Chapter 17 Moisture, Clouds, Precipitation
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Water vapor
• Odorless, colorless gas
• Freely mixes with other gases
• Can change from one state of matter to another
Waters changes of states
Ice, liquid water, water vapor
Calorie
Amount of energy required to raise 1 gram of water 1 degree Celsius
Latent Heat
Energy absorbed or released during a change of state
Mixing ratio
Mass of water vapor in a unit of air compared to remaining mass of dry air
Relative humidity
• Ratio of the air’s actual water vapor content to its water vapor capacity (at a given temperature and pressure)
• Adding or removing water vapor
• Varies with temperature
Dew point temperature
Temperature to which air has to be cooled in order to reach saturation and then begin to condense
Adiabatic Temp changes
Cooling or warming of air caused when it expands/compresses, not because heat is added/subtracted
- Parcel – few hundred cubic meters, independent of surrounds
• Dry: rate of cooling/warming in unsaturated air
• 1°C per 100 meters
• Wet: rate of temperature change in saturated air

Orographic lifting
Air forced to rise over a mountain or barrier
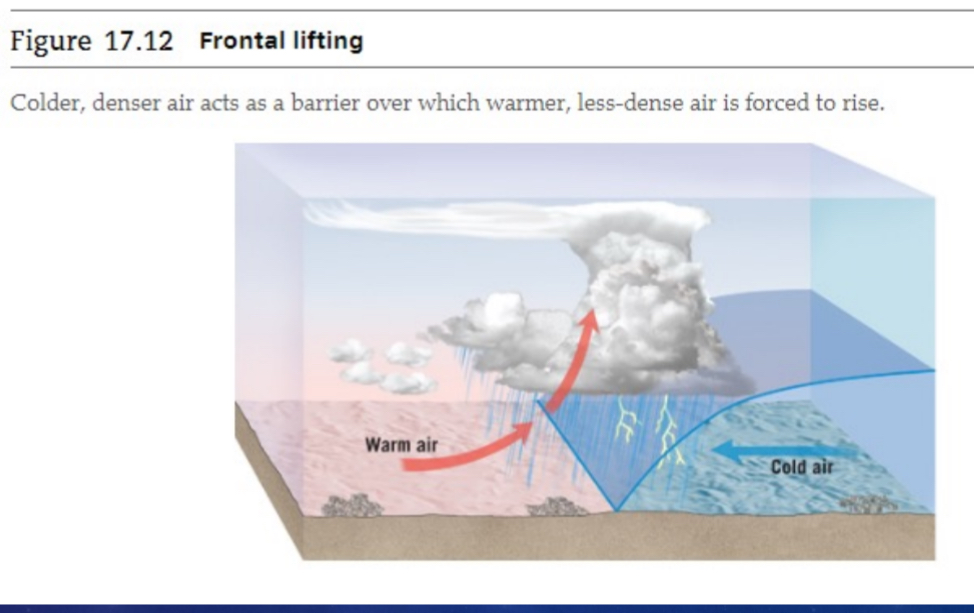
Frontal lifting
Warmer, less-dense air forced over cooler, denser air

Convergence
Pileup of horizontal airflow resulting in upward movement
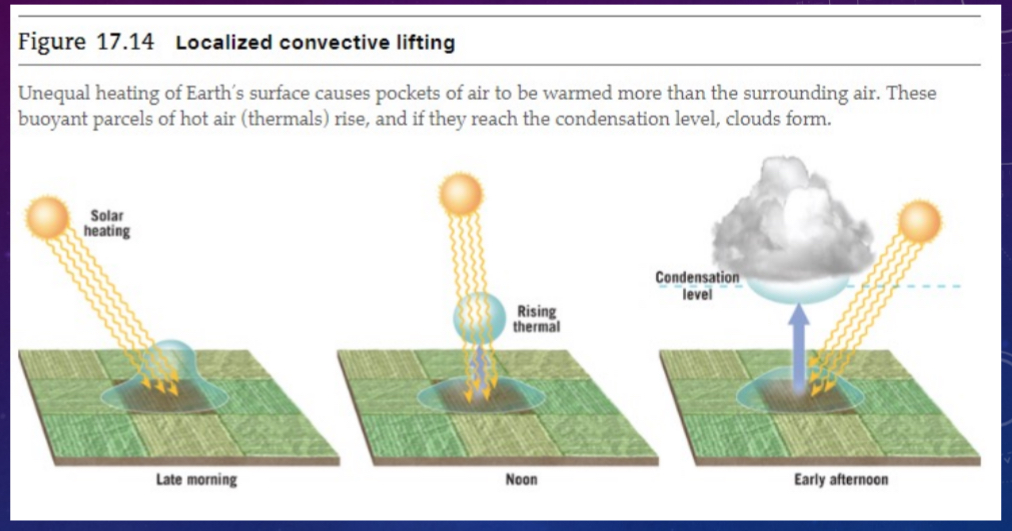
Localized convection lifting
Unequal surface heating causes localized pockets of air to rise due to buoyancy
Stable air
air that resists vertical displacement
Unstable air
air that does not resist vertical displacement
Cloud condensation nuclei
microscopic particles that serve as surfaces on which water vapor condenses
Hygroscopic nuclei
those that have a high affinity for water, such as salt particles; will absorb water
Clouds
visible aggregates of minute droplets of water or tiny crystals of ice
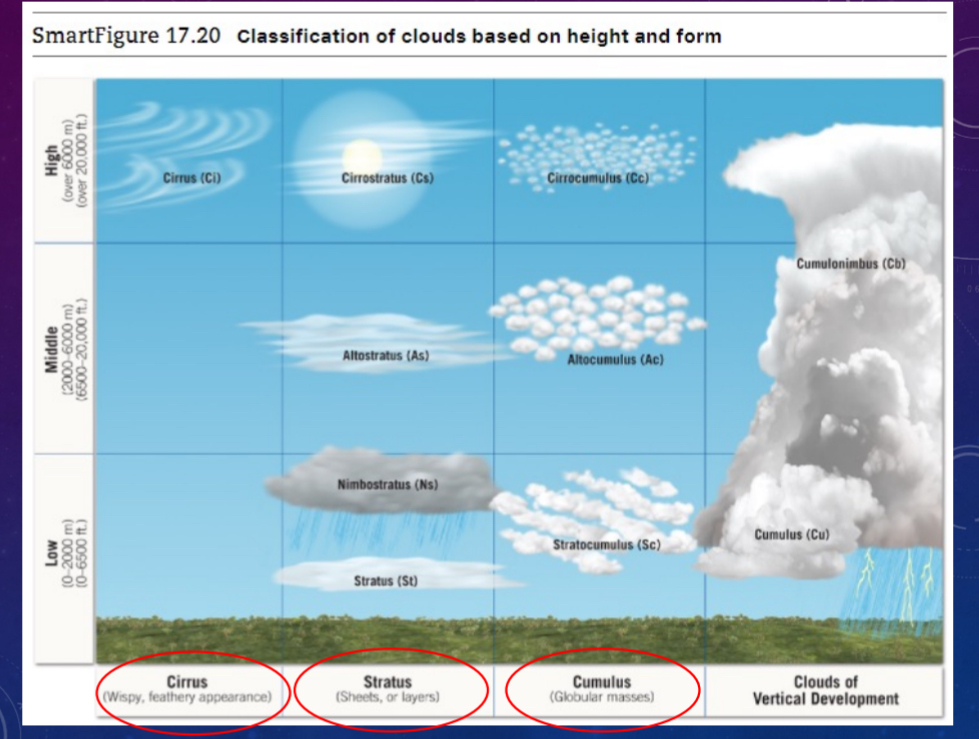
Cloud types
How precipitation forms
Cloud droplet grow to larger precipitation