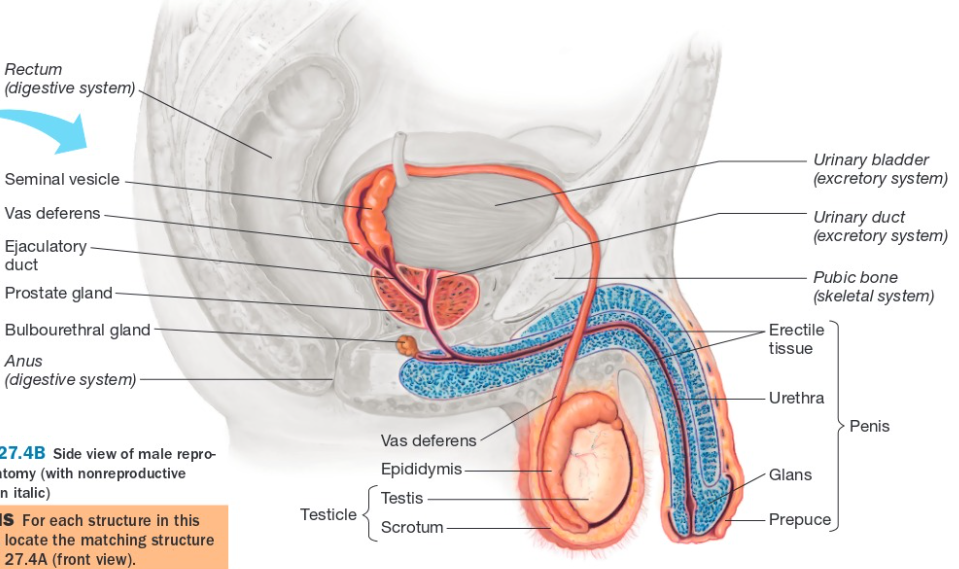
The Male Reproductive System
1/19
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
testes
the male gonads that produce immature sperm
scrotum
a sac that contains the testes outside of the body
testicle
testes + scrotum
what is the role of the scrotum?
the sperm can only be formed in temperatures slightly cooler that the body temperature; the scrotum helps keep the cells that make sperm cool since it’s outside of the body.
if it’s cold, however, the muscles in the scrotum contract, bringing the testes closer to the body, to bring more heat to the testes in order for sperm to be produced properly
epididymis
coiled tube that takes in the immature sperm made from the testes and develop the immature sperm until they are matured.
matured sperm are stored here.
ejaculation
the process of expelling fluid with sperm from the penis through contractions that push the sperm from the epididymis through the vas deferens
vas deferens
a pathway which the sperm travels through that connects from the epididymis up and around the bladder
ejaculatory duct
a short pathway made through the convergence of the vas deferens and the seminal vesicle into the urethra
urethra
the path through which urine and the sperm come out through the penis
the three main glands in the male reproductive system
seminal vesicle, prostate gland, bulbourethral glands
seminal vesicles
a pair of short ducts that secrete mucus with fructose that provide the sperm energy to travel through the female reproductive tracts
prostate gland
a structure that secretes this thin, whitish fluid that ensures the sperm stays healthy
bulbourethral glands
structure that secretes clear, alkaline (basic/ bitter) mucus, a fluid that is travels through the penis before ejaculation that contains some sperm
semen
fluid made of sperms and fluids and mucus secreted by the 3 glands during orgasm (a point of climax in which there is involuntary movements of the reproductive tissues in organ)
why is it beneficial that the semen is more basic?
a more basic semen neutralizes the acid in leftover urine in the urethra as well as in the vagina, preventing the sperm from dying
penis
male reproductive organ with a shaft with erectile tissue with a head with sensitive glans
the prepuce for men, the foreskin that covers the head, is typically removed through circumcision
erection
the firmness of the penis due to the high amounts of blood flushing into the organ creating great pressure on the veins, blocking it from transporting blood back
impotence (erectile dysfunction)
inability to have an erection
causes of impotence
age
drugs
alcohol
psychological issues
nervous system issues
circulatory system issues
male reproductive system (overall)