(CIE A2 Biology) Desired gene isolation (based on SaveMyExams revision notes)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
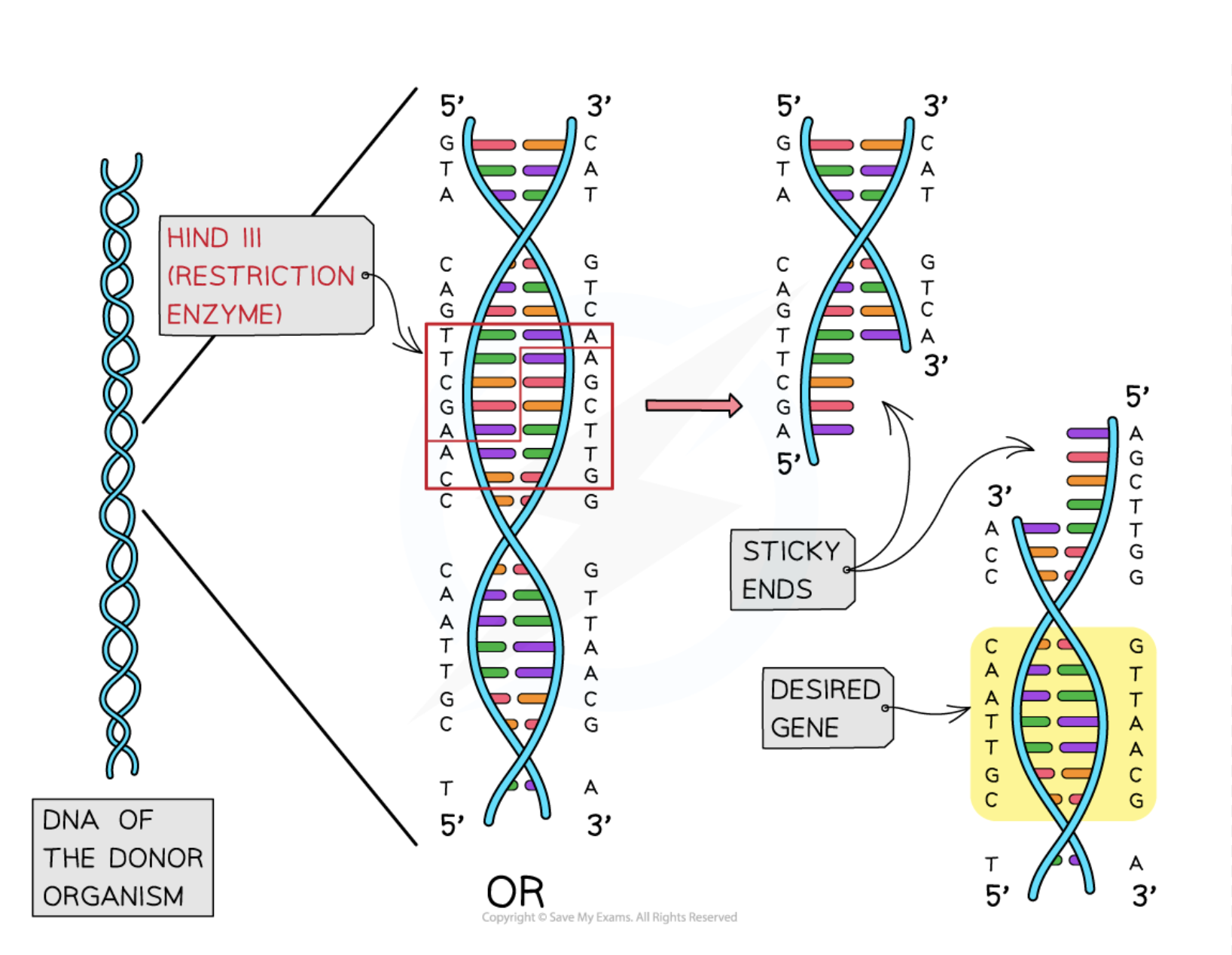
Restriction Endonucleases
A class of enzymes found in bacteria that cut viral genetic material and isolate genes from donor DNA.
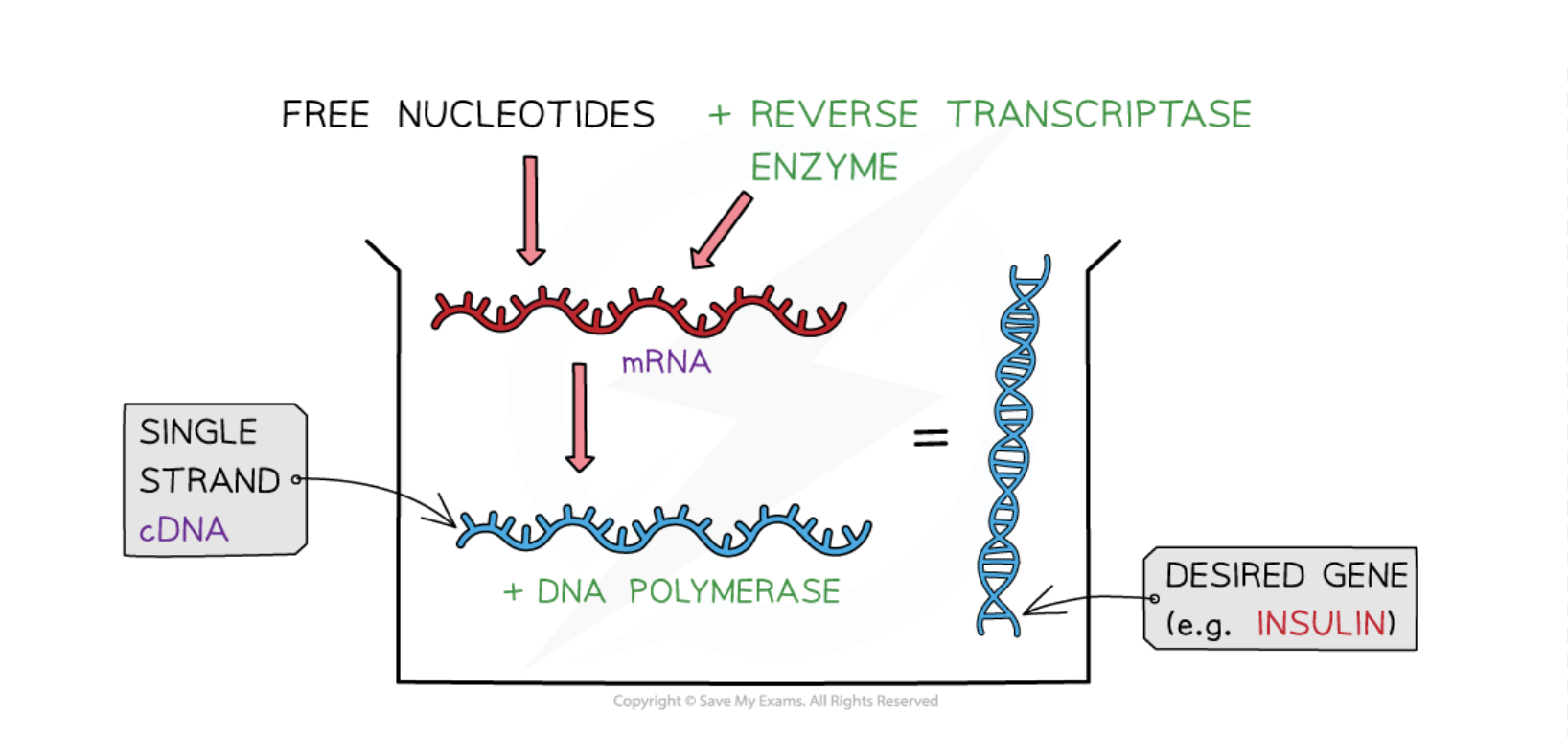
cDNA (complementary DNA)
Single-stranded DNA synthesized from mRNA using reverse transcriptase.
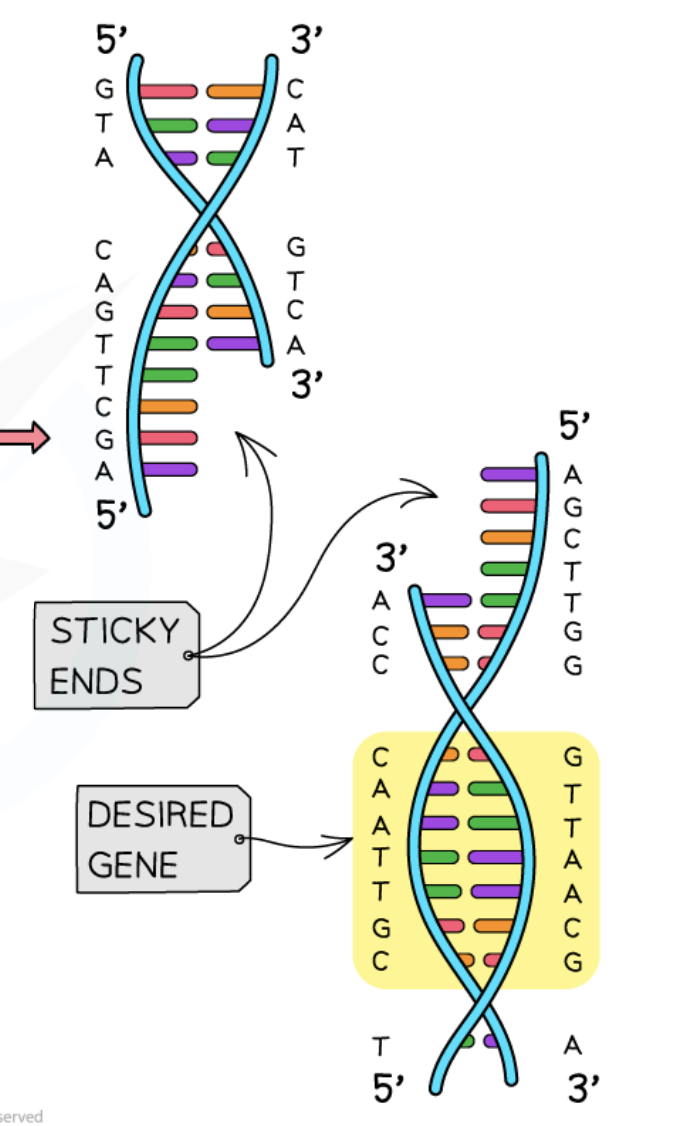
Sticky Ends
DNA fragments with overhanging sequences that facilitate easier insertion of genes into other DNA.
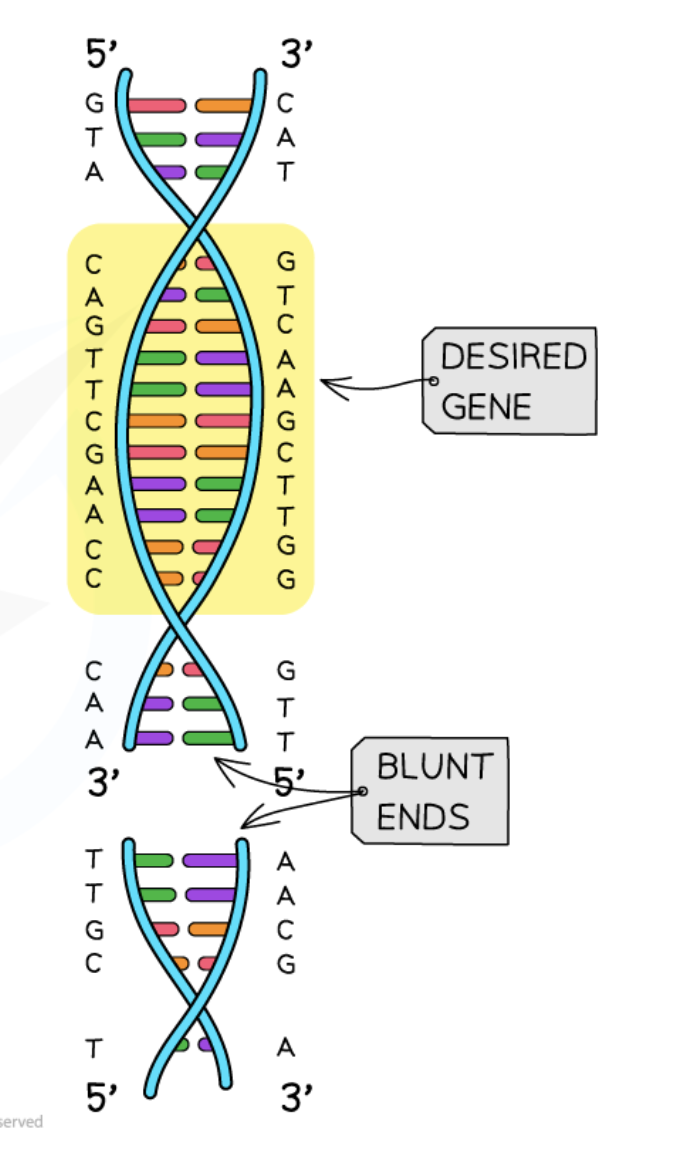
Blunt Ends
DNA fragments with straight cuts in the sugar-phosphate backbone, making them less efficient for insertion.
Reverse Transcriptase
An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of mRNA into cDNA.
DNA Polymerase
An enzyme that converts single-stranded cDNA into double-stranded DNA.
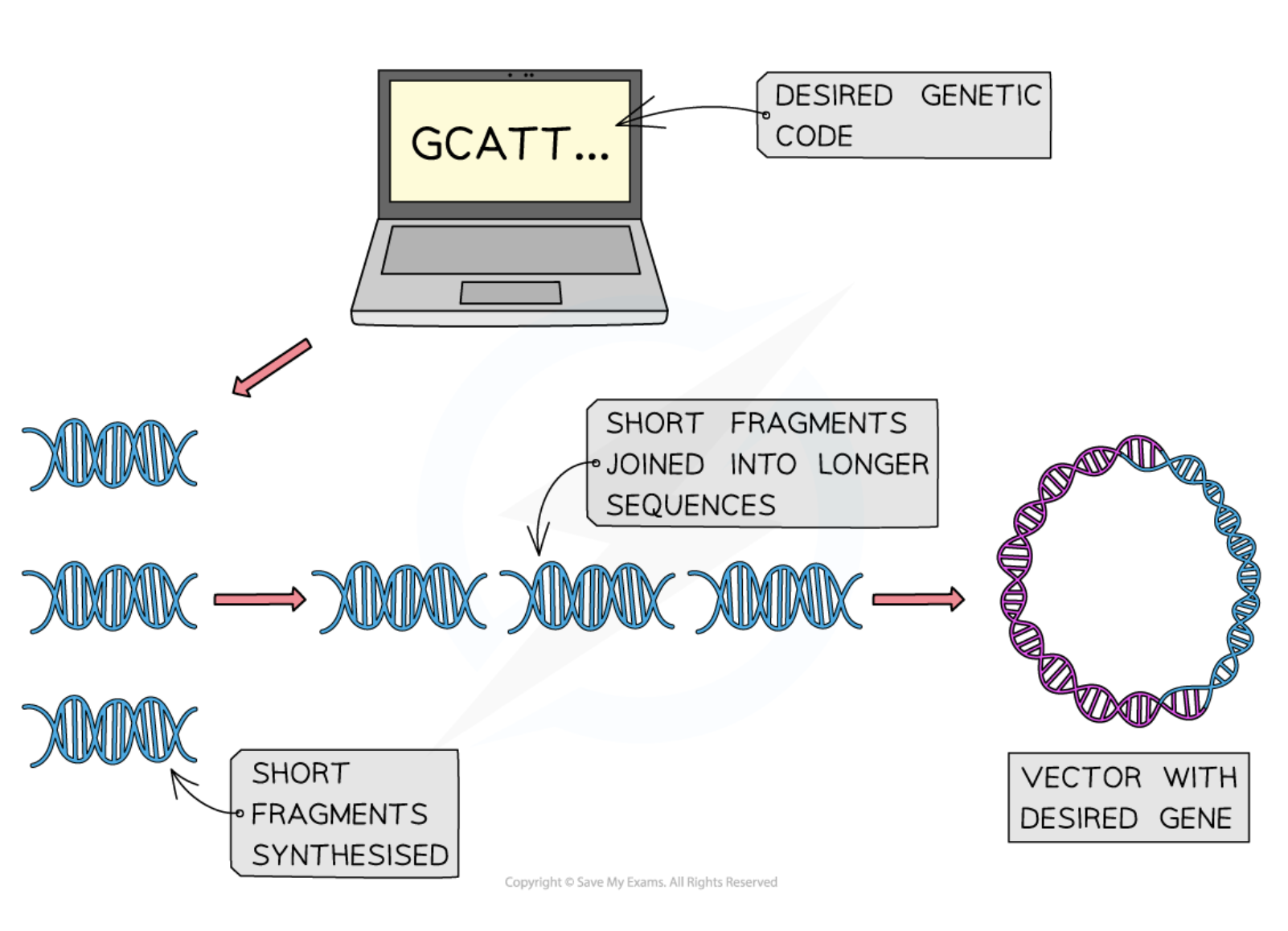
Artificial Gene Synthesis
The process of creating genes using computers to generate nucleotide sequences based on known genetic codes.
Retroviruses
Viruses that use reverse transcriptase to transcribe their RNA into DNA.
Nucleotide Sequence
A specific order of nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule that encodes for genes.
Vector
A vehicle, such as a plasmid, used to artificially insert genes into an organism.