Lecture 23: Hypothalamus
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Hypothalamus Functions

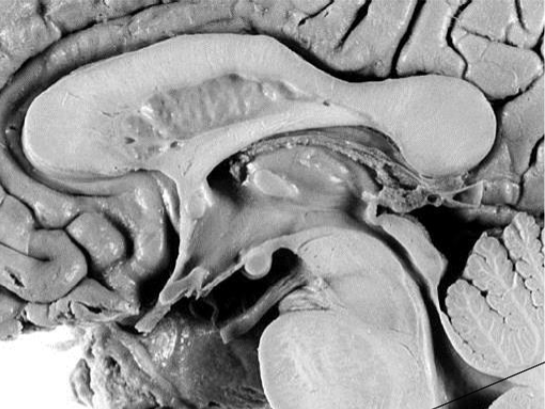
Optic chiasm
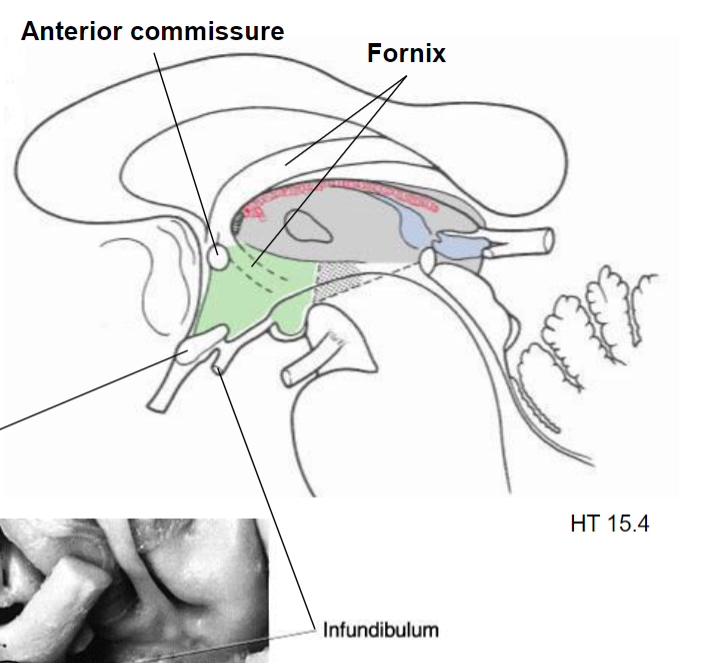
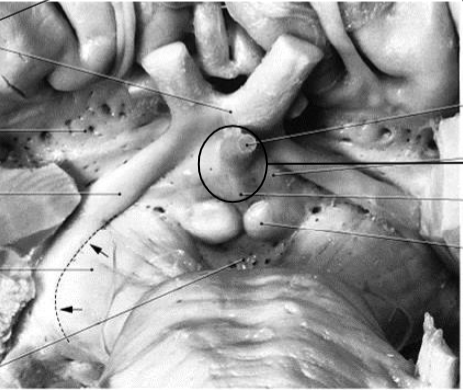
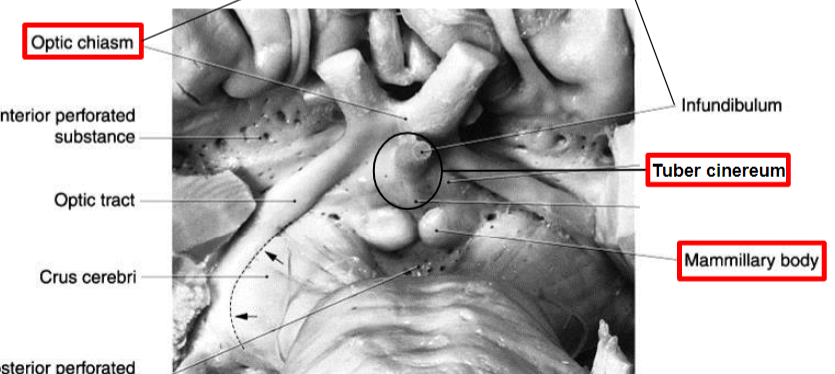
Preoptic area

ventrolateral preoptic n

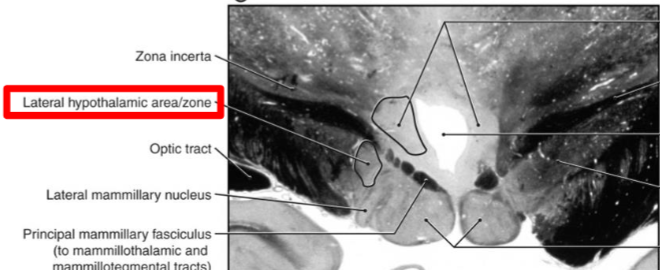
Lateral Zone

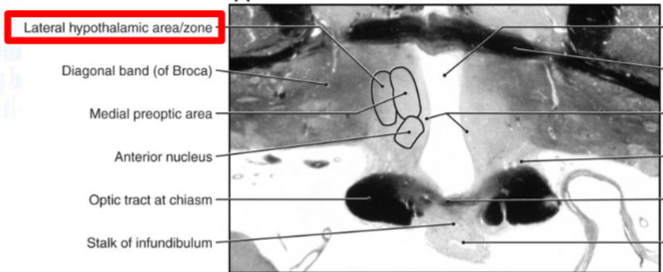
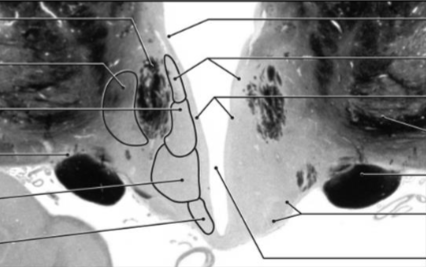
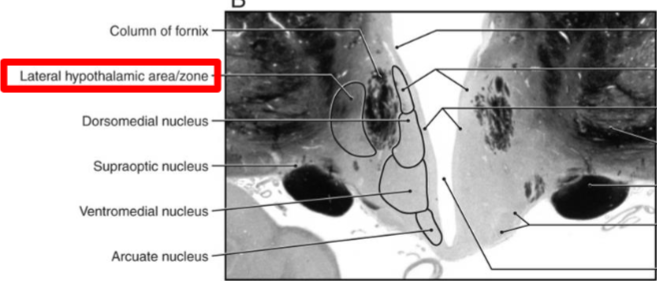
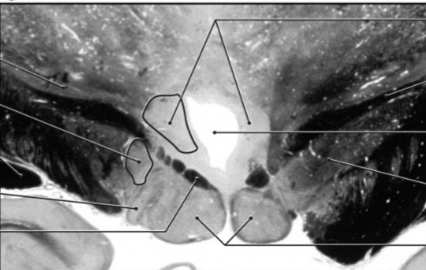
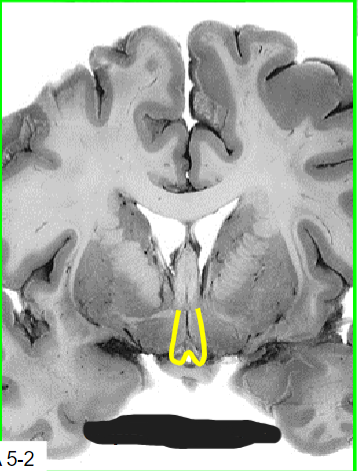
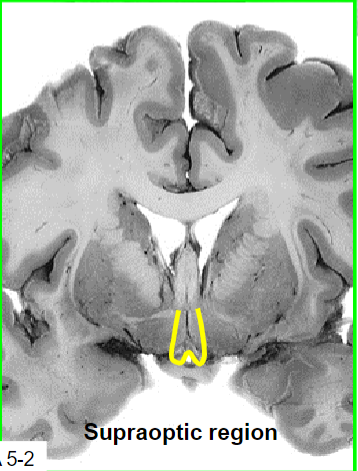
Medial zone, supraoptic region
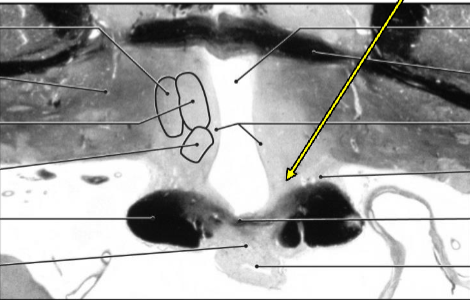

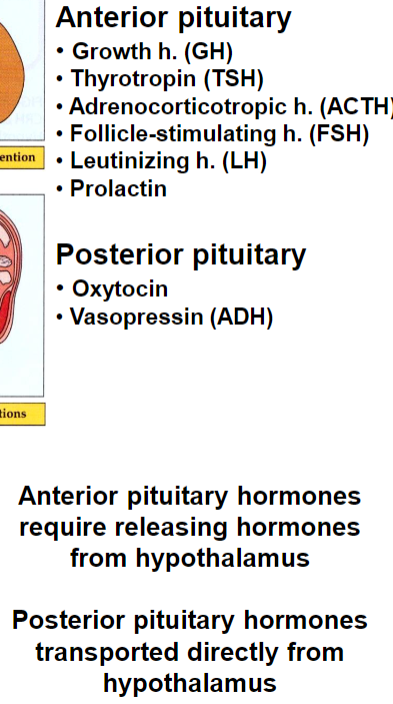
Oxytocin & vasopressin (ADH)
part of water balance reflex; respond to changes in blood osmolality
Lesion of the supraoptic or paraventricular nucleus, or shearing of the infundibulum/hypophysial stalk, leads to diabetes insipidus (excessive water consumption and excessive urination)
Oxytocin & vasopressin are also involved in uterine contraction, milk letdown, pair-bonding, and social cognition
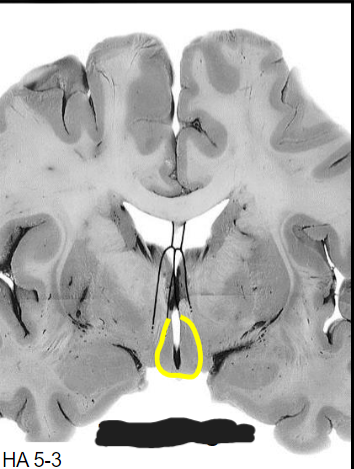
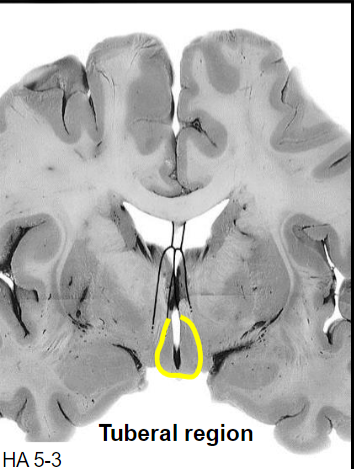
Medial zone, tuberal region

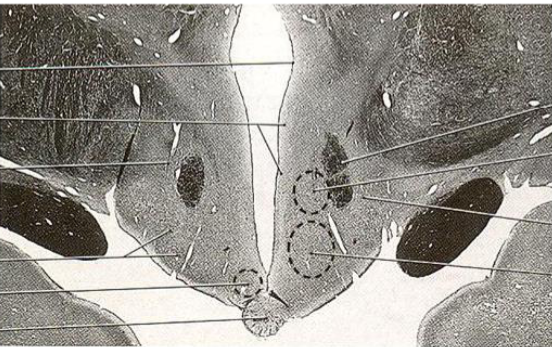
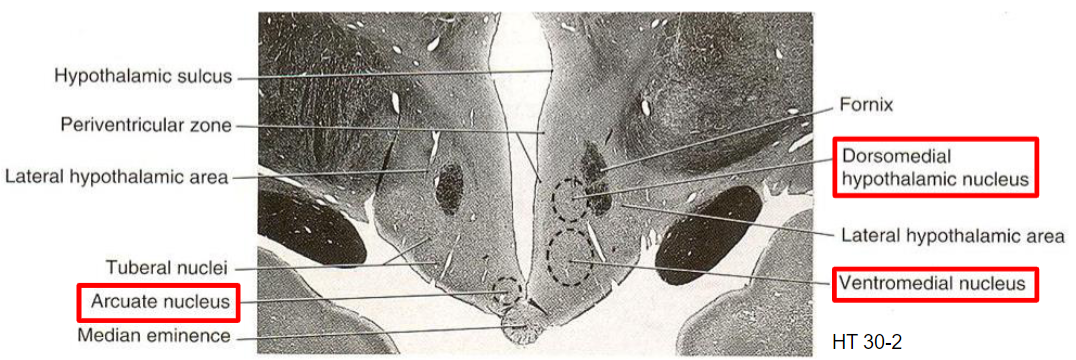
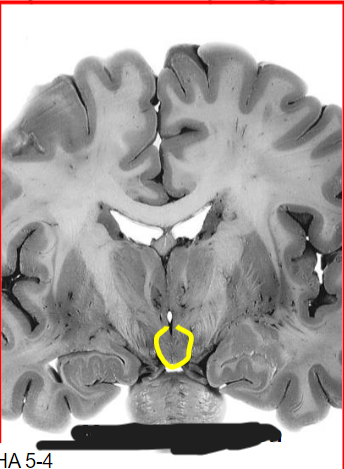
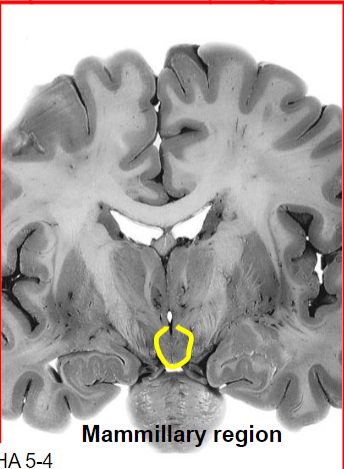
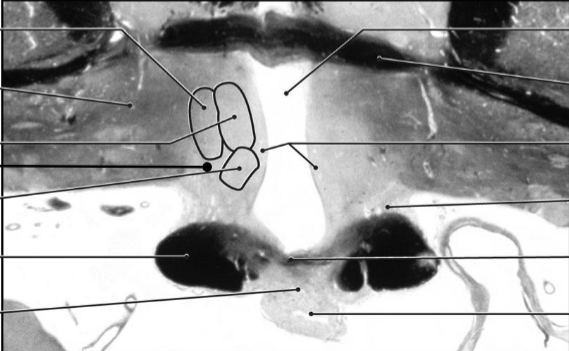
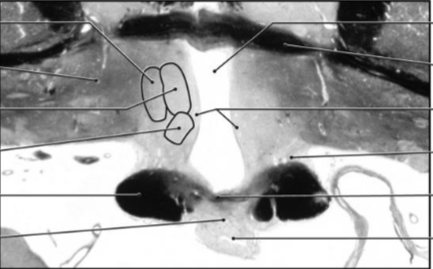
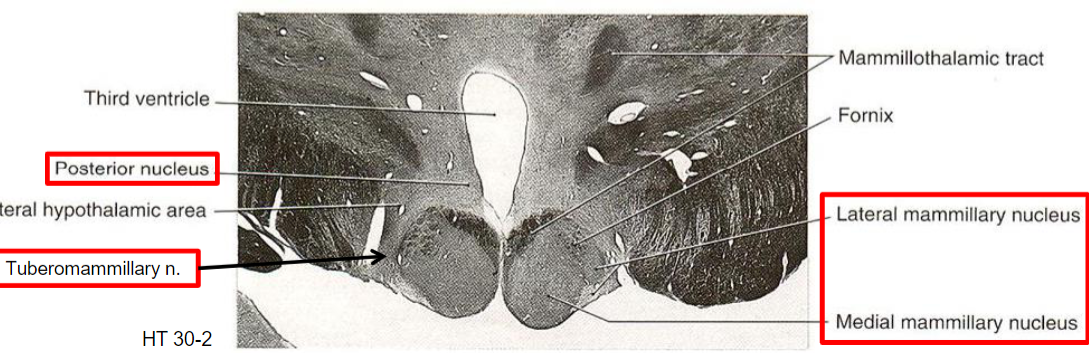
Medial zone, mammillary region

Periventricular zone
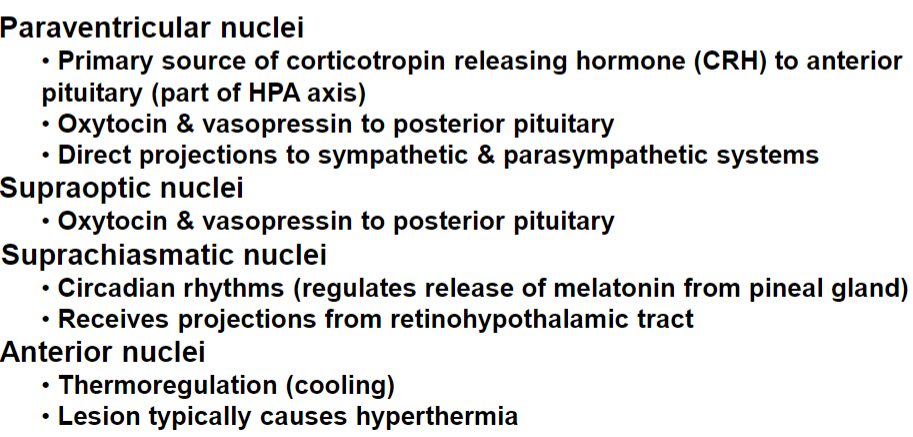
Periventricular nuclei:
Releasing hormones to anterior pituitary
Small projection to brainstem autonomic nuclei
Descending Efferent Projections from the Hypothalamus
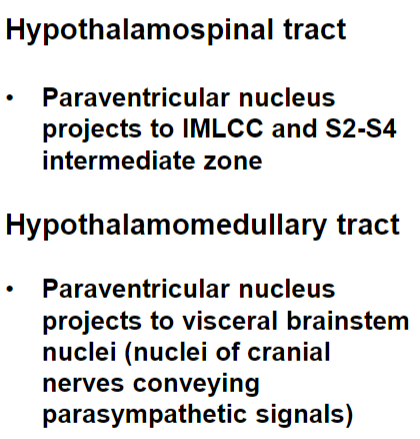
tuberoinfundibular tract

supraopticohyophysial tract

Anterior and Posterior Pituitary Hormones
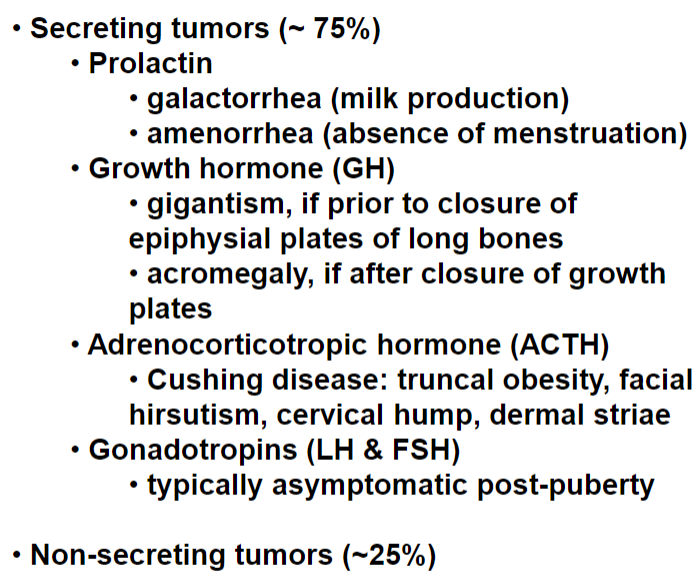
Pituitary adenomas
Bitemporal hemianopia
Pituitary Gland

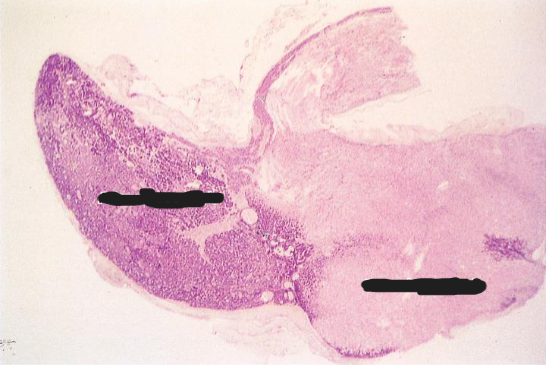
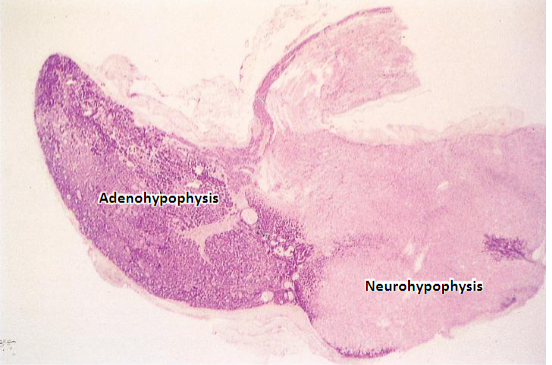
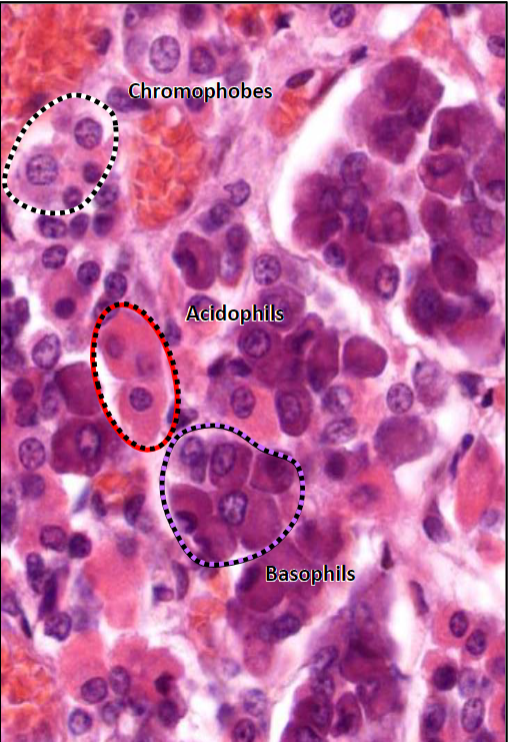
Adenohypophysis
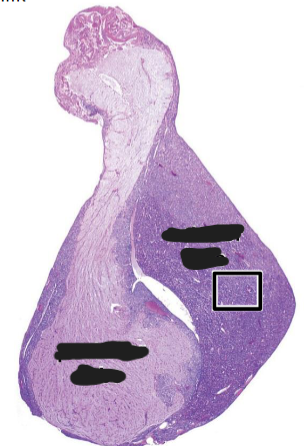
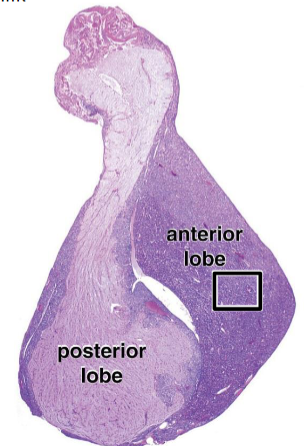
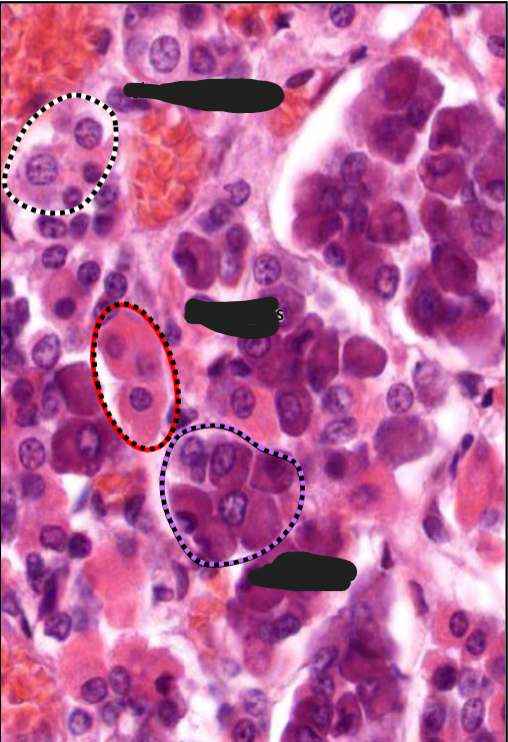
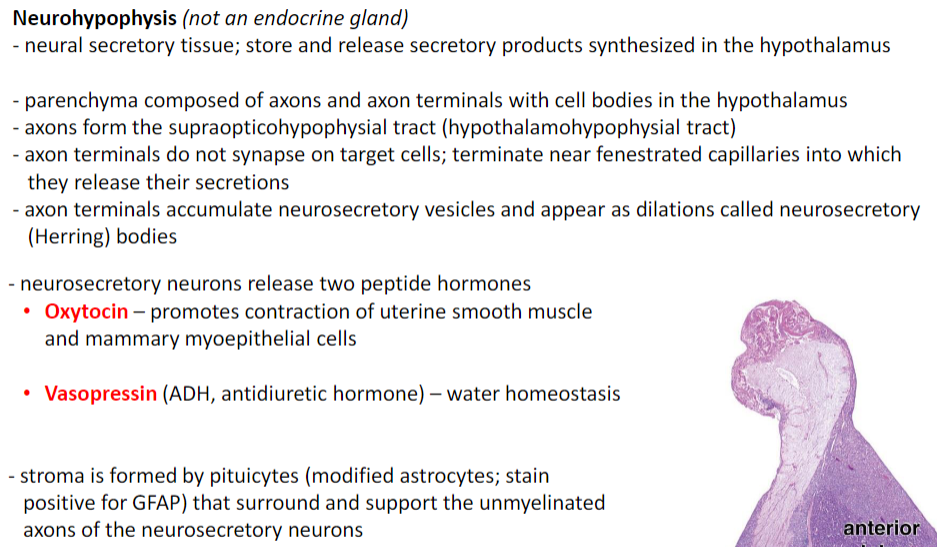
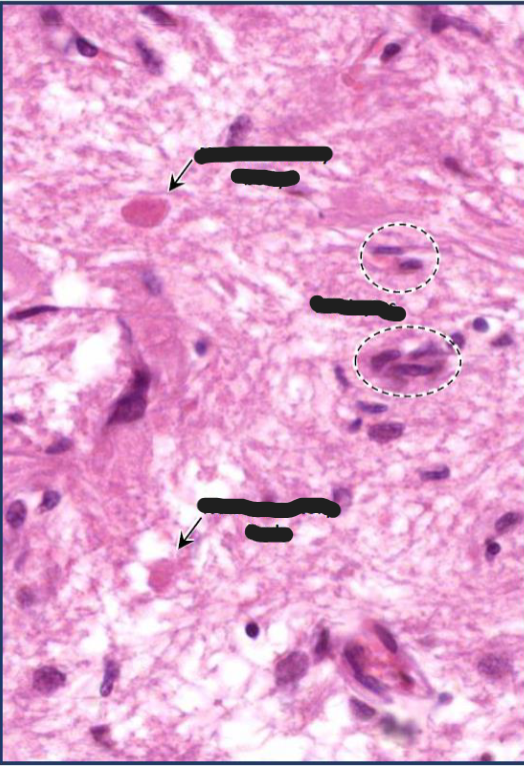
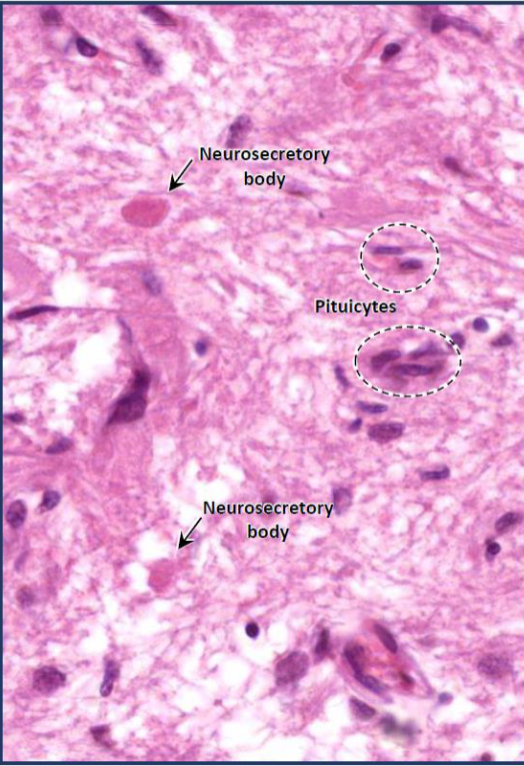
Neurohypophysis
Suprarenal Gland Overview
dense CT capsule; supported by reticular CT
outer cortex and inner medulla
adrenocortical insufficiency or Addison’s disease causes degeneration of the adrenal cortex while typically sparing the medulla
Most common cause is autoimmune

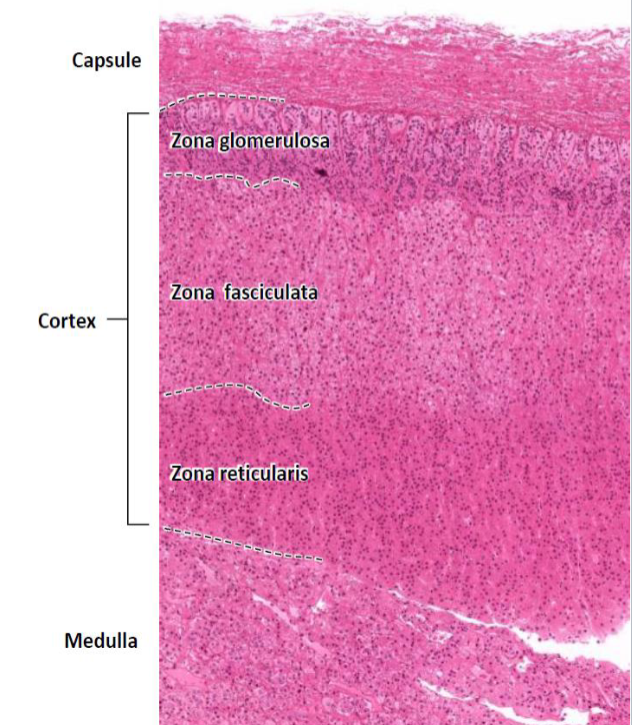
Suprarenal Gland

pheochromocytoma
rare, benign tumors of chromaffin cells
Production of excessive amounts of catecholamines causes potentially life-threatening hypertension and cardiac arrhythmias
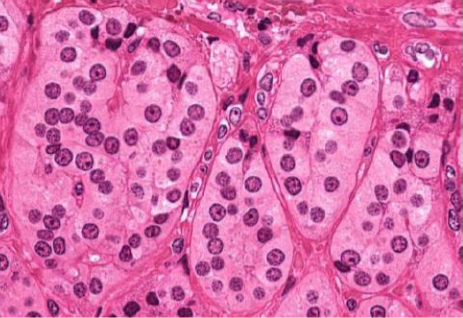
Zona Glomerulus: balls of cells
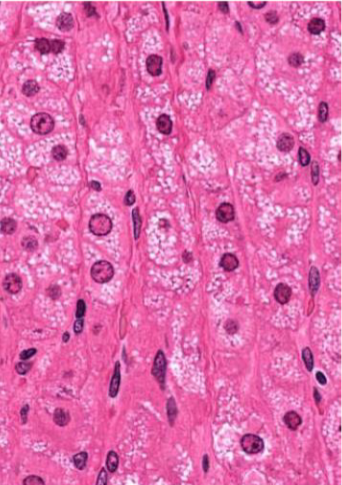
Zone fasciculus: ropes of cells
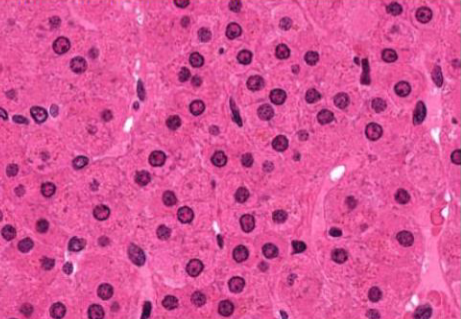
Zone reticularis: networks of cells
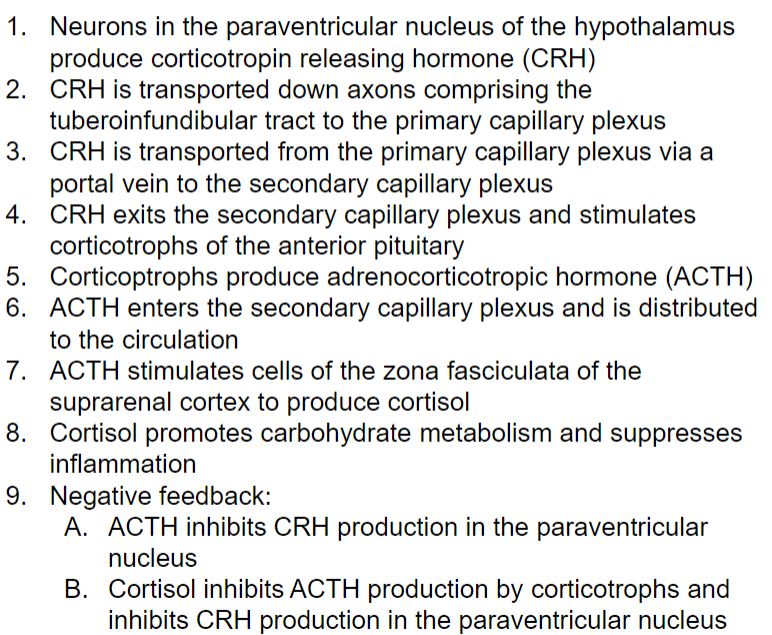
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis
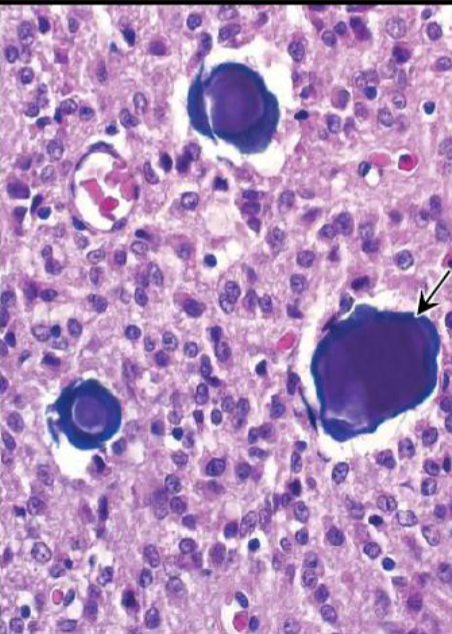
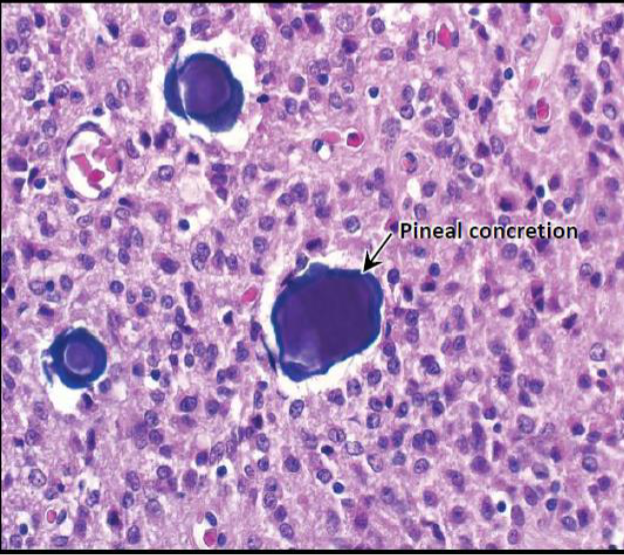
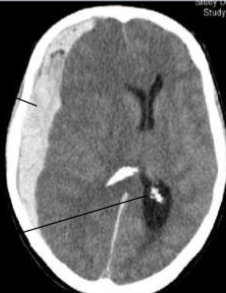
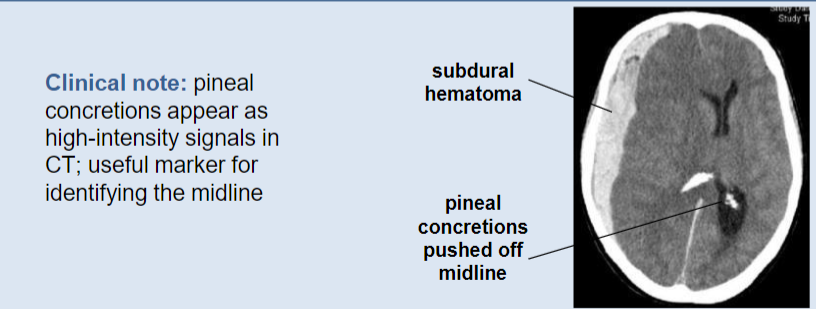
Pineal Gland