B8 - Retroviruses Introduction
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What type of genome do Retroviruses have?
Positive sense single stranded RNA genomes
Why is retroviruses’ genome transcription/replication unique?
Retroviruses convert their ssRNA genome into dsDNA using reverse transcriptase
How were retroviruses classified in the past?
Oncoretroviruses
Lentiviruses
Spumaviruses
How are retroviruses classified now?
Orthoretrovirinae
Oncoretroviruses
Lentiviruses
Spumaretrovirinae
Spumaviruses
Why were Lentiviruses named that way?
Because they are characterised by long incubation periods and ‘Lenti’ is Latin for slow
Why were Spumaviruses named that way?
Because infected cells looked ‘foamy’ in culture and ‘Spuma’ is Latin for foamy.
What are the 6 Genera of retroviruses?
Alpha retrovirus
Beta retrovirus
Gamma retrovirus
Delta retrovirus
Epsilon retrovirus
Lentivirus
Of the 6 retrovirus genera, which are able to infect humans?
Only Delta retroviruses and Lentiviruses
What are the four core proteins which all retroviruses contain and what are their functions?
Gag
Precursor to internal structure proteins
Pro
Viral protease
Pol
Precursor to Integrase (IN) and Reverse Transcriptase (RT)
Env
Precursor to envelope glycoproteins
What is the difference between Simple retroviruses and Complex retroviruses?
Both contain the general 5’-gag-pro-pol-env-3’ scheme
However, complex retroviruses also contain accessory genes which contribute to pathogenicity
Retrovirus genomes contain PBS regions. What are these?
PBS - Primer Binding Site
Specific tRNA binds here and serves as a primer for reverse transcription
Retrovirus genomes contain Leader regions. What are these?
Leader sequences
Contains genome packaging signals and 5’ splice donor signals
Retrovirus genomes contain PPT regions. What are these?
PPT - Polypurine tract
Important for cDNA generation
What is the retrovirus cell entry mechanism?
Entry initiated by interaction of Env proteins with specific cell surface receptors
Followed by fusion of viral and cellular membranes which allows entry of the capsid into the cytoplasm
Retrovirus RNA looks like 5’CAP-R-U5------------U3-R-AAA3’.
Once converted to cDNA, what does it look like?
U3-R-U5---------------U3-R-U5
What are Long Terminal Repeats? (LTRs)
The U3-R-U5 regions found in retrovirus cDNA after Reverse Transcription
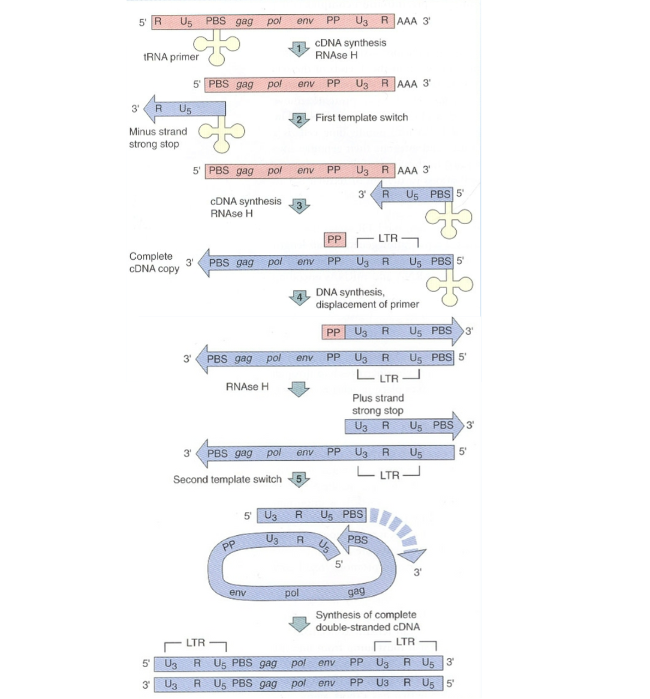
What is the first step of retrovirus cDNA generation?
tRNA primer binds to PBS site and U5 and R sequence are replicated first using tRNA primer
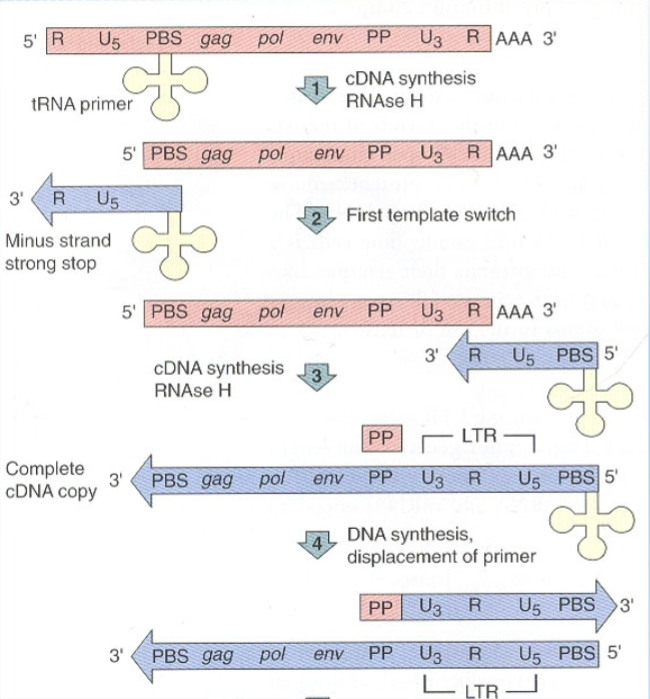
After the U5 and R sequences have been replicated using the tRNA primer, what is the second step of retrovirus cDNA generation?
The tRNA primer releases from the RNA and moves to the 3’ end by aligning with the 3’ R sequence.
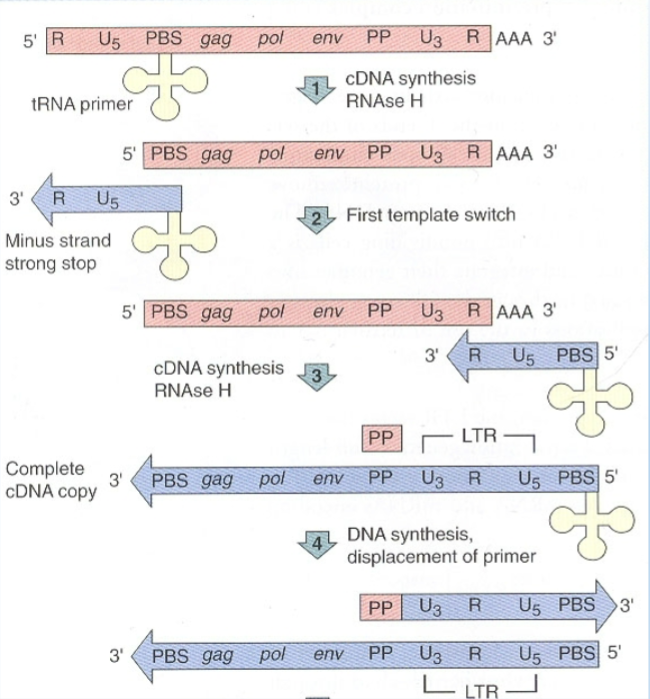
After the tRNA primer releases from the RNA and moves to the 3’ end, what is the third step of retrovirus cDNA generation?
cDNA replication occurs and replicates the whole RNA genome.
Almost all the genomic RNA is removed however the PP sequence is left behind
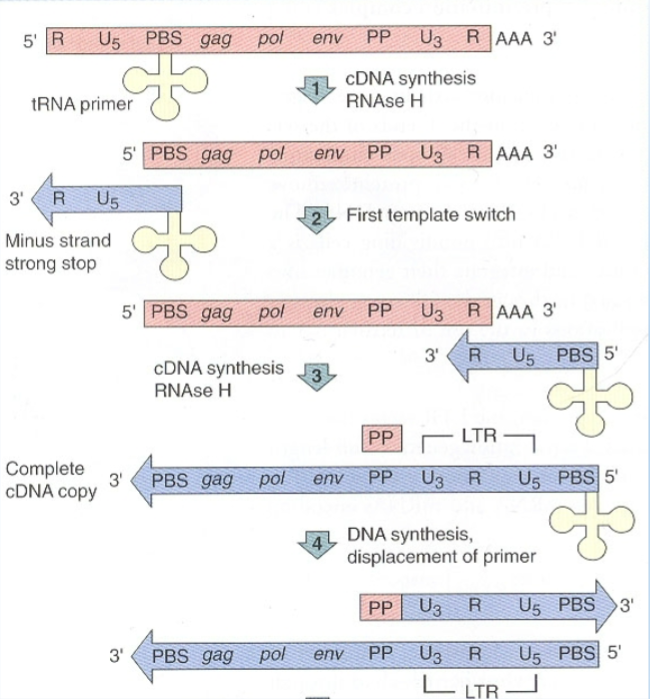
After cDNA replication occurs and replicates the whole RNA genome, what is the fourth step of retrovirus cDNA generation?
The PP sequence is used to generate part of the second cDNA strand
PP sequence is then removed by RNaseH and replaced with DNA
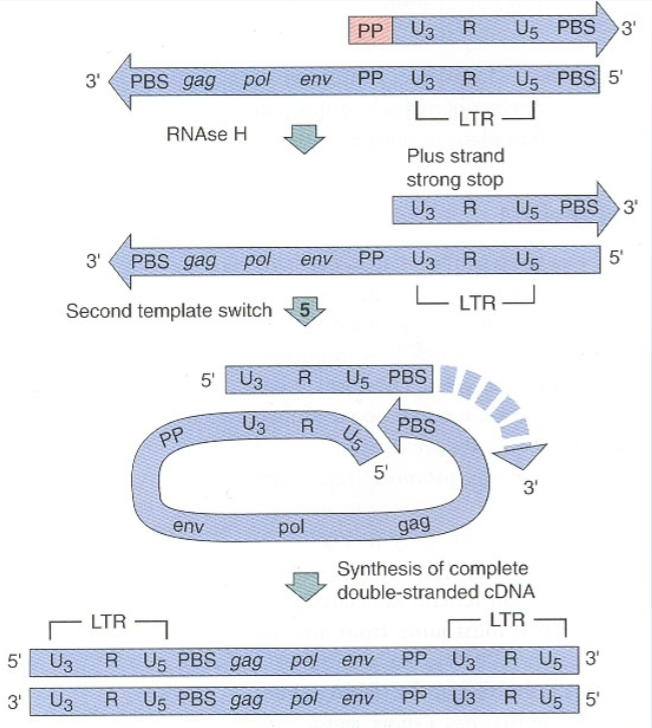
After the PP sequence is used to generate part of the second cDNA strand, what is the fifth step of retrovirus cDNA generation?
The partly double stranded DNA anneals to its own tail which contains a complementary PBS sequence
This allows for complete synthesis of the second cDNA strand
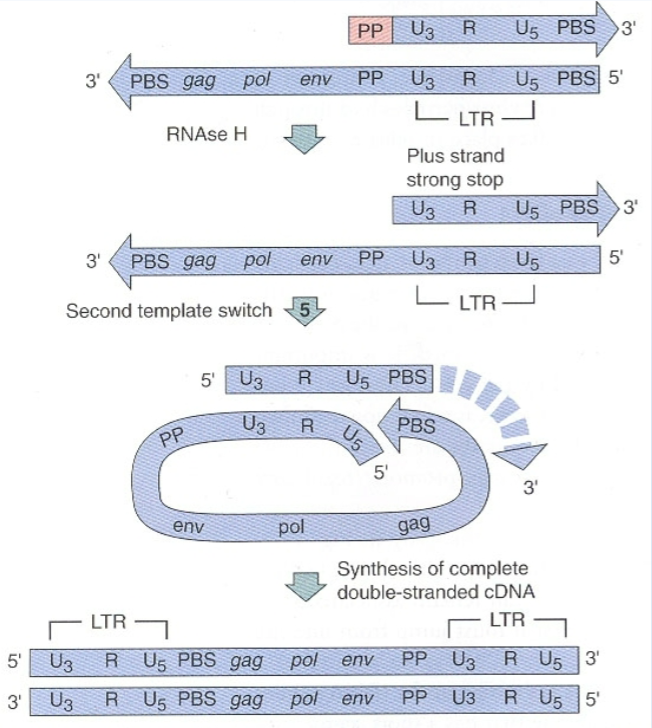
What is the complete process of retrovirus cDNA generation?
Which retrovirus Genera require nuclear membrane disruption for cDNA integration?
Onco/Deltaretroviruses require nuclear membrane disruption
Which retrovirus Genera can access the nucleus via a nuclear pore for cDNA integration?
Lentiviruses can access the nucleus via a nuclear pore
What is the first step of retrovirus cDNA insertion into host genome?
cDNA migrates to the nucleus in a complex with integrase protein.
After cDNA migrates to the nucleus in a complex with integrase protein, what is the second step of retrovirus cDNA integration?
Integrase cleaves two nucleotides from the 3’ end of the cDNA to produce a sticky end.
After Integrase cleaves two nucleotides from the 3’ end of the cDNA to produce a sticky end, what is the third step of retrovirus cDNA integration?
Integrase cleaves host genomic DNA and separates the breaks by several base pairs to form a more jagged cut
After Integrase cleaves host genomic DNA, what is the fourth step of retrovirus cDNA integration?
Integrase ligates host DNA to the 3’ end of the retroviral cDNA via sticky ends
Host proteins will then fill the gaps and ligate the retroviral cDNA to host DNA
What is a DNA Provirus?
Integrated form of the viral genome in host chromosomes.
Transcriptionally active
How is retroviral mRNA expressed following integration of the genome?
5’ LTR serves as a promoter region for host RNA pol II
3’ LTR serves as a polyadenylation/transcription stop signal
This produces a full length, capped mRNA with a polyA tail
What can retroviral mRNA serve as a messenger for?
Gag, pro and pol proteins
But NOT env proteins
Why is splicing necessary in retroviruses?
Only one promoter region present so some genes require splicing
What is used to splice retroviral mRNA?
Cellular spliceosome
How is Gag expressed from retroviral mRNA?
ORF followed by a (suppressible) leaky STOP codon
How is Pro-Pol expressed from retroviral mRNA?
ORF in different reading frame compared to Gag
Retroviral gag and pol are polyproteins which need to be cleaved. What cleaves them?
Cleaved post-transcriptionally by pro protein
Final maturation of retroviral capsid may not occur until after budding. True or False?
True.
Expression of what retroviral polyproteins leads to capsid assembly in the cytosol?
Gag and gag-pol polyproteins
Why are immature retroviral capsids not infectious?
No free Reverse Transcriptase or Integrase as they are still in their polyprotein form which hasn’t been cleaved yet
What cellular proteins do retroviruses utilise to facilitate budding?
Utilise ESCRT (Endosomal Sorting Complex Required for Transport)