bio 300 biodiver LAB exam 1
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
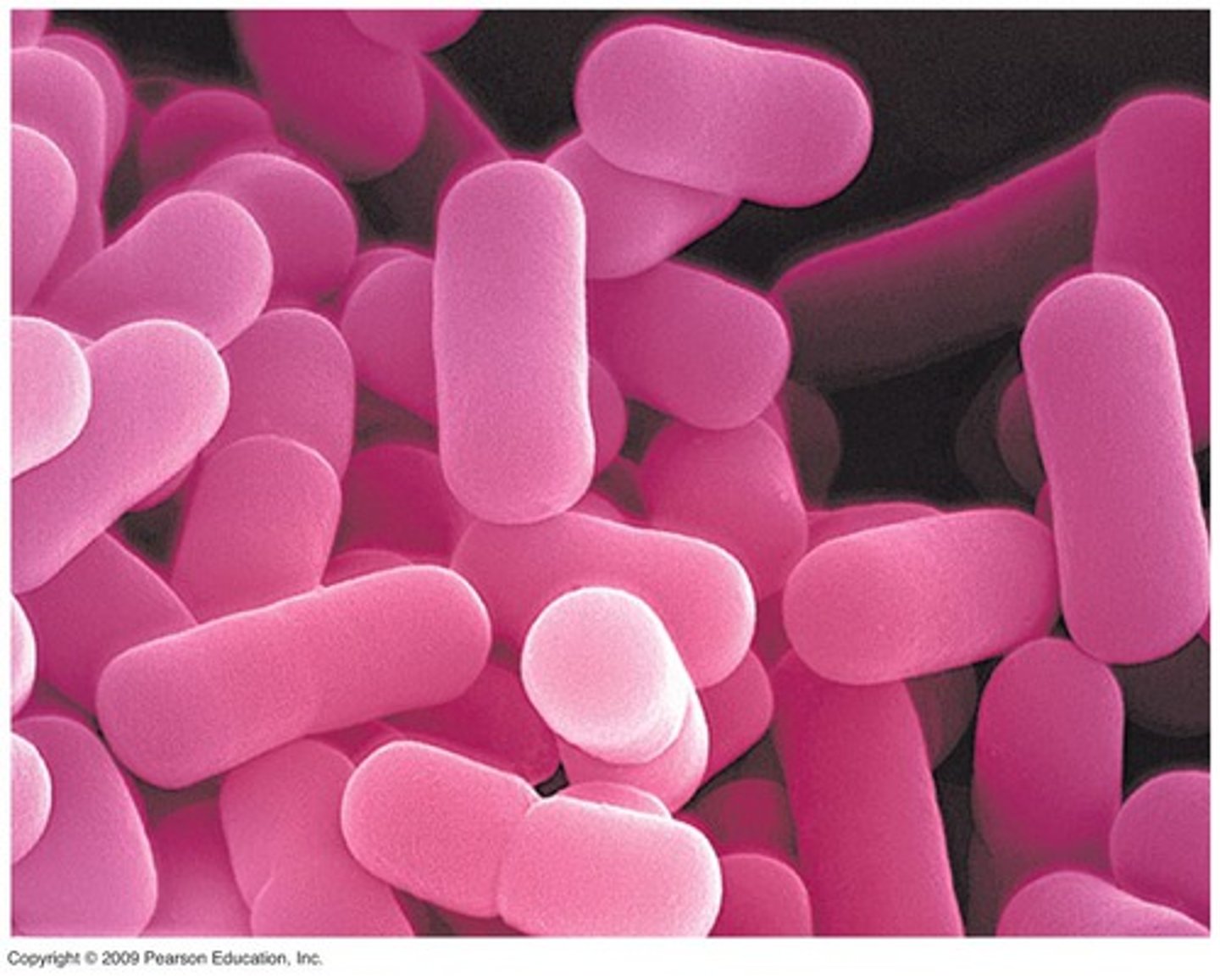
Prokaryote shape: bacilli
rod shaped
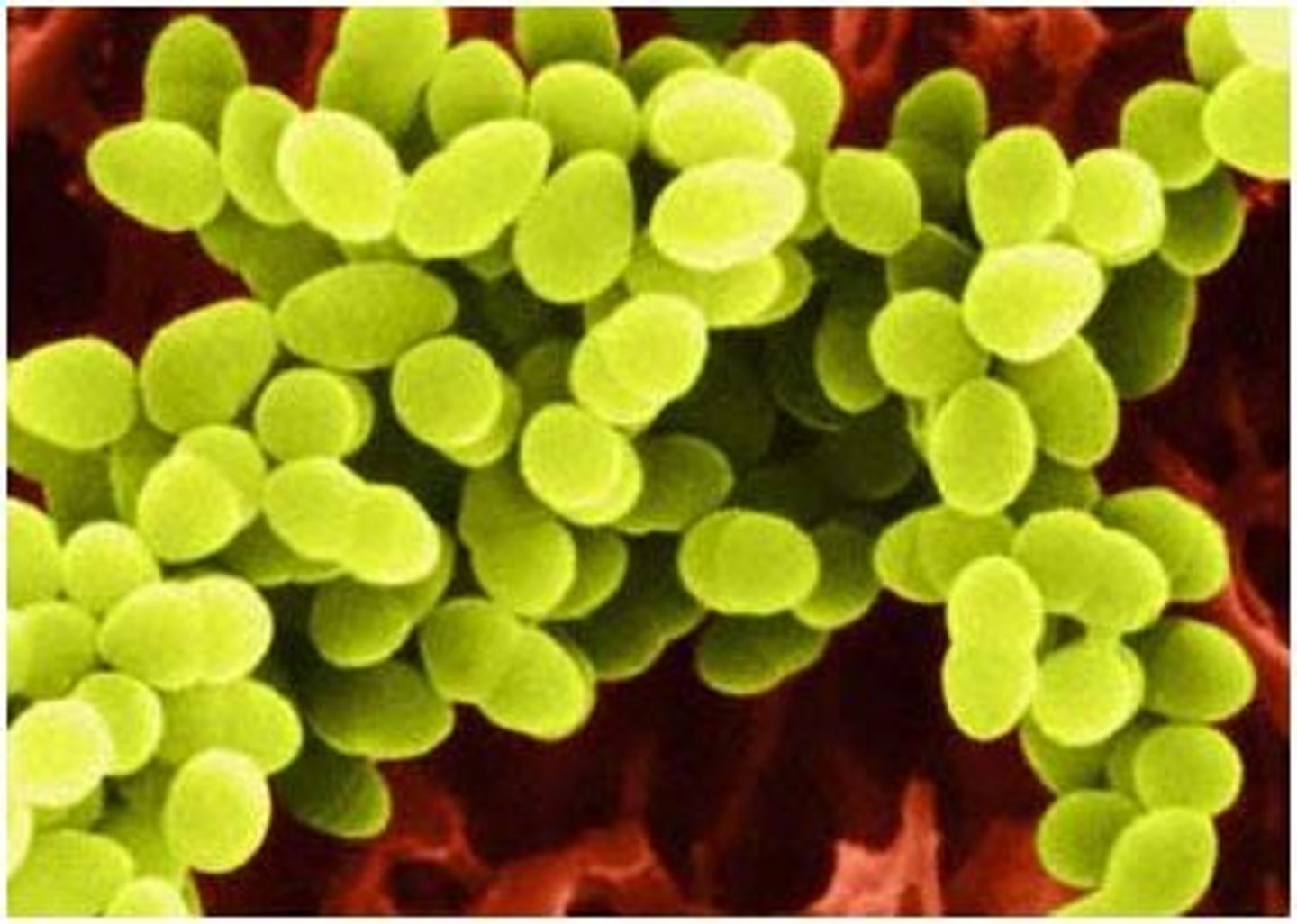
Prokaryote shape: cocci
spherical
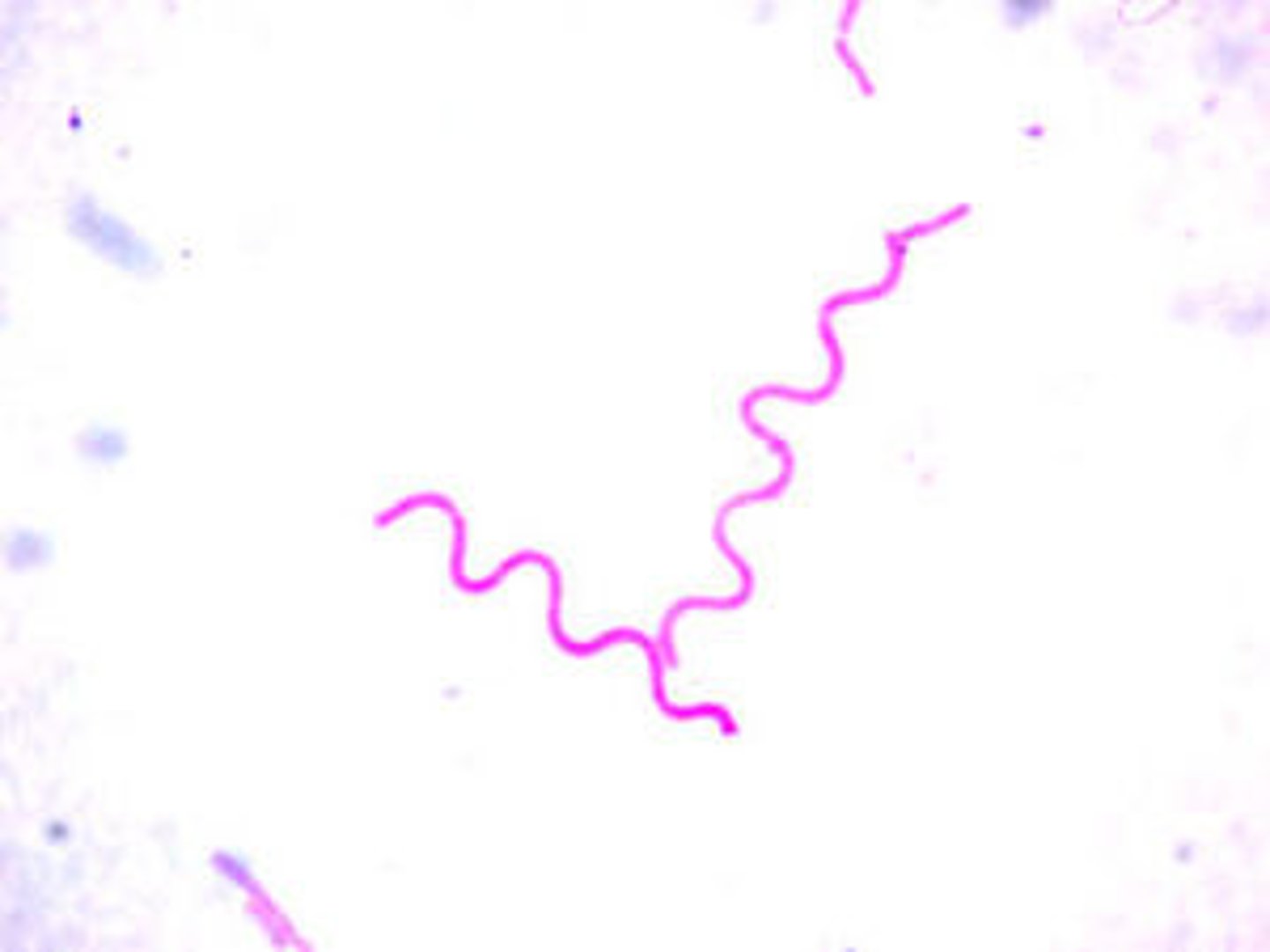
prokaryote shape: spirillum
Pleiomorphic bacteria
-lack a cell wall
-varied cell shapes
Gram positive cell wall
thick layer of peptidoglycan
gram negative cell wall
thin peptidoglycan layer
Chemoheterotrophs
An organism that must consume organic molecules for both energy and carbon.
photoheterotroph
An organism that obtains energy from sunlight and carbon from organic sources.
photoautotroph
organism that uses energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water to carbon compounds
facultative
organism that can survive with or without oxygen
Halobacterium salinarum
•Extreme halophile
•Photoheterotroph
•Bacteriorhodopsin: nonphotosynthetic light-harvesting pigment that can generate ATP
•Consumes amino acids or other organic acids; is therefore heterotrophic
Protists
Any Eukaryote that is not a land plant, animal, or fungus Most are microscopic and unicellular they are Unicellular or multicellular Autotrophic or heterotrophic Asexually or sexually reproducing Sessile or motile, via cilia, flagella, or pseudopodia
Physarum polycephalum
Plasmodial slime mold
Moves hydrostatically using pseudopods
Feeds and moves primarily through chemotaxis
Can change into a resting state conditions
sclerotinumin poor
Displays complex decision making without a brain: Makes feeding "decisions" based on quality and quantity
Remembers where it has been and finds optimal pathways to food sources

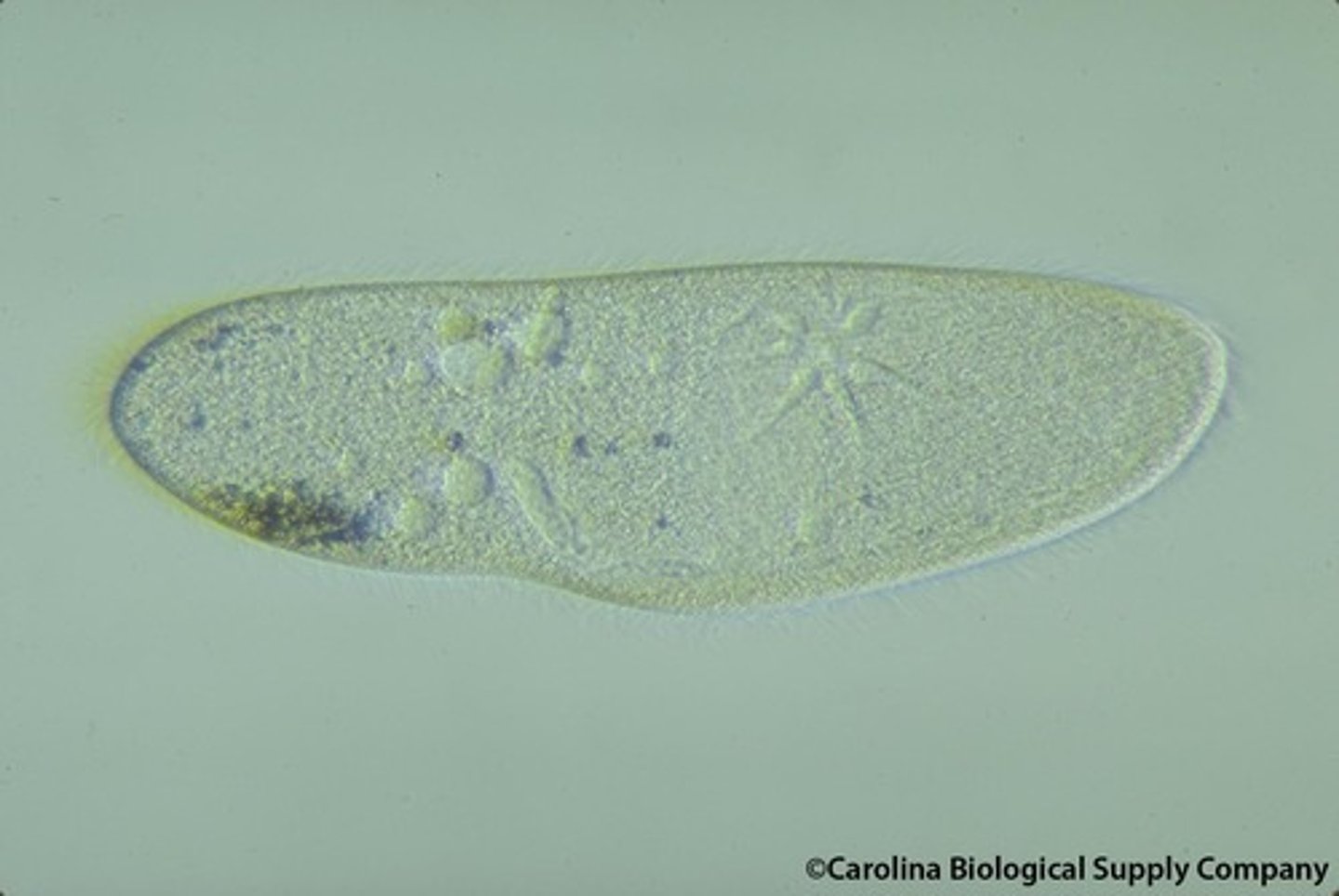
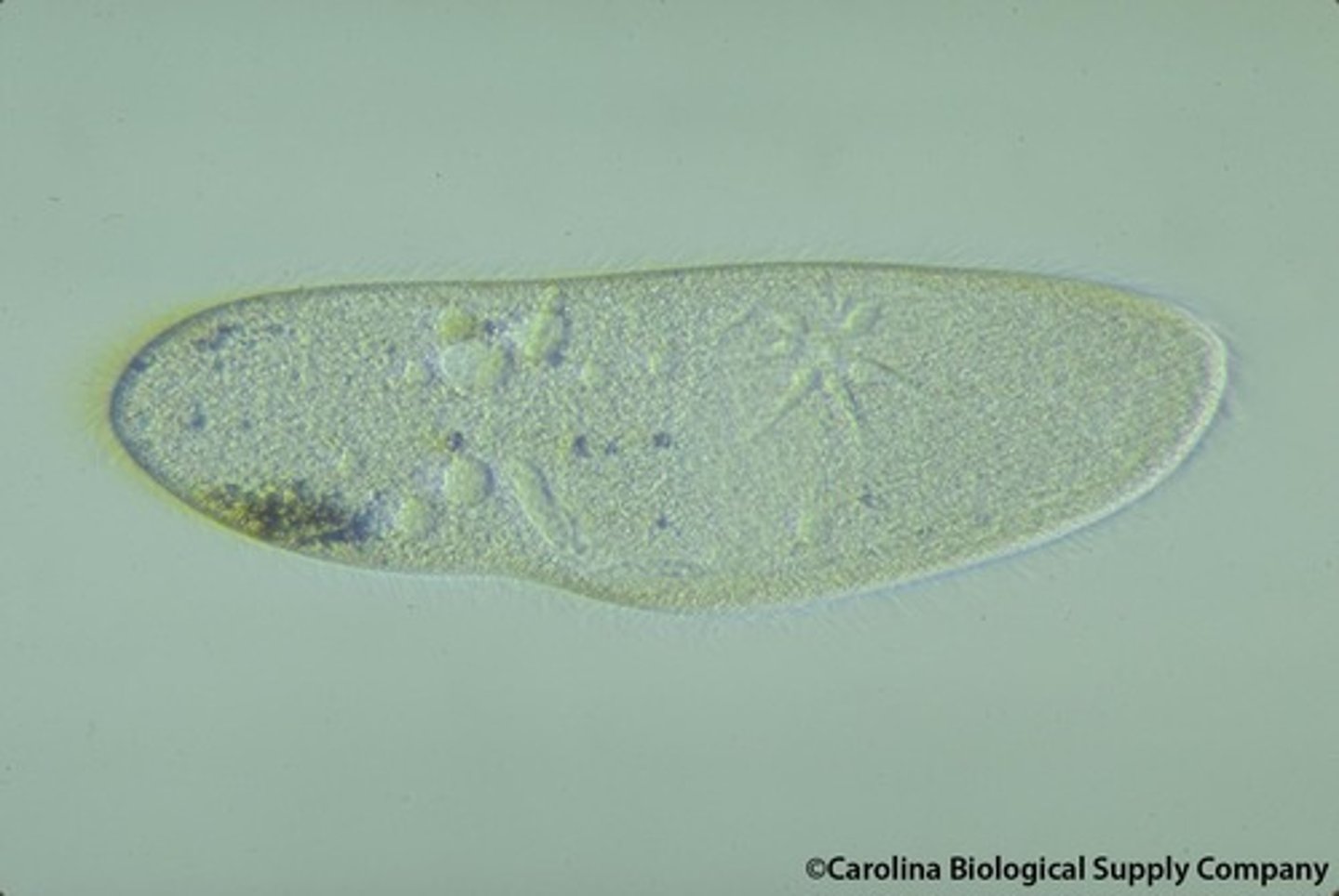
Paramecium (Alveolates)
Large, unicellular, heterotrophic, ciliated protist
Easy to see nuclear envelope and digestive vacuoles
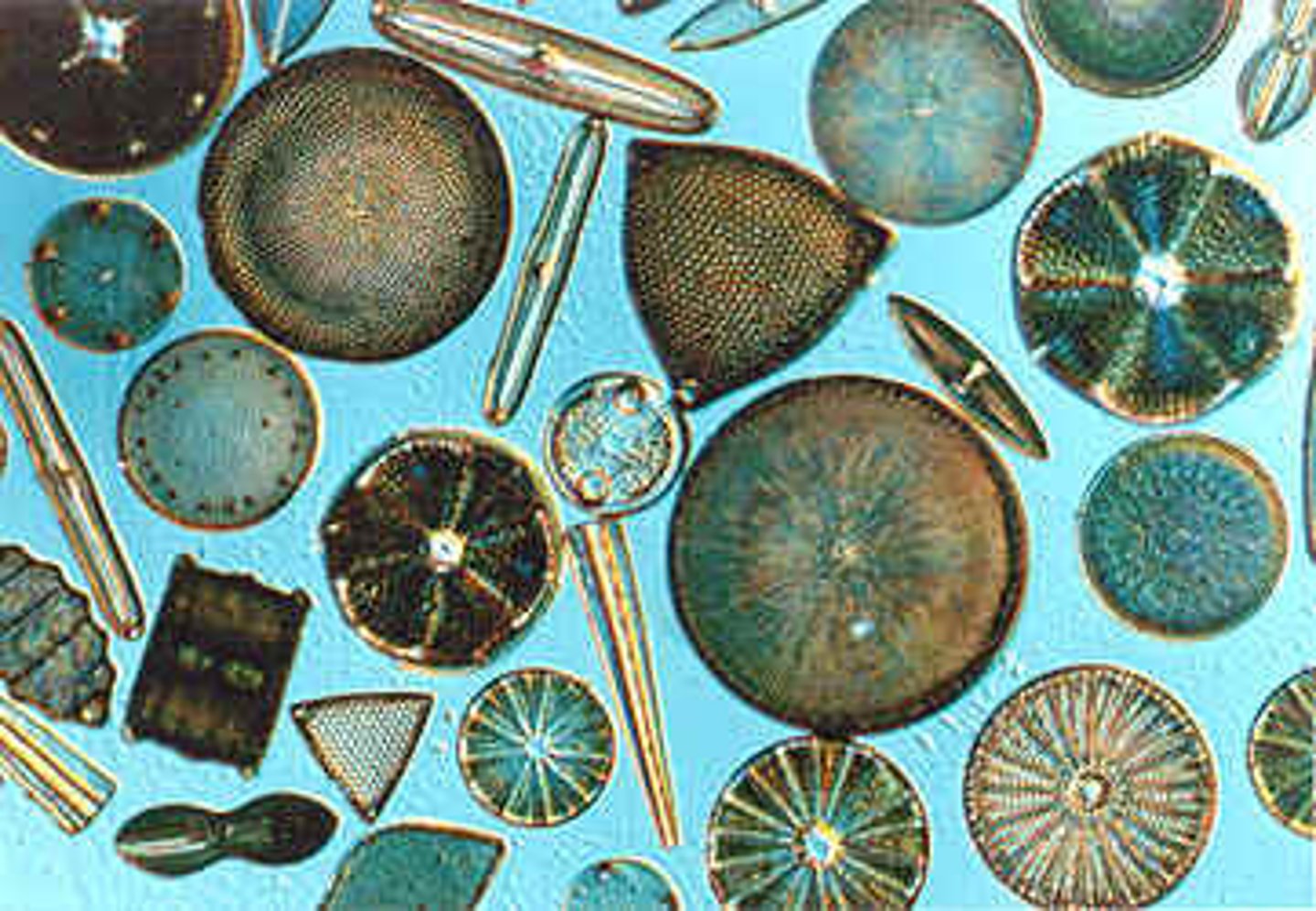
Biomineralized Protists: Diatoms ( Stramenopiles )
Fresh or saltwater photoautotrophs
Tests are made of silicon dioxide: SiO2 glass
Each daughter cell receives ½ of the test in mitosis
Diatomaceous earth Powdered diatom fossils
Can be taken by mouth for various nutritional uses
good as an insecticide, scrubbing agent, or toothpaste!
Foraminifera
Supergroup Rhizaria
Marine chemoheterotrophs
Create calcium carbonate (CaCO3) shells called tests
Tests have elaborate patterns that are species specific
Tests create deepsea limestone deposits
Pseudopods extend through the tests for feeding and movement
Multicellular Protists: ( Stramenopiles )
Not a fungus, but looks and behaves like one
Multicellular, saprobic or parasitic
Body is a mass of cellwide filaments called hyphae
Coenocytic: multiple nuclei in one plasma membrane
Similar to Physarum
Can reproduce sexually
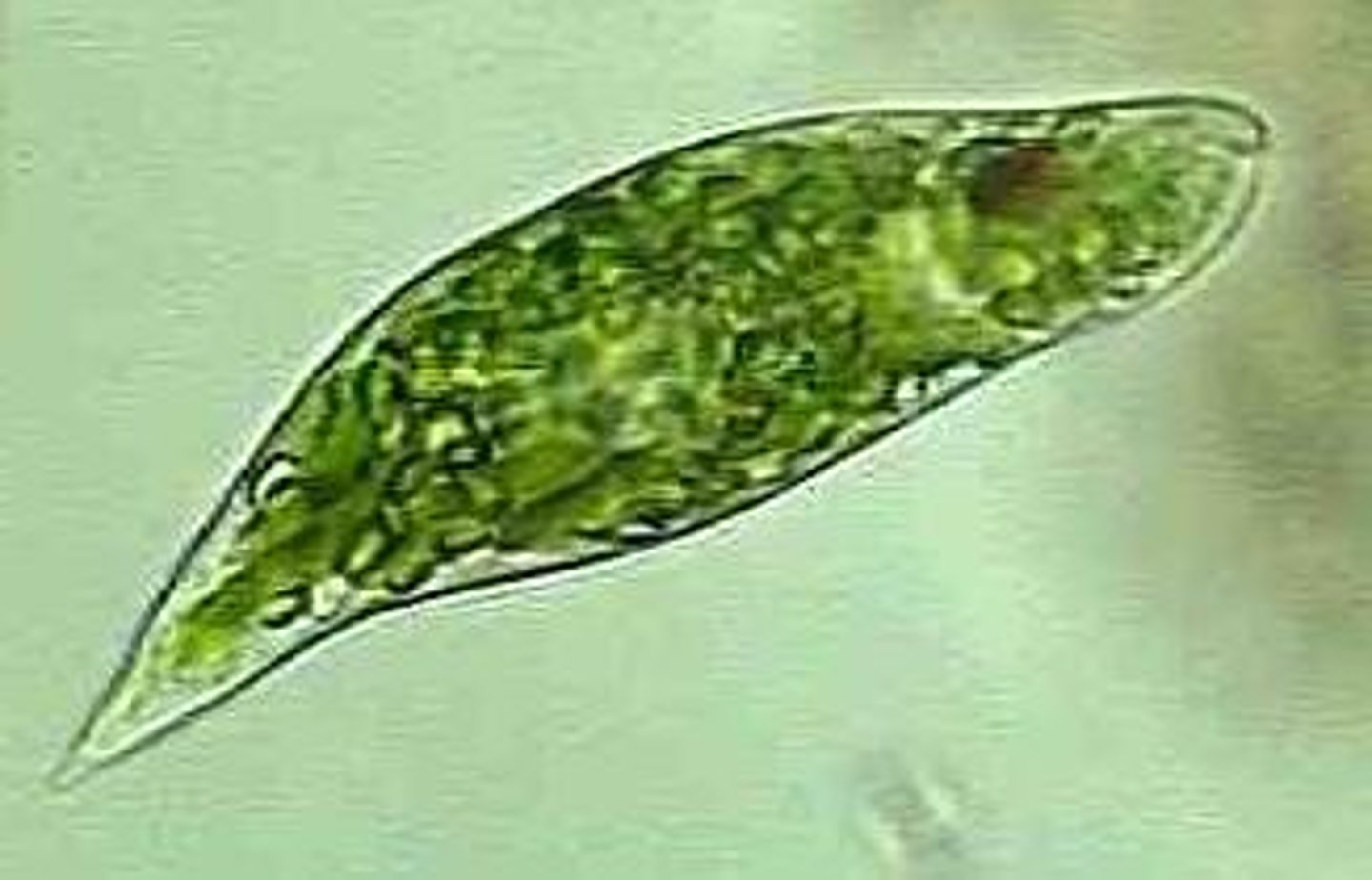
Unicellular Protists: euglenids
Unicellular and flagellated
Facultative heterotrophs
Can obtain energy heterotrophically or autotrophically
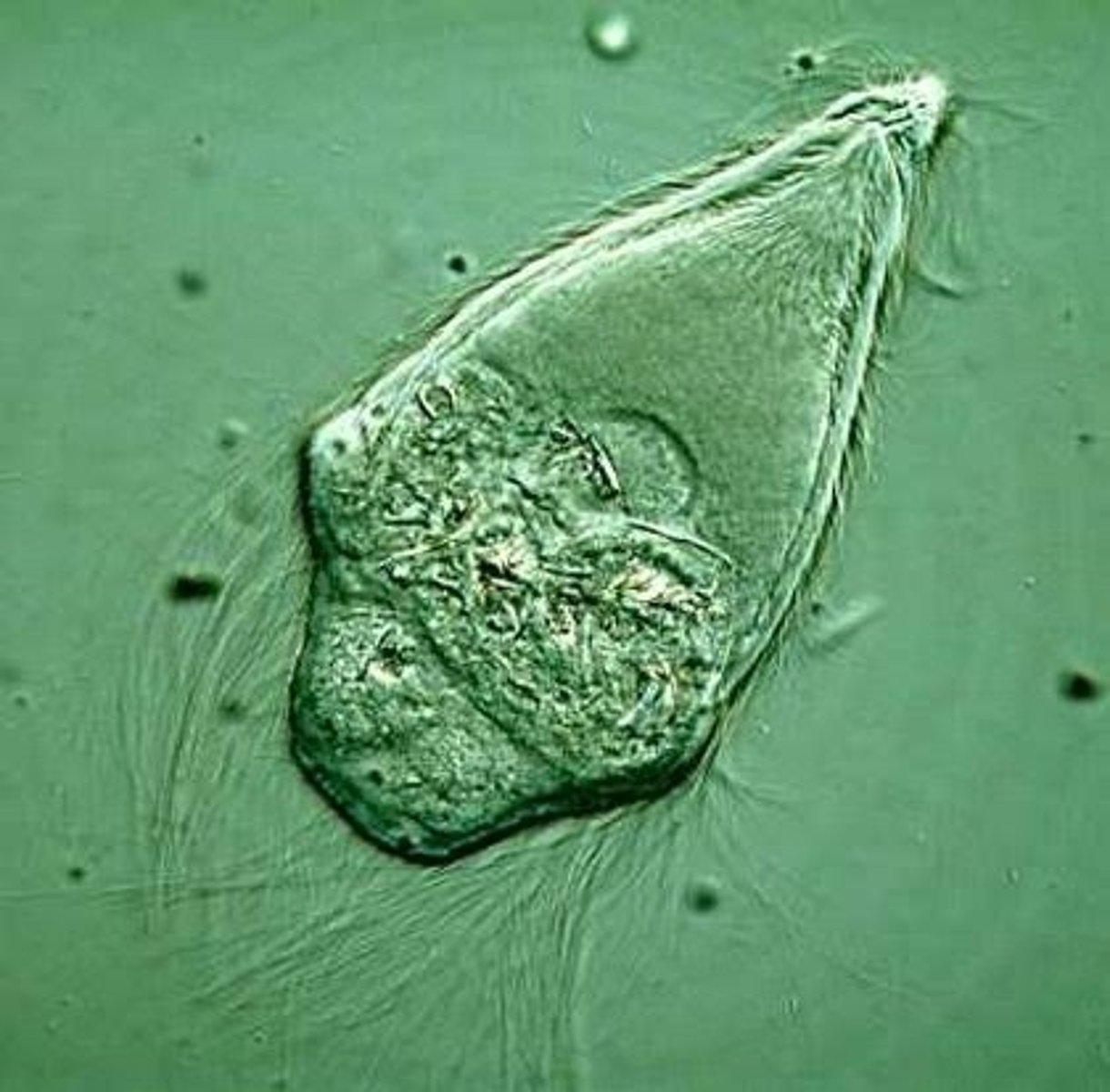
unicellular protsists: Trichonympha
Unicellular and parasitic
No mitochondria
Endosymbiont of termites
Helps termites digest wood pulp
Many family members cause human disease
Multicellular Protists: • Fucus ( Stramenopiles )
Capable of photosynthesis, but is not a plant Brown algae (kelp)
Restricted to marine environments
Reproduces sexually using gametic meiosis
Multicellular specialization
Fronds = "leaves"
Stipe = "stem"
Holdfast = "roots"
green algae
Evolutionarily grouped with land plants
taxonomically grouped with protists
Shared characteristics with land plants:
Chlorophylls a and b
Cellulosic cell walls
Storage of starch in chloroplasts
produce 50-70% of all oxygen in our atmosphere
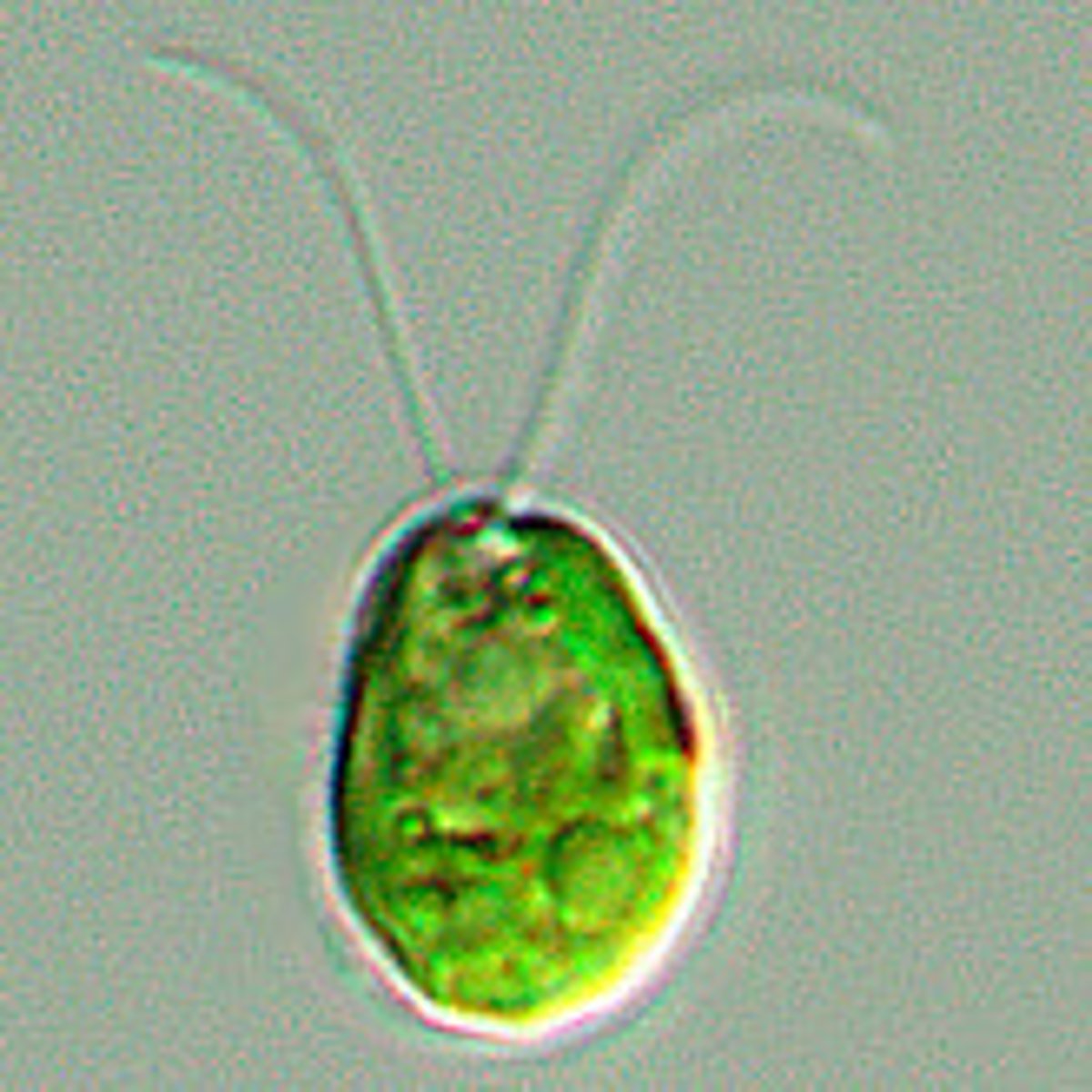
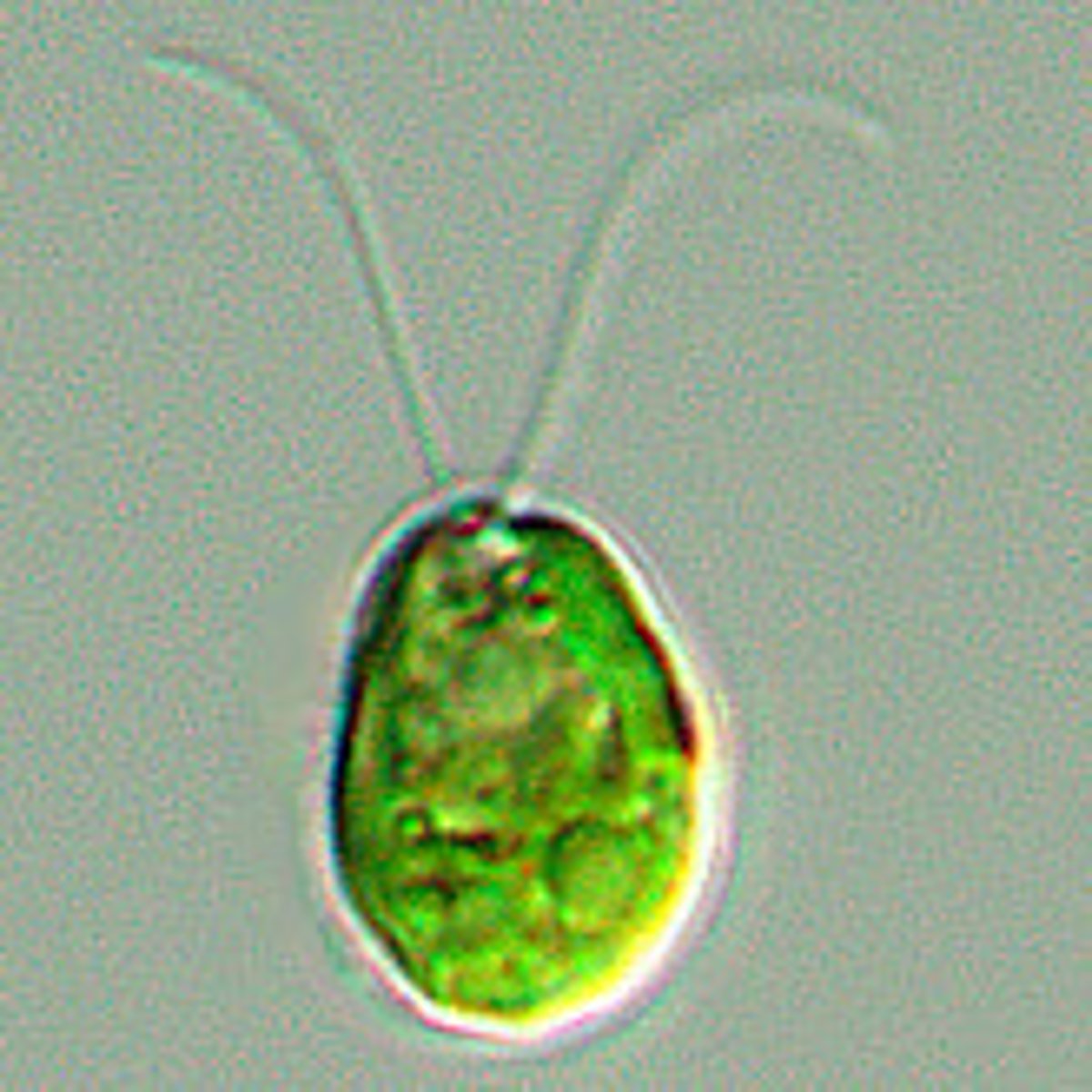
Chlamydomonas
Chlorophytes Motile, unicellular, freshwater genus of green algae
Have both asexual (mitosis) and sexual (gametic meiosis) forms of reproduction
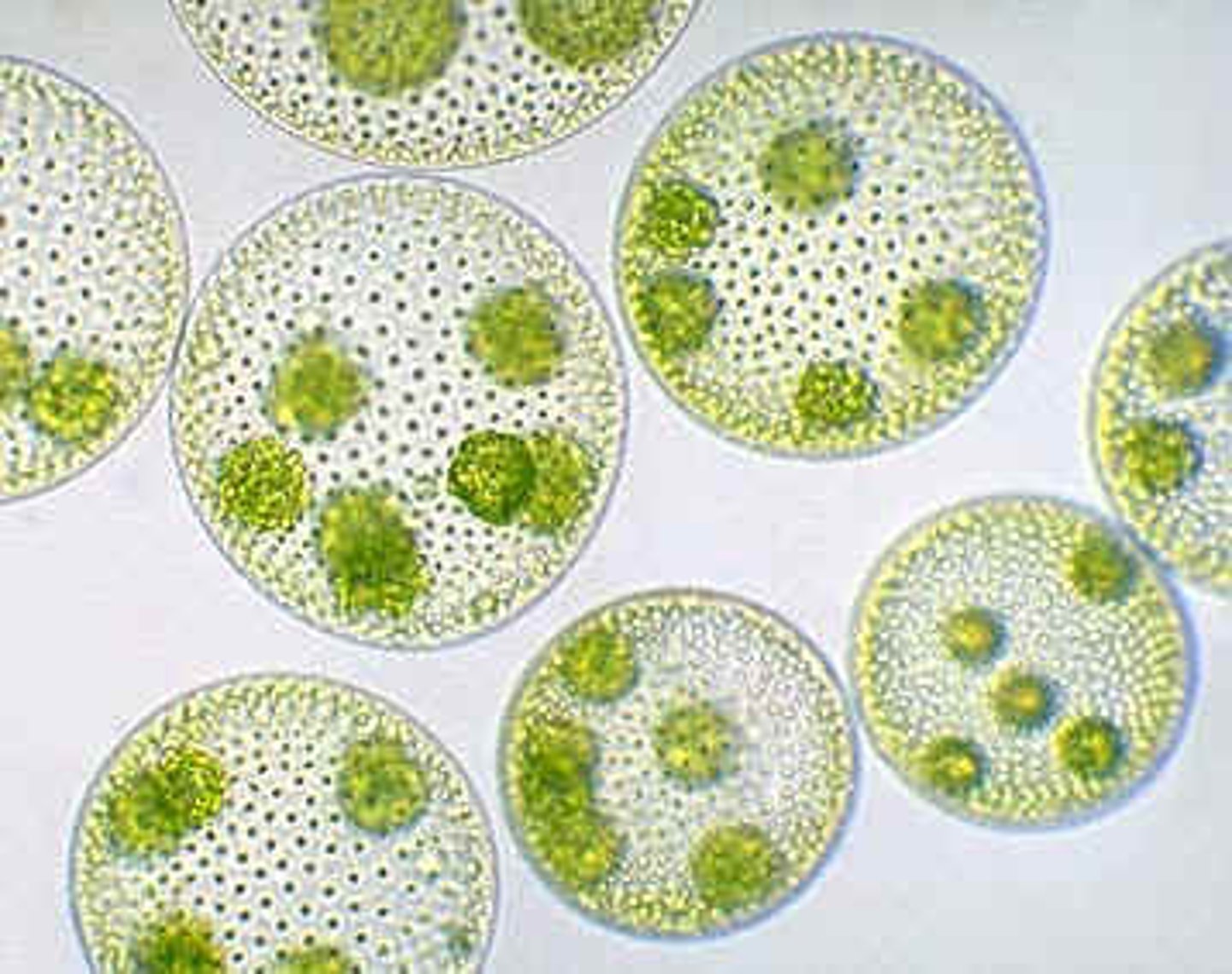
volvox
Motile colonial green algae (chlorophyte)
Hundreds to thousands of haploid cells in a gel matrix
Asexual (vegetative) reproduction
Daughter colonies form inside parent colonies
Sexual reproduction: Gametes form at end of growing season
Dormant zygotes undergo meiosis before germination
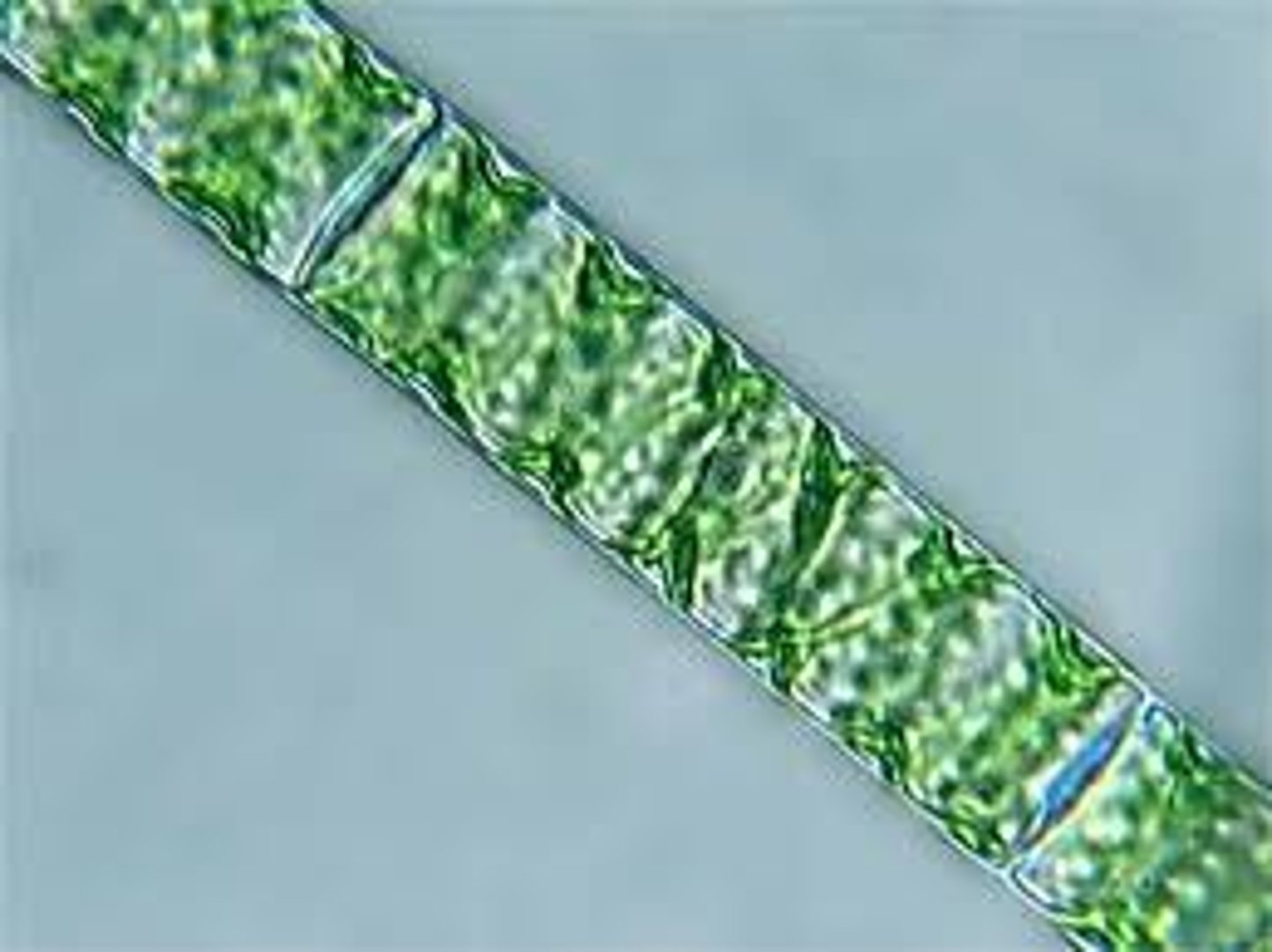
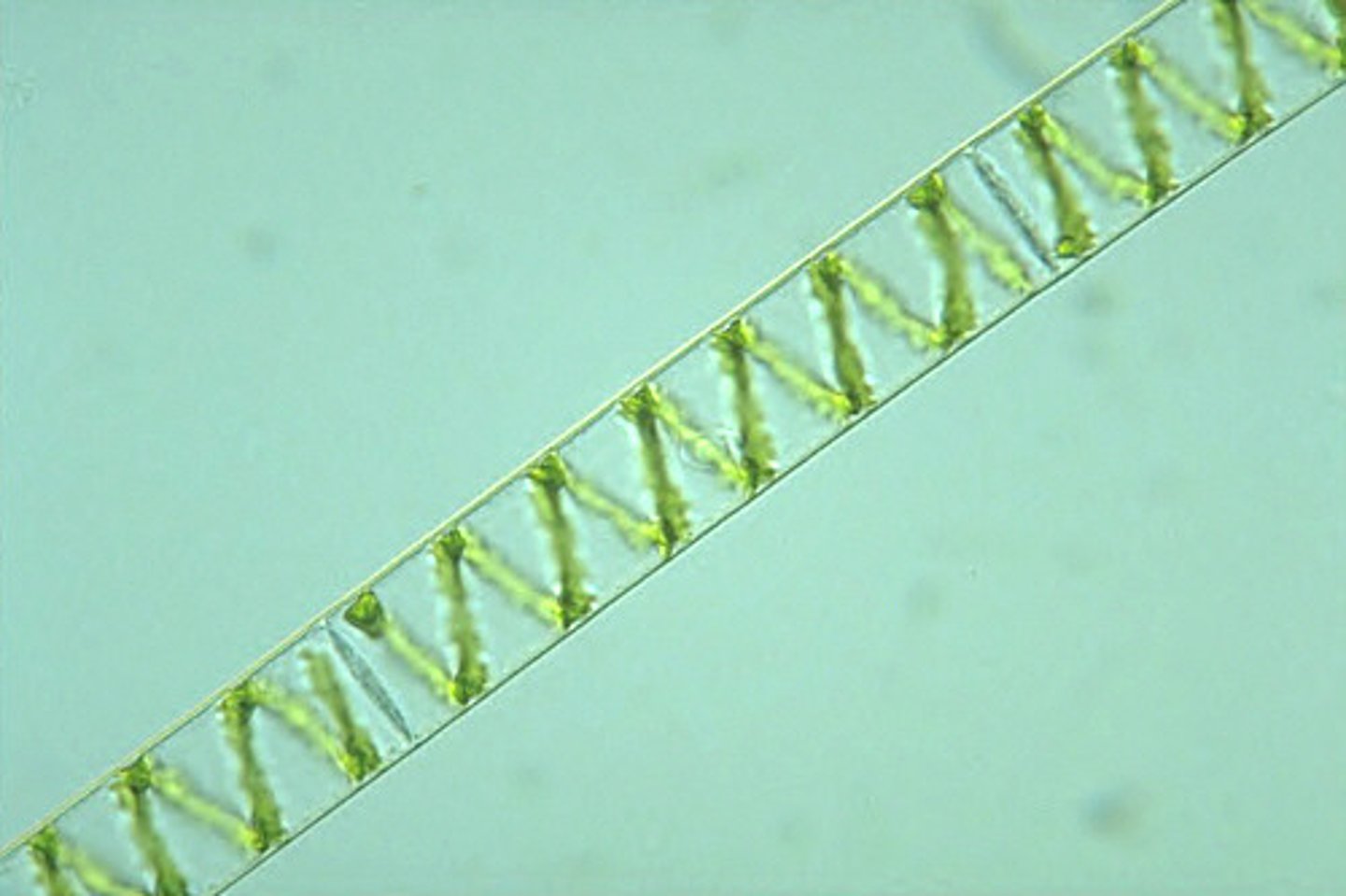
Spirogyra
Freshwater green algae (chlorophyte)
Asexual (vegetative) reproduction
Fragmentation of filaments
Sexual reproduction
Conjugation
chara
Charophyte considered the most closely related group of green algae to land plants (based on genetic data)
Freshwater green algae
Develop CaCO3 deposits on cell walls (biomineralized)
earning them the nickname "stoneworts"

non-vascular land plants
Structures to deal with water scarcity:Cuticle Stomata Spores,
Vascular tissue
Sexual reproduction
increasing efficiency from water
All land plants undergo sporic aka, alternation of generations
Land plants protect the embryo in maternal tissue
Photosynthetic efficiency increases in more complex plants
nonvascular simple plants
3 types: all of them release spores into the air
Liverwort ( Hepatophyta Hornwort )
Antherophyta
Mosses
liverworts: genus marchantia
Thallus flat mass of tissue
Dominant phase of the life cycle is the haploid gametophyte
Pores on the upper surface allow for gas exchange
Asexual reproduction,
Gemma cups Produces clones of the plant
Sexual reproduction
Antheridia (male) and archegonia (female) produce sperm and egg, respectively
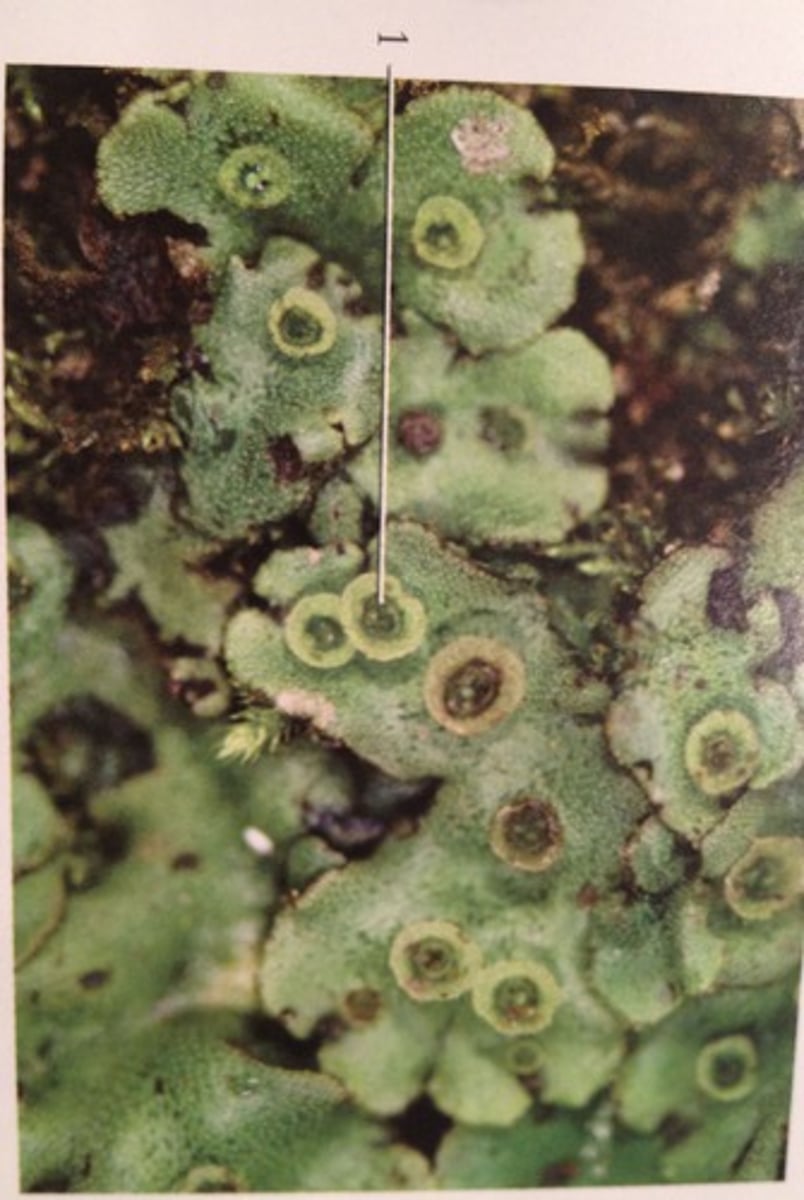
Liverworts: Antheridia and Archegonia
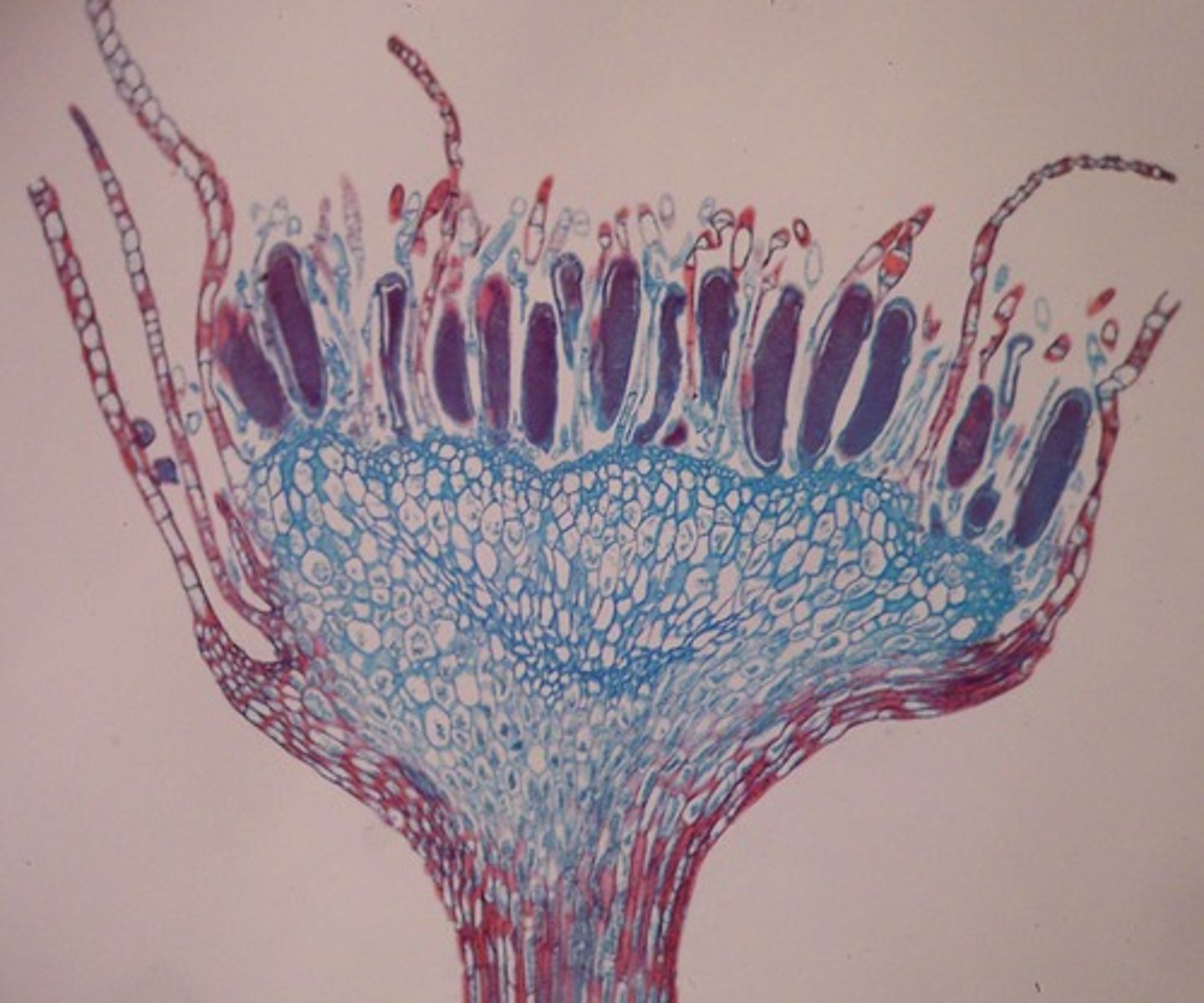
anthridia:
Produced in disks on stalks
Houses male gametes
Breaks open to allow sperm to swim away or disperse in raindrops.
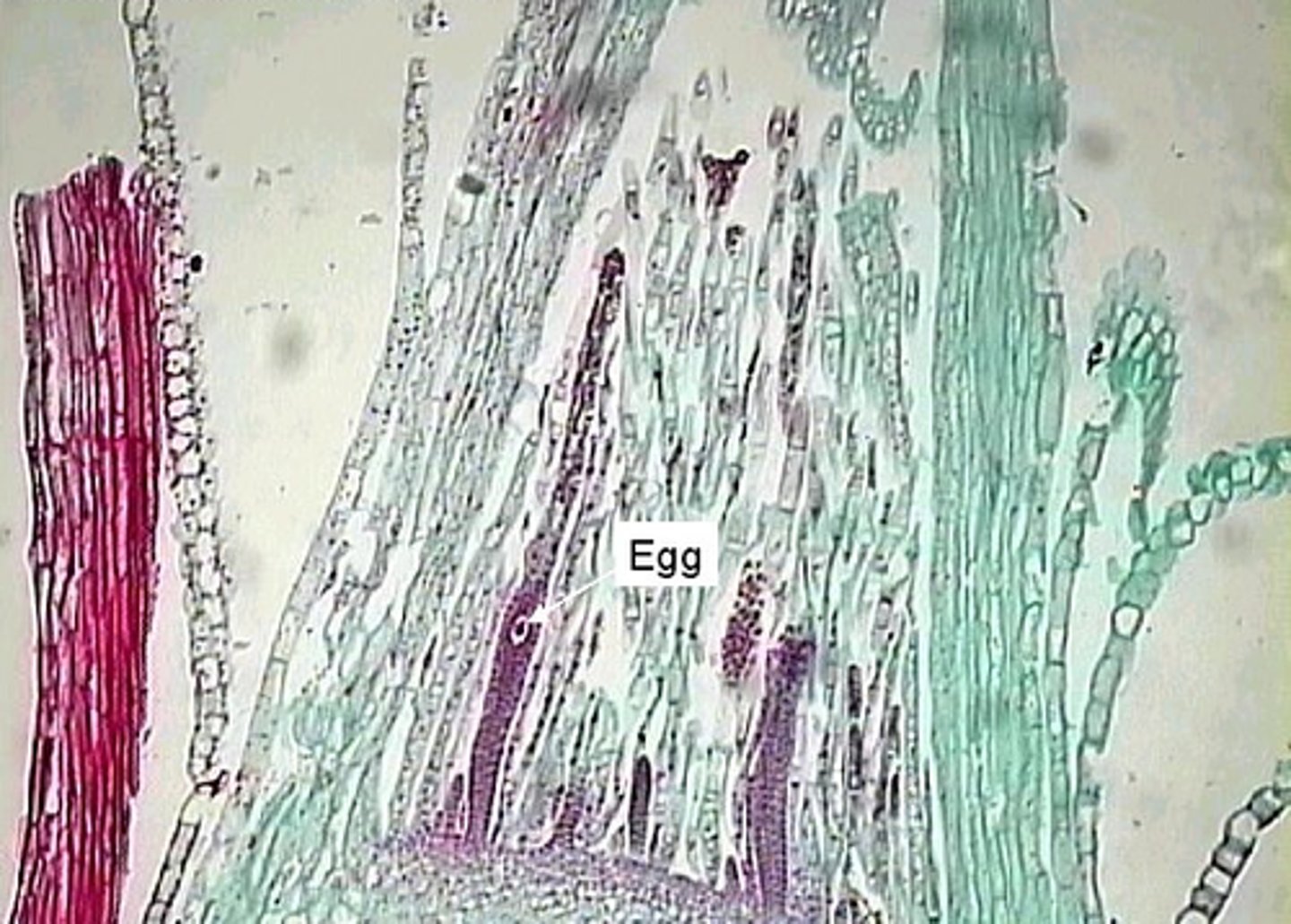
archegonia:
Produced on the under surface of stalked finger like structures
Produces a multicellular sporophyte when eggs are fertilized
Sporophyte is attached to and nutritionally dependent on the female gametophyte
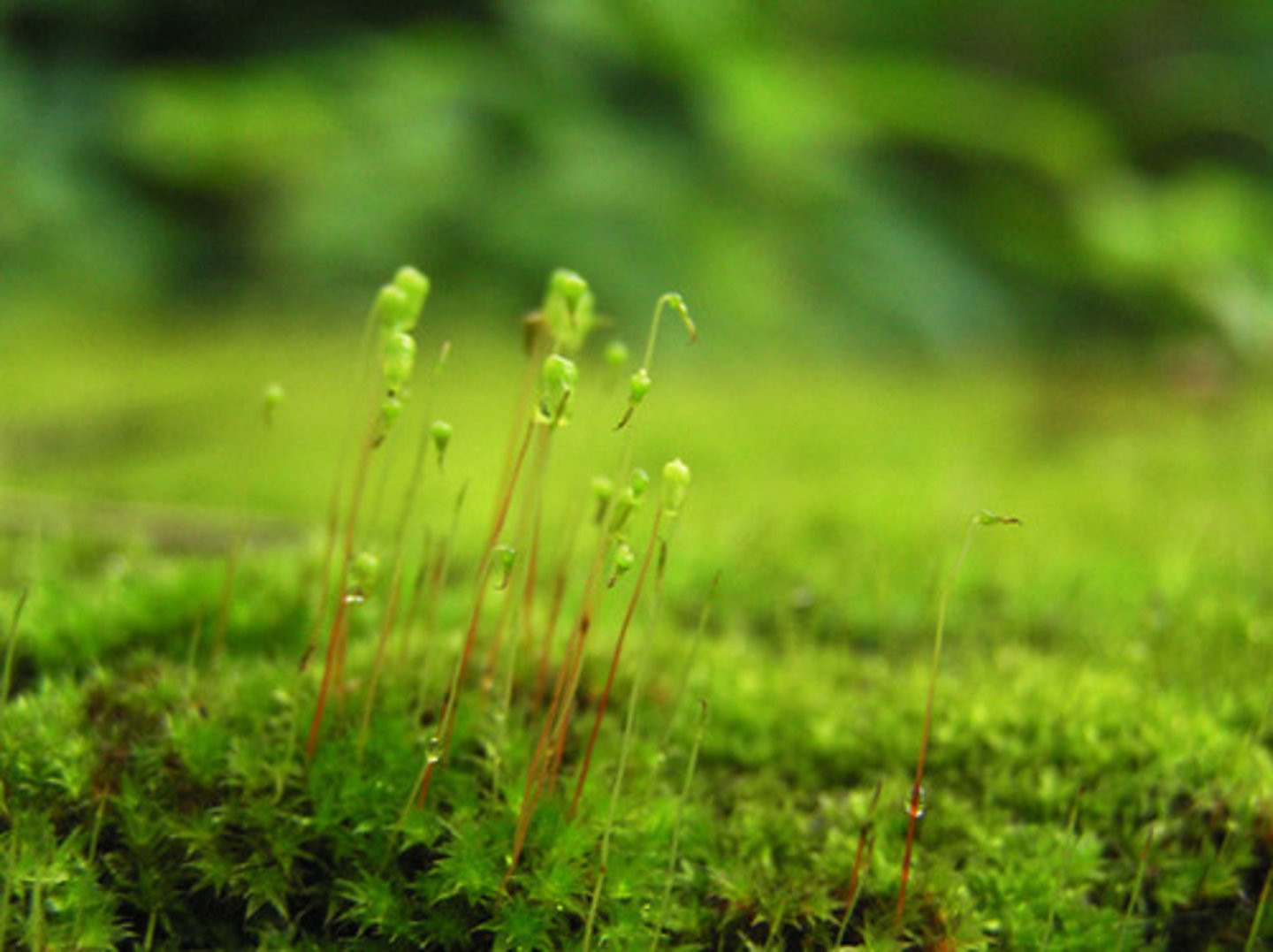
mosses
Leafy green non vascular plant
Dominant phase of the life cycle is the haploid gametophyte. •
Produces a nonphotosynthetic sporophyte, nutritionally dependent upon the gametophyte Sporophyte forms the sporangium
Specialized diploid organ where meiosis occurs, forming haploid spores

Ceratopteris richardii
Reaches sexual maturity in 2 weeks
It secretes a pheromonelike substance ( antheridogen ) which controls the differentiation of male or hermaphroditic sexual forms
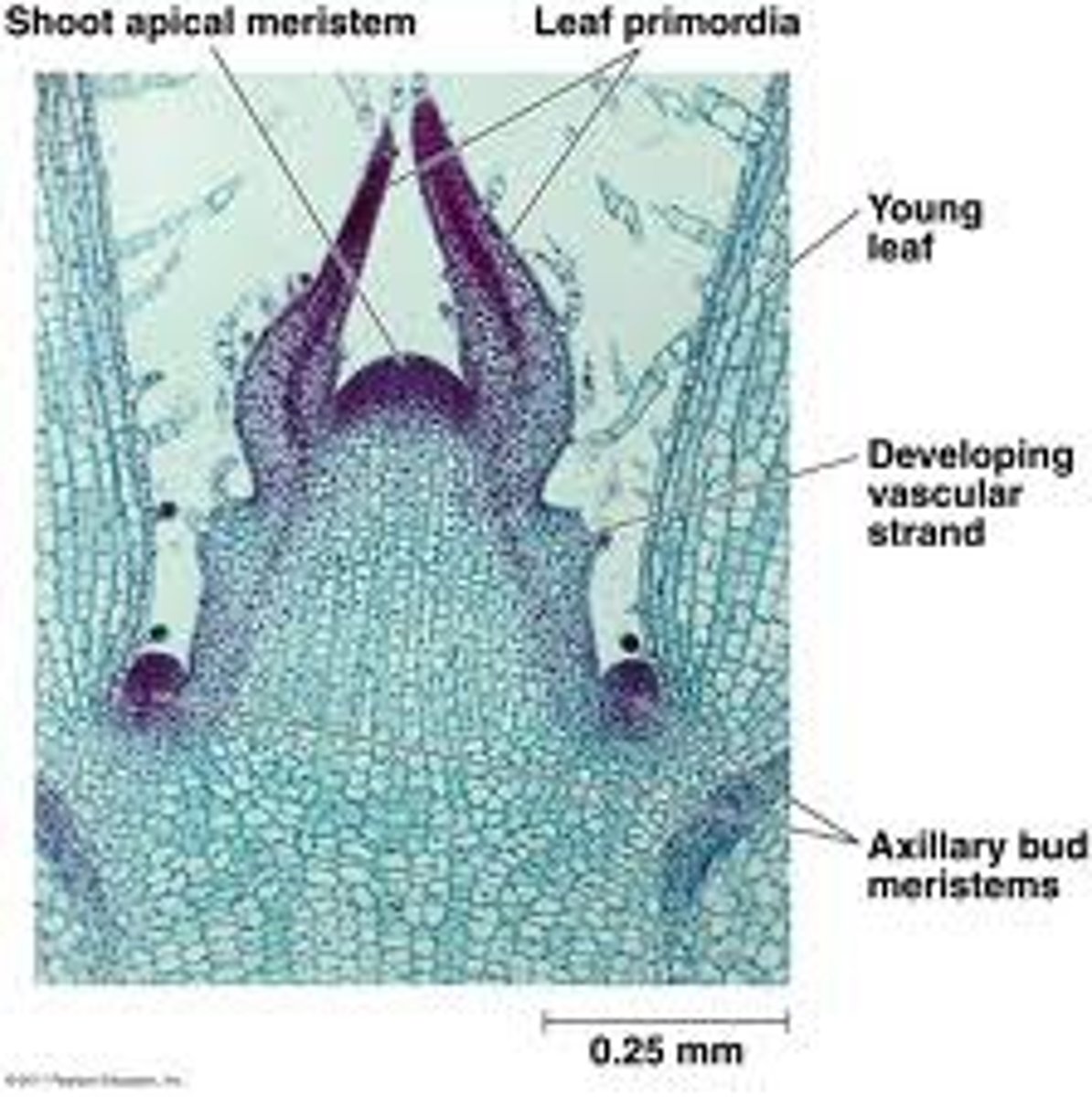
seedless vascular plants primary growth
• Primary growth = branching apical growth; responsible for vertical growth
• Growth through cell division in mitotic zones called apical meristems located in apices (stem/root tips) of the plant
Axillary bud = meristematic tissue laid down by shoot apical meristem at the node between the stem and (eventual) leaf
Primary growth gives rise to primary tissues are composed of 3 functional groups:
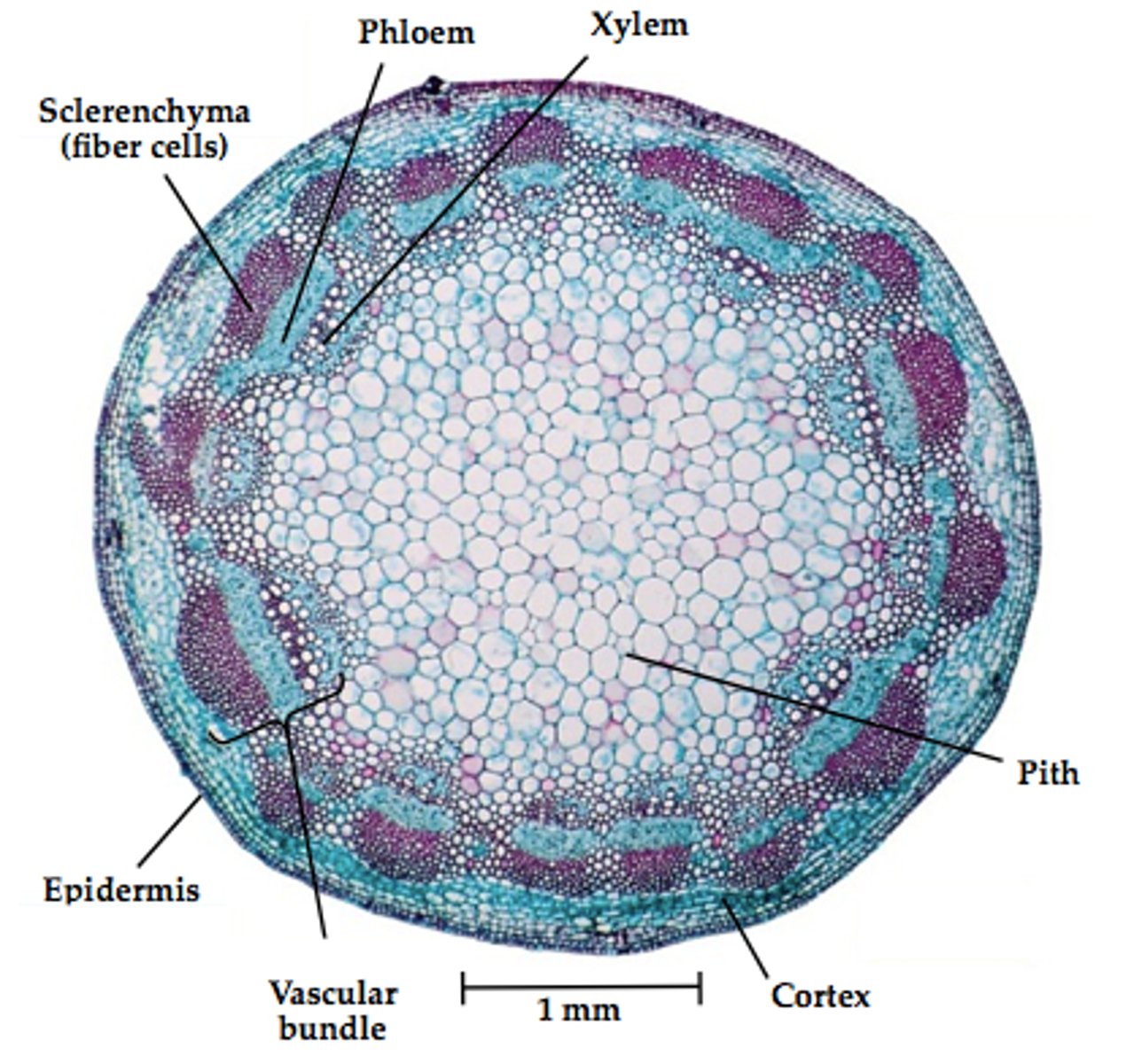
Dermal tissues (epidermis)
Vascular tissues (xylem and phloem)stem, roots, and leaves
Ground tissues (fill spaces between dermal & vascular -- pith, cortex, mesophyll, parenchyma, sclerenchyma...)
secondary growth and vascular tissues
increases lateral girth in stems and roots; growth comes from the vascular cambium • • meristem
Appears between primary xylem and phloem
Generates new vascular tissue • • xylem (wood) grows toward the interior of the stem, phloem grows toward the exterior of the stem
xylem
carries water and dissolved ions upwards to stem & leaves
Relies on specialized waterconducting cells, collectively called tracheary elements:
Vessel elements in angiosperms=Tracheids
gymnosperms Cells are dead at maturity & heavily reinforced with lignin, providing structural support
Phloem
carries sugars from leaves downwards to other parts of the plant
2 specialized cell types:
Sieve elements
Companion cells
lycophyte leaves
Microphylls
not anatomically true leaves, though functionally similar derives from protosteleno leaf gap; single vein
Homosporous strobili
Composed of many, densely packed leaves (sporophylls) with attached sporangia
Sporangia contain spores of IDENTICAL size
Shed spores will produce BISEXUAL gametophytes
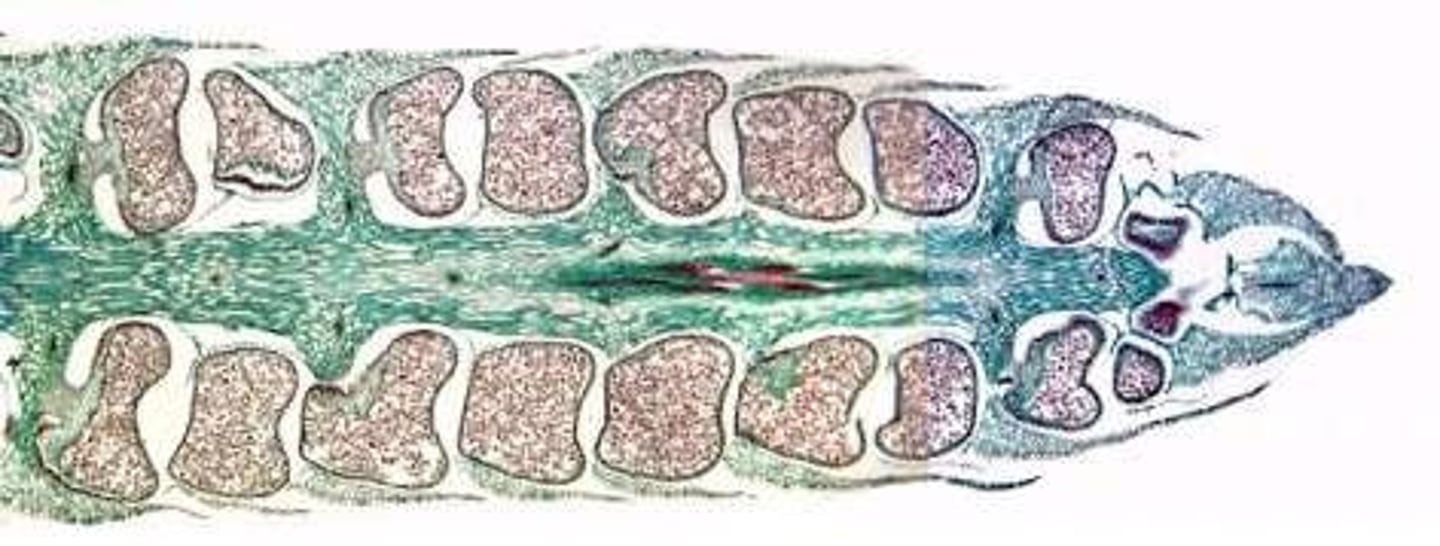
Heterosporous strobili
MEGASPORANGIA
Produce larger spores (megaspores) that germinate into FEMALE gametophytes
MICROSPORANGIA
Produce smaller spores (microspores) that germinate into MALE gametophytes
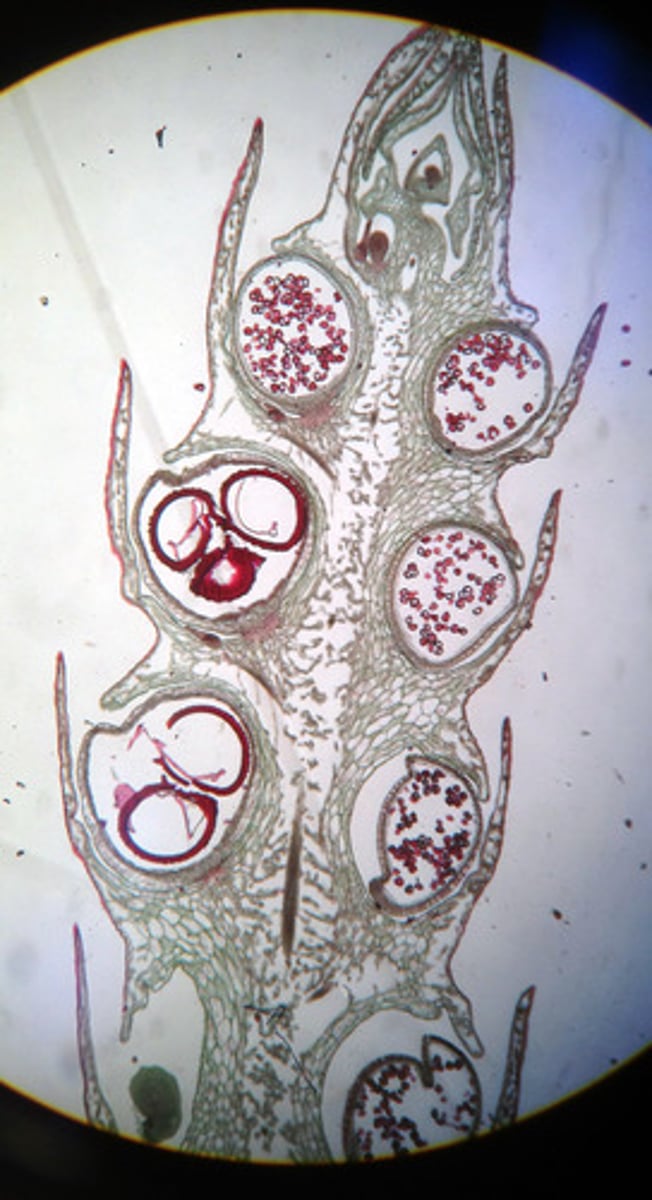
Leptosporangiate Ferns
Highly vascularized true leaves (megaphylls) -possess leaf gap •Vascular tissue is arranged in a siphonostele •Possess rhizomes and roots
Fern Leaves
Develop from coiled buds (fiddleheads)
May be divided or undivided into one to several levels of pinnae (leaflets)
Sporangia are borne on undersurface of fronds or on highly modified, non photosynthetic fronds
Clusters of sporangia = sori (singular sorus)
Indusium (thin protective sheet)
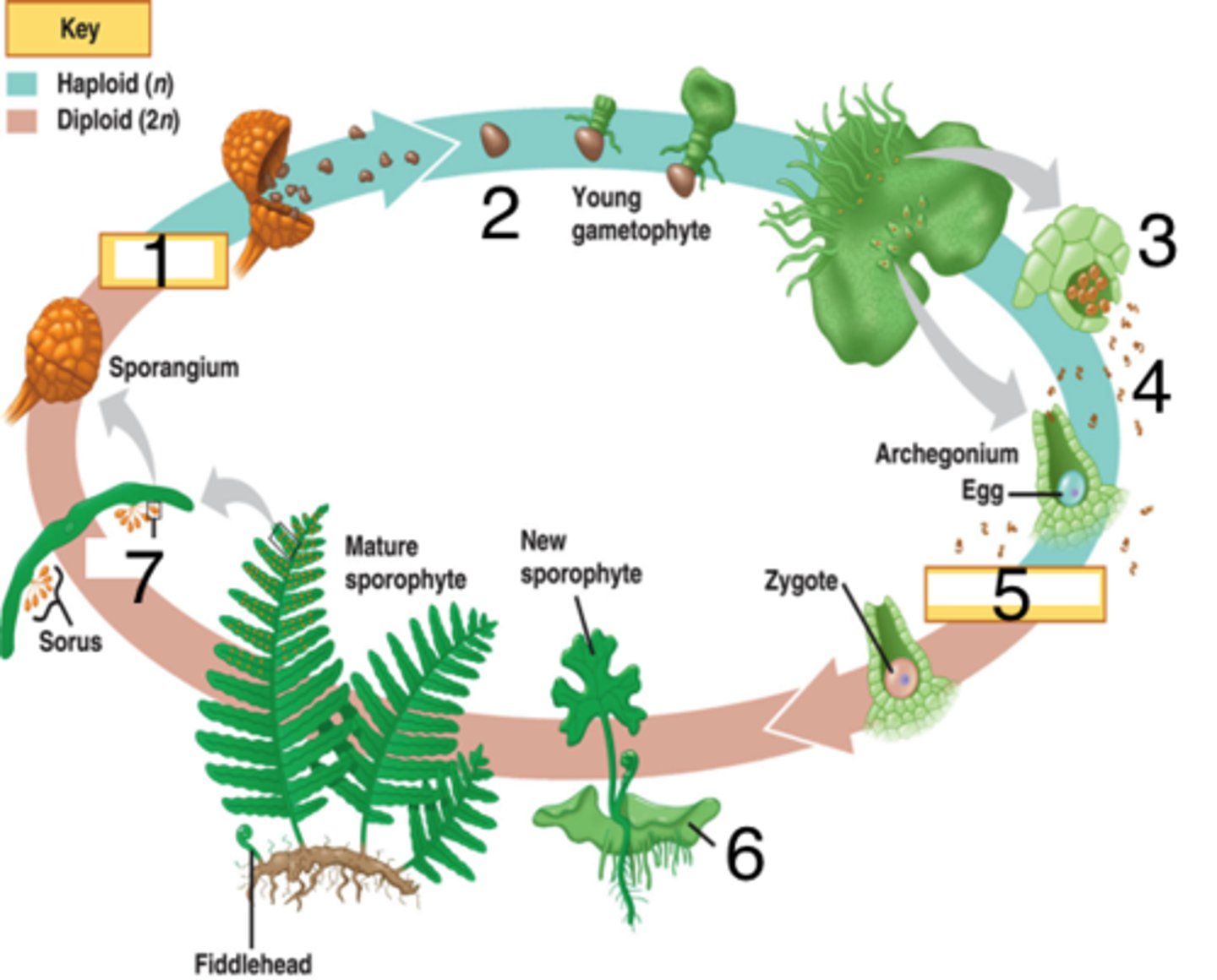
fern life cycle
1). Zygote develops into leafy fern plant.
2) the sporophyte. 3
) Spores are released from spore cases and grow into tiny, heart-shaped gametophytes. Each gametophyte has both male and female structures.
4) Sperm swim to another gametophyte to fertilize eggs.
true leaves
Leaf gap
Complex vasculature
Axillary bud (lateral shoot bud)
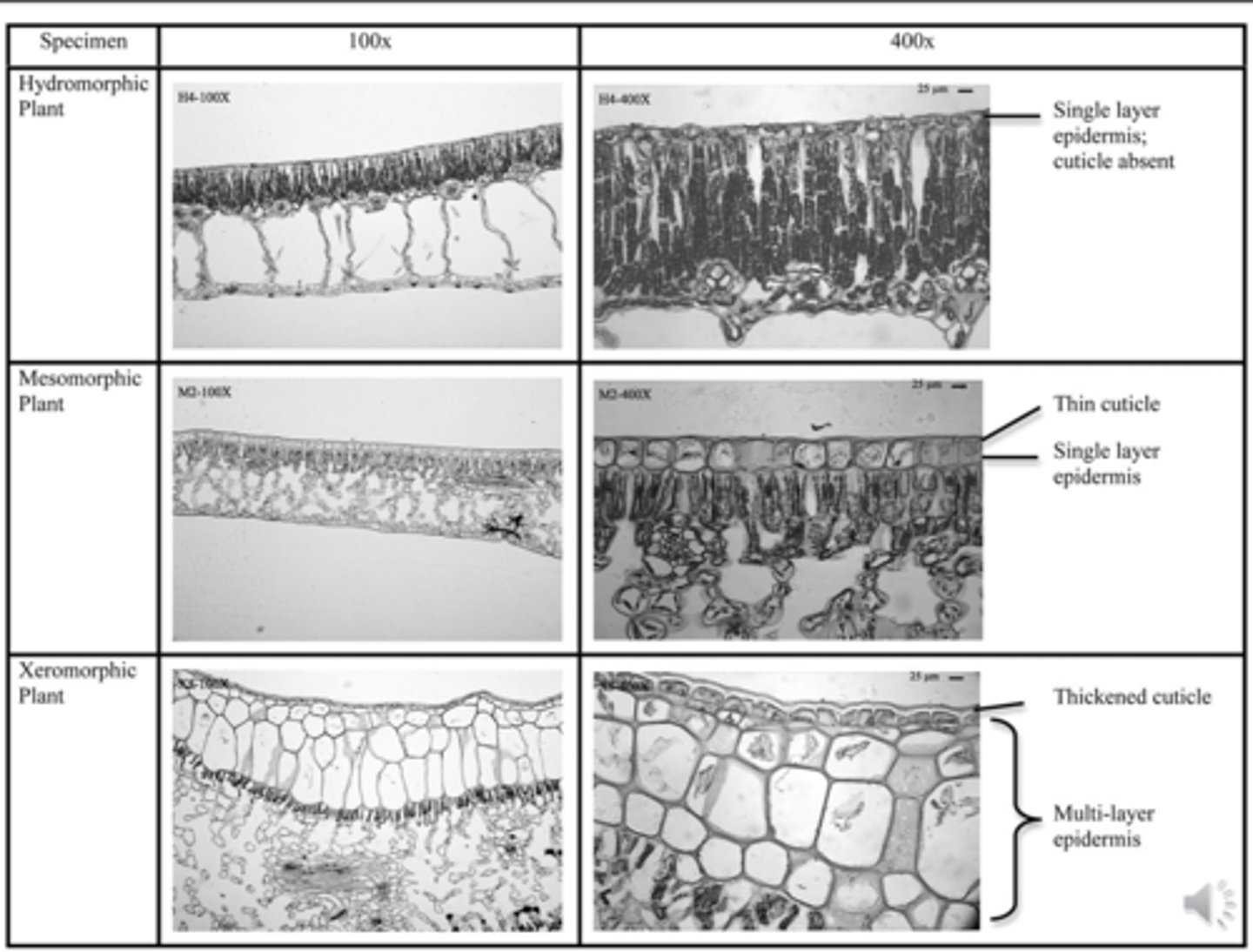
Xeromorphic Leaves
Dry environments Designed to prevent water loss
Thick cuticle
Tight palisade
Stomatal crypt
Increases humidity Examples: Nerium (oleander) and Pinus (pine)
Hydromorphic Leaves
Aquatic environment
Leaves either in the water or on the surface of the water
Stomata on upper surface Inside of leaf is filled with water
Little structural support
May contain sclereids walls
Example: Nymphaeabundles of cells with thick, tough (water lily)
Mesomorphic Leaves
Intermediate environment
Standard architecture
Easy to distinguish top from bottom
Palisade is on top
Most stomata on underside of leaf
Example: Syringa (lilac)
seed-bearing plants
Angiosperms and gymnosperms
Together form a major group of plants called spermatophytes
All heterosporous, meaning they possess: Small male microstrobili, Large female megastrobili
Spores are retained in sporophyte (2n) parent rather than being cast off to the environment
Spores grow into tiny multicellular gametophytes (n)
Parent provides protection and nutrition for fertilized zygote to become new sporophyte (2n)
gymnosperms
Fruitless seed plants
Female gametophytes develop on exterior of sporophyte plant body
No ovary; seeds are unprotected
angiosperm
Flowering plants (>90% of all plants on earth; ~300,000 species)
Major groups: monocots and dicots
Characteristics:
Flower (key)
Fruit (mature ovary)
Double fertilization resulting in 3n endosperm (stores nutrients) and 2n zygote
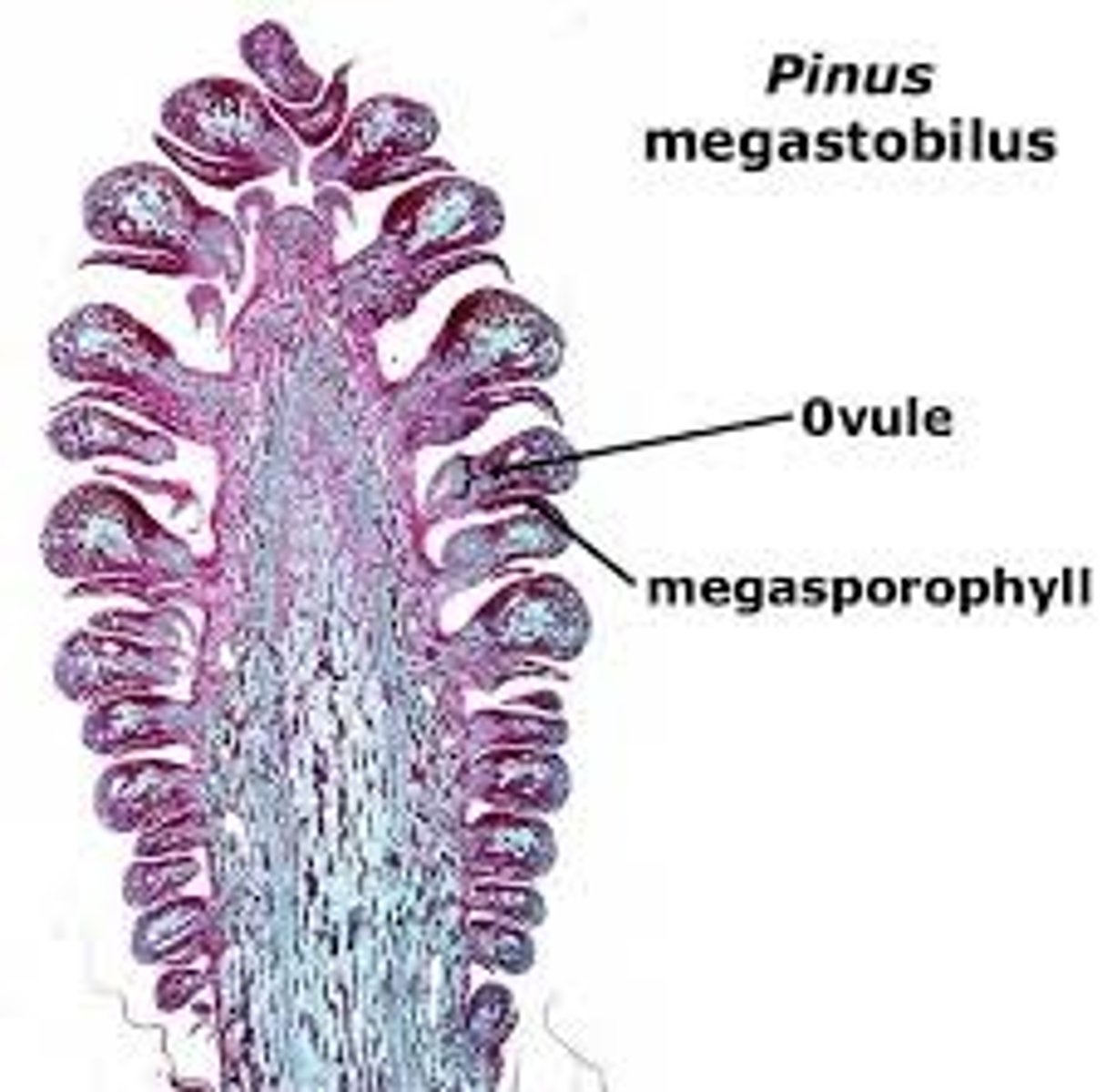
female pinecone
Each ovuliferous scale contains 2 ovules (megasporangia and integuments)
Within the 2n megasporangium is a single meiosis to produce haploid megaspores megasporocyte , which divides by Rest of the cells make up nucellus (2n tissue) of the megasporangium Only one megaspore survives and develops into the megagametophyte (through mitosis)
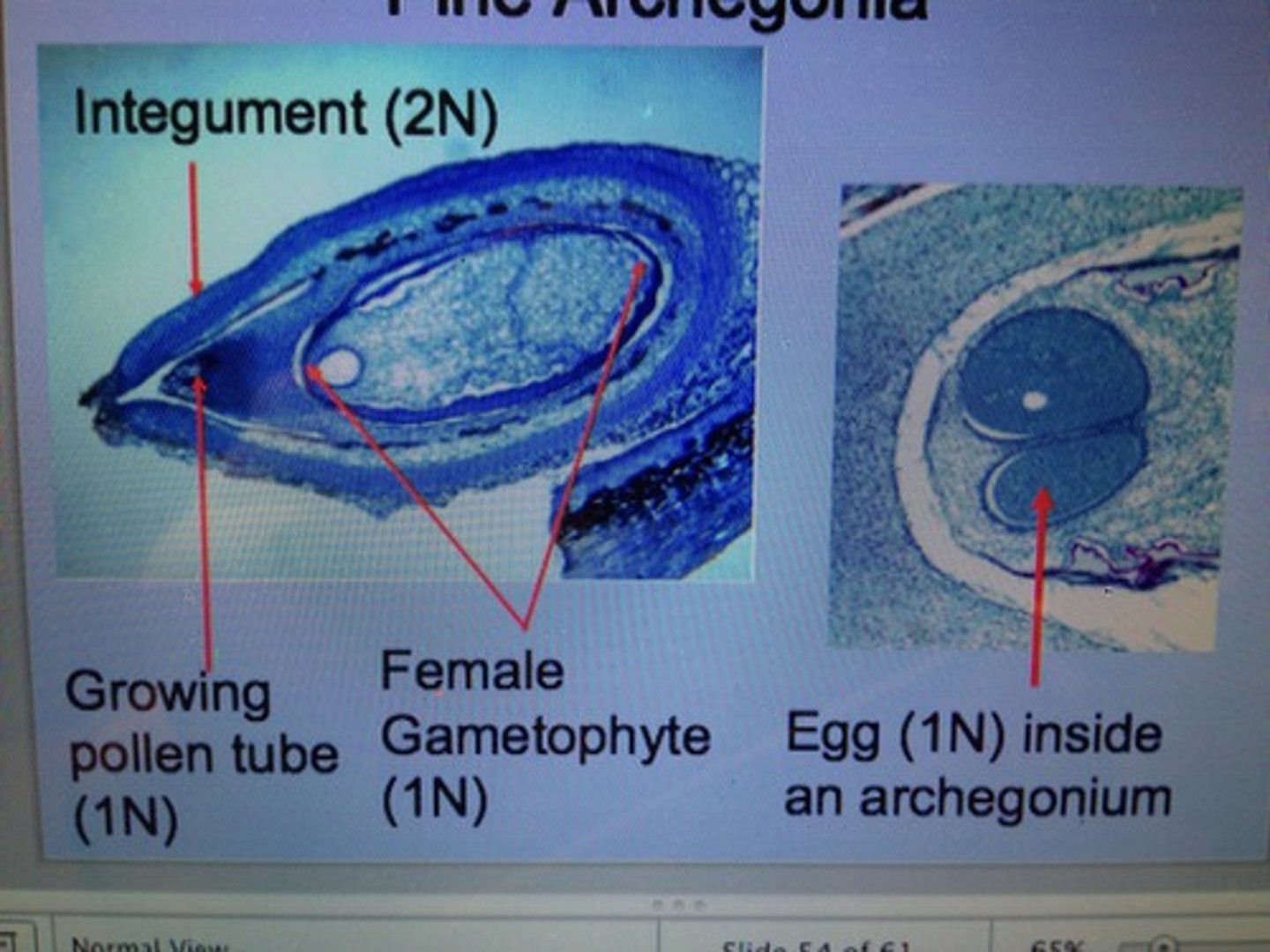
Pine Archegonia
Two or more (each with an egg) develop within the maturing gametophyte.
Mature ovule consists of: Integument Thin layer of remaining nucellus
Megagametophyte, containing archegonia with enclosed egg
Micropyle = a pore at the end of the ovule
Space between the micropyle and nucellus is the pollination (micropylar) chamber, through which pollen tubes will grow
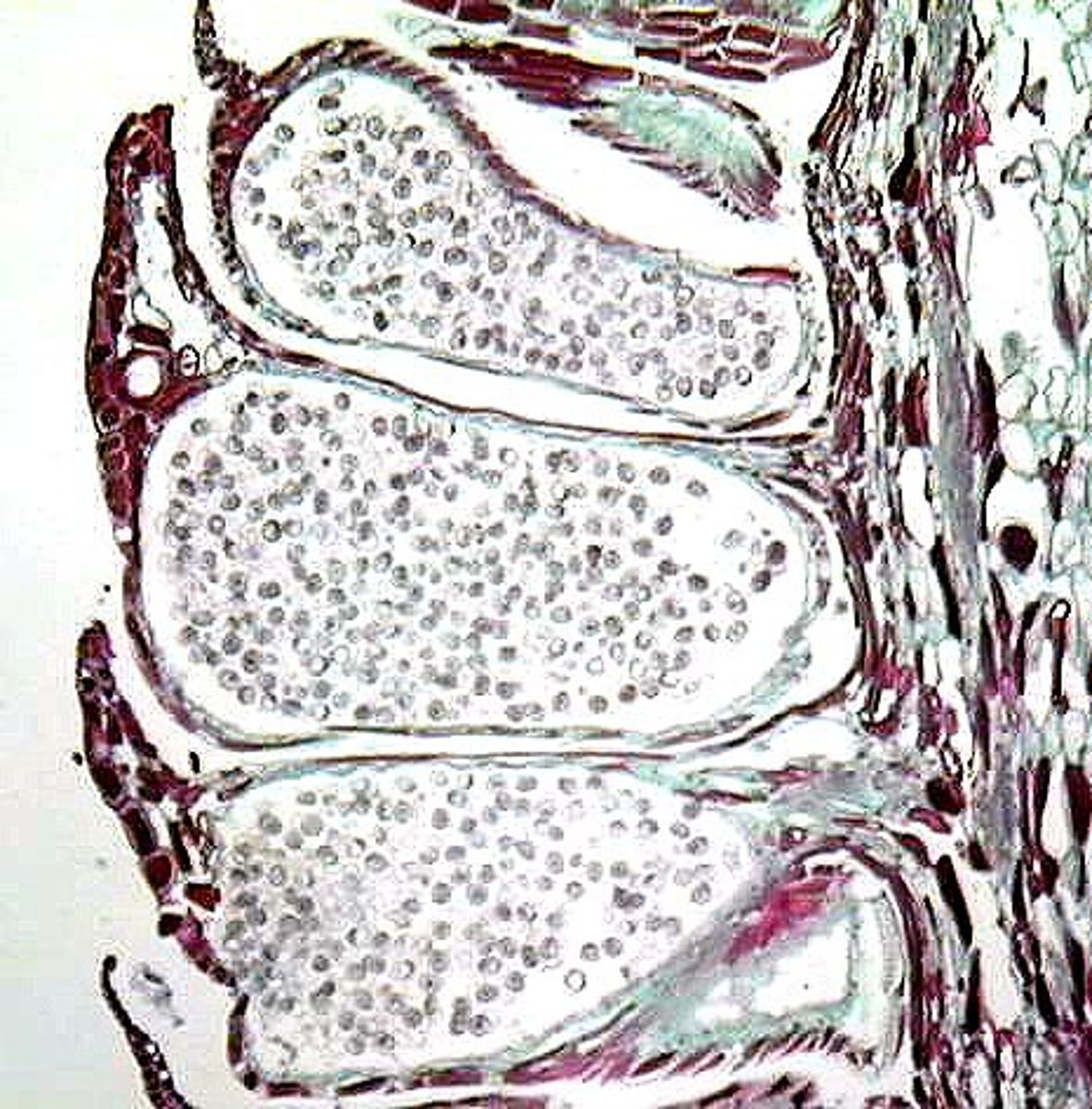
male pinecone
Two (or more) microsporangia develop on underside of microsporophylls
Microsporocytes within microsporangia undergo meiosis to make microspores
Through mitosis, microspores develop into immature male gametophytes called pollen grains
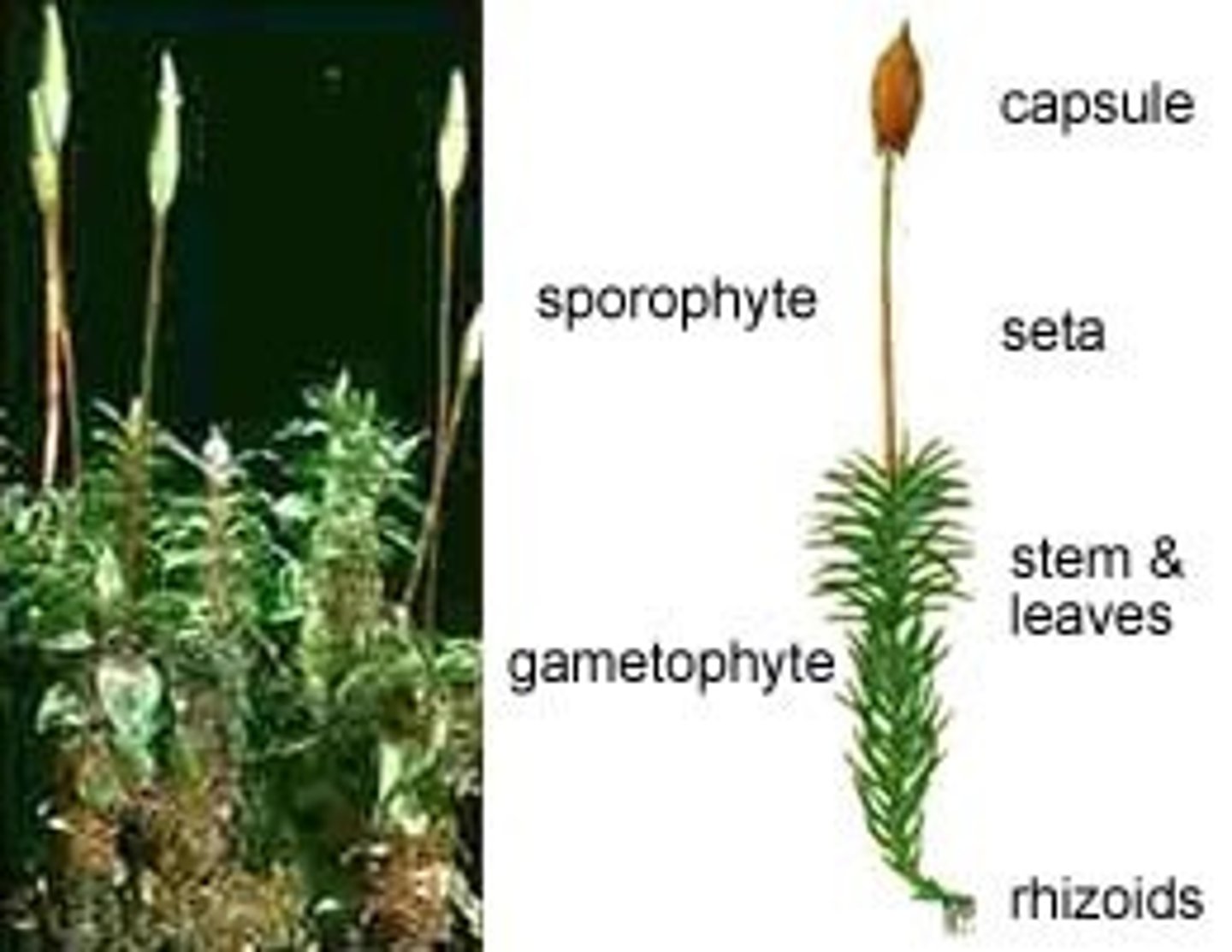
moss life cycle
A sporophyte has a specialized capsule that holds the spores which grow into separate male and female gametophytes.
Antheridia produce sperm on the male gametophytes and the archegonia produce eggs on the female gametophyte.
Antheridium fertilizes the egg of the archegonia which grows into a new sporophyte.
obligate anaerobes
organisms that cannot live where molecular oxygen is present
Anabaena azollae
what organism turns the water red
halobacterium salinarum
methods we used to classify species of bacteria
process of generating a phylogenetic tree from genetic data.
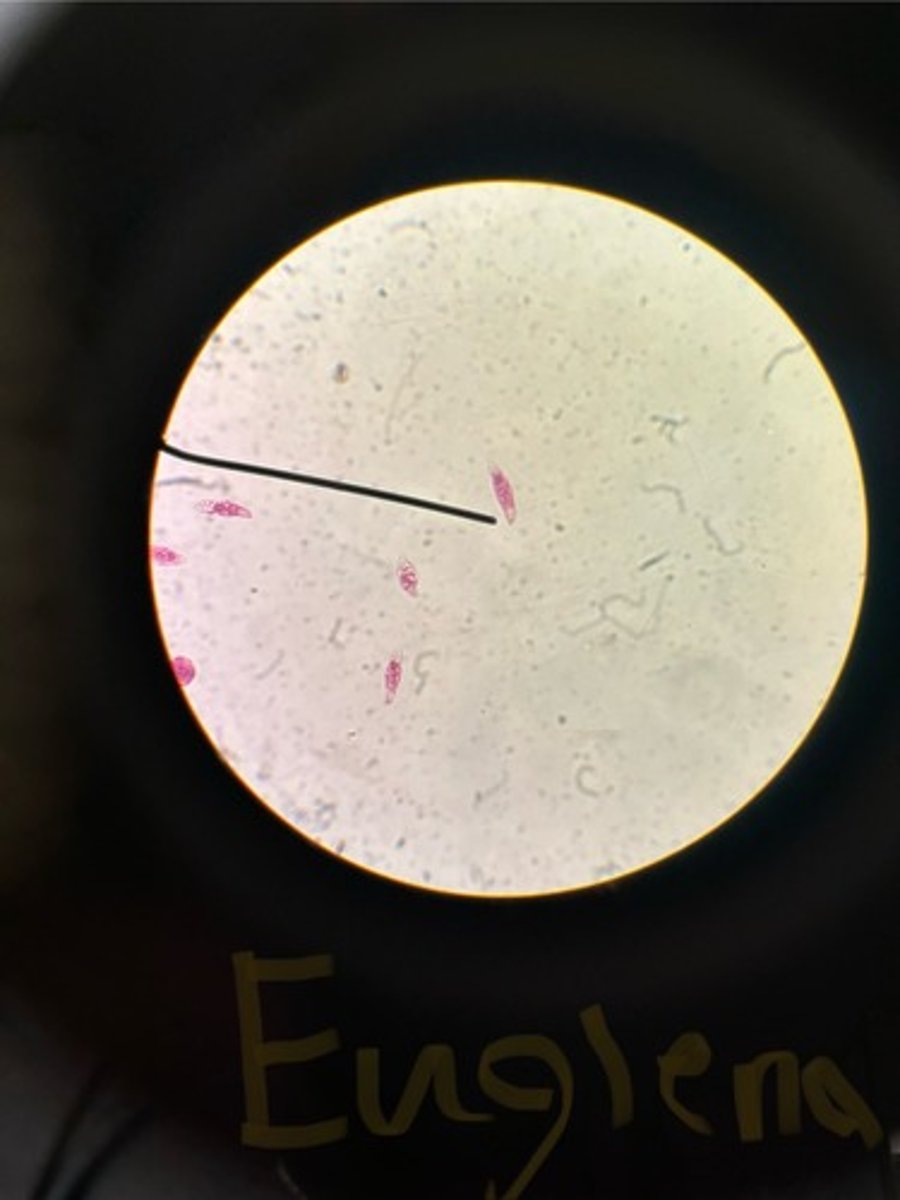
Euglena (stained)
Saprolegnia
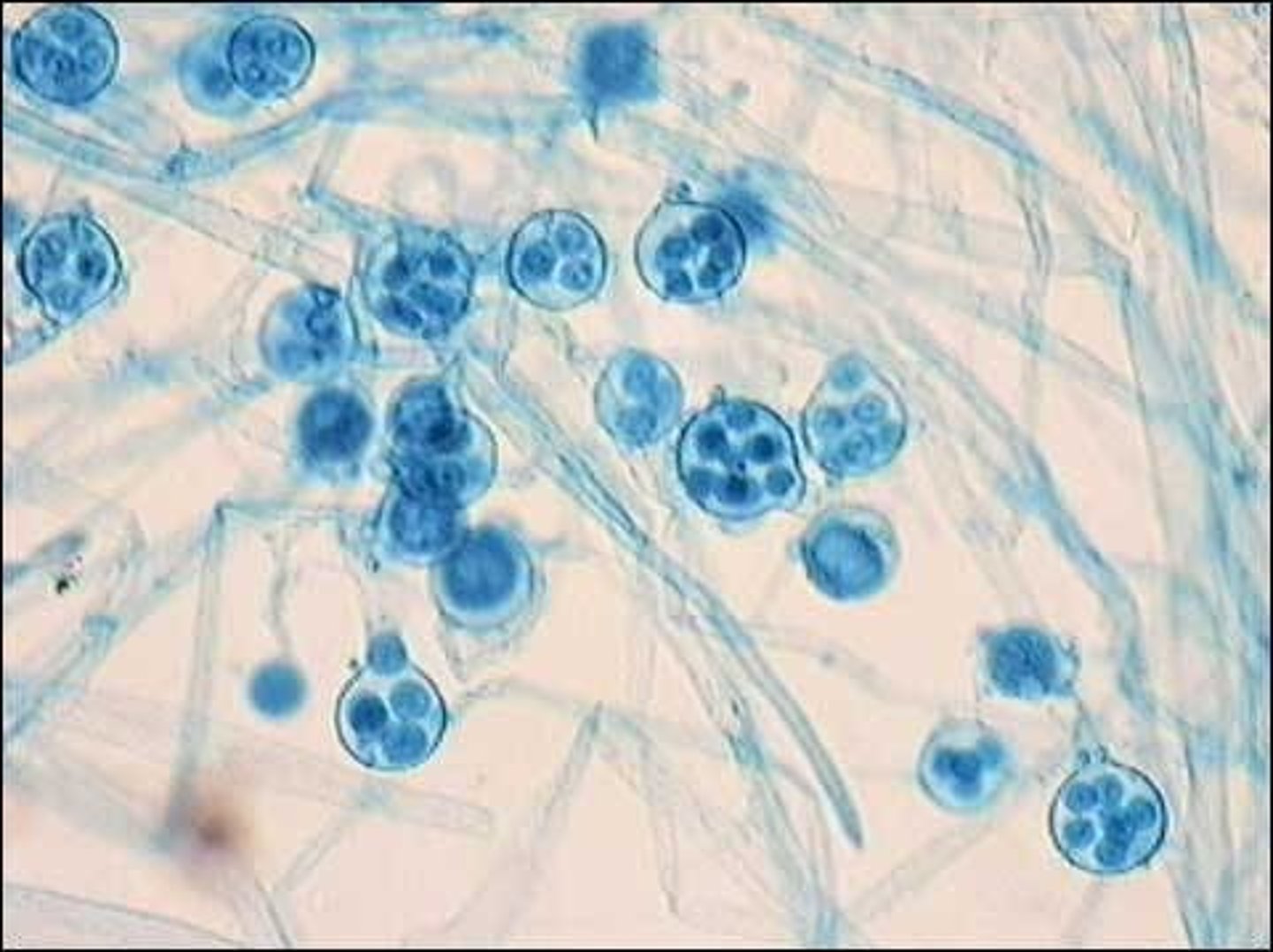
What is Saprolegnia important to?
crop and fish diseases
Diatoms

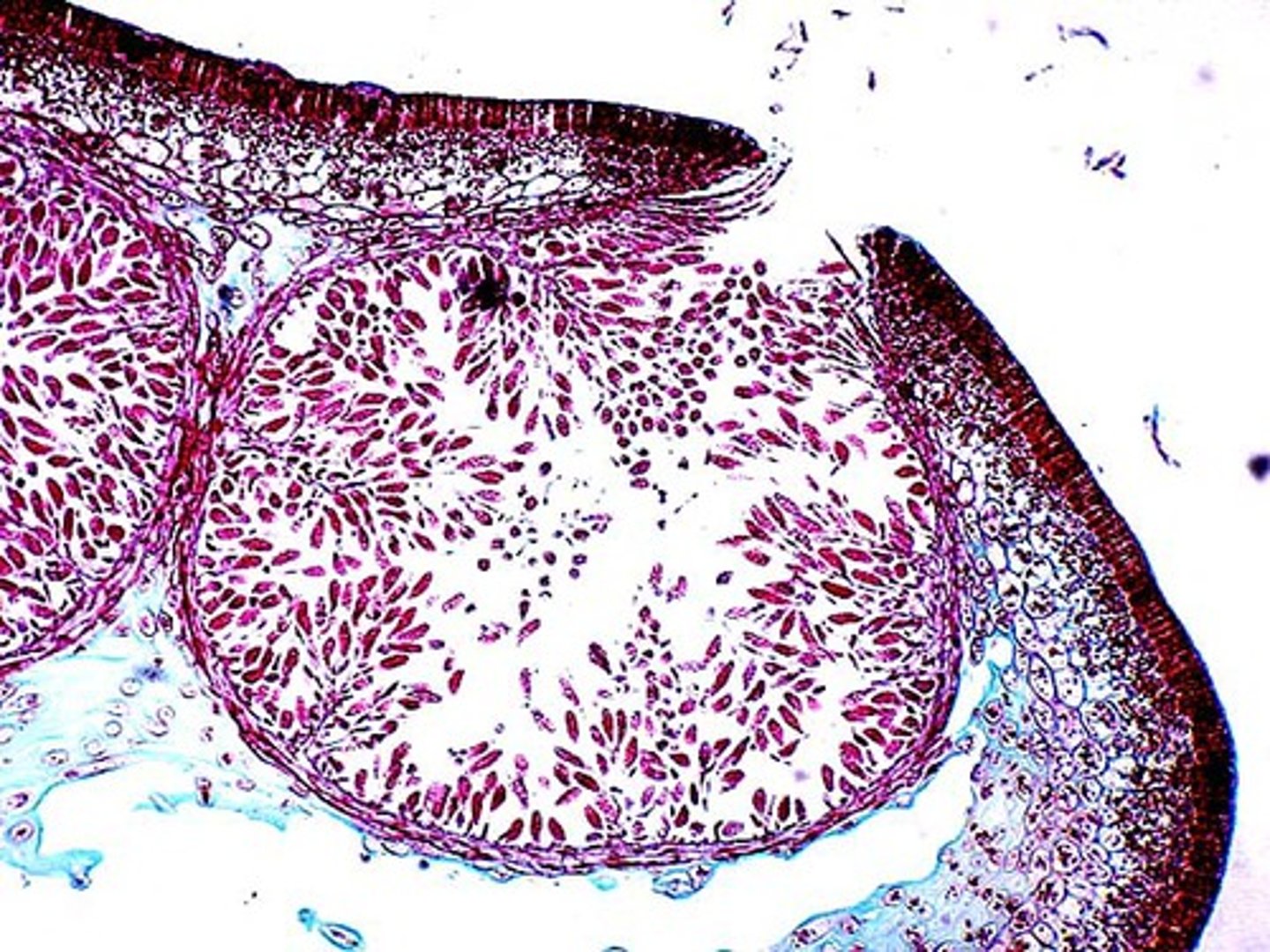
male fucus
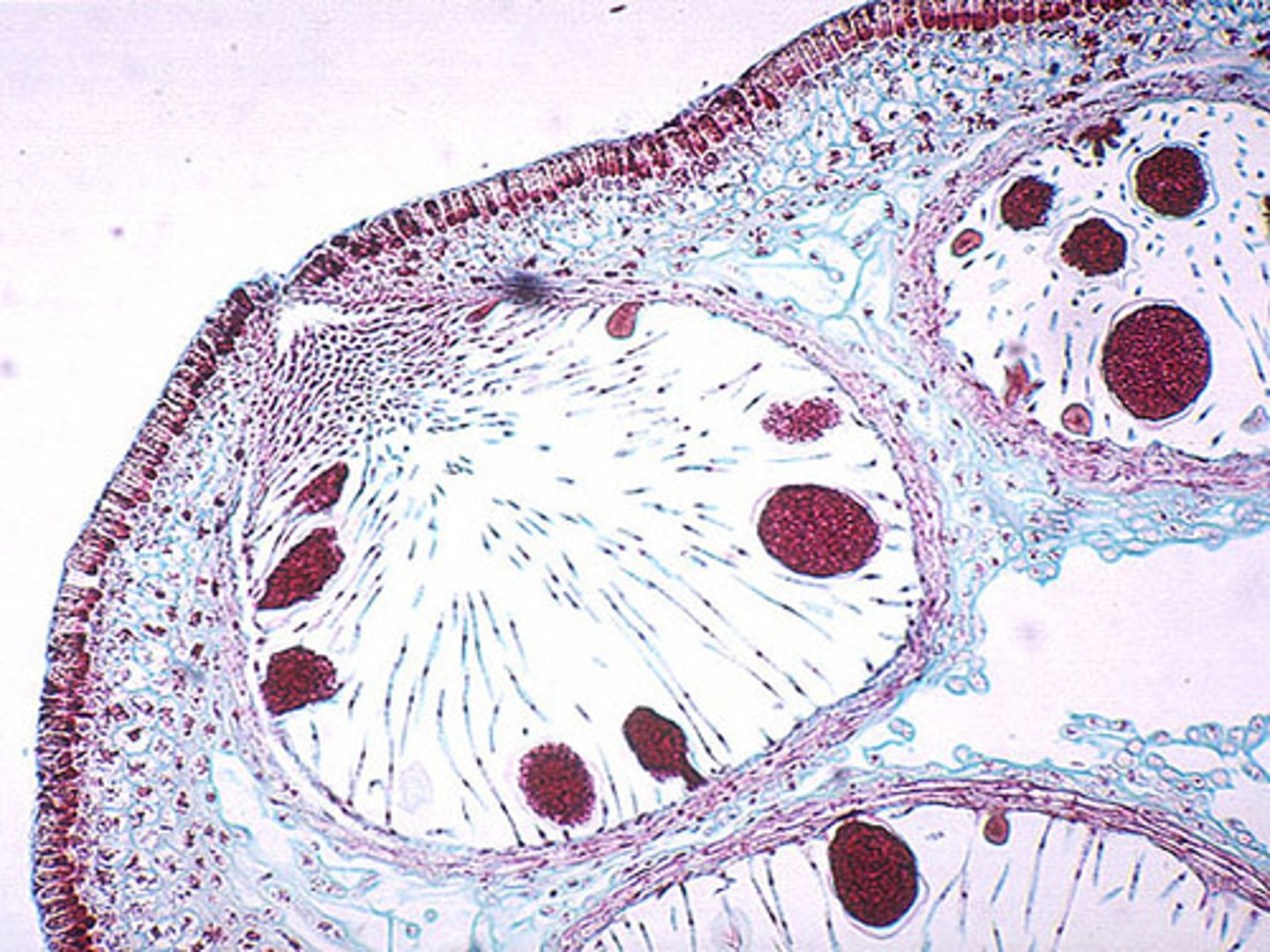
female fucus
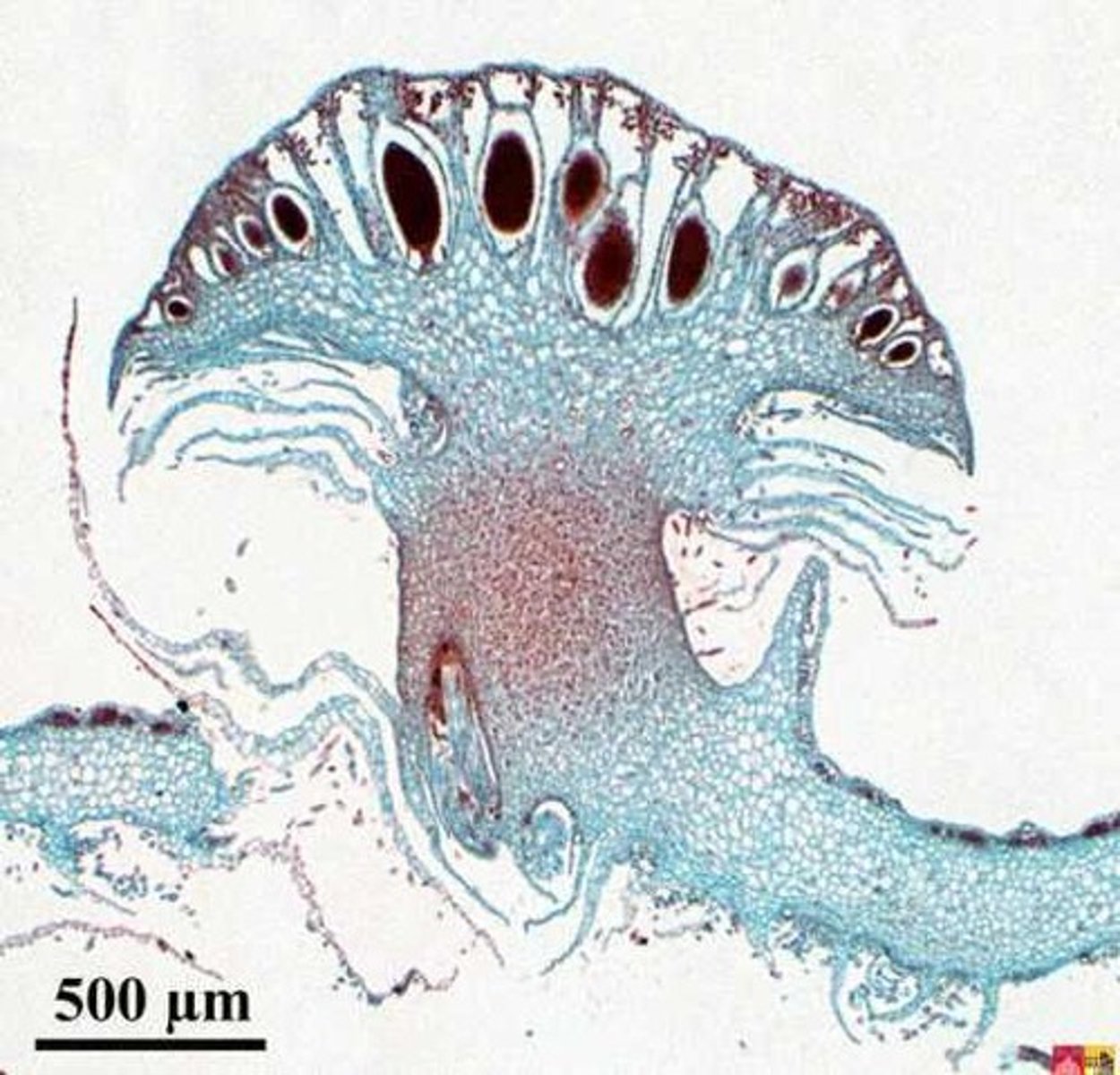
Liverwort
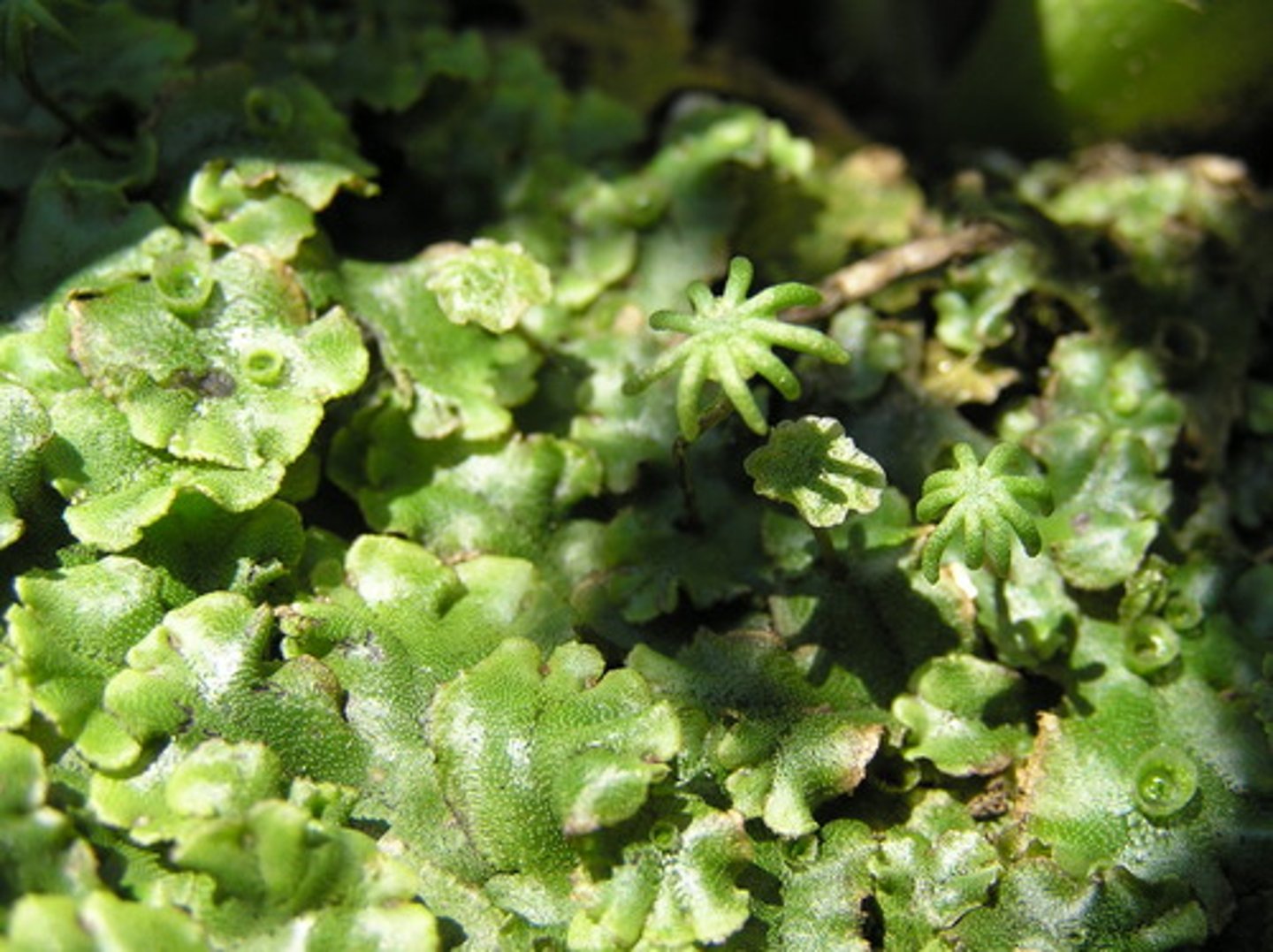

liverwort has what
a thallus and gemma cup
thallus
body of a plant with no differentiated tissue
gemma cup
cup-like structures containing gemmae
gemmae
small multicellular reproductive structures
Chlamydomonas
liverwort (marchantia)
archegonia (female)
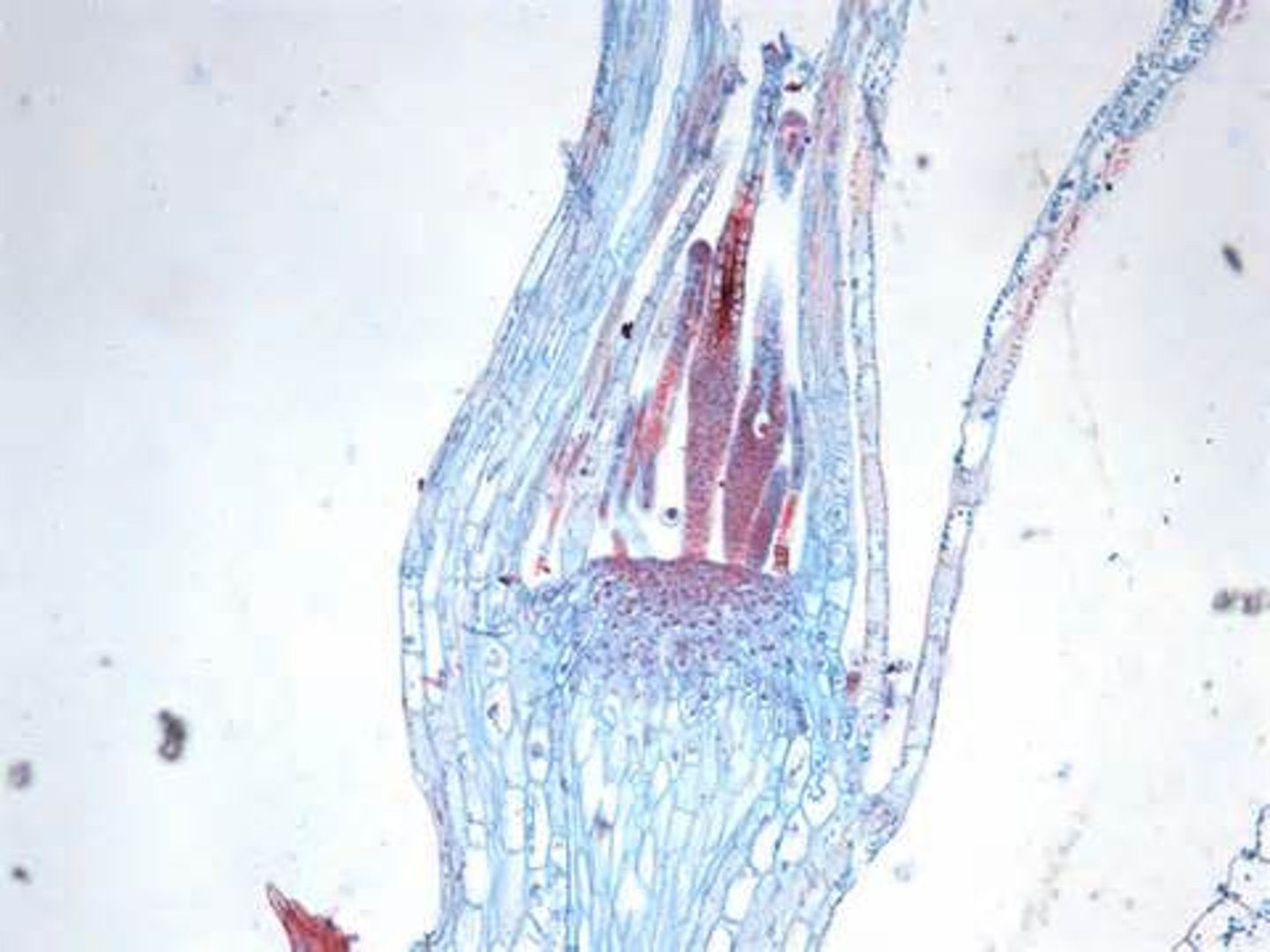
coleus shoot tip
moss with sporophytes

apical meistem
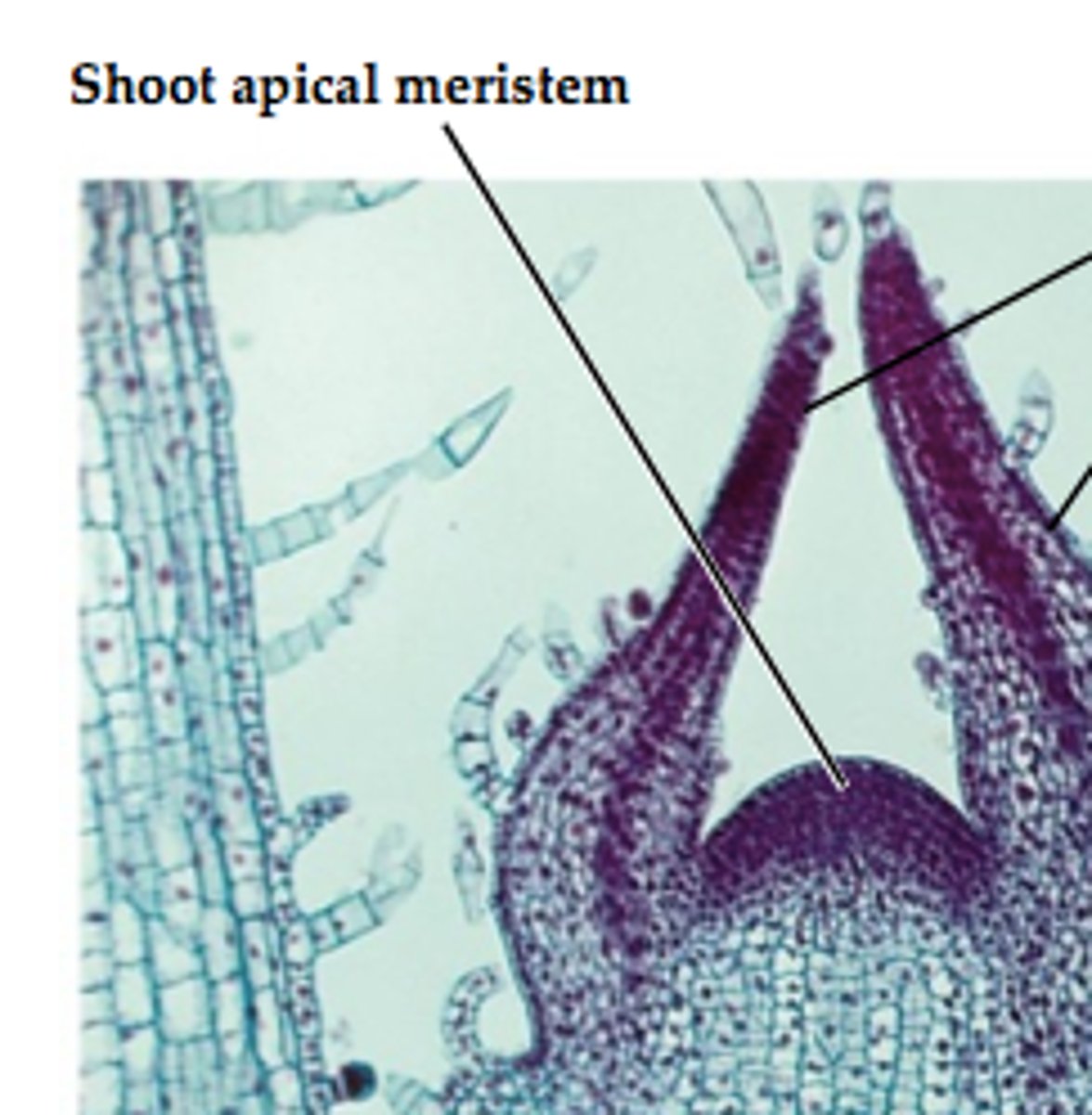
axillary buds
new growth from the side of the stem
eustele
different types of stele
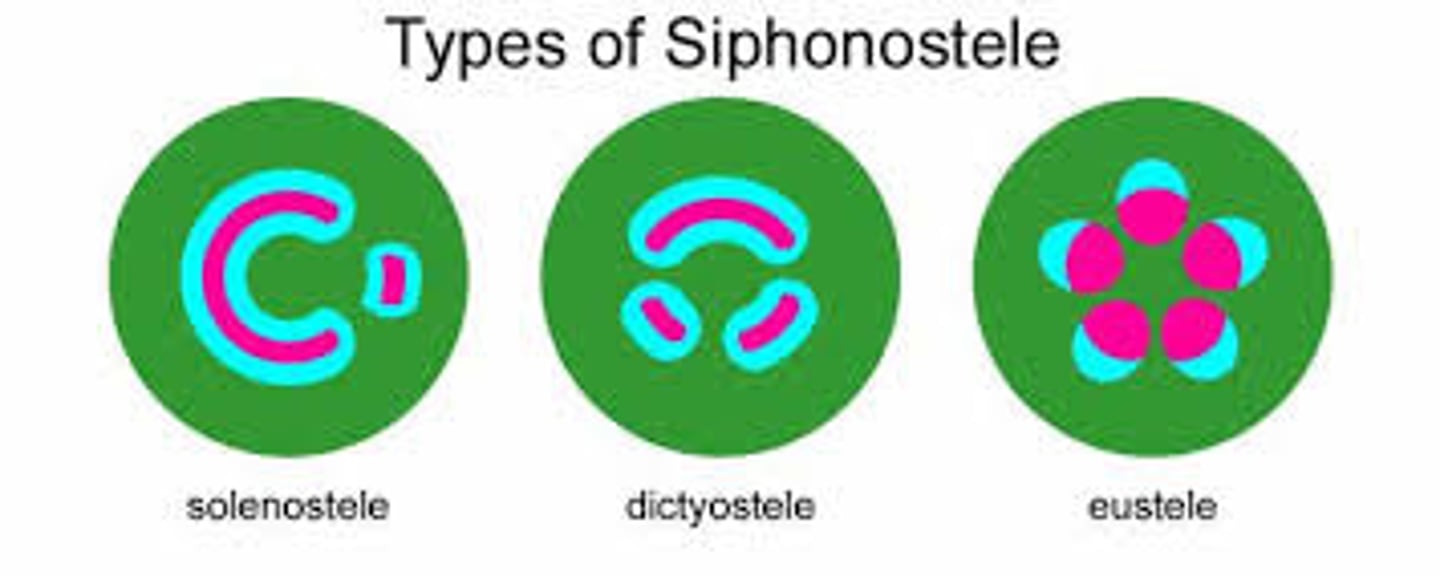
Siphonostele
sori
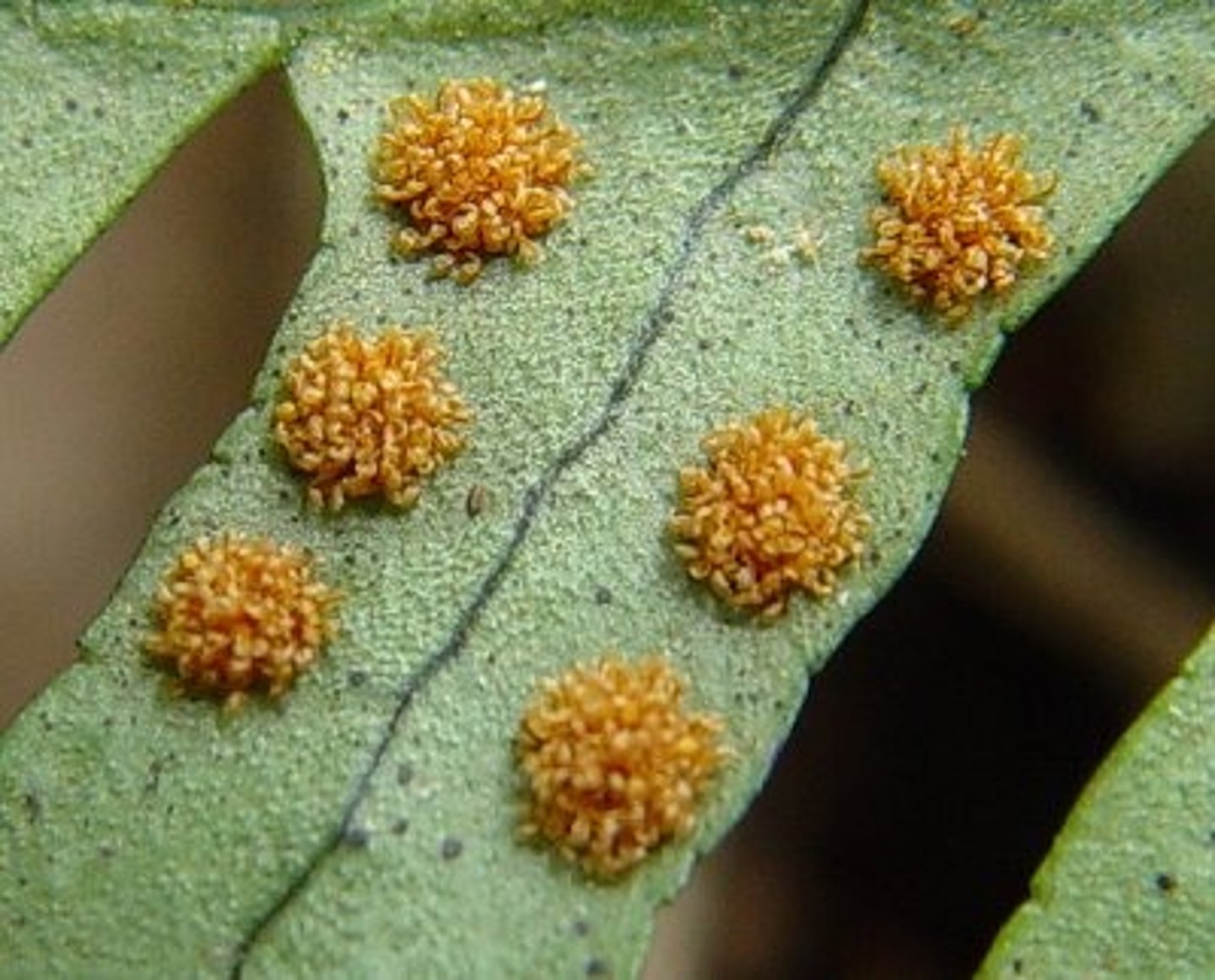

what are sori used for
reproduction, spreading spores
apical bud
A bud at the tip of a plant stem; also called a terminal bud.
•What is the name of the plant we are growing on our agar plates?
CERATOPTERIS
•We will see two sexes. What are they?
HERMAPHRODITE AND MALE
•What do we hypothesize about the sex ratio?
MORE MALES THAN HERMS AS CONCENTRATION INCREASES
•We will see two genotypes. What are they?
WILD TYPE AND POLKA DOT
•What do we hypothesize about their survival rates?
MORE WILD TYPES THAN POLKA DOTS
TYPE OF PLANT
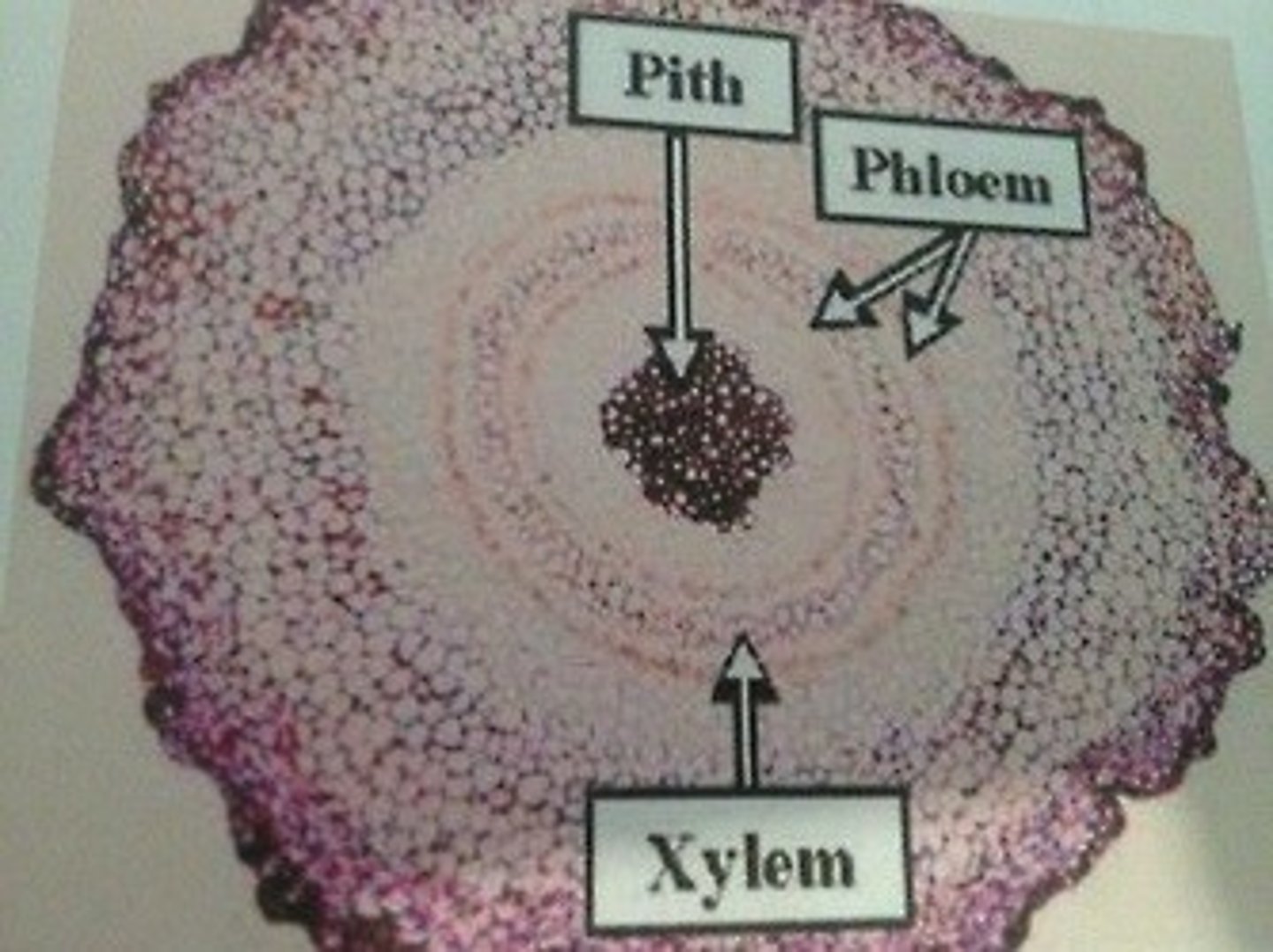
Phloem
carries sugar to the roots
xylem
carries water to the leaves
stomata
Small openings on the underside of a leaf through which oxygen and carbon dioxide can move
amoebozoa
what group is plasmodial slime mold
Paramecium
euglena
trichonympha
stramenopiles
not a fungus but behaves like one
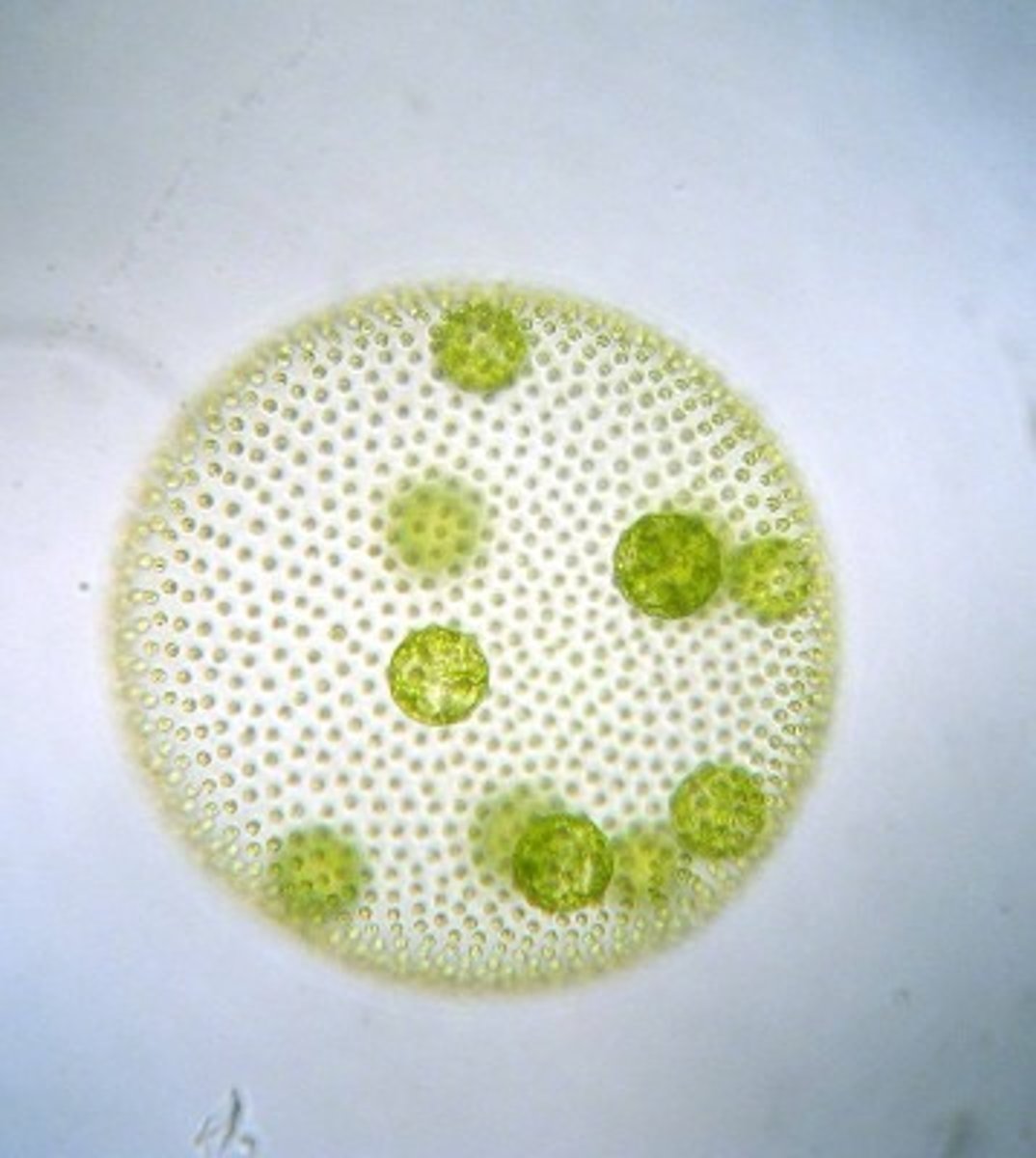
volvox
spirogyra
Antheridial Head (male)
Archegonial Head (Female
where is the xylem
towards the inside of the plant, the phloem is on the outside