Topic 2: Hardy Weinberg & Changes in Gene Pools (21.1, 21.2)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms

Genetic Diversity
genotypic and/or phenotypic traits that distinguish individuals within a population
4 sources of genetic diversity/variation?
Sexual Reproduction (recombination)
Crossing over
Different Alleles
Random Mutations
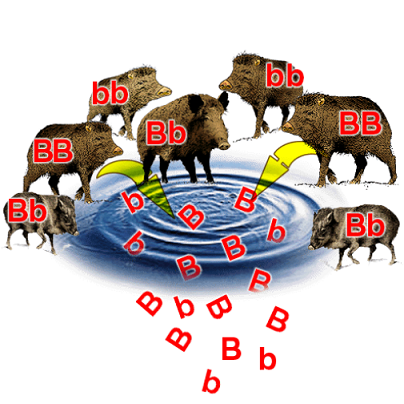
Gene Pool
The total collection of ALL genes and their alleles present in a population.
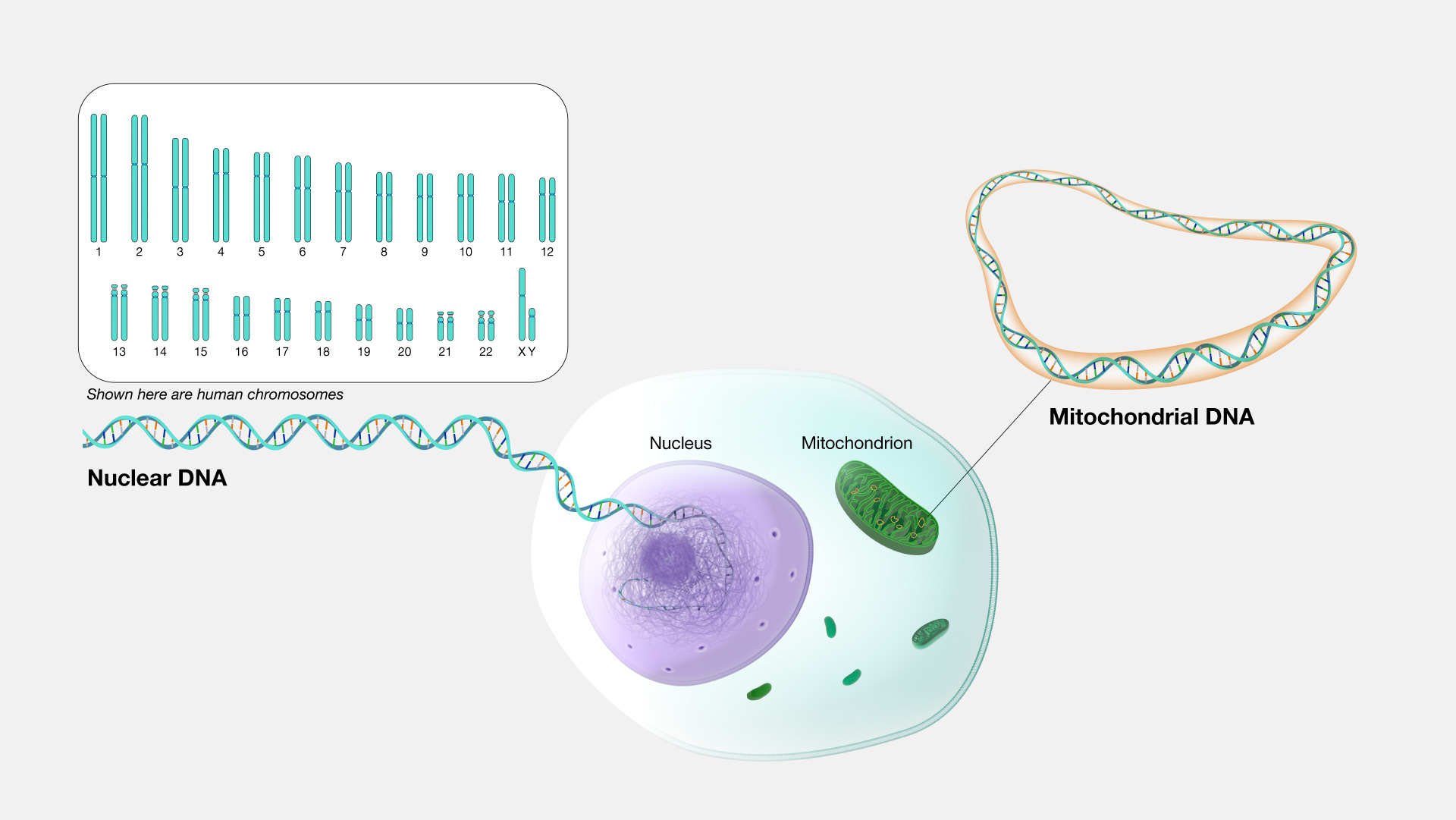
Genome
The complete set of genetic information in an organism's DNA, including all of its genes, non-coding regions and mitochondrial & chloroplast DNA
Importance of a large gene pools?
A large gene pool has greater genotypic diversity. Therefore it is better able to resist environmental challenges.
A smaller gene pool (inbreeding) makes populations less able to adapt and survive with environmental challenges
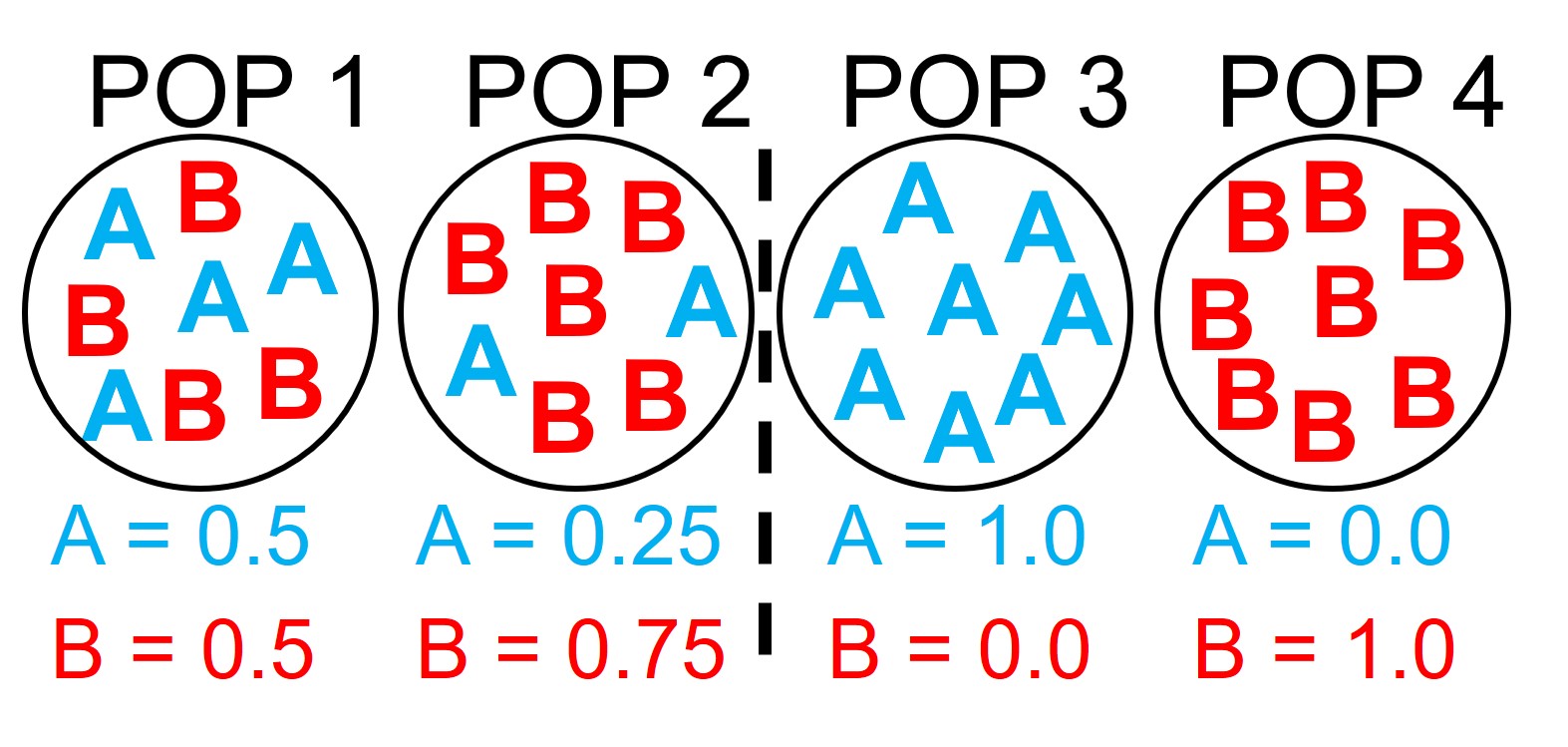
Allele Frequency
The proportion of a particular allele in a given population (A or a)
It is expressed as a decimal, percent or fraction, and the frequencies of all alleles for a gene must add up to 1.
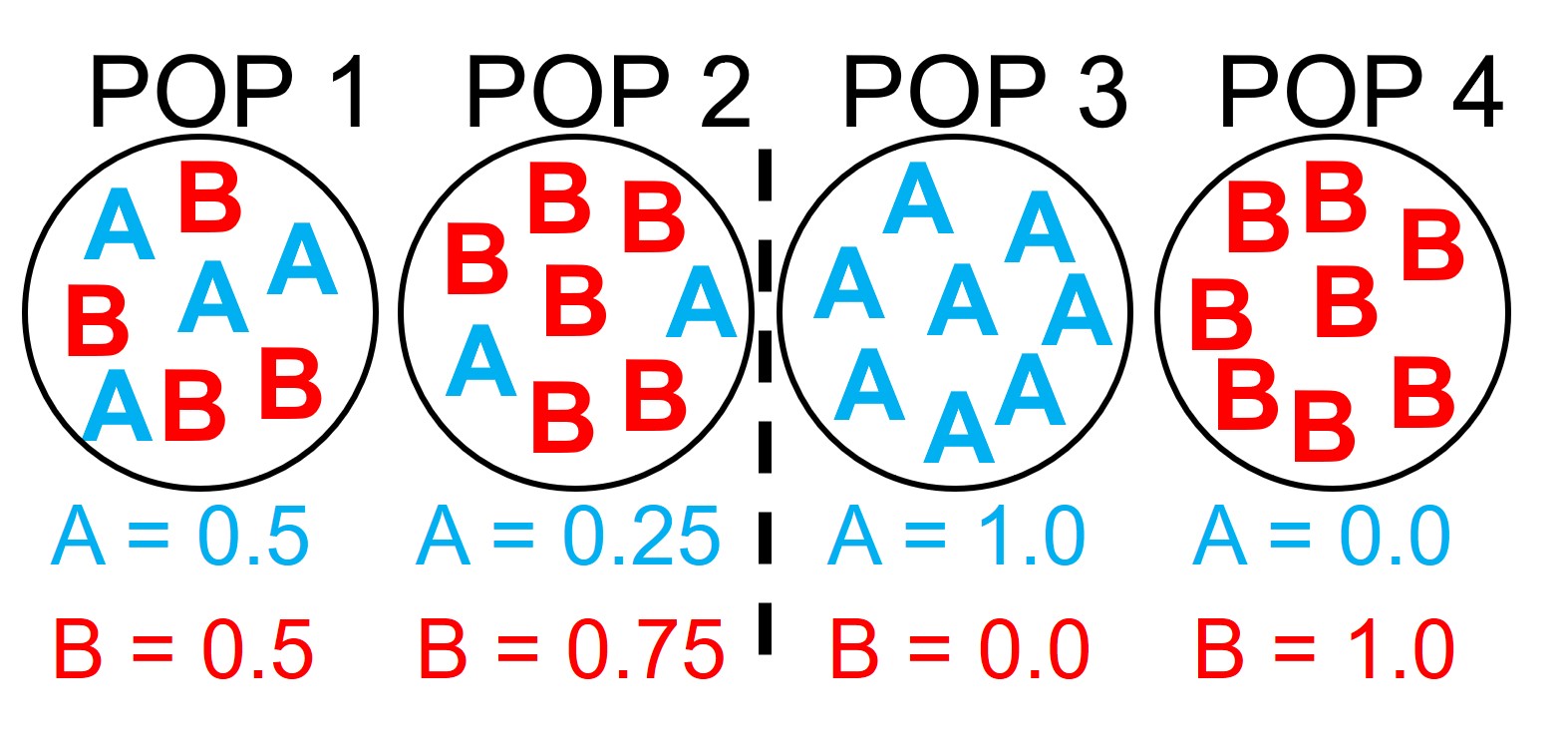
Fixed Frequency
When ONLY one allele exists as a gene in the population.
Its frequency is 100% (1.0).
What does the Hardy-Weinberg Principle state?
in a large, randomly mating population, the allele and genotype frequencies will remain constant from generation to generation if certain conditions are met (virtually impossible)
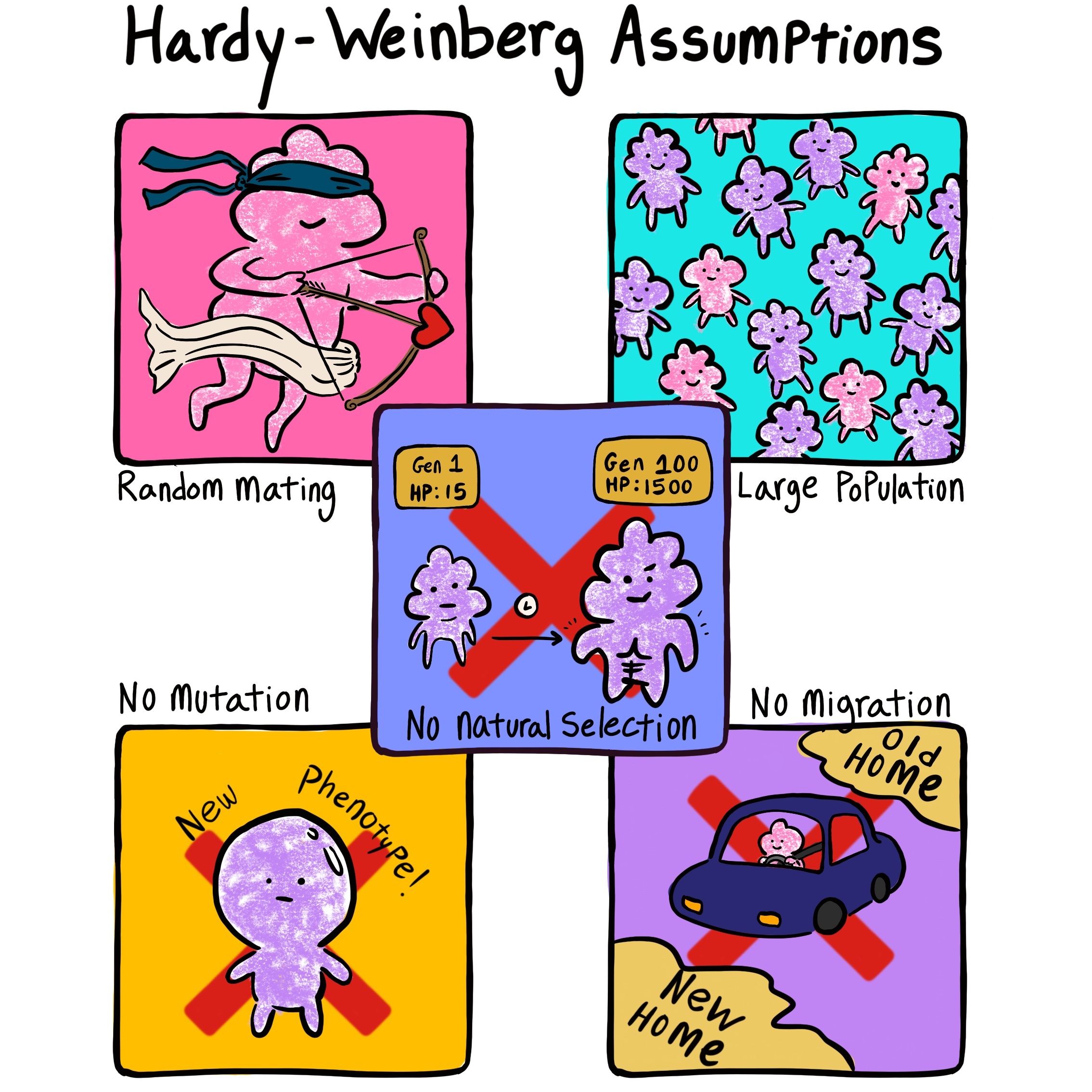
What are the 5 conditions required for an Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
No mutation: so no new alleles are introduced
Large population size: alleles don’t die out easily
No gene flow (migration): so different populations don’t mix and introduce new alleles
Random mating: so no one has a better chance of mating and passing on favourable alleles to the next generation
No natural selection: so no one with better phenotypes have greater reproductive success.
Why is the Hardy-Weinberg Principle important?
It provides a starting point to determine whether evolution is occurring in a population.
For a gene with ONLY two alleles (A,a) what is the Hardy-Weinberg allele frequency equation?
p + q = 1
p = frequency of allele A
q = frequency of allele a.
What is the Hardy-Weinberg genotype frequency equation?
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
p2 = frequency of homozygous dominant genotype (AA)
2pq = frequency of heterozygous genotype (Aa)
q2 = frequency of the homozygous recessive genotype (aa)
What does frequency mean?
Decimal form between 0 and 1
How do you *calculate genotype frequency in a gene pool?
*(One of many ways)
Count the number of individuals with a specific genotype (AA, Aa, or aa)
Divide that by the total number of individuals in the population.
How do you *calculate allele frequency in a gene pool? *(One of many ways,)
Count the number of each desired allele in the population
Divide by the total number of alleles.
How do you *calculate phenotype frequency in a gene pool?
*(One of many ways)
Count the number of individuals with a specific observable trait (phenotype)
Divide that by the total number of individuals in the population.
How are all three different types of frequencies different?
Allele frequency looks at alleles only (A vs a)
Genotype frequency looks at gene combinations (AA, Aa, aa)
Phenotype frequency looks at observable traits (dominant or recessive expression).
How do these frequencies relate to evolution?
If allele, genotype, or phenotype frequencies change over time, evolution is occurring.
If they stay the same, evolution is not occurring and maintains genetic equilibrium
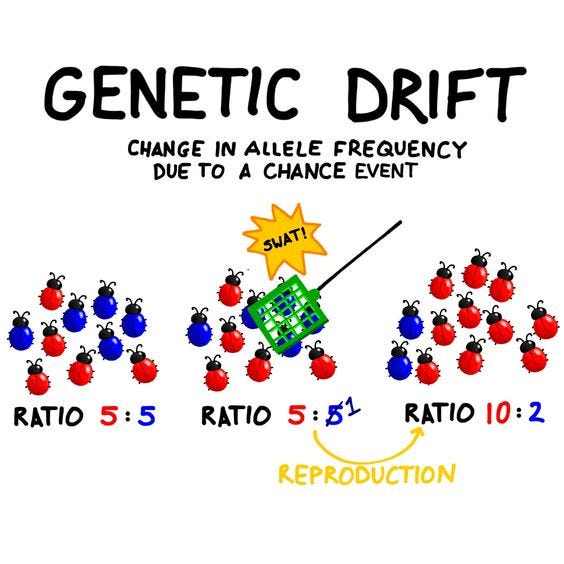
Genetic Drift. What part of Hardy-Weinberg does it oppose?
Changes in the allele frequency of a population due to random chance.
It opposes the condition to have a ‘Large Population’, b/c it reduces the allele frequency due to random chance.
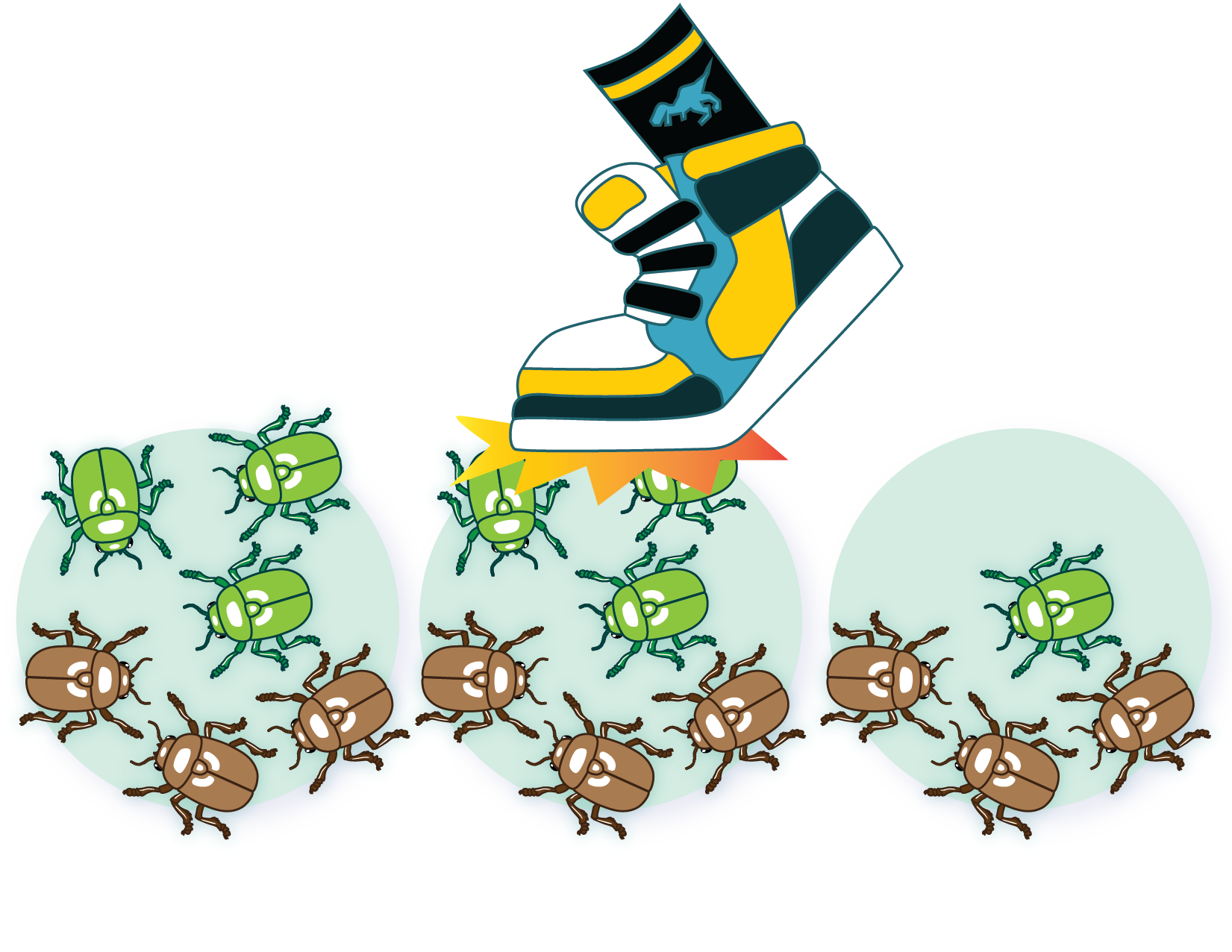

Why does genetic drift affect small populations more strongly?
Smaller the population, greater the change in allele frequencies due to random chance, leading to homozygosity, and reduced genetic diversity.
2 types of genetic drifts?
Bottleneck Effect
Founder Effect
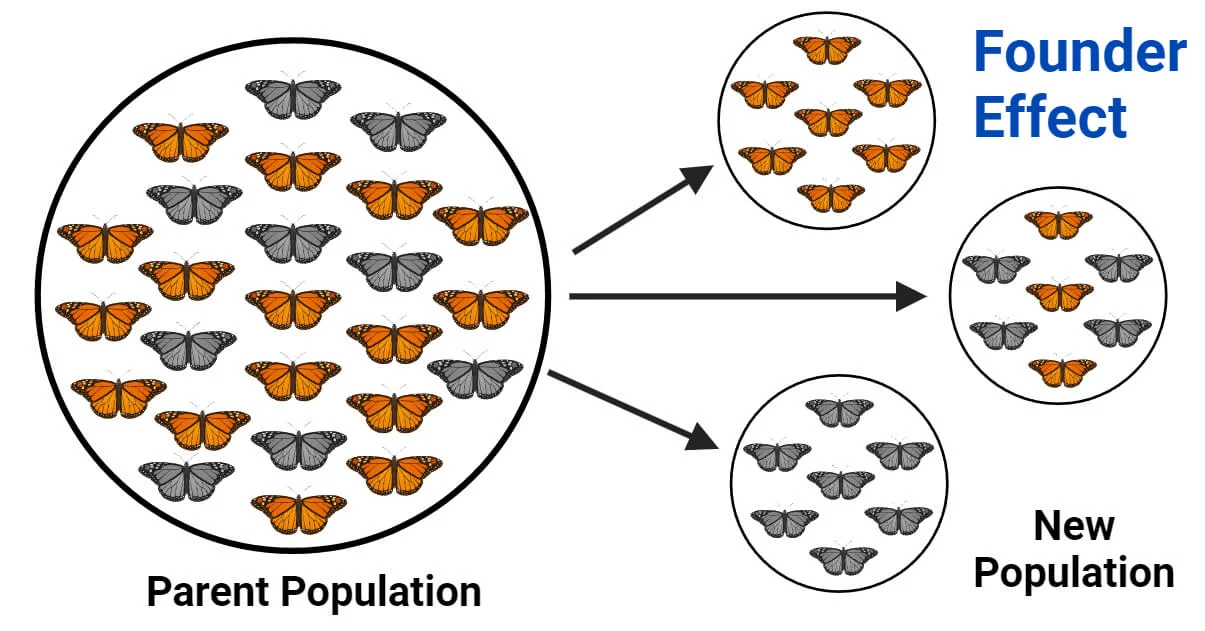
Founder Effect
When a few random individuals from a large population establish a new population.
*Their allele frequencies may differ from the original population.
Example of the founder effect? (Humans)
The Amish community in Pennsylvania: descended from 30 random founders, one carrying a rare recessive allele for short limbs.
Today this allele is prominent compared to most populations.
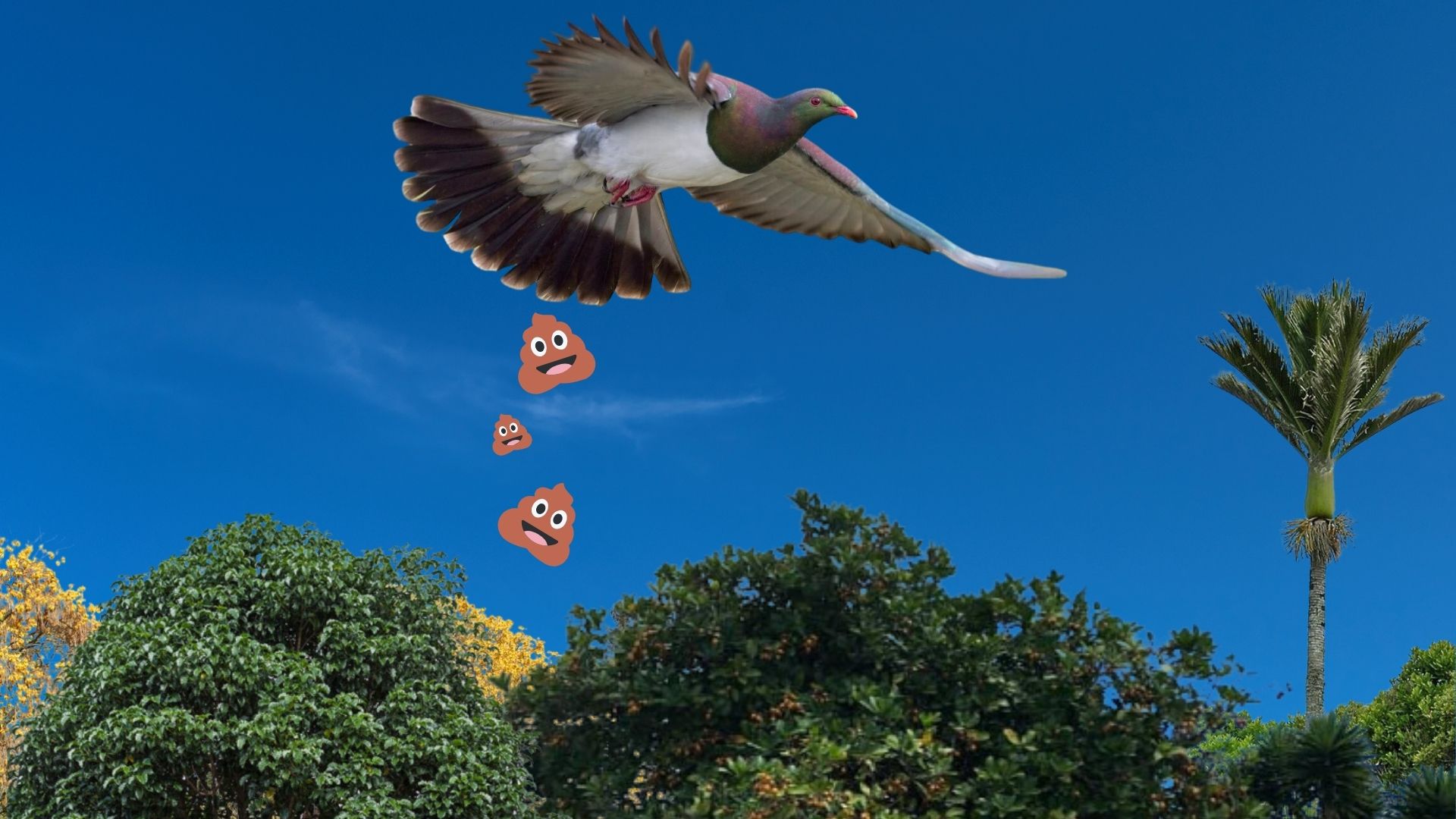

Example of the founder effect? (nature)
A few seeds carried by the bird poop is carried into a island, establishing a new plant population, different from its original.
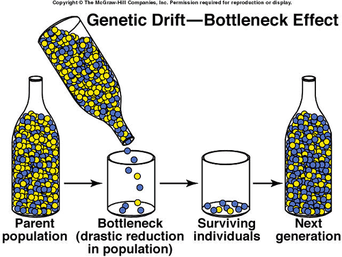
Bottleneck Effect
A drastic reduction in population size due to severe environmental events. The reduction of alleles are due to chance.
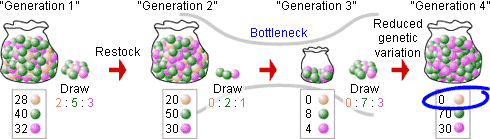
How does genetic drift (bottleneck effect and founder effect) influence evolution?
It influences evolution by increasing the chance of allele fixation, due to reduced genetic variation.
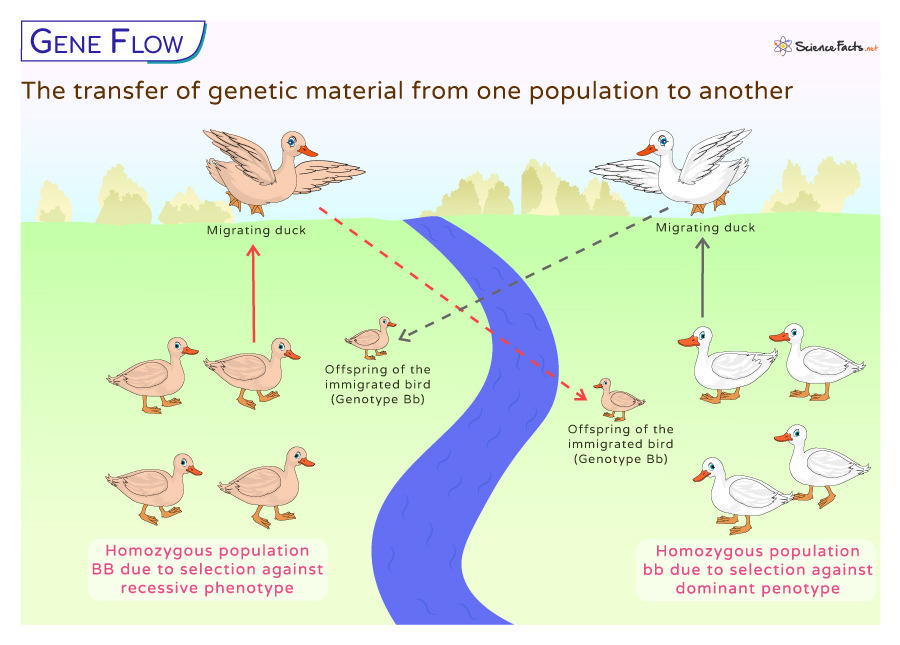
Gene Flow. What part of Hardy-Weinberg does it oppose?
When an organism migrates or mates w/o entering, with another population. This removes or adds alleles to that population altering its allele frequencies.

Why does Hardy-Weinberg oppose mutations?
B/c it introduce new alleles. If it’s beneficial mutation, natural selection would increase it’s frequency, altering the population's gene pool.
What is the relationship between mutations and natural selection?
Mutations provide new genetic variations (different phenotypes). While natural selection selects beneficial phenotypes.
They work together to enhance reproductive success and increase it’s frequency.
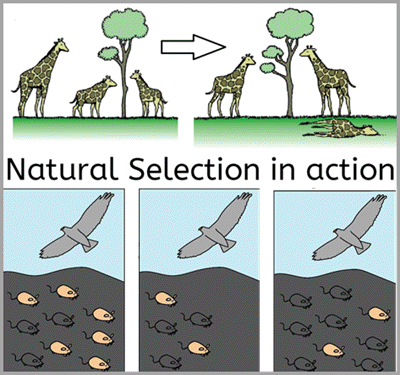
What does natural selection act on?
On individuals and their phenotypes; not directly on their alleles.
Why does Hardy-Weinberg oppose non-random mating?
B/c when certain individuals mate more than others, it contributes more, altering the gene pool of future generations.
Sexual selection
A form of non-random mating where favoured phenotypes influence mating success. Includes sexual dimorphism.
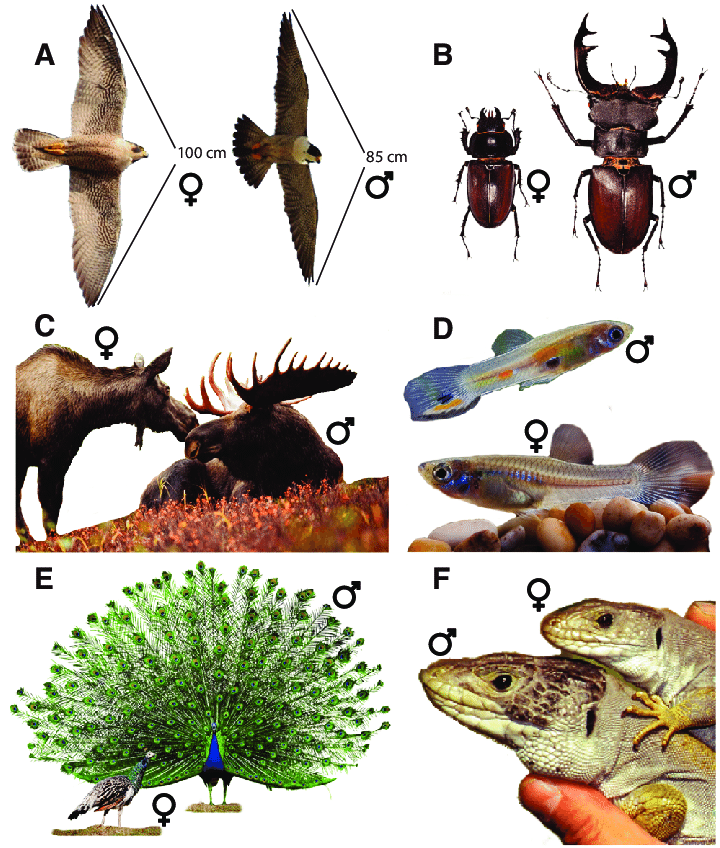
Sexual Dimorphism
Striking physical or behavioural differences between males and females of a species

Give examples of in sexual selection.
Female choice of males with bright plumage, songs, or displays
Male-male competition using weapons or territorial defence