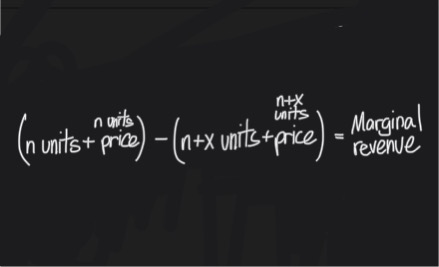Economics | Introduction to Economics Review
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Economics
The study of scarcity—how people try to satisfy what appears to be unlimited wants through careful use of limited resources
Time, money, clothes, food, and shelter are examples of what?
Scarcity
Air, sleep, and shelter are examples of what?
A need
A want is a way of expressing what?
Desire
Utility
Capacity to be useful or provide satisfaction
What does the paradox of value mean?
Some necessities have little monetary value, while some non-necessities have much higher monetary value
According to the paradox of value, for something to have value, what two things must it be?
It must be scarce and have utility
Wealth is the accumulation of tangible products that have what characteristics?
Scarce, useful, and transferrable from one person to another
According to the trade offs and opportunity cost definition, there are ___ & ___ to everything we do.
Benefits & costs
Trade offs are
alternative choices
What economic question is being answered if a company chooses to produce pencils as a product?
What to produce?
What economic question is answered if a company chooses to hire people to produce pencils?
How to produce?
What economic question is answered if a company chooses to sell their pencils to highschool students?
For whom to produce?
Natural resources, livestock, sunshine, and climate (fixed) are examples of what factor of production?
Land
Tools, equipment, machines, factories that produce capital goods are examples of what factor of production?
Capital
What is capital a result of?
Production
People working (varies in size) is an example of what factor of production?
Labor
Innovators responsible for much of the change in the economy are examples of what factor of production?
Entrepreneurship
What is the process of creating goods and services when all four factors are present?
Production
This diagram represents various combinations of goods and services an economy can produce when all productive resources are fully employed
The production possibilities curve (or PPC/PPF)
One thing the PPC shows: identifying possible ___
opportunities
One thing the PPC shows is: fully employed ___
resources
One thing the PPC shows is: ___ cost
opportunity
One thing the PPC shows is: the cost of ___
choice
One thing the PPC shows is: ___ growth
economic
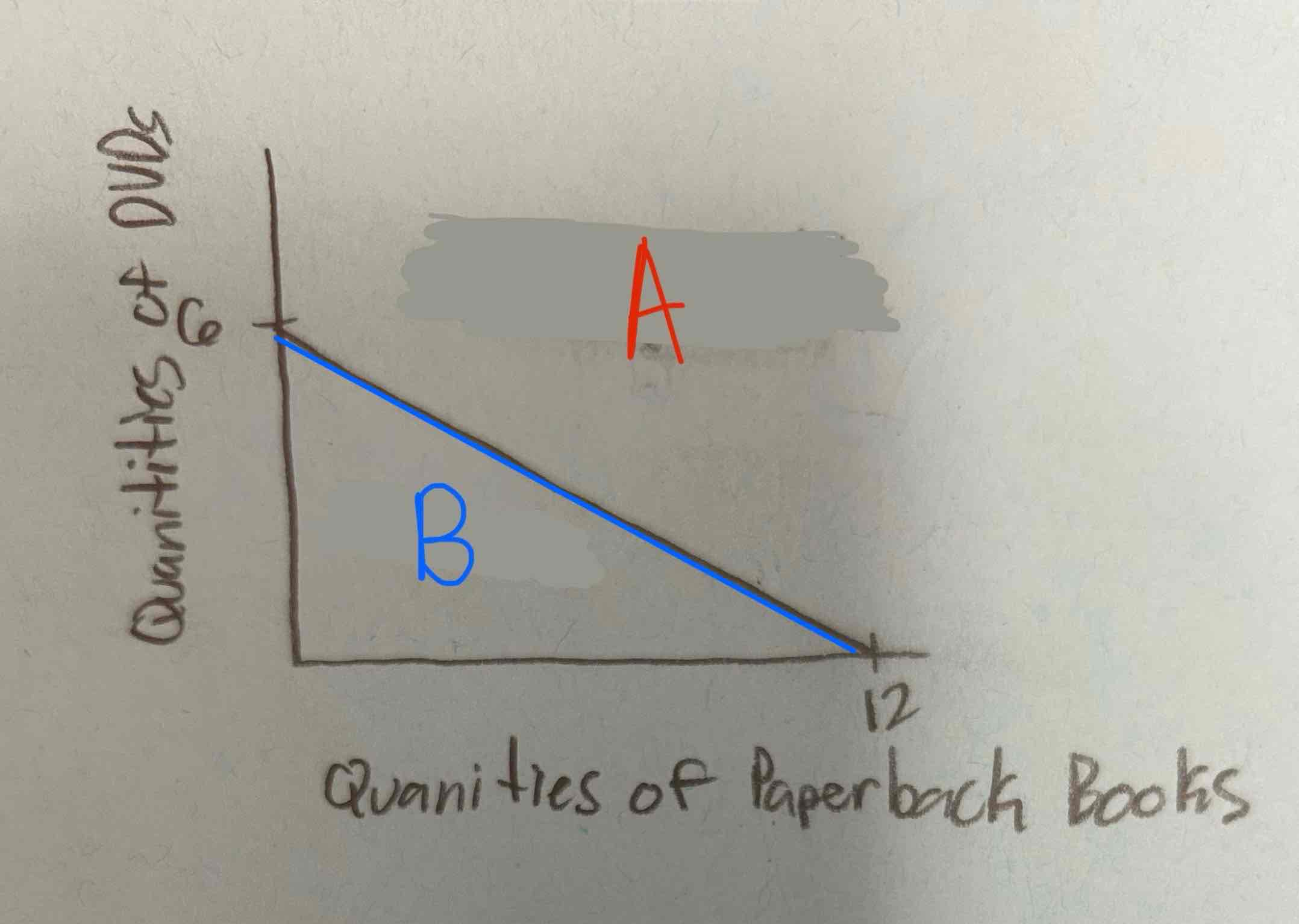
Look at the following PPC curve of a bookshop.
What spot on the graph is attainable?
B
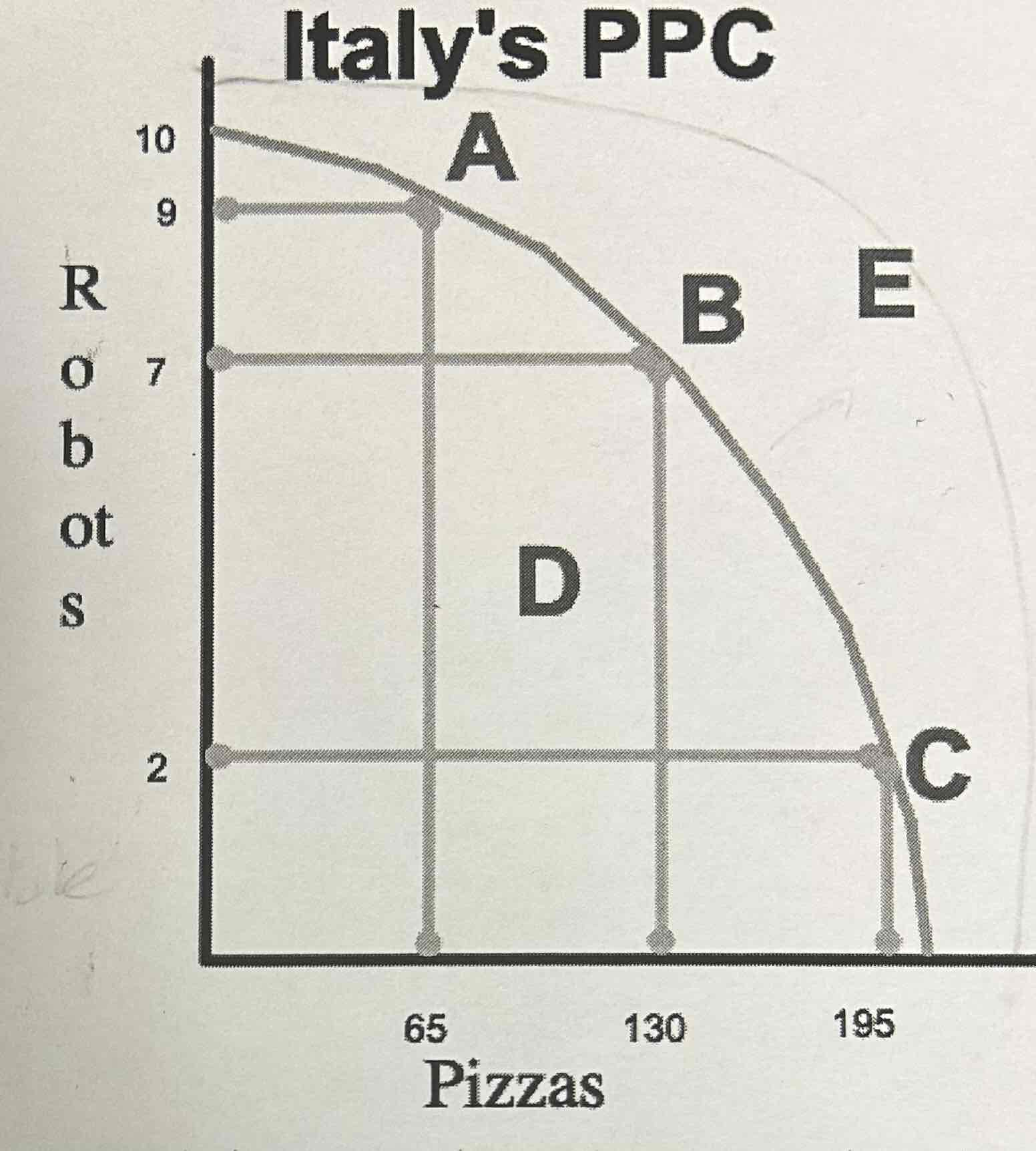
The following graph shows Italy’s PPC
What point(s) are attainable and desirable?
A, B, & C because they fall on the curve which means that resources are being used efficiently
The following graph shows Italy’s PPC
What point(s) on the graph are attainable, but not desirable?
D is attainable, but it’s not desirable because it falls below the curve which means resources aren’t being used efficiently
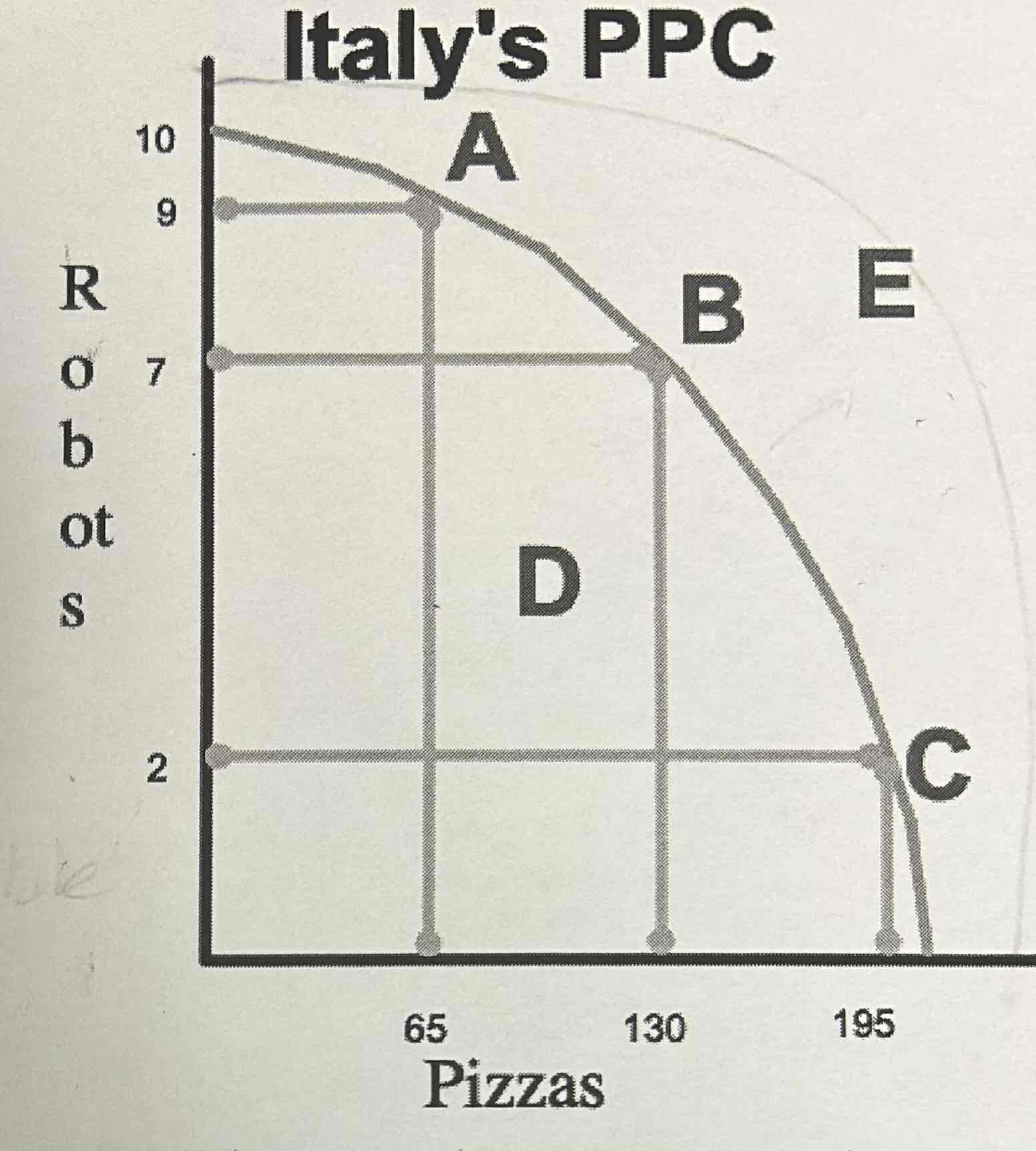
The following graph shows Italy’s PPC.
Which point(s) are unattainable? Are these points desirable?
E is unattainable, but desirable. This point can be attained by increasing factors of production.
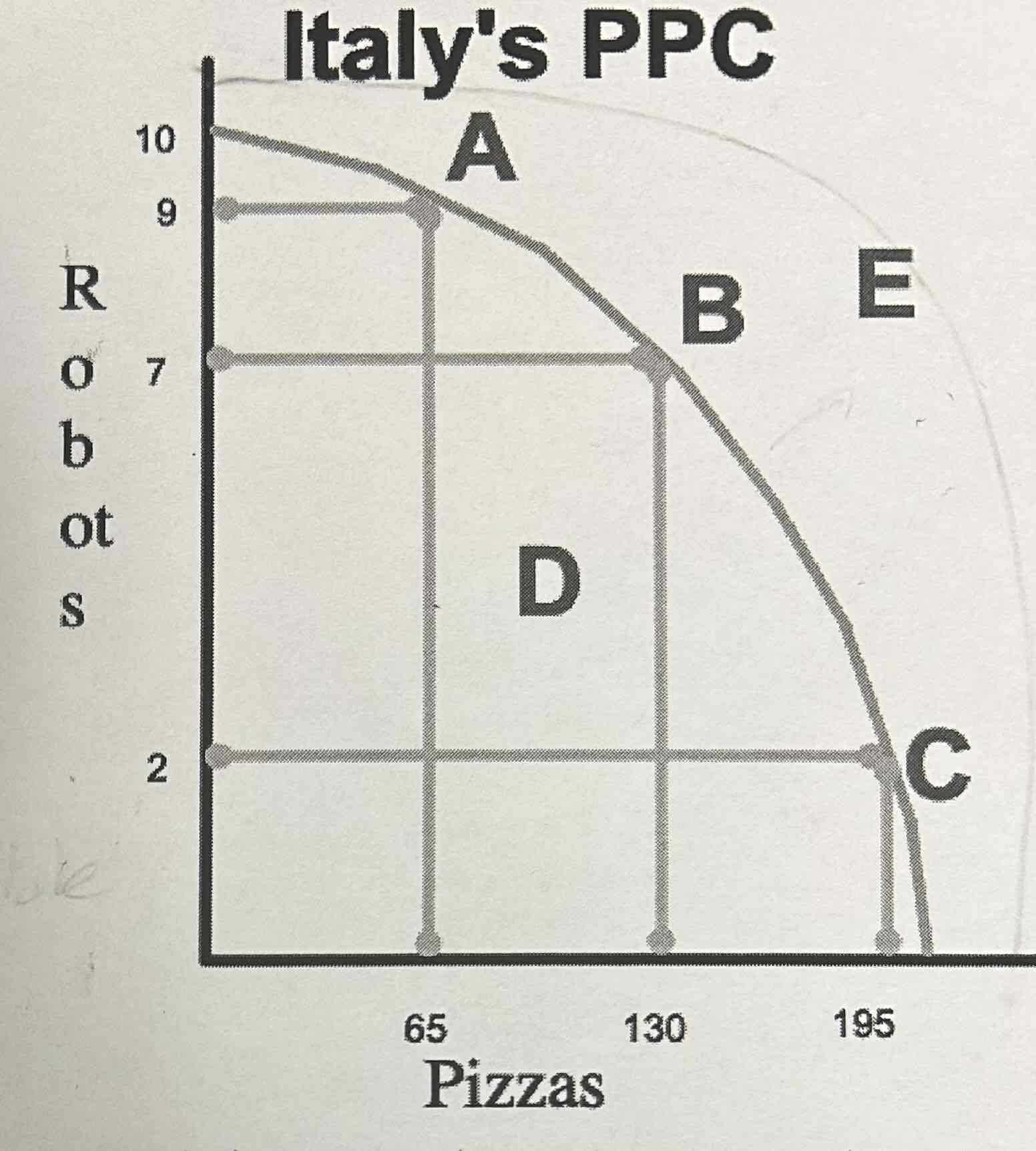
The following graph shows Italy’s PPC.
Which point means more consumption in the future?
E
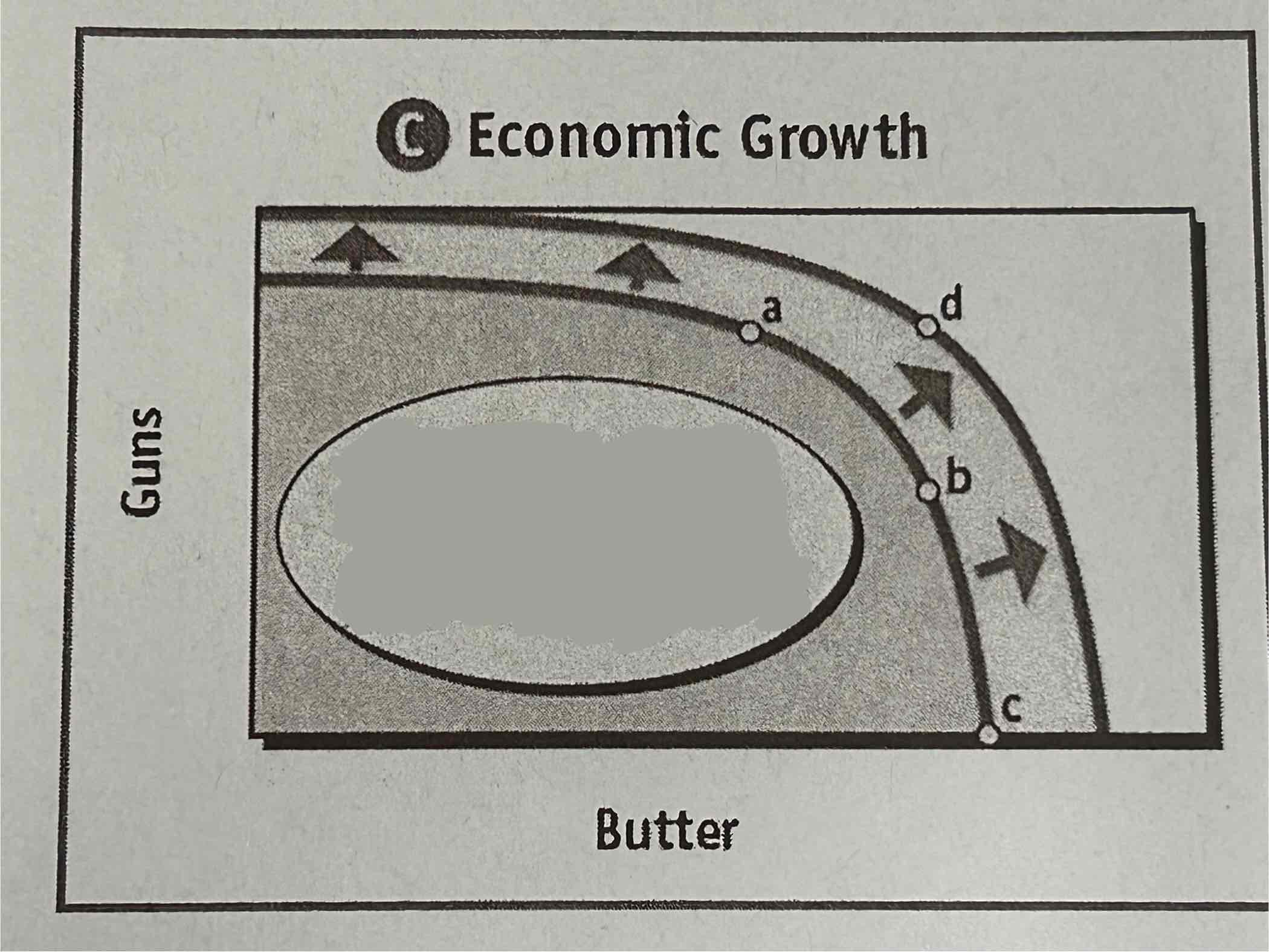
The PPF below is showing how production possibilities could expand.
How can production possibilities expand?
By increasing the factors of production
Economic Systems
Organized way where a nation provides for the wants and needs for its people
What happens in the factor/resource market?
Households sell, firms buy
What happens in the product market?
Firms sell, households buy (products and/or services)
Traditional economies
An economy where tradition determines how the economy functions and how resources are distributed
Command economy
An economy where the central authority makes decisions
Market economy
An economy where a county’s people and businesses act according to their self interests
Mixed economy
A mix of the command & free market economies
What type of economy are most economies today?
Mixed economy
What makes the U.S. a mixed economy? Give an example.
People have the freedom to sst up a business, however the government regulates what businesses can exsist.
What is the revenue gained by producing one additional unit of a good or service
Marginal revenue
What is the cost added by producing one additional unit of a product or service?
Marginal cost
Marginal cost equation
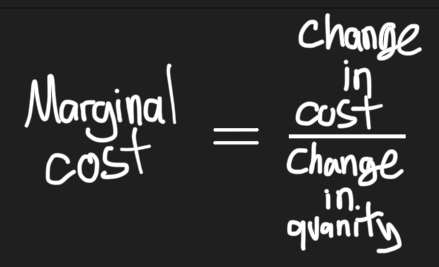
Marginal revenue equation