Econ 必記 (j2)
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What are macroeconomics aims?
sustainable and inclusive economic growth
full employment
price stability
What is deflation?
refers to a situation of sustained1 decrease in the general price level
What is inflation
refers to a situation of sustained1 increase in the general price level
How to calculate inflation rate?

What is consumer price index?
measure of the price level of a basket of goods and services purchased by an average household with respect to a base year.
What is economic growth?
refers to the increase in national output of a country over a period of time
indicators: GDP and GNI
What is gross domestic product (gdp)?
measure of the monetary value of final goods and services produced within the geographical boundaries of the country over a year
What is gross national income (GNI)?
GNI (GNI = GDP + net factor income from abroad) or GNP is the monetary value of final goods and services produced by the residents of a country over a year
production process may take place either within the country itself or in another country
refers to GDP plus factor incomes earned by residents overseas minus factor incomes earned by non-residents in the domestic economy
What is nominal GDP?
GDP valued at the current prices
What is real GDP?
GDP valued at a chosen base year’s price level
How to calculate GDP or GNI per capita?
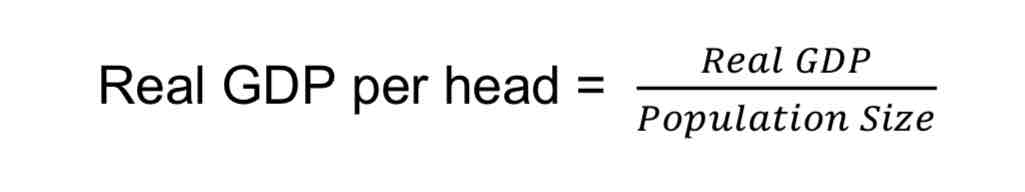
How to calculate economic growth rate?

What is unemployment?
unemployment occurs when people in the working age population who are available for work and are actively looking for a job but are without a job
How to calculate unemployment rate?

What is trade balance (BOT)?
balance of trade (BOT) is a statement of the transactions of goods and services between one country and the rest of the world
BOT = value of exports of goods and services (X) – value of imports of goods and services (M)
positive BOT means the country is having a trade surplus while a negative BOT means a trade deficit
What is exchange rate?
exchange rate (or foreign exchange rate) is the amount of one country’s currency that can be exchanged for another (price of one currency in terms of another)
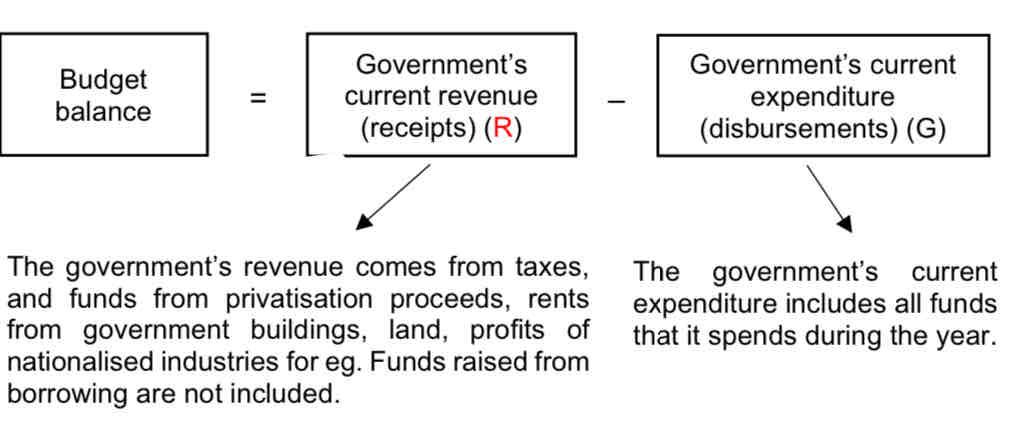
What is budget balance?
budget balance of a country is the difference between general government revenues and expenditures showing how much in a given year government spending is financed by the revenues collected
How to calculate gov budget?
What is standard of living?
material well-being and non-material well-being of the people in the country
What are the indicators of standard of living?
material and non material well being
HDI
Gini coefficient
real gdp per capita
What is material well being?
standard of living refers to the level of material well-being of an individual, determined by the quantity of goods and services enjoyed by an individual
What are the factors determining material well being?
cost of living differences
reliability of data differs
size of the hidden/ underground economy differs
size of non-market economy differs
What is non material well being?
non-material well-being refers to the quality of life enjoyed by individuals which is influenced by environmental factors such as degree of urban crowding & crime rates, and by socio-economic factors such as life expectancy and leisure hours
What are the factors determining non material well being?
infant mortality rate
quality of personal and family life
quality of environment
unemployment rates
What is gini coefficient?
commonly used indicator that measures the income inequality
measures the extent to which the distribution of income among individuals or households within an economy deviates from a perfectly equal distribution (value lies between 0 and 1)
a value of 0 represents perfect income equality where every household has the same income
a value of 1 represents perfect income inequality – where one household has all the income in the economy
the greater the value of the Gini coefficient, the greater is the income inequality
most of the benefits of growth may not be enjoyed by the majority of the population, majority of the population may have a much lower standard of living than the minority
Why is gini coefficient considered in standard of living?
if a country has a high gini coefficient, improvement in standard of living is likely to be experienced by only a small proportion of the country’s entire population, thus, having good economic performance in terms of economic growth, price stability and employment is not necessarily the only determinant of standard of living in a country
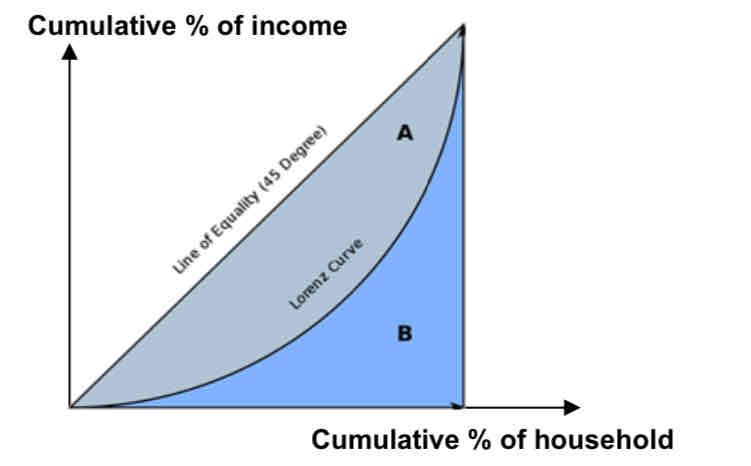
How to calculate gini coefficient?
Lorenz curve is a graph on which the cumulative percentage of total income is plotted against the cumulative percentage of the corresponding population (households),
area between the line of equality (45 degree line) and the Lorenz curve divided by the area under the line of equality (45 degree line)
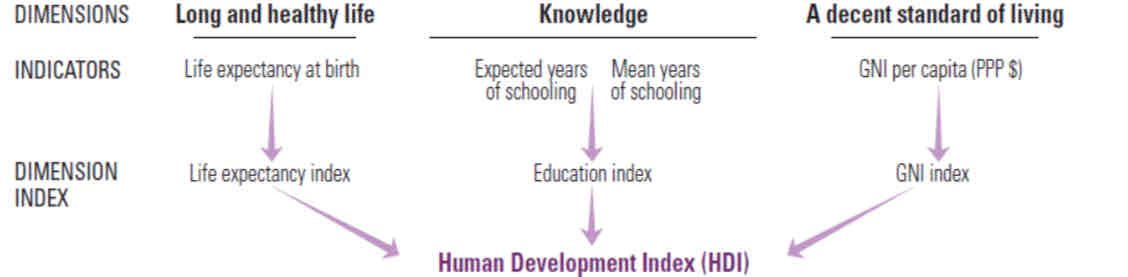
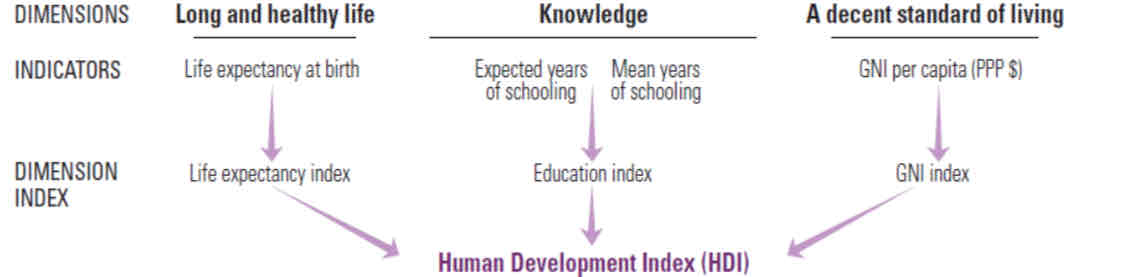
What is human development indicator (HDI)?
composite indicator to reflect standard of living
summary measure of average achievement in three key dimensions of human development – a long and healthy life, being knowledgeable and having a decent standard of living
How is HDI interpreted?
HDI index is expressed as a value between 0 and 1, where 1 is the best possible score and zero is lowest possible score
high values of HDI scores are associated with good health care systems, widely-available education and a productive economy
higher the HDI index (i.e. closer to 1) the higher will be the level of standard of living,vin terms of both material and non-material aspect
as an increase in a country’s HDI value would have been attributed to an increase in life expectancy index, education index and/or GNI index
How is HDI assessed?
health dimension is assessed by life expectancy at birth,
education dimension is measured by mean years of schooling for adults aged 25 years and more and expected years of schooling for children of school entering age
standard of living dimension is measured by gross national income per capita
What are the limitations of HDI?
HDI is not a complete measure of welfare because it does not consider issues like quality of education, inequality, political, social and economic freedom, human rights, protection against violence and discrimination, and opportunities for creativity which can obscure important differences in human development
How does higher HDI result in higher standard of living?
increase in a country’s HDI value due to an increase in real GNP (or GNI) per capita (PPP$) would imply a higher material standard of living for every individuals as the citizens have greater ability to consume more quantities of goods and services in the country
How does higher HDI result in higher of non material SOL?
citizens face a relatively high level of non-material well-being as reflected by higher life expectancy index and/or education index
How does higher HDI result in higher literacy?
country as reflected by the higher education index,
it means that there are more job opportunities available for the educated individuals which may mean higher future incomes to be earned,
individuals may also be more able to enjoy better quality goods and services
also implies that the people in a country will be able to read and appreciate aesthetics or literacy work, enjoy the fine arts and engage in pursue of their own aspirations
ability to pursue self-realisation is a non-material aspect of SOL
How does higher HDI result in higher life expectancy?
individuals have access to better nutrition healthcare services and hence are more able to enjoy a higher quality of life
How does infant mortality rate determine non material well being?
infant mortality rate is measured as number of deaths of children under one year of age, expressed per 1 000 live births
fall in the infant mortality rate in a country is another measure of improvements in a country’s non-material standard of living
decreasing levels of infant mortality rate are associated with better access to healthcare and nutrition over time, more optimal living conditions including better sanitation and higher levels of education, implying improvements over time in the quality of life experienced by the residents of a country
decreasing infant mortality rate is a measure of improvements in non-material standard of living in a country
How does unemployment rate determine non material well being?
level of unemployment in an economy can also determine the non-material well-being in an economy
with a greater number of unemployed people, the quality of life of individuals would worsen as they may be more stressed about finding employment
higher levels of crime are also associated with higher unemployment rates in
an economy which worsens quality of life
How does quality of personal and family life determine non material well being?
increase in real income per capita over 2 periods may overstate the increase in standard of living if the increase in national income is accompanied by a longer average working week, higher stress level at work, more working mothers and a decrease in quality family life
How does quality of environment determine non material well being?
increase in real income per capita may not increase the standard of living if it is accompanied by negative externalities. Negative externalities such as pollution and congestion are likely to arise as the economy grows and expands. Hence, although people may be on average, better off in terms of spending power, they may be worse off when environmental factors are considered
Why is real GDP used instead of norminal GDP?
nominal GDP could have risen over time, but general price levels could have risen at a faster rate, thus eroding the real purchasing power of the individual and living standards in the economy
real GDP refer to the value of final goods and services produced within a country measured at constant base year price
by measuring GDP at constant base year prices, its value has been adjusted for price changes
Why is per capita used in GDP?
a rise in quantity or volume of goods and services produced does not necessarily imply an improvement in the quantity or volume of goods enjoyed by an individual if the number of residents in the country rose faster
thus to consider the effect of changes in the size of the nation’s population, compute per capita income - the amount of goods and services available to each individual in the nation.
How does cost of living difference determine material well being?
most commonly used measure to compare standard of living of different countries is the real income per head expressed in terms of a common currency
country with higher real income per head does not necessarily mean that its residents will enjoy higher standard of living
as official or nominal exchange rate is over-valued or under-valued due to several reasons.
real income per head figures does not consider the differences in the cost of living between countries
How does difference in reliability of data determine material well being?
lack of facilities and expertise in data collection and analysis in developing economies lead to tendencies for their GDP figures to be inaccurate compared to developed economies.
making the comparison of standard of living between developing and developed economies more difficult, than in comparing economies at similar stages of development
How does difference of size of hidden/ underground economy determine material well being?
official real income may understate the actual change in output because of the existence of a hidden/ underground economy
people may not declare to the tax authorities the incomes they earn in an attempt to evade paying tax and people may not declare economic activity because it is illegal such as smuggling of goods
size of the hidden economy varies between economies, it is influenced, among other things, by tax rates on income and the penalties imposed for illegal activity
difference in the size of the hidden economy can make international comparison of economic growth rates and living standards difficult
How does difference of the size of non market economy determine material well being?
omissions become serious when one is comparing living standards between developed countries and developing countries
I’m developing countries, a large part of the production of the agricultural sector is not traded and therefore does not appear in national income statistics, their people consume what they themselves produce, thus existence of a relatively large non-monetary sector in developing economies
this means that the official income figures will grossly underestimate the country's output, which is in contrast to the highly-monetised developed economies
to make meaningful comparison of living standards between developed and developing countries, there is need to estimate the non-market activities of developing countries and include them in the countries' national income statistics, however, it is difficult to impute a value for each non-market activity
How does difference in type ot goods produced determine material well being?
country with higher national income does not guarantee higher living standards
type of products which raises people's living standards may differ between countries
production is desirable to the extent that it enables the country to consume more
How does difference in income distribution determine material well being?
countries with similar per capita incomes may still have very different standard of living for the majority of their population, if their distributions of income are not the same (rich ppl can pull up average) making the per capita income higher than other countries with more even distribution of income
Define AS
total output of goods and services produced by an economy fro given general price level
AS is at __ spare capacity at intermediate range
limited
There is __ at intermediate range (about employment)
approaching of full employment of resources
AS is at __ spare capacity at horizontal range
excess
There is __ at horizontal range (about employment)
large amount of unemployment resources
There is __ at horizontal range (about employment)
full employment rate
AS is at __ spare capacity at vertial range
no / approaching no
Explain shifts in the horizontal segment of AS curve
there is changes in unit cost of production that is not associated to the a chage in productive capacity of an economy
as such when there is decrease in price of a factor of production,
unit cost of production decreases
and producers are more willing and able to produce more
this results in an increase of AS along the horizontal range
Describe the factors that shift the vertical proportion of AS curve
change in quantity of resources
change in quality of resources
change in state of technology
Describe changes in quantity of resources in AS
investment by private sector (by domestic and/or overseas firms) and public sector (government) which raises the stock of capital (e.g. capital accumulation), enables increased production (increases the economy’s ability to produce) and increases the economy’s productive capacity
immigration and population growth/greater population of working age which increases the quantity of labour, enables increased production and increases the economy’s productive capacity
effective supply-side policies which create the right environment for households to supply factors of production and for firms to produce output and increases the economy’s productive capacity
Describe changes in quality of resources in AS
investment of human capital increases quantity of labor, thus leads to more output / hour
this increases economy’s productive capacity
Describe changes in state of technology in AS
higher level of spending on new technology enabled economy to produce in greater volume using same quantity of scare resources
this increases productive capacity
What is definition of AD
total demand for all goods a d services produced by a country for given general price level
AD= C + I + G + (X-M)
Describe consumption expenditure
consumption expenditure (C) refers to the spending by households on consumer goods such as food, clothing, household appliances and services
C increases, AD increases
State the factors of consumption expenditure
consumer confidence
demographic
income
access to credit
technology changes
Describe technology changes in terms of C
technological advances have enabled the creation of new products and services and added value to existing ones, thereby increasing consumption
there will be creation of new products and services and increased convenience and accessibility
Describe demographics in terms of C
changes in demographics significantly impact aggregate consumption in an economy, as different demographic groups have varying consumption patterns, savings behaviors, and overall economic need
Describe income in terms of C
increase in the level of income in the country would result in households having a greater amount of money to spend on goods and services
increase disposable income
which increases purchasing power
Describe consumer confidence in terms of C
consumers are optimistic about the overall state of the economy, they are likely to make more purchases even without any changes in income, due to perceptions of greater job security and expectations of promotions /higher incomes
Describe access to credit in terms of C
interest rate is the cost of borrowing money.
Interest rates charged by banks can affect households’ access to credit to make expensive (or big-ticket) purchases
interest rate decreases, more households would be attracted to borrow money to fund these purchases, increasing consumption expenditure
changes in interest rates can also affect consumption via changes in returns on saving
when interest rate decreases, the returns on saving money would fall or the opportunity cost of spending would decrease, households will be incentivised to spend rather than save
Describe investment expenditure
investment expenditure (I) refers to the spending by the firms on capital goods and net additions to stock
Describe the factors of investment expenditure
access to credit
expected return of investment
Describe access to credit in terms of I
interest rate is the cost of borrowing money or the cost of credit
determined by the demand and supply of loans
it is an important factor influencing investment by businesses that depends on borrowed capital
volume of investment is inversely related to the rate of interest
there is a fall in interest rate, this implies a fall in the cost of borrowing for firms to finance their investment spending
as such, projects with lower expected returns (which were previously unprofitable) will now appear profitable
hence, firms will be more willing to invest, resulting in an increase in the volume of investment, which in turn increases investment expenditure
Describe expected returns of investment in terms of I
economic outlook and technological changes can affect the expected return of investment, If business outlook or the level of technology improves, expected yield or return of investment will increase and this means that there will be more investment at each interest rate than before leading to an increase in investment expenditure
economic outlook
political stability > decrease confidence
infrastructure
ease of doing business
skills of workforce > attractive
technological changes
creation of investment opportunities
enhancement
competitive pressure and need for innovation
Describe government expenditure
refers to the government’s spending on goods and services
G increase, AD increase
State the factors of government expenditure
state of the current economy
government’s plans for the future economy
size of the government’s budget
State the definition of net exports
net exports is the difference between export revenue (X) and import expenditure (M) on goods and services
export revenue is the expenditure by foreigners on domestically produced goods and services, exports revenue therefore contributes directly to the country’s national income
meanwhile, import expenditure is the expenditure by locals on foreign produced goods and services, it does not generate income for the country, import expenditure has to be deducted from the computation of a country’s national income
State factors of exports revenue
foreign protectionism rate
foreign national income
relative price levels exchange
exchange rate
State factors of import expenditure
local protectionism
relative price levels
exchange rate
domestic expenditure rate