased respiratory drive, deconditioning, obesity, anxiety
What is the purpose and cause of coughing?
- purpose: clear and protect airway
- Causes: airway irritants, airway diseases, parenchymal disease, heart failure, drug induced issues
What does coughing clear secretions indicate?
- Viral infections, allergies
What does coughing thick yellow or green secretions indicate?
- bacterial infection
What does coughing thick, cloudy, and sticky secretions mean?
- TB
What is hemoptysis? What are the pulmonary and non-pulmonary causes of this?
- Coughing or spitting up blood
- Pulmonary causes: Airway, parenchymal, vascular, impaired coagulation, and pulmonary endometriosis
- Non-pulmonary: nasopharynx, GI issues
Where id diaphragm pain referred to?
- Shoulder
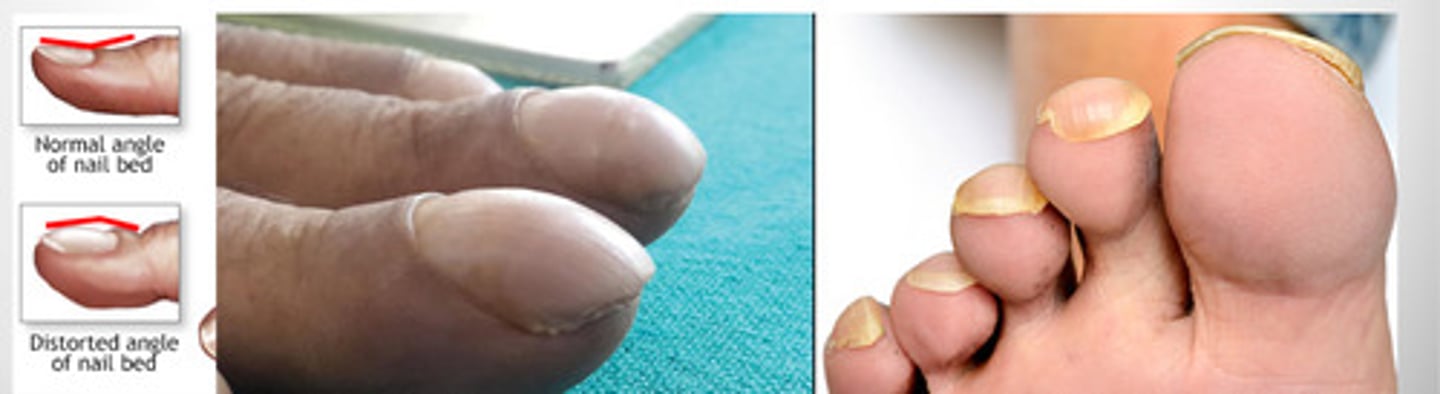
What is nail clubbing and why does it happen?
- Occurs due to lack of blood flow which means low O2
What does dyspnea mean in terms of WOB, what occurs in the nostril here?
- Dyspnea leads to increased WOB and nasal flaring
What is the appearance of cystic fibrosis?
- Barrel chests, hypertrophy accessory muscles, forward head, shoulder protraction, decreased core and spine stabilization/endurance, LE muscle tightness, Tripod/forward lean in sitting/standing
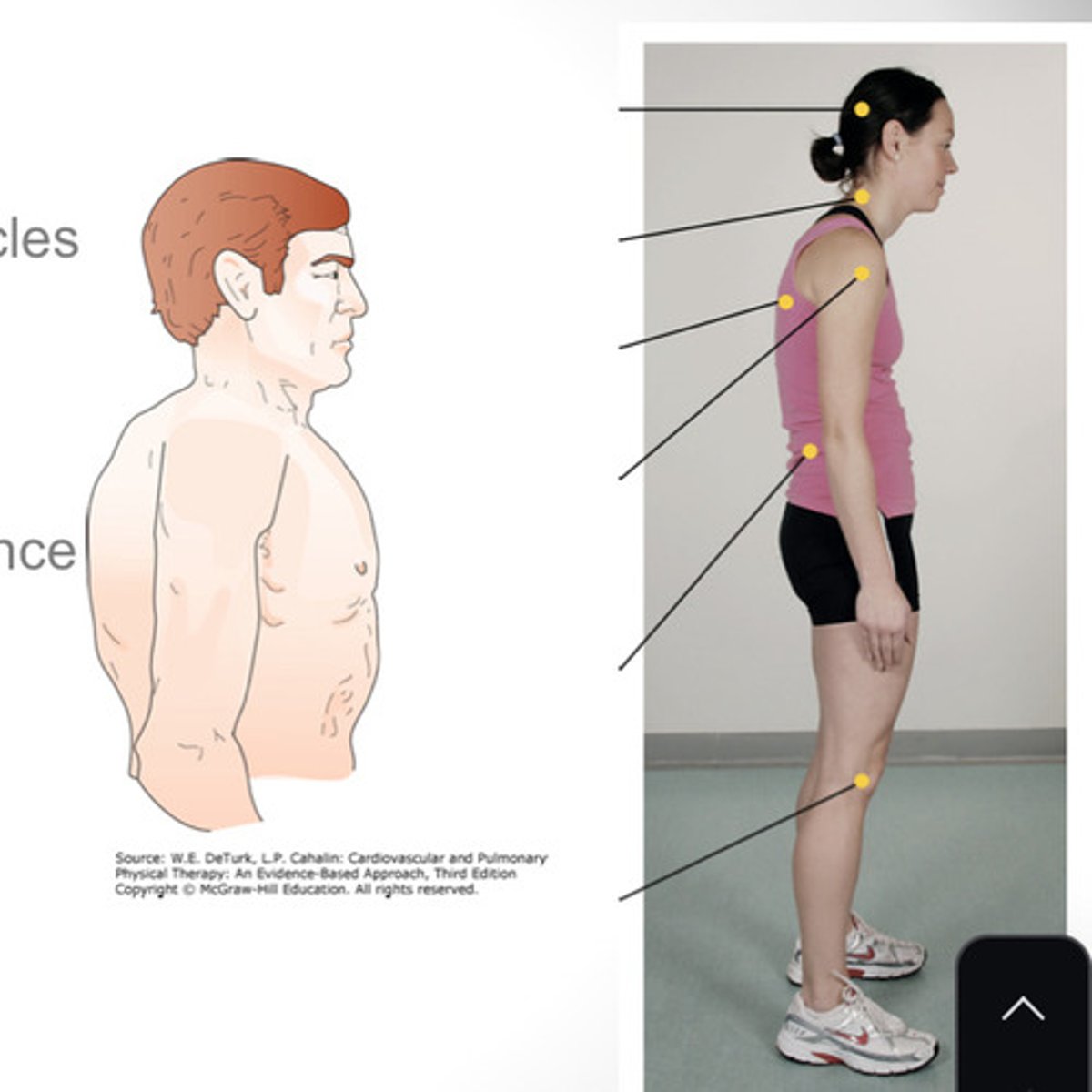
What is the appearance of obstructive lung diseases?
- generalized muscle wasting, barrel chest, accessory muscle use, forward leaning posture, protracted head and scapula, T/S kyphosis, scapular elevation, cyanosis, tripod position
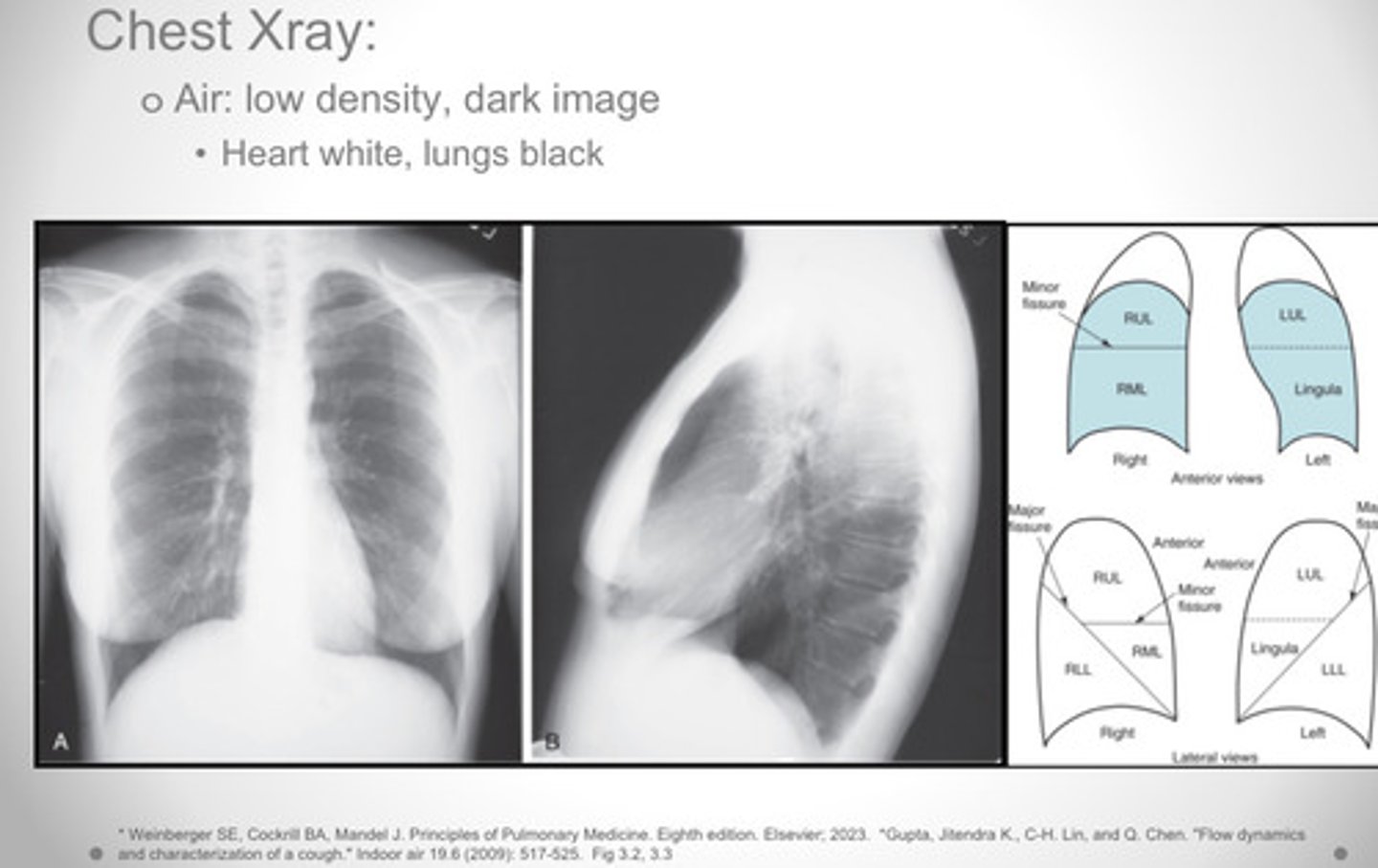
What does a chest X Ray look like?
- Air: low density so it forms a dark image
- heart, bones, etc. are dense and white
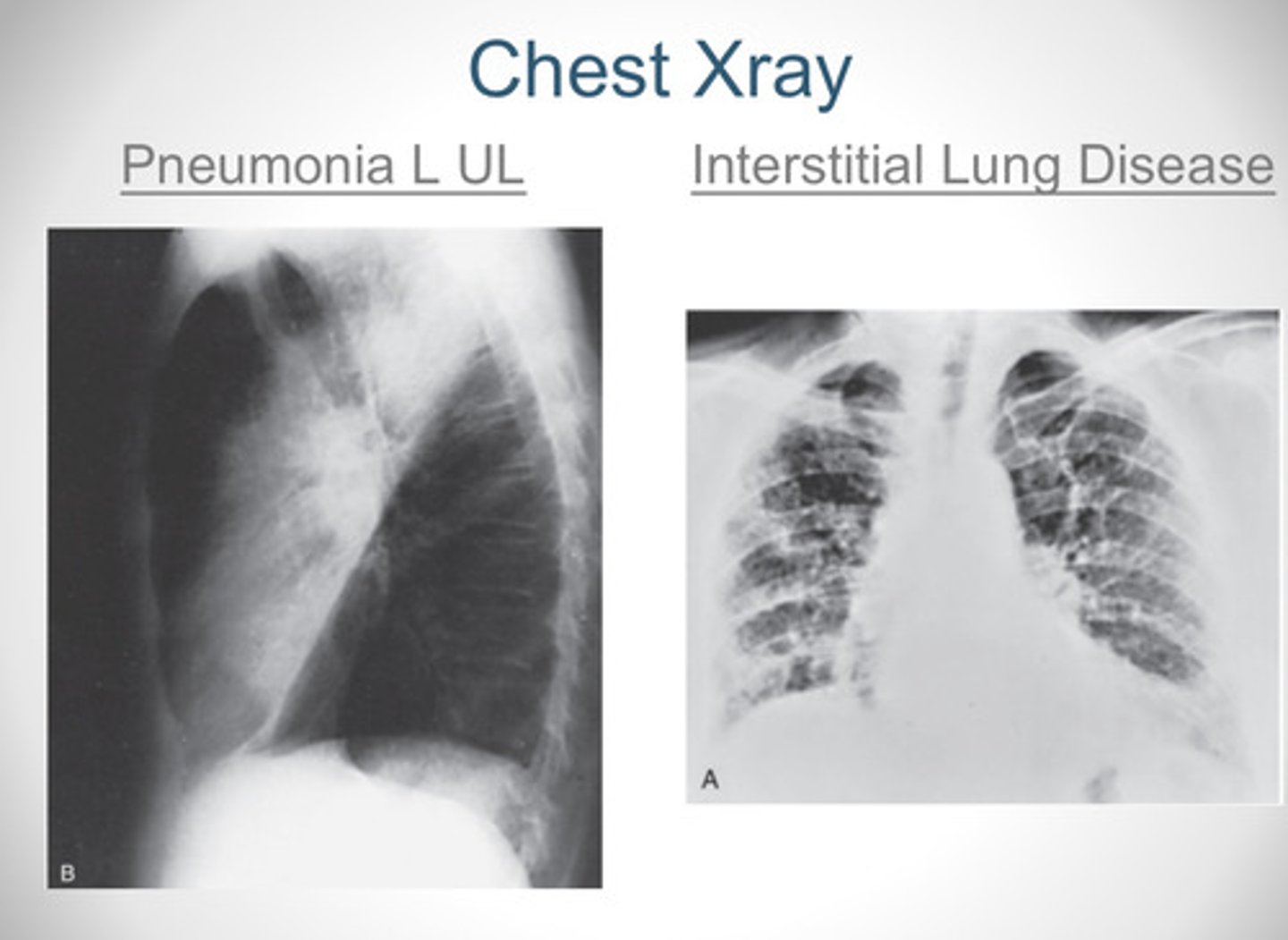
What does pneumonia look like on an X-Ray? How about interstitial lung disease?
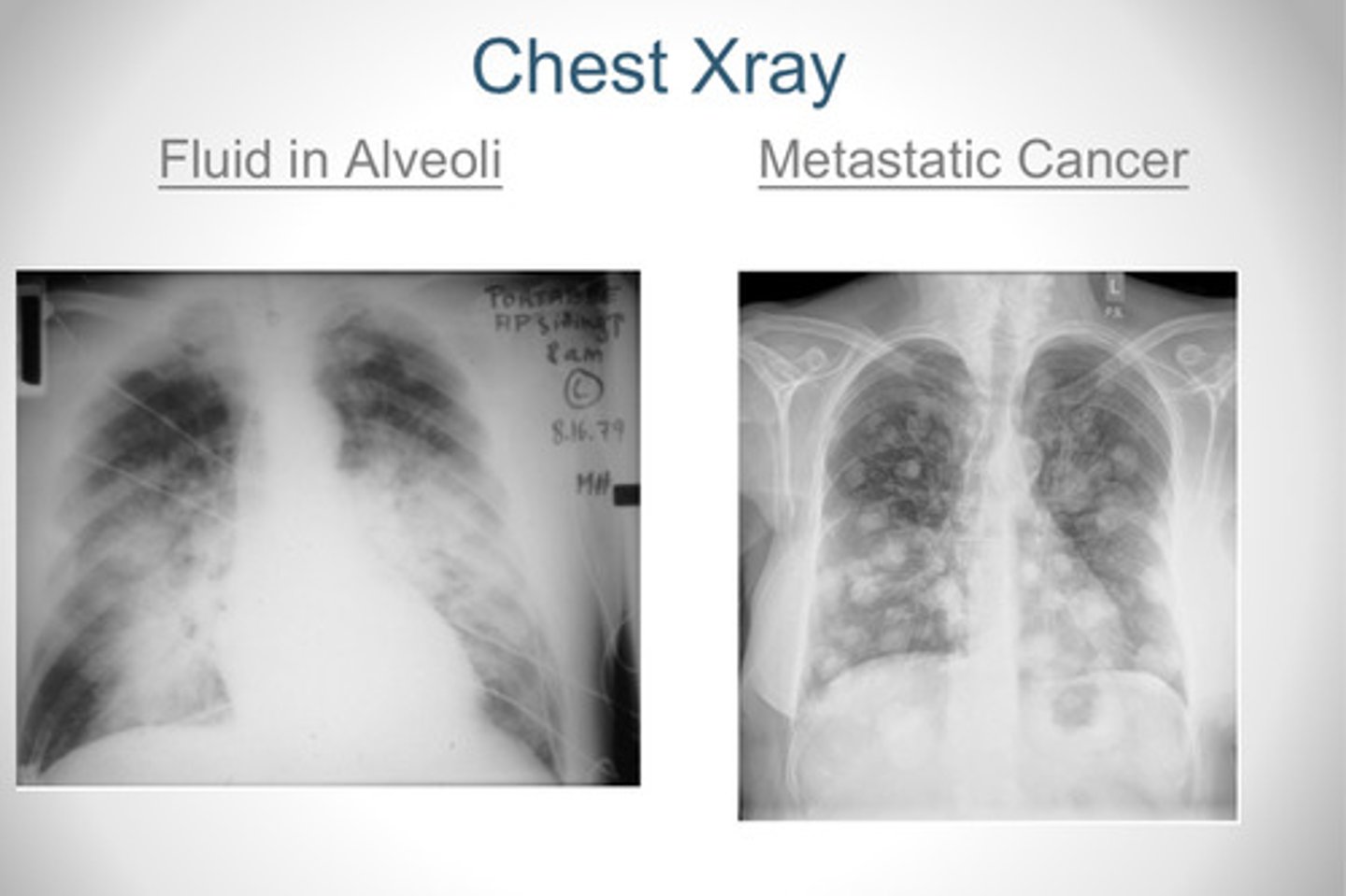
What does fluid in the alveoli look like? What about metastatic cancer?
What is the purpose of a V/Q scan?
- The purpose is to assess ventilation and perfusion of the lungs
—— The Dx: pulmonary embolism, regional lung function
- This is done via IV and inhaled radio-isotope
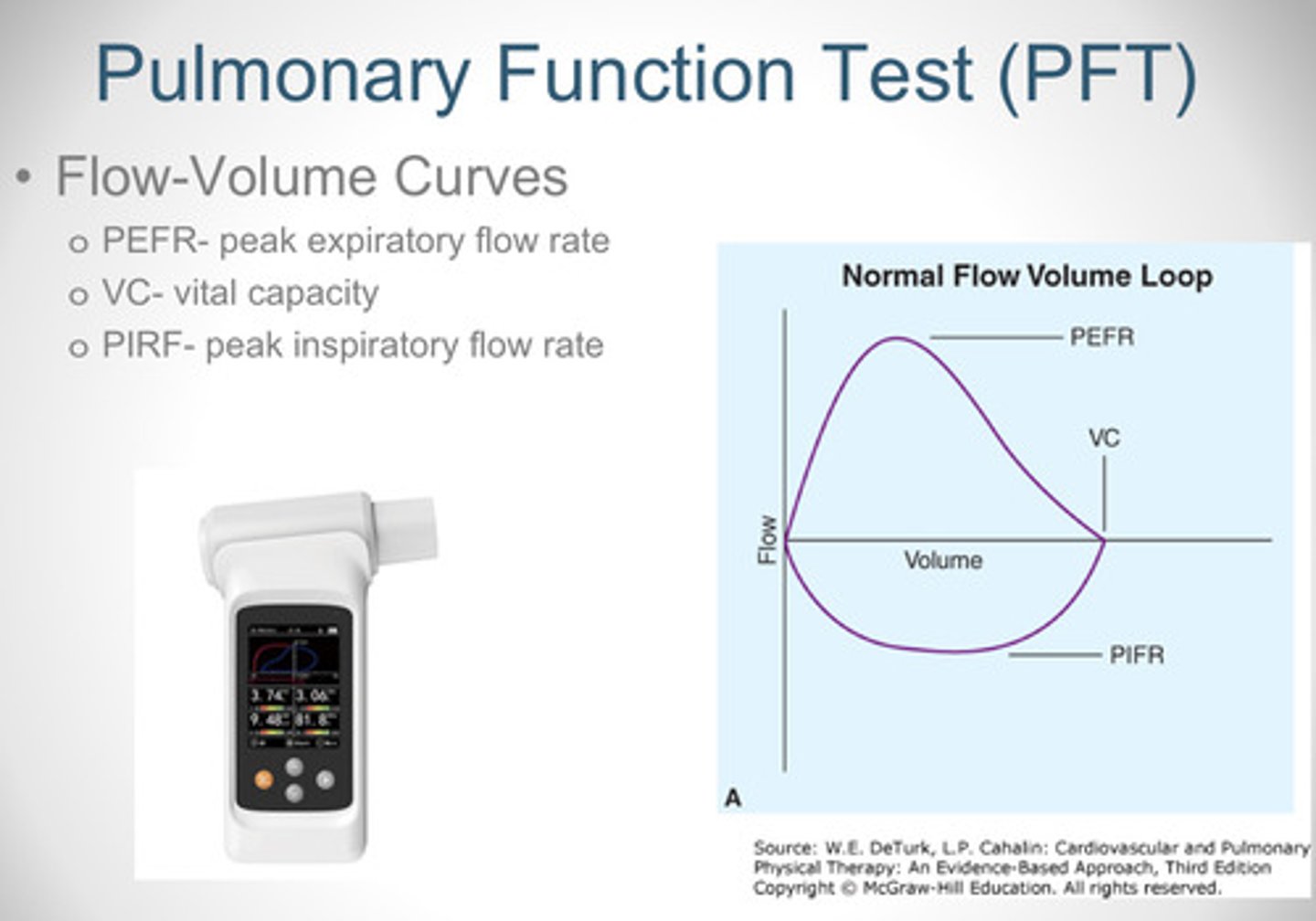
What is the purpose of a pulmonary function test?
- assess volume and flow during inhalation and exhalation
- Polmonary disorders have characteristic changes in volumes and flow volume curves
What does a PEFR, VC, and PRRF mean in a pulmonary function test (PFT)?
- PEFR: peak expiratory flow rate
- VC: vital capacity
- PIRF: peak inspiration flow rate
Review ABGs from ex phys
What is the purpose of a chest wall excursion?
- Assess the motion of chest wall during inhalation and exhalation
- Measure at 3 spots:
—— upper: fourth rib and thumbs as sternal angle
—— middle: xiphoid process
—— Posterior at 10th rib
What is normal diaphragmatic excursion?
- Normal is 3-5cm
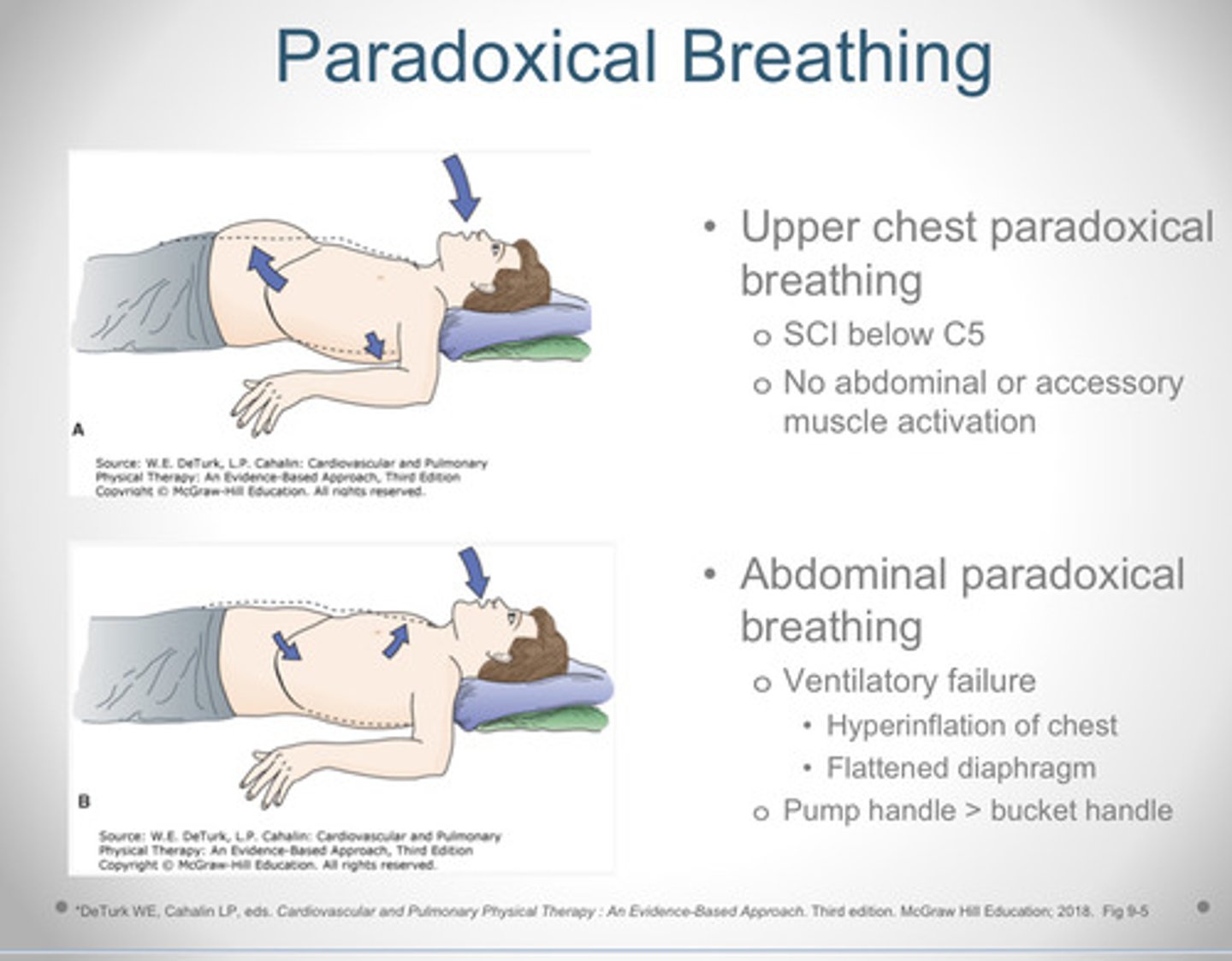
What is paradoxical breathing in the upper chest and abdomen?
- upper chest paradoxical breathing: SCI below C5, no abdominal or accessory motion innervation
- Abdominal paradoxical breathing: Ventilatory failure: hyperinflation of chest, flattened diaphragm. Pump handle is above the bucket handle
What is egophony?
"Aaaa" is heard as the patient says "eeee" indicates consolidation
What is bronchophony?
when you hear the patient say "99" more clearly or louder than normal
What is whispered pectoriloquy?
a whispered phrase heard through the stethoscope that sounds faint and inaudible over normal lung tissue
Learn all of the sounds on pages 32-33
Why is traditional exercise testing used in this setting?
- Typically this is a cycle ergometer or treadmill
- Has the purpose of understanding the cause and severity of dyspnea, understanding O2 and CO2 relationships during rest and exercise determine level of exercise tolerance, investigate presence of heart disease
- Vitals plus ABG we want to see here