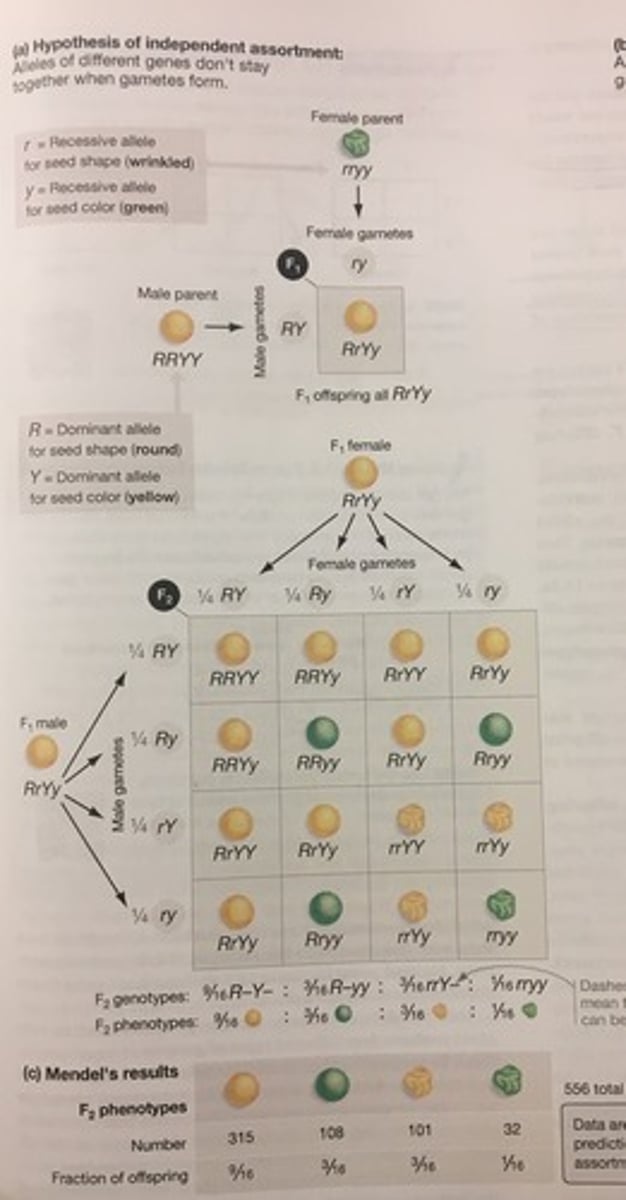
10.2 Mendelian Genetics basic punnetts (Glencoe Biology),
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

30 Terms
Genetics
Scientific study of heredity
Heredity
Passing on of characteristics from parents to offspring.
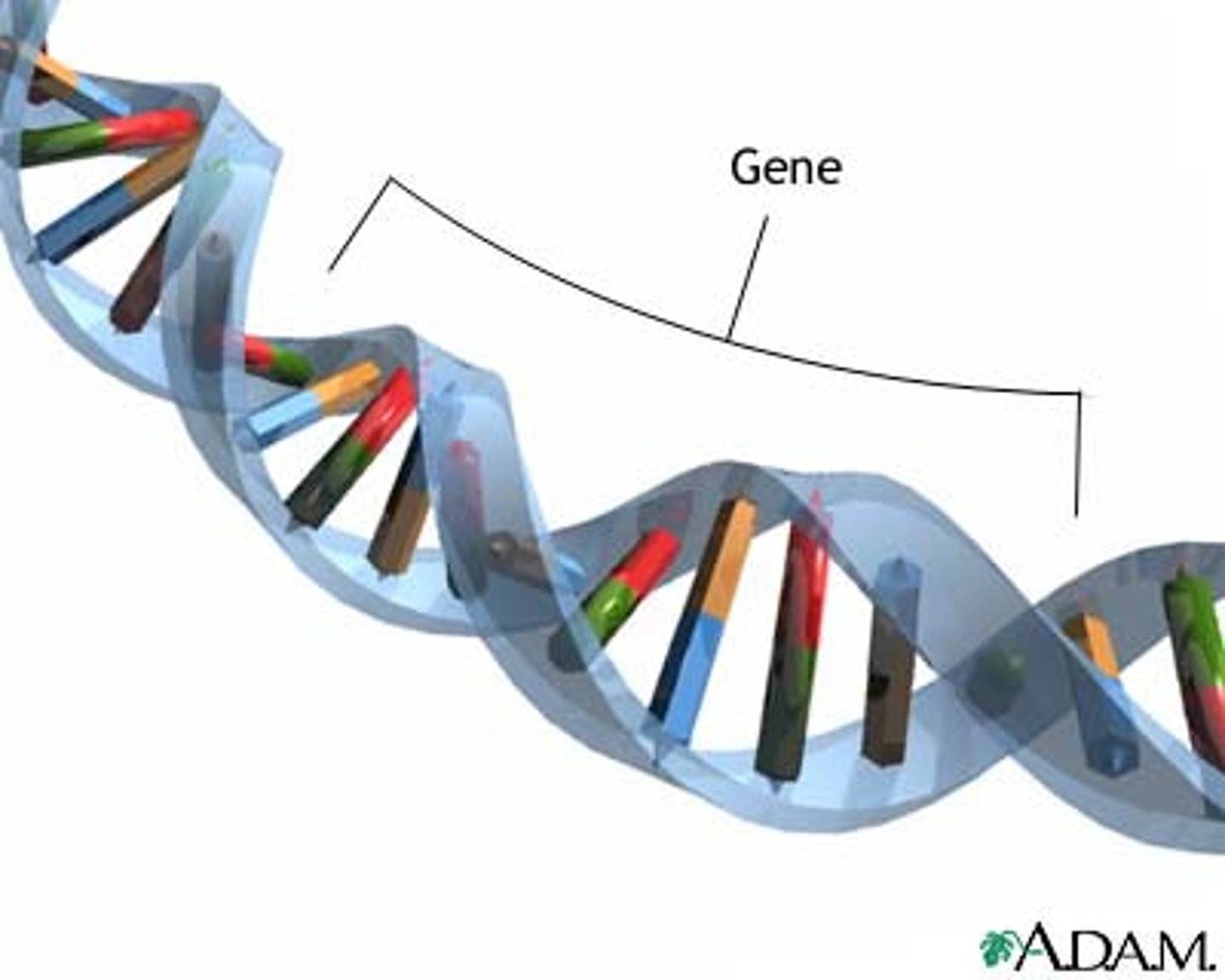
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait
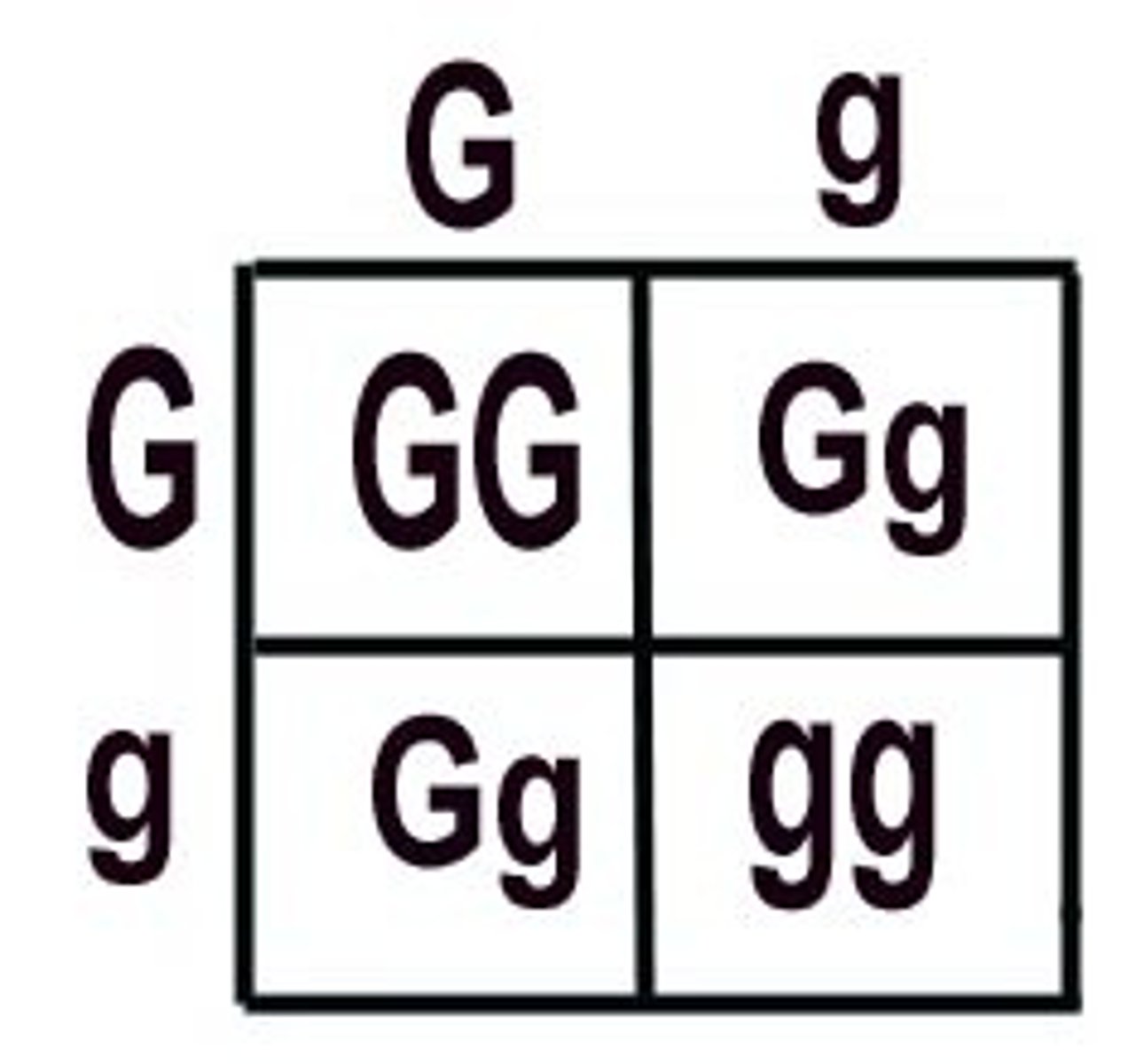
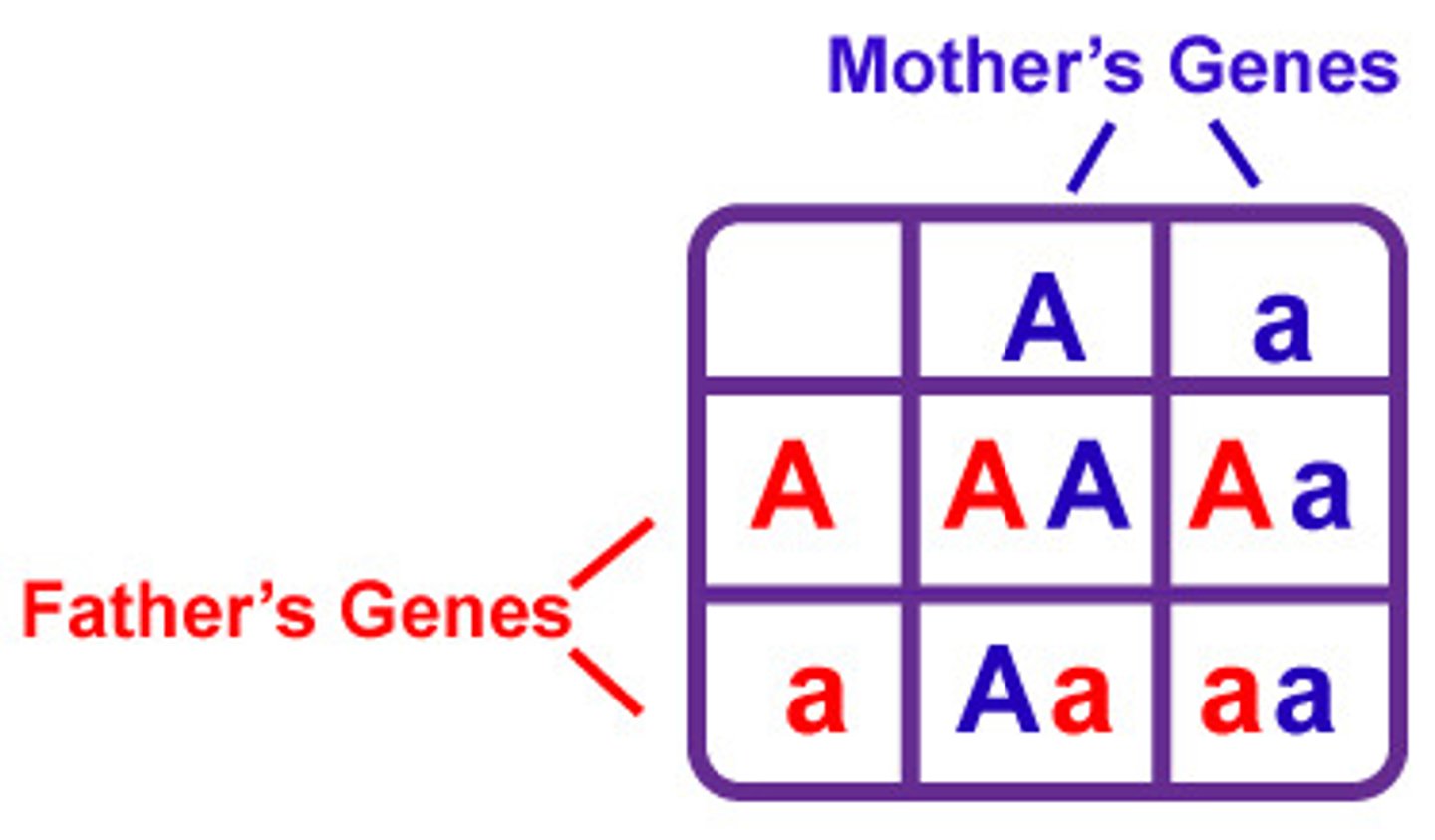
Punnett square
A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross
monohybrid cross
crosses that examine the inheritance of only one specific trait
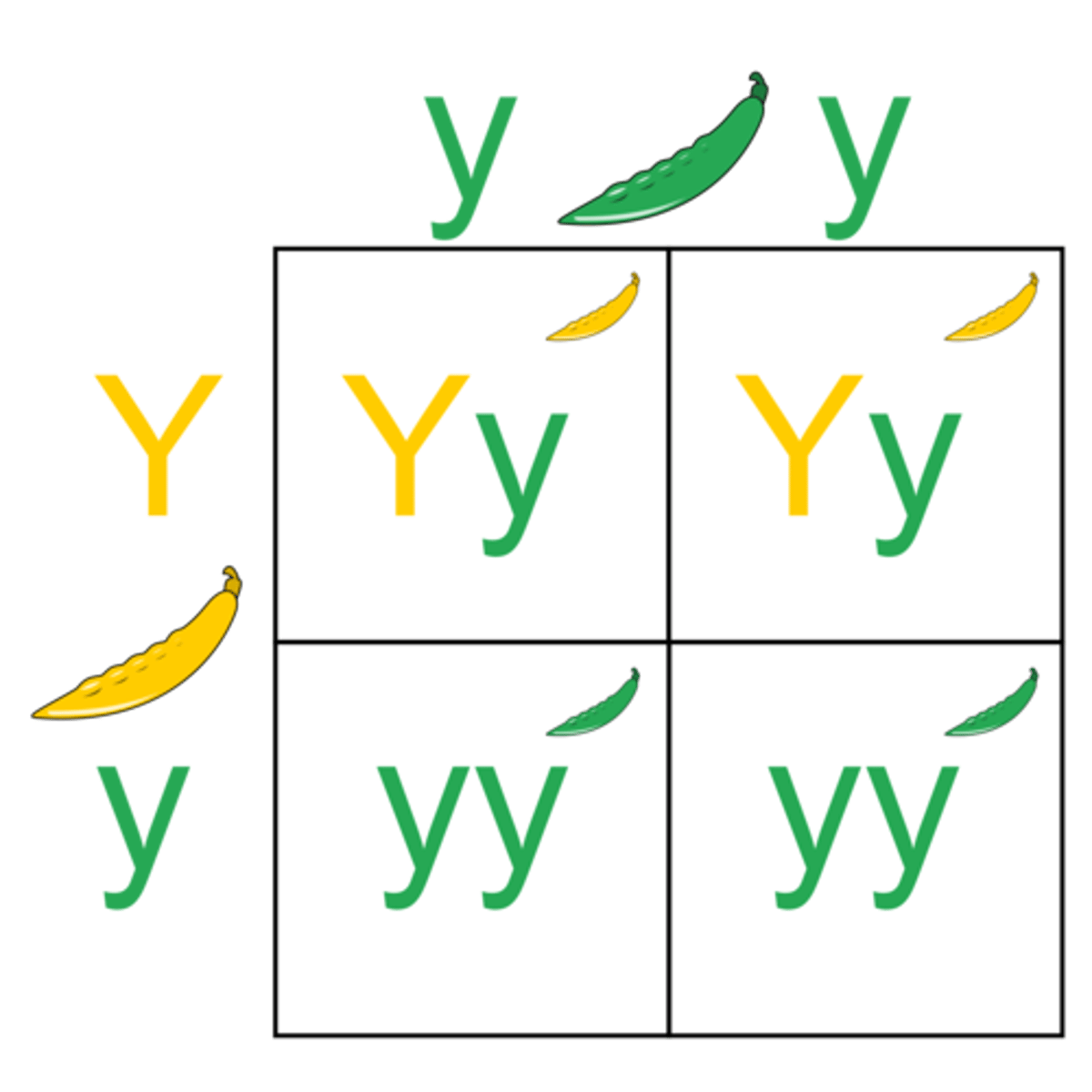
Allele
Alternate variants of a gene. Each parent contributes an allele (letter) to an offspring.
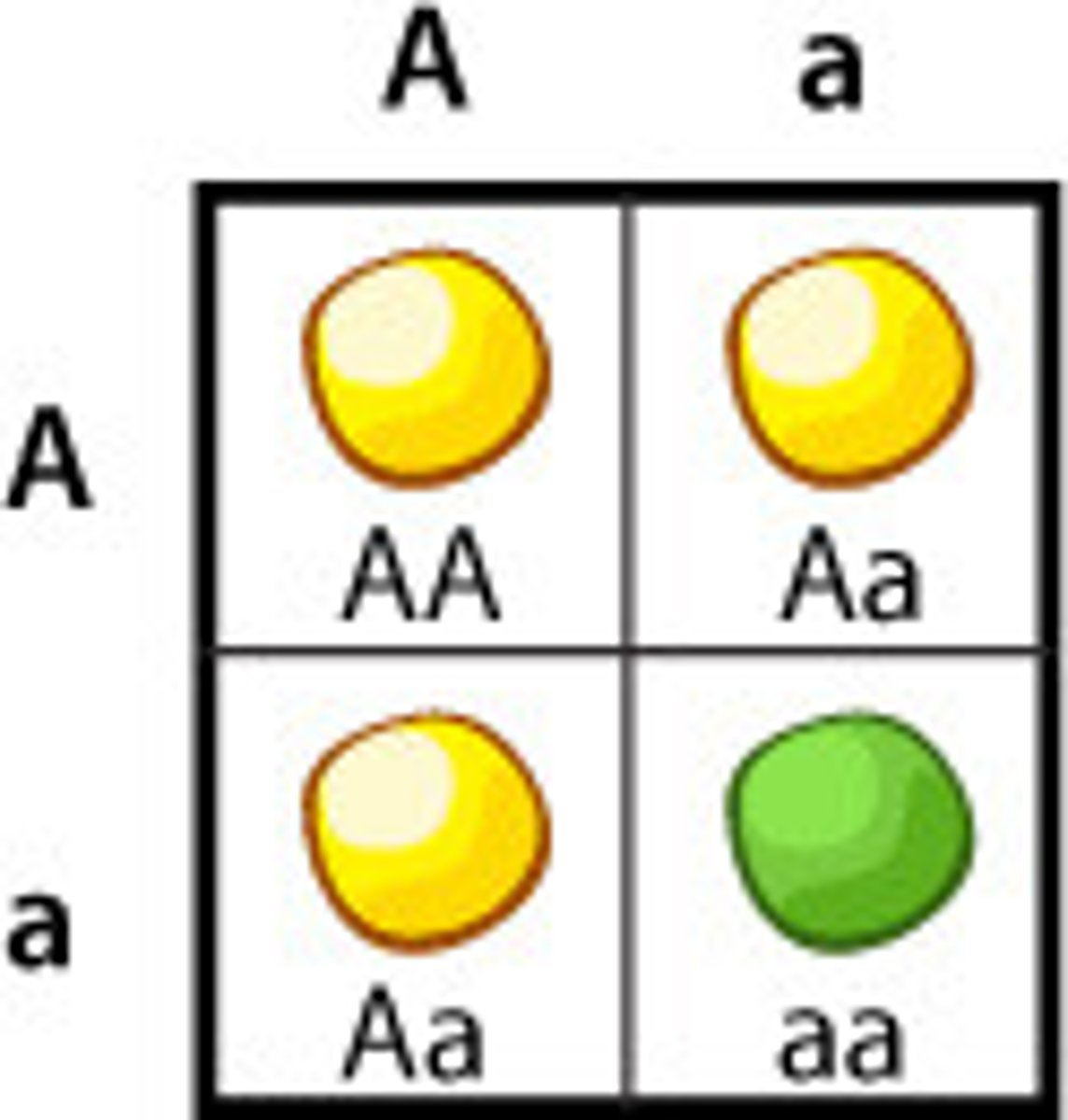
Dominant
A trait that overpowers or covers up a recessive trait.
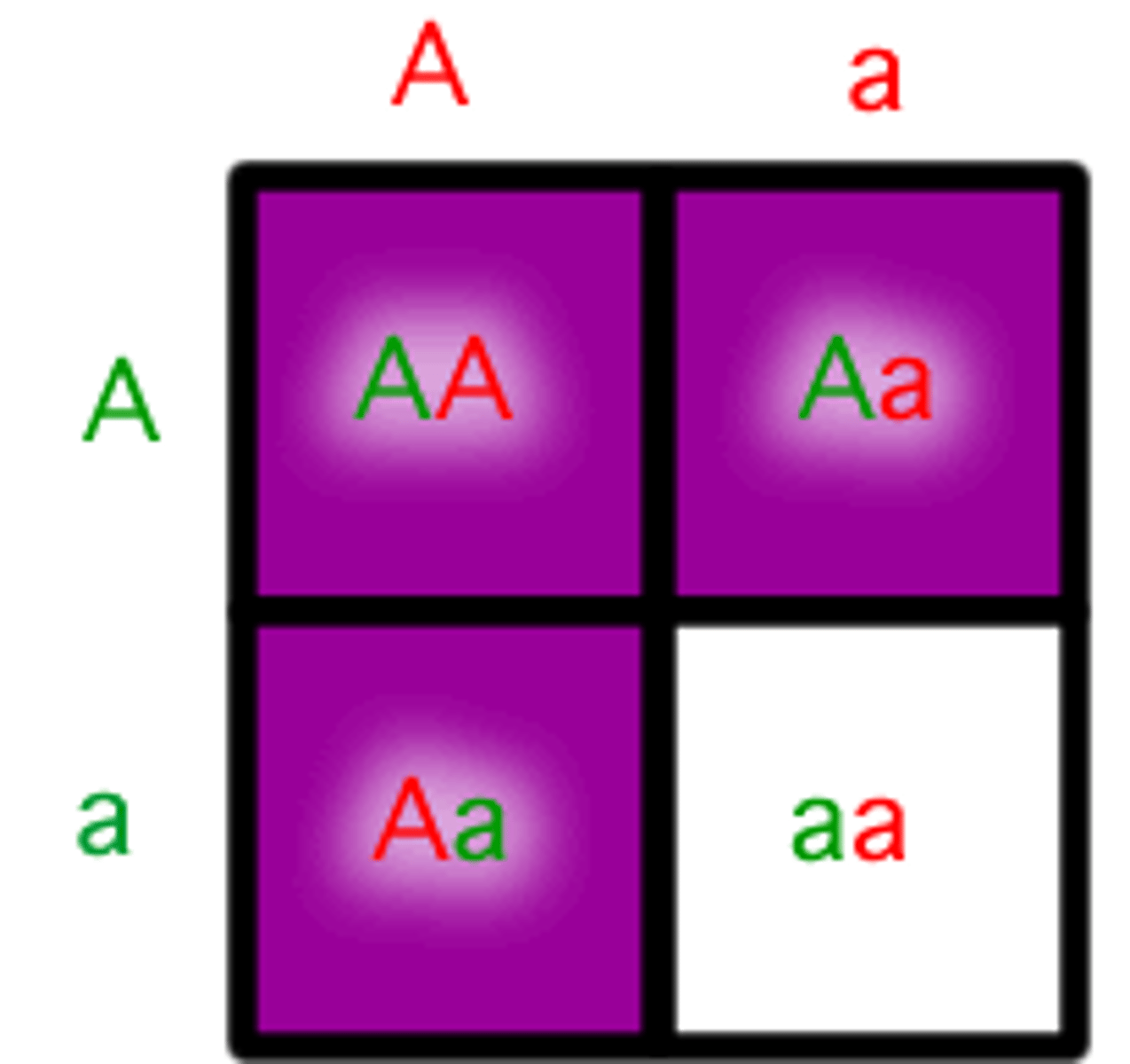
recessive
An allele that is masked when a dominant allele is present.
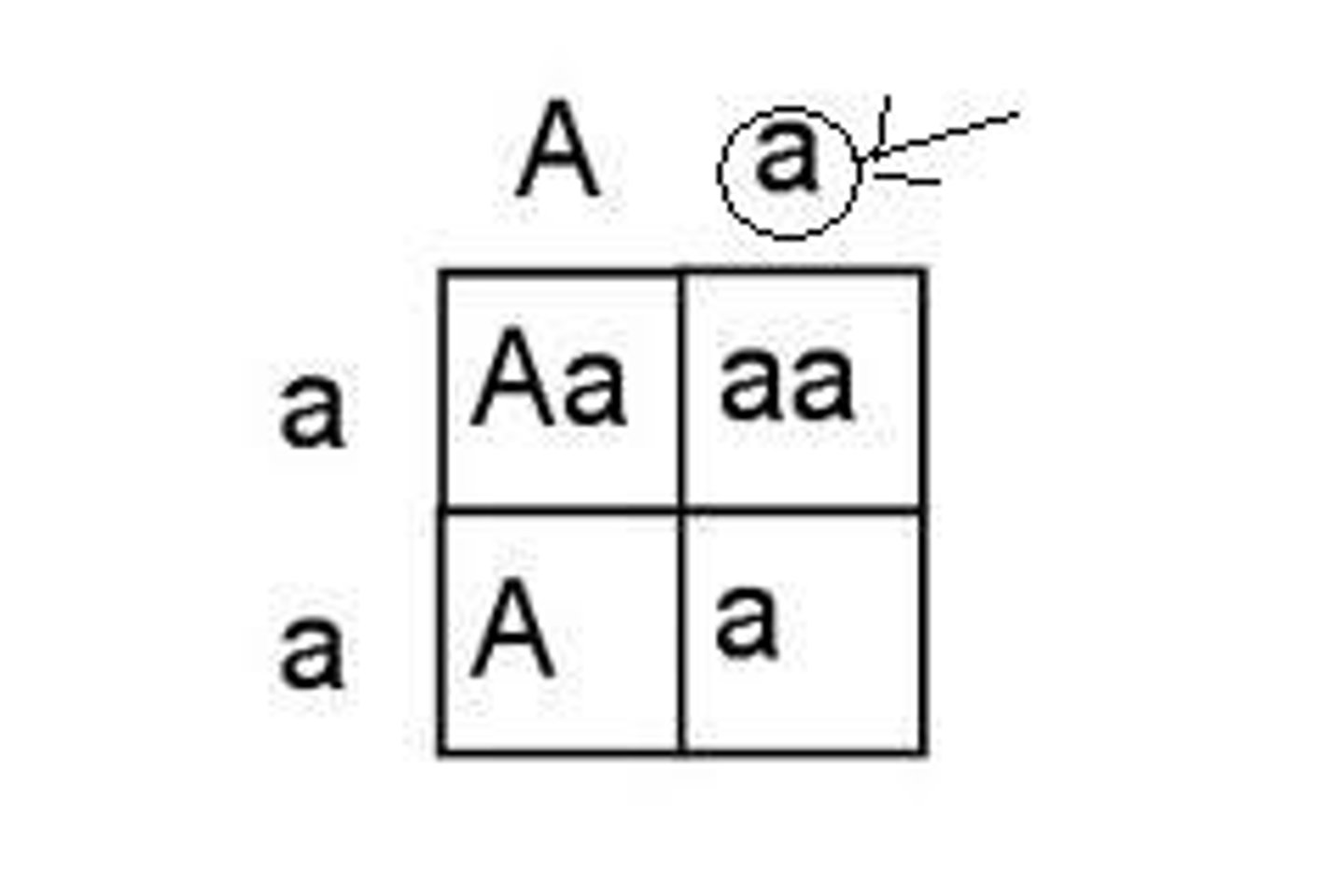
genotype
Genetic makeup of an organism. Say the letters ie. Pp => say "Big p little p"
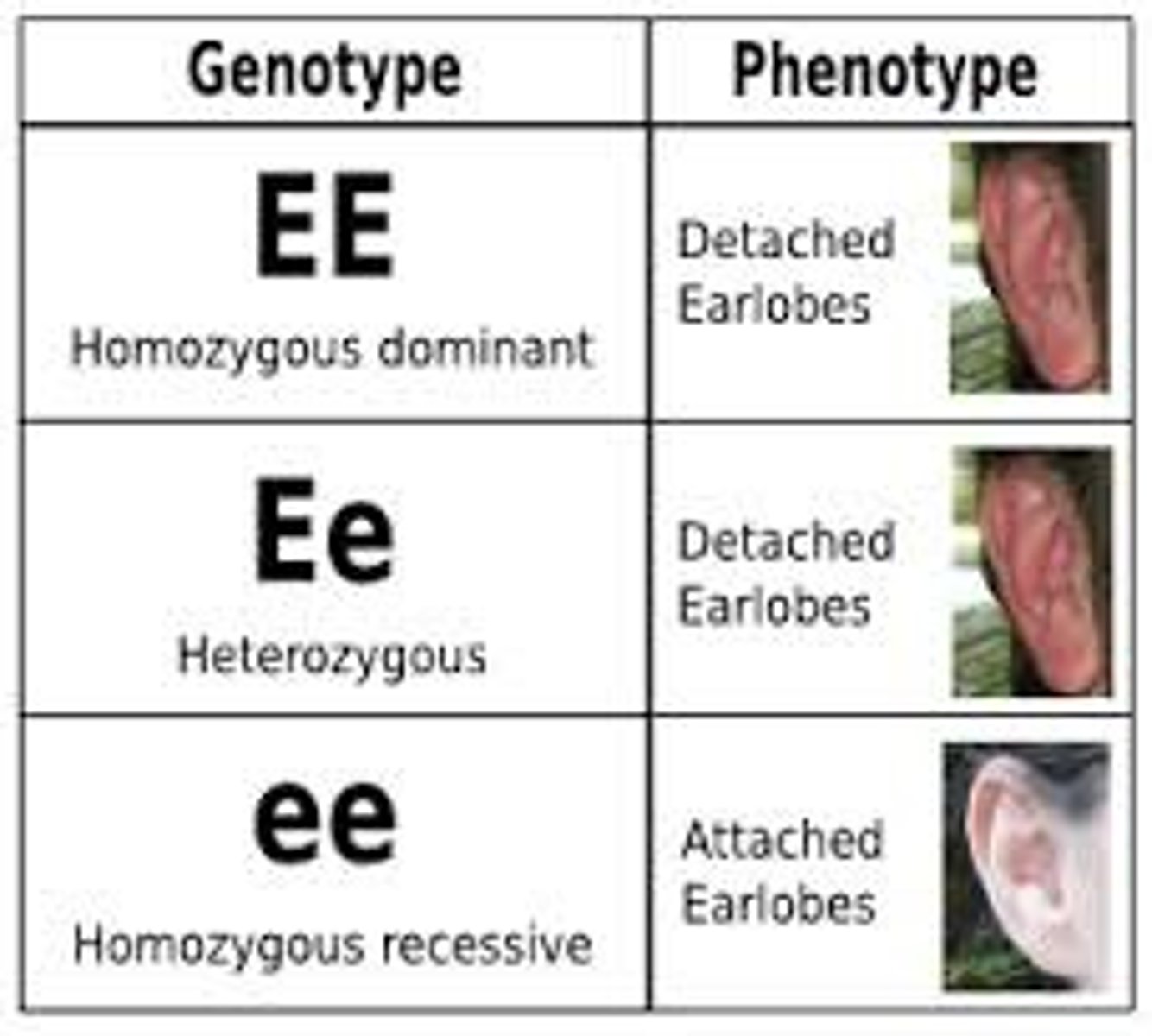
Phenotype
PHysical outcome of a genetic cross. The trait that showed up due to the letters in a Punnett
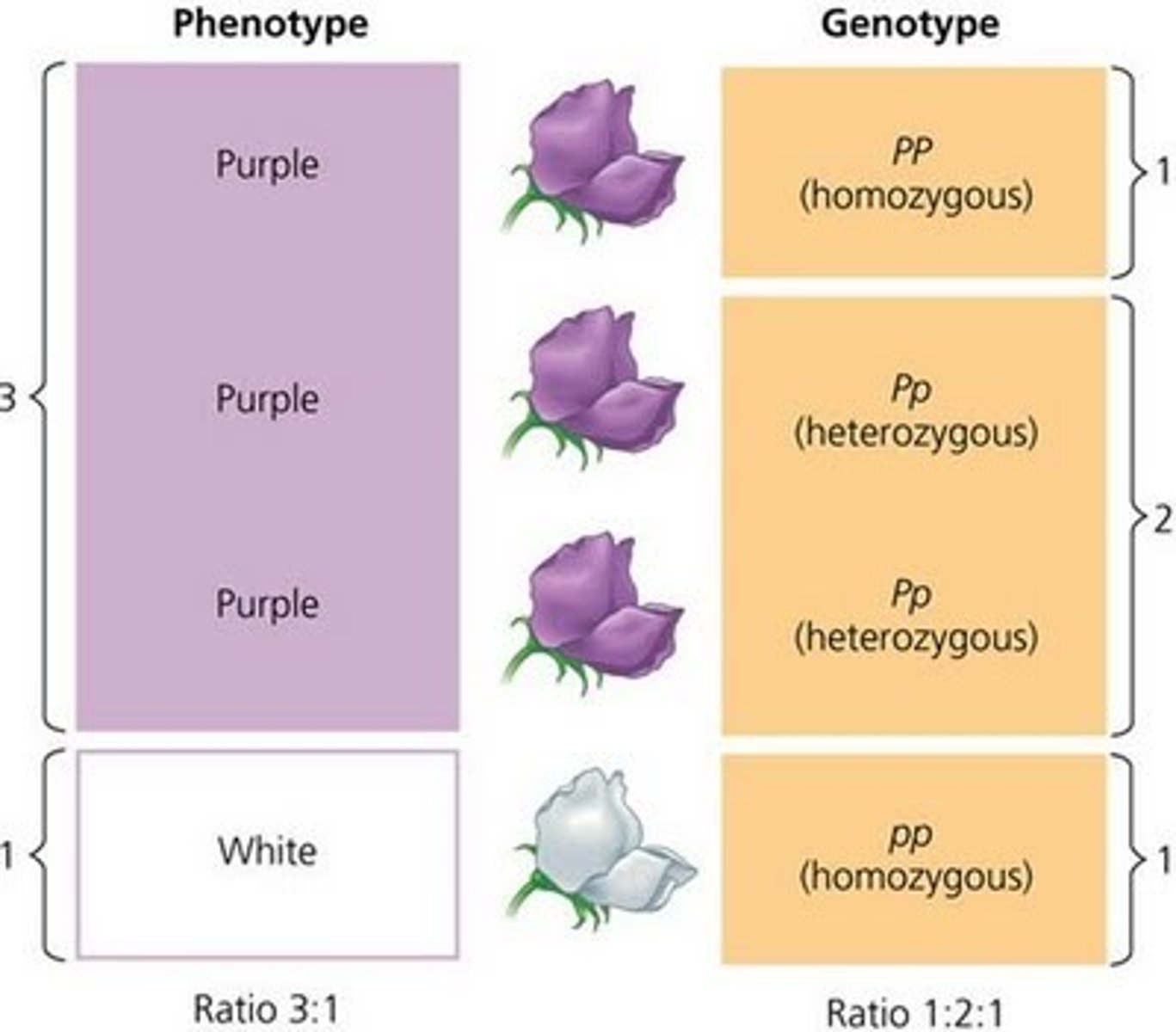
trait
Characteristic that is inherited
Homozygous
When there are two identical alleles for a trait. Same letters AA
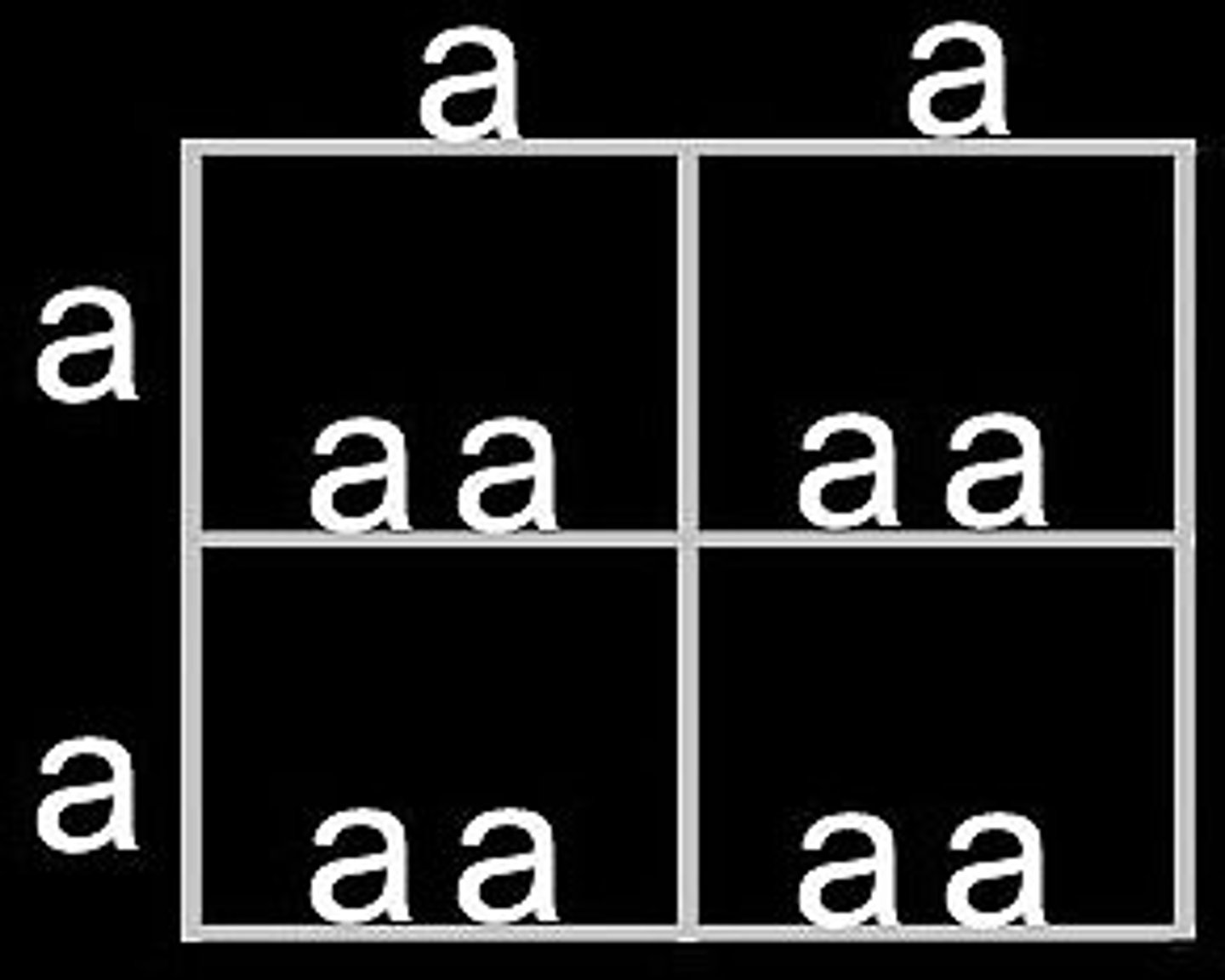
Heterozygous
When there are two different alleles for a trait. Different letters. ie. Aa or Bb.
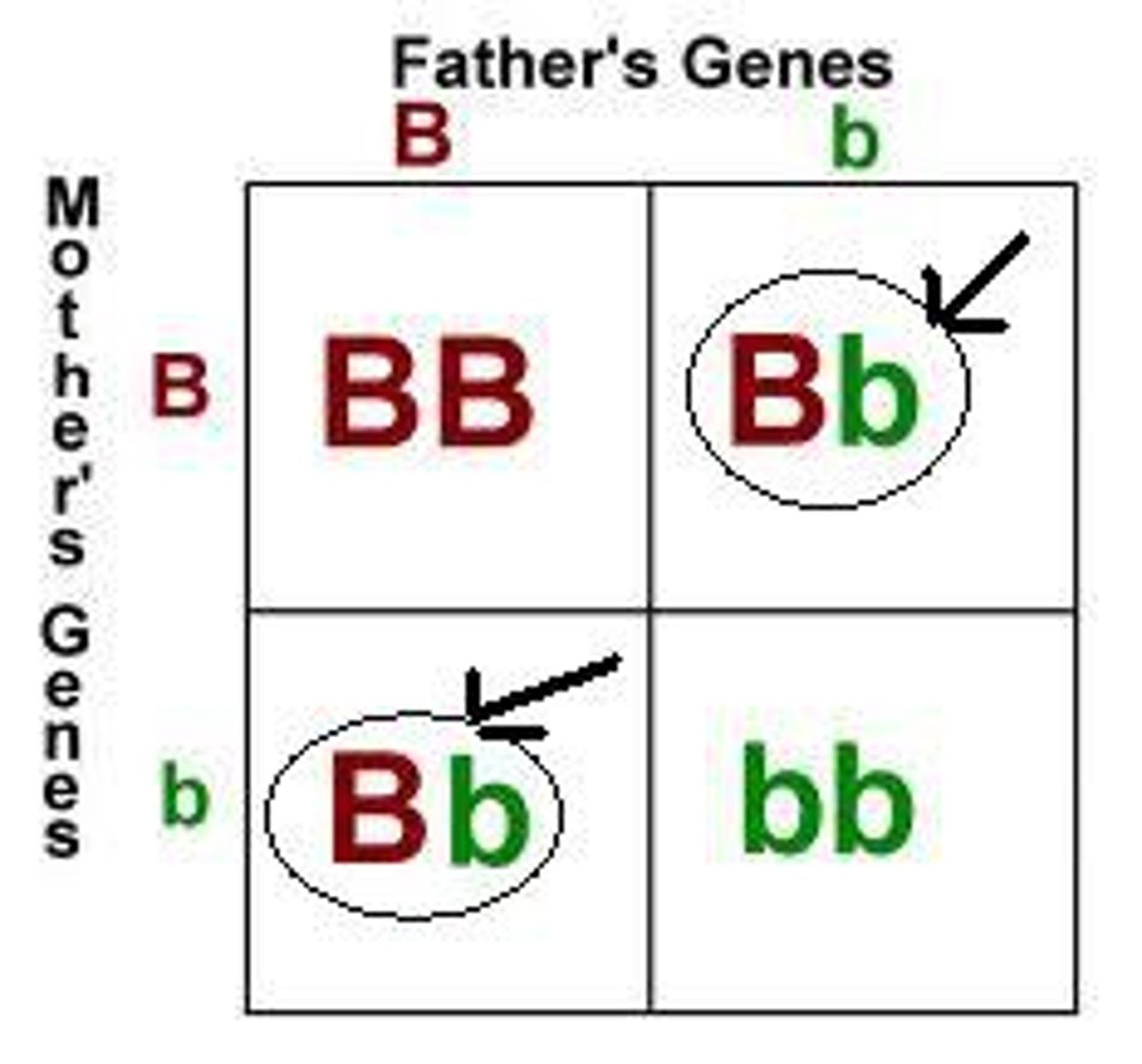
phenotypic ratio
the ratio of phenotypes that could appear in offspring. i.e. 3 out of 4 will be tall, one will be short
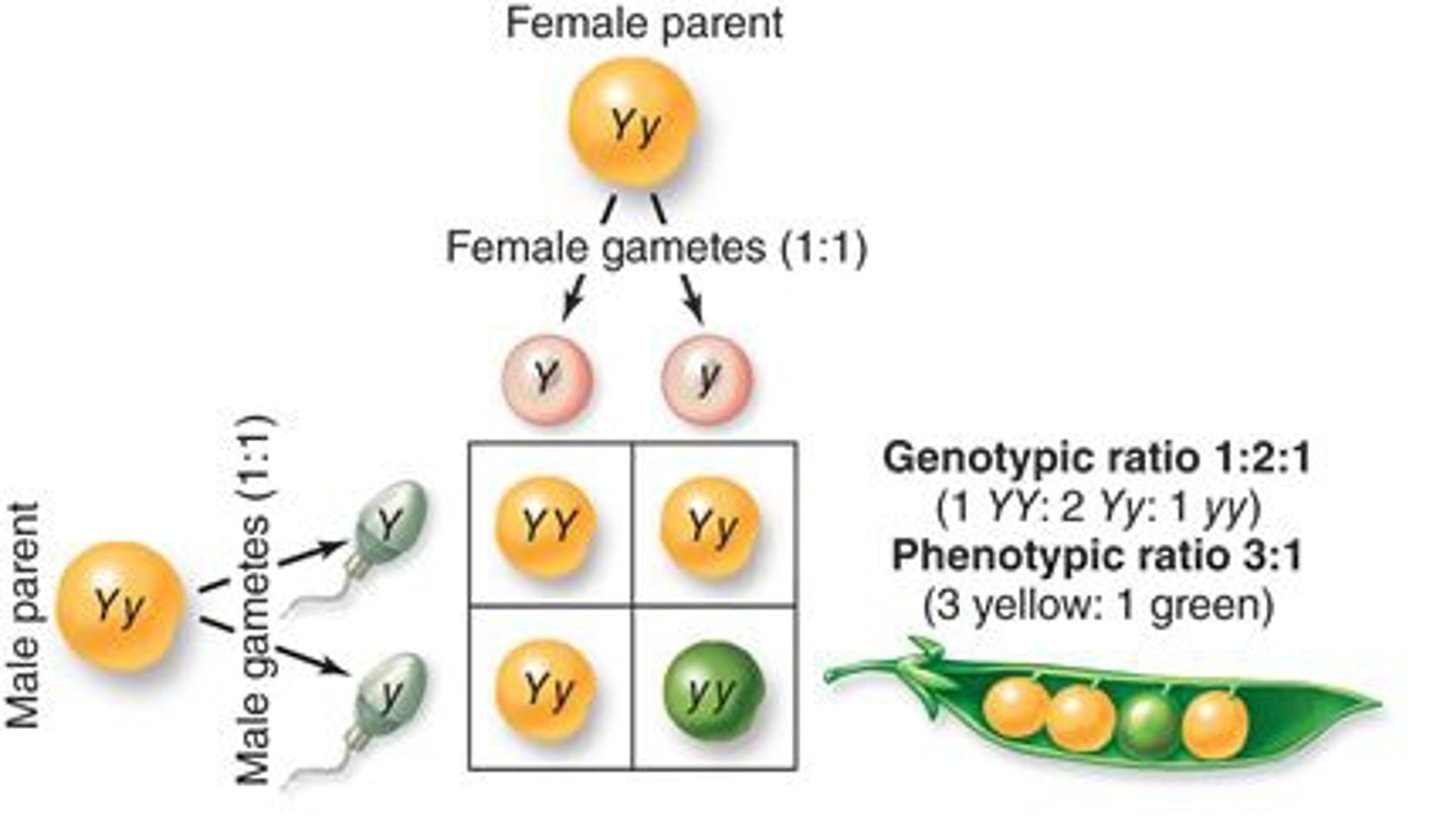
genotypic ratio
the ratio of the genotypes (think letters) that appear in offspring. i.e.. 1 will be TT, 2 will be Tt, and 1 will be tt. 1:2:1 ratio
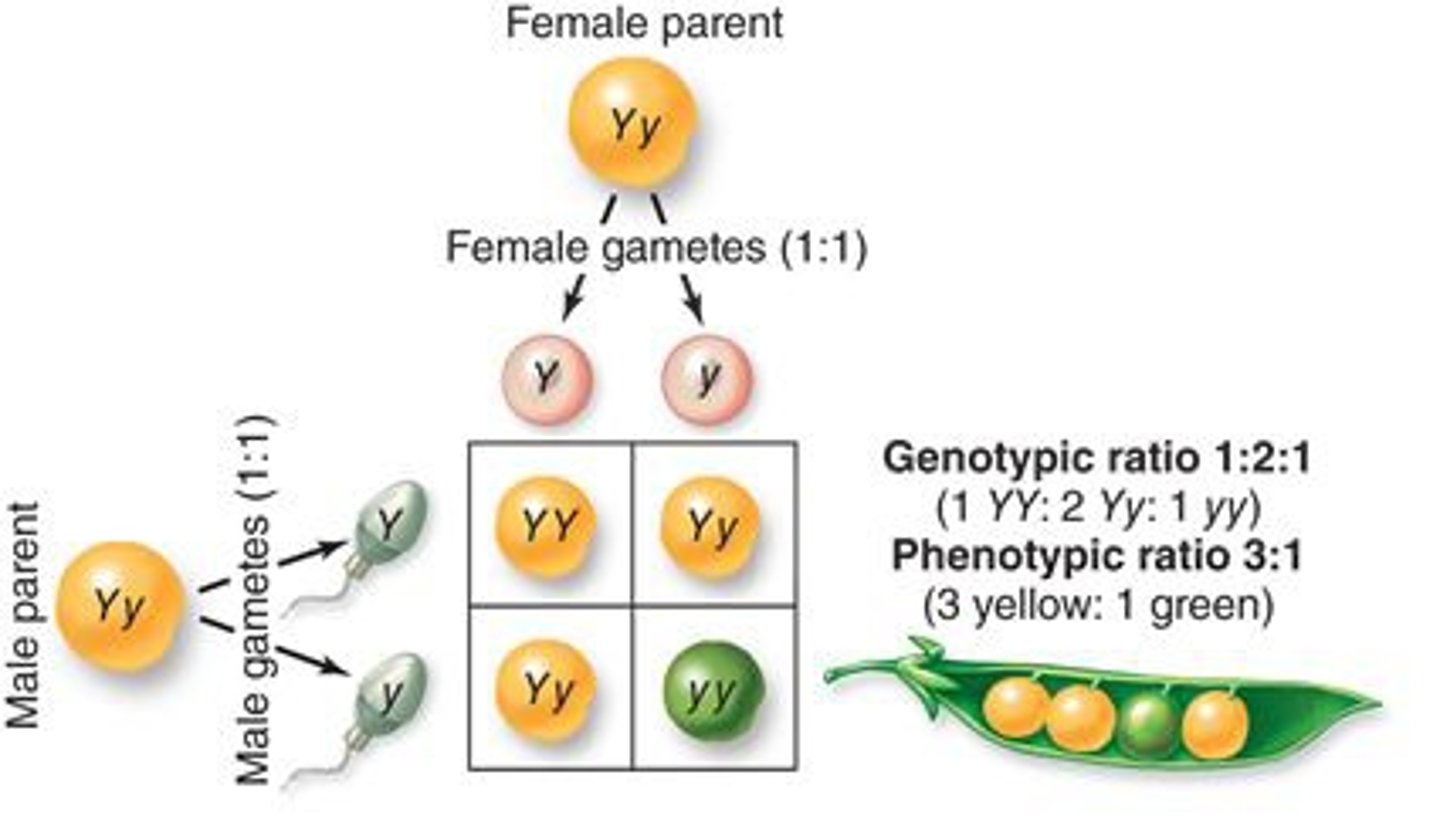
Offspring
A baby. In Punnetts it is what is found inside the boxes.
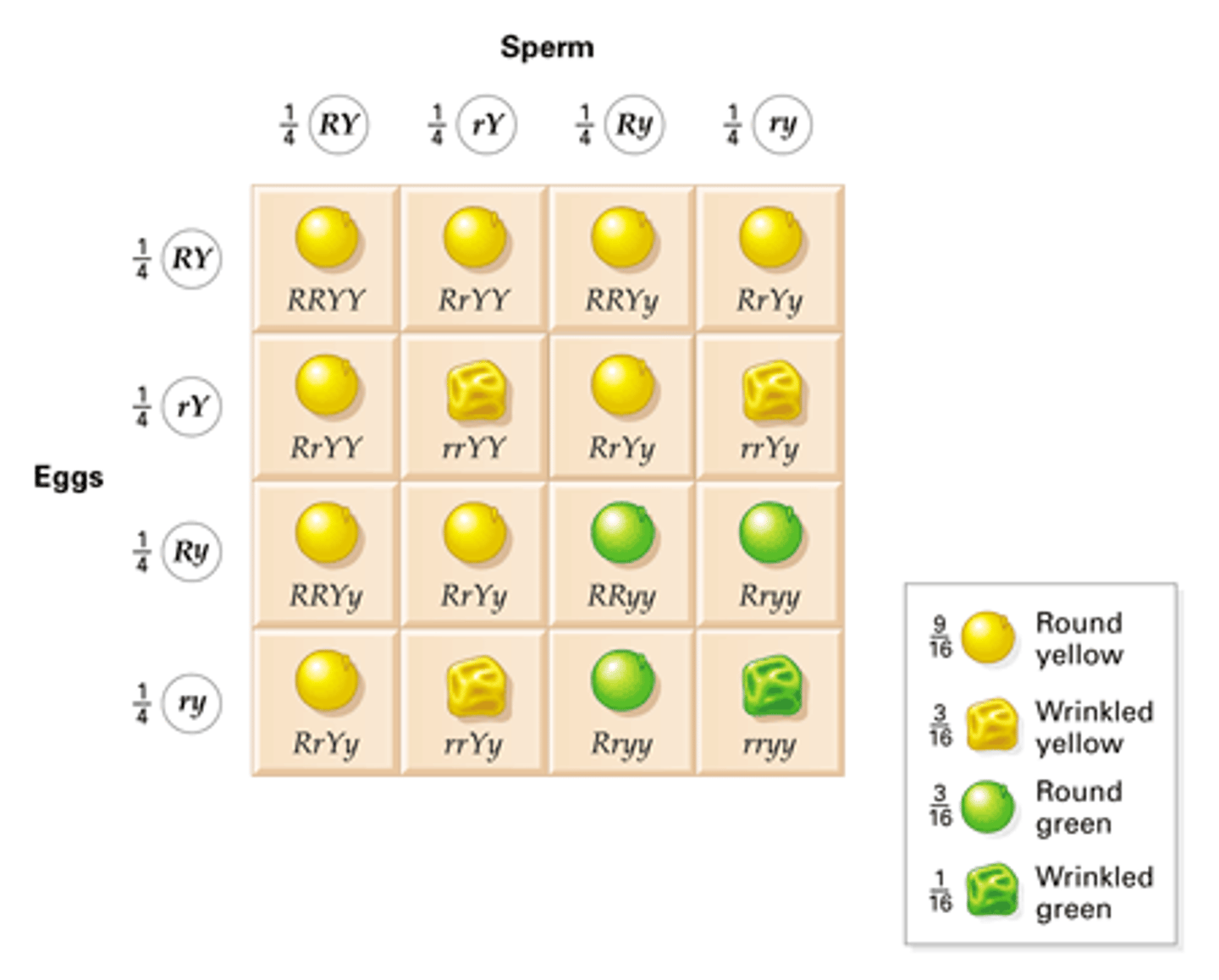
dihybrid crosses
A cross between two individuals, concentrating on two definable traits
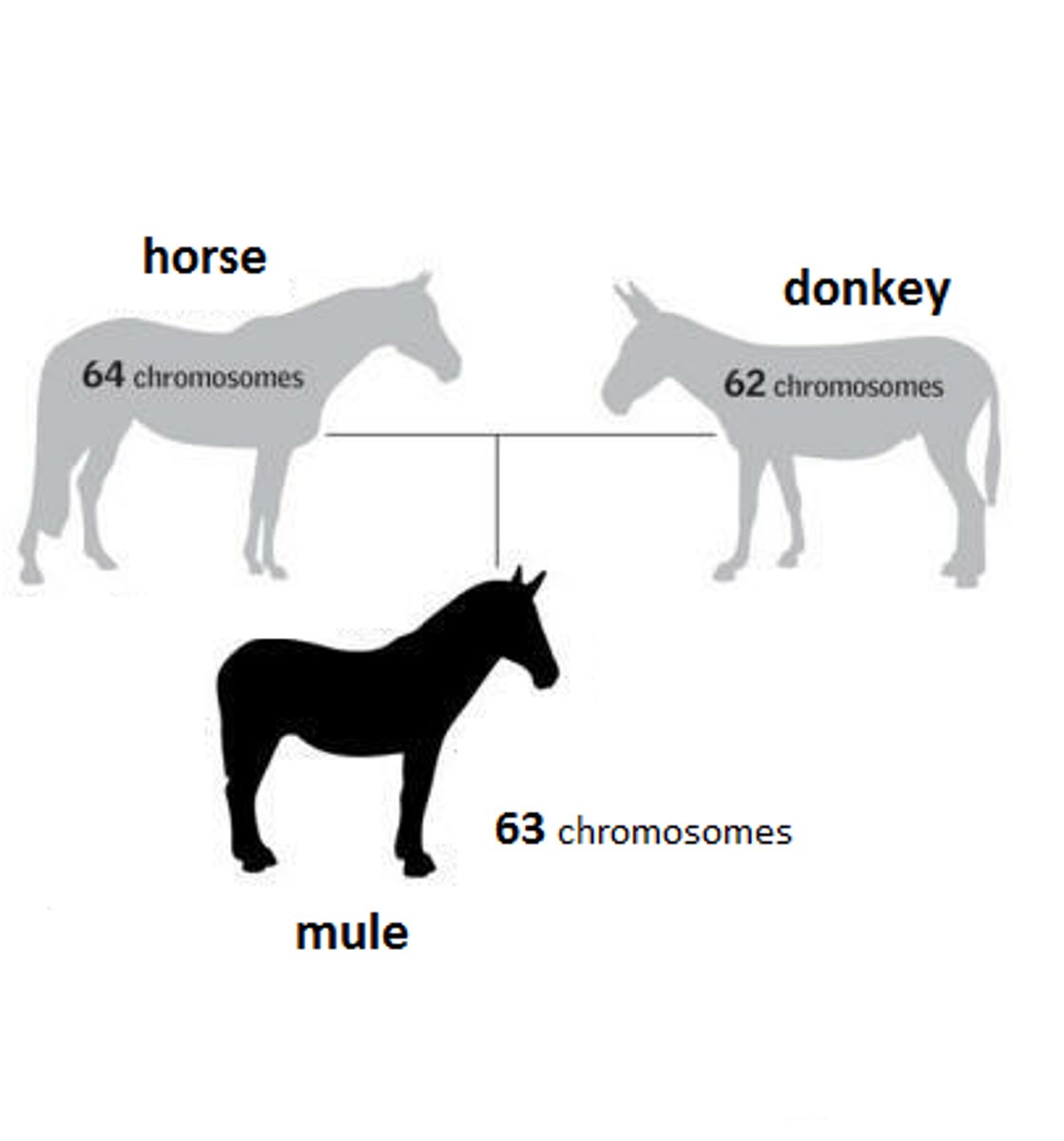
Hybrid
Offspring formed by parents having different forms of a trait.
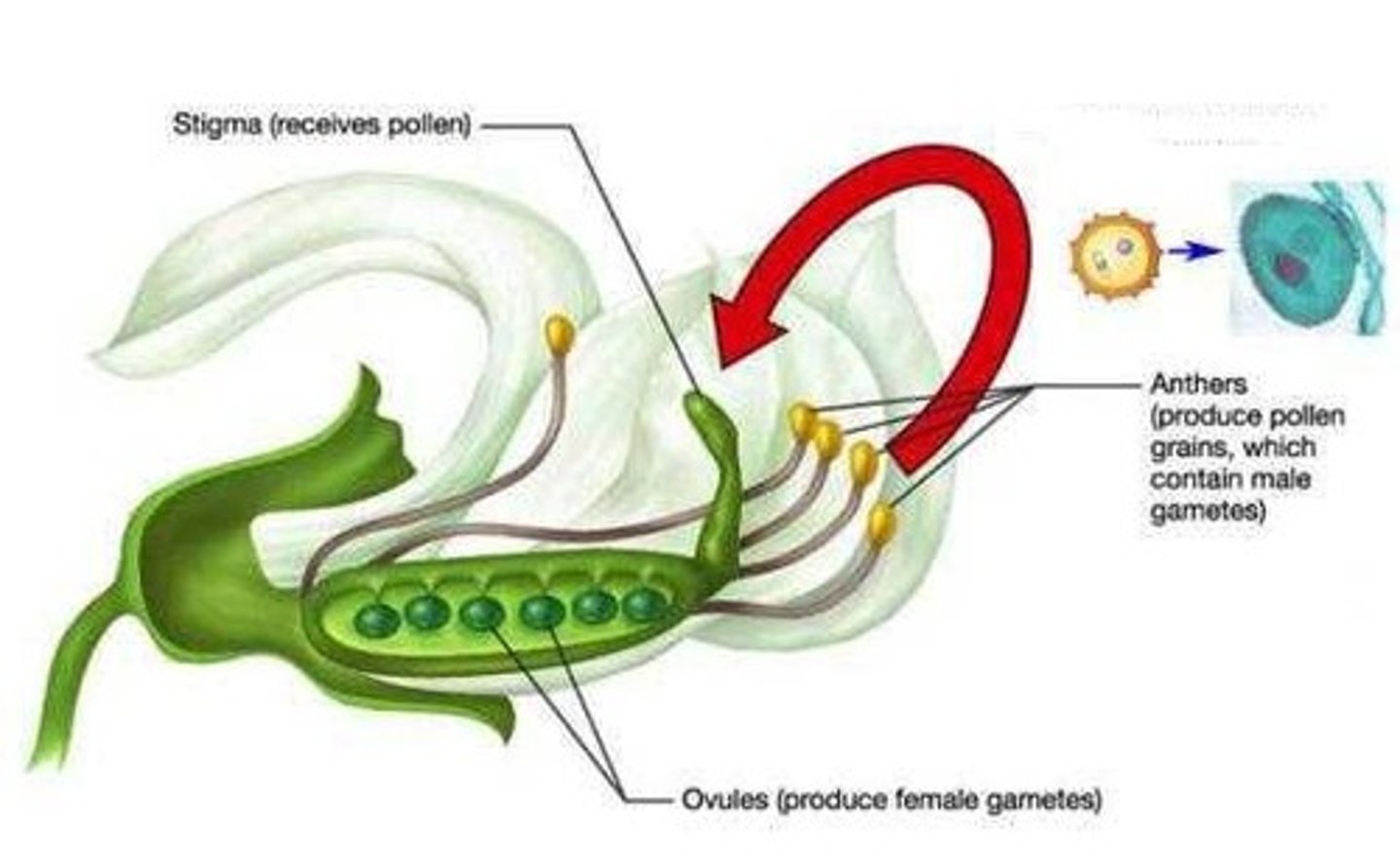
Pollination
The transfer of pollen from male reproductive structures to female reproductive structures in plants
Fertilization
Fusion of male and female gametes.
Gregor Mendel
"The Father of Genetics"

self-pollination
Self fertilize. The pollen and eggs involved in fertilization came from the different flowers of the same plant.
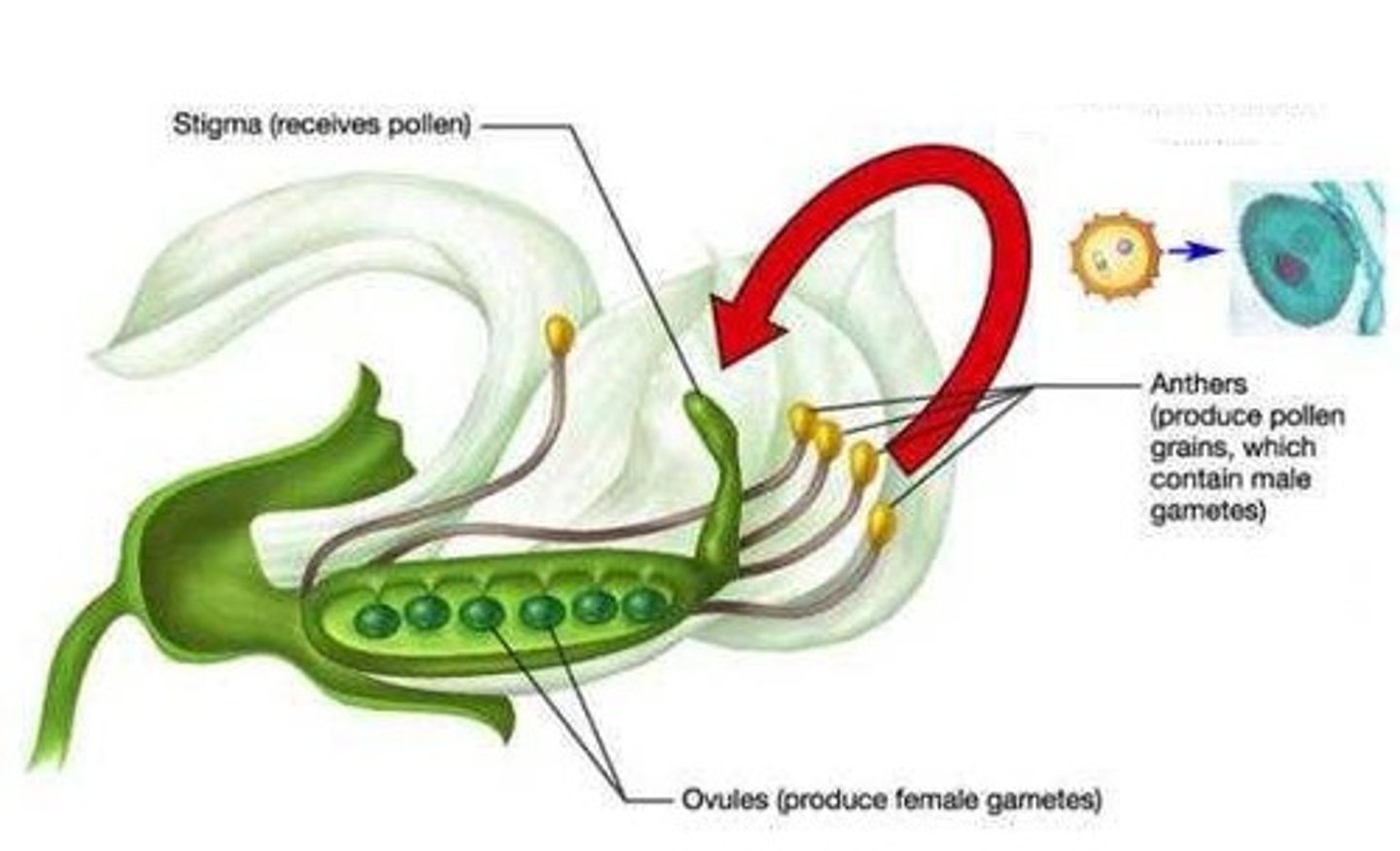
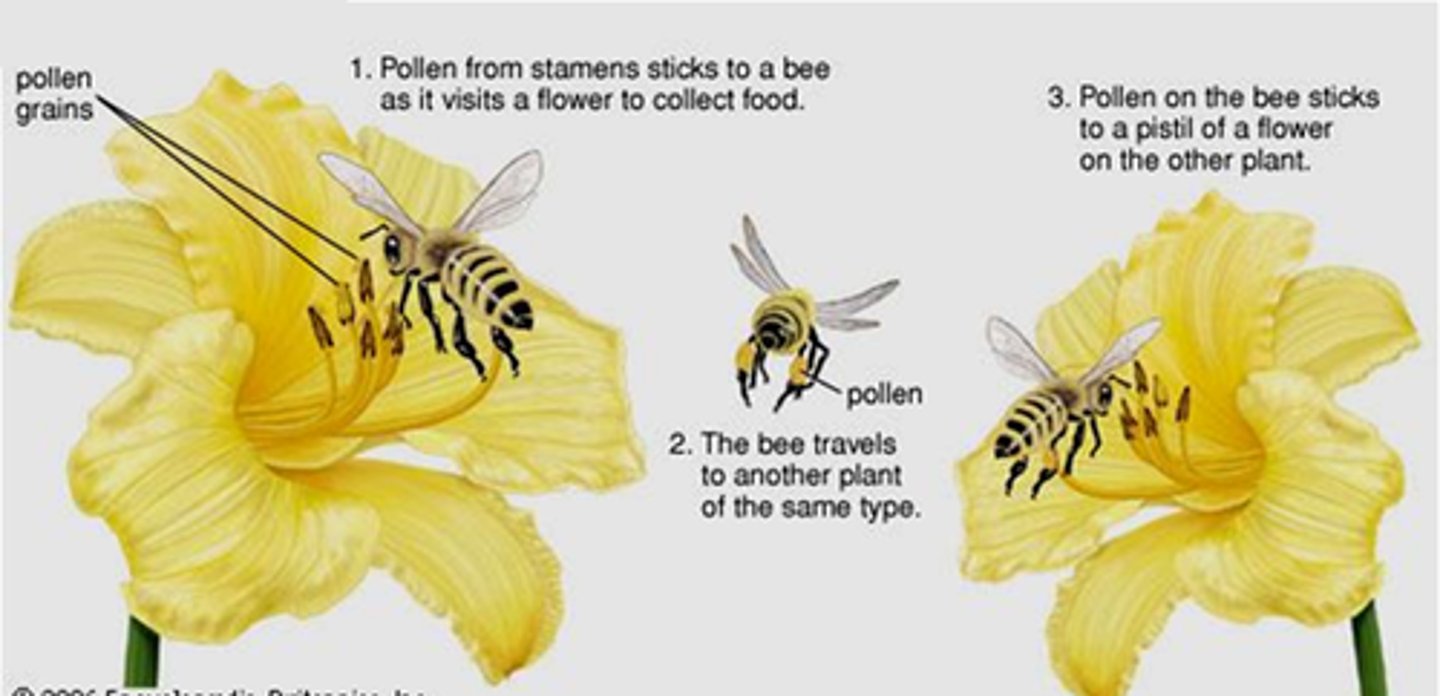
cross-pollination
Fertilization between two different plants. The pollen and eggs involved in fertilization came from two different plants

probability
A number that describes how likely it is that an event will occur
Gregor Mendel's "law of independent assortment"
Law stating that pairs of genes separate independently of one another in meiosis
Gregor Mendel's "law of segregation"
the two copies of each hereditary factor segregate so that offspring acquire one factor from each parent.
P Generation
parental generation, the first two individuals that mate in a genetic cross
F1 Generation
the first generation of offspring obtained from an experimental cross of two organisms
F2 Generation
the offspring of self-pollinated F1 generation plants
gamete
A haploid cell such as an egg or sperm. Found on the outside of punnett squares