Illicit Drugs Overview
1/175
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
176 Terms
Drug
a natural or synthetic substance that is designed to produce a specific set of psychological and/or physiological effects on the human body or animals
Illicit
forbidden by law, rules, or custom
Drug abuse
when a drug is consumed for purposes other than what intended for, usually psychoactive effects
1906: Pure Food and Drug Act
Did not allow states to transfer drugs across state lines that were mislabeled/adultured
1914: Harrison Act
Regulated the sale of opium and cocaine
1930: Bureau of Narcotics
Enforced taxes on imported drugs
1956: Narcotic Drug Control Act
Increased penalties on drugs
1970: Comprehensive Controlled Substance Act
Uniform Controlled Substances Act - state level control of illicit substances
Pharmacological effects
Factors used by FDA to evaluate how to schedule/classify illicit drugs
Ability to produce psychological dependence and physical addiction
Factors used by FDA to evaluate how to schedule/classify illicit drugs
A legitimate medical use for the substance
Factors used by FDA to evaluate how to schedule/classify illicit drugs
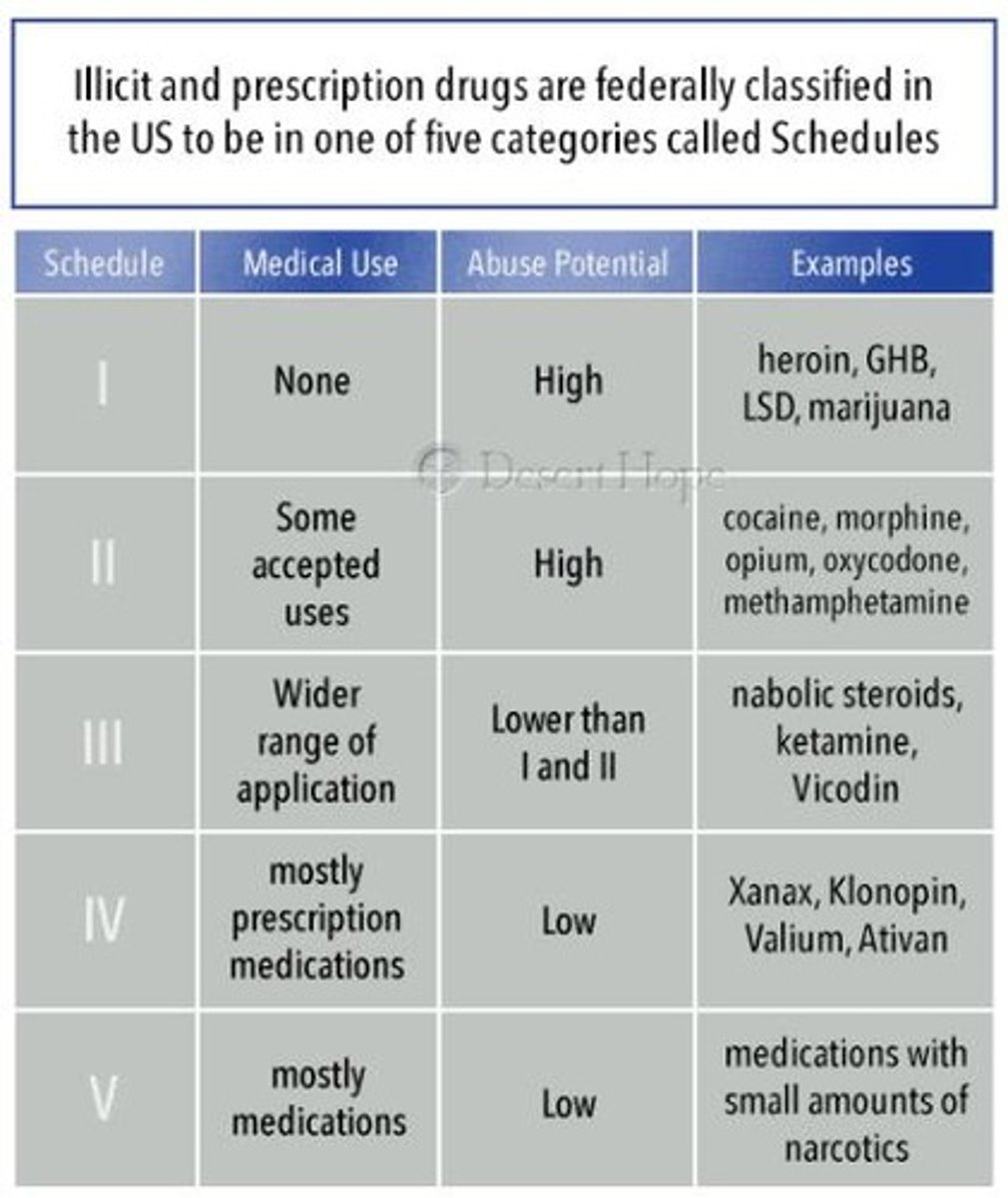
Five Schedules
based on potential for abuse, pharmacology, and medical use
Naturally Occurring
found in nature in plants (marijuana, shrooms)
Plant Extracts
naturally occurring, but needs to be extracted (cocaine)
Semi-Synthetic
derived chemically from a natural substance (LSD)
Synthetic
totally man-made (ecstasy)
Stimulants
elevate one's mood
Depressants
de-elevate one's mood
Narcotic
relieves pain
Hallucinogen
alters mind
Forensic Toxicology
study of harmful effects of drugs
Postmortem Toxicology
analysis of biological samples after death to identify poisons and determine their amounts
Human Performance
evaluation of drug effects on athletes and others
Doping Control
monitoring for drug use in sports
Workplace Drug Screening
testing employees for drug use
Toxicology
study of harmful effects of drugs
Pharmacology
study of how drugs enter the body and how distributed and eliminated
Poison
substance that causes illness or death of a living organism (toxic effect)
Pharmacokinetics
what happens to the drug by the organism - how it moves in and out of the body
Pharmacodynamics
what happens to the organism when a drug is taken
Absorbance
how drugs are introduced to the body; passage of drugs through tissue into bloodstream
Alcohol (Oral)
into stomach and then absorbed mostly in the upper part of the small intestine
Alcohol (In bloodstream)
into the brain, can then affect the nervous system
Distribution
anywhere there is blood, which is everywhere
Concentration of drug
is not the same; more blood = more drug; depends on chemical and physical properties
Higher concentration
in brain, heart, liver
Alcohol distribution
to all parts of the body in approximate proportion to the water content of each part
Metabolism
effect of the liver on the drug
Alcohol metabolism rate
90% of alcohol is metabolized at 0.015% per hour
Excretion/Elimination
Primarily through urine - water soluble metabolites; exhales, sweat, bile, breast milk; control of the liver and kidneys
Addiction
psychological dependence of a drug
Dependence
physical need for the drug to function - failure to provide drug causes withdrawal
Synergism
total effect on the body of 2+ drugs taken together is greater than taken separately
Tolerance
body's organ systems adapt to a drug, need more of the drug for the same level of effect
Screening Test
Alcohol - field sobriety (walking line, saying alphabet backwards, etc.) & portable breath test
Confirmatory Test (Alcohol)
Breath Test Instrument (BRAC); living person at the police station
Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC)
postmortem; GCMS - headspace
Confirmatory Test (Drugs)
Mass Spectrometry - coupled with GC or LC depending on the drug
Combustion Reaction
fuel (flammable objects/substances) and oxygen produces carbon dioxide, water, and energy
Exothermic Reaction
releases energy
Flash Point
lowest temperature at which a liquid gives off enough vapors to form an ignitable mixture with air
Rich vs. Lean
Smoke occurs when there is an incomplete combustion in a fire - 'fuel rich'
Flashover/Backdraft
occurs when the fire burns with a limited supply of oxygen and then is suddenly ventilated, resulting in an explosive fire
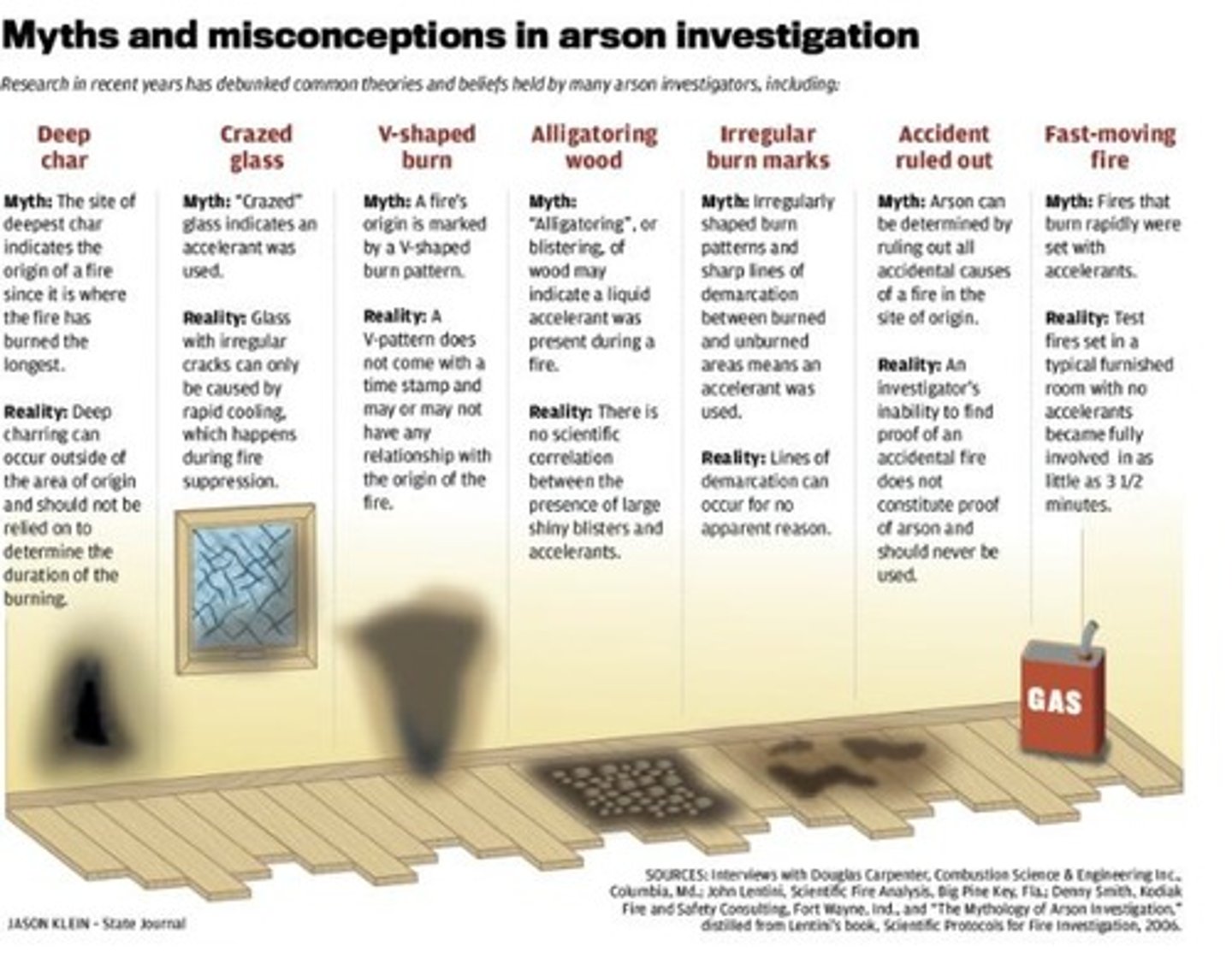
Types of Fires
Natural, Accidental, Deliberate/Incendiary
Ignition Types
Self-ignition, Direct ignition, Electrical, Weather-related, Mechanical
Arson
A deliberate/incendiary fire that was set with criminal intent
Paint
A substance composed of three main components: binder, pigment, and vehicle.
Binder
Allows paint to be distributed across a surface.
Pigment
Color component of paint, which can be organic and/or inorganic.
Vehicle
Forms a continuous film binding pigment to the surface, consisting of solvents, resins, and additives.
Solvents
Evaporate after application, leaving a hard polymer on the surface.
Architectural Paints
Household paints.
Product Coatings
Manufacturing process and automobile paints.
Pretreatment/Electrocoat
Zinc pretreatment that provides corrosion resistance.
Primer
Provides corrosion resistance, pigment, and a smooth surface for the next layer.
Topcoat/Basecoat
The layer that provides color.
Clearcoat
Provides UV protection.
Paint Chips/Flakes
Evidence indicating that layers are present, considered most important.
Paint Smears
Evidence from the top layer, often from a sideswipe.
Special-Purpose Paints
Paints that serve functions beyond protection and aesthetics.
Art Paints
Paints used for artistic purposes, relevant in authentication and forgery cases.
Collection of Paint Evidence
The process of comparing a known paint source with an unknown sample.
Physical Properties Examination
Involves assessing layer sequence, thickness/ratio of layers, and color of layers.
Chemical Properties Examination
Involves assessing solubility and components of paint.
Pyrolysis-GC
Used for analyzing the entire paint chip.
Infrared Microspectrophotometry
Analyzes organic compounds of each paint layer.
Soil
Contains both organic (humus) and inorganic (minerals) substances.
Forensic Geologist
A professional who associates soil from a crime scene to a source and compares samples.
Class Evidence
Evidence that is considered circumstantial.
Area of collection
Depth & width
Representative sample
Homogenized sample
Physical Properties
Characteristics such as particle size, distribution, color, and mineral identification
Particle size
The dimension of individual particles in a sample
Particle distribution
The arrangement of particles within a sample
Color
The visual appearance of a sample based on light absorption and reflection
Mineral identification
The process of determining the minerals present in a sample
Chemical Properties
Characteristics that define the chemical composition of a sample
SEM/EDS
Scanning Electron Microscopy/Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy - used to analyze elements
HPLC-UV-Vis
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Ultraviolet-Visible detection - used for profiling organic substances
Infrared
A technique useful for obtaining spectra of organic and inorganic soil components
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
An instrumental analysis method to look at tiny particles and determine elemental composition
Glass manufacturing
The process of creating glass products such as sheet glass, container glass, and glass fibers
Fracture match
A method of matching broken glass pieces based on their edges
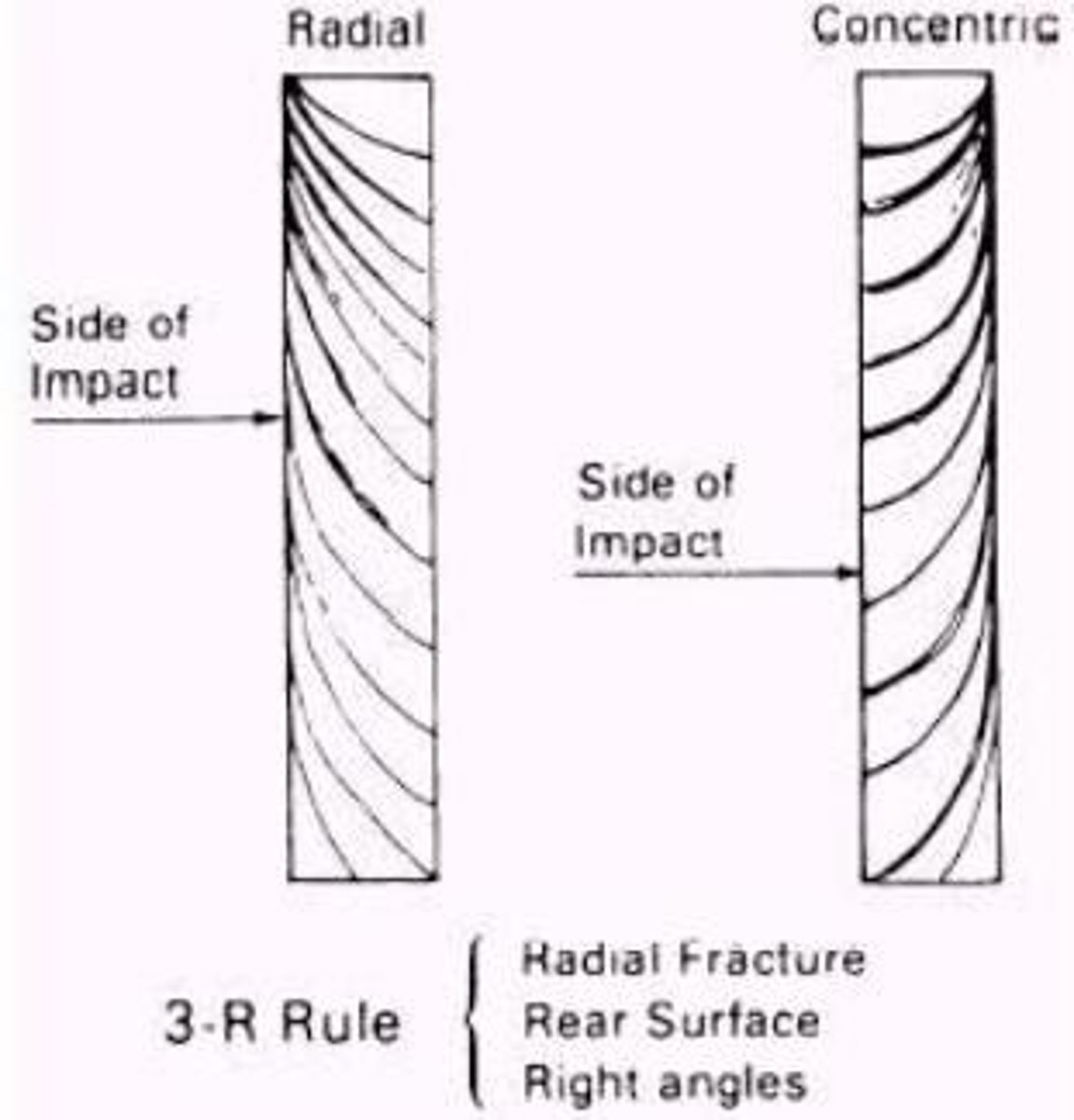
Radial Lines
Fractures that spread out from the impact point
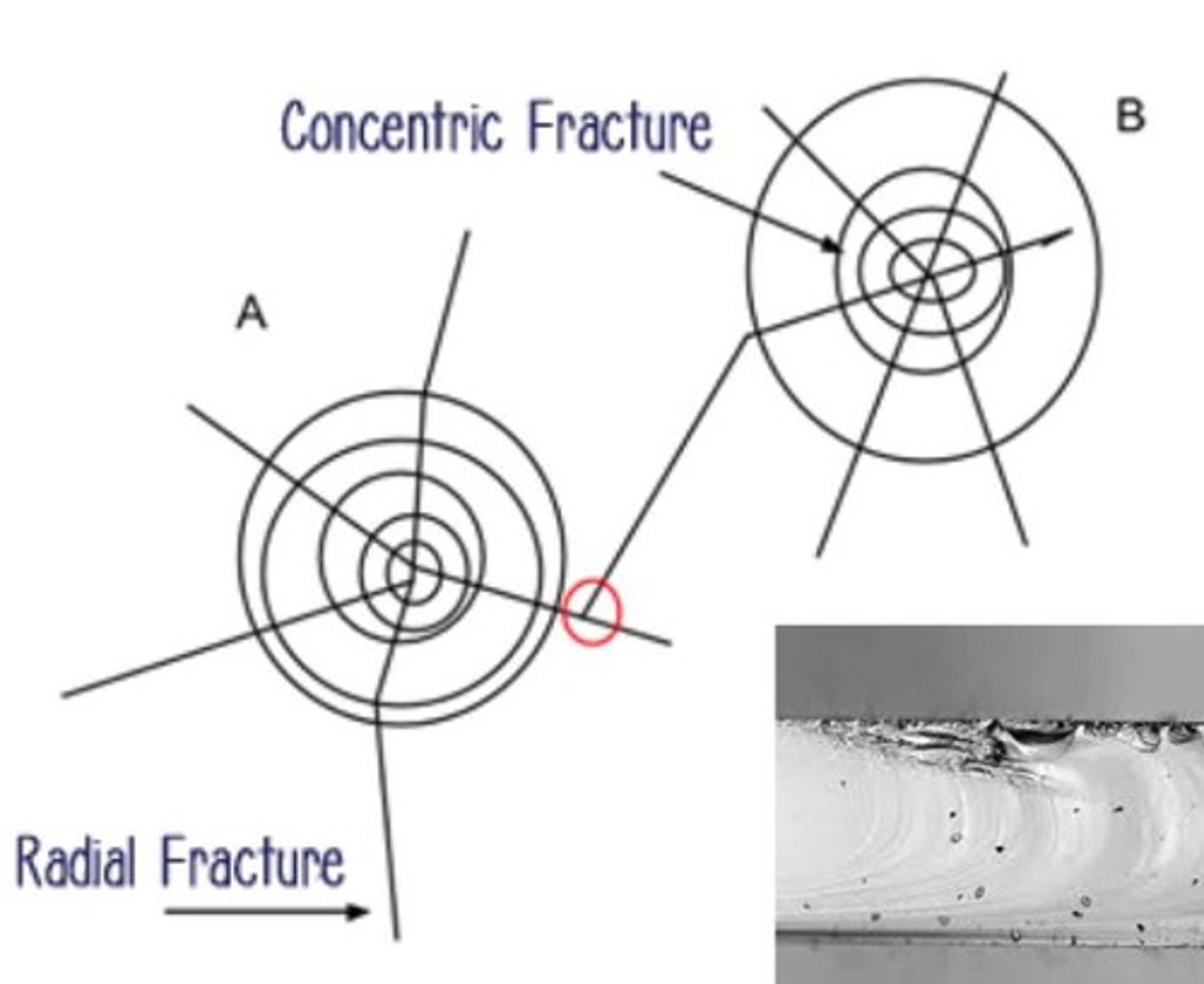
Concentric Lines
Circles that form around the impact point on glass
Wallner Lines
Marks on the inside edge of glass that indicate stress
Becke Line Method
A technique that requires knowledge of temperature, refractive index of oil, and a single known wavelength
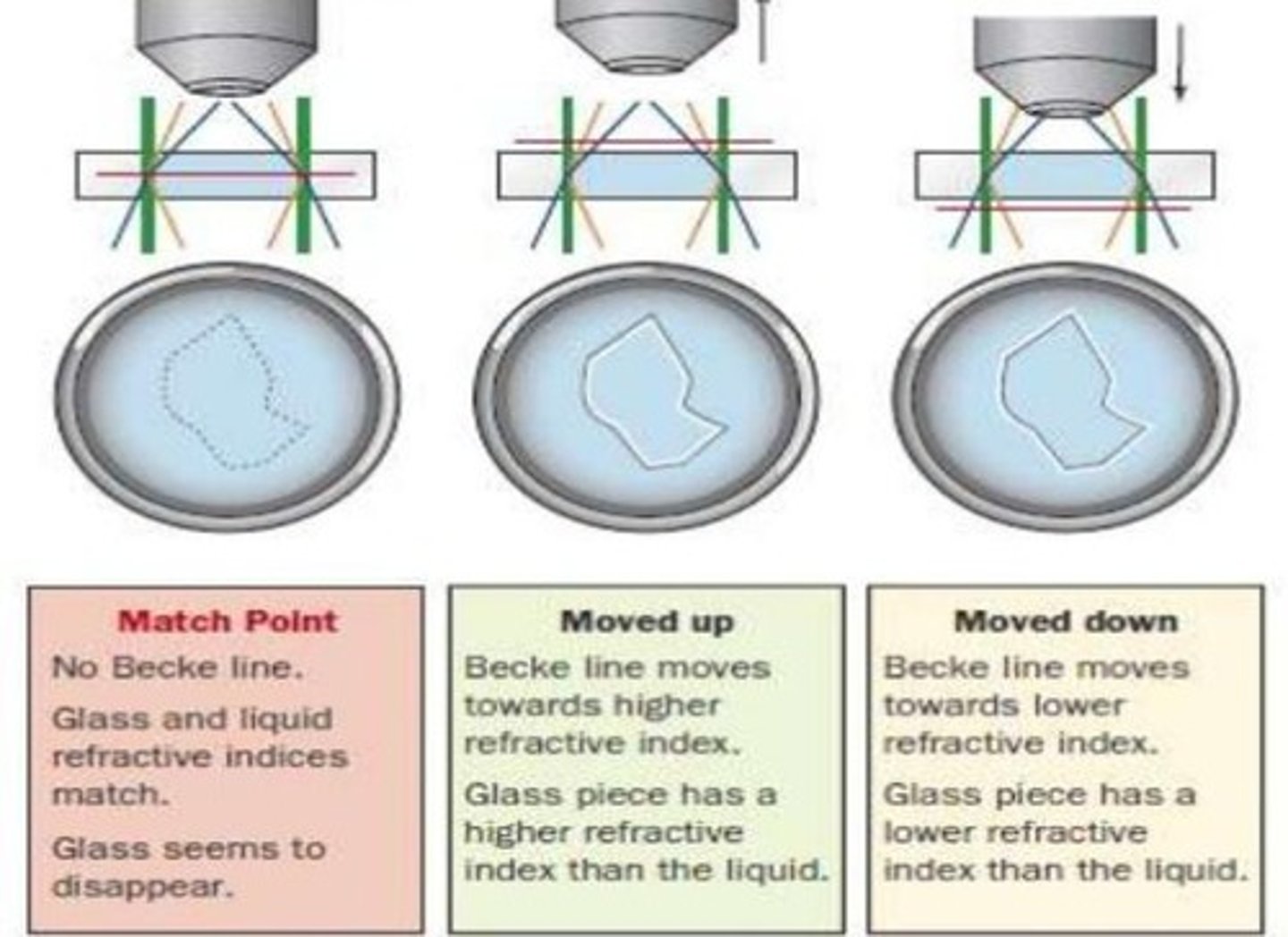
Elemental Composition
The makeup of a material in terms of its elements
Amorphous solid
A solid that lacks a defined crystalline structure
Silicon Oxides
Compounds made of silicon and oxygen, commonly found in glass