Business - 1.3 Marketing mix and Strategy
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Name the marketing mix
Product
Promotion
Price
Place
What is the design mix
Function
Aesthetics
Cost
How do changes in social trends affect the design mix?
Changes in social trends can influence consumer preferences, leading to shifts in function, aesthetics, and cost considerations in the design mix to better meet market demands.
waste minimisation
re-usable products
recyclable
sourced ethically
The challenges of product design
Adapting one element can affect other components. E.G reducing cost may have an impact on the product's quality or functionality.
Advantages of adapting designs to reflect social needs
helps businesses cut cost - reducing waste
reflecting social trends = sell larger quantities
USP
What are the aims of promotion (anagram)
Awareness
Interest
Desire
Action
AIDA
Define promotion
Aims to inform customers and potential customers about the product/ service and persuade them to buy it
What is above the line promotion
Above the line promotion = forms of advertising through mass media channels such as TV, radio, newspapers, and the internet, aimed at a wider audience.
What is Below the line promotion
All other forms of advertising that is not advertising - sales promotion, public relations, merchandising, direct selling and trade fairs
What factors influence promotion?
the target audience
technology
promotional budget
the message
Define - brand
a brand is a product with unique characteristics that distinguish it from other products, often associated with a name, logo, or design that creates a lasting impression in the minds of consumers.
Define branding
branding is creating an image of the product in the mind of the consumer ; which gives the product identity
Types branding
Sponderships
Emotional Branding
viral marketing
What is the importance of branding
Added value - enables higher price to be charged - increases in profitability - competative advantage - lowers vulnerability in competition and creates stronger bond
Reduced PED - strong branding persuades customers that substitutes are less acceptible - reducing PED - less price inelastic - higher total revunue
define - Distribution (place)
distribution refers to how the product gets to the customer.
What are the 4 parties in a distrinution network
Agents
retailers
Wholesalers
Distributer
Intermediaries = takes some of the profit and responsibility
Describe the 4 stages of distribution
Producer - wholesaler - retailer - consumer
retailer doesnt have purchasing power to buy from manufacturer = wholesaler provides producers to get their product into retai
wholesaler bears the distribution costs
wholesalers provide storage facilties ; reduce producers stock holding cost
Describe the 3 stage of distribution
Producer - retailer - consumer
Advantages of 3 stage distribution include lower costs, reduced inventory requirements for producers, and increased market reach for retailers.
Disadvantages of 3 stage distribution channels include less control over product placement, reliance on retailer performance, and potential for reduced profit margins.
Describe two stage distribution channels
Producer to consumer = disintermediation (no middle man)
Advantages -
producers sell directly to the consumer = no intermediaries = producer can control their markup = can be sold at a competative price
producers close relationship = direct feedback = can react faster to change in consumer needs + market conditions
lower costs for consumers, increased profit margins for producers.
What factors effect the appropriate distribution channel
nature of the product
stage of the life cycle
market coverage
customer expectation and preferances
What influences price
Levels of competition and their prices - best value product = prices competitive
PED - PED = elastic total revenue can change if there is a price change
PED inelastic = USP, strong branding can set higher prices = higher total revenue
Stage in the Product Life Cycle -
What are the 7 types of Pricing strategies
Price skimming - price high to low - attract early adopters - higher sales revenue
Penetration Pricing - low initial price - penetrate new market ( new products only) = gain market share
Cost plus = cost of the product + markup = selling price
Predator pricing = illegal - setting low prices to cut out competition
Phycological pricing= e.g "£1.99 vs £2.00”
Competative pricing - setting prices based on competitors' prices in the market.
discriminative pricing = setting different prices for the same product based on factors such as customer segment
Define - Marketing strategy
a plan of activities to achieve a marketing objective
define niche market
where a business targets to a smaller segment of a large market, where the customers have specific wants and needs
define mass market
where a business sells into a large part of the market, where there are similar products to offer
define outbound marketting
includes any strategy that involves pushing out a message to customers - above and below the line methods
define inbound marketing
Includes any technique that attracts potential customers to a website
What are the stages of the “product life cycle”
introduction
growth
maturity
saturation
decline
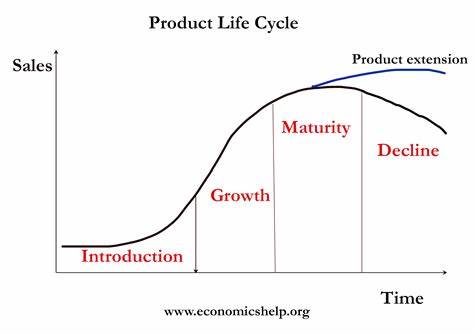
PPA - product portfolio analysis
can be used to track the development of multiple products over time - taking into account growth sales and market conditions
The boston Matrix - what are the axis
Market growth and market share
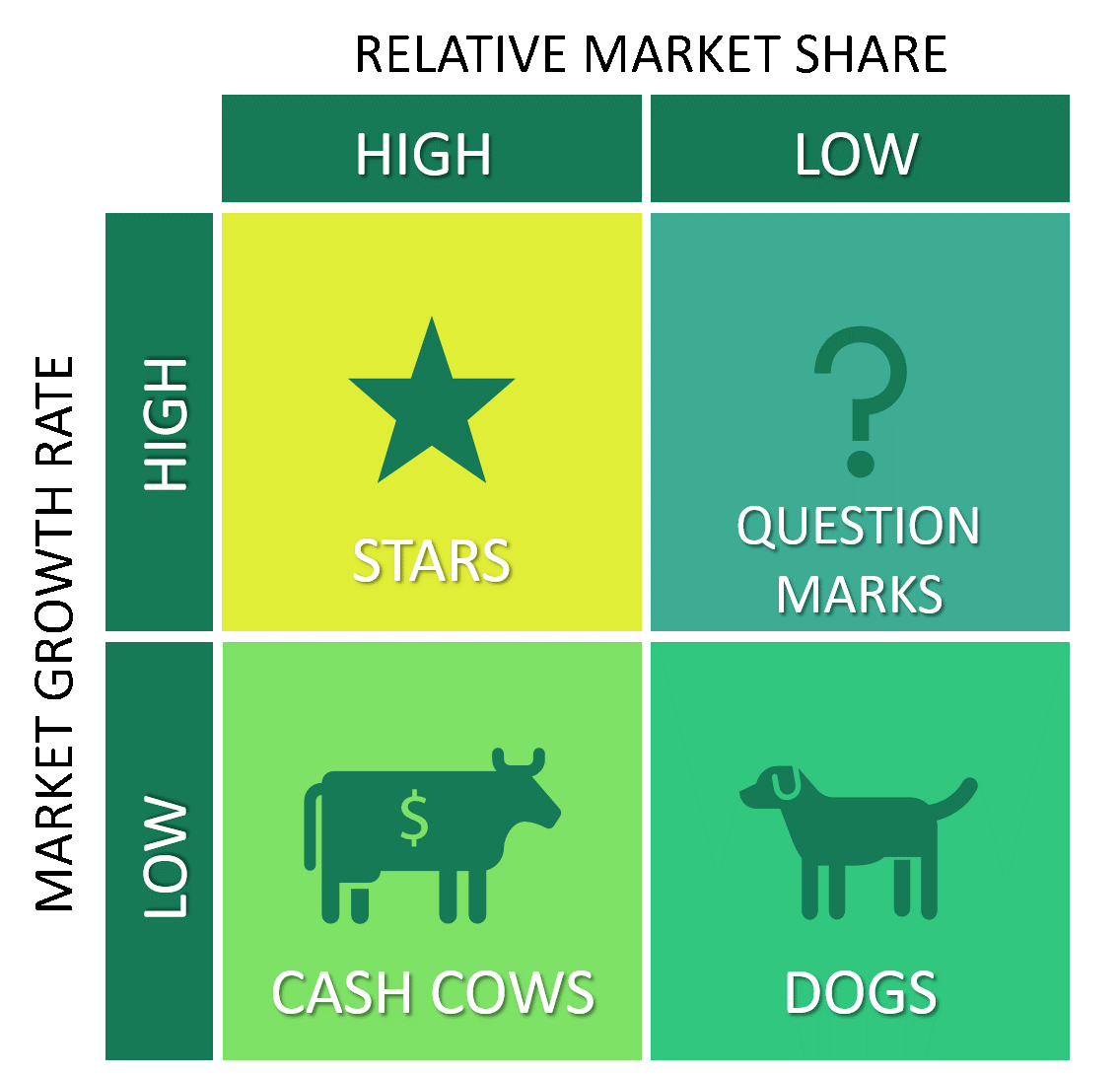
What are the 4 boston matrix components
Problem child (question mark)- high growth, low market share
Dogs - low market growth, low market share
cash cows - low market growth, high market share
stars - high market growth high market share