Altered Cells and Tissues
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PTT. 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What Are The Basic Components of a Cell?
Cytoplasm, Nucleus, Cell membrane.
Function of the Cytoplasm
Where cell works occurs, surrounds nucleus/holds organelles in a colorless fluid of water, nutrients, ions, gases, and wastes
Function of the Nucleus
Largest organelle; holds DNA, proteins, and enzymes. Controls metabolism/reproduction.
Function of the Plasma Membrane
Encloses cell; controls what comes in/out of cell. Made of lipids, carbs & proteins.
What are the 8 Organelles of a Cell?
Lysosome, Peroxisome, Proteosome, Ribosomes, Mitochondria, Golgi Apparatus, Endoplasmic Reticulum.
What are the 8 functions of the cell?
Movement, conductivity, ingestion, secretion, excretion, respiration, reproduction, communication.
Define Anabolism.
Energy using process of metabolism
Define Catabolism.
Energy producing process of metabolism.
What Are The 3 Stages of Cellular Metabolism?
Digestion → Glycolysis & Oxidation → Citric Acid Cycle
What is Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)?
Energy source used for muscle contraction & active transport of molecules across cellular membranes.
Facilitated Diffusion
Molecules move across the membrane with help from carrier or channel proteins, no energy needed.
Active Transport
Movement of molecules against concentration gradient (low → high) using energy (ATP) and transport proteins.
What are the three types of passive transport?
Diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis.
Passive Transport.
Movement of molecules across the cell membrane without energy, from high to low concentration.
Osmosis
Water moves through a semipermeable membrane along a concentration gradient, moving from an area of higher to one of lower concentration
Diffusion
Particles move from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration until equilibrium is reached.
What is endocytosis?
The process by which cells take in materials from their surroundings.
Types:
Phagocytosis
Pinocytosis
What is exocytosis?
When a cell releases substances from inside to outside the cell.
Four Types of Tissues?
Nerve, epithelial, connective, muscle.
Hyperplasia
Increase in the number of cells.
Metaplasia
Changing of one cell type to another.
Dysplasia
Actual change in cell size, shape, uniformity, arrangement & structure
Hypertrophy
Increase in cell size
Atrophy
Decrease in cell size
Define Morphology
The study of the form, structure, & shape of cells or tissues.
What Are Some Causes of Cellular Injury & Death?
Toxins, Infection, Physical, Serum deficit Injury. (TIPS)
What is Cell Injury?
Cells are not able to maintain normal or adaptive state.
•May be reversible/may be irreversible → cell death
Ischemia
Lack of blood supply to a tissue or organ.
What is free radical injury to cells and its main causes?
Cell damage from unstable molecules that steal electrons → UV/radiation, incomplete oxygen reduction, drug/chemical metabolism
What are asphyxial (hypoxic) injuries?
Injuries caused by lack of oxygen to tissues.
Cause: Can result from suffocation, choking, strangulation, or drowning.
Effect: Cells are unable to produce enough energy, leading to cell damage or death.
Key Term: Hypoxia = low oxygen levels in tissues.
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death that occurs naturally in the body.
Key Features:
Cell shrinks
Blebbing of the cell membrane
Nuclear fragmentation
DNA breakdown
Necrosis
Uncontrolled cell death caused by injury, infection, or toxins, often triggering inflammation.
Caseous Necrosis
A type of tissue death with a cheese-like appearance, often seen in TB.
Liquefaction necrosis
Necrotic tissue softens and turns liquid due to enzymes breaking down cells, most commonly in the brain.
What happens in fat necrosis?
Necrosis of fat tissue where lipases break triglycerides into fatty acids, which combine with ions to form chalky, opaque “soaps”. Often caused by trauma to fatty areas.
Coagulative Necrosis
Accidental cell death usually from ischemia or infarction, where cell structure is preserved because enzymes are denatured. Common in kidneys, heart, & adrenal glands.
What is gangrene?
Dead or dying body tissue(s) that occur because of inadequate blood supply.
Dry Gangrene
Minimal bacterial invasion, dry/wrinkled, dark brown or black tissue.
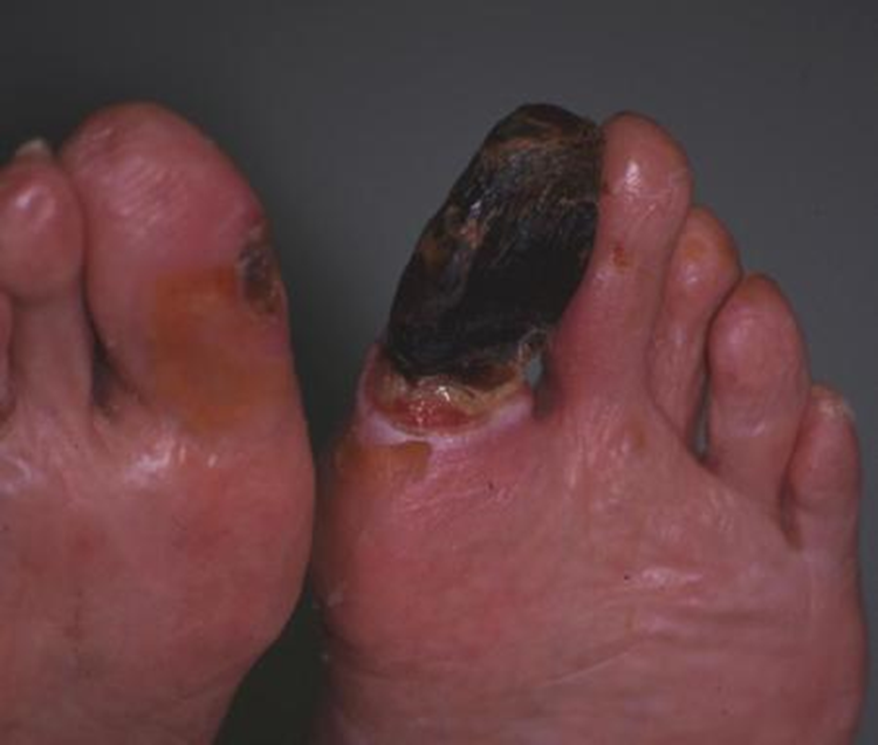
Wet Gangrene
Much lytic activity from bacteria, liquid center forms, internal organs as well as extremities affected.
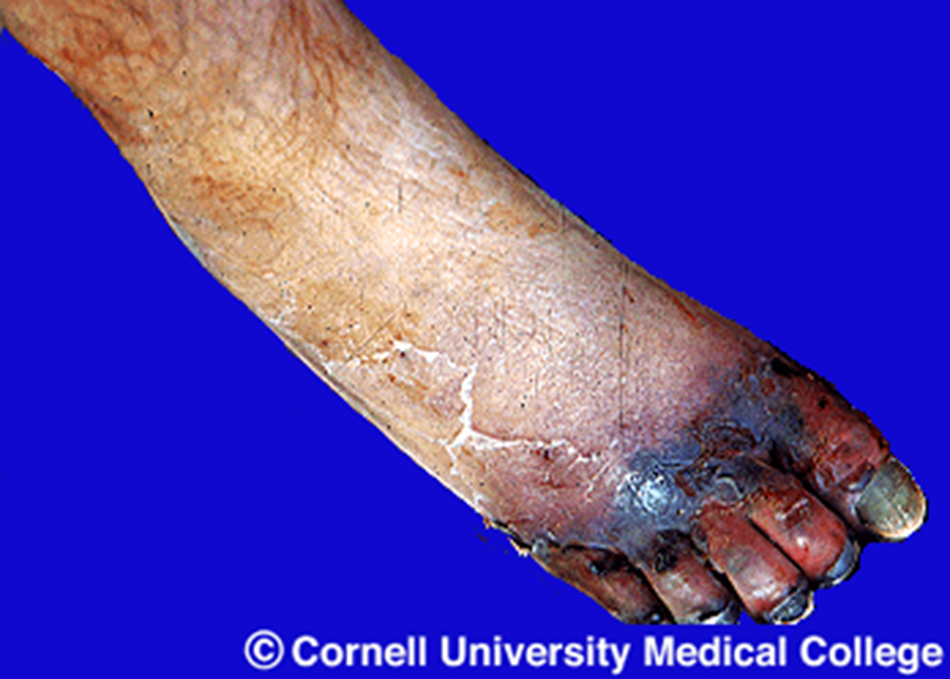
Gas gangrene
Anaerobic bacteria Clostridium w/ severe trauma, may be fatal, toxins released from bacteria, gas bubbles released.
Somatic Death
Death of the entire organism, marked by the permanent stop of respiration and circulation.