Chemistry - Redox reactions ✅
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Including: redox reactions, oxidation states, Electrochemical cells, Galvanic cells, Standard electrode potential, and Electrolytic cells
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
reactions that can be modelled as redox reactions
single replacement reactions, combustion, corrosion, decomposition, combination and electrochemical processes
what do redox reactions involve
oxidation of one substance and reduction of another substance
What reactant in a reaction will be reduced
reactant with the most positive E0 value
What reactant in a reaction will be the reducing agent
reactant with the most negative E0 value
What reactant in a reaction will be oxidised
Reactant with the most negative E0 value
What reactant in a reaction will be the oxidising agent
reactant with the most positive E0 value
What does O.I.L. stand for
Oxidation is lost (loses electrons)
What does R.I.G. stand for
Reduction is gained (gains electrons)
In an oxidation reaction, what side are the e- on
e- on product side of equation
In a reduction reaction, what side are the e- on
e- on reactant side of equation
What is the reduced agent in this reaction: Zn(s) + 2H+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + H2(g)
Zn as electrons are gained
What is the oxidised agent in this reaction: Zn(s) + 2H+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + H2(g)
H as electrons are lost
what is a reducing agent
a substance which gives e- to the other species and is oxidised
What is a oxidising agent
a substance which takes e- from the other species and is reduced
When are oxidation states used to determine redox reaction half equations
In an equation involves more than two chemical species
What can oxidation states be assigned to
atomic species or to individual atoms within a molecular species
What does an oxidation state/number represent
The charge that an atom would have if it was an ion, shows the number of electrons gained or lost by an atom
What is the oxidation state of a free element (e.g. Na, P, S)
zero
What is the oxidation state of a simple ion (e.g. Mg2+, N3-)
the charge on the ion
What is the oxidation state of main group metals
the charge on their ion
What is the oxidation state of Hydrogen and exceptions
+1 (except of metal hydrides, oxidation state is -1)
What is the oxidation state of oxygen and exceptions
-2 (except in compounds with fluorine, oxygen is positive, in peroxides, oxidation state is -1)
What is the oxidation state of halogens and exceptions
-1 (except in compounds with oxygen or another halogen above them in group 17)
what does the sum of oxidation numbers of all atoms in a neutral compound (e.g. CO2) equal to
zero
What does the sum of oxidation numbers of all atoms in a polyatomic ion (e.g. SO42-) equal to
The charge on the ion
Which element is assigned the negative oxidation state
the most electronegative element
How can the ability for an atom to lose/gain electrons be predicted
the atom’s position in the periodic table
What properties can be used to explain an atom’s ability to lose or gain electrons
valence electrons, consideration of energy and the overall stability of the atom
What conditions are needed to show redox reactions as half equations
acidic conditions
How can redox reactions be represented
balanced half-equations
What does a galvanic cell do
converts chemical potential energy to electrical energy and spontaneous reactions occur
What is an anode in a galvanic cell
The electrode where oxidation occurs and negatively charged
What are half-cells in a galvanic cell
an electrochemical cell, where either oxidation or reduction occurs
What is an cathode in a galvanic cell
The electrode where reduction occurs and is positively charged
What is the electron movement in a galvanic cell
from anode to cathode
what do salt bridges contain
ions that are free to move so that they can balance charges formed in the two half-cell compartments
What is the flow of molecules in a salt bridge
Cations move towards the cathode and anions toward the anode
EMF formula
EMF (E0 cell) = E0 reduction – E0 oxidation
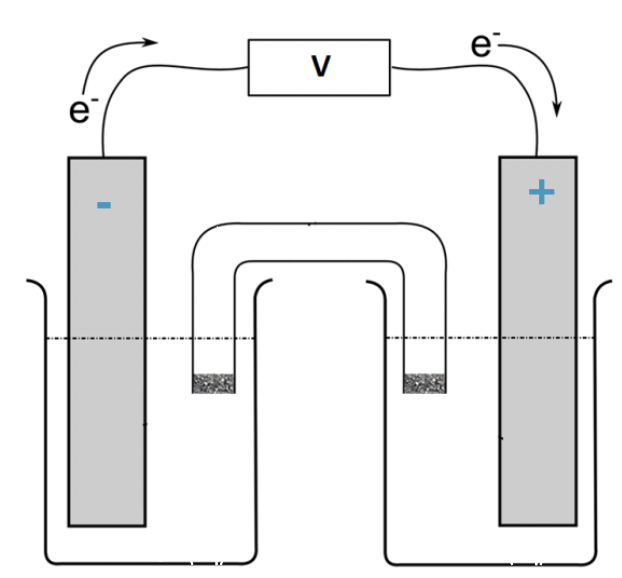
which side (left or right) is the anode and the charge
left, negative charge
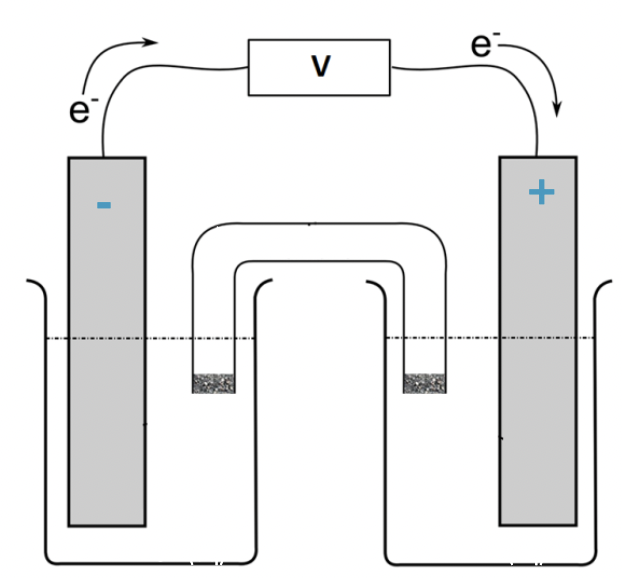
which side (left or right) is the cathode and the charge
right, positive charge
What is a fuel cell
constant supply of reactants, inert electrodes which do not take part in any of the reactions, products are gaseous, liquid or aqueous, produces a current for as long as it has reactants
What do galvanic cells generate
an electrical potential difference
Another term for galvanic cell
voltaic cell
what is a electrochemical cell
a device in which chemical energy is converted into electrical energy
What is a galvanic cell
a type of electrochemical cell in which chemical energy is converted into electrical energy
what would happen if there was no salt bridge in a galvanic cell
each half cell would have a build up of charge taking place, accumulation of charge would stop the reaction very quickly
Other terms for potential difference
electromotive force or voltage
Standard conditions for potential differences
Pressure of 100kPa, Solution concentrations of 1 molL-1, Temperature of 25°C
what is the strongest reducing agent in a reaction
equation with the most negative E0 value
what is the strongest oxidising agent in a reaction
equation with the most positive E0 value
Where does oxidation occur in a galvanic cell
the negative electrode (anode)
Where does reduction occur in a galvanic cell
the positive electrode (cathode)
What components are required to make a voltaic cell
two half-cells connected by a salt bridge
In electrochemical cells, what is the movement of electrons
from anode (oxidation reaction) to cathode (reduction reaction)
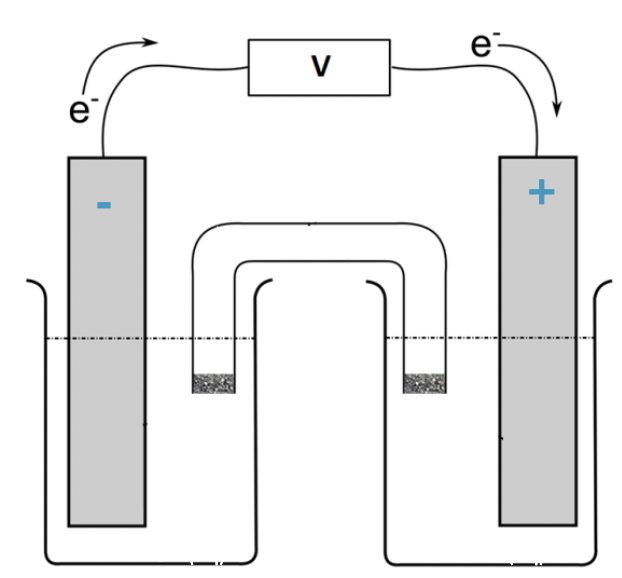
where is the positive electrode (right or left)
right
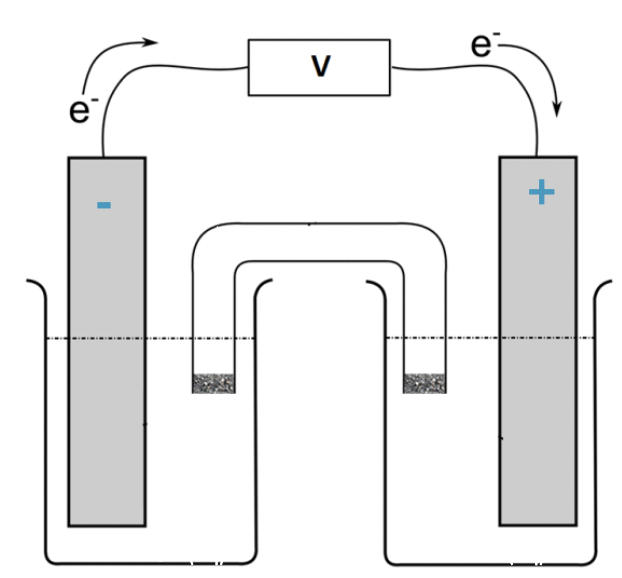
where is the negative electrode (right or left)
left
what can cell potential values (at standard conditions) be used for
compare cells constructed from different materials
As half equations’ E0 becomes more negative, what does this mean for strength of the agent
will be a stronger reducing agent as E0 values becomes more negative
As half equations’ E0 becomes more positive, what does this mean for strength of the agent
will be a stronger oxidising agent as E0 values becomes more positive
When is a reaction spontaneous
What the E0 value is a positive number (red-ox)
What doe electrochemical cells consist of
oxidation and reduction half-reactions connected via an external circuit
Two types of electrochemical cells
Galvanic and electrolytic
difference between galvanic and electrolytic cells
Galvanic cells produce energy through spontaneous reactions, electrolytic cells produce energy through non-spontaneous reactions
what do electrolytic cells create
convert electrical energy into chemical energy
5 parts of a electrolytic cell
electrolyte, anode, cathode, porous barrier, voltage
what is required for an electrolytic cell to produce a reaction
an external electrical potential difference
two scales of electrolytic cells
small-scale and industrial situations
two examples of electrolytic cells
metal plating and the purification of copper
Porous barrier
separates the products whenthe reaction takes place in a single container
why must an ionic compound be molten (liquid) in electrolysis
a solid ionic compound can not conduct electricity
How many reactants does molten NaCl provide
2
what is electrolysis
a process that produces a non-spontaneous redox reaction by the passage of electrical energy from a power supply through a conducting liquid
Which electrodes are used in electrolysis of molten salt and why
platinum metal or graphite as they allow electron the pass to and from the power supply, and as they are inert they do not react
disadvantage of using a molten electrode
the process requires much more energy
Why are aqueous solutions of salts often used instead of molten salts
it is impractical to produce the high temperatures that are required for the electrolysis of molten salts
what is present in aqueous electrolysis as another reactant
water
what are the reactants in electrolysis of of sodium chloride solution
Na+, Cl-, H20
what are the strongest oxidising and reducing agents in the electrolysis of aqueous NaCl
H2O and H2O
Why does water compose the two half equations in the electrolysis of aqueous NaCl
Because it is both the strong reducing agent and the strongest oxidising agent on the SEP table
what are the reactants in electrolysis of copper sulfate solution
CU2+, (SO4)2-, H2O
what are the strongest oxidising and reducing agents in the electrolysis of copper sulfate solution
oxidising agent is Cu2+ and reducing agent is H20
essential components of an electrolytic cell
source of electric current and conductors, positive and negative electrodes, and the electrolyte
When can the SEP table not be used in electrolysis
If an aqueous solution is concentrated (conc. > 1M)
what happens when electrolysis is performed under non-standard conditions
the electrode potentials of each half-equation changes
two types of electrodes that can be used
reactive and inert
what are reactive electrodes
electrodes that are consumed in the cell reaction
what are the possible reactants in electrolysis of CuSO4(aq) with copper electrodes
Cu2+, (SO4)2-, H2O, Cu
what is electrolysis used for in chemical industries
electroplating and electrorefining
another term for electroplating
metal plating
what components in an electrolytic cell are needed for electroplating
An electrode of the metal is at the anode and the electrolyte solution contains ions of the metal to be plated.
another term for Electrorefining
purification
in the purification of copper what is found at the two electrodes
Anode: Blister copper (impure Cu) and cathode: Copper (pure Cu)