Reactions of amino acids
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
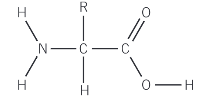
What are amino acids? Show the general structure
Amino acids are organic compounds containing both amine (NH2) and carboxylic acid (COOH) functional groups
What do amino acids form?
Proteins
What is meant by α-amino acids?
The amine group and carboxyl group are connected to the same C atom (i.e. amine group connected to the second carbon atom, next to the carboxyl group)
There are 20 common amino acids in the body. What makes these different and how?
The side chain, R, attached to the same α-carbon atom
The different R groups cause different properties
What is the general formula of an α-amino acid?
RCH(NH2)COOH
What is meant by the β-carbon in an amino acid?
The second carbon atom (excluding the one used for carboxyl group)
What is the solubility of amino acids like?
Soluble in both acids and bases
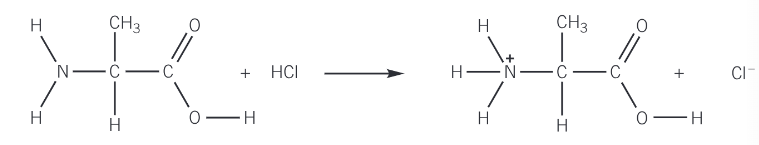
What happens when amino acids react with acids?
Amino acid + acid → salt
Amine group can react with an acid to form a salt
Amine group acts as a nucleophile due to the lone par on the nitrogen, which reacts with a haloalkane
Show the reaction between alanine (2-aminopropanoic acid) and HCl
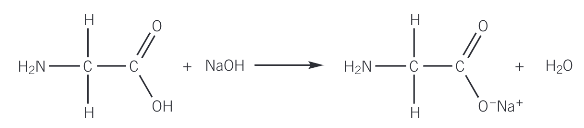
What happens when amino acids react with bases?
Amino acid + bases → salt
The carboxylic acid group reacts with the base to form with a salt
What happens when amino acids react with alcohols? Give the conditions needed
Amino acid + alcohol → ester
Carboxylic acid group reacts with alcohols
Conditions:
Concentrated sulfuric acid
Heat
Give 3 other things amino acids can react with
Metals
Metal carbonates
Metal oxides
Show the reaction of glycine (aminoethanoic acid) with sodium hydroxide
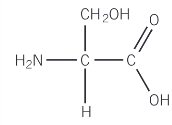
Show the reaction of serine with excess ethanol and a small amount of sulfuric acid
Carboxylic acid group is esterified to produce an ester
Acidic conditions protonate the basic amine group of the ester
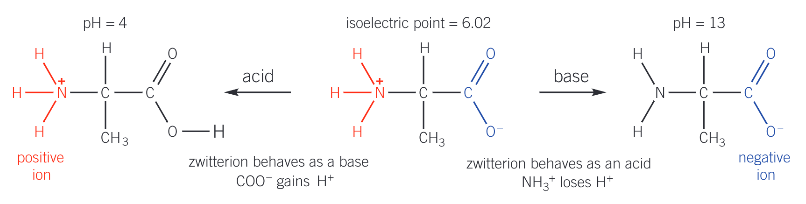
What is a zwitterion?
An internal salt formed when the basic amine group can accept a proton from the carboxylic group to form an ion containing both a positive and negative charge
E.g. alanine
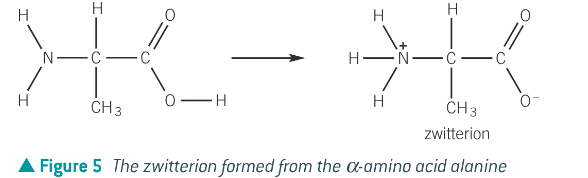
Why does a zwitterion have no overall charge?
The positive and negative charges cancel out
What is the isoelectric point of an amino acid?
The pH at which the amino acid has no net charge and the zwitterion is formed
What happens when an amino acid is added to a solution with a pH:
greater than its isoelectric point
lower than its isoelectric point
greater: amino acid behaves as an acid and loses a proton
lower: amino acid behaves as a base and gains a proton