BIOL 108 Topic 7: Evolution of populations
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Do individuals evolve?
NO, natural selection acts on individuals but only populations evolve via natural selection.
What is the smallest unit of evolutionary change?
Population
What is a population?
A group if individuals of the same species that live in the same area and interbreed, producing fertile offspring.
What is microevolution?
The change in allele frequencies in populations over generations.
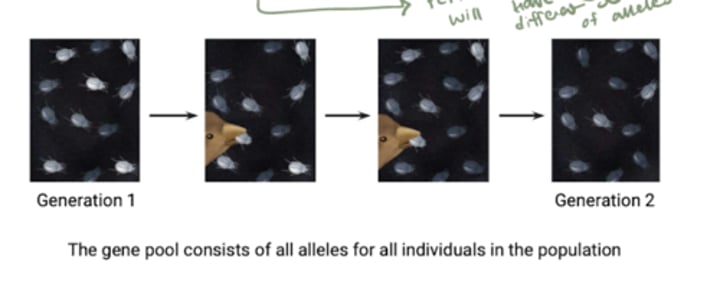
What is a gene?
A gene (more accurately, genetic locus) consists of two alleles in diploid individuals.
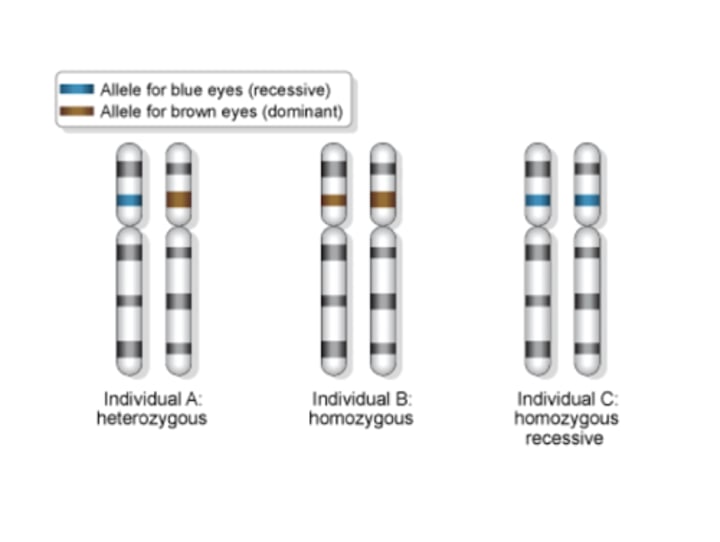
What are alleles?
Different forms of a gene corresponding to different DNA sequences in each form.
How many alleles are there per chromosome?
One
How many chromosomes are donated from each parent?
In sexually reproducing diploid species, one chromosome from each parent.
Do alleles blend or remain separate?
Remain separate; apparent blending is the result of incomplete dominance.
What is the more complete definition of population?
A localized group o individuals of a single species that interbreed (share alleles) and produce fertile offspring.
What do individuals represent?
Different combinations of alleles drawn from the gene pool, that is, from all the alleles present in all individuals in the population.
What may happen if different populations of the same species are isolated?
distinct gene pools
What is the prerequisite for evolution?
Variation in heritable traits
What is one of the three main components of biodiversity?
genetic diversity (variation)
Why is genetic variation advantageous to a population?
It enables adaptation of the population to the environment via natural selection.
What causes genetic variation?
Genetic variation among individuals is caused by differences in genes or other DNA segments
-individuals have a specific genotype (combination of alleles)
What is phenotype a product of?
Inherited genotype and environmental influences.
Can natural selection act on variation?
Natural selection can only act on variation with a genetic component.

How do new genes and alleles arise?
By mutation or gene duplication
What are the sources of genetic variation?
1. Mutations
2. Sexual reproduction
What are mutations?
Changes in an individual's DNA sequence
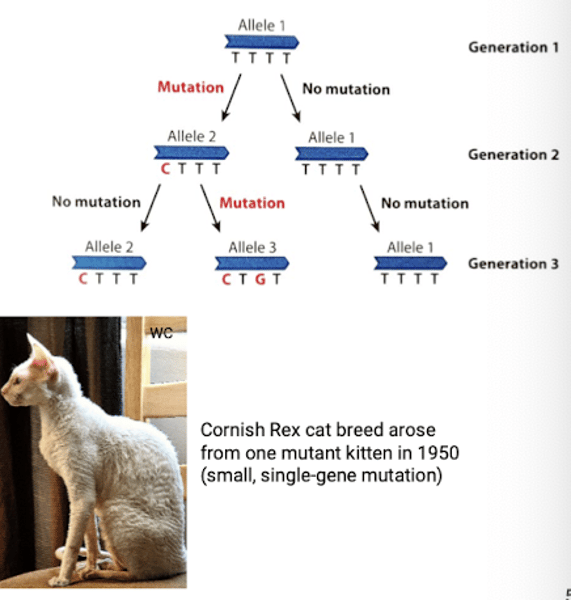
What are mutations caused by?
1. Small scale (e.g. point mutation) or chromosomal (e.g. insertion/deletion) errors in DNA replication
2. Structural damage to DNA (e.g. radiation).
What are the only mutations that can be passed on to the next generation?
Only mutations in cells that produce gametes (eggs or sperm) can be passed onto the next generation.
Do mutations occur randomly?
Yes
Do selection pressures cause the "right" mutations?
NO
What do mutations create?
New alleles
Does a mutation necessarily have to have an effect?
No; a single mutation can have no effect (no change in phenotype) or can have a large effect (lethal)
-most mutations have negligible effect.
What 3 things can a mutation be?
1. Deleterious ('bad')
2. Neutral
3. Advantageous ('good') in the current situation.
What is an example of an advantageous mutation in the current situation?
A neutral mutation may later be advantageous or disadvantageous if the environment changes, i.e. selective pressures change.
What kind of mutation is typically harmful?
Chromosomal mutations that delete, disrupt, or rearrange many loci are typically harmful.
What kind of mutation is typically less harmful?
Duplication of small DNA segments increases genome size and is usually less harmful.
What can duplication of DNA segments result in?
Duplication of genes that can take on new functions by further mutation.
What is whole genome duplication?
A process of genome doubling, is an important driver of evolution by supplying genetic material and increasing genome complexity.
What is most evolutionary change based on the accumulation of?
Many mutations with small individual effects.
How high are mutation rates in animals and plants?
Low
-human genomes accumulate around 60-100 new mutations per generation.
How are mutation rates in prokaryotes?
Much lower
-but mutations accumulate quickly in prokaryotes because they have very short generation times.
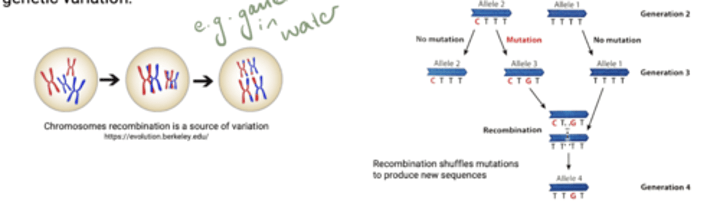
How is sexual reproduction a source of genetic variation?
Can shuffle existing alleles into new combinations.
How does sexual reproduction shuffle existing alleles into new combinations?
1. Random mating between organisms; random fertilization.
2. Recombination of homologous chromosomes during meiosis shuffles existing genetic material to create new combination of alleles.
What is more important in producing genetic variation?
In sexually reproducing organisms, recombination of alleles in more important than mutation in producing genetic variation.
What are the factors that alter allele frequencies in populations?
1. Natural selection
2. Genetic drift
3. Gene flow
What does natural selection cause?
Adaptive evolution, where a population becomes more adapted to its environment under natural selection.
What is non-adaptive evolution?
Any change in allele frequency that does not lead a population to become more adapted to its environment.
What causes non-adaptive evolution?
Genetic drift and gene flow, since their effects on allele frequencies are primarily random
What two things are also non adaptive?
Mutations and recombination, but they don't impact allele frequencies in populations.
What is the only cause of adaptive evolution (adaptation)?
Natural selection
What is adaptation?
Feature or trait (selected through natural selection) that provides an advantage (higher relative fitness) to an individual possessing it.
What is relative fitness?
The contribution an individual makes to the gene pool of the next generation, relative to the contributions of other individuals.
What does natural selection act on?
Existing variation
What does differential reproductive success of individuals in a population result in?
The alleles of those species to be passed to the next generation in greater proportions.
What are the three modes of natural selection?
1. Directional selection
2. Disruptive selection
3. Stabilizing selection
What does directional selection favour?
Individuals that differ from the current mean phenotype of a population in one direction.
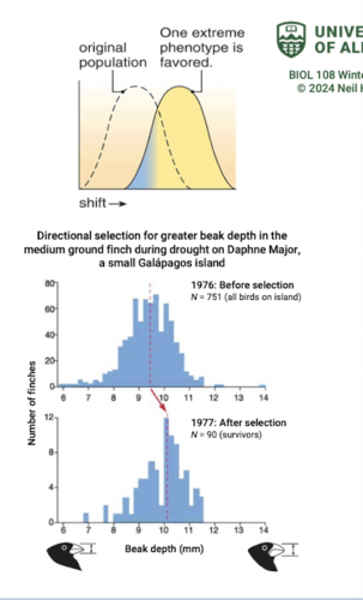
What happens under directional selection?
A population's genetic variant shifts toward a new phenotype with higher relative fitness when exposed to selection pressures.
What does directional selection occur in response to?
Consistent selective pressure, i.e. a steady change in environment.
What shifts under directional selection?
The frequency distribution of phenotype shifts under directional selection.
-directional shift in the mean of the population
-doesn't affect the amount of genetic variation in a population.
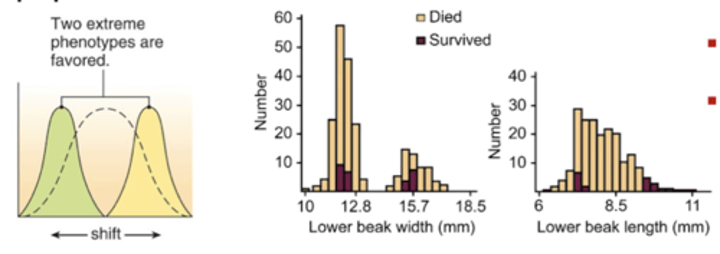
What does disruptive selection favour?
Favours individuals at both extremes of the phenotypic range.
What phenotypes are less fit than either extreme phenotype?
Intermediate (average) phenotypes.
-results in two or Moore divergent phenotypes.
What does disruptive selection maintain?
Maintains genetic variation in the population.
Explain an example of disruptive selection for beak size in the black-bellied seedcracker (Pyrenestes ostrinus).
The black-bellied seed cracker population has divergent diets and feeding efficiencies on their principal food, sedge seeds (Scleria spp.).
-small beaked birds specialist on softer seeded species, while large beaked birds specialize on hard seeded species.
-juvenile birds that survive have either relatively small or relatively large beaks
-Birds with intermediate beak size cannot use either kind of seed efficiently and survive poorly.
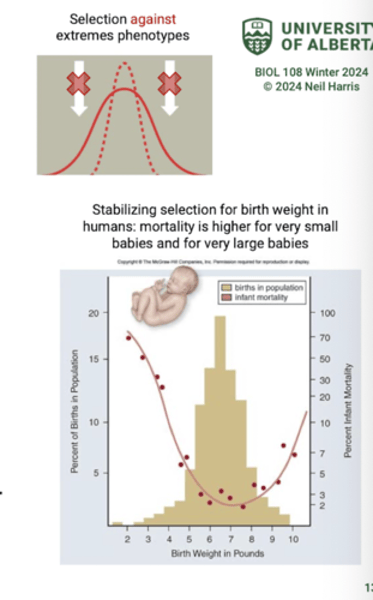
What does stabilizing selection favour?
Intermediate or common variants by selecting against extreme phenotypes that deviate from the current population mean.
What does stabilizing selection conserve?
Conserves functional genetic features by selective pressure against deleterious variants.
In stabilizing selection what happens to the mean of the population?
Stays the same, but genetic variation in the population decreases.
What is the affect on evolutionary change in stabilizing selection?
little or no evolutionary change in the population.
How common is stabilizing selection? What does it remove?
Very common: removes deleterious mutations (removes individuals with lower fitness).
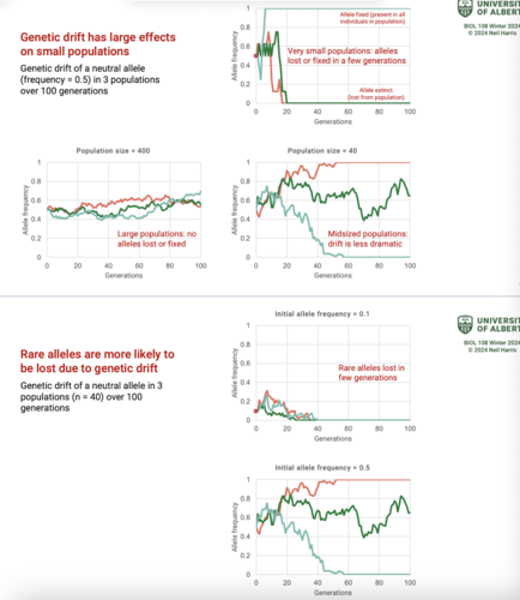
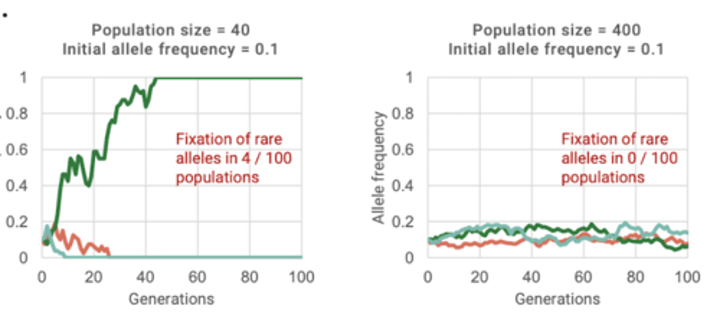
What is genetic drift?
Random changes in allele frequency in a population.
-allele frequencies "drift" (fluctuate unpredictably) from one generation to the next.
Where is genetic drift more likely?
In small populations.
-The smaller the sample, the greater the chance of deviation from a predicted result.
In genetic drift what can random events do?
Random events can differentially remove certain alleles.
What alleles are more likely to be lost in genetic drift?
Rare alleles are more likely to be lost due to genetic drift.
In genetic drift what happens to genetic variation?
Reduces genetic variation in a population through loss of alleles.
What does genetic drift cause? What does it not create?
Genetic drift causes evolutionary change but does not create adaptations (non-adaptive).
What are two examples of genetic drift?
founder effect and bottleneck effect
What is the bottleneck effect?
A sudden reduction in population size due to a change in the environment.
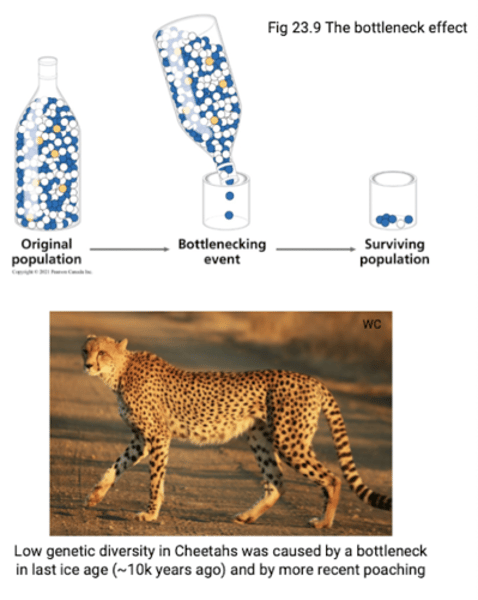
With the bottleneck effect how is population size reduced?
Population size is reduced within its natural range.
e.g. catastrophe destroys most of the population's habitat
What kind of population is the bottleneck effect concerned with?
Large population —> few individuals.
-only these few individuals contribute alleles to the next generation.
Explain the example of the bottleneck effect with greater prairie chickens.
Greater prairie chickens once lived throughout Canadian and US prairies (extirpated in Canada)
-Loss of prairie habitat caused a severe reduction in the population of greater prairie chickens (bottleneck)
-some prairie populations remain throughout US prairie states
-the bottleneck reduced genetic variation in the surviving populations (loss of fertility)

What is the founder effect?
The founder effect occurs when a few individuals become isolated from a larger population.
-allele frequency in the original population is unchanged
What happens in the founder effect?
The small founding population has a small fraction of the total gene pool present in the original population.
In the founder effect what is the difference between the allele frequency in the founder population vs. the original population?
Allele frequencies in the small founder population differ from those in the larger originating population.
-e.g. increased frequency of Huntington's disease in human populations founded by a small group of European migrants
The next four cards are a summary of the effects of genetic drift: Who does genetic drift have the largest impact on?
Small populations
How does genetic drift cause allele frequency to change?
At random
What can genetic drift lead to?
A loss of genetic variation within populations
What can genetic drift cause?
Harmful alleles to become fixed in small populations
What is gene flow?
the movement of alleles between populations of a species.
How can alleles be transferred?
Through the movement of fertile individuals (e.g. dispersals of animals or seed) or gametes (e.g. pollen).
What does gene flow introduce into the receiving population?
New variation
-counteracts genetic drift but may slow adaptation of the receiving population.
What does gene flow reduce over time/
Reduces variation between populations over time.
-populations become more similar (homogenous) to each other.

Diagram of gene flow.
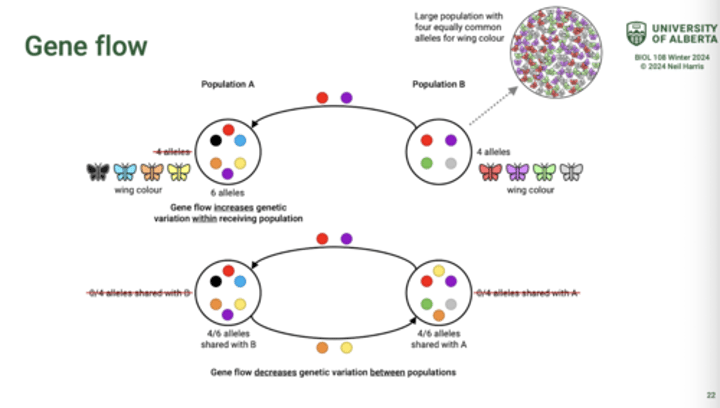
What can gene flow decrease?
The fitness of the receiving population.
e.g. gene flow supplies new alleles to populations with limited genetic variation
What is an example of gene flow increasing the fitness of a receiving population?
The spread of alleles fro resistance to insecticides
-insecticides are used to target mosquitoes carrying diseases (e.g. malaria)
-mosquito populations become insecticide-resistant via natural selection.
-the flow of insecticide resistance alleles into new populations causes an increase in fitness in the receiving population.
What are three factors that alter allele frequencies in populations and bring about most evolutionary change?
1. Natural selection (adaptive)
2. genetic drift (non-adaptive)
3. Gene flow (non-adaptive)
What are two other factors tat bring about evolutionary change?
1. Extirpation of populations reduces a specie's genetic diversity
2. Global extinction of a species (complete loss of genetic diversity)

What is neutral variation?
Genetic variation that does not confer a selective advantage or disadvantage
-natural selection does not affect the frequency of neutral mutations.
What nine things maintain genetic variation in populations in spite of natural selection and genetic drift?
1. Mutation
2. Recombination (crossing-over of chromosomes during meiosis).
3. Independent assortment of alleles during meiosis.
4. Random mating between organisms (sexual reproduction)
5. Random fertilization (sexual reproduction)
6. Recessive alleles are hidden from selection in heterozygote individuals
7. Disruptive selection (natural selection)
8. Gene flow (between populations)
9. Balancing selection
What is balancing selection?
occurs when natural selection maintains stable frequencies of multiple alleles in the gene pool of a population.
-varying habitats (e.g. dry areas vs. wet areas) over the range of a population may promote the maintenance of alleles at intermediate frequencies.
What are two mechanisms of balancing selection?
1. Heterozygotę advantage
2. Frequency-dependent selection
When does heterozygote advantage occur?
When an organism with two different alleles of a particular gene (heterozygote) has greater fitness than an organisms with two identical copies of either allele (homozygote)
What tends to happen with heterozygote advantage?
Natural selection will tend to maintain two or more alleles at that locus.
What can heterozygote advantage result from?
Stabilizing or directional selection.
What is an example of heterozygote advantage?
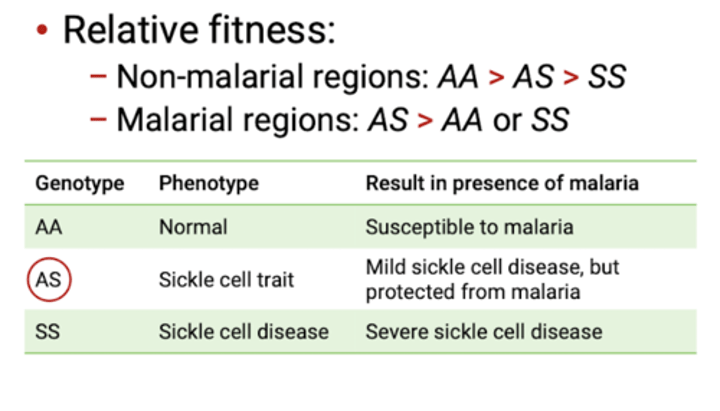
Sickle cell disease
-A allele: normal hemoglobin and functional, round red blood cells
S allele: Mutation induces hemoglobin aggregation, causing sickle cells, which causes chronic anemia.
-Sickle cell (S ) allele causes mutations in hemoglobin but also confers malaria resistance.
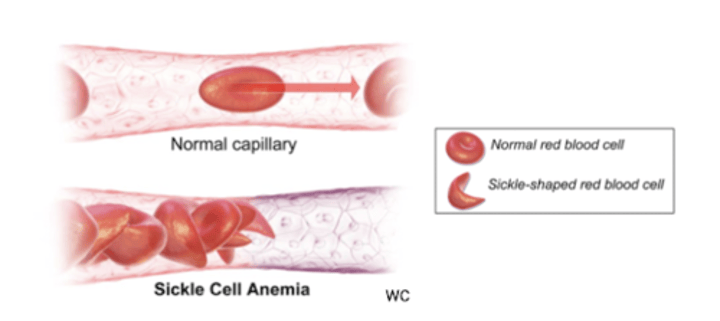
Who has an advantage in malarial regions?
Heterozygous individuals (AS) have an advantage over homozygous individuals (AA or SS)
What is frequency dependent selection?
Under frequency-dependent selection, the fitness of a phenotype is proportional to its frequency in the population