Homologous Recombination
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Homologous Recombination requires
• Homologous sequences share high levels of sequence identity
• e. g. maternal and paternal copies of a chromosome
• e.g. sister chromatids after replication
• Antiparallel strands from homologous chromosomes can base-pair with one another
same order of genes nearly identical sequences slight differences due to replication errors, etc
this can happen anywhere there is homology (not just at ends)
Homologous Recombination is
an essential part of meiosis I
• Recombination that results in “crossing over” leads to diverse combinations of alleles in gametes
• This is one way that offspring are genetically different from their parents
• Connections between homologous pairs provide tension needed for meiosis to proceed
Homologous recombination requires
double- strand breaks
• Double-strand breaks are induced during meiosis I
• 5’ exonuclease creates an overhang
• The longer strand can base-pair with the homologouschromosome (Rad51-mediated)
diagram steps
paired homologous chromosomes
Spo11, Mre11 nuclease complex
one chromosome cut and ends processed
further processing of 5' ends by nuclease
RecA-like protein catalyzes strand exchange
dna synthesis
Both strands base pair with
strands from the homolog
• DNA Polymerase extends 3’ overhangs
• Ligase joins strands
• Four more single-strand cuts must be made so that the homologs can separate
• The pattern of cuts determines whether the HR results in a crossover or not
• Either way, the site of recombination has a region of heteroduplex
diagram 2 steps
capture of second strand
additional DNA synthesis
additional DNA synthesis followed by DNA ligation
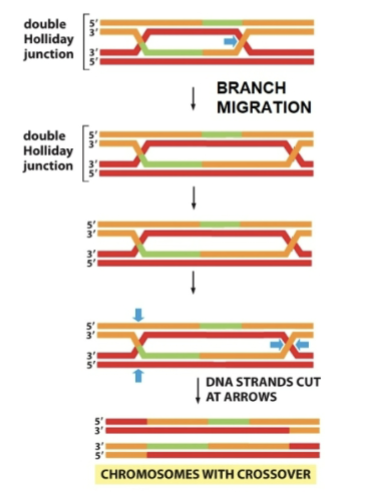
double Holliday junction
DNA strands cut at arrows
chromosomes with or without crossover
without crossover: arrows both pertical
with: vertical left, horizontal right
Strand cutting and ligation
does not always occur at the site where new strand synthesis ends
These junctions can migrate
Mismatch repair can
fix any mismatches that arise in heteroduplex regions
• Mismatch repair proteins are active during meiosis
• Selection of the “correct” strand is random at each site of repair
• This can lead to over-representation of a given allele in the gamete population, but does not always because the reciprocal heteroduplex may be
repaired to favor the opposite allele
mismatch repair diagram
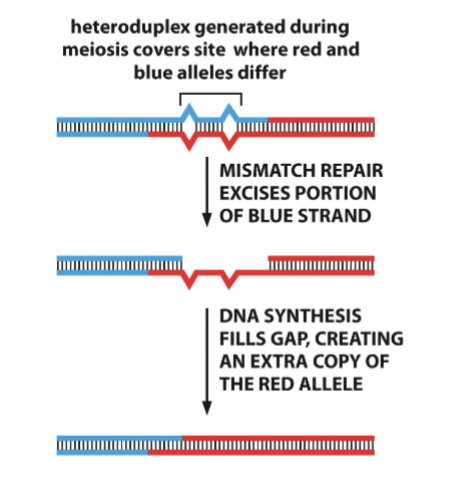
mismatch diagram text
heteroduplex generated during meiosis covers site where red and blue alleles differ
mismatch repair excises portion of blue strand
dna synthesis fills gap, creating an extra copy of the red allele