GEOGRAPHY global systems and global governance單詞卡 | Quizlet
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
globalisation
how the world is becoming more interconnected
globalisation advantages
1. access to new markets
2. spread of knowledge and technology
3. promotes economic growth
globalisation disadvantages
1. increased competition
2. exploitation of labour and resources
3. imbalanced trade
4. domestic job losses
globalisation timeline
1944 - world bank was set up
1948 - jamacan/indian people (ex-colonies) migrated to the UK due to the smaller workforce after ww2
1975 - the UK joined the EU - improves trade
1990 - first window's personal computer was sold - more interconnected through technology
1996 - internet available at home
2001 - 9/11 - deglobalisation due to higher security in airports
2004 - start of facebook - global social media platform
2011 - china becomes world's second largest economy
global systems
systems put in place to make the world work together (international trade)
global governance
attempts to regulate and control global systems (activity by the UN)
poverty AO1
1. since 1990 extreme poverty ($1.90 per day) has halved to now 21%
2. 1.4 billion people still live in poverty
5 global flows
1. capital
2. labour
3. information
4. services
5. products
measuring globalisation
1. KOF index 2002
2. AT kearney
flows of capital
movements of money (investment, trade, business production)
4 flows of capital
1. IMF - supports global financial stability & promotes economics growth
2. the world bank - gives out money (loans) for development & aid
3. core areas - HICs
4. periphery areas - LICs/MICs/NEEs
core regions and periphery regions diagram
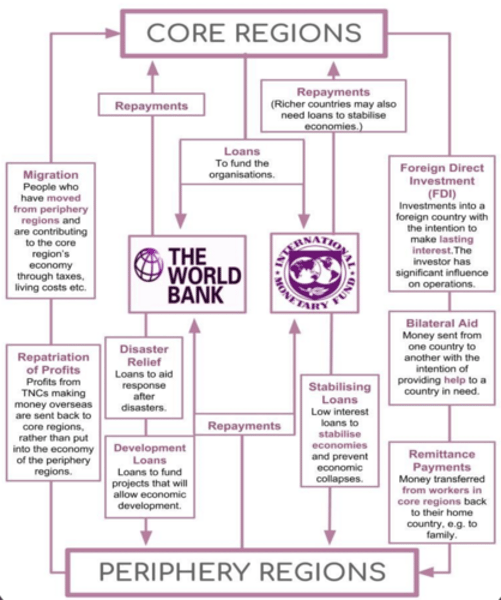
sources of capital flows
1. FDI - TNCs investing in infrastructure in LICs
2. repatriation of profits
3. aid - multilateral, bilateral, NGOs
remittances
money migrants send back to family and friends in their home countries - somalia's GDP is 85% reliant on remittances from their families working in overseas TNCs
flows of people
movement of people/labour (migration)
flows of people AO1
1. today 3-4% of the world's population are international migrants
2. 1.6% of LICs are made up of international migrants
brain drain
the loss of highly skilled workers from less developed countries to HICs due to higher wages in HICs
brain drain example
trained mechanics in the poor areas of china moved to the car industries in europe (volkswagen) due to higher wages & living standards - this leaves china lacking mechanics
flows of labour
movement of migrants mainly seeking better employment opportunities (economic migrants)
flows of labour example
movements of labour to the oil-rich middle easter states (qatar, bahrain, saudi arabia)
flows of labour AO1
1. 2 million indians live in the UAE, accounting for 30% of the population, contributes to $15 million a year sent back to india through remittances
2. mexico and the USA are interdepedent due to economic benefits
3. today 1/5 if the USA population is hispanic
south-south flows
movements between LICs and NEEs, fast growing economies such as nigeria & south africa are seen as attractive by asian manufactoring companies, increasing volumes of south-south trade, UN data shows south-south movements are equal to north-south trade
flows of products
flows of physical goods from one country to another - improved by globalisation, outsourcing
flows of products AO1
1. HICs account for 60% of global exports
2. sub-saharan africa account for 2% of global exports
containerisation
the process of using large shipping containers to transport goods - makes global transportation cheaper due to greater carrying capacity and therefore reduced trips

flows of information
internet, phone calls, social media, international news - experience other cultures, aware of global events, seek better employment opportunities
trade agreements
have made globalisation accelerate as they make trading cheaper & easier, are all overlooked by the WTO to ensure they are fair
trade blocs
groups of countries in a trading agreement allowing them to have certain advantages (reduced tariffs & higher quotas) - NAFTA, EU
SDTs
help developing countries trade with greater trade HICs since they struggle to trade with powerful nations because they are prevented by tariffs & quotas, countries must be a member of the WTO
SDTs advantages
1. helped many countries to develop services & tourist industries
2. diversifies their economies
SDTs disadvantages
1. don't consider all the issues in LICs
2. takes 8-10 years to apply
3. can flood markets with cheap, lower quality goods and undermine the HIC markets
SEZs (special economic zones)
areas within a country that have special rules (do not follow the general trading rules), have lower tariffs & taxes, this attracts FDI
flows of electronic waste
electronic waste moves from HICs to LICs, LICs have fewer health and safety laws (ghana receives 200,00 tones of electric waste annually, contributes to poor health, breaking apart items & burning them releasing toxic chemicals)
global trade AO1
1. china is the number 1 exporter of goods, valued at $2.3 trillion in 2017
2. just 10 nations (including USA, china, japan & germany) account for more than half of all global trade
slovakia case study
1. since 2007 has been the world's largest producer of cars
2. 3 major TNC car assembly plants
3. to remain a large producer of cars during globalisation it joined NATO, the EU and the WTO
4. this reduced barriers of trade through a reduction of tariffs
5. KOF index riose from 61.9 in 1996 to 83.5 in 2015
6. exports take up 91.9% of their exports
TNC
a business with operations in more than one country
characteristics of a TNC
HQ often in HICs and factories in LICs, large firms have expanded their businesses globally by building branch plants overseas achieving economic growth through mergers & take-overs - apple's HQ are in california while the factories are in china/taiwan, 90% of apple's profits are sent back to california, does not benefit china/taiwan
where TNCs operate
1. primary sector - commercial farming
2. secondary sector - samsung, sony, BMW, unilever
3. tertiary sector - banks, insurance, investment & media cooperations (HSBC)
4. quaternary sector - medical research is increasingly conducted in india by western firms (pfizer)
the role of TNCs in global systems
1. help group nations together through their production & supply chains (the UK & malaysia are linked together by the TNC dyson - they are sold in the UK but manufactured in malaysia)
2. build up their businesses by buying foreign firms
3. 'sweat shops' don't actually operate in TNC buildings - employee exploitation may happen further down the supply chain
4. most TNCs are assembly industries
why do TNCs trade/operate globally?
1. they can get around trade barriers & tariffs
2. lower production costs - LICs have lower set up costs and cheaper land & labour
3. resources - some TNCs need to locate near raw materials
4. reach foreign markets - they place themselves close to markets they want to tap into
primary sector TNC spatial organisation characteristics
1. based where there are unexploited natural resources (developing economies)
2. new technology (fracking) can make new reserves of raw materials
primary sector TNC spatial organisation examples
royal dutch shell (NL/UK) & BP (UK)
secondary sector TNC spatial organisation characteristics
1. manufacturer in developing countries
2. low labour costs
3. easier to train workers (less skill needed)
4. strong work ethic & little regulation
secondary sector TNC spatial organisation examples
kia motors (south korea), toyota (japan), apple (USA)
tertiary sector TNC spatial organisation characteristics
1. low labour costs
2. good education
3. able to move freely
tertiary sector TNC spatial organisation examples
BT (UK), holiday inn (USA)
quaternary sector TNC spatial organisation characteristics
1. in the country of origin
2. highly skilled workers for research
3. expensive technology needed
quaternary sector TNC spatial organisation examples
glaxosmithkline (USA), pfizer (USA)
outsourcing
when TNCs contract work to other countries
vertical integration
the company owns the whole supply chain and has complete control at every point
horizontal integration
when the company diversifies & takes over other companies so it has a wider range at the same level of production
the negative impacts of TNCs
1. labour exploitation - cheap, flexible labour in LICs
2. urbanisation - building factories in cities draws young workers to the city, suffering the rural areas
3. people in the country of origin face unemployment as the jobs go overseas
4. local businesses cannot compete with the TNCs and go out of business
5. money leaves the country - the economy could shrink as TNCs send their profits to their home country
6. TNCs might commit tax avoidance - they can afford lawyers to find loopholes - no government revenue
7. pollution - china suffers from serious air pollution due to their manufacturing industry
8. agricultural TNCs replace rainforests with plantations (palm oil)
9. natural resources exploited
the positive impacts of TNCs
1. creates employment for poor locals
2. offer training and a minimum local wage for employees - these are transferrable skills
3. reduces economic vulnerability
4. TNCs bring money back to their country of origin - can be reinvested into the national economy
coca-cola case study
1. number 1 manufacturer of carbonate soft drinks in the world
2. first sold in atlanta in 1886
3. bottles were first sold in 1894 and cans in 1955
4. head-quarters in atlanta georgia USA
5. coca-cola was first shipped overseas in 1923
6. by ww2 coca-cola was being bottled in 44 countries
7. they sell nearly 400 different products
8. coca-cola owns smart water, costa coffee & innocent
9. 70% of their sales are generated outside of north america
10. coca-cola expanded with fanta in 1950 and sprite in 1961

positives of coca-cola TNC
1. they offer training & education to workers - improves employment
2. they run community schemes in africa & south-east asia
3. many of the bottling firms are local companies and so all the profits stay in the host country
negatives of coca-cola TNC
1. less strict environmental restrictions in LICs - coca-cola takes advantage of that
2. harsher working conditions - employees get very few benefits & work long hours for very little pay
3. depletion of local ground water due to utilisation of natural water resources
world trade food commodity case study: bananas
1. 4th most important food product in LICs
2. large quantity of energy - 90 calories
3. 1 banana provides more than an adult's daily potassium requirement
4. 5th most traded agricultural product
5. 80% of exported bananas come from latin america or the caribbean
6. ecuador remains the greater exporter

bananas environmental impact
1. bananas are susceptible to disease and so are treated with chemicals - the soil becomes contaminated
2. deforestation can occur to clear land for plantations
bananas economic impact
1. around 90% of the cost paid by the consumers in the HICs stays in the rich north - it never reaches the producer
2. 42% of the profits is taken by the retailer (large supermarket TNCs like tesco or walmart)
3. in the past 80% of banana trade was dominated by 4 large US TNCs
4. large TNCs grow bananas in ecuador and colombia with vertical integration - they own the plantations and have their own transport - this causes economies of scale where they can produce at very low prices to the USA and EU
bananas trade war
1. in 1975 the EU made a SDT agreement with 71 ACP countries (the lome convention)
2. these countries were given tariff-free access to EU markets to import bananas
3. this protected the smaller family-run farms in the carribean & africa since the latin american TNCs supplied 75% of the EU market at the time and only 7% came from the carribean
4. in 1992 the latin american TNCs filed a complaint to the WTO that the EU practise with the ACP countries was unfair
5. the WTO ruled against the EU in 1997 forcing the EU to reduce the tariffs on the latin american bananas
spatial distribution of bananas
1. grown in hot (27ºC) and wet (2000-2500mm of rainfall per year) tropical areas
2. domestic suppliers - brazil, india, africa
3. commercial suppliers - central america & the carribean
4. the main importers of bananas are the USA and EU - in 2013 each consumed about 27% of the total exports