Lecture 9 and 10 Ocular Anatomy
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
eye
the organ of sight
-an extension of the central nervous system
-contains all four basic tissue types
anteroposterior diameter
~24mm
from front to back of eye
horizontal diameter
~23.5mm
from lateral to medial sides of the eye
vertical diameter
~23 mm
from top to bottom of the eye
anatomic equator
Divides the globe into two unequal halves
-Approximately 13 to 14 mm behind the limbus
13 years of age
what age does the eye reach normal adult size?
eye position in the orbit
anteriorly and slightly closer to the roof than the floor
-more fat in the floor of the orbit
the lateral orbital rim
protects the posterior 1/2 of the globe from the temporal side
lateral portion of the eye
what portion of the eye is most exposed ad more prone to injury?
visual axis
An imaginary line passing from the midpoint of the visual field to the fovea centralis.
orbital axis
line down the center of the orbit
-in line with optic nerve
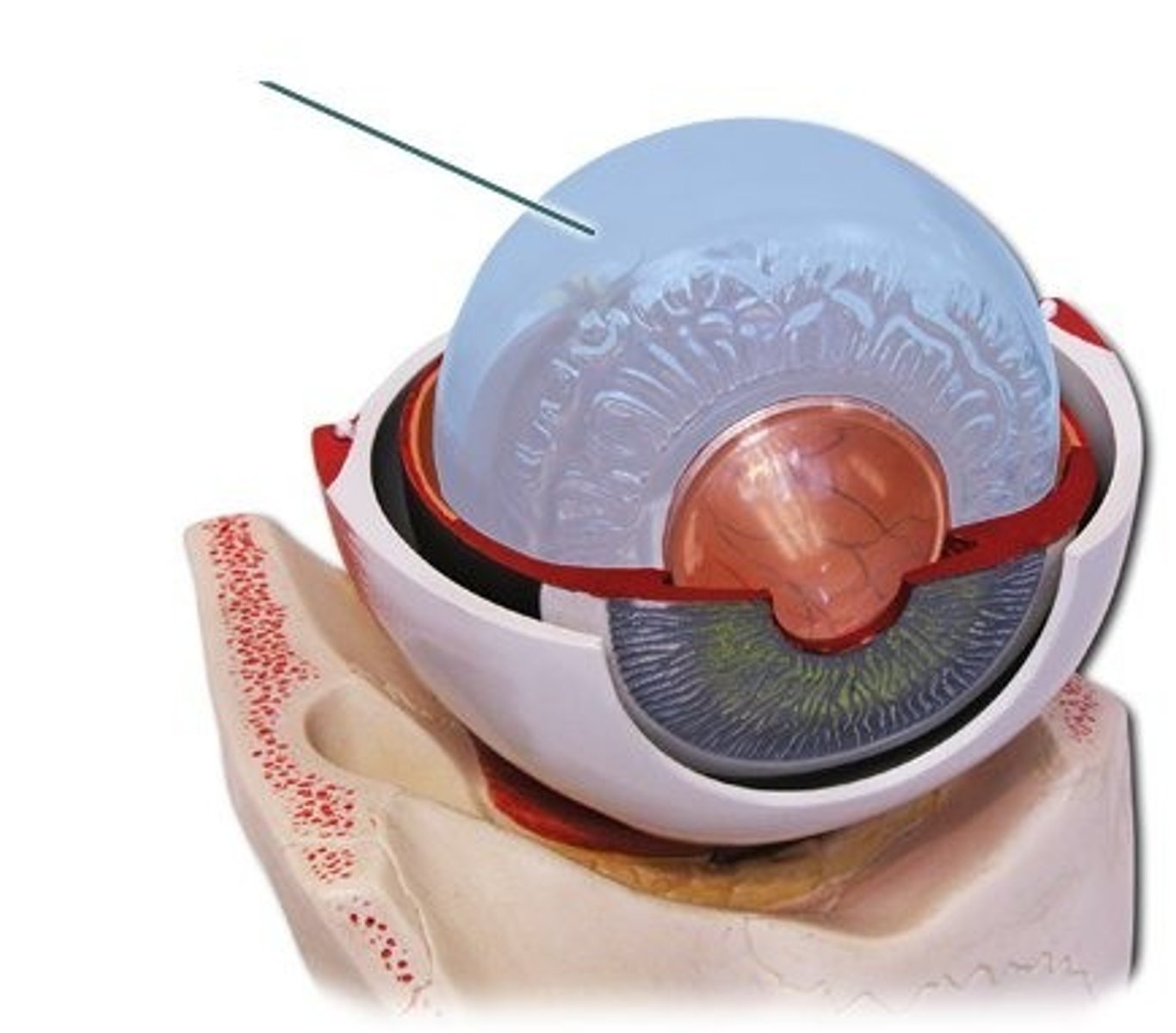
ocular tunics
-Fibrous
-Vascular or Uveal
-Neural or Retina
fibrous tunic
composed of the transparent cornea anteriorly and the opaque sclera posteriorly
-both made of collagen but the arrangement contributes to the colors
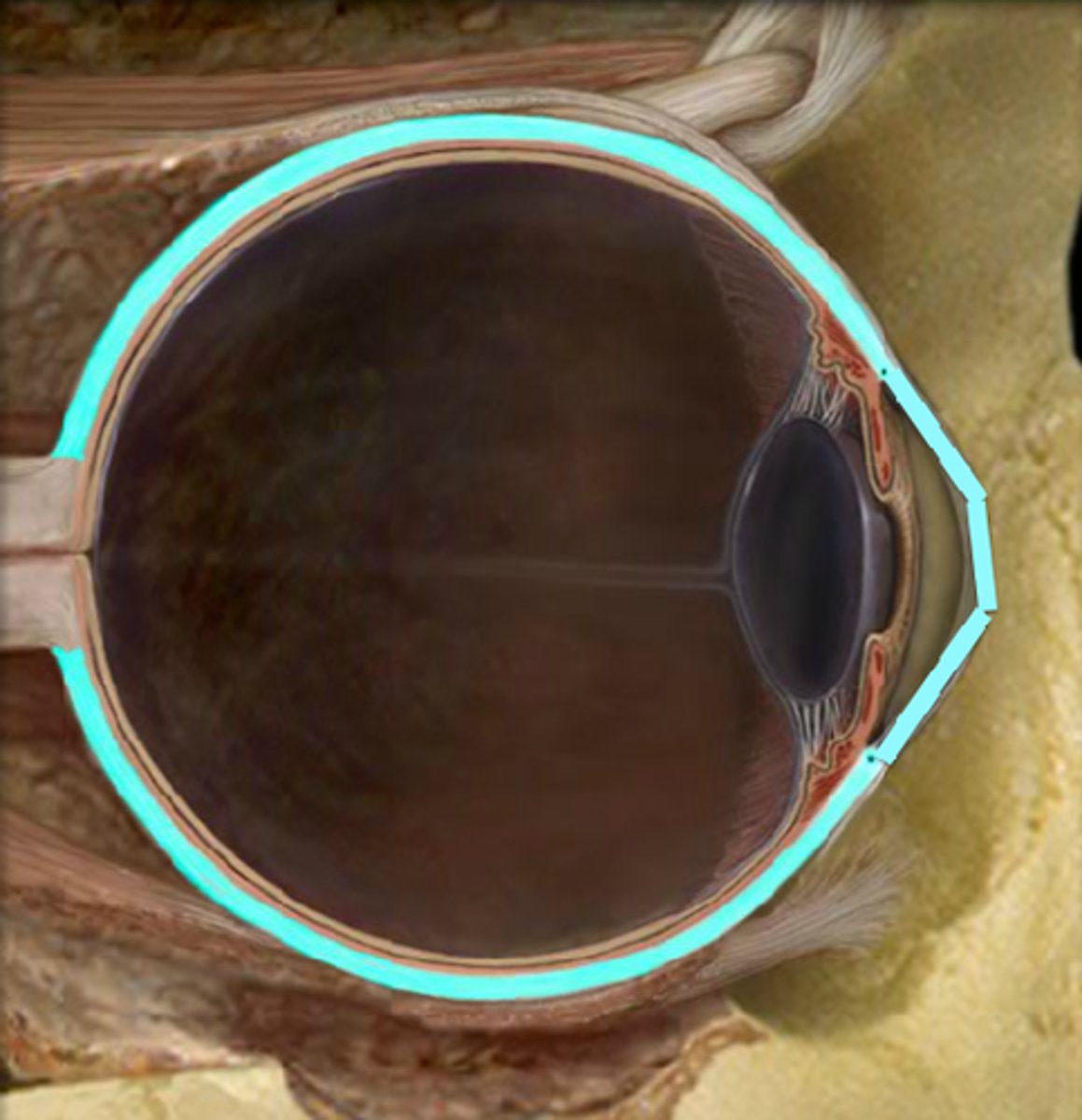
Corneoscleral limbus
where the cornea and sclera merge
sclera function
provides the attachment sites for intraocular structures and extraocular muscles
-uveoscleral outflow pathway for aqueous humor
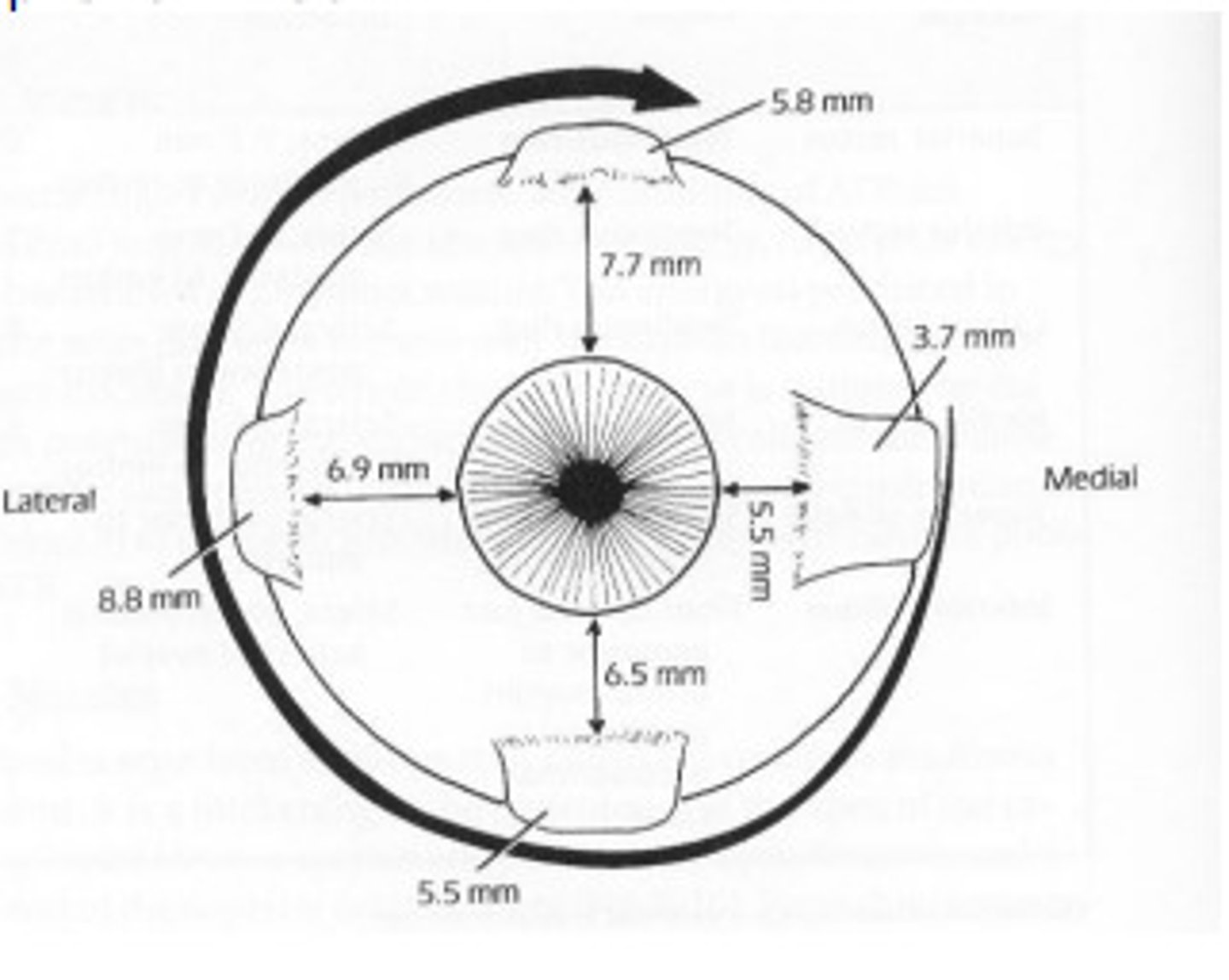
scleral aperatures
allow for passage of blood vessels and nerves to enter and exit the eye
scleral thickness
non-uniform
-greatest around the optic nerve 1 mm
-thinnest just posterior to the insertion of the rectus muscles 0.3 mm
-Continues to increase until it reaches the corneoscleral limbus 0.8 mm
where is the sclera most vulnerable to rupture?
just posterior to the insertions of the rectus muscles (where it is thinnest)
spiral of tillaux
The insertion pattern of the rectus muscles
layers of the sclera
-Stroma
-Lamina Fusca
Episclera
fibrovascular layer situated between the sclera and tenon's capsule
-provides nutrients to sclera
-Thickest anteriorly and thins progressively towards the tendinous insertions of the rectus muscles
Tenon's Capsule
connective tissue
-the socket in which the globe is suspended; kept intact for ocular prosthesis
Cornea
The clear tissue that is part of the fibrous tunic.
-Tough, highly innervated
-Avascular
-Major Refractive component of the eye
Where is the cornea thickest?
periphery
~670 um
where is the cornea thinnest?
center
~520-550 um
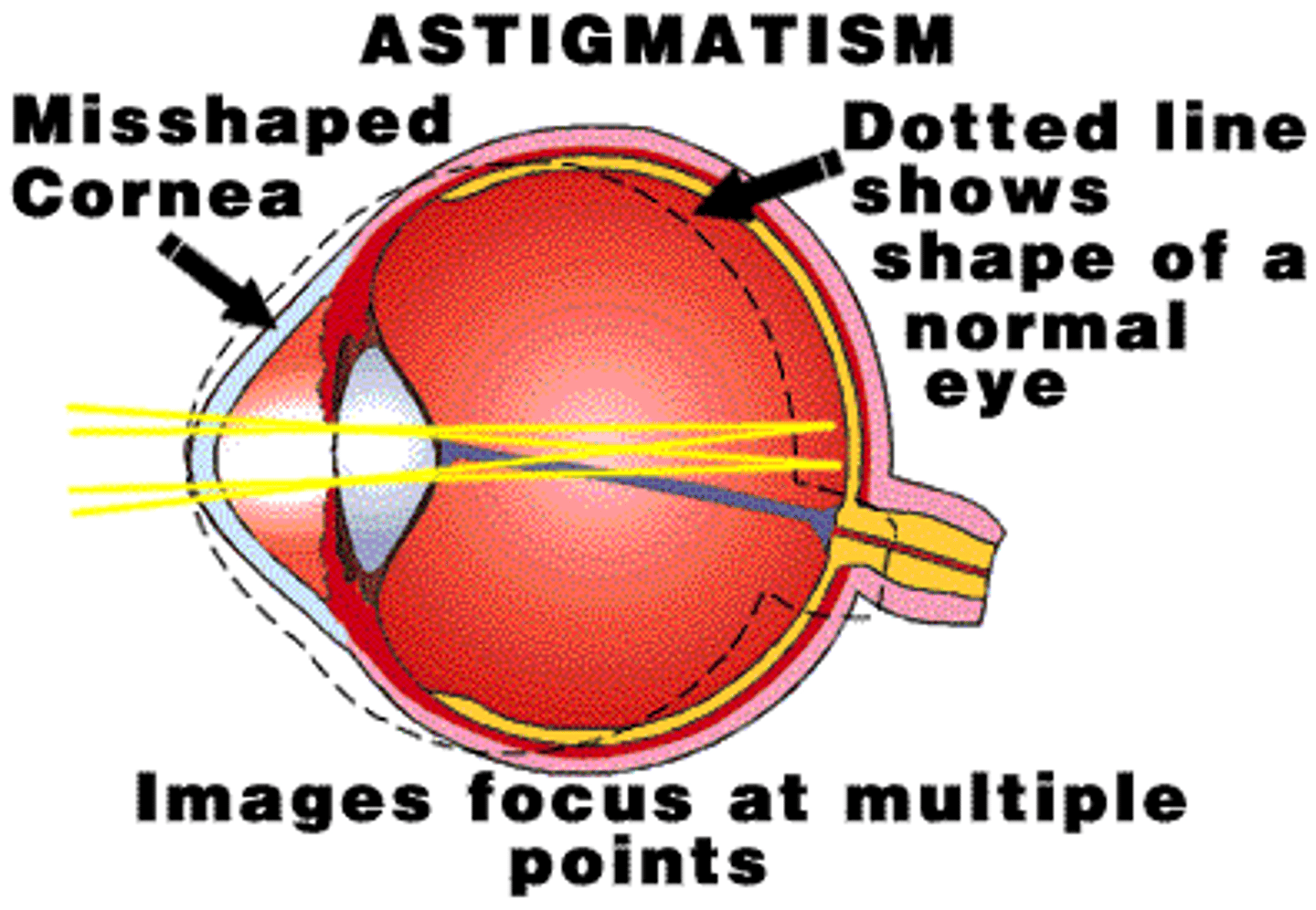
astigmatism
unequal curvature of the cornea
-prevents light from being focus to a single point on the retina
Corneal tear film
-Lipid Phase (surface)
-Aqueous Mucinous phase
-Glycocalyx
Lipid phase
aggregates of lipid held together by hydrophobic forces
Aqueous Mucinous Phase
-both soluble and gel-forming mucins
-interact with a base layer of epithelial membrane-bound mucins
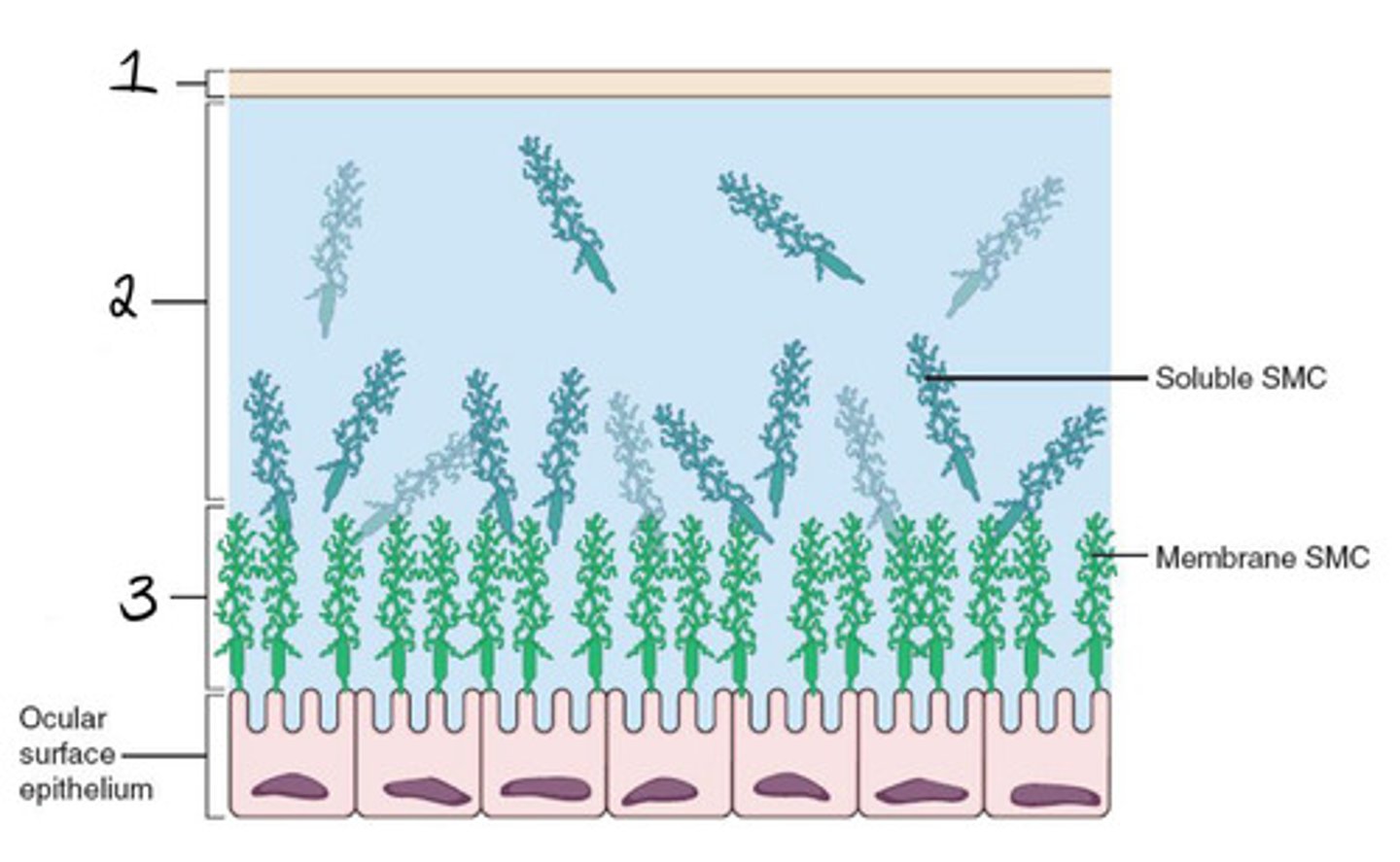
Glycocalyx
-secreted by epithelial cells
-includes several trans membranous mucins
-directly related to cornea
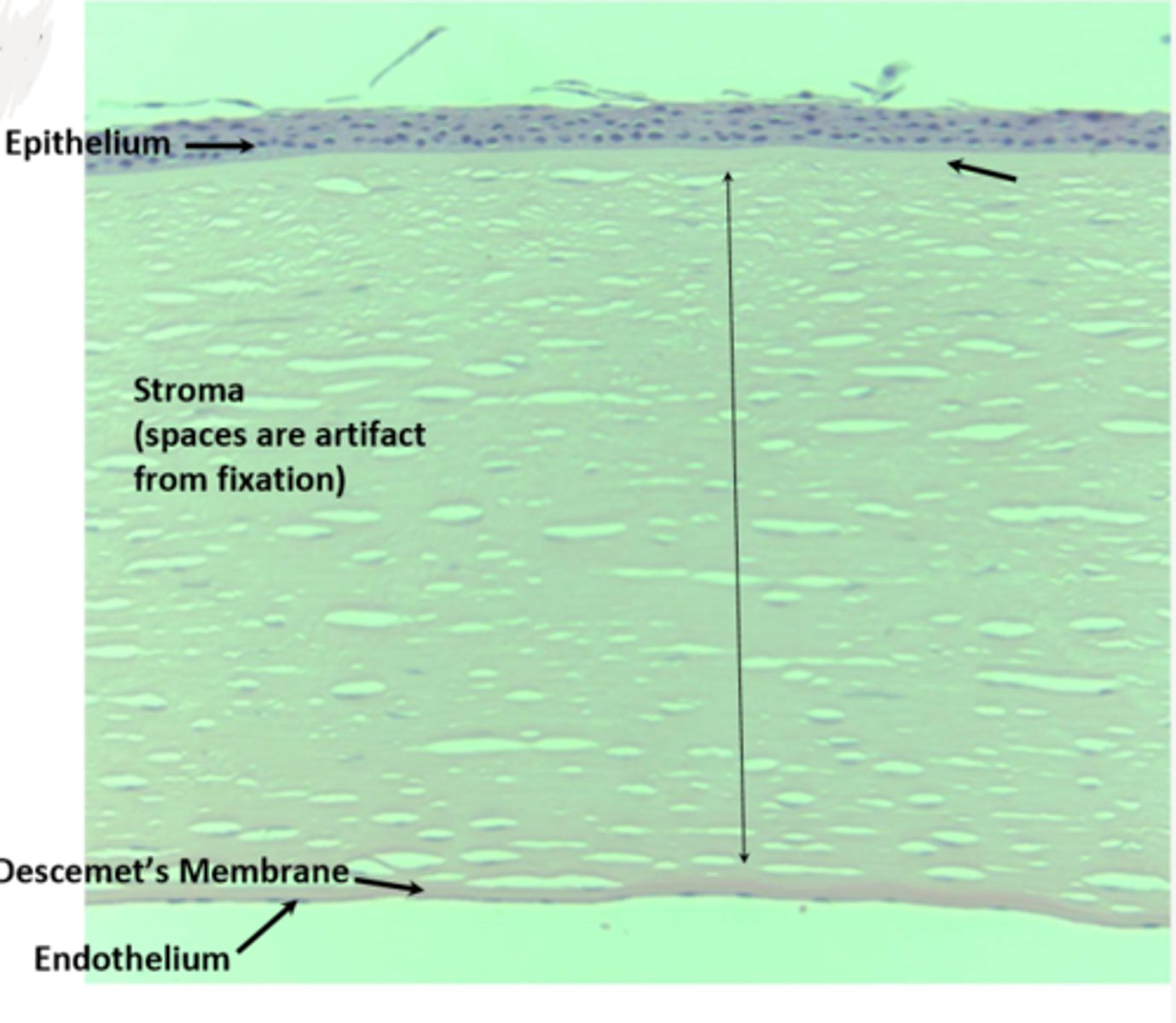
5 layers of cornea
-Anterior epithelium
-Bowman's Layer
-Stroma
-Descemet's Membrane
-Endothelium
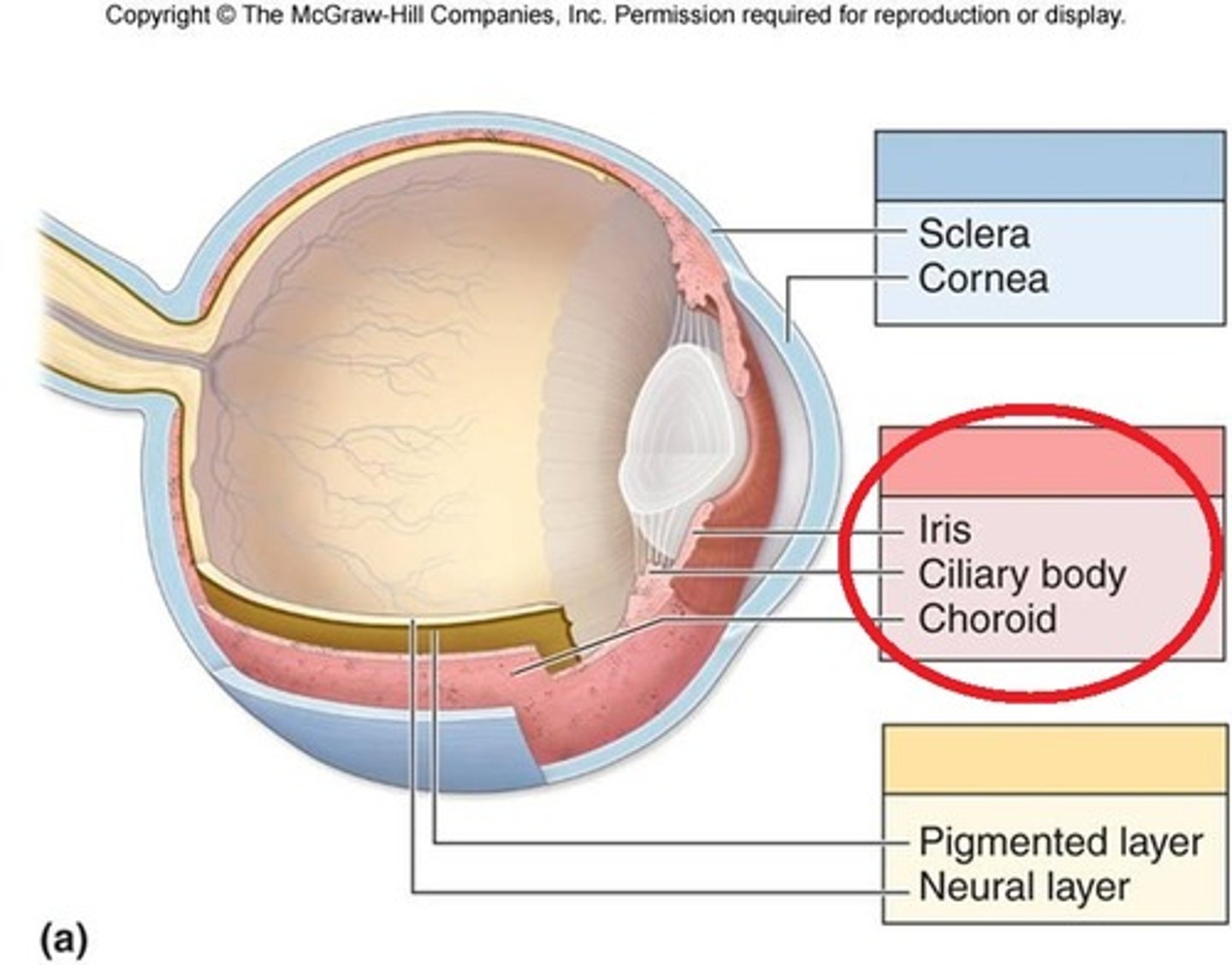
Vascular Tunic
heavily pigmented and highly vascularized
composed of
-Iris
-Ciliary body
-Choroid
Iris
regulates the amount of light reaching the retina via its aperture, the pupil, and has been likened to a diaphragm in an optical system
what divides the aqueous compartment into anterior and posterior chambers?
the iris
Ciliary body
-formation and secretion of aqueous humor
-Synthesis of lens zonules and vitreous during fetal development
-Acts as a fulcrum for the lens zonules
-Major role in accommodation
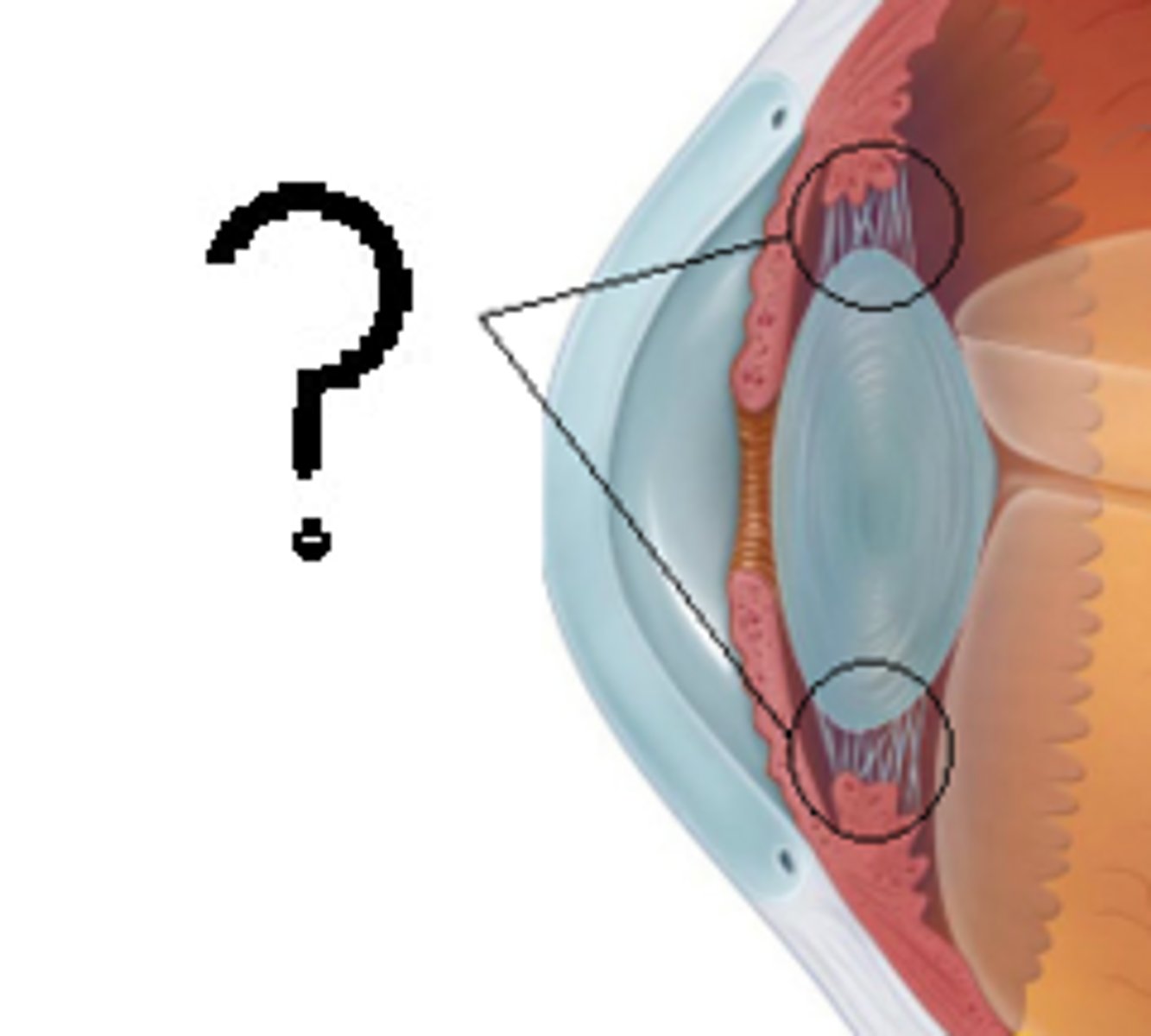
Parts of the Ciliary Body
Pars plicata and pars plana
Pars Plicata
part with ciliary processes
Pars plana
Smooth, flat part of the ciliary body
irregular oblong spheroid
shape of the globe
ciliary processes
hair-like processes that extend from its inner border to into the posterior chamber
choroid
composed of blood vessels, melanocytes, connective tissue, and a mucinous extracellular fluid
What is the sole source of nutrients for photoreceptors in the retina?
choroidal vasculature
Location of choroid
between sclera and retinal pigment epithelium
why is the choroid brownish in color?
dense melanocyte population
Neural tunic
innermost layer of the eye composed of the retina
-responsible for converting light into a neural signal by the process of phototransduction
retina
contains the first three cells of the visual pathway
-composed of 10 layers
what forms the optic nerve?
axons of the retinal ganglion cells
retinal ganglion cells
the third layer of retinal neurons whose axons leave the eyeball and form the optic nerve.
-the output cells of the retina
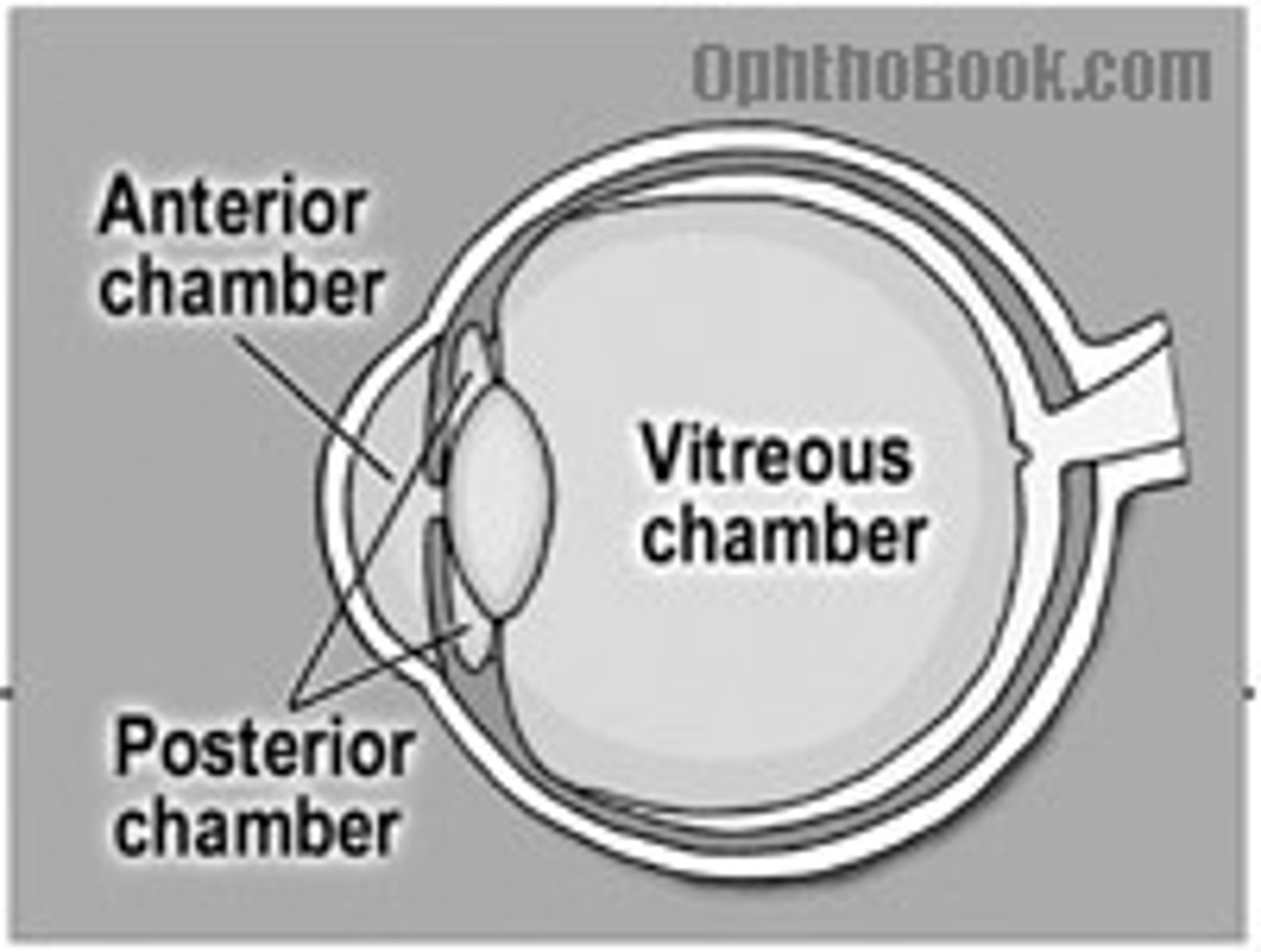
Anterior chamber
between cornea and iris, filled with aqueous humor
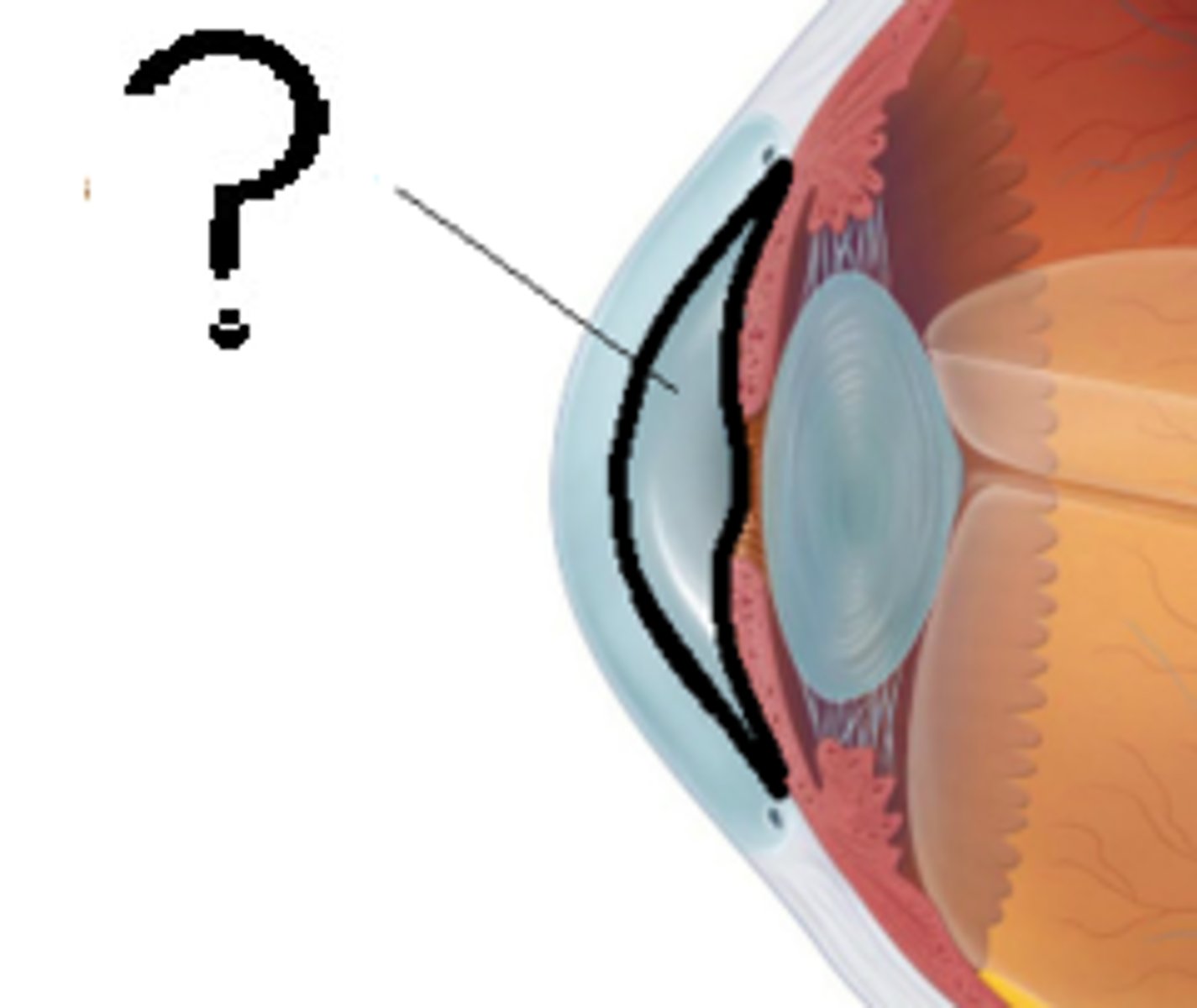
what is responsible for keeping normal pressure in the eye?
trabecular meshwork
posterior chamber
between iris and lens, filled with aqueous humor
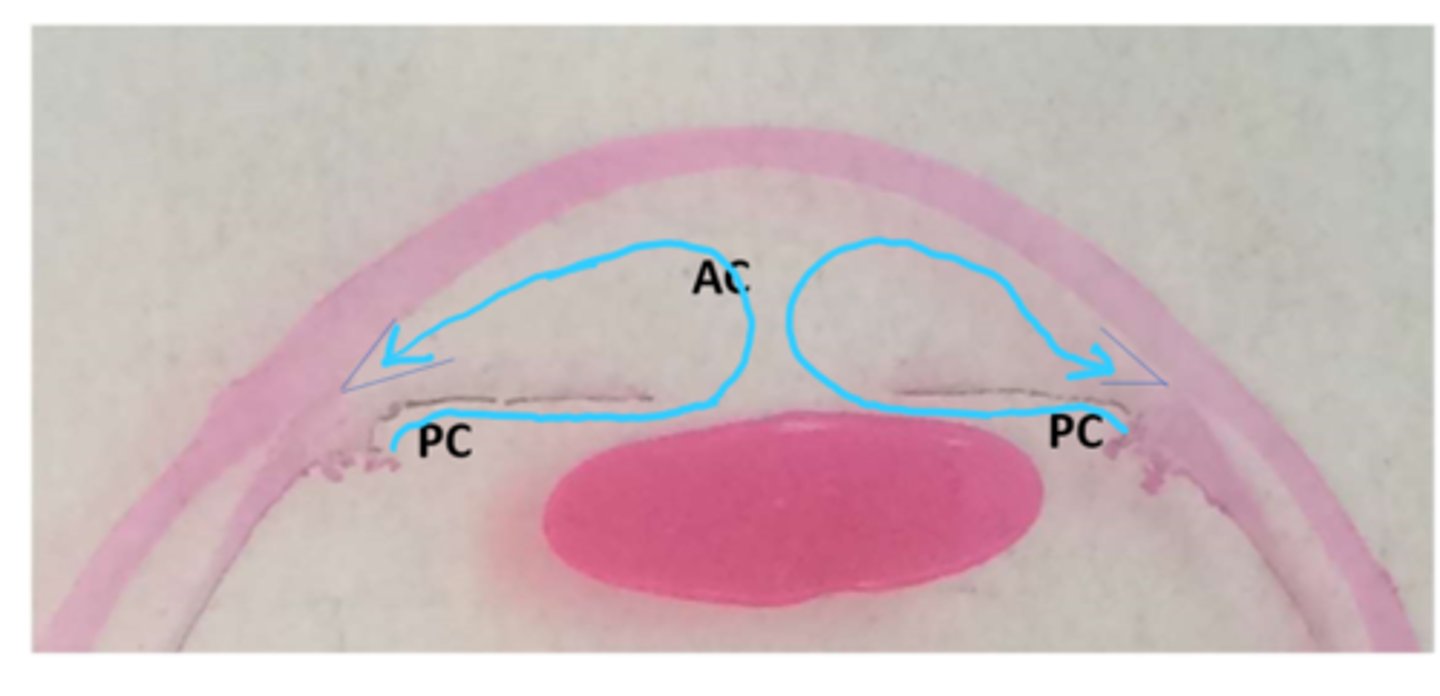
flow of aqueous humor
unidirectional from posterior chamber through pupil to anterior chamber
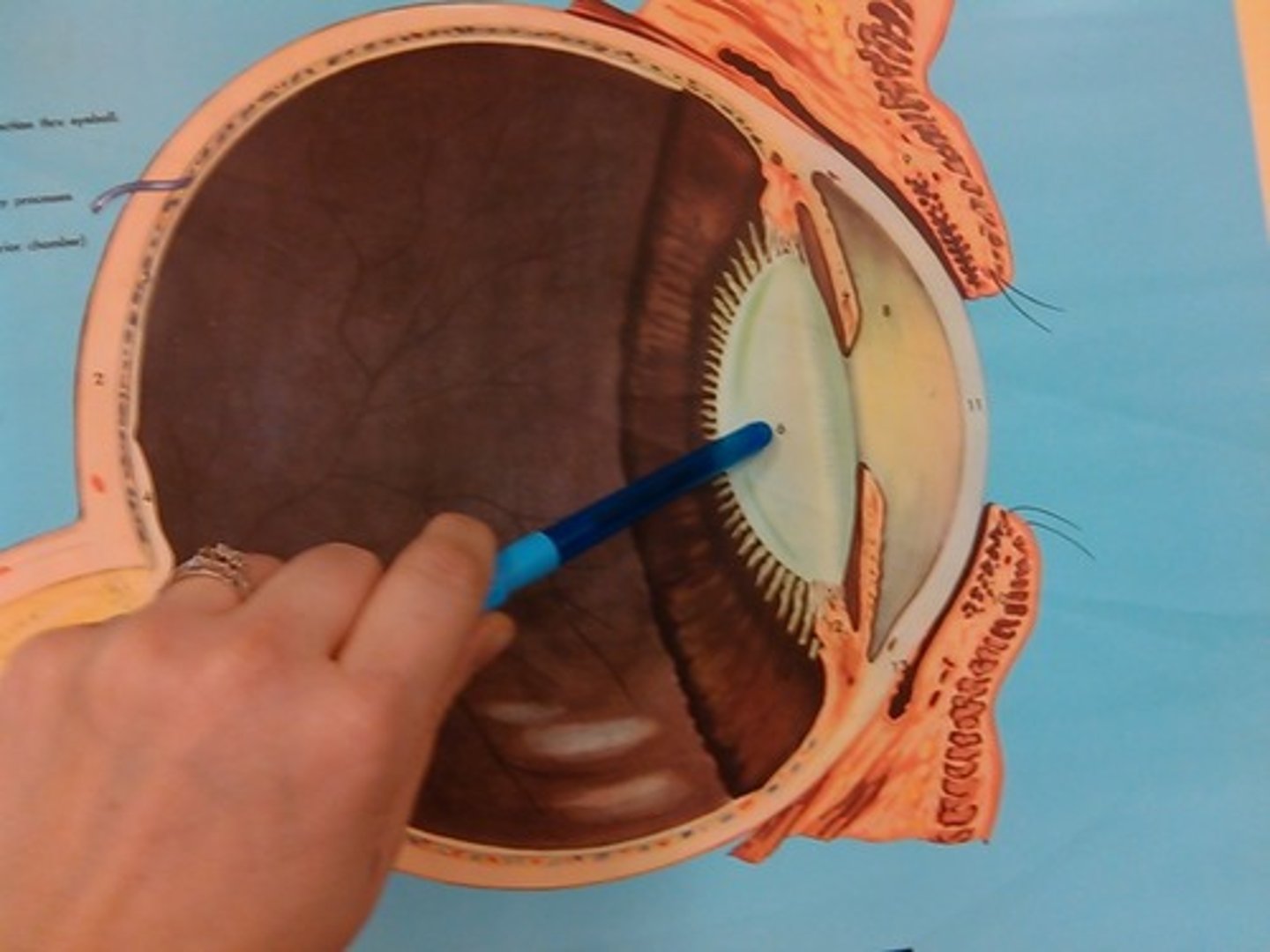
crystalline lens
biconvex structure that is located posterior the iris and pupil and anterior to the vitreous body.
-Focusing element of the eye's optical system
vitreous chamber (body)
between the lens and the retina
filled with vitreous humor
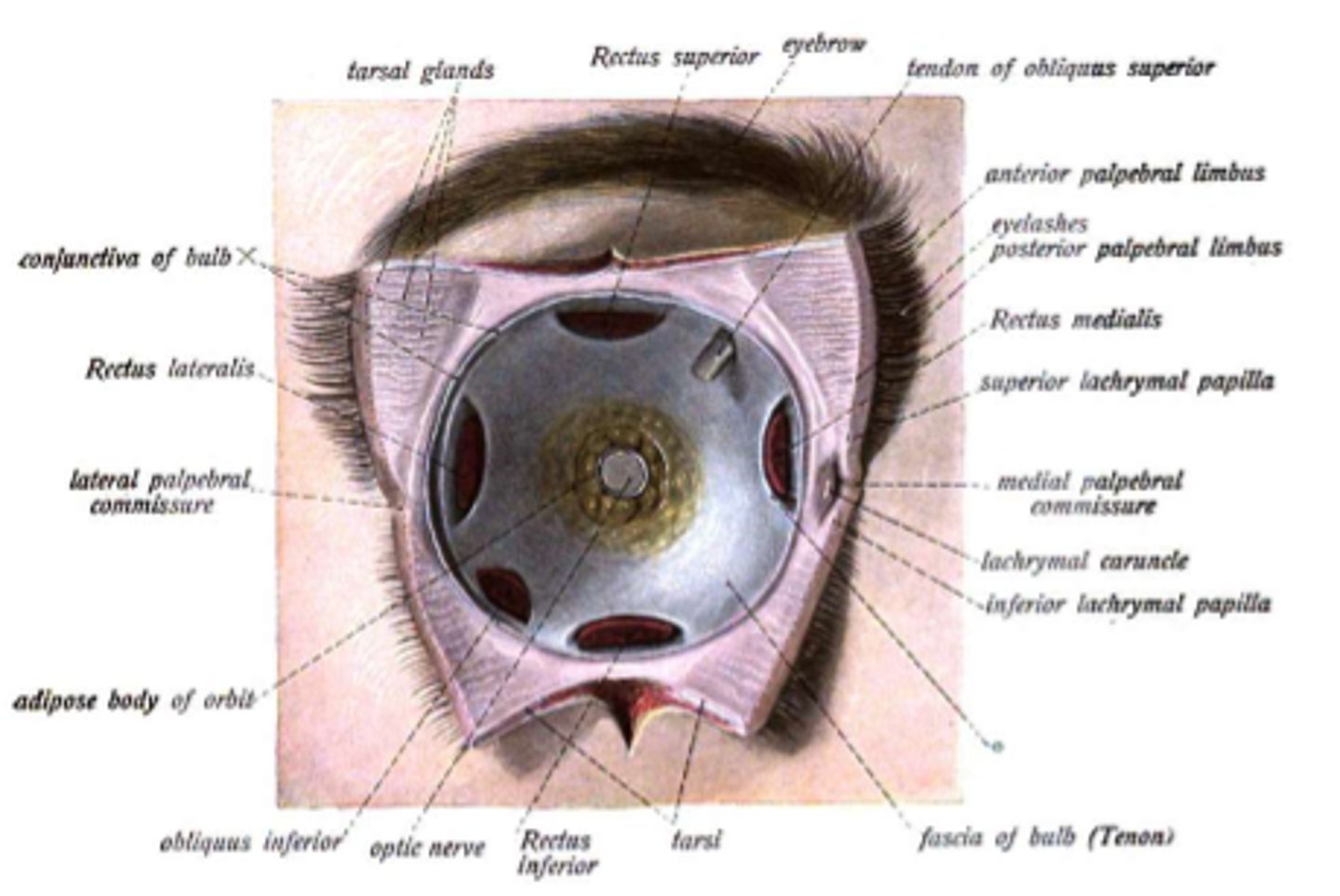
ocular adnexal structures
-eyelids
-conjunctival sac
-lacrimal apparatus
-orbital contents
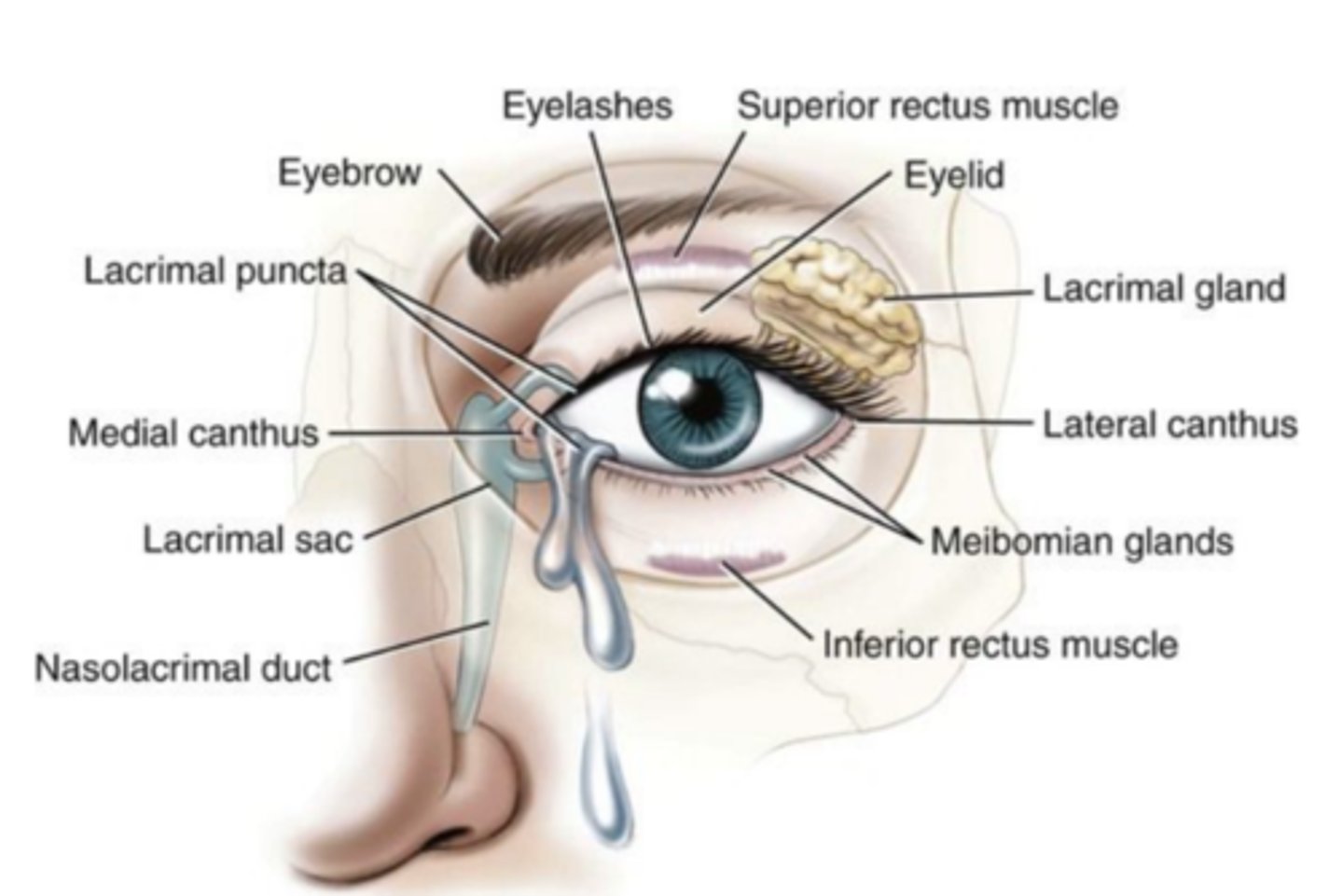
eyelids
(palpebrae) two movable flaps of skin which cover and uncover each eyeball.
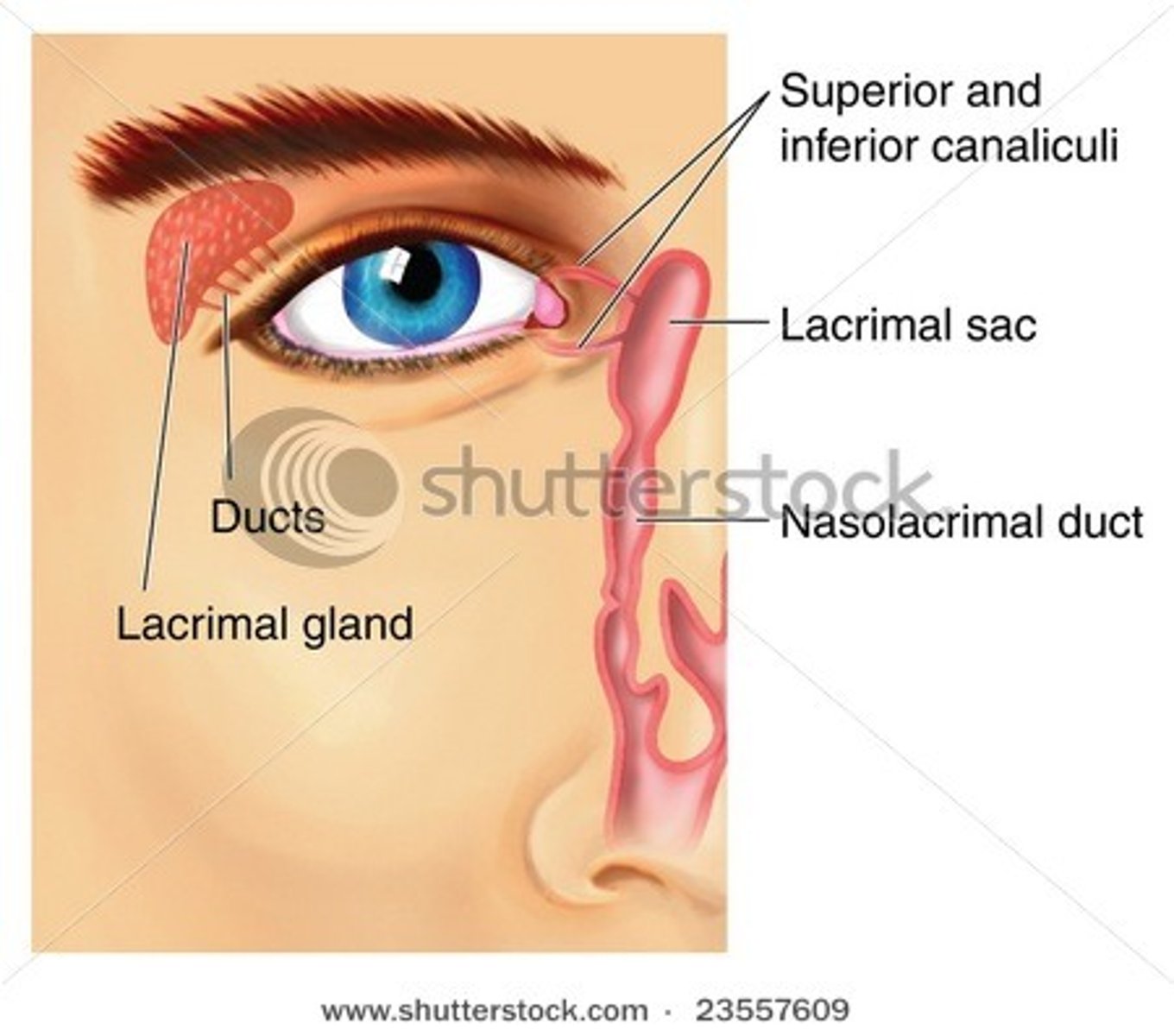
lacrimal apparatus
the structures that produce, store, and remove tears
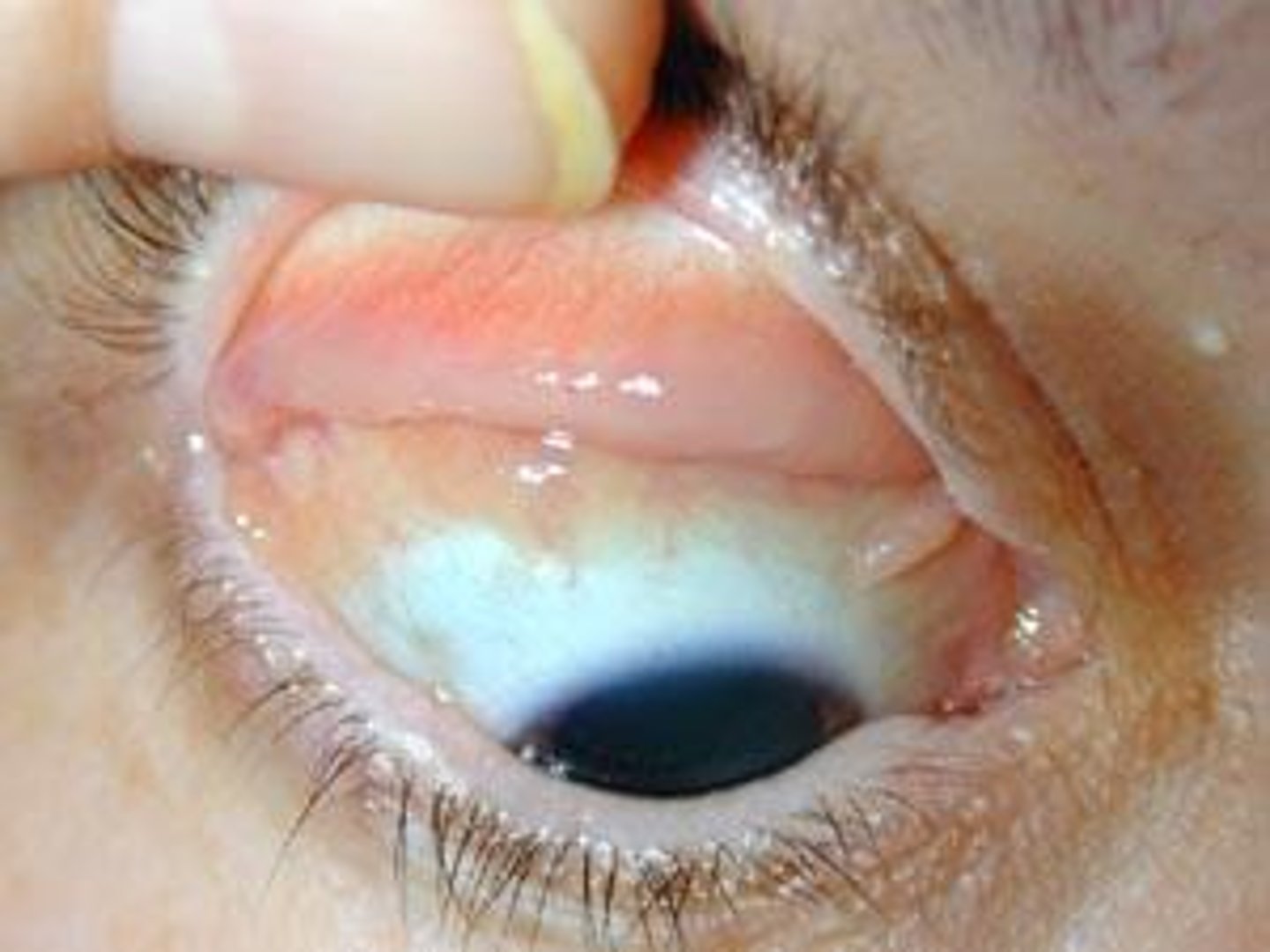
conjunctiva
Delicate membrane lining the eyelids and covering the eyeball
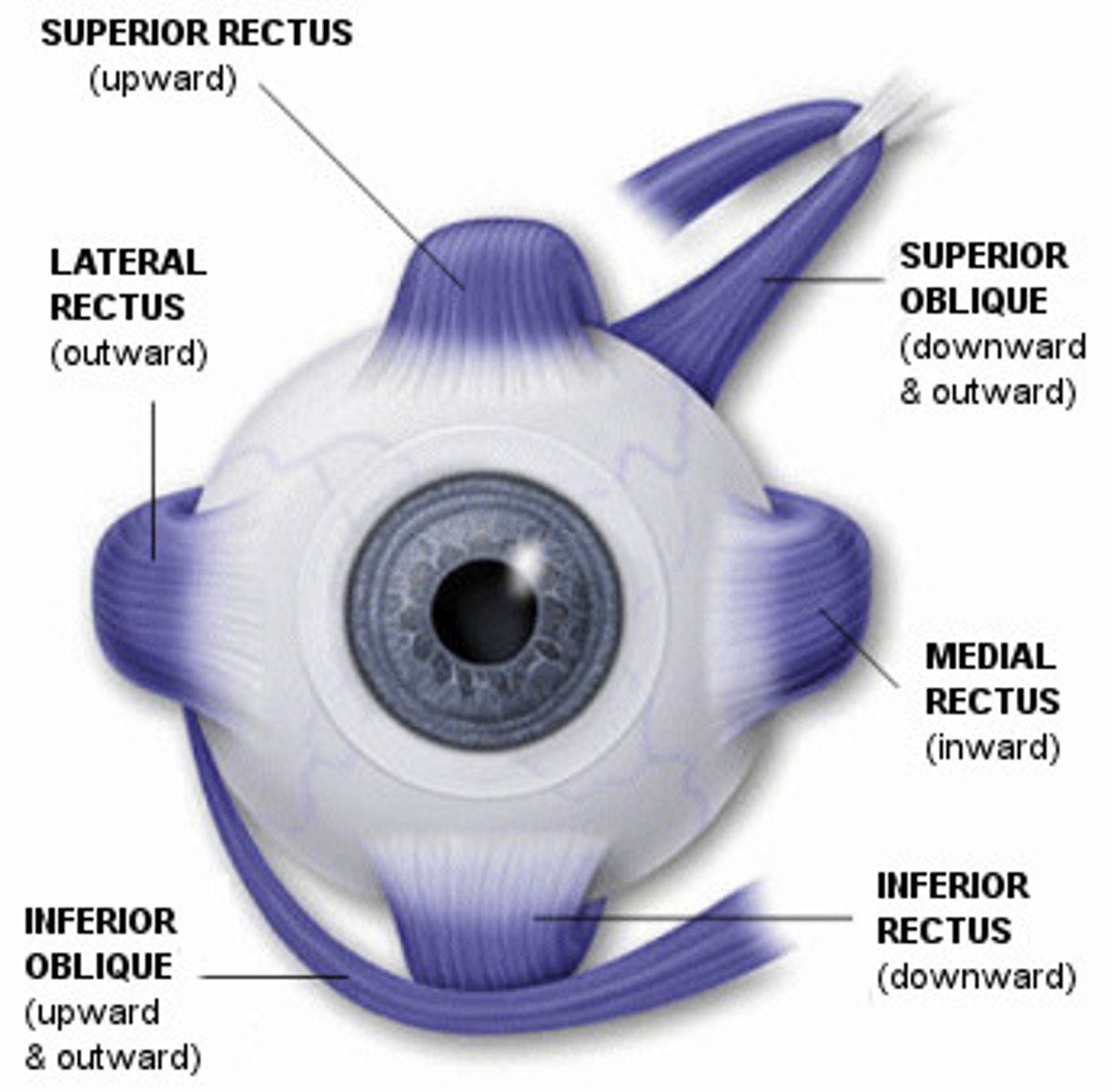
extraocular muscles
-Superior rectus
-Inferior Rectus
-Medial Rectus
-Lateral Rectus
-Superior Oblique
-Inferior Oblique
Internal Carotid Artery
artery that branches off to ophthalmic artery
Ophthalmic Artery
main arterial blood supply to orbit and eye
where does the ophthalmic artery enter the orbit?
via optic canal/foramen
cranial nerves associated with eye and orbit
-Optic Nerve CNII
-Oculomotor Nerve CNIII
-Trochlear Nerve CN IV
-Trigeminal Nerve CN V
-Abducent Nerve CN VI
-Facial Nerve CN VII
cranial nerve II
Optic Nerve;
Sensory
Vision
CN 3, 4, 6
oculomotor, trochlear, abducens
responsible or eye movements
Cranial Nerve V
sensory information of eye
e.g. pain, touch
CN VII
motor innervation to orbicularis oculi - a muscle of facial expression