Cranium
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
function of cranium
supports and protects the brain
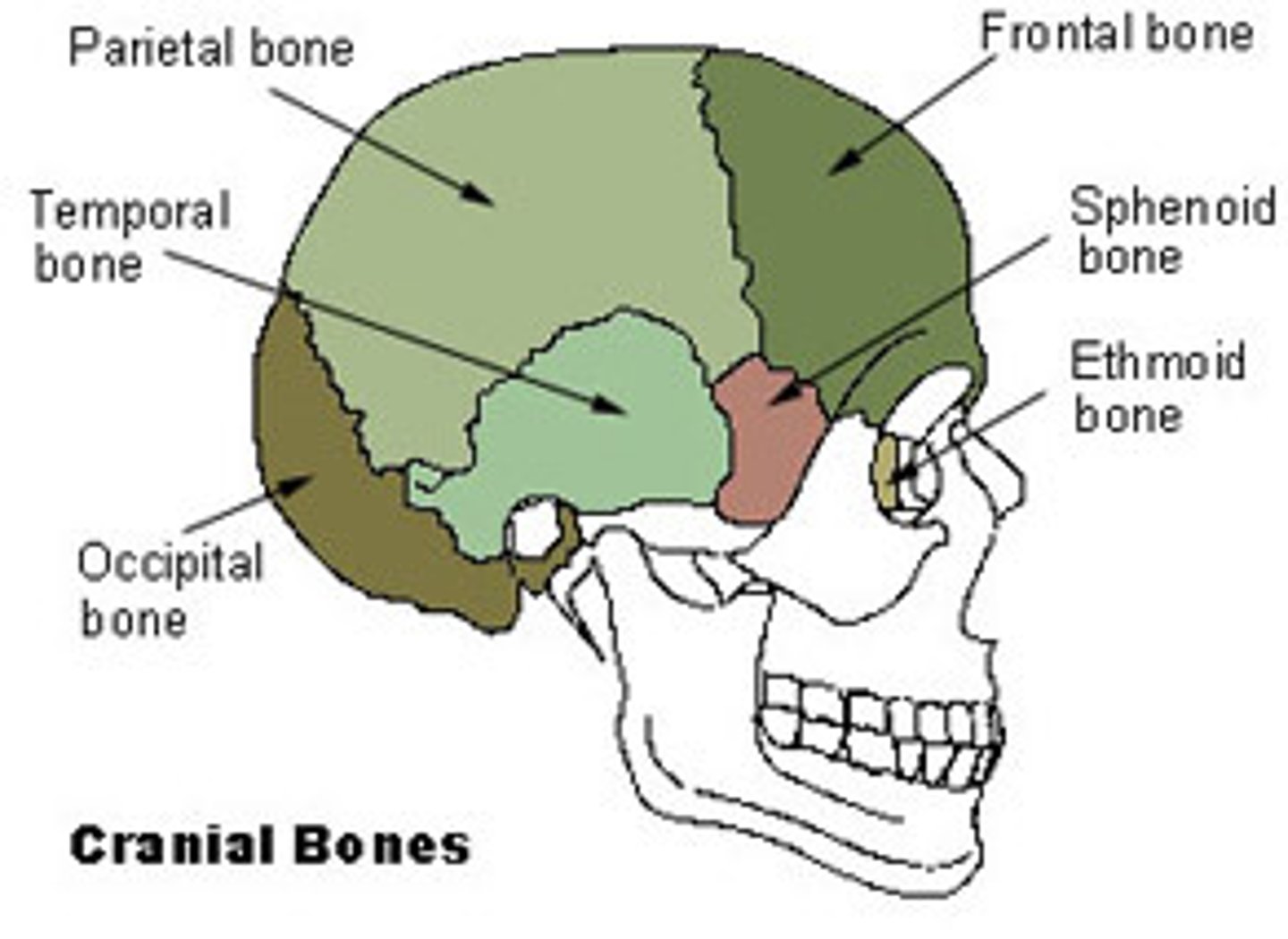
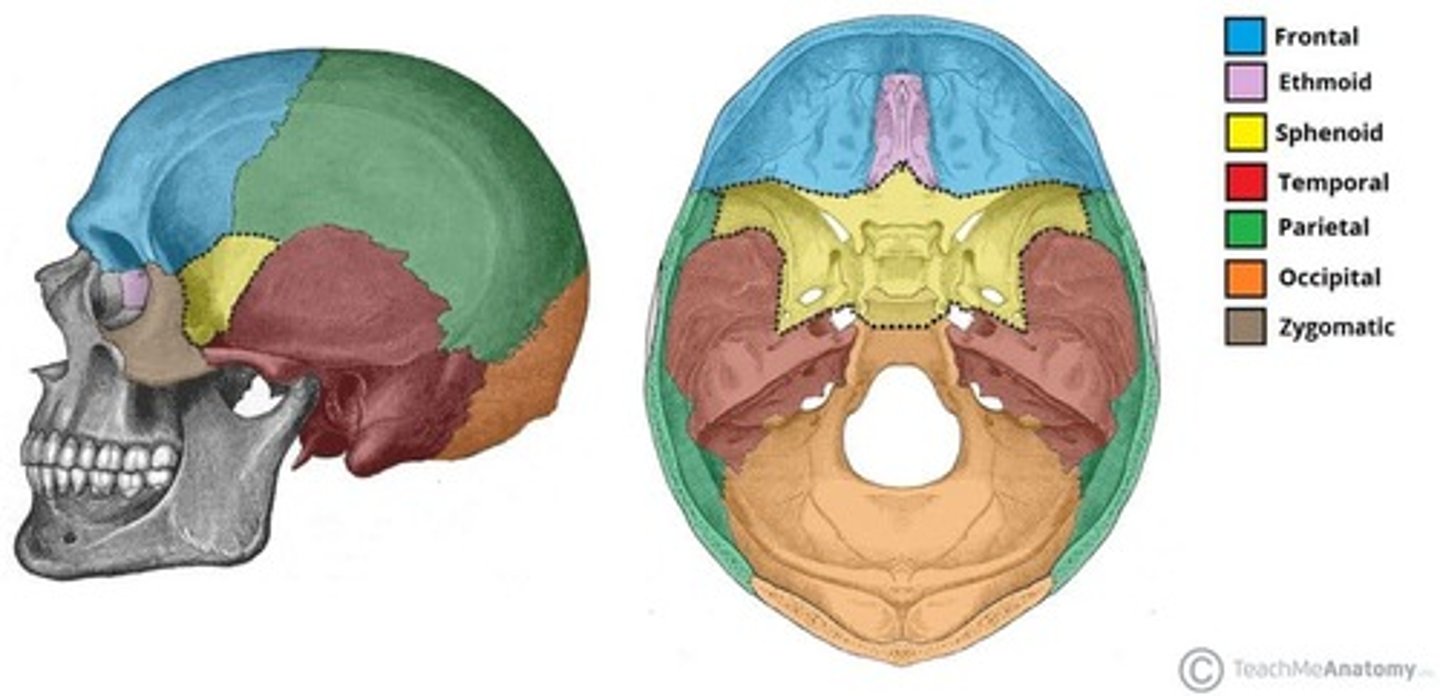
Bones of the cranium (8)
frontal, parietal (2), occipital, temporal (2), sphenoid, ethmoid
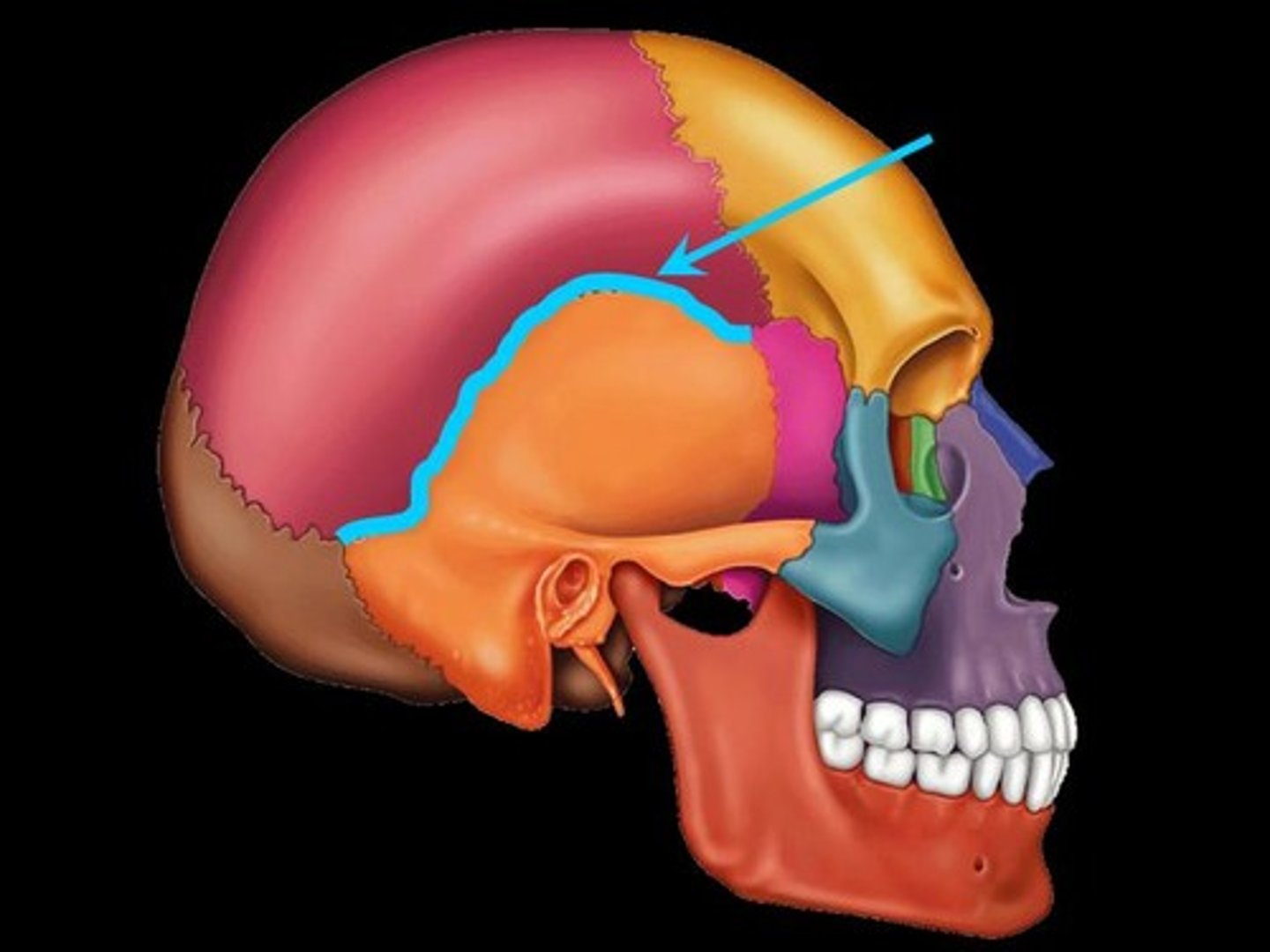
squamous suture
Between parietal and temporal bones
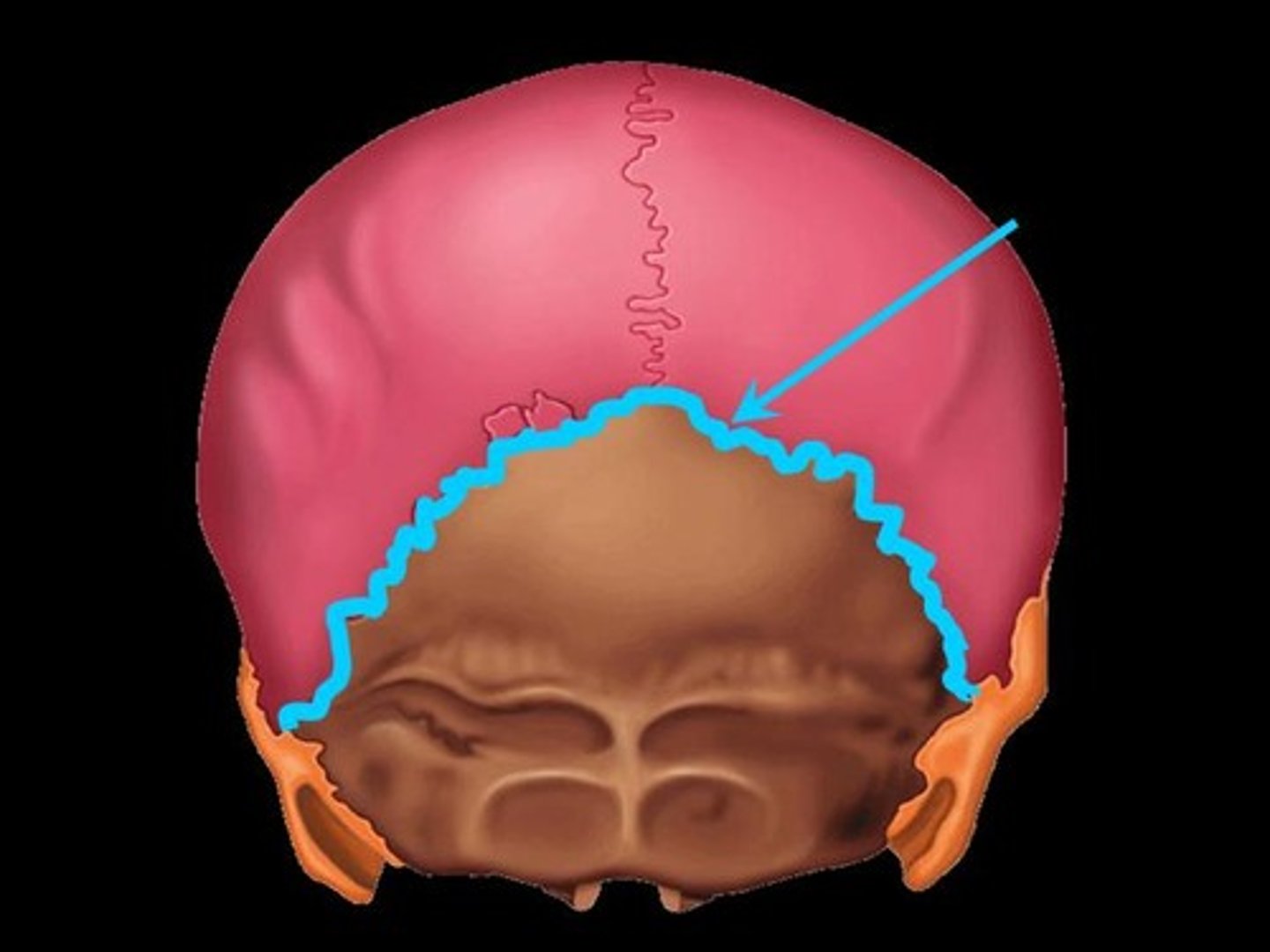
lambdoid suture
between parietal bones and occipital bone
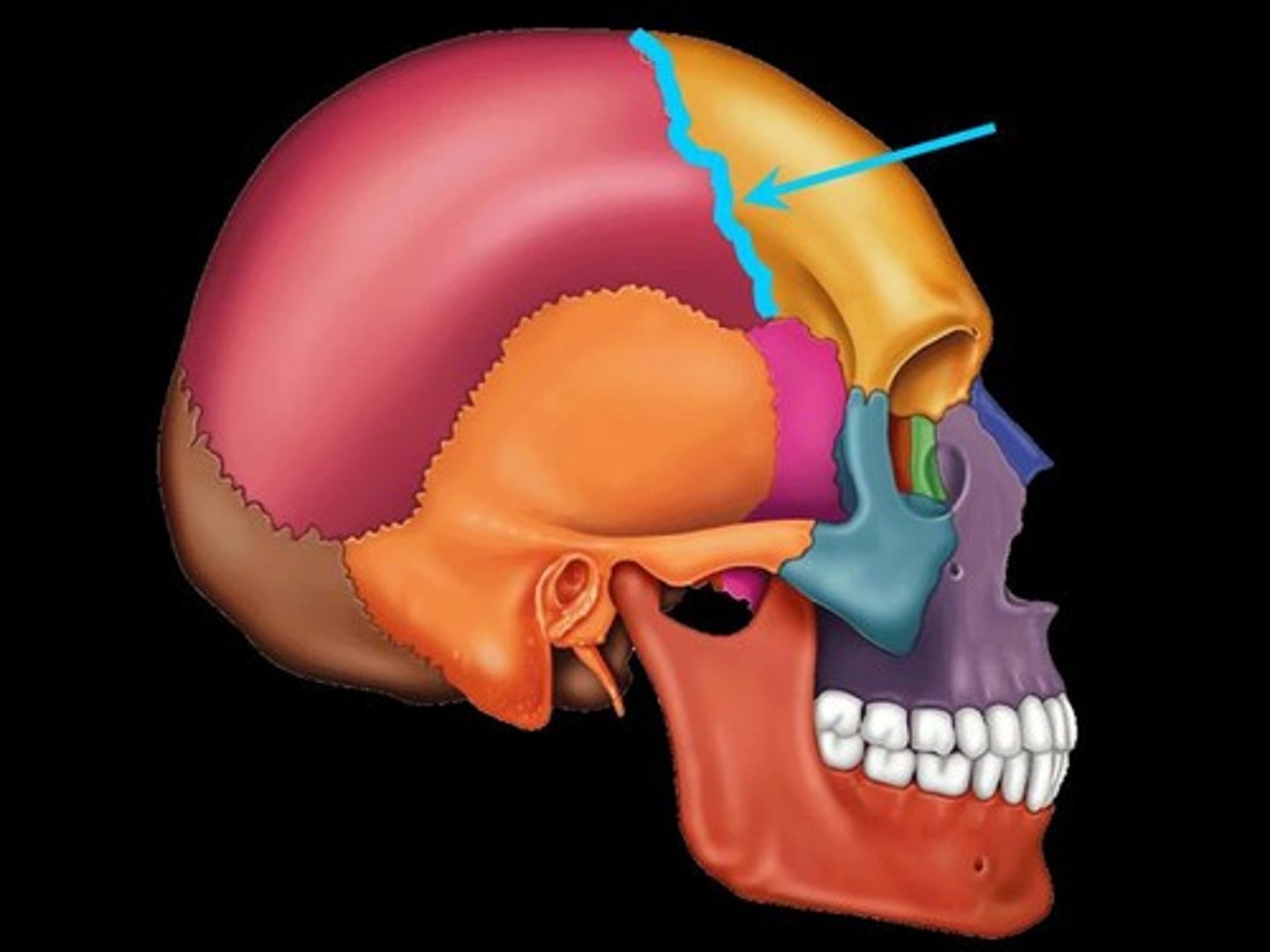
coronal suture
between frontal and parietal bones
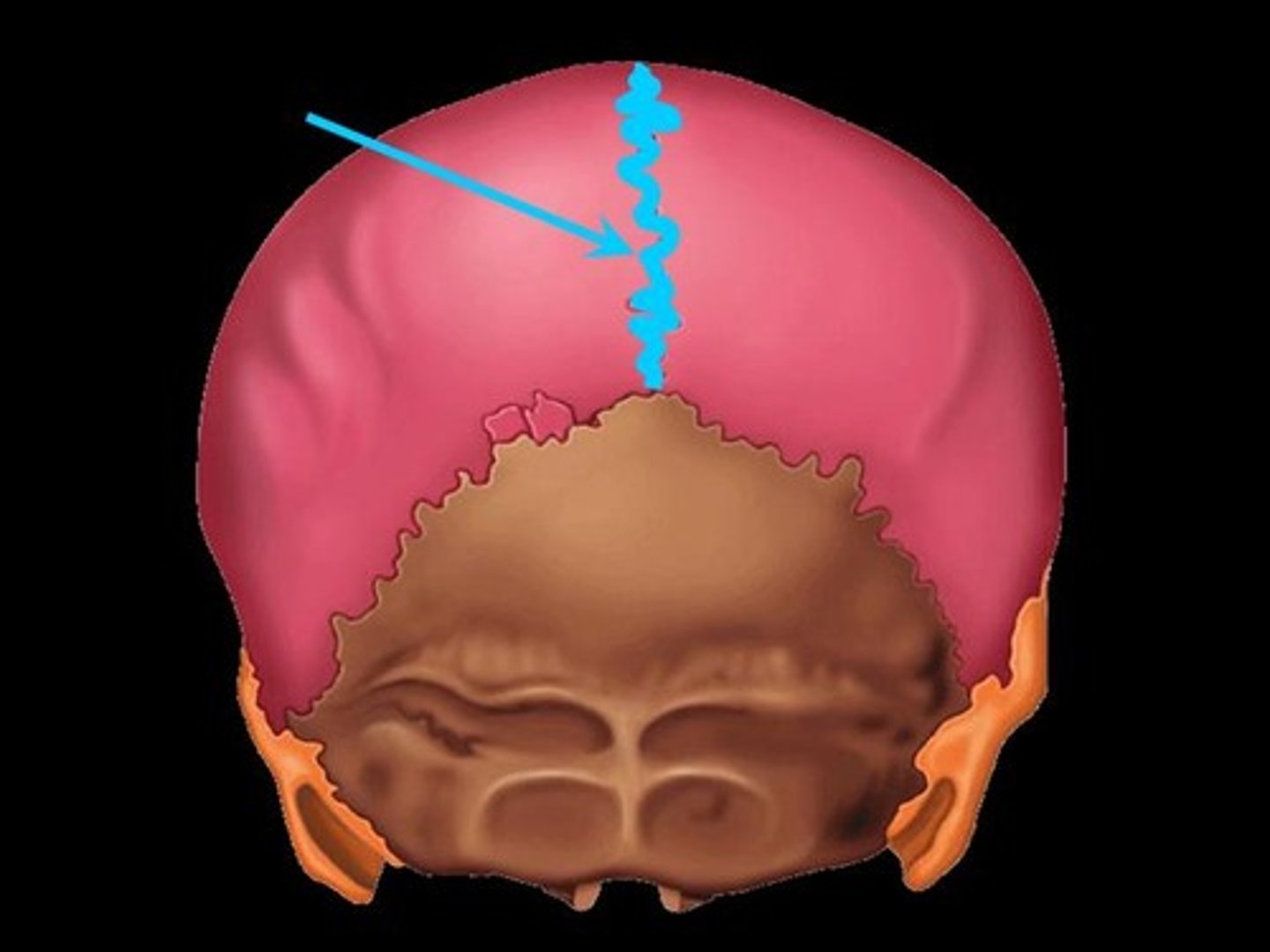
sagittal suture
between the two parietal bones
fontal (anterior) fossa
primary frontal bone
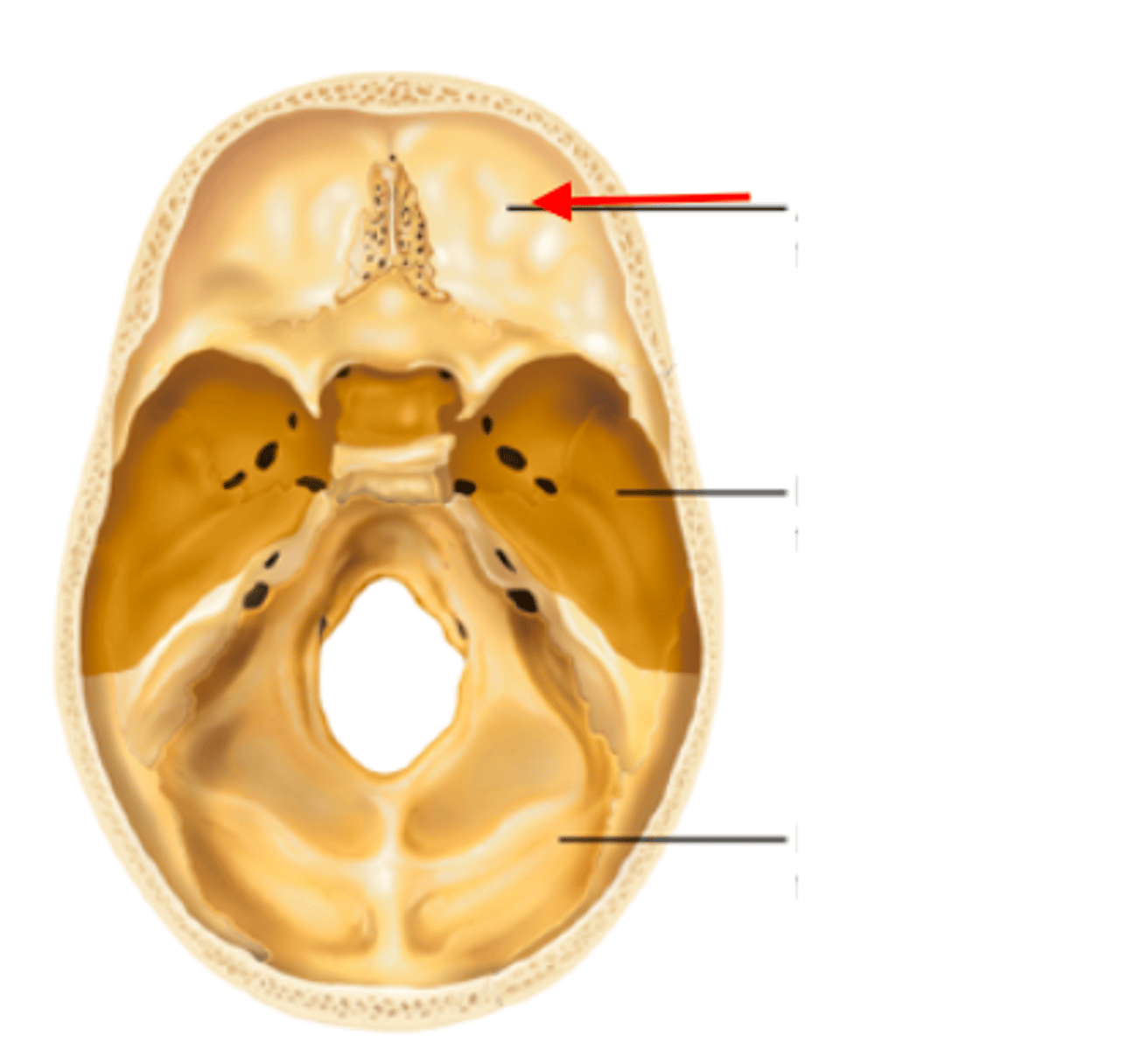
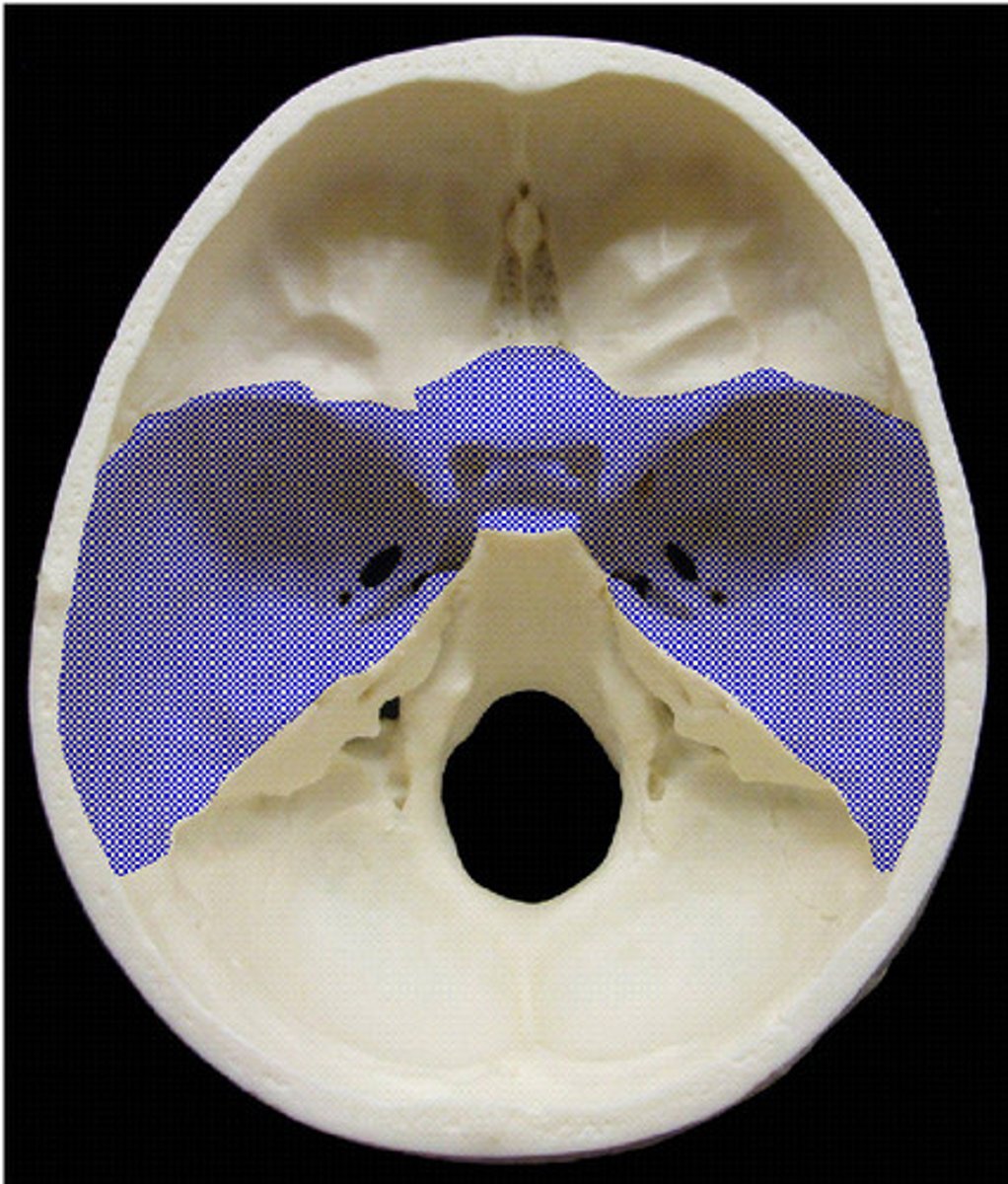
middle ( temporal) fossa
primary body of sphenoid and temporal bones
posterior (Infratentorial) fossa
formed by occipital and temporal bones
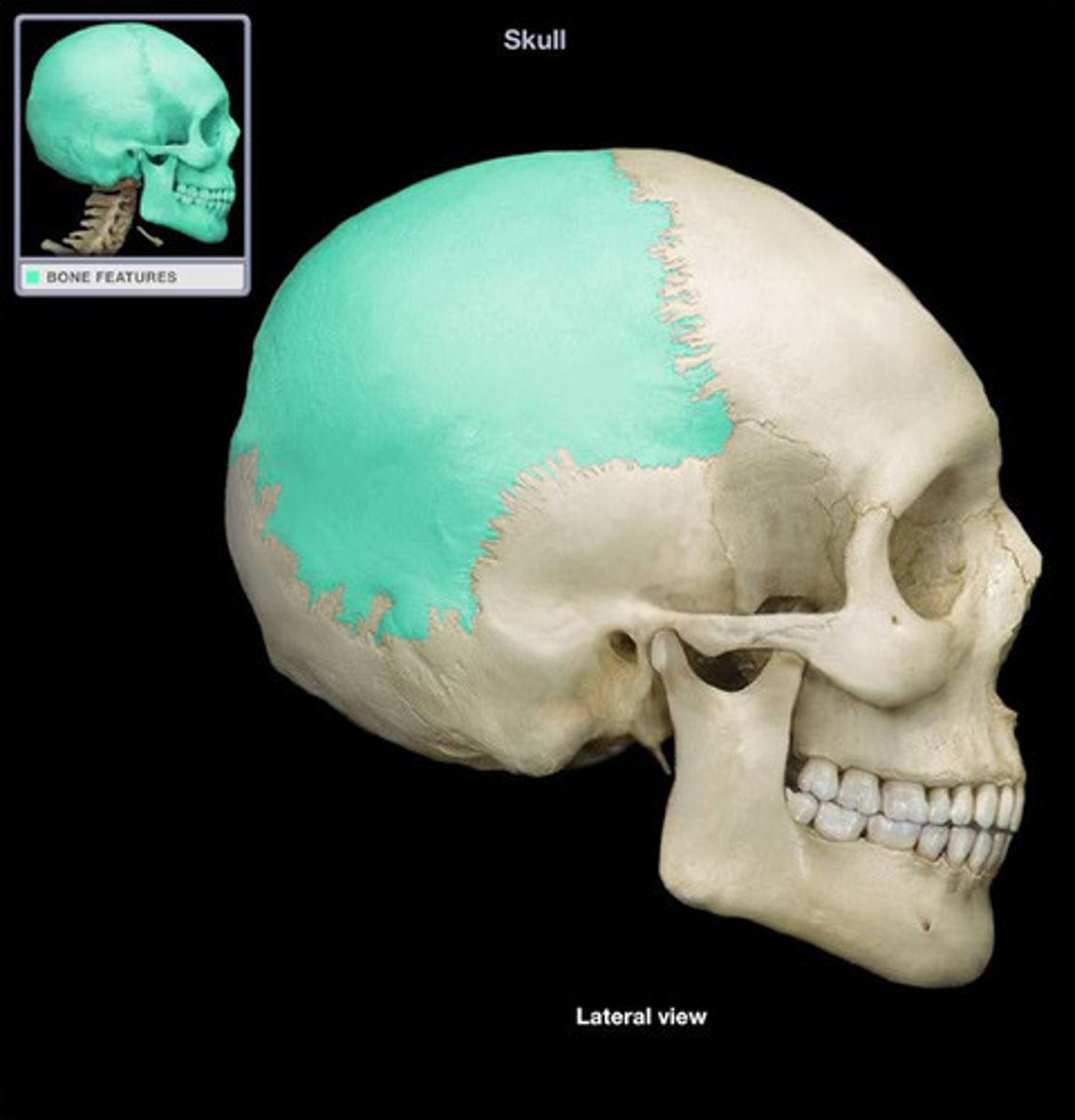
parietal bone of skull
-paired
-forms the lateral part and roof of the cranium
vertex
superior point
found between parietal bones
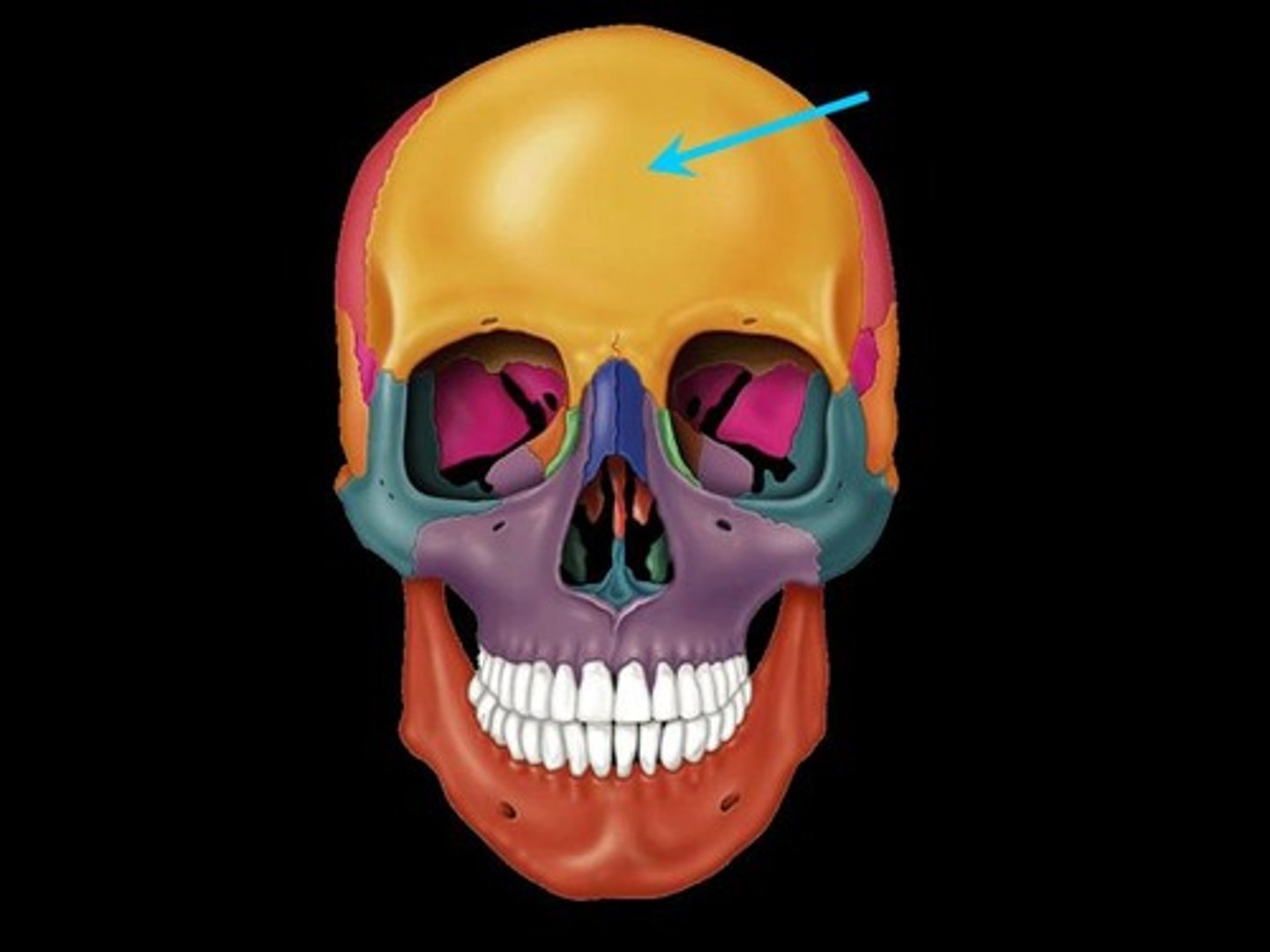
frontal bone
Forms the forehead (vertical)
orbital plate
roof of each orbit, part of the frontal bone
Where are the frontal sinuses located?
located at anterior midline
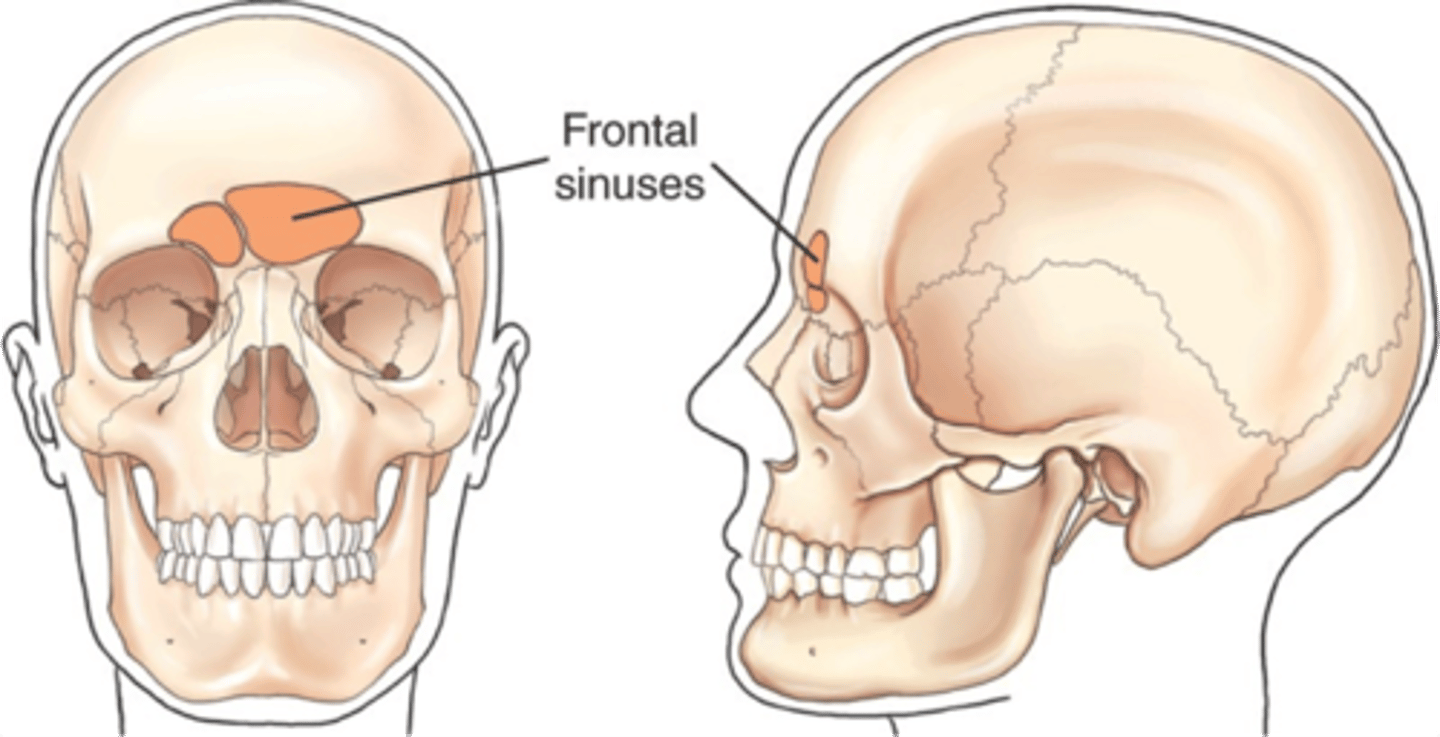
What are the frontal sinuses?
Air-filled spaces within the frontal bone.
Where do the frontal sinuses drain?
middle meatus and nasal cavity
Supraorbital notch/foramen
passage for nerves and arteries
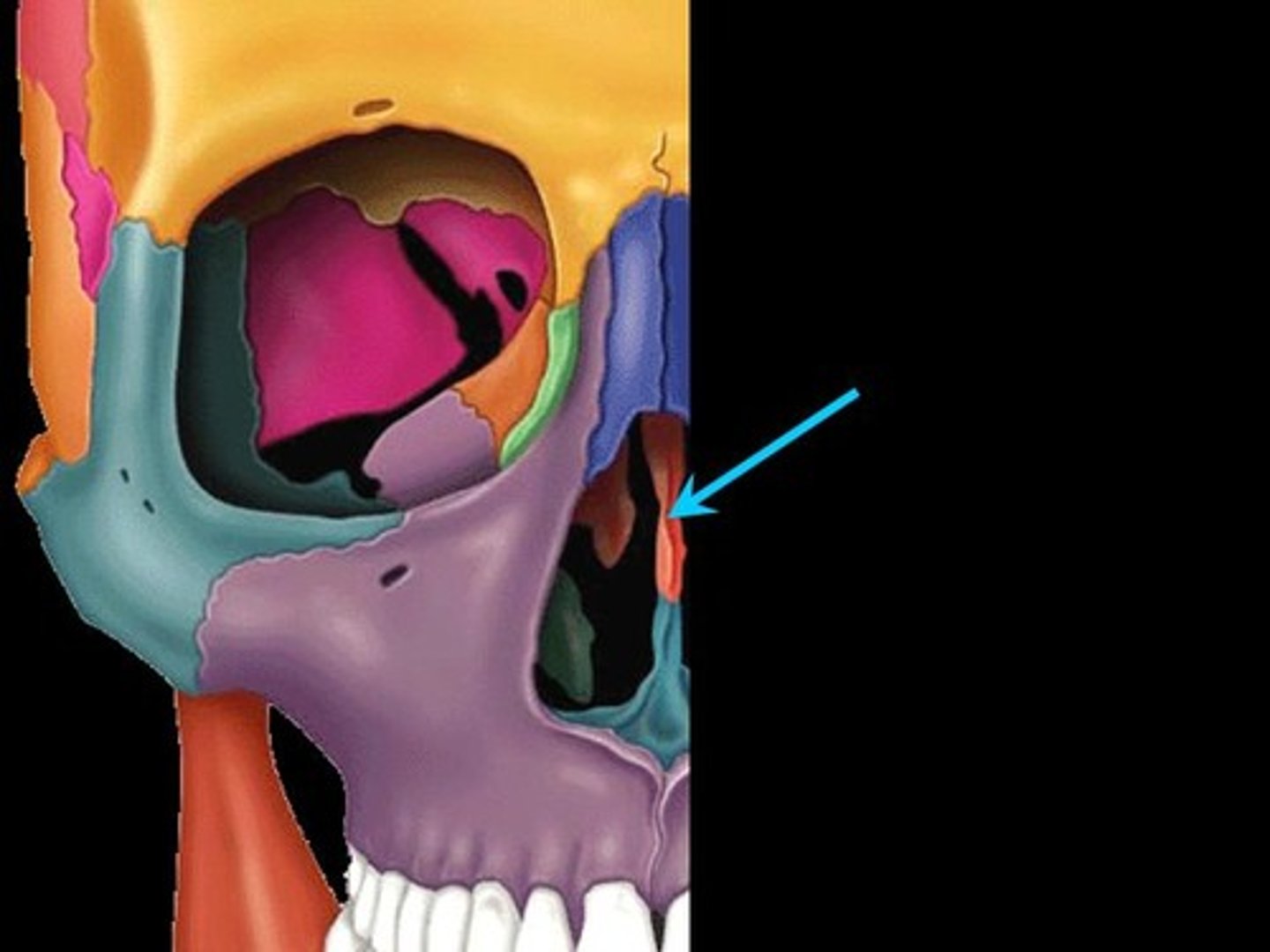
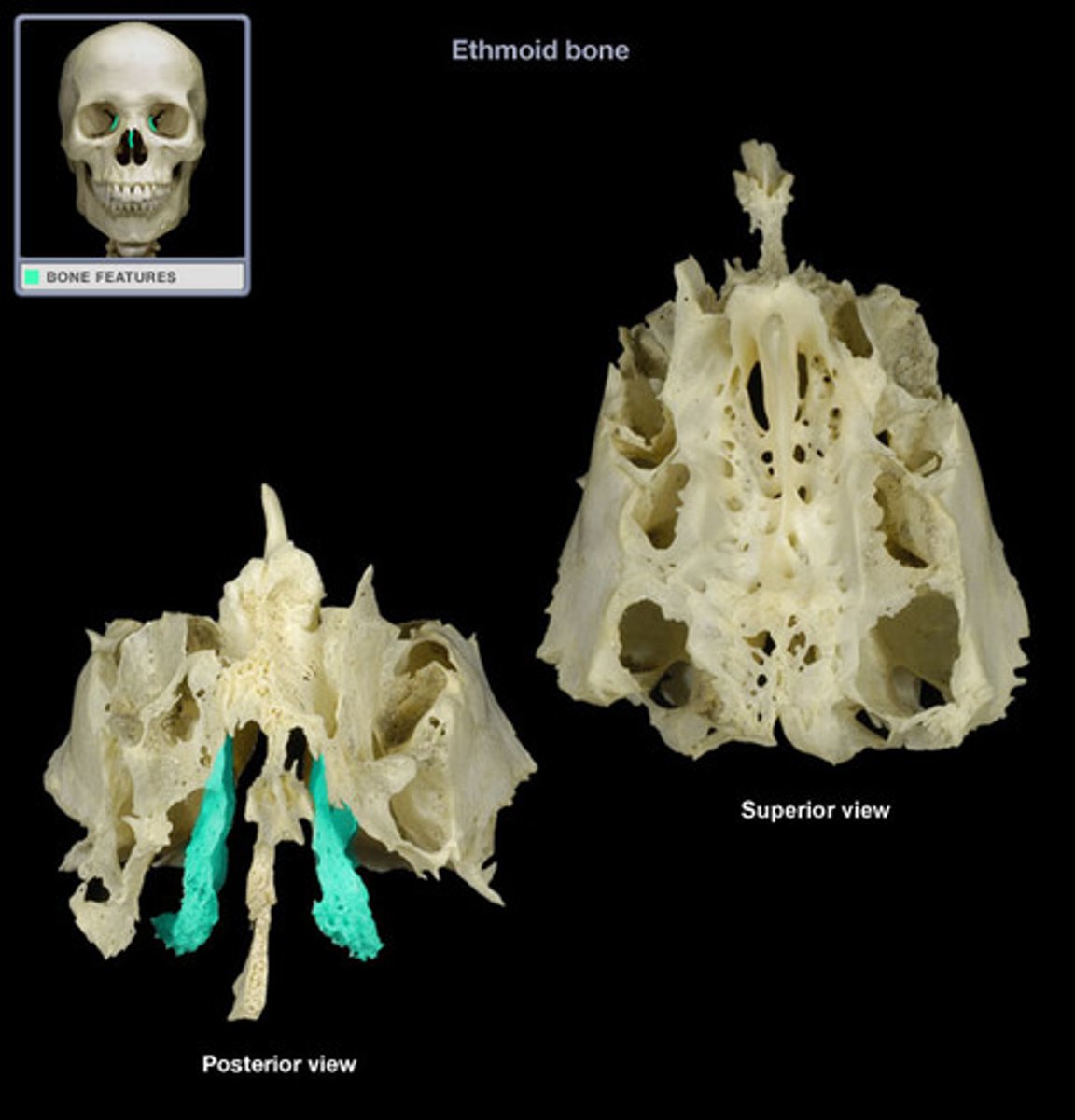
Ethmoid bone
-smallest cranial region
-cube shaped
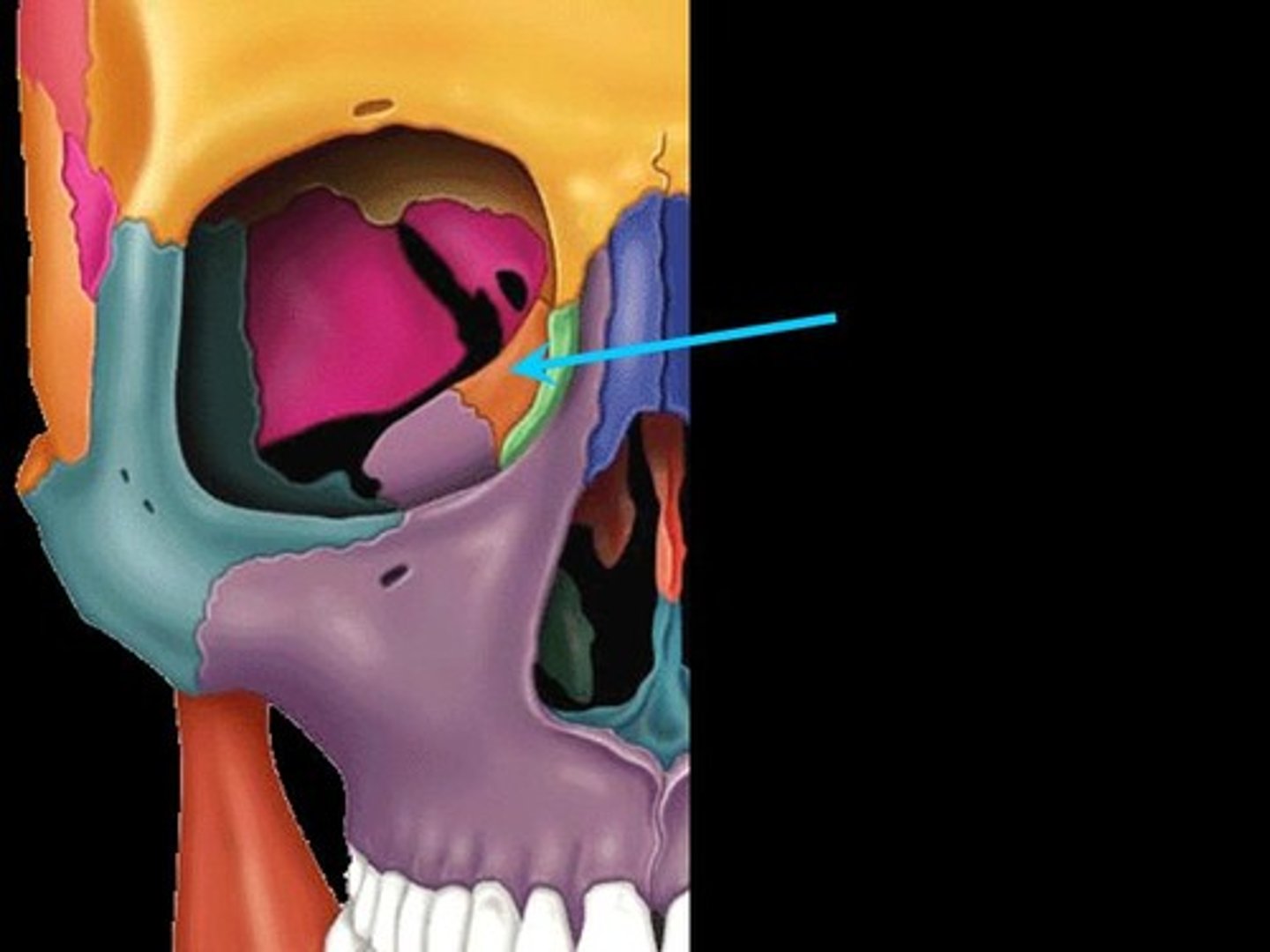
Where is the Ethmoid bone Located
between the orbits
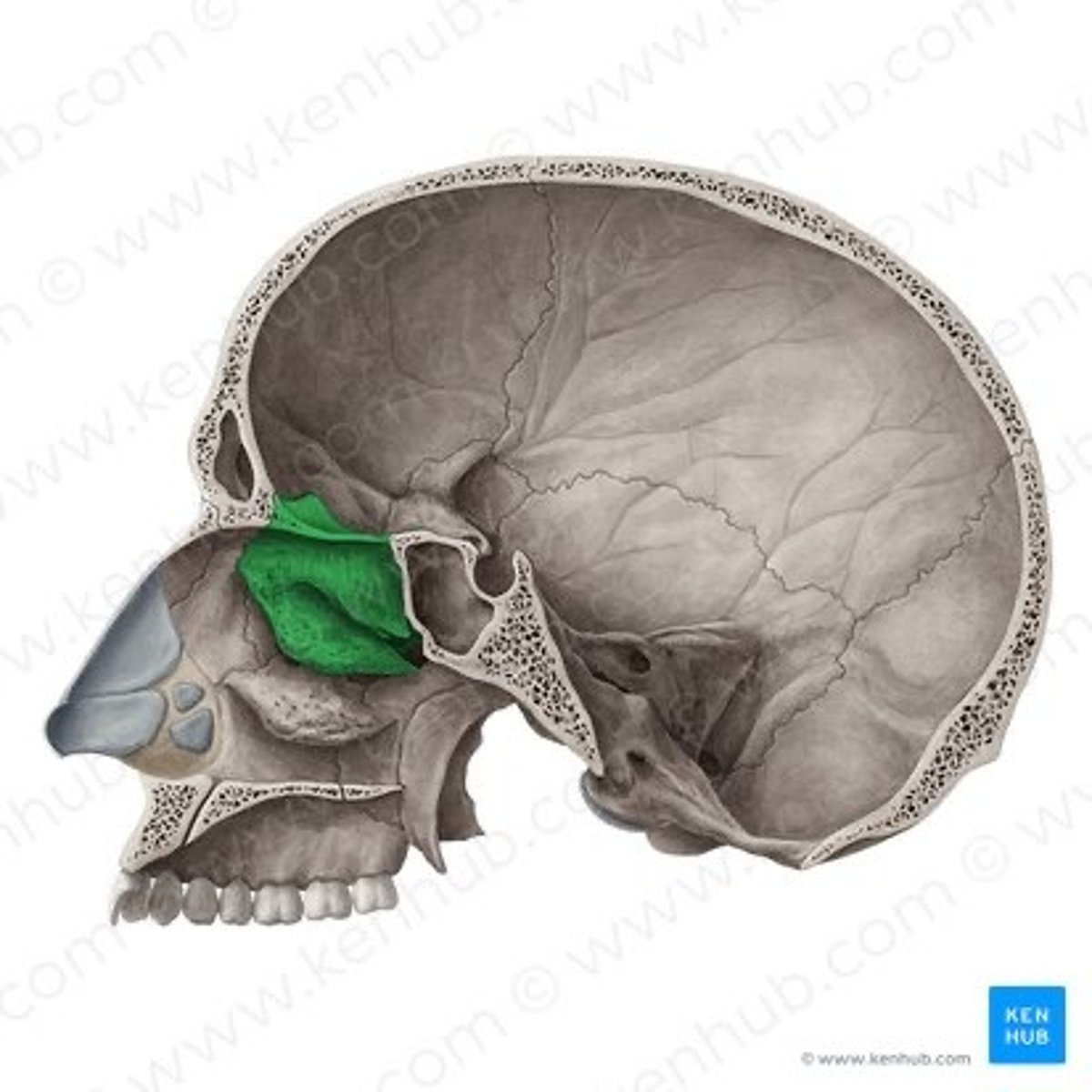
What do Ethmoidal sinuses contain?
3-18 air cells
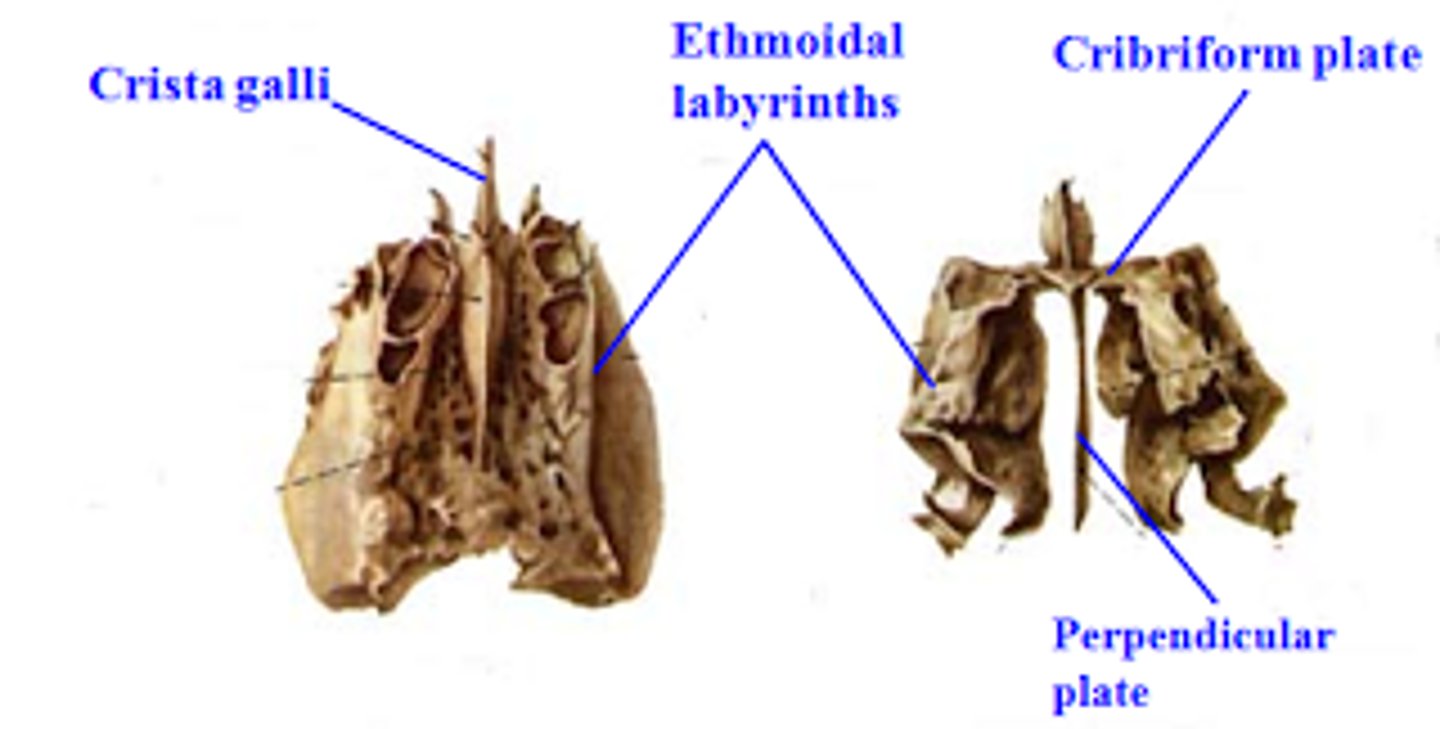
cribiform plate
horizontal portion of ethmoid bone
What does the cribiform plate contain?
many formina for passage of OLFACTORY nerves
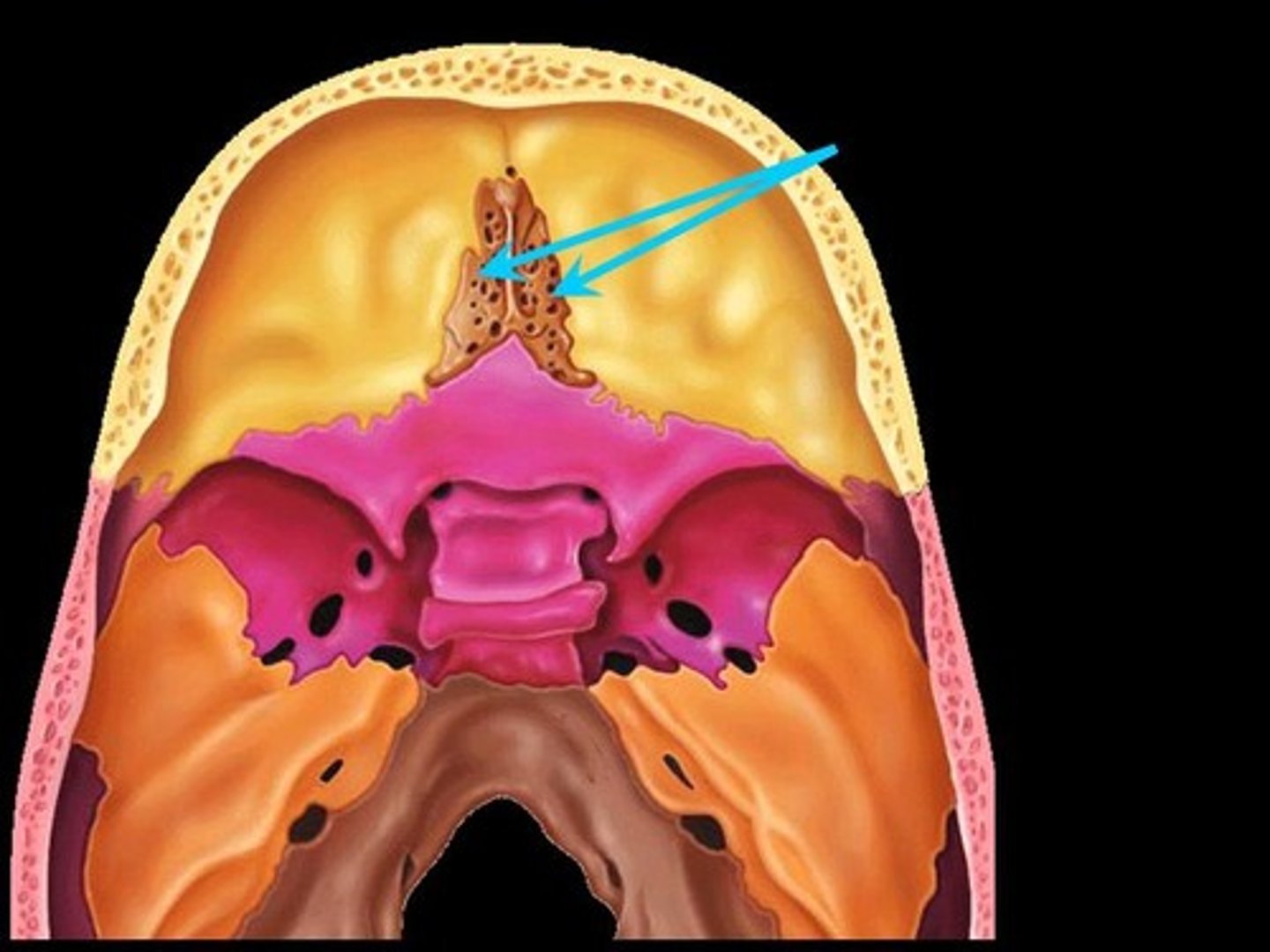
Where is the cribiform located?
on the floor of the anterior cranium
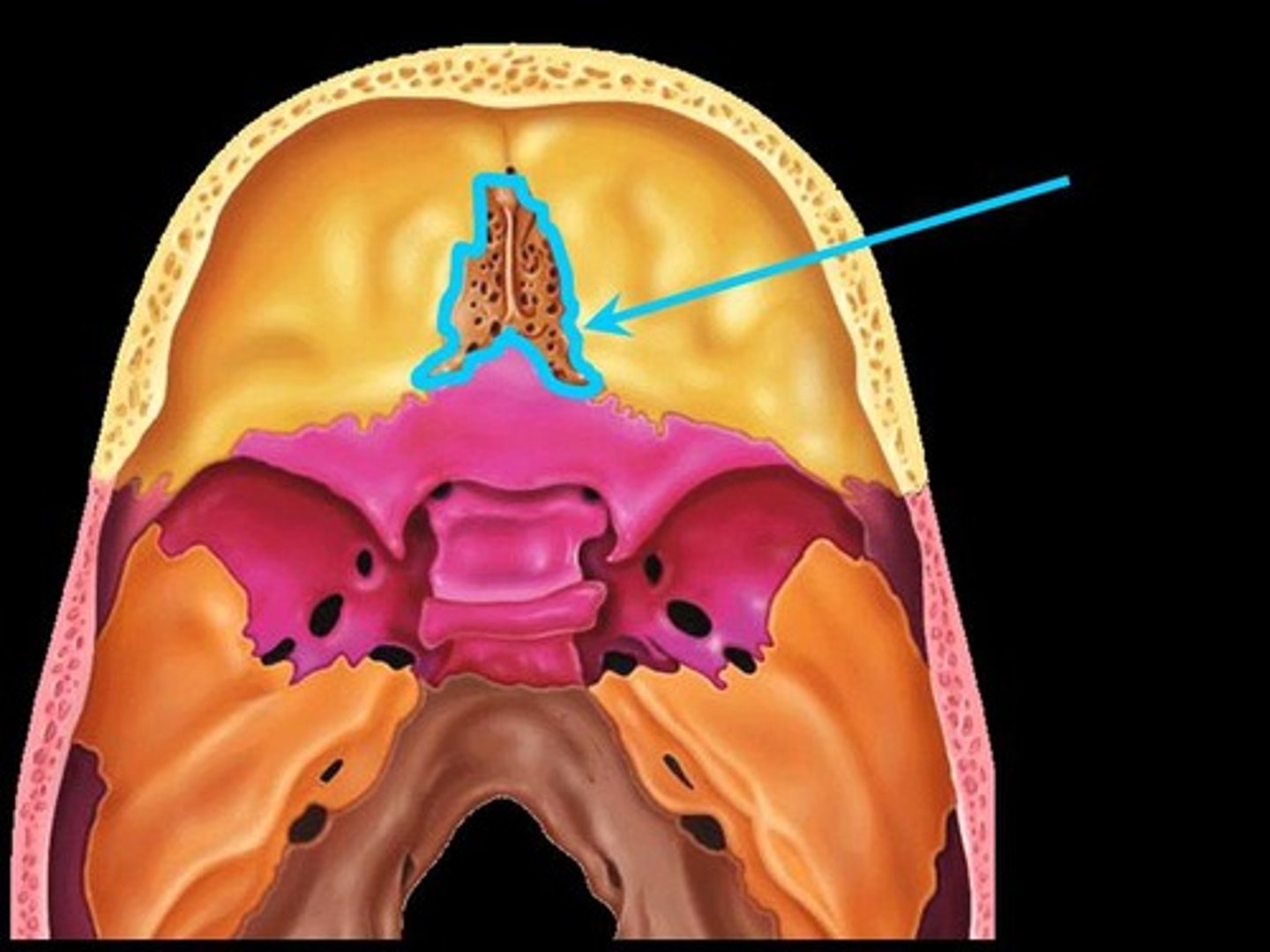
Crista galli
first vertical portion of Ethmoid bone
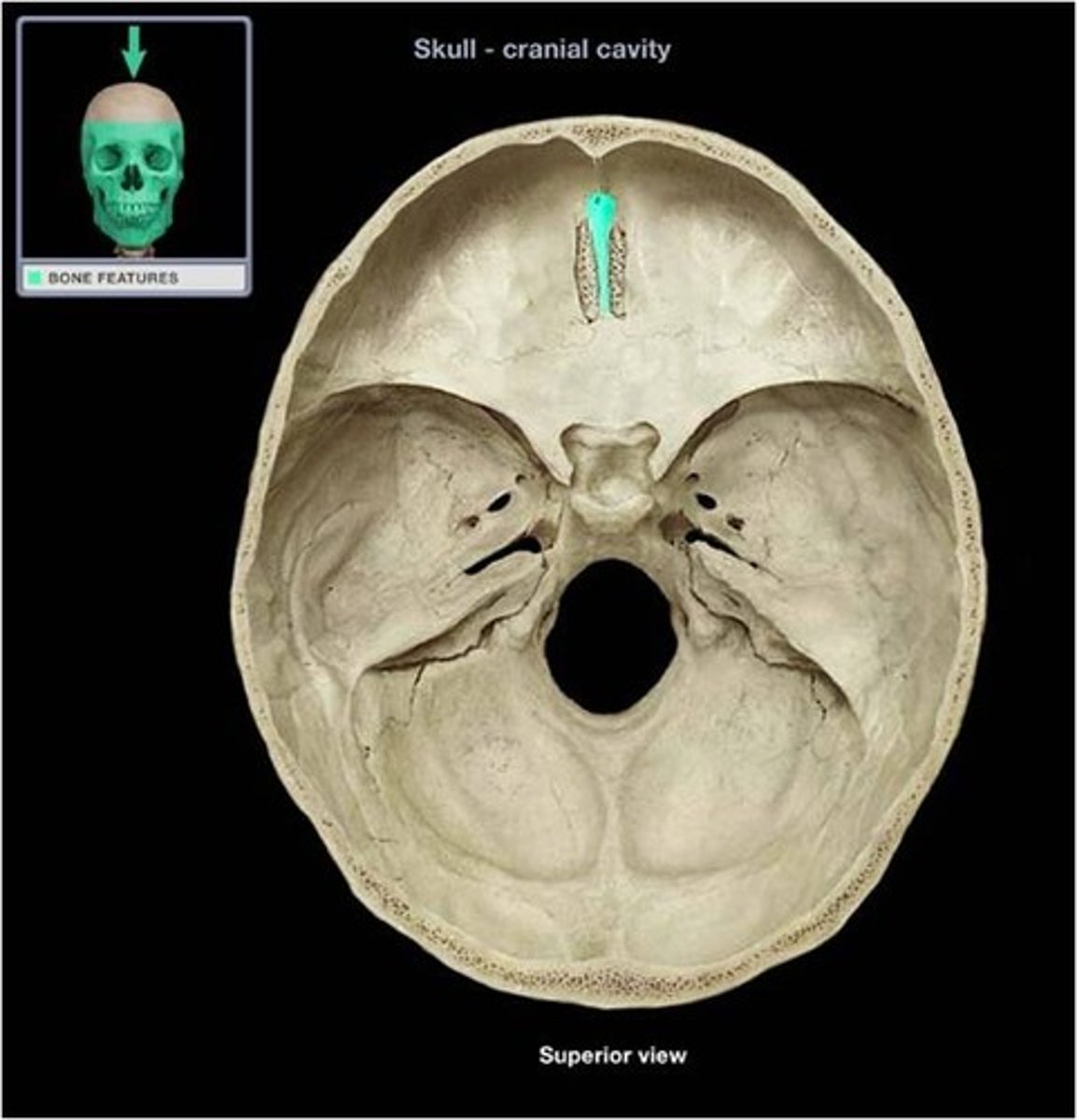
crista galli location
project superiorly from cribriform plate
attaches to falx cerebri
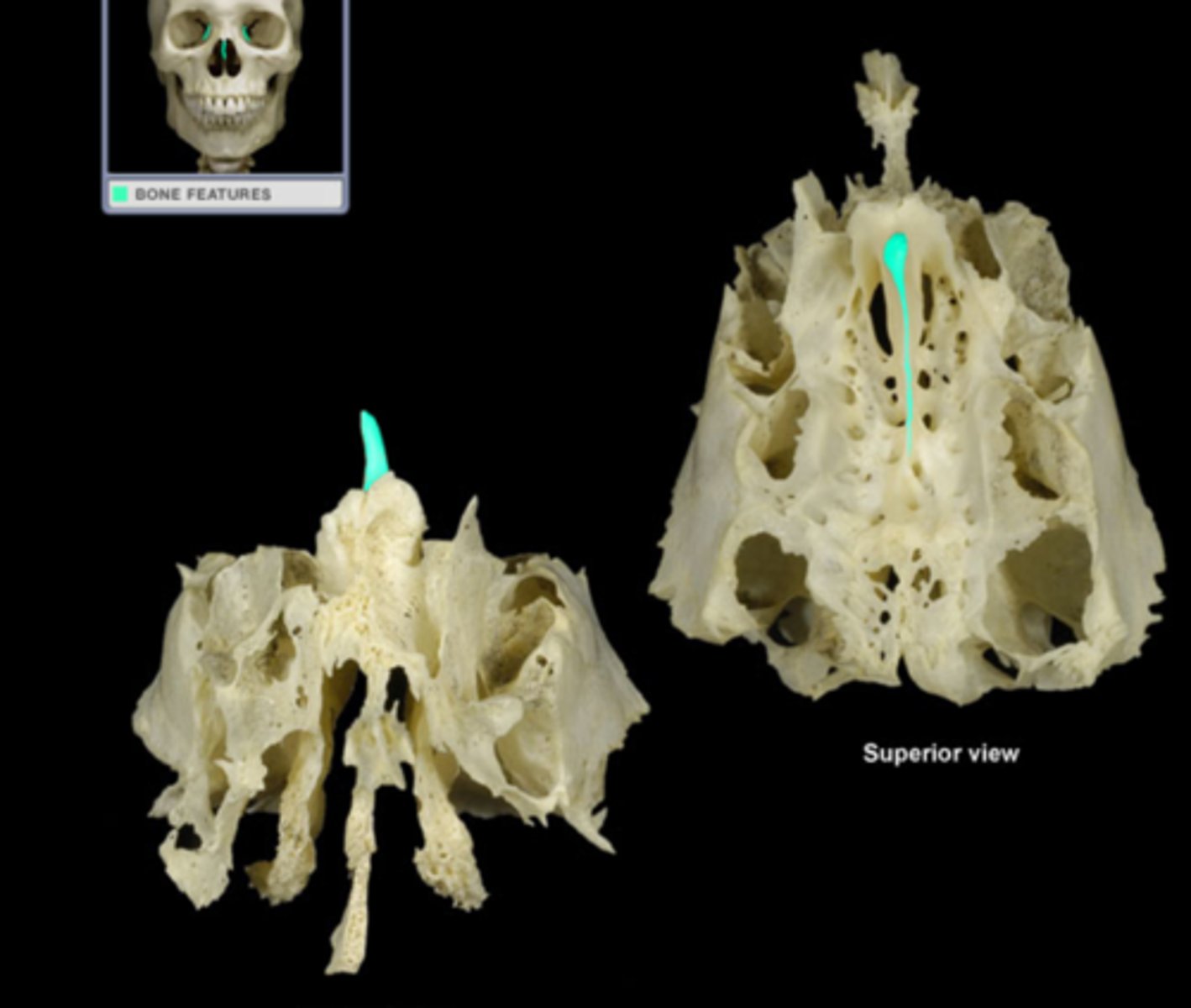
perpendicular plate
second vertical portion of the ethmoid
perpendicular plate location
-projects inferiorly from cribriform plate
-forms portion of bony nasal septum
labryinths
-The lateral portion of the ethmoid
- contain ethmoid air cells in ethmoid sinuses
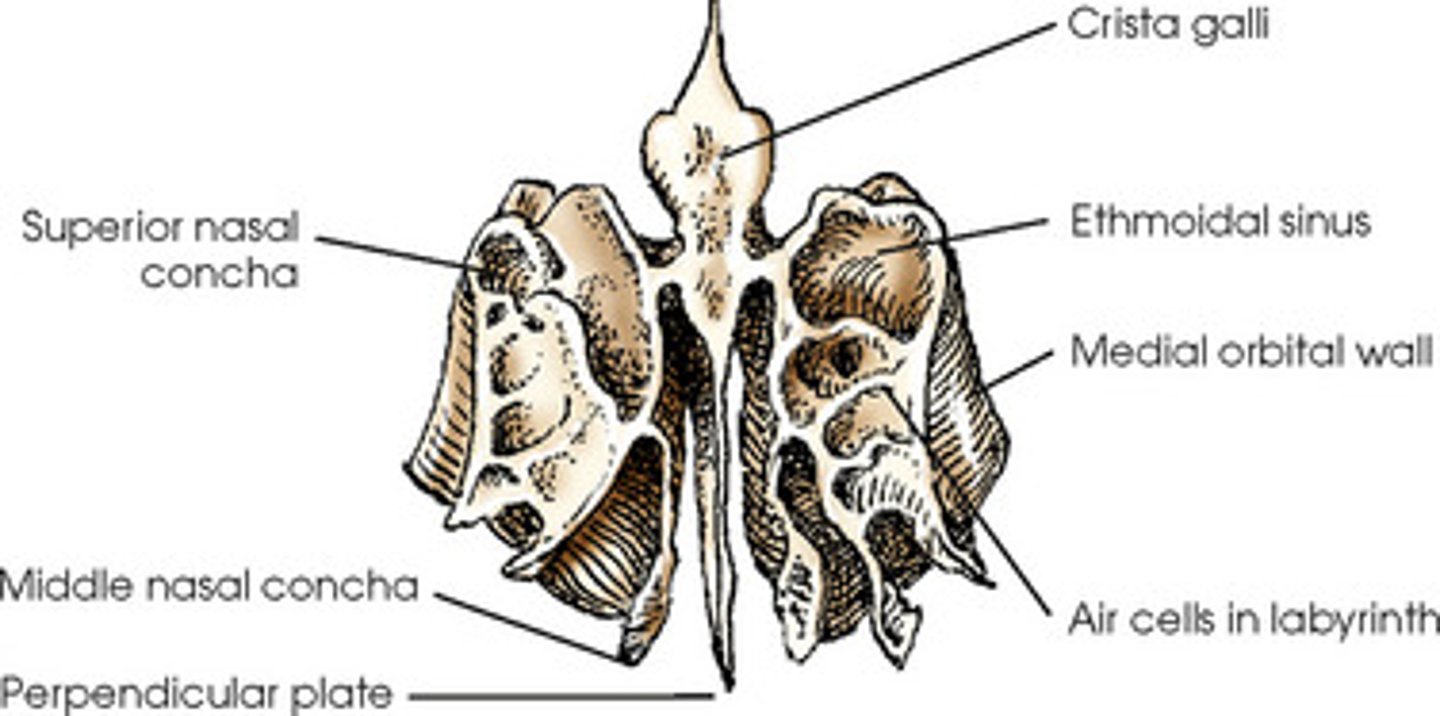
superior and middle nasal conchae
thin sea shell-shaped bones located on the labyrinth portion of the ethmoid
superior and middle nasal conchae purpose
allow for humidification of air going into the lungs
sphenoid bone
ONLY bone to articulate with ALL cranial bones
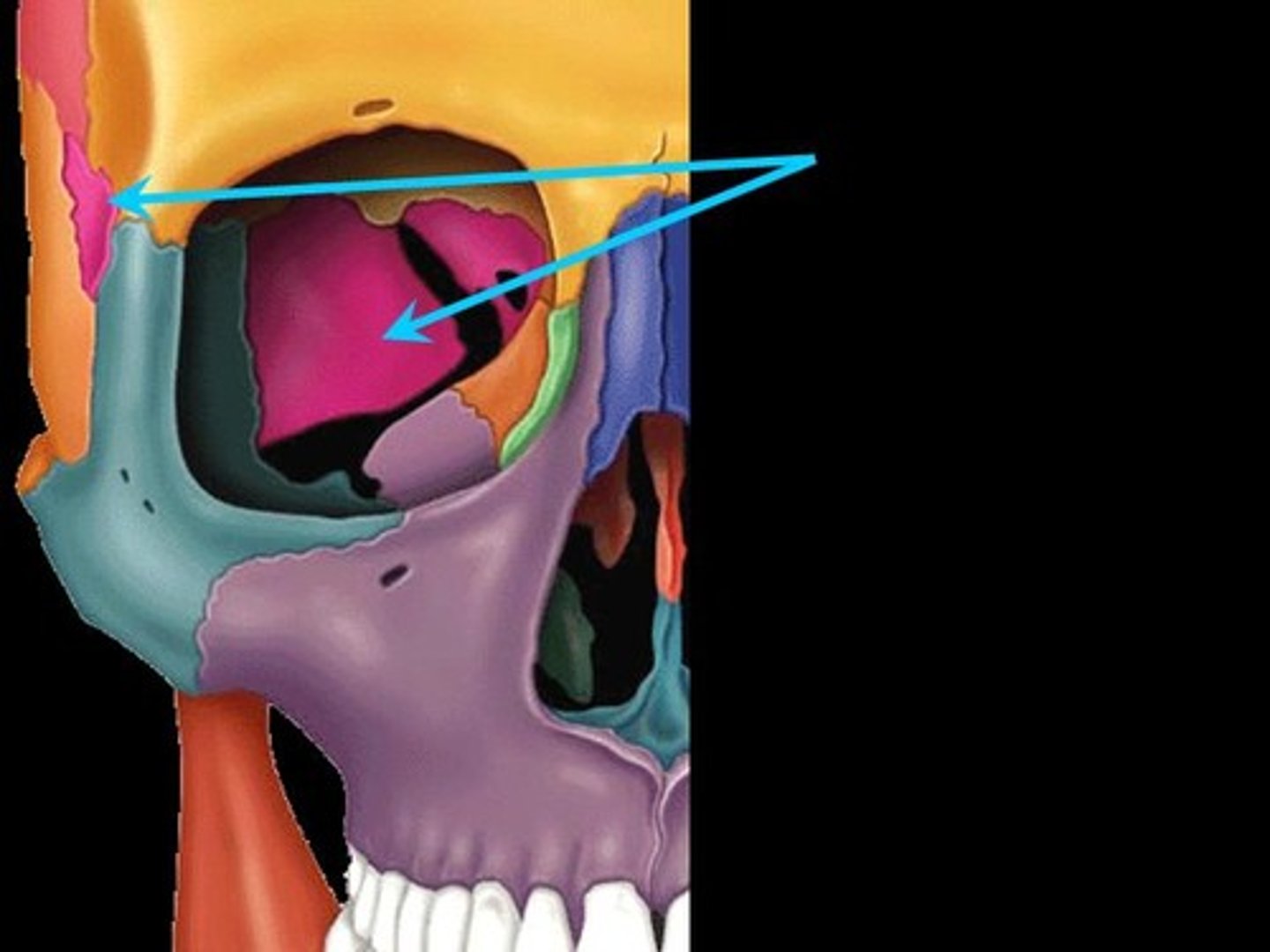
What does the sphenoid bone form?
majority of the base of the skull/ middle fossa
Location of sphenoid bone
midline of cranium
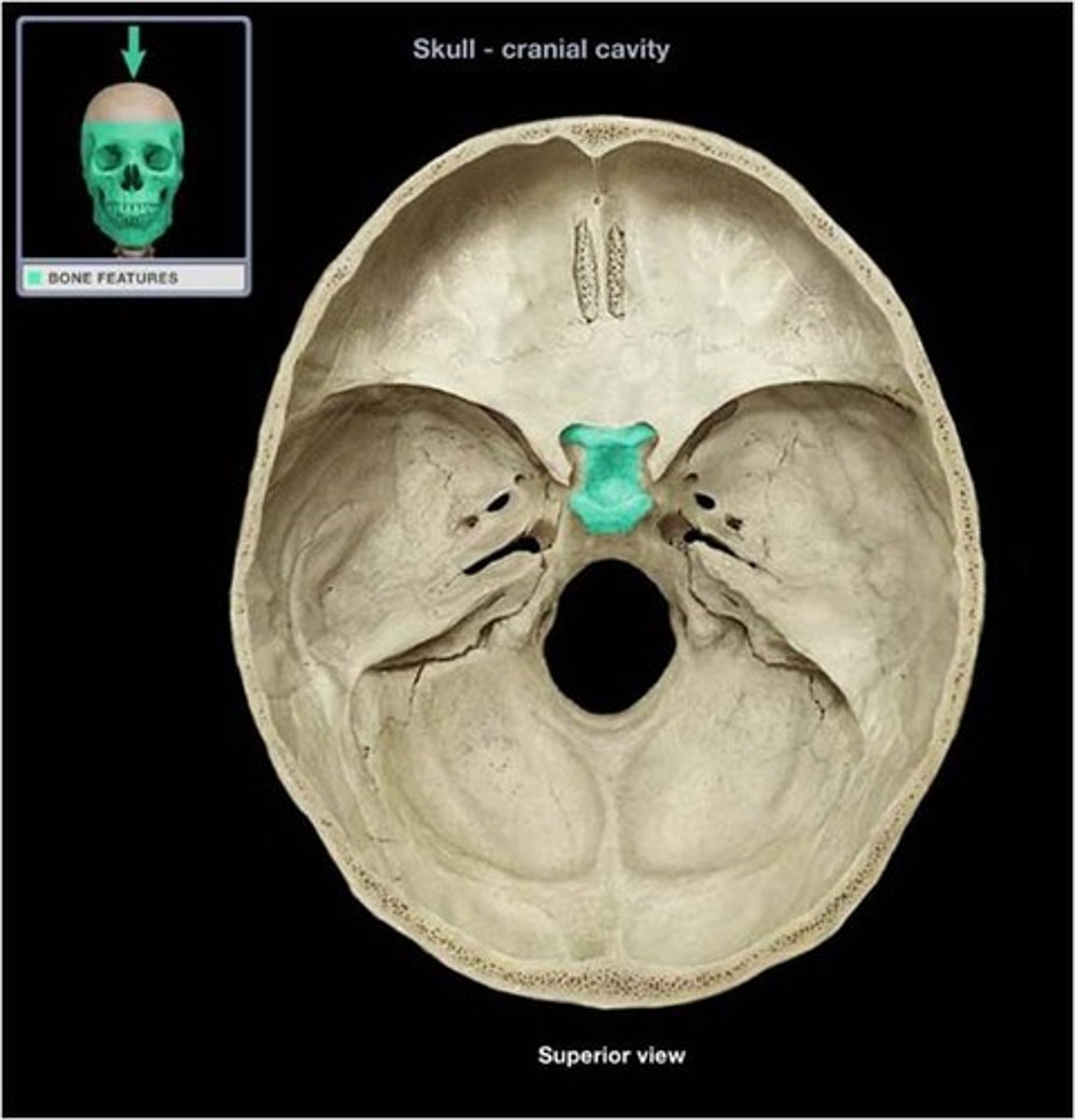
Sella turcica
depression in the sphenoid bone where the pituitary gland is located
pituitary gland
master endocrine gland
What surrounds the sella turcica?
anterior and posterior clinoid processes
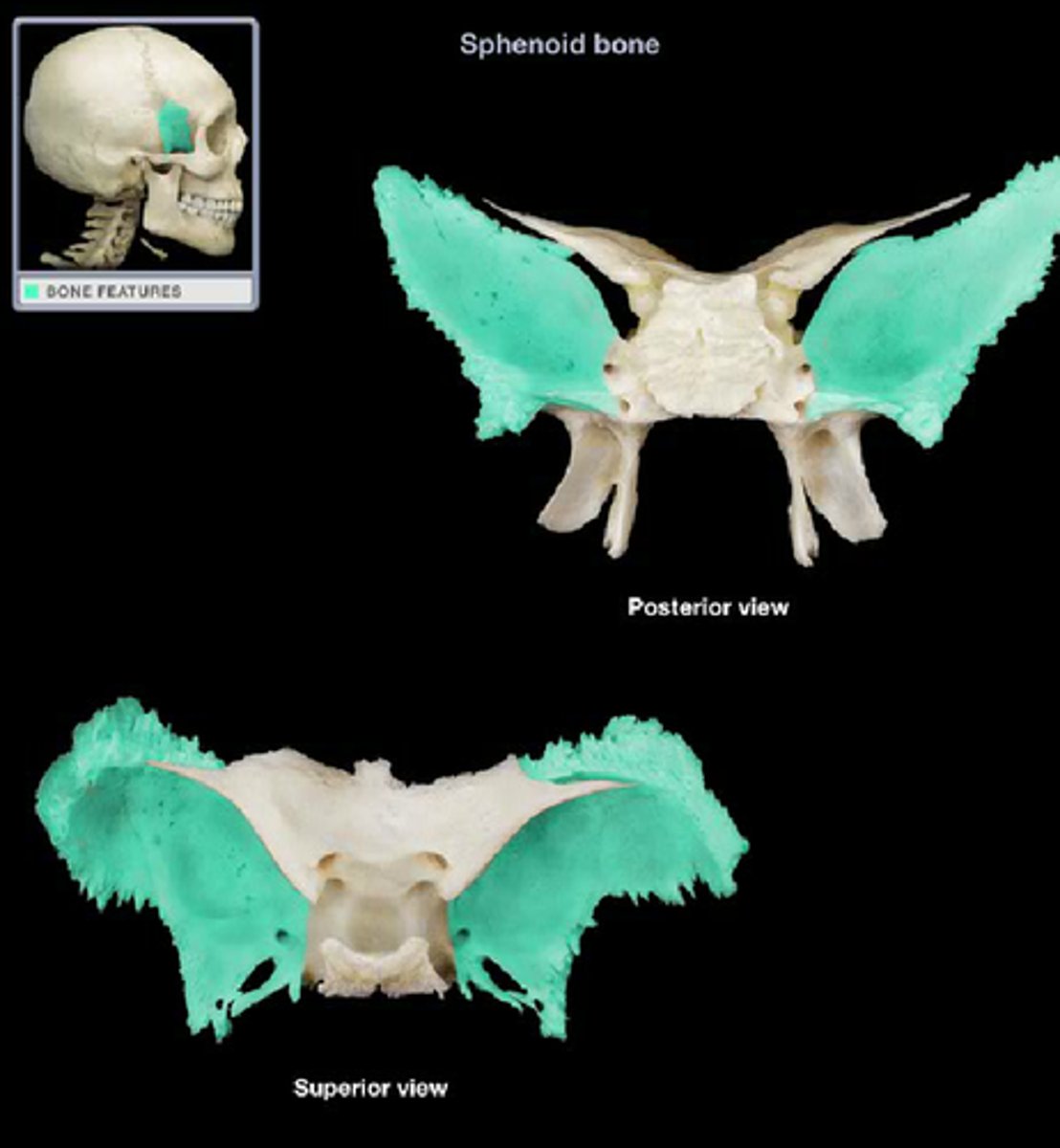
Where are the lesser wings of the sphenoid located?
lateral projections anterior and superior to sella turcica
What do the lesser wings of the sphenoid form?
posterior orbital wall
What do the lesser wings of the sphenoid contain
OPTIC CANAL
What passes through the optic canal found in the lesser wings portion of the sphenoid?
OPTIC NERVE and opthalamic
optic nerve
vision
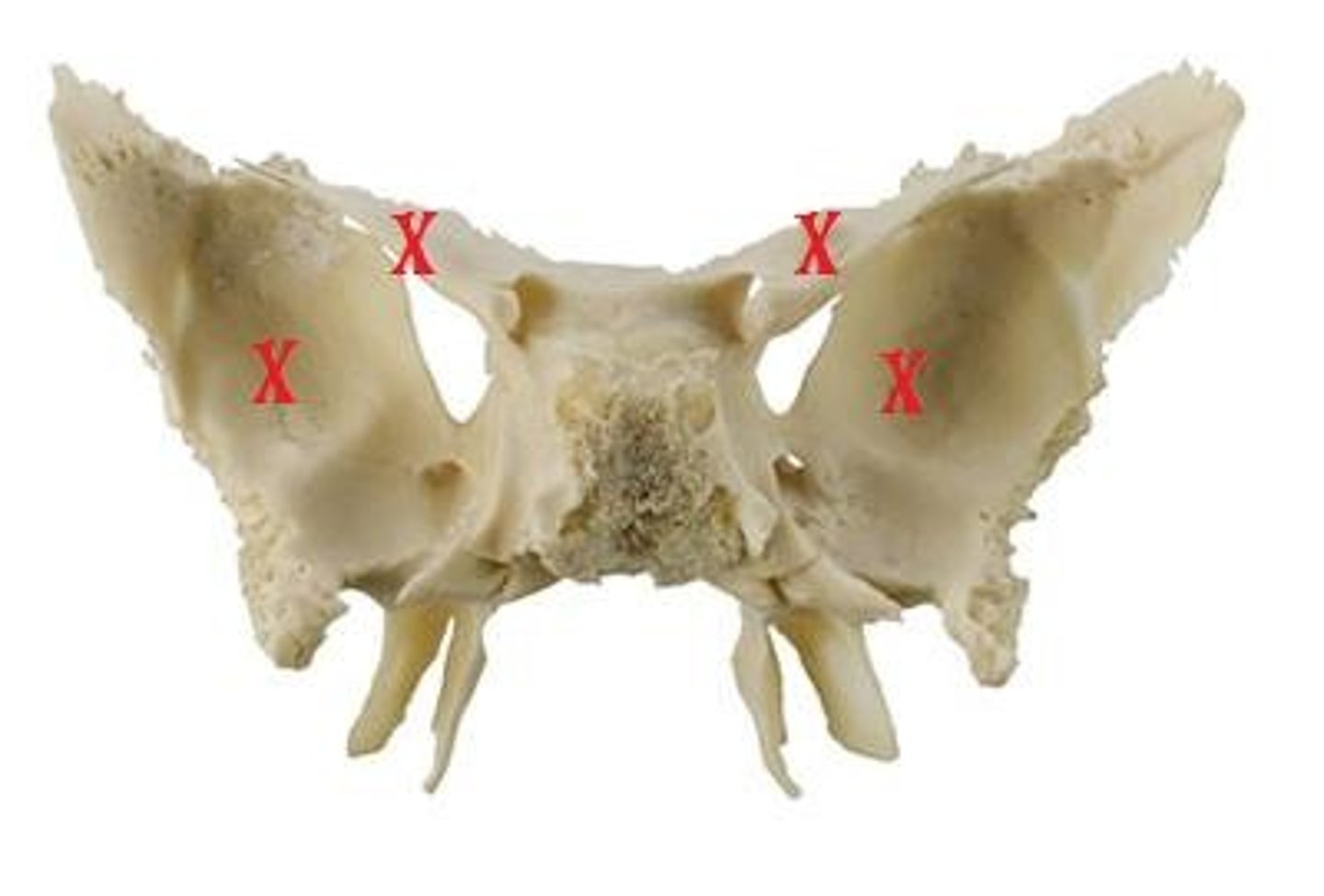
Greater wings of the sphenoid
Are projections that project inferior and laterally•
Pterygoid processes
Serves as an attachment site for pterygoid muscles used in moving the lower jaw.
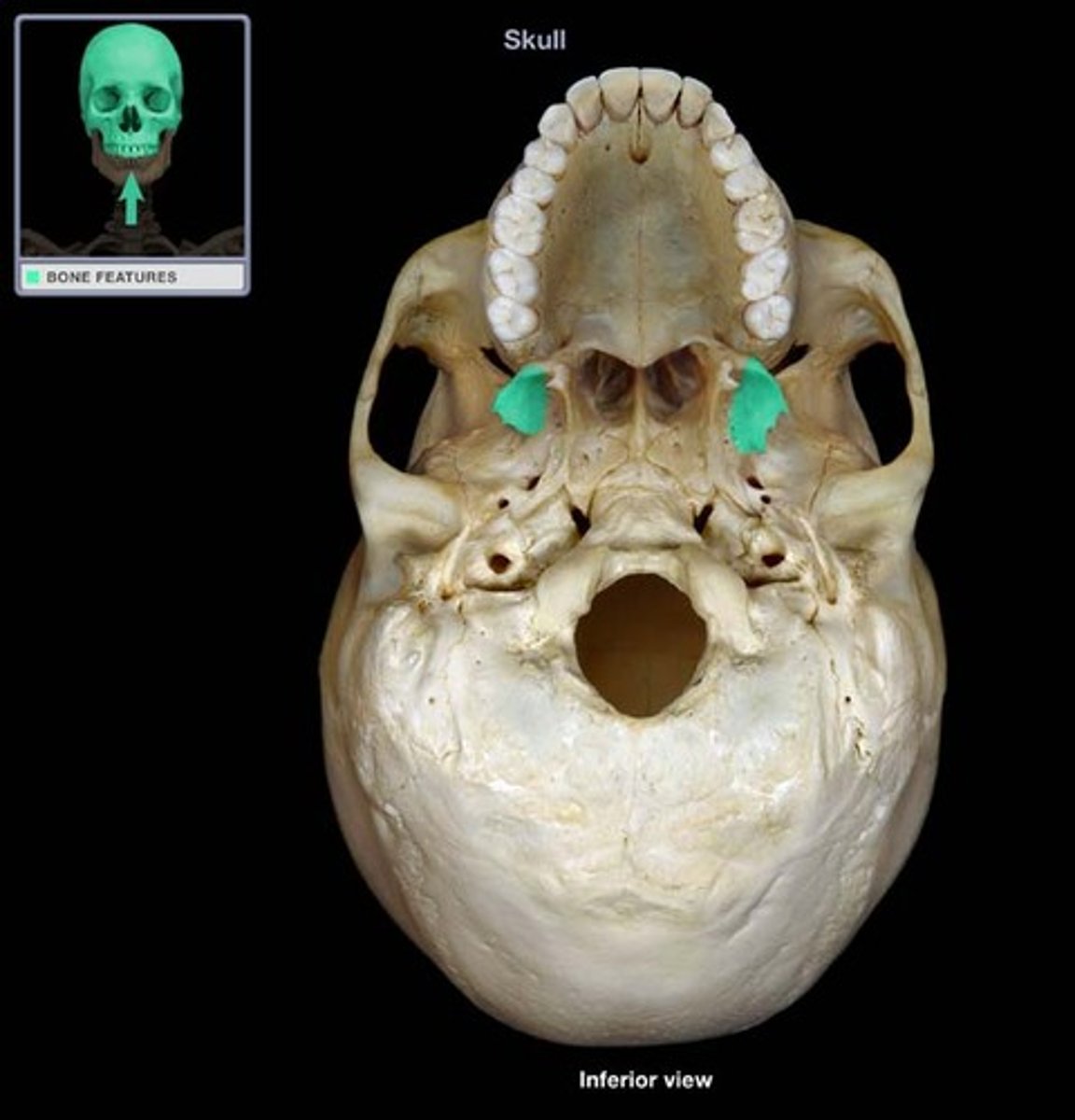
Pterygoid processes location
Extend downward from the sphenoid bone from the junction between the greater wings and the body
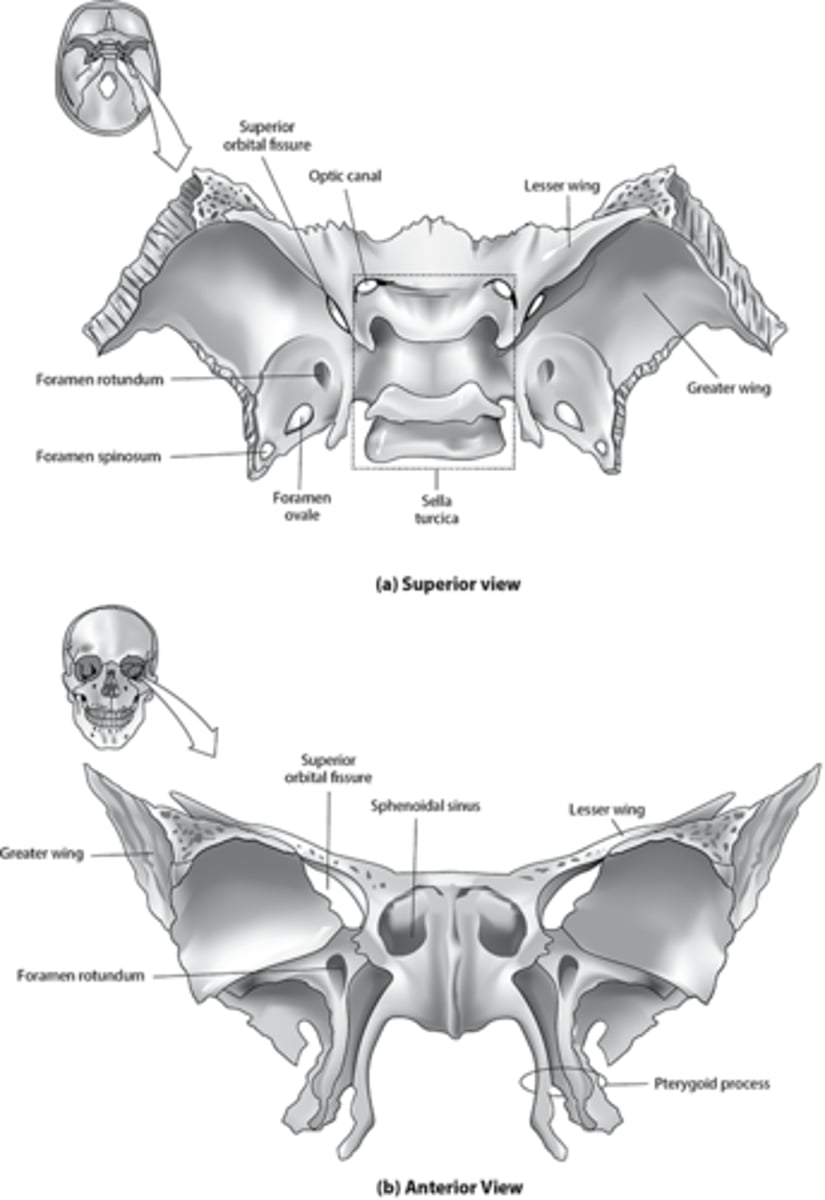
What is the sphenoid sinus?
An air-filled space located within the central portion of the sphenoid bone.
Where is the sphenoid sinus located in relation to other paranasal sinuses?
It is the most posterior of the paranasal sinuses.
located inferior to the sella turcica
Sphenoid foramina location
in sphenoid
What does the Sphenoid foramina transmit
nerves and vessels
The sphenoid foramina includes
lacerum
superior fissure (L. superior part of sphenoid)
rotundum: (L. middle portion of sphenoid)
spinosum(L. inferior portion of sphenoid)
ovale (R. inferior portion of sphenoid)
optic (R. superior portion of sphenoid)
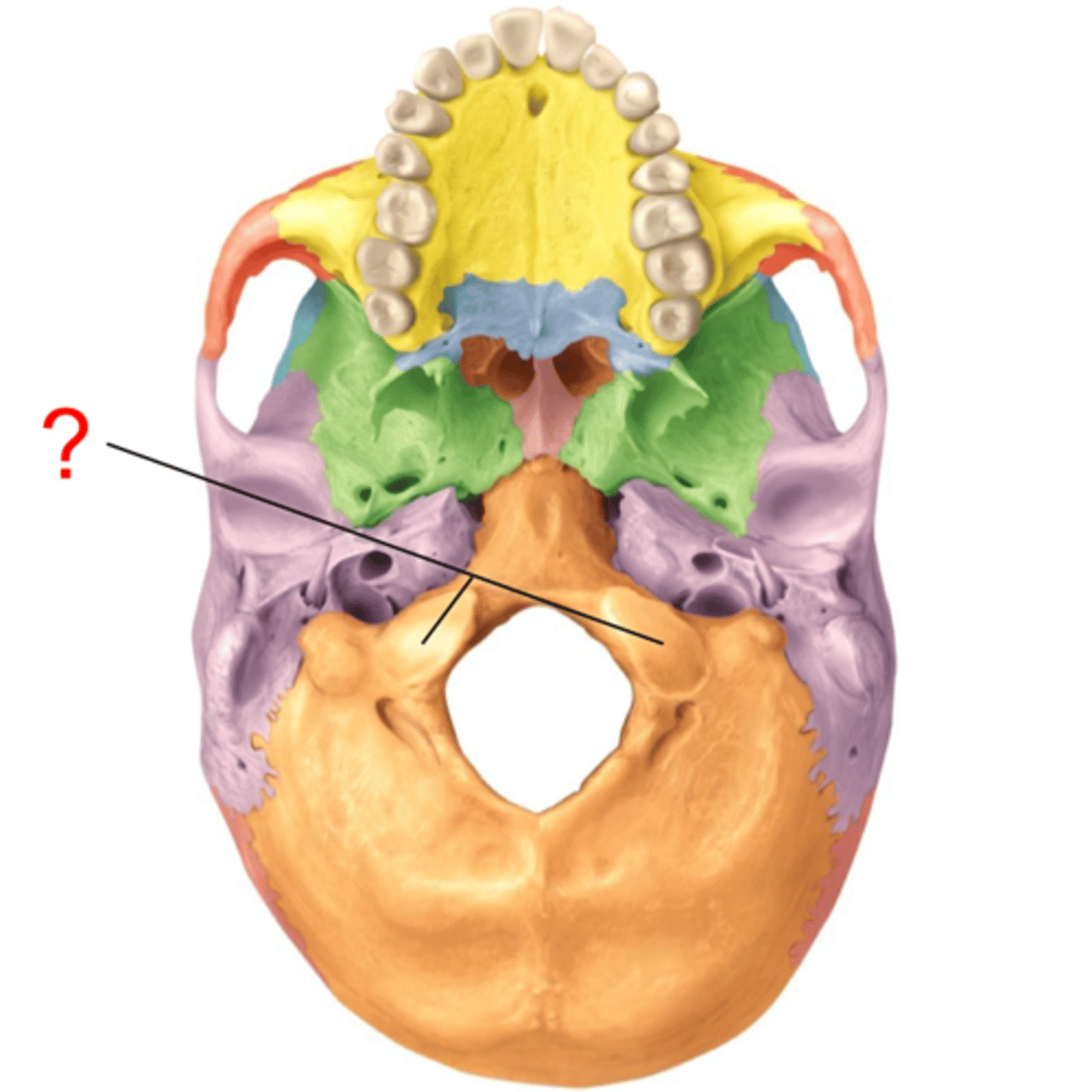
Occipital bone
forms the inferioposterior portion of the cranium
4 parts of occipital bone
squamous, 2 occipital condyles, basilar portion
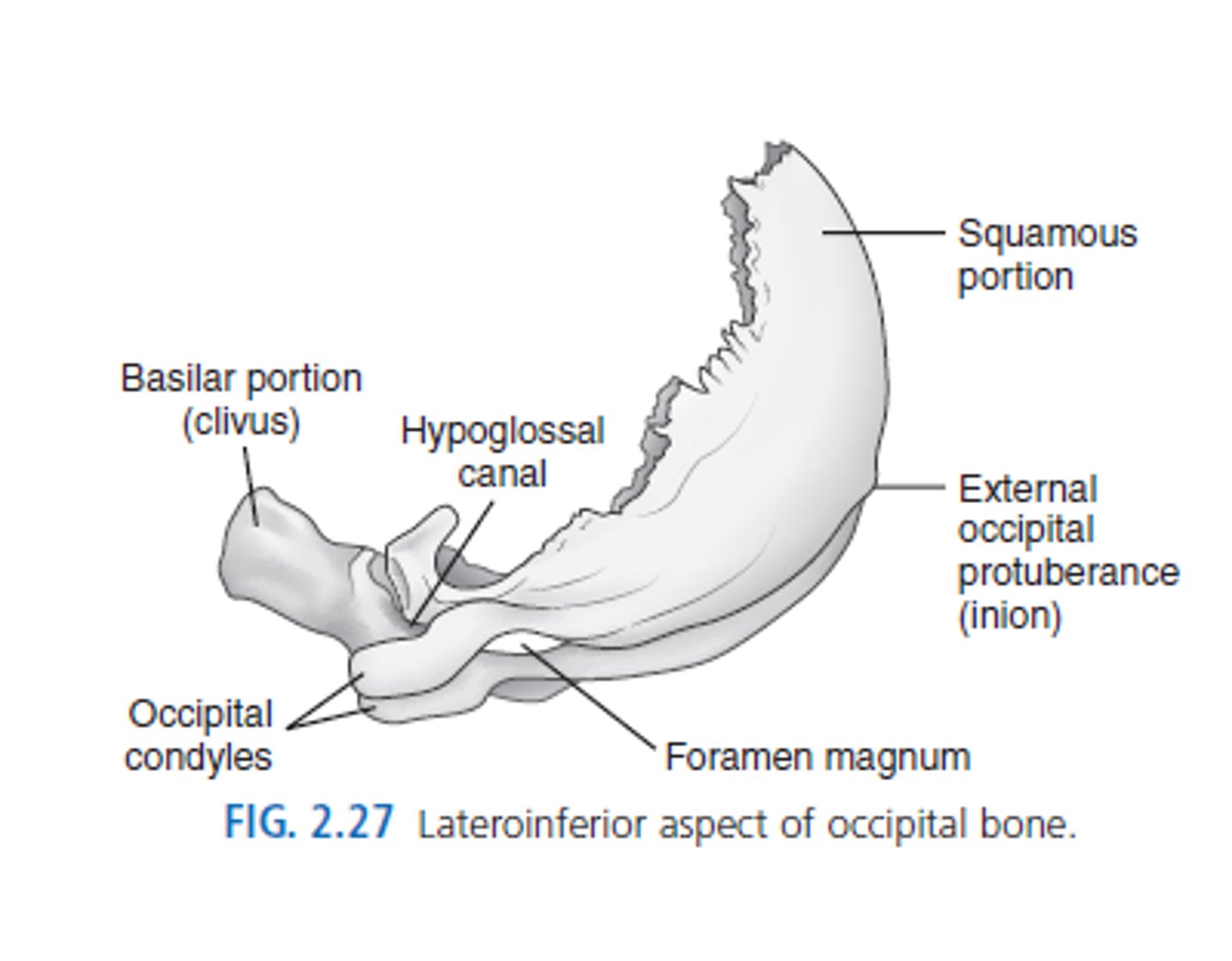
lateral occipital condyles of occipital bone
-2
-articulate with c1 of spine (atlas)
squamous part of occipital bone
The largest part of the occipital bone
includes external occipital protuberances (EOP)
clivus
- found in occipital bone
-Bony structure at the base of the skull.
-slopes down into foramen magnum
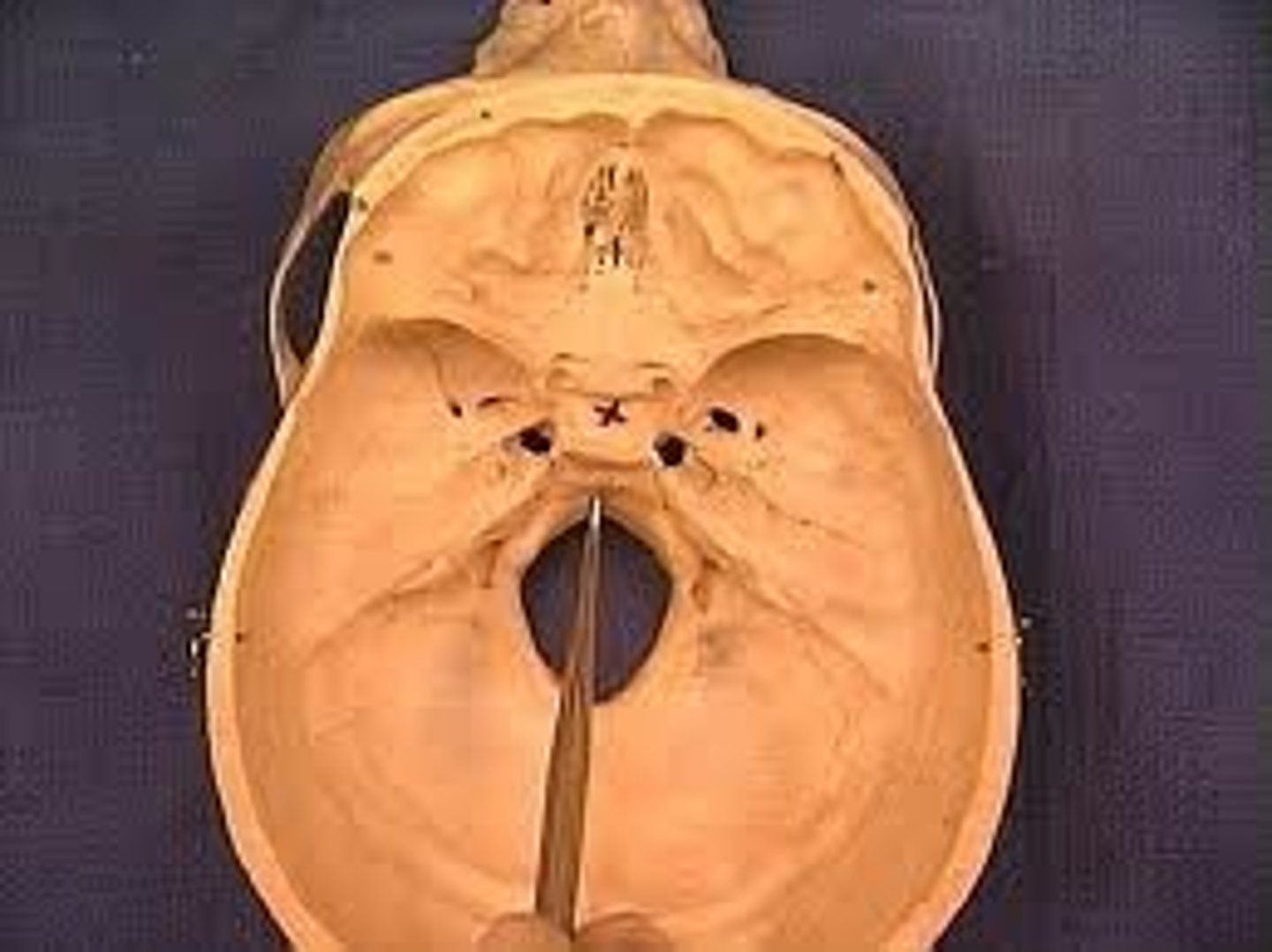
clivus purpose
provides a platform for brainstem
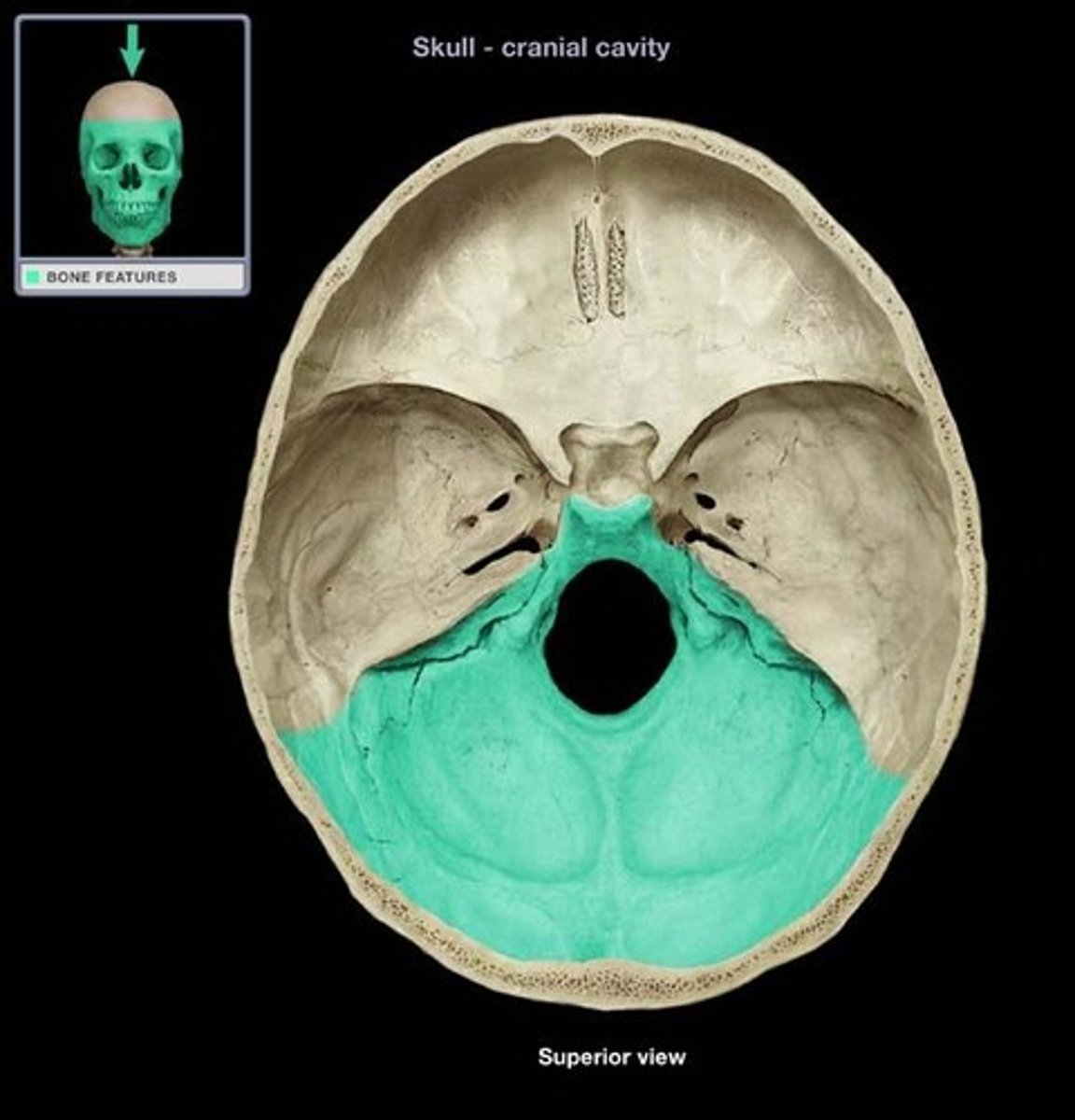
foramen magnum
inferior portion of the occipital bone
largest opening in skull
foramen magnum location
base of skull in occipital bone
Foramen magnum functioin
allows brainstem to continue as spinal cord
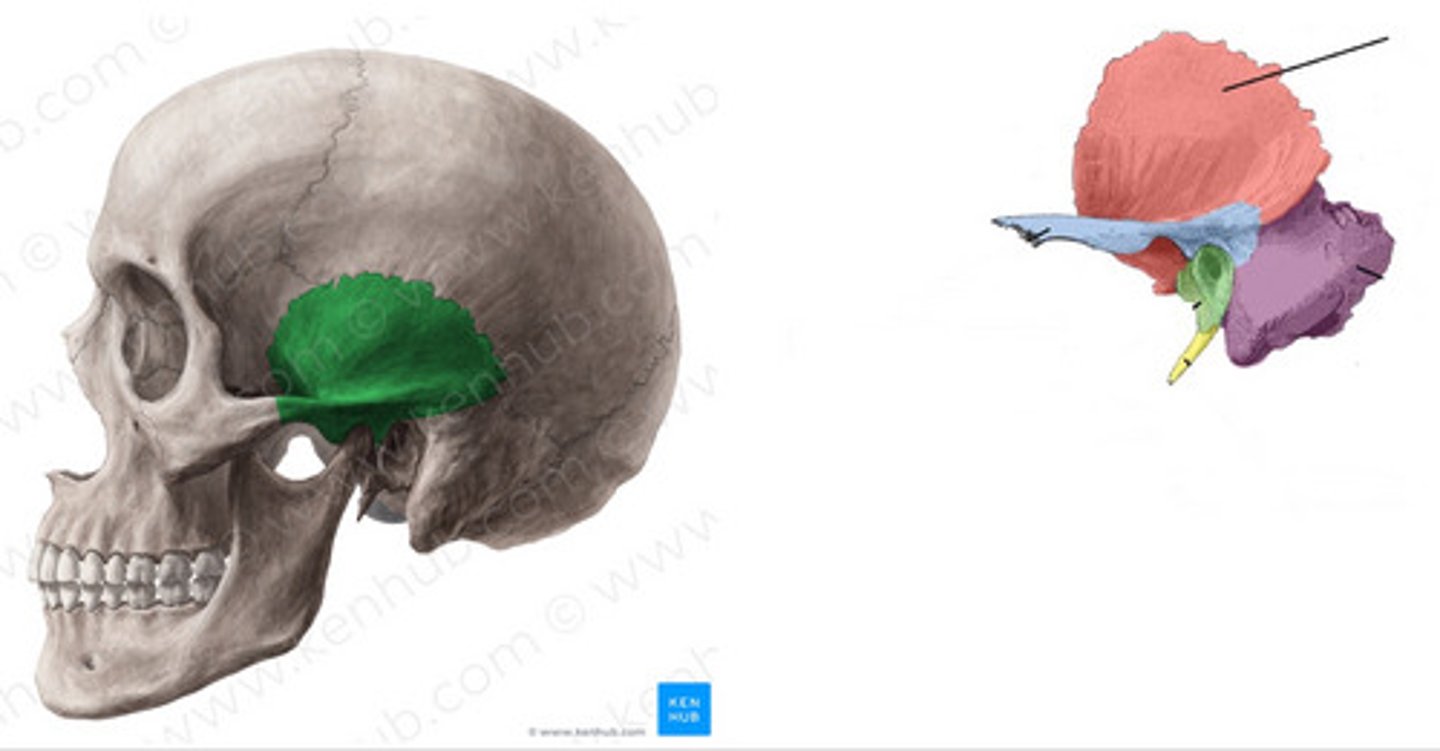
temporal bone
-forms the inferior lateral wall of the cranium and the most middle cranial floor
-paired
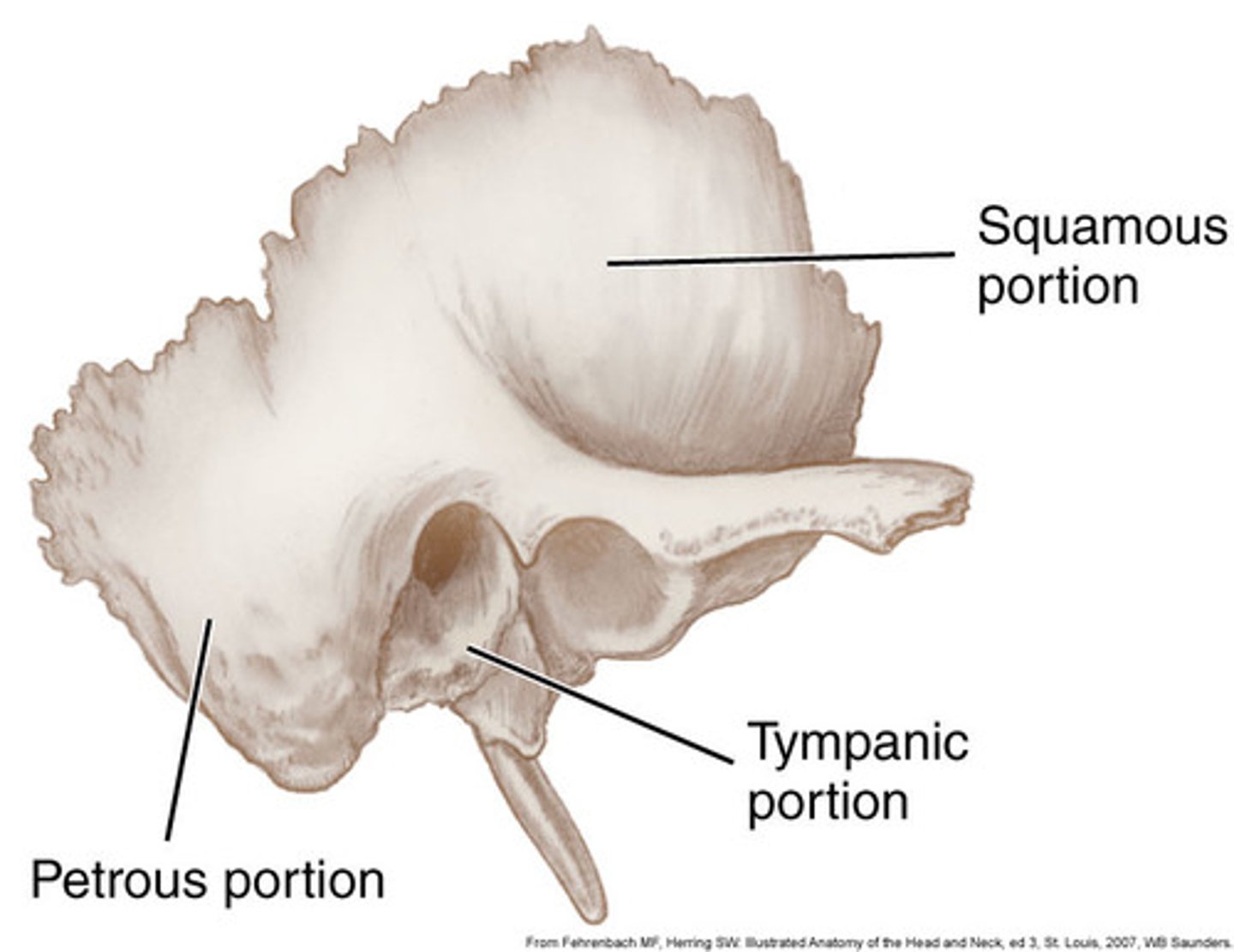
Four portions of the temporal bone
squamous, tympanic, mastoid, petrous
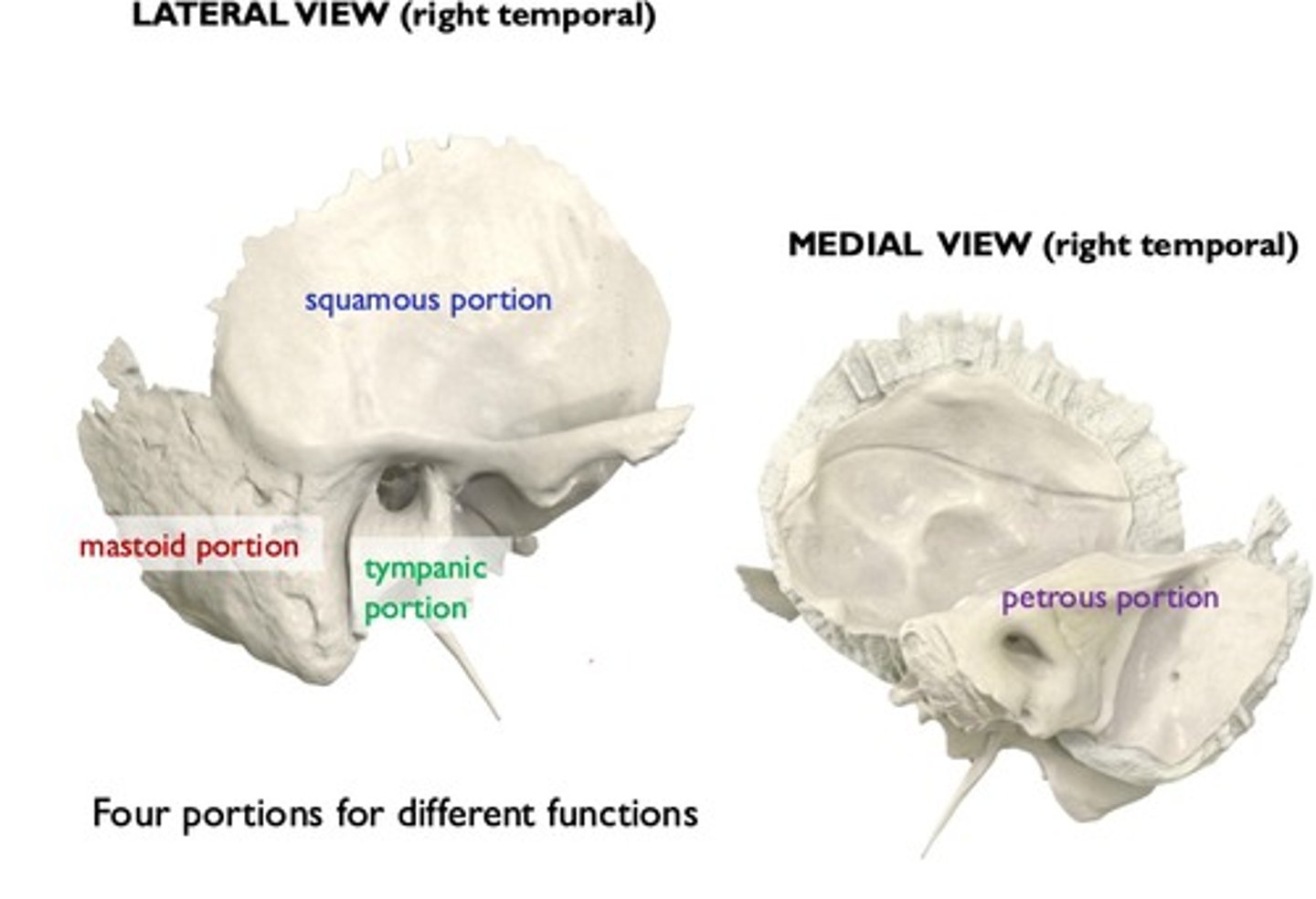
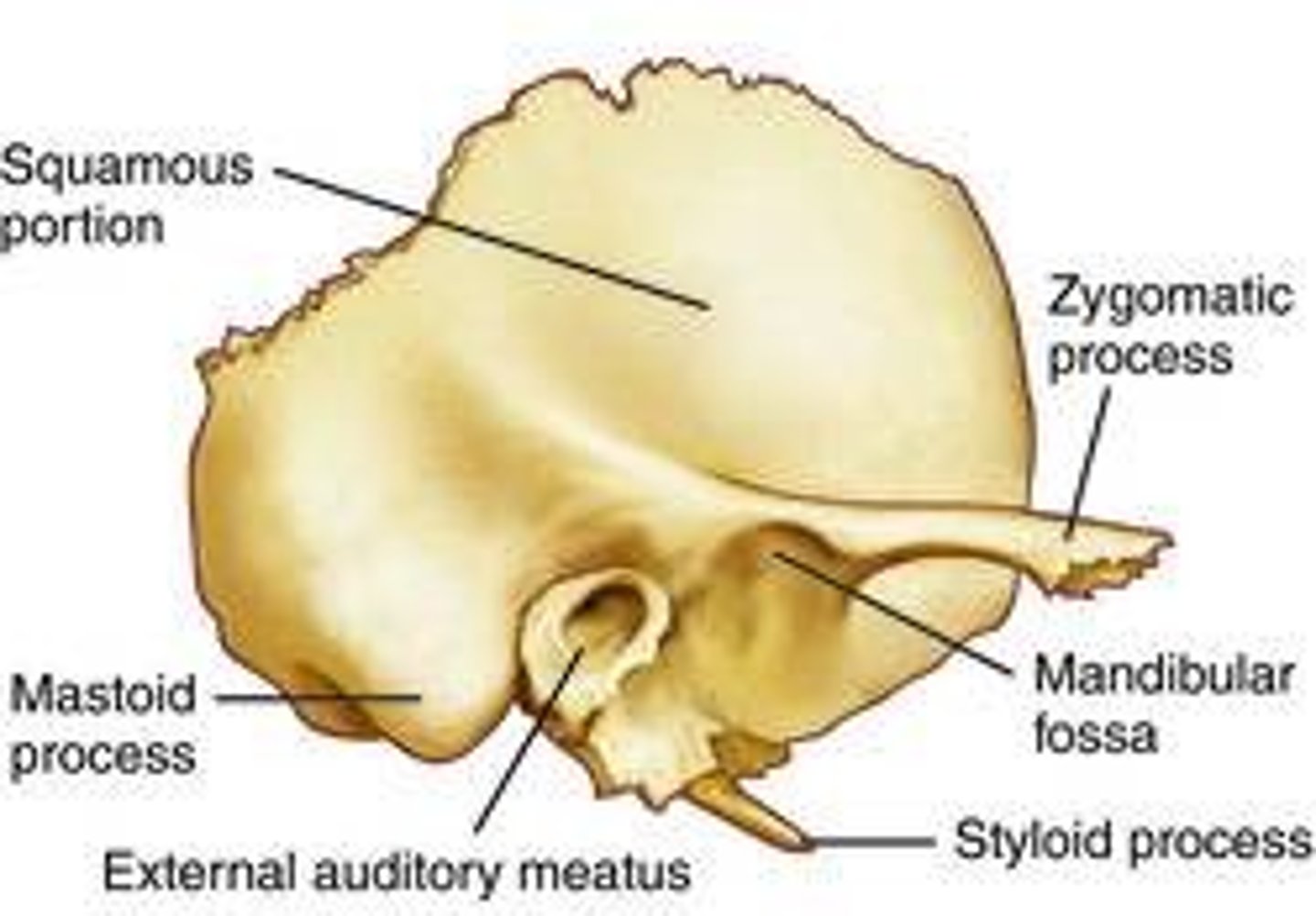
squamous portion of temporal bone
-largest
-contains zygomatic process
tympanic portion of temporal bone
-2
-form the majority of External Auditory Meatus (EAM)
What is the EAM and where is it located?
-ear canal
-located lateral side of the cranium
mastoid portion of temporal bone
-contains mastoid process (3)
- encloses mastoid air cells
petrous part of temporal bone
houses the middle and inner ear structures for hearing
densest
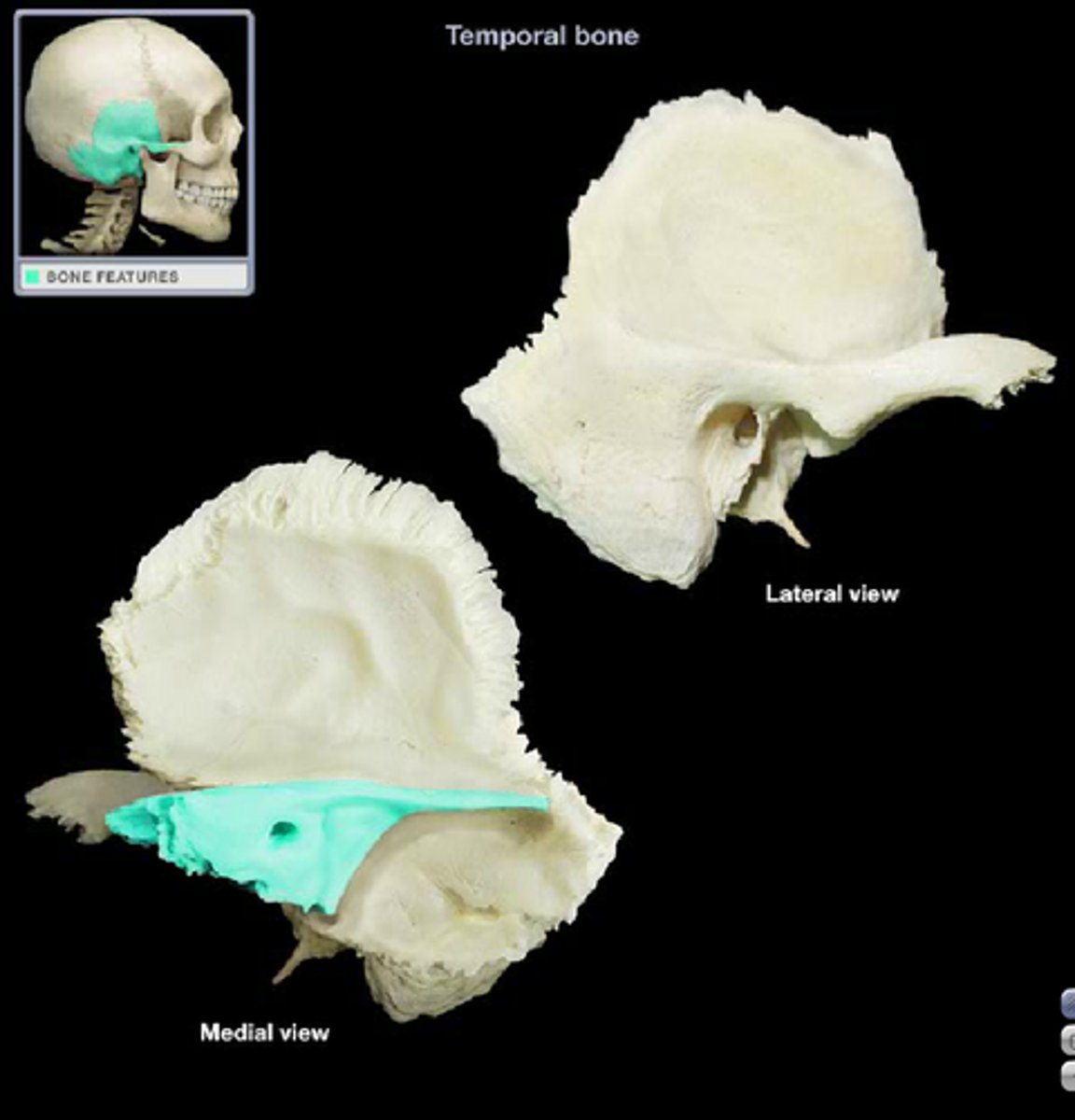
What does the petrous contain
the styloid process
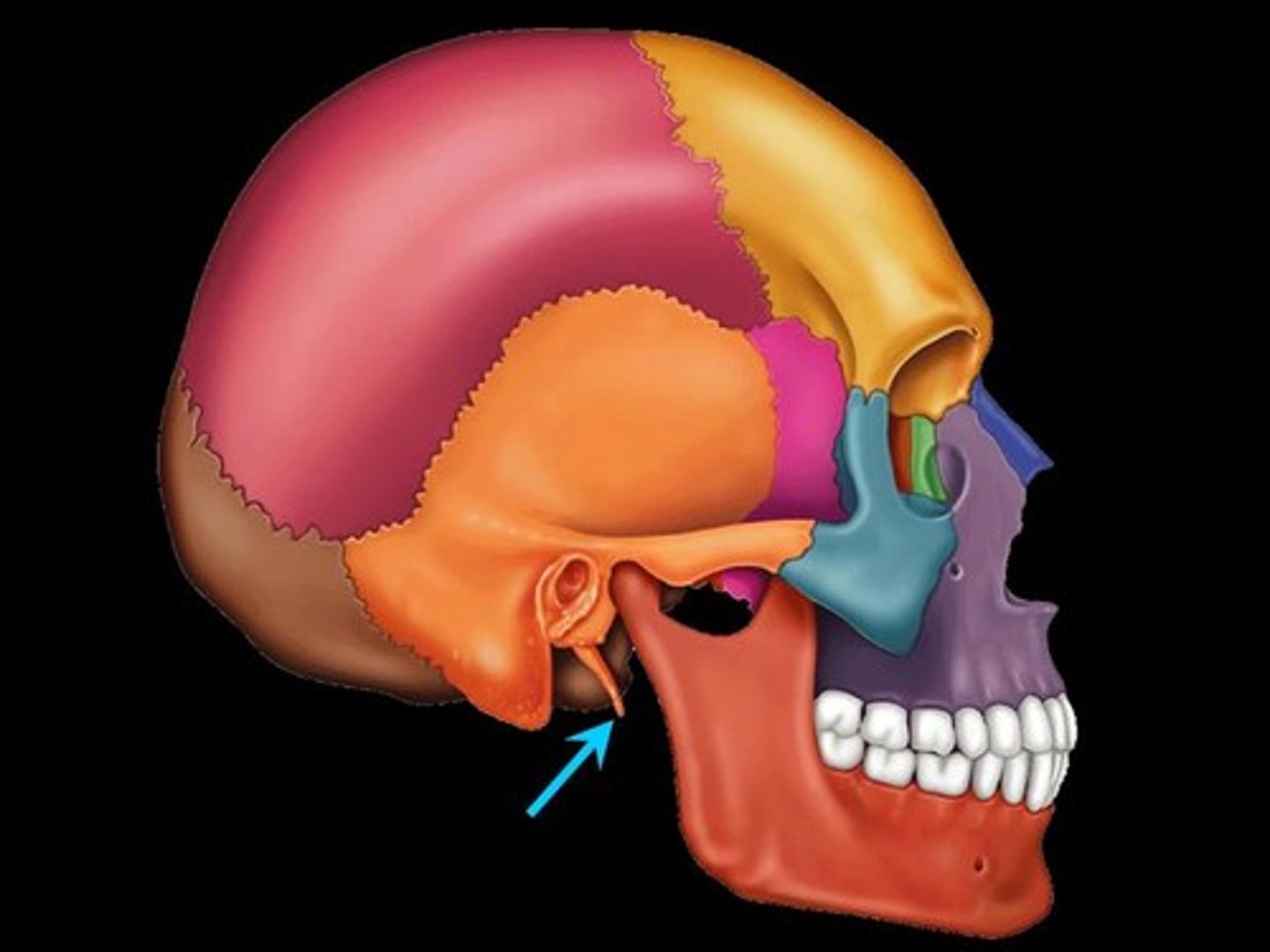
structure of ear
outer ear, middle ear, inner ear
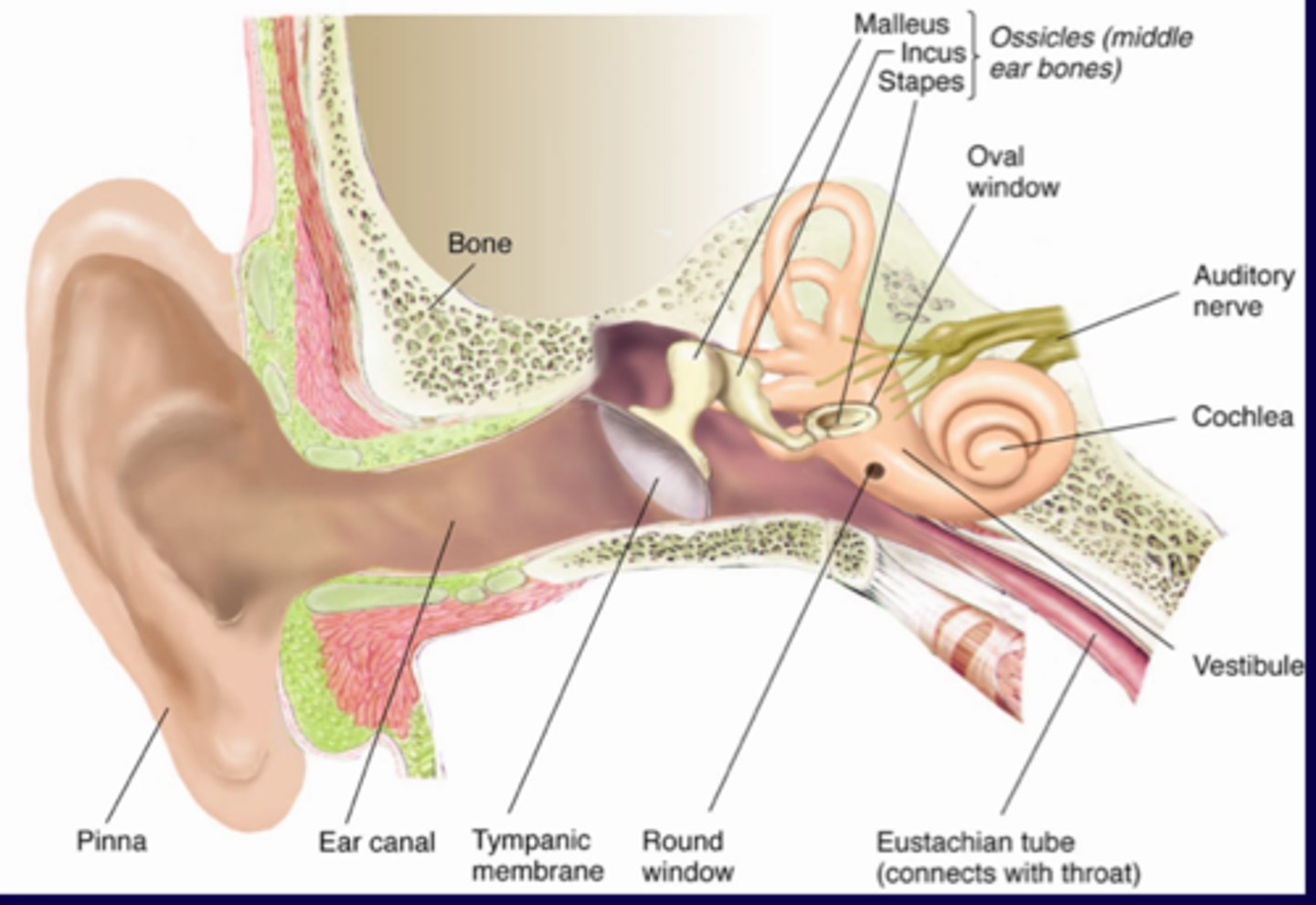
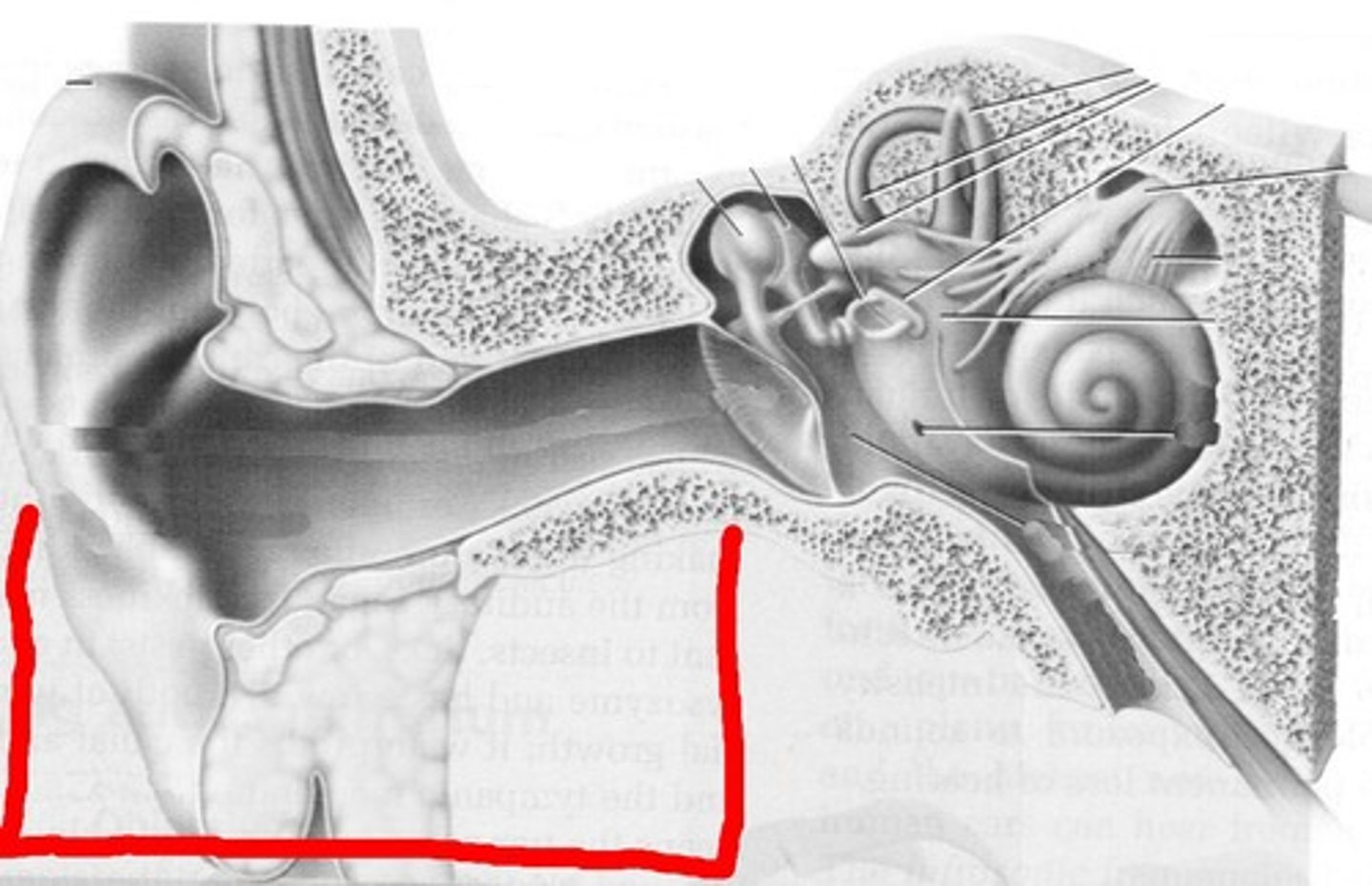
External Ear consists of
auricle and external acoustic meatus (EAM)
middle ear
air filled cavity in the temporal bone
middle ear consists of
Eustachian tube
tympanic membrane
ossicles bones
Eustachian tube
auditory tube
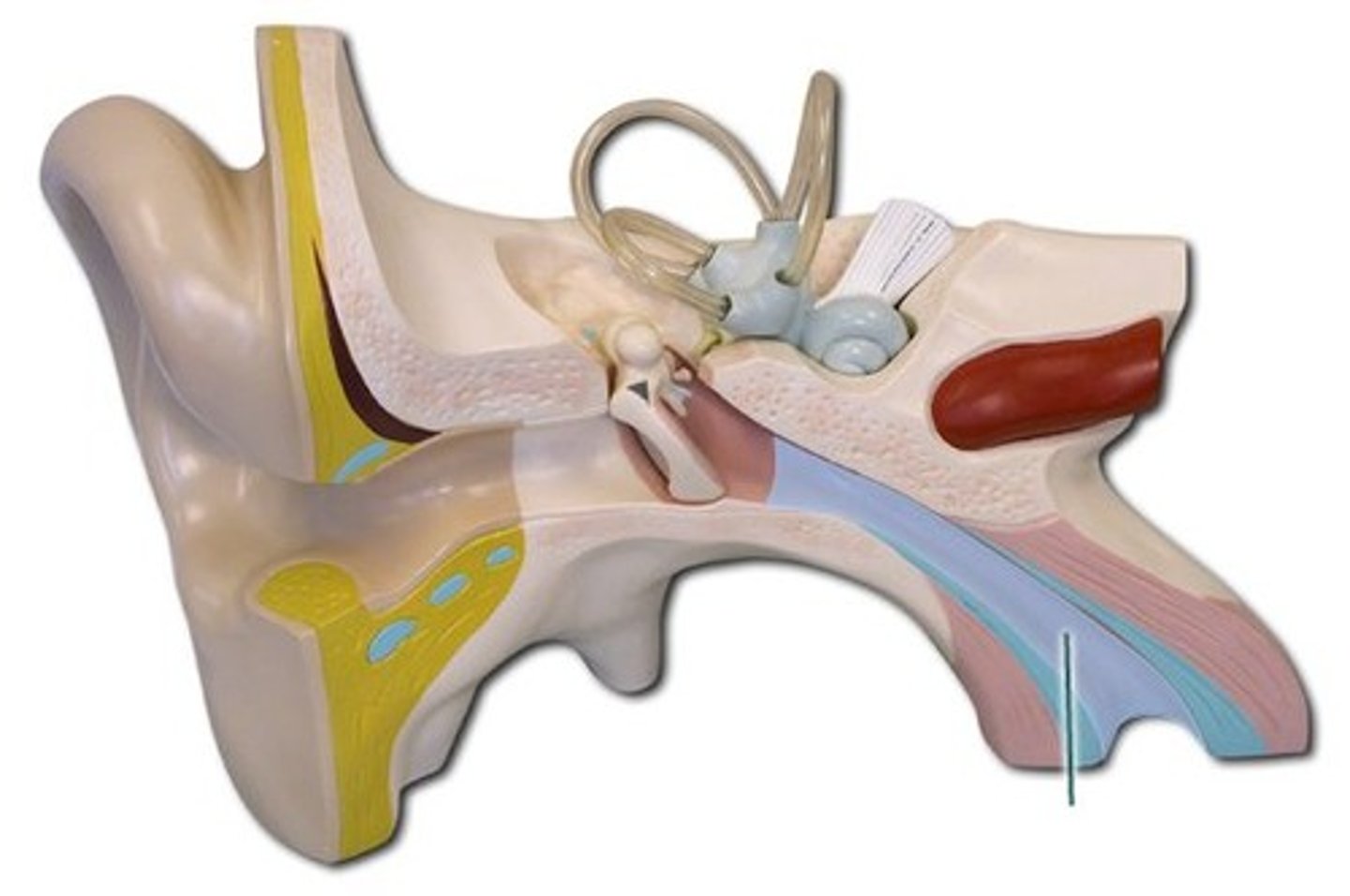
what does the eustachian tube connect the middle ear to?
nasopharynx
what role does the eustachian tube play
plays role in pressure equalization
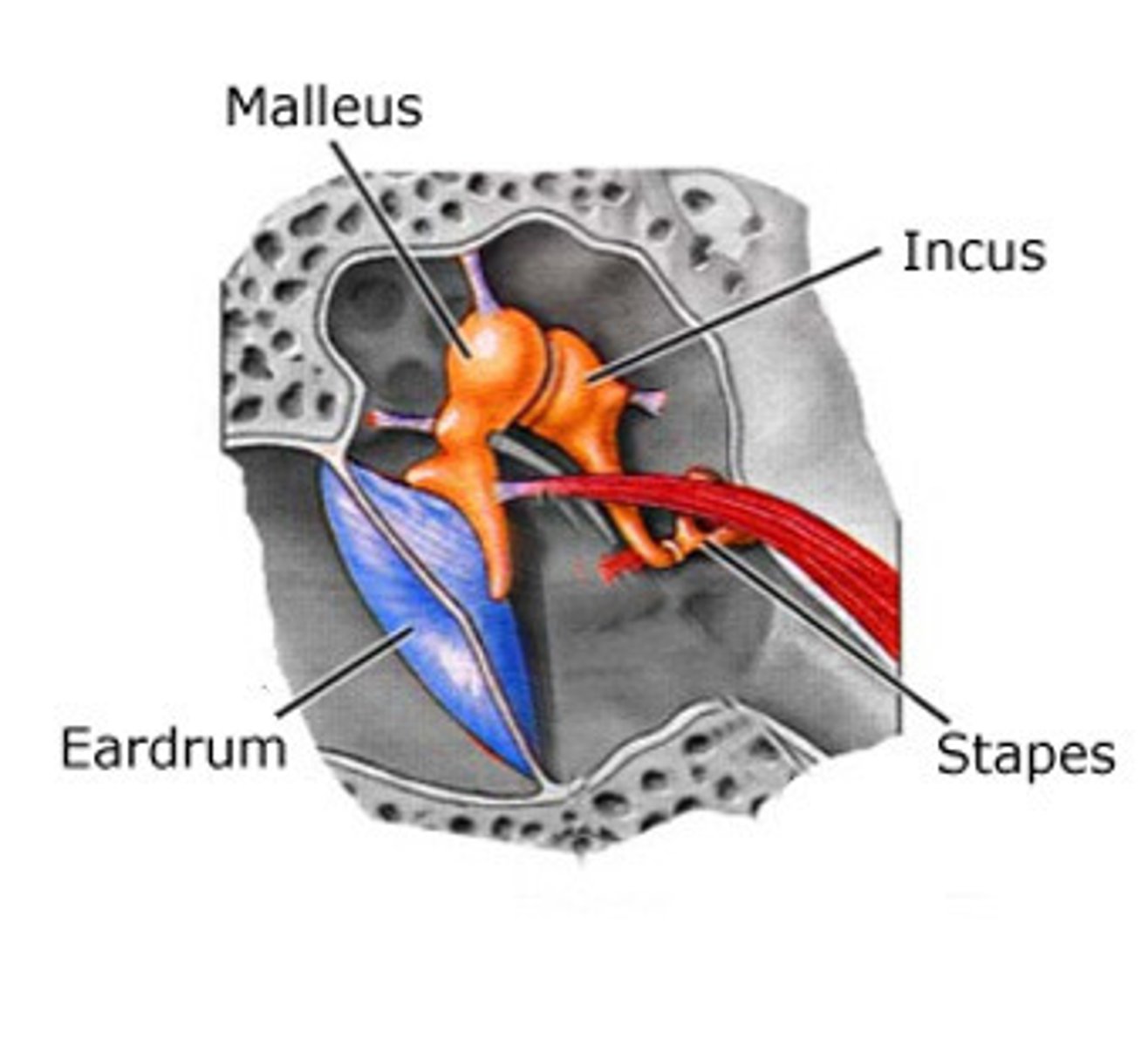
Tympanic membrane
eardrum
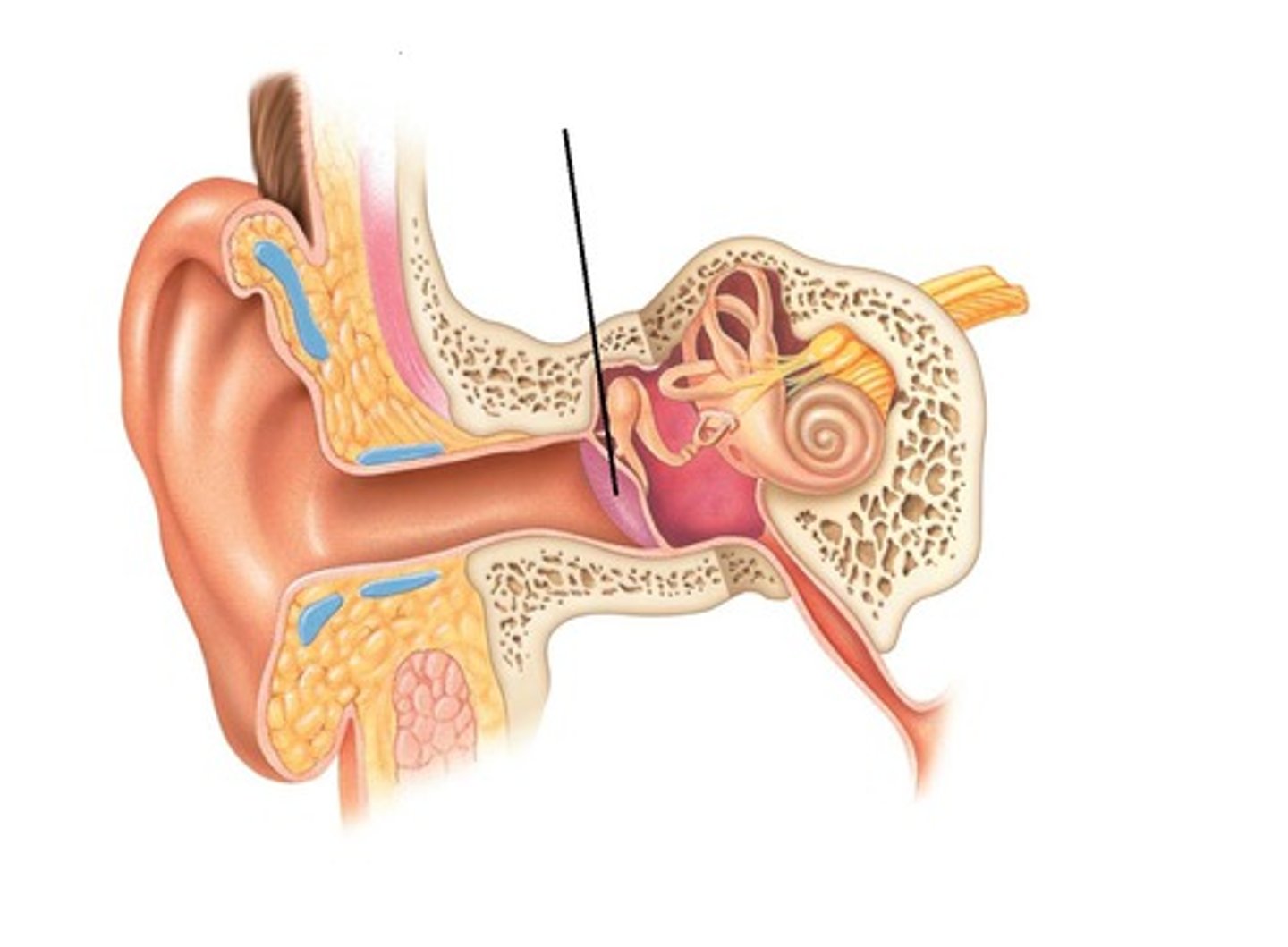
Ossicles
malleus, incus, stapes
inner ear
fluid filled
What does the inner ear consist of
cochlea, vestibule, semicircular canals
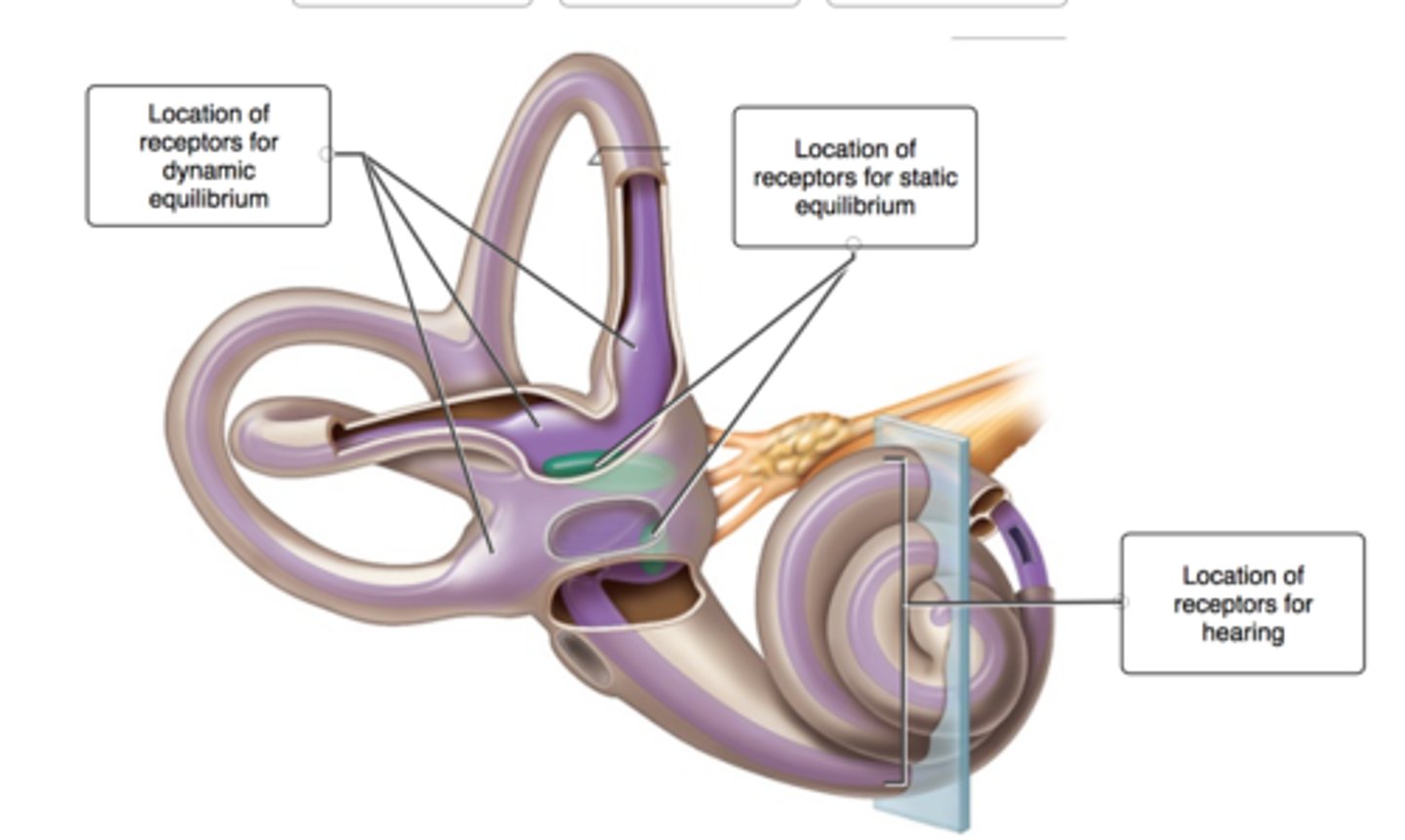
vestibule and semicircular canals
controll balance and equilibrium
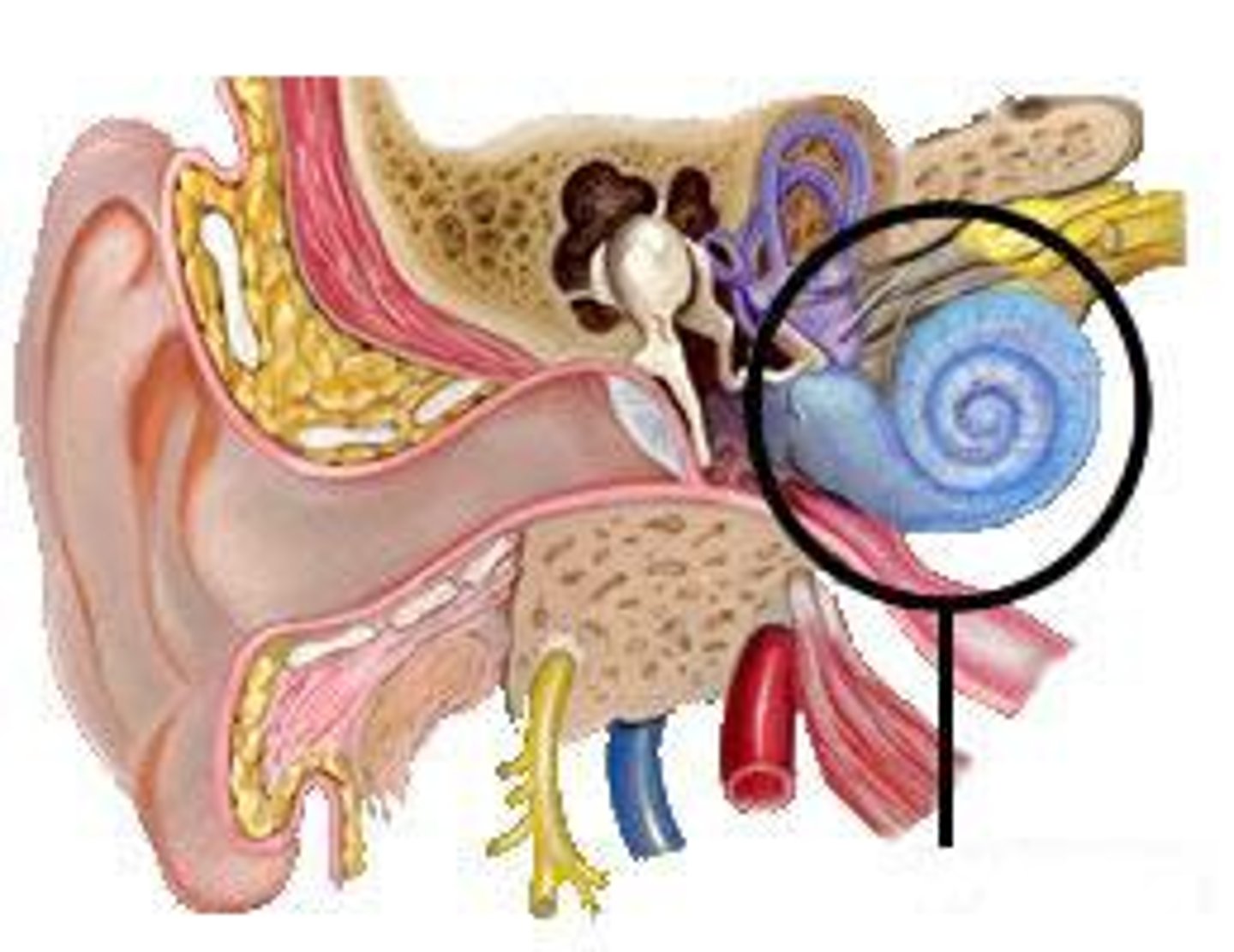
cochlea
responsible for hearing