IMSE 421 - Exam 2
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CH. 8, 9, 11
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
The increment’s internal rate of return is greater than MARR
Using an incremental rate of return (IRR) analysis, the decision to replace the “current best” by the “challenger” is based on what decision rule?
a. The internal rate of return of the increment is greater than the external rate of return.
b. The increment’s internal rate of return is greater than the previous increment’s internal rate of return.
c. The increment’s internal rate of return is greater than 0.
a. The increment’s internal rate of return is greater than MARR.
A
A company is considering 2 alternatives, one of which must be implemented. Of the 2 projects, A has the higher maintenance cost, but B has the higher investment cost. The appropriate (and properly calculated) incremental IRR is 17.6 percent. Which alternative is preferred if the minimum attractive rate of return is 20 percent?
a. A
b. B
c. The company is indifferent between A and B.
d. Cannot be determined from the information given.
MARR
Consider the calculation of an external rate of return (ERR). The positive cash flows in the cash flow profile are moved forward to t=n using what value of i in the (F|P i, n-t) factors?
a. 0
b. The unknown value of ERR (i’)
c. MARR
d. IRR
Both (a) and (b)
If a well-behaved investment alternative’s internal rate of return (IRR) is equal to MARR, what must be true about the other measures of worth for this alternative?
a. PW=0
b. AW=0
c. (a) only
d. (b) only
e. Both (a) and (b)
An initial negative cash flow followed by all positive cash flows
An investment is guaranteed to have a unique value of IRR if what is true?
a. Alternating positive and negative cash flows
b. An initial negative cash flow followed by all positive cash flows
c. A unique value for ERR
d. A positive PW at MARR
ERR has only a single root, but IRR can have multiple roots
Consider the IRR and ERR measures of worth. If we define a root to mean a value for the measure that results in PW=0, then what is true?
a. Both IRR and ERR can have multiple roots.
b. IRR has only a single root but ERR can have multiple roots.
c. ERR has only a single root but IRR can have multiple roots.
d. Both IRR and ERR have only a single root.
Order the alternatives from lowest to highest initial investment
When conducting an incremental analysis, what step must always be taken immediately prior to beginning the pairwise comparisons?
a. Order the alternatives from highest to lowest initial investment
b. Order the alternatives from lowest to highest present worth
c. Order the alternatives from lowest to highest internal rate of return.
d. Order the alternatives from lowest to highest initial investment
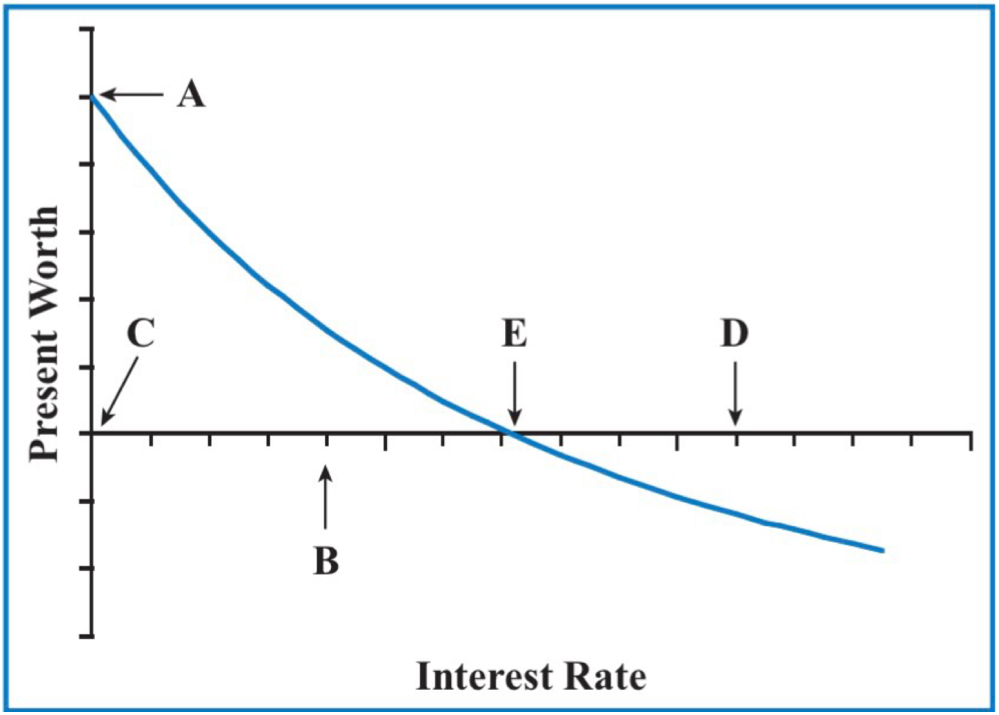
The IRR of the investment is greater than 20 percent
If the interest rate at B is 20 percent, then what describes the analysis of the investment?
a. The IRR of the investment is less than 20 percent.
b. The IRR of the investment is equal to 20 percent.
c. The IRR of the investment is greater than 20 percent.
d. None of the above are true.
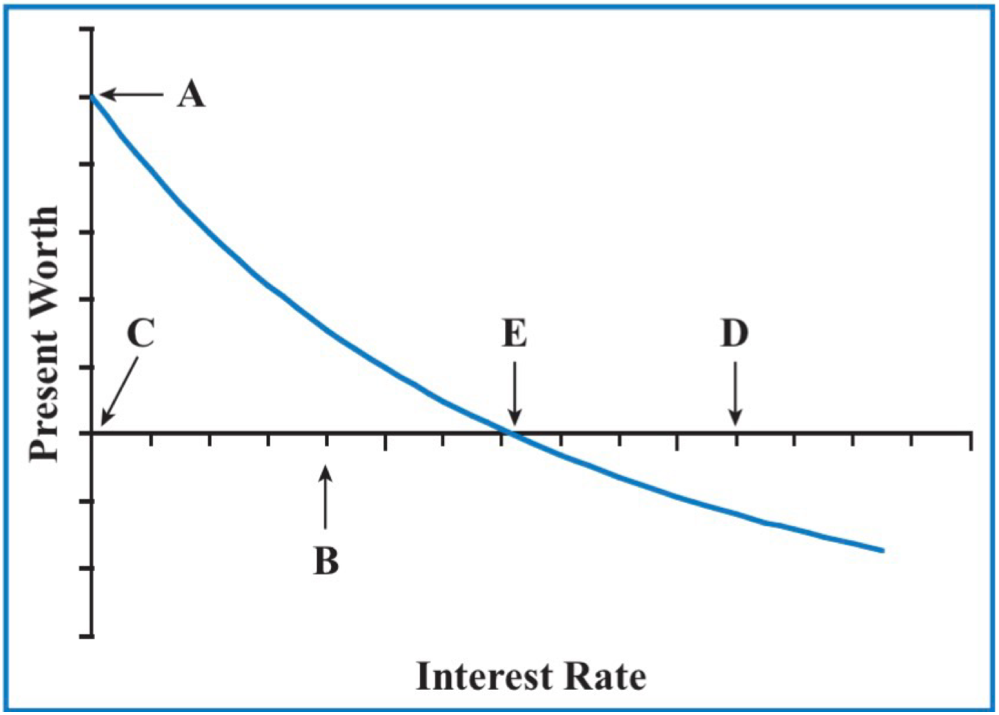
E
The IRR of this investment is located at which point?
a. A
b. C
c. D
d. E
Not enough information is given to determine which alternative is preferred
If the IRR of Alternative A is 18 percent, the IRR of Alternative B is 16 percent, and MARR is 12 percent, what is correct?
a. Alternative B is preferred over Alternative A.
b. Alternative A is preferred over Alternative B.
c. Not enough information is given to determine which alternative is preferred.
d. Neither Alternative A nor Alternative B is acceptable.
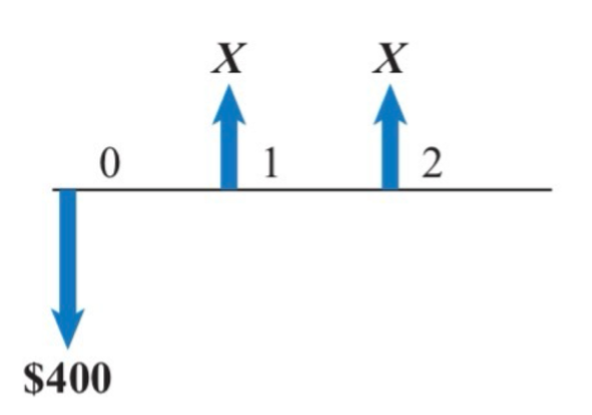
$246
Consider the following cash flow diagram. What is the value of X if the internal rate of return is 15 percent?
a. $246
b. $255
c. $281
d. $290
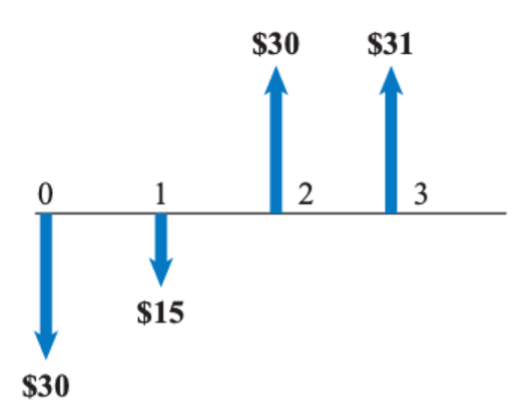
15 percent
What is the internal rate of return of the following cash flow diagram?
a. 20 percent
b. 18.2 percent
c. 17.5 percent
d. 15 percent
10 percent to 12 percent
A snow-cone machine at an ice cream shop costs $15,000. The machine is expected to generate profits of $2,500 each year of its 10-year useful life. At the end of the 10 years, the machine will have a salvage value of 0. Within what interest rate range does the IRR fall?
a. Less than 10 percent
b. 10 percent to 12 percent
c. 12 percent to 14 percent
d. Greater than 14 percent
$28,580
A lumber company purchases installs a woodchipper for $200,000. The chipper is classified as MACRS 7-year property. It’s useful life is 10 years. The estimated salvage value at the end of 10 years is $25,000. Using MACRS depreciation, compute the first-year depreciation.
a. $17,500
b. $20,000
c. $25,007.50
d. $28,580
$17,500
A lumber company purchases and installs a woodchipper for $200,000. The chipper is classified as MACRS 7-year property. It’s useful life is 10 years. The estimated salvage value at the end of 10 years is $25,000. Using straight-line depreciation, compute the first-year depreciation.
a. $28,571.43
b. $20,000
c. $17,500
d. $25,000
Depletion
The concept similar to depreciation that is applied to natural resources is called what?
a. Depletion
b. Declining balance
c. Amortization
d. MACRS
$1,728
An X-ray machine at a dental office is MACRS 5-year property. It costs $6,000 and has an expected useful life of 8 years. The salvage value at the end of 8 years is expected to be $500. Assuming MACRS depreciation, what is the book value at the end of the third year?
a. $1,584
b. $1,728
c. $3,916
d. $4,272
It must have a basis (initial purchase plus installation cost) greater than $1,000
What is not a requirement for an asset to be depreciable?
a. It must have a life longer than 1 year.
b. It must have a basis (initial purchase plus installation cost) greater than $1,000.
c. It must be held with the intent to produce income.
d. It must wear out or get used up.
Double declining balance and straight-line
MACRS-GDS deductions are a combination of which other methods of depreciation?
a. Sum-of-years’-digits and straight-line
b. Sum-of-years’-digits and declining balance
c. Double declining balance and 150 percent declining balance
d. Double declining balance and straight-line
$72,576
Production equipment used in the bottling of soft drinks (MACRS-GDS, 10-year property) is purchased and installed for $630,000. What is the depreciation deduction in the fourth year under MACRS-GDS?
a. $90,720
b. $78,687
c. $72,576
d. $48,510
a and c only
Which of the following is (are) required to calculate MACRS-GDS depreciation deductions?
a. Property class
b. Salvage value
c. First cost
d. Annual maintenance costs
e. a and c only
f. b and c only
g. a, b, and c
h. a, b, c, and d
$67,682
The depreciation deduction for year 11 of a 15-year property with a 20-year class life is $4,000. If the asset’s salvage value is estimated to be $5,000 and MACRS-GDS is used to calculate the depreciation deduction for year 11, what was the asset’s initial cost?
a. $42,105
b. $67,682
c. $72,682
d. $80,000
$80,000
The depreciation deduction for year 11 of a 15-year property with a 20-year class life is $4,000. If the asset’s salvage value is estimated to be zero and straight-line depreciation was used to calculate the depreciation deduction for year 11, what was the asset’s initial cost?
a. $42,105
b. $67,682
c. $72,682
d. $80,000
For MACRS-GDS, an estimate of the salvage values is required
What is not true about depreciation?
a. Depreciation is not a cash flow.
b. To be depreciable, an asset must have a life longer than 1 year.
c. A 5-year property will generate a regular MACRS-GDS depreciation deduction in 6 fiscal years.
d. For MACRS-GDS, an estimate of the salvage values is required.
Cannot be determined with the information given
The depreciation allowance for a $100,000 MACRS-GDS asset was $8,550 after its third year. What was the depreciation allowance after its second year?
a. $8,550
b. $9,500
c. $18,000
d. Cannot be determined with the information given
$370,000
A company owns a 6-year-old gear hobber that has a book value of $60,000. The present market value of the hobber is $80,000. A new gear hobber can be purchased for $450,000. Using an insider’s point of view, what is the net first cost of purchasing the new gear hobber?
a. $310,000
b. $370,000
c. $390,000
d. $450,000
$450,000
A company owns a 6-year-old gear hobber that has a book value of $60,000. The present market value of the hobber is $80,000. A new gear hobber can be purchased for $450,000. Using an outsider’s point of view, what is the net first cost of purchasing the new gear hobber?
a. $310,000
b. $370,000
c. $390,000
d. $450,000
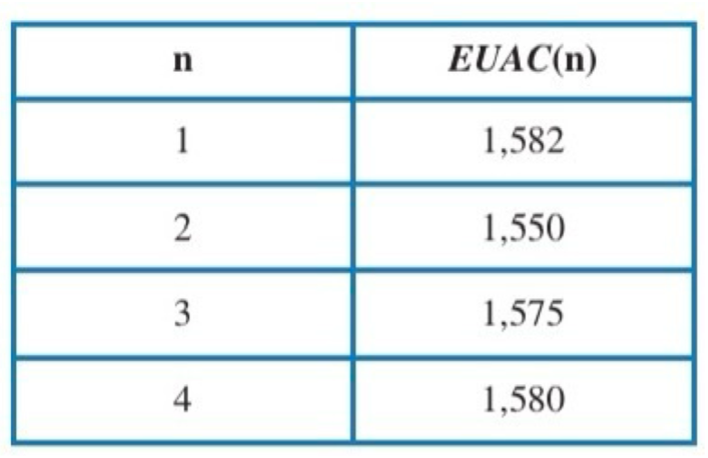
2 years
In evaluating a piece of equipment for its optimal replacement interval, the following table of equivalent uniform annual costs is obtained, What is the optimal replacement interval for the equipment?
a. 1 year
b. 2 years
c. 3 years
d. 4 years
Ten years, because maintenance costs don’t increase
A radiology clinic is considering buying a new $700,000 X-ray machine that will have no salvage value after installation, since the cost of removal will be approximately equal to its sales value. Maintenance is estimated at $24,000 per year as long as the machine is owned. After 10 years, the X-ray source will be depleted, and the machine must be scrapped. Which of the following represents the most economic life of this X-ray machine?
a. One year, since it will have no salvage after installation
b. Five years, since the maintenance costs are constant
c. Ten years, because maintenance costs don’t increase
d. Cannot be determines from the information given
Supply chain approach
What is not an approach to replacement analysis?
a. Cash flow approach
b. Insider viewpoint
c. Outsider viewpoint
d. Supply chain approach
Shortest life
The most common approach to determining the planning horizon for replacement analysis is which of the following?
a. Shortest life
b. Median life
c. Longest life
d. Least common multiple
$16,000
A company owns a 5-year-old turret lathe that has a book value of $20,000. The present market value of the lathe is $16,000. A new turret lathe can be purchased for $45,000. Using a before-tax analysis and an outsider’s point of view, what is the first cost of keeping the old lathe?
a. $29,000
b. $45,000
c. $20,000
d. $16,000
$29,000
A company owns a 5-year-old turret lathe that has a book value of $20,000. The present market value of the lathe is $16,000. A new turret lathe can be purchased for $45,000. Using a before-tax analysis and an insider’s point of view, what is the first cost of keeping the old lathe?
a. $29,000
b. $45,000
c. $25,000
d. $16,000
Operating and maintenance costs and capital recovery costs
What 2 cost categories form the trade-off that leads to an optimal replacement interval?
a. Direct costs and indirect costs
b. Insider costs and outsider costs
c. Operating and maintenance costs and capital recovery costs
d. Sunk costs and opportunity costs
Increase
Increasing the magnitude of the initial investment tends to _______ the optimum replacement interval.
a. Decrease
b. Increase
c. Reverse
d. Not affect