1.3. Transport and Kinematics
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Key concepts of transport phenomena
Equilibrium state corresponds to…
Adjacent particles with non-uniform quantities tend to…
The return to equilibrium is due to…
Molecular interactions transport…
From the macroscopic POV…
Equilibrium state corresponds to… (key concepts of transport phenomena)
a uniform distribution within a volume of fluid of its physical quantities
Adjacent particles with non-uniform quantities… (key concepts of transport phenomena)
tend to equilibrium when placed in contact
The return to equilibrium is due to… (key concepts of transport phenomena)
local molecular interactions in a way that depend on the molecular structure of the medium
Molecular interactions… (key concepts of transport phenomena)
transport physical quantities across the boundaries
From the macroscopic POV… (key concepts of transport phenomena)
the non-uniform distribution of a generic quantity C between one fluid particle and the next one can be seen as a continuous variation.
So, a general law for the flux can be derived.

Transport is a ___ process
statistical
Irreversibility is …
macroscopic
The physical quantities that can be exchanged:
Mass
Heat → related to kinetic energy of molecules → temperature
Momentum
Quantities driving the transport
Fraction of molecules of a given species (concentration)
Kinetic energy (temperature)
Momentum (velocity)
What is the general expression for the flux?
the total rate of transfer of a given quantity
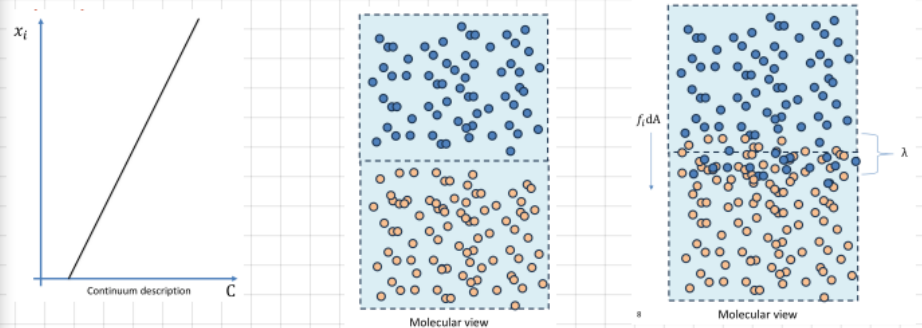
Write the general expression of the flux (total rate of transfer of a given quantity):
fi=-kij*(dC/dxj)
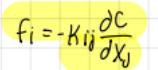
If the system is isotropic…
the general expression for the flux becomes: fi=-kappa*(dC/dxi)
kappa being the transpor coefficent → depends on the medium’s molecular properties
What is C and what are its units? (transport of mass)
C: species concentration (%)
Transport of mass from conservation laws, formula?
(dC/dt)=-(kappa_D/N)*grad²C=-K_D*grad²C
N is the total number of molecules per unit volume
K_D is the diffusivity coefficent (length² * time^-1)

Transport of mass for an ideal gas, formula?
K_d prop to lambda (u²)^1/2
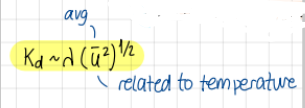
What is C and what are its units? (transport of heat)
C: temperature (K)
In transport of heat, what does f_i equate to? (2 formulas)
f_i=q_i (Heat flux(J/(sm²)))
f_i=kappa_n*(dT/dxi) (kappa_n being therman conductivity)
Transport of heat from conservation laws, formula?
(dT/dt)=-(kappa_h/(C_P*rho))*grad²*T=-K_H*grad²*T
Cp is the specific heat (heat capacity at P cte)
K_H is the thermal diffusivity (length² * time^-1)

Transport of heat for an ideal gas, formula?
K_H prop to lamda*(U²)^1/2

Definition of viscosity
Viscosity is the resistance of a fluid to flow (deformation rate) due to internal friction
Hypothesis of transport of momentum, viscosity
Simple shear flow (velocity and velocity gradient in one direction)
What is C and what are its units? (transport of momentum)
u (m/s)
In transport of momentum, what does f_i equate to?
f_i=tau_i (N/m²) → net transfer of i-components of momentum per unit time and unit area (flux)
In transport of momentum, what does tau_i equate to?
tau_i=mu*(du/dxi)
mu is dynamic viscosity (kg/(ms) or Pa*s)
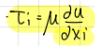
Transport of momentum from conservation laws, formula?
(Du/Dt) prop to (mu/rho)*grad²*U
where upsilon=mu/rho is the dynamic viscosity
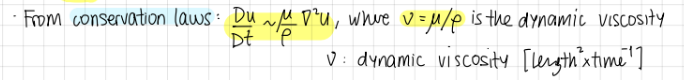
Transport of momentum for an ideal gas, formula?
upsilon prop to lambda*(U²)^1/2

Southerland’s law (transport of momentum)
mu(T)=(mu/mu0)*sqrt(T) for gases
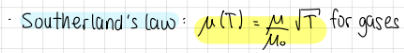
Viscosity facts
What is viscosity coefficent or dynamic viscosity?
What does kinematic viscosity (the ratio between viscosity and density) represent?
Viscosity varies with ___, variation is different for …
What is the Prandtl’s number?
What is kinematic viscosity?
The ratio between viscosity and density
What is viscosity coefficent or dynamic viscosity?
is the resistance of a fluid to flow (deformation rate)
What does kinematic viscosity (the ratio between viscosity and density) represent?
it represents the momentum diffusivity concept
Viscosity varies with ___, variation is different for …
Temperature; air (increases with temperature) and water (decreases)
What is the Prandtl’s number?
is the ratio between momentum and thermal diffusivity concept
Prandtl’s number formula
Pr=upsilon/K_H=(C_p*mu)/(kappa_H)
constant in gases
around 0.7 for air

Forces acting on a fluid particle
Body forces
Surface forces
Body forces characteristics
Typically due to external fields (conservatives or not)
Proportional to particle volume
ex: gravity, electromagnetic, …
a non-local force, comes externally

Surface forces characteristics
Due to local (molecular) interactions
Proportional to body surface
Both normal (pressure) and tangential actions
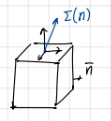
Gauss’s theorem: for a ___ domain, the following relation can be demonstrated to hold:
grad*a=divergence
if grad*a=0 → everything that goes in, goes out

Material (or Lagrangian) derivative (formula)
formula
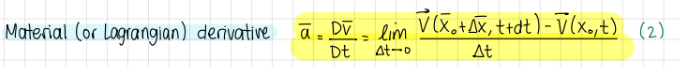
Eulerian derivative (formula)
formula
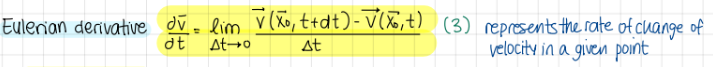
Total derivative 2 (formula)
formula
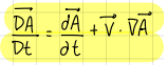
if d/dt=0
the aerodynamic system is steady/stationary
stationarity also depends on…
the reference frame
The total derivative is obtained from…
the sum of the variation in time of the considered variable plus the variation to the spatial gradients
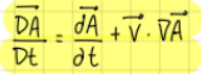
The total derivative is gotten from…
a mathematical connection between the material and eulerian derivatives
what are A and v? (total derivative)
A: vector field (or scalar fluid)
v: velocity vector
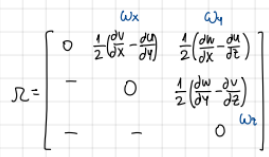
What is vorticity?
the curl of the velocity vector
Vorticity formula:
formula
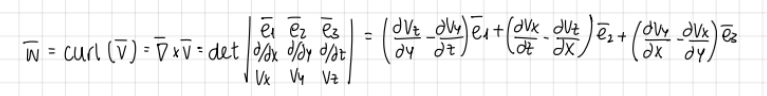
regarding vorticity, in 2D:
d/dz=0 → Vz=0
how many components of vorticity?
formula and graph
deformation of a fluid particle: draw diagram and write equations
diagram and equations
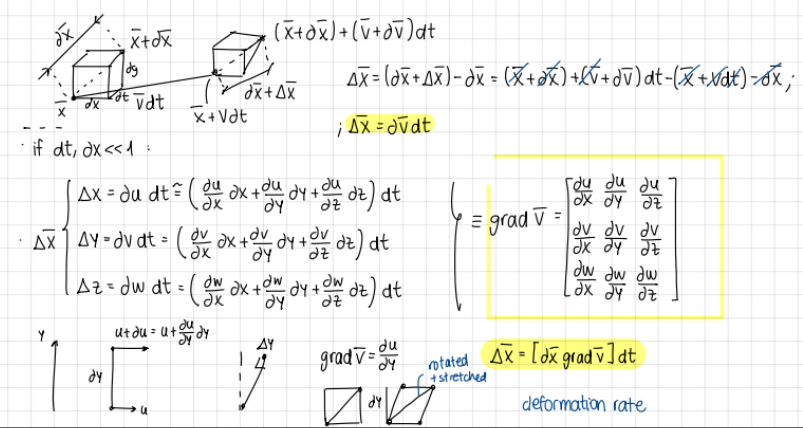
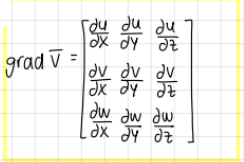
write the tensor of the gradient of the velocity vector (deformation of a fluid particle)
tensor
deltaX equal to (deformation of a fluid particle)
formula
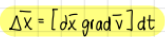
a tensor is symmetric if…
A=A^T
a_ij=a_ji
A_sym=1/2*(A+A^T)

a tensor is antisymmetric if…
b_ij= -b_ji
A_antisym=1/2*(A-A^T)
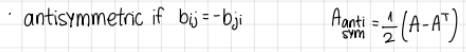
gradient of velocity vector is equal to… (formula)
gradV=E+omega
E symmetric
omega antisymmetric
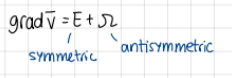
tensor of E
tensor

tensor of omega
tensor
what does deltax equal to when total deformation?
deltax= (dx*gradv)*dt
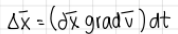
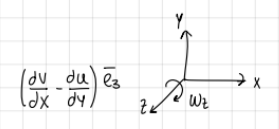
Formula for rotation rate of a particle around a given point?
formulas
omega= twice the rotation rate of a particle around a given point
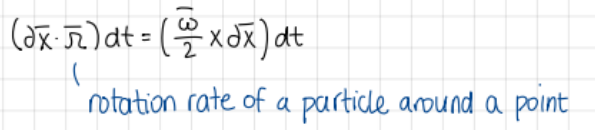
Development of rotation rate and vorticity (formulas and diagrams)

What are streamlines?
streamlines are the lines tangent to the velocity field
formulas and diagram of streamlines

what are pathlines?
pathlines are the trajectory followed by a particle
formula and diagram of pathlines

What are streaklines/smokelines?
they are the locus at a given time t of the position of the particles that at t=0 have passed by x0

how do pathlines, streamlines and streaklines relate if the flow is stationary?
pathline=streamline=streakline
What is a stream tube?
is the identified region where streamlines don’t get out and the mass flow does not go through the surface (constant mass flow)
Vortex lines/tubes characteristics
They’re tangent to the vorticity vector
Vortex lines are material lines (inviscid flow)