Intergumentary systems
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What are the two main tissues of the skin?
Epithelial tissue (epidermis) and connective tissue (dermis).
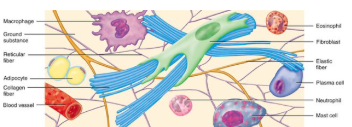
Connective tissues
Most abundant and widely distributed
Binds structures and provides support and protection, stores fat, fills spaces, makes blood cells, protects against infections and repairs tissue damage
Cells are spread apart with an abundance of extracellular matric lying between them
Largest organ
The skin is made up of 2 square metres and weighs 4.5 KG
What makes up the intergumentary system
The skin and its associated structures and organs
2 types of tissues of the skin
Epithelial tissue
Connective tissue
2 distinct layers of the skin
Epidermis (Made up of stratified squamous epithelium)
Demis (Made up of connective tissues, smooth muscle tissue, nervous tissue and blood)
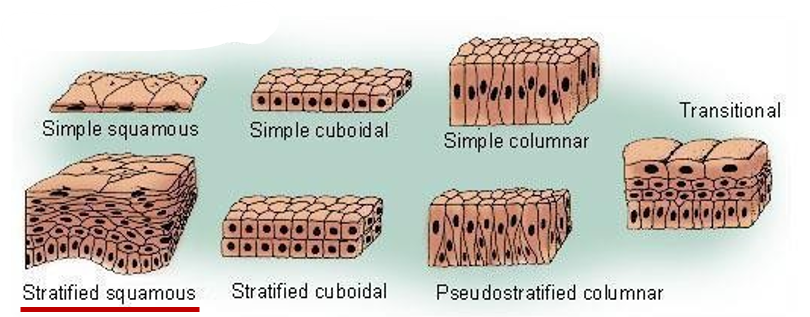
Types of epithelium
Stratified squamous epithelium: Many cell layers which makes the tissue relatively thick
Cells divide in the deeper layers and new cells push older ones farther outward where they flatten
Epidermis (superficial layer of skin)
Functions of the skin
Protection and touch
Protective barrier against microorganisms
Sense of touch arises from the nerves within the skin
Temperature regulation
Key role for homeostatic mechanism which regulates body temperature
Synthesis of vitamin D
Wound healing
Depends on the nature and extent of the injury excretion and absorption
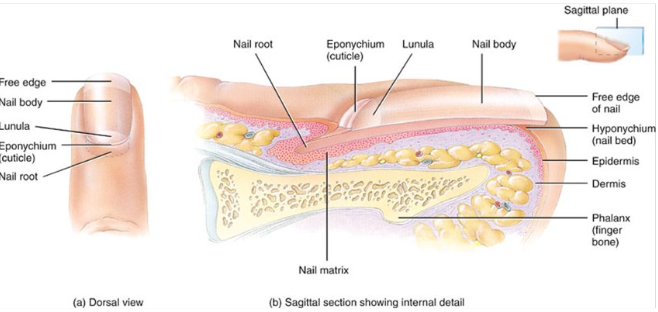
Structure of nails
Purpose is to protect coverings
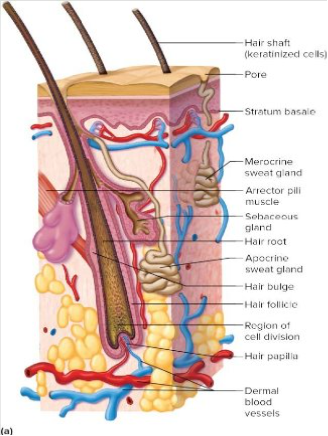
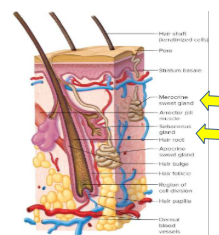
Structure of hair follicles
Each hair develops from a group of stem cells at the base of a hair follicle
Hair follicle contains a hair root which can extend into the subcutaneous layer
The hair will stand up due to cold temperatures6
Exocrine glands
Secretes substances into ducts and onto the surface (sweat, saliva, mucus and milk)
Examples of exocrine glands
Sweat glands-Sudoriferous glands
Oil glands-Sebaceous glands
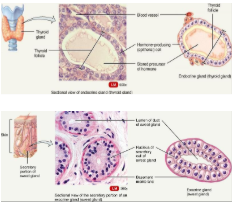
Exocrine VS endocrine glands
Both are made up of epithelial tissue
Exocrine glands secrete substances into the interstitial fluid and bloodstream (hormones)
Exocrine glands secretes substances into the ducts and onto the surface (sweat, saliva, mucus and milk)