Developmental and Acquired Defects OMFR
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
cleft lip
Defective fusion of the medial
nasal process with the maxillary
process
cleft palate
Failure of the palatal shelves to
fuse
Orofacial clefts
Could be from maternal alcohol/smoking/anticonvulsant therapy, or syndromes
bifid uvula
Very common, can also be combined with submucous palatal cleft (when bone not continuous but mucosa over everything)
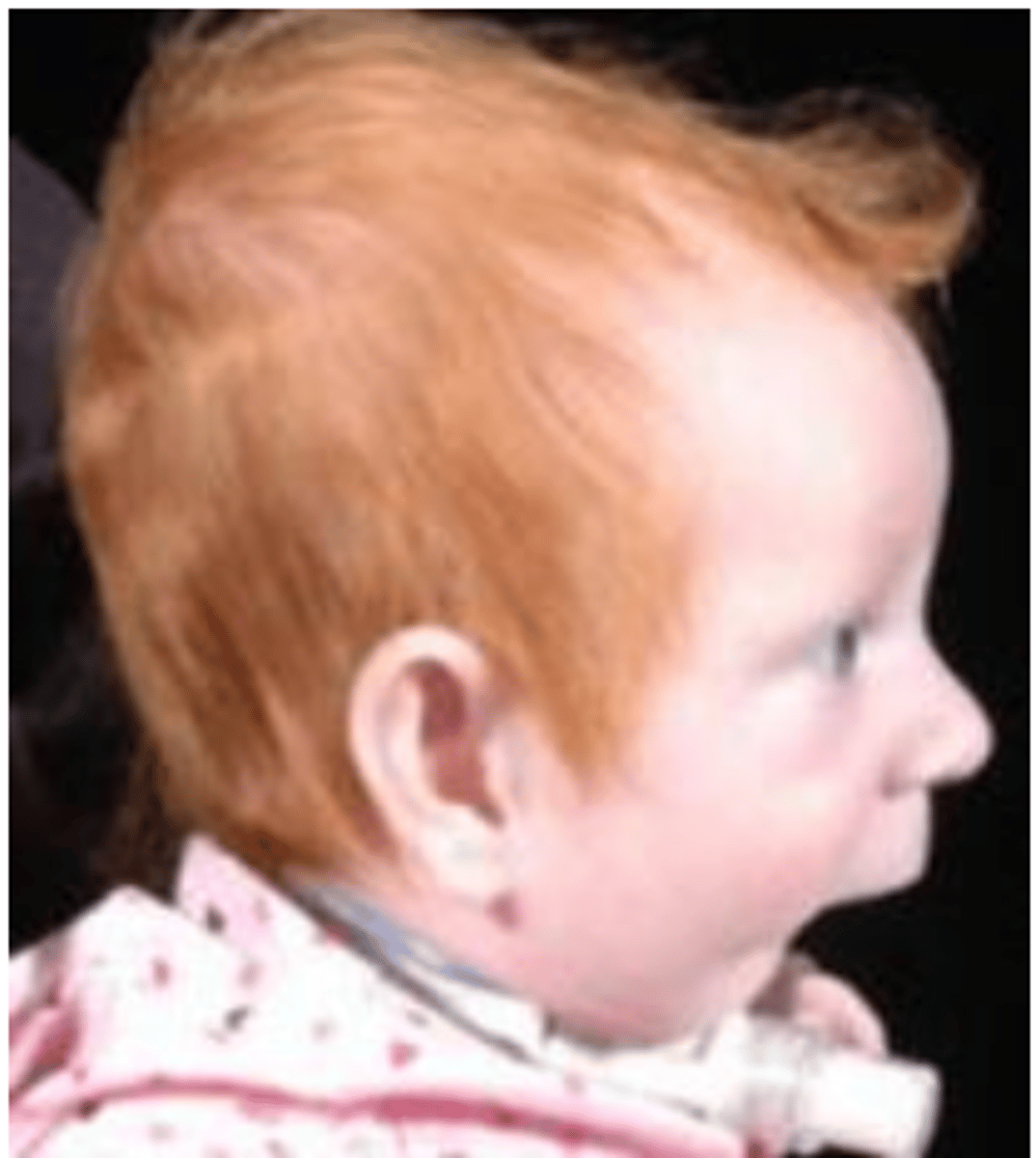
Pierre robin
• CP
• Mandibular micrognathia (small mandible)
• Glossoptosis (airway obstruction from posterior/lower displacement of tongue)
Probably from constraints in utero

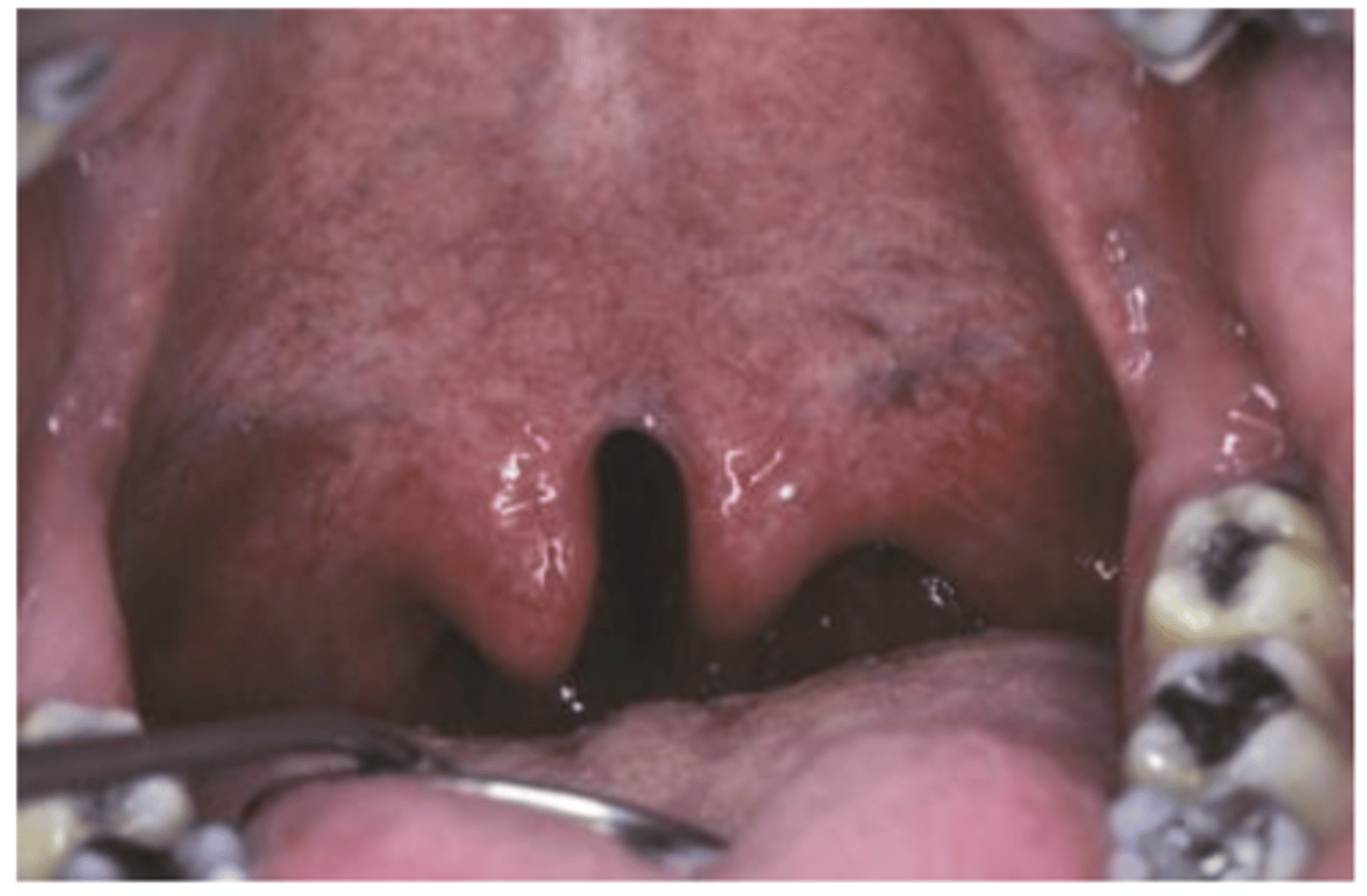
paramedian lip pits
• Rare congenital invaginations of
the lower lip
• Bilateral and symmetric
Could be part of van der Woude or kabuki syndrome
van der woude
if paramedian lip pits are inherited AD with CL and/or CP it is called
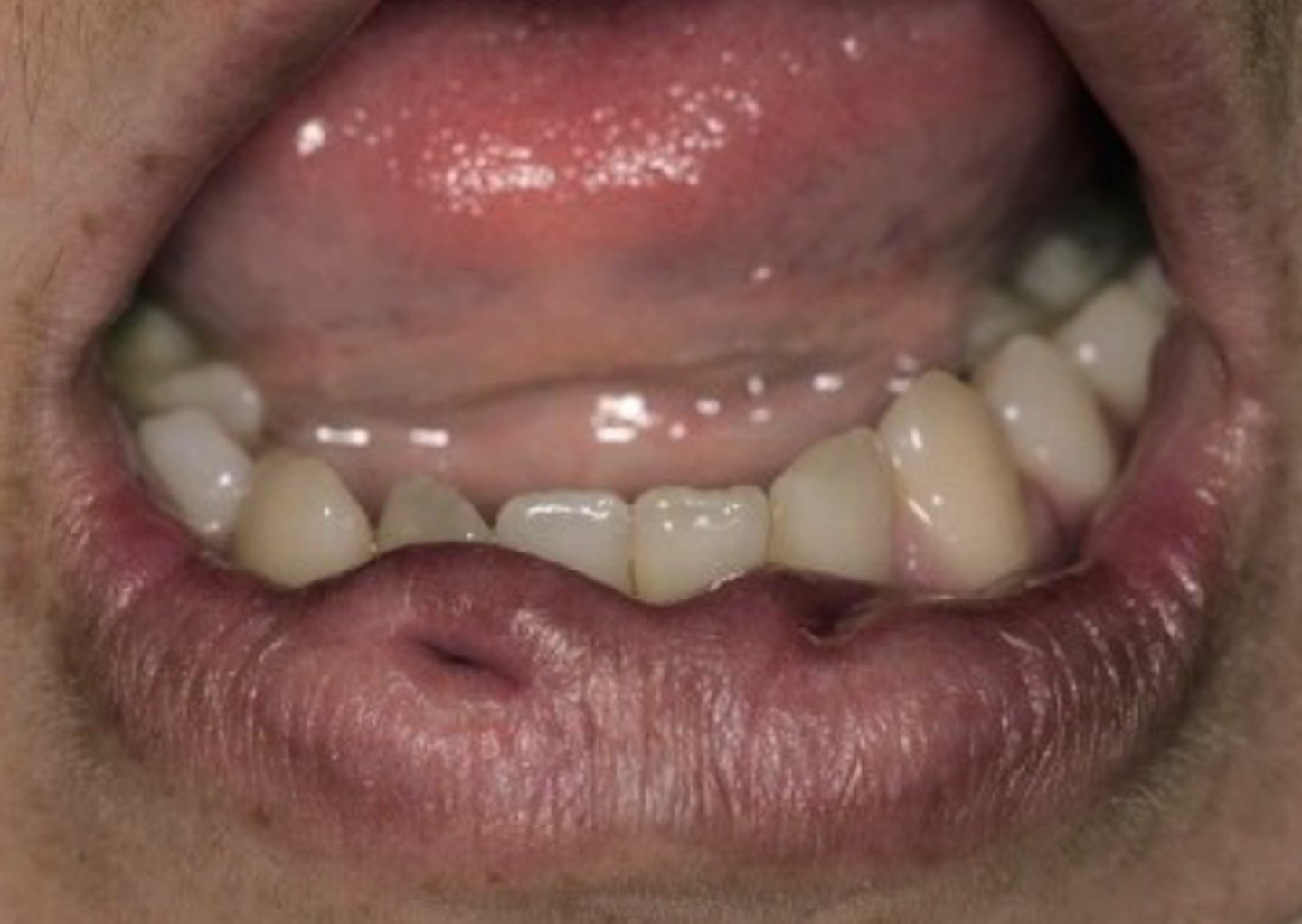
double lip
• Redundant fold of tissue on the
mucosal side of the lip
• Most cases are congenital, but
may be acquired
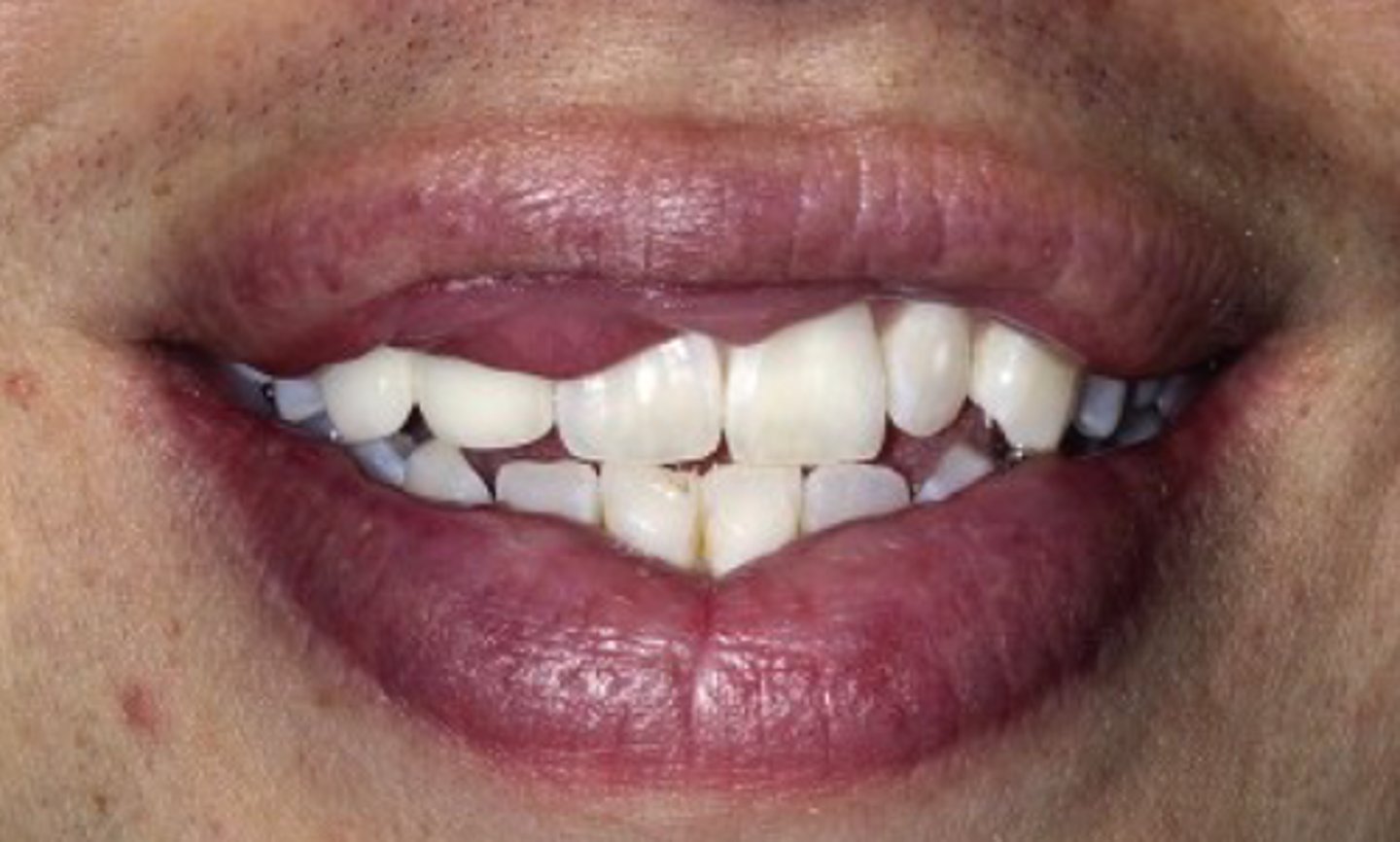
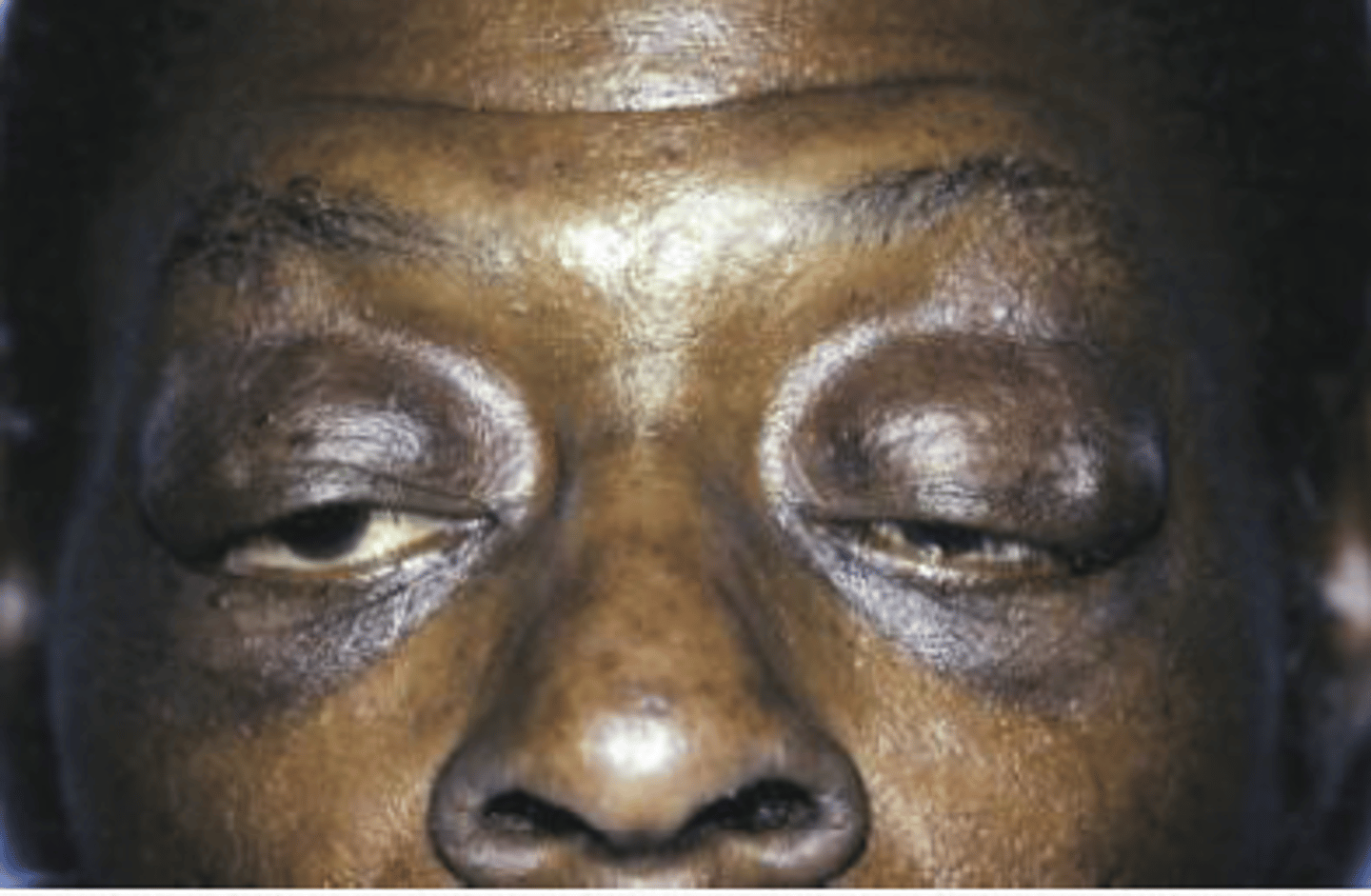
ascher syndrome
• Double lip
• Blepharochalasis
• Nontoxic thyroid enlargement
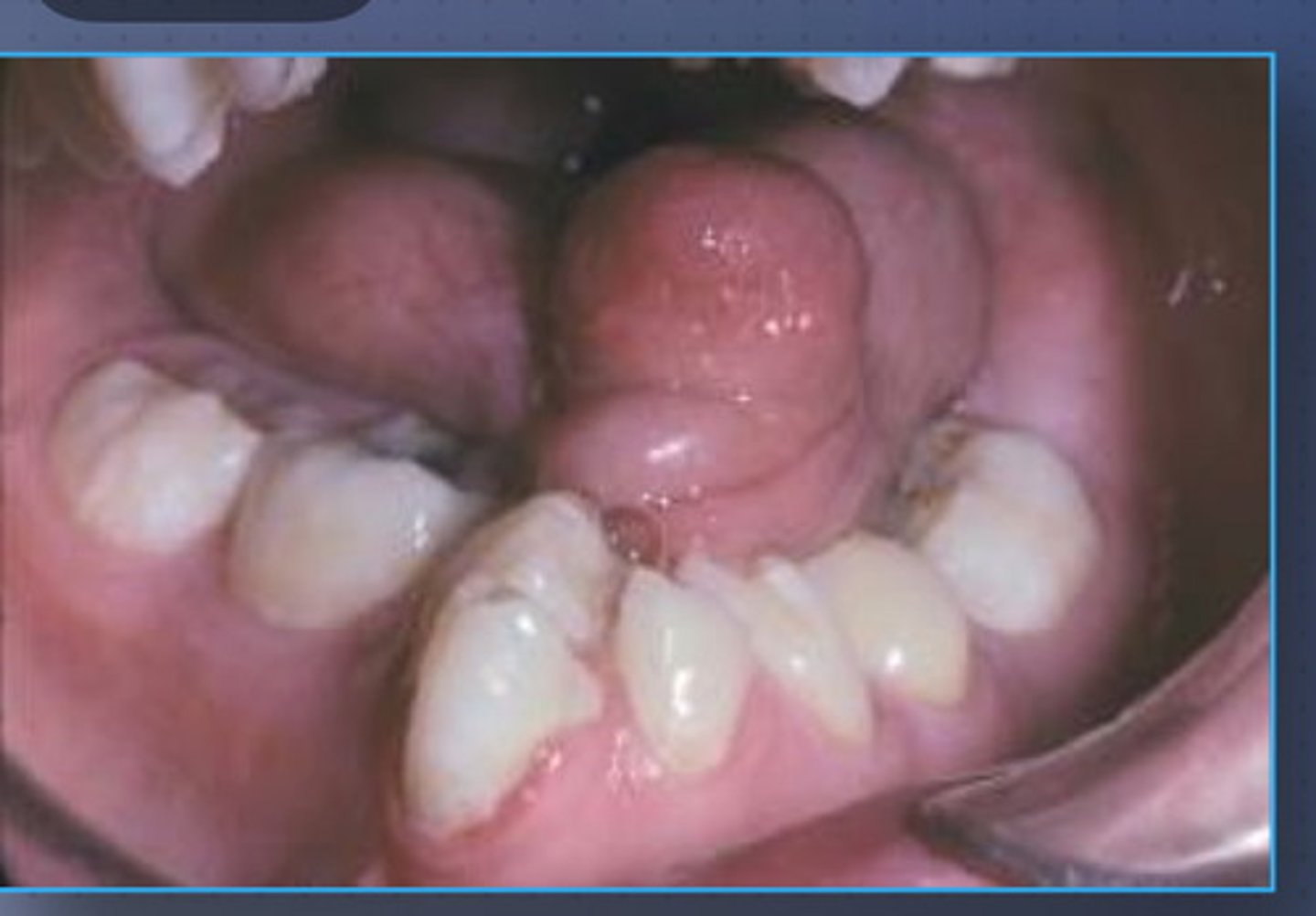
microglossia
• Uncommon developmental
condition of unknown cause that
is characterized by an
abnormally small tongue
• May be isolated or part of a
syndrome
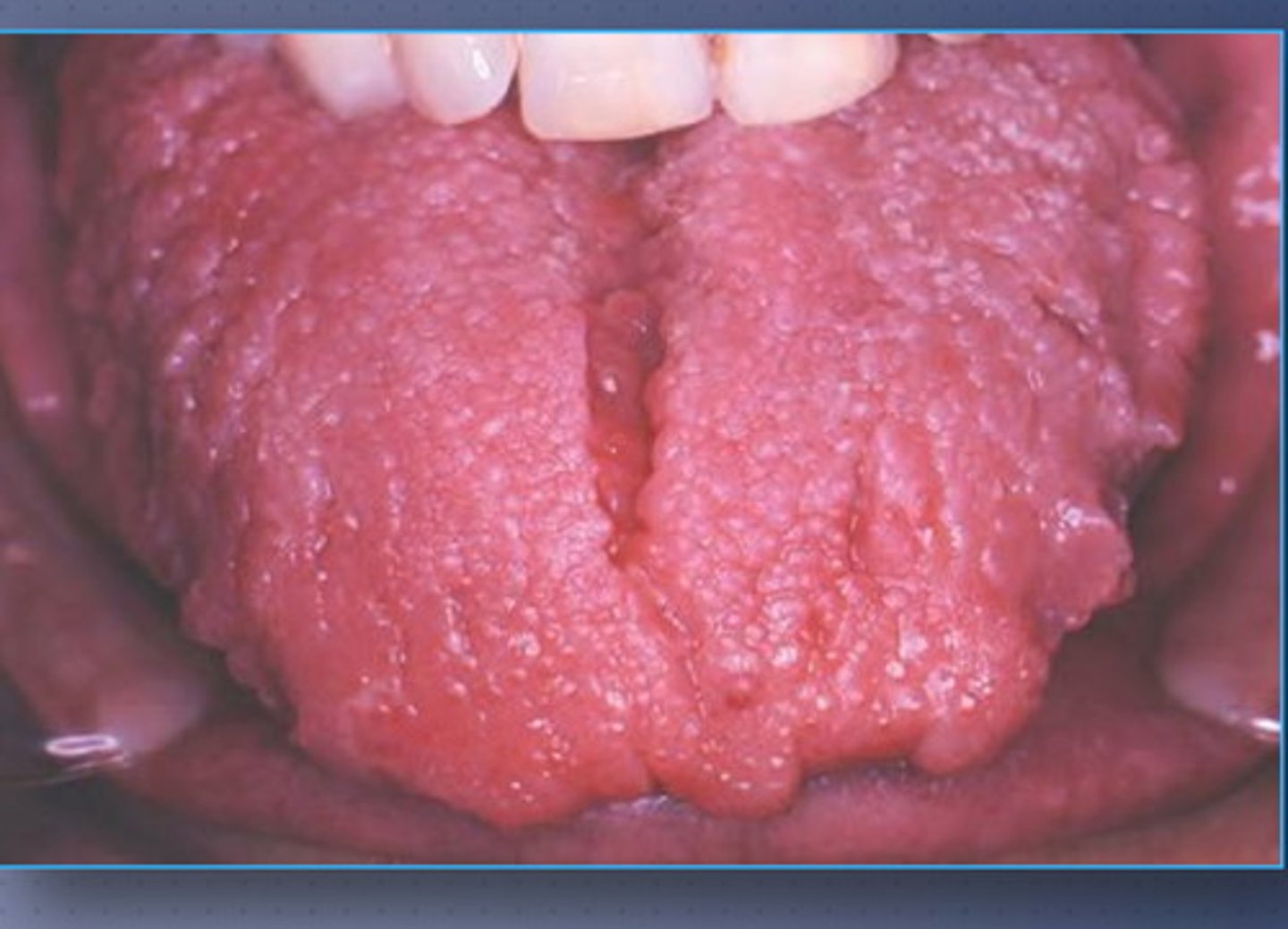
macroglossia
• Enlargement of the tongue
• May be congenital or acquired
Common with Down syndrome
down syndrome
macroglossia is commonly associated with ...
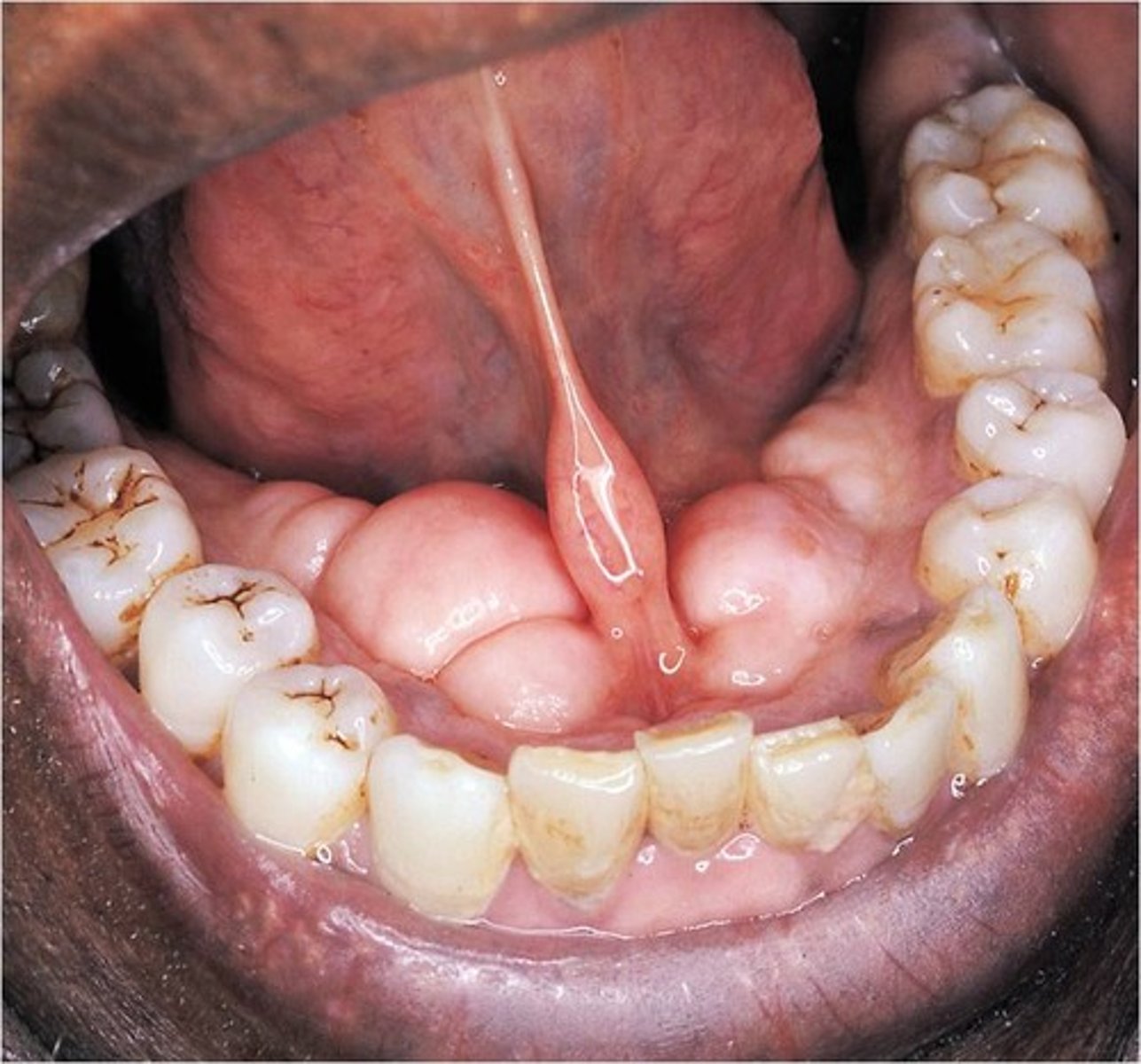
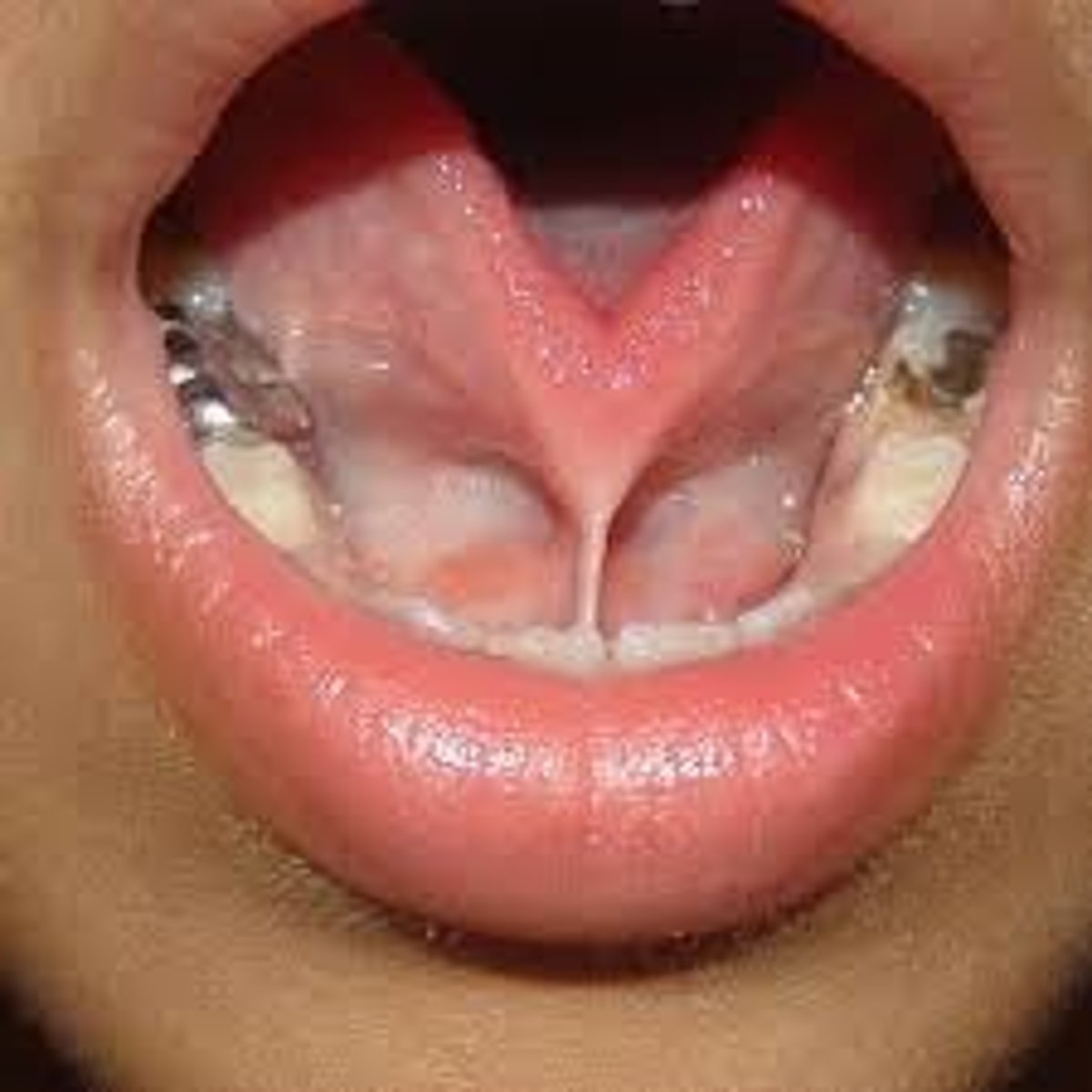
Ankyloglossia
• Short, thick lingual frenum
resulting in limitation of tongue
movement
no
in most cases in treatment necessary for ankyloglossia
females
lingual thyroids are 4-7x more likely in ...
lingual thyroid
• If the primitive gland does not descend normally, ectopic thyroid tissue may be found between the foramen cecum and the epiglottis
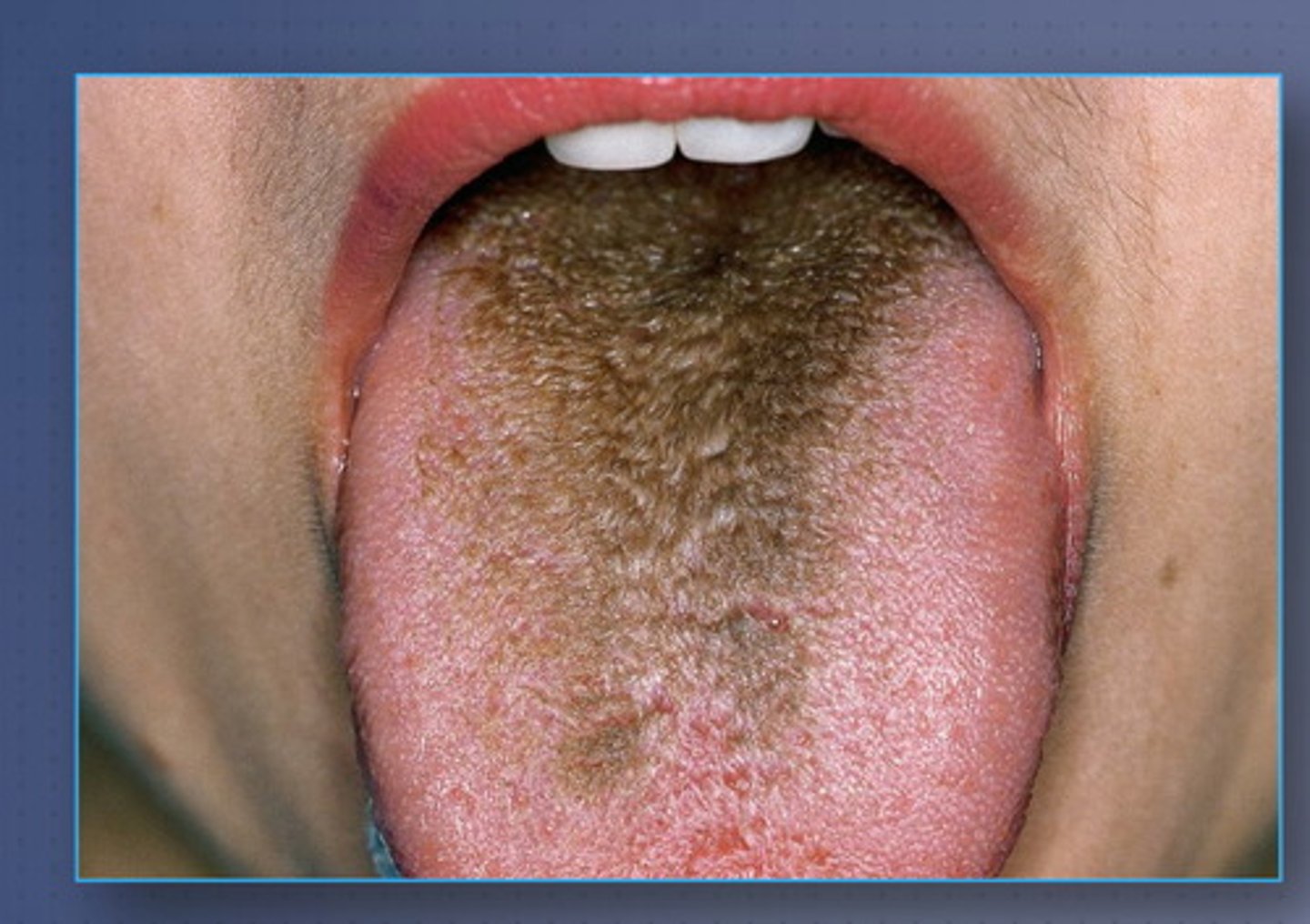
hairy tongue
Marked accumulation of keratin
on the filiform papillae of the
dorsal tongue, resulting in a
hair-like appearance
Not from fungal infection
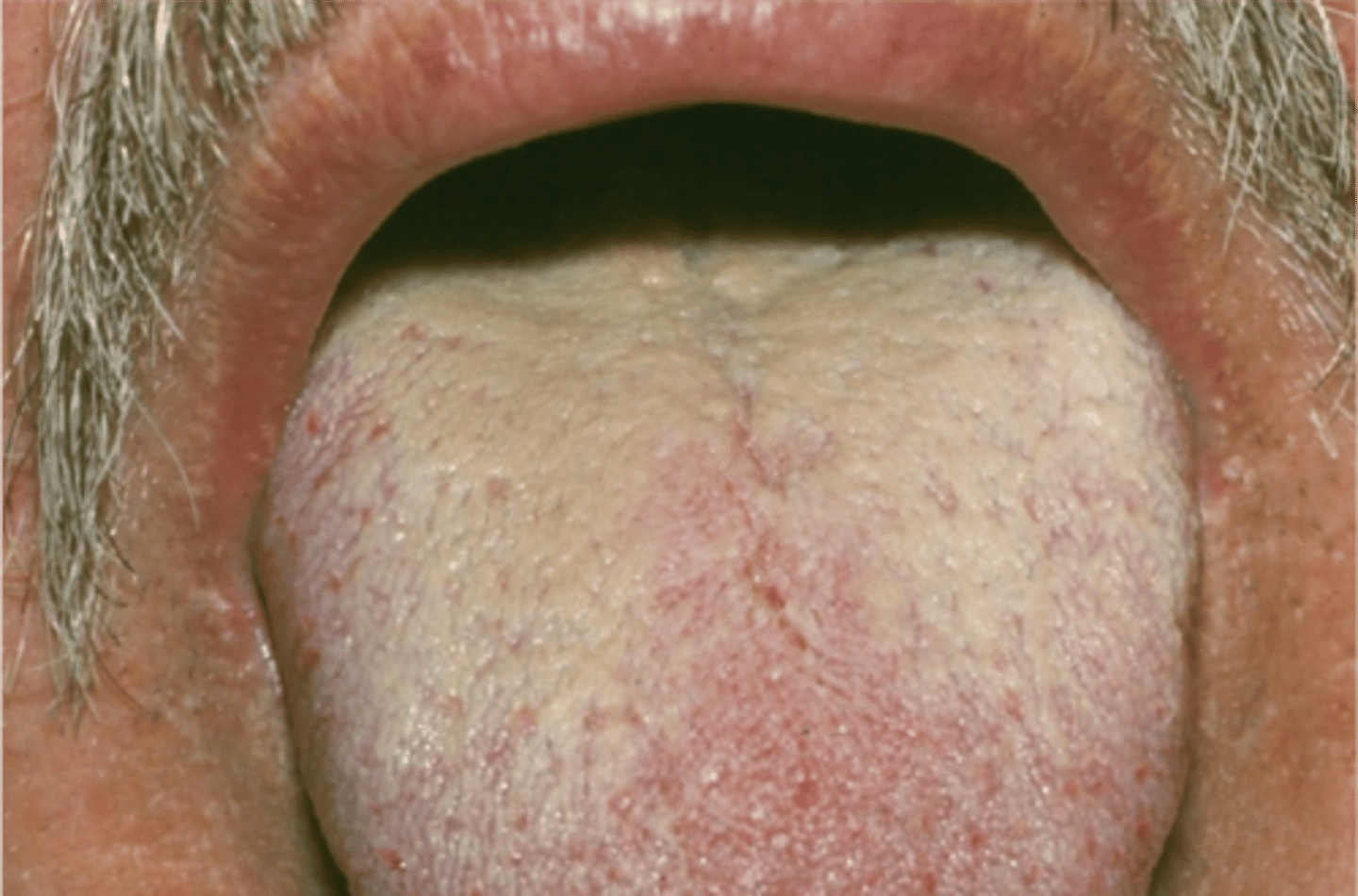
coated tongue
Numerous bacteria and
desquamated epithelial cells
accumulate on the dorsal
tongue surface, but without the
hair-like filiform projections
candidiasis; antifungal
coated tongue can be misdiagnosed as
..... and treated
unnecessarily with ....
medications
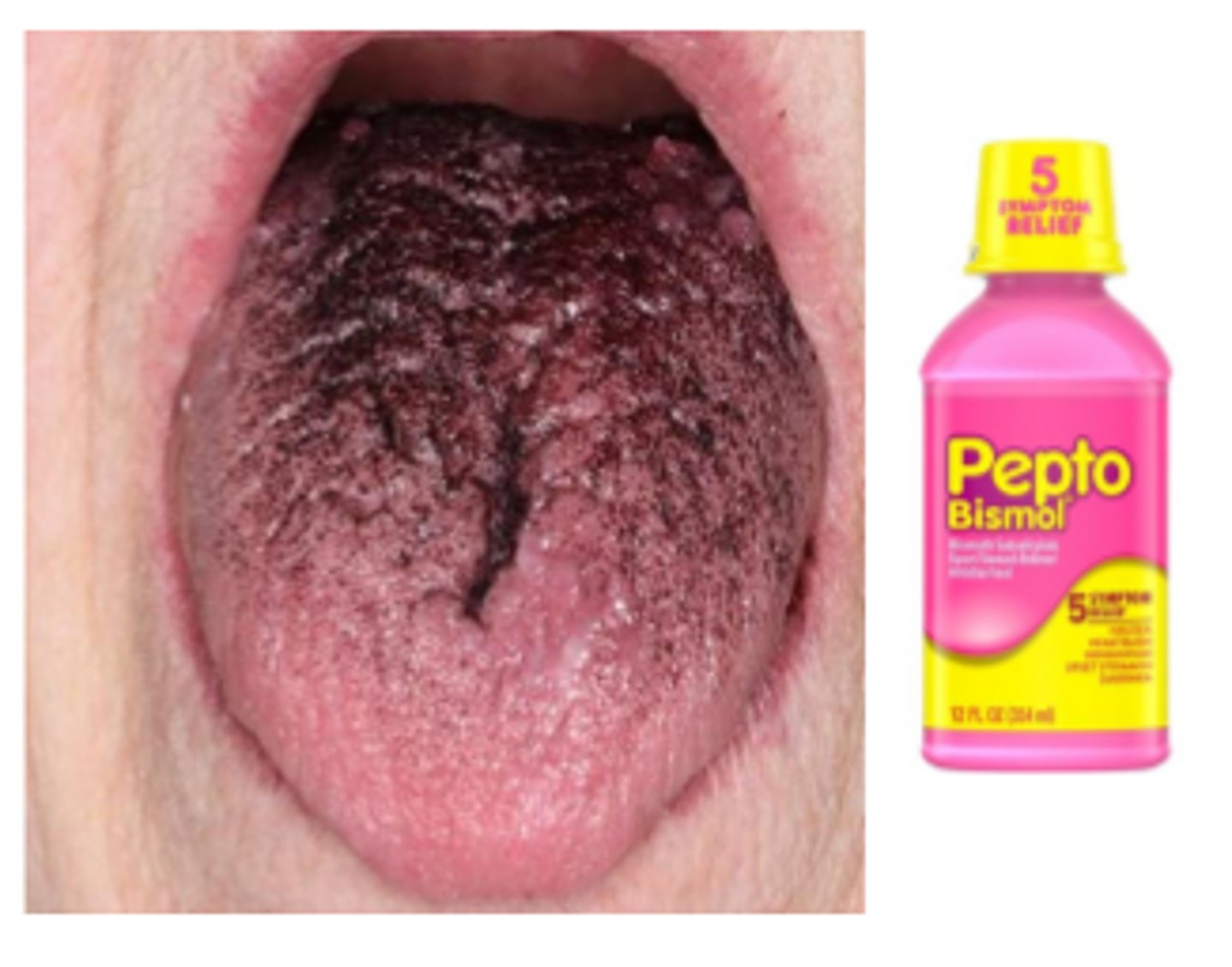
black coated tongue
• Black staining of the dorsal
tongue without elongation of
the filiform papillae
• Can occur in patients who use
Photo bismol or some other antibiotics
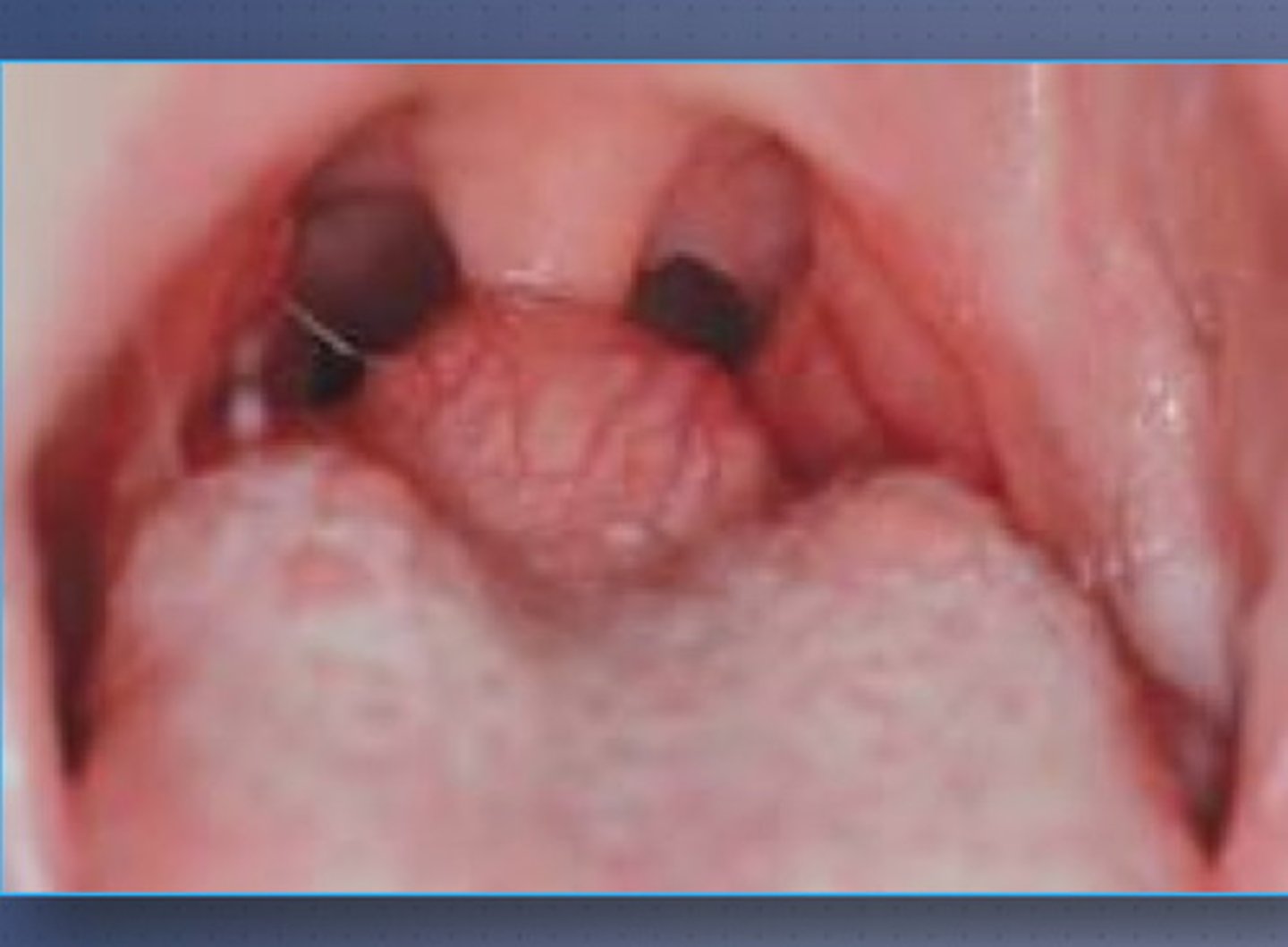
varices
• Abnormally dilated and tortuous
veins
• Age is an important etiologic
factor
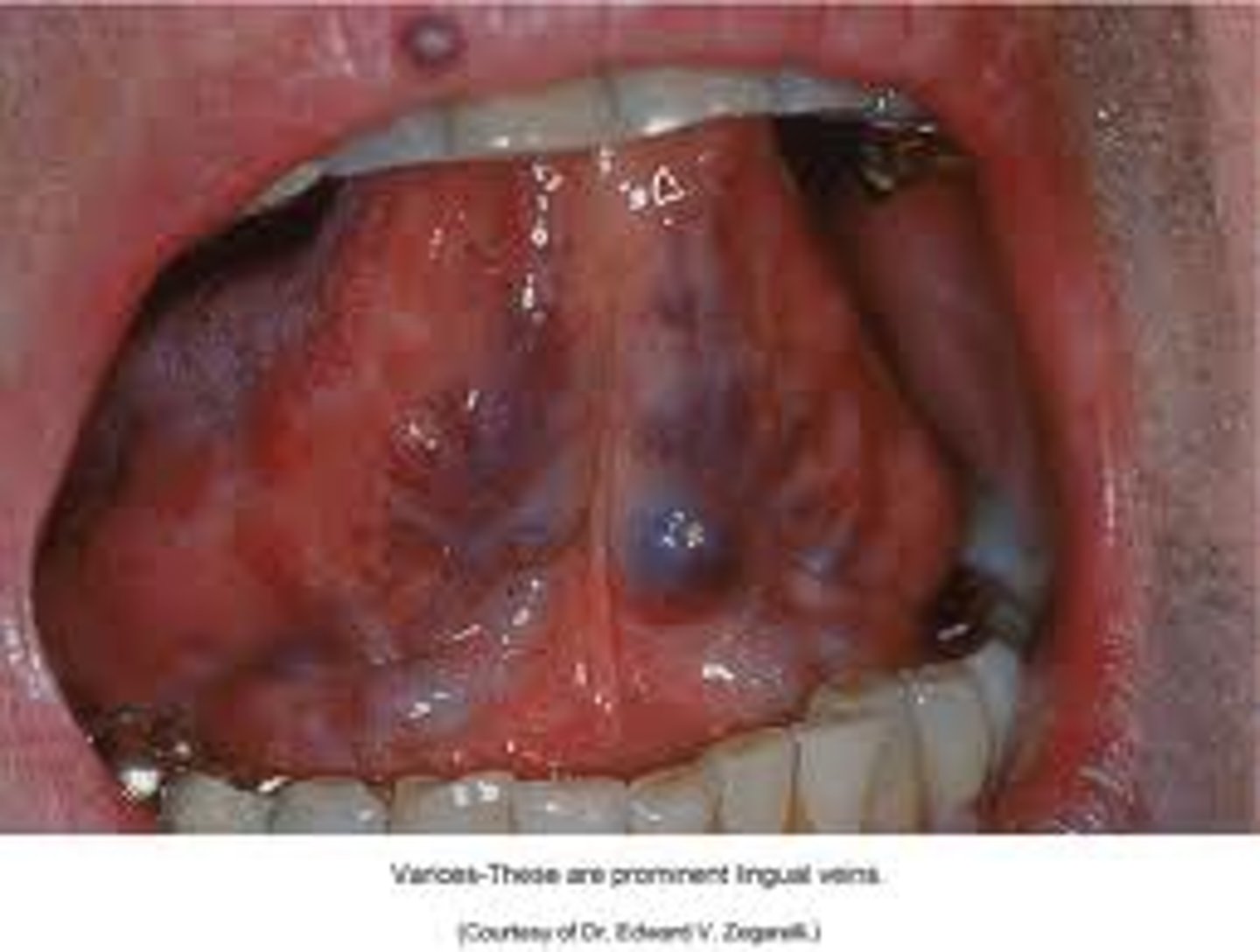
sublingual
The most common type of oral
varicosity is the .... varix
caliber persistent artery
• Common vascular anomaly
• A main arterial branch extends
up into the superficial
submucosal tissues without a
reduction in its diameter
• Seen more frequently in older
adults
eagle syndrome
• Elongation of the styloid process
or mineralization of the
stylohyoid ligament complex is
reported in 18% to 84% of the population increasing in
incidence with age
• Usually bi-, but may be unilateral
- only called ..... if there are symptoms present
stafne defect
• Focal concavity of the cortical bone on the lingual surface of the
mandible
• Believed to be developmental, but does not appear to be present
from birth
• Contain a portion of the submandibular gland
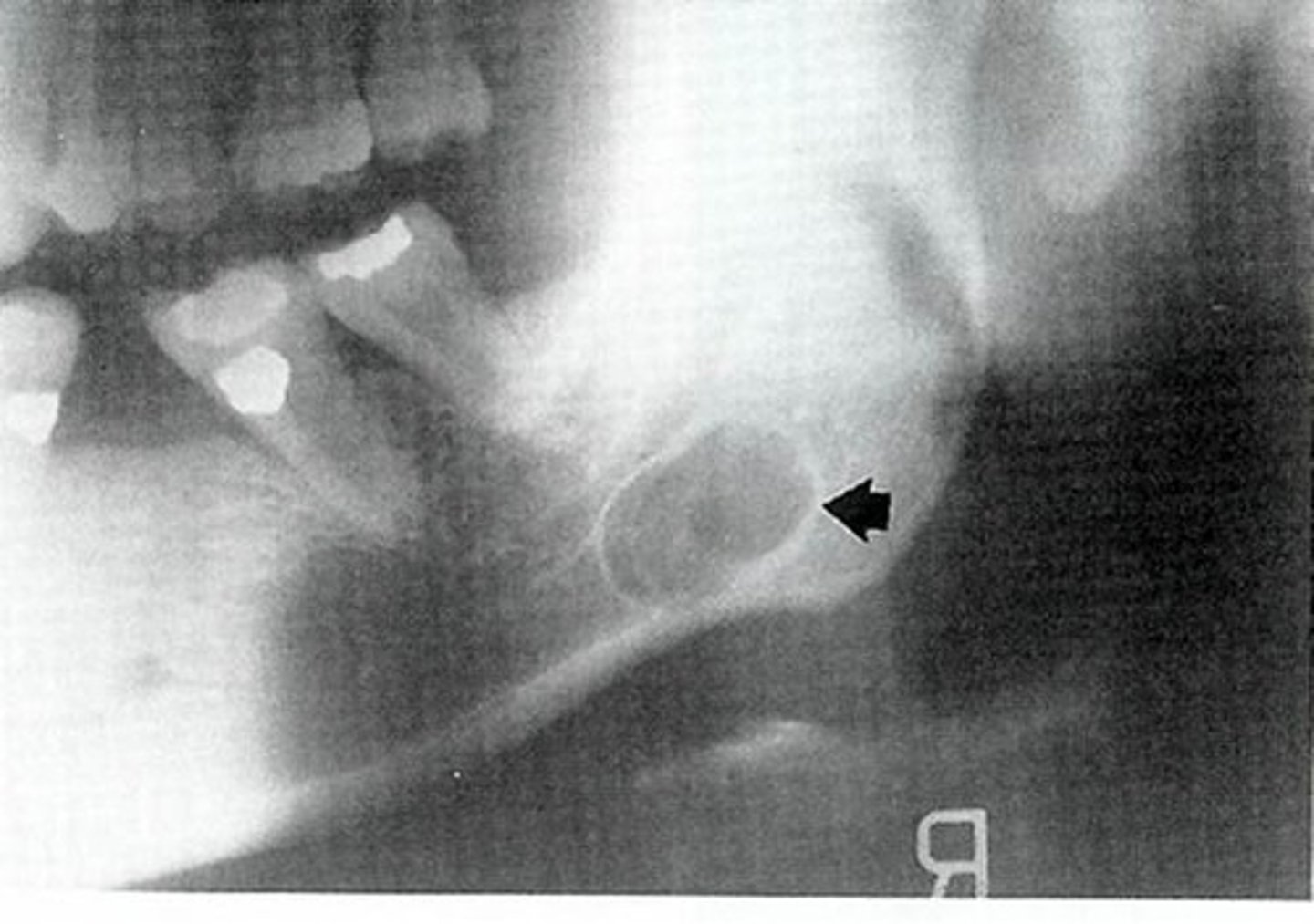
males
is stafne defect more common in males or females
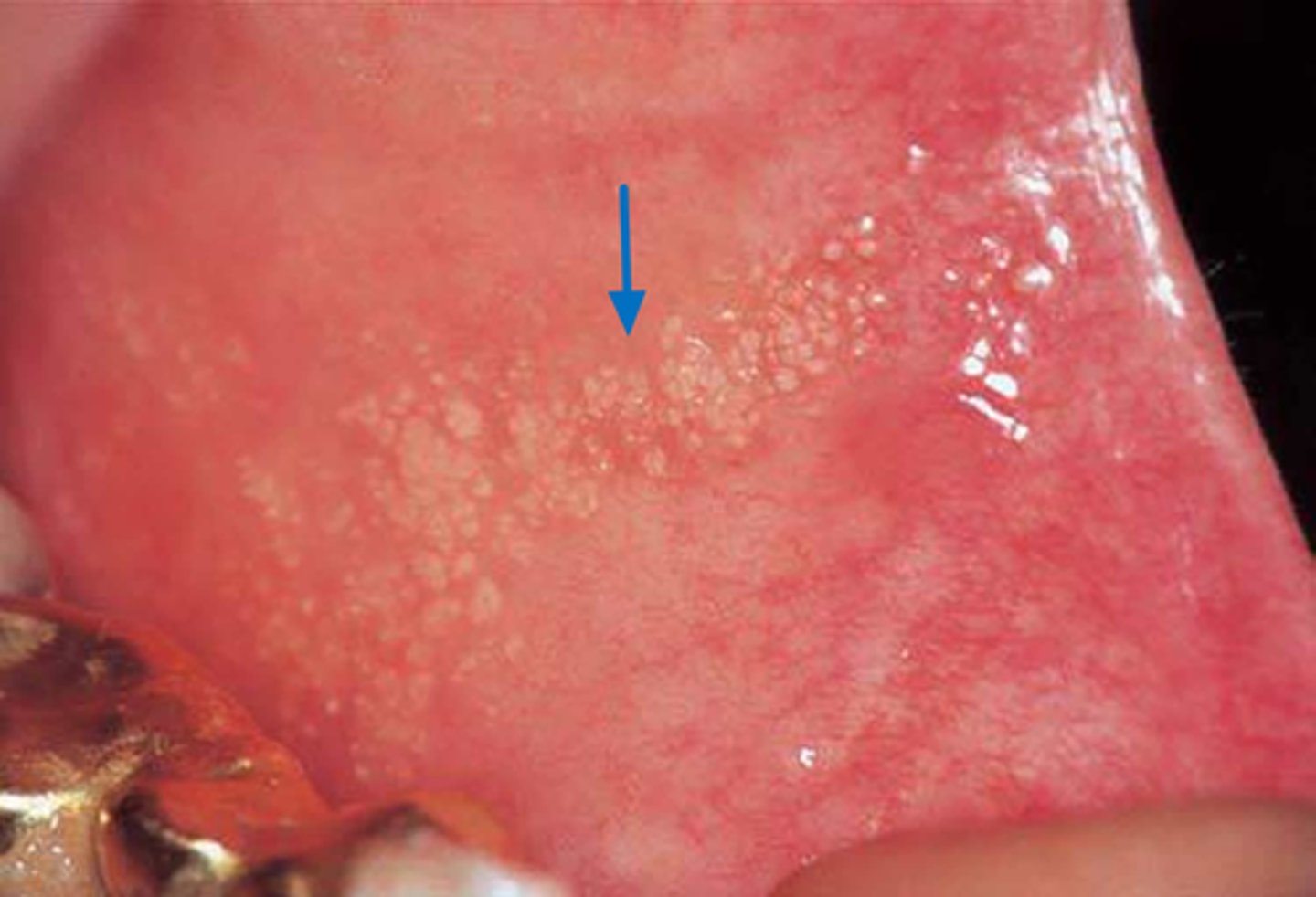
fordyce granules
• Sebaceous glands that occur on the oral mucosa
• Sebaceous glands are considered to be dermal adnexal structure so
those found in the oral cavity have been considered to be "ectopic"
• However, Fordyce granules have been reported in more than 80% of
the population
• SO THEY ARE NORMAL
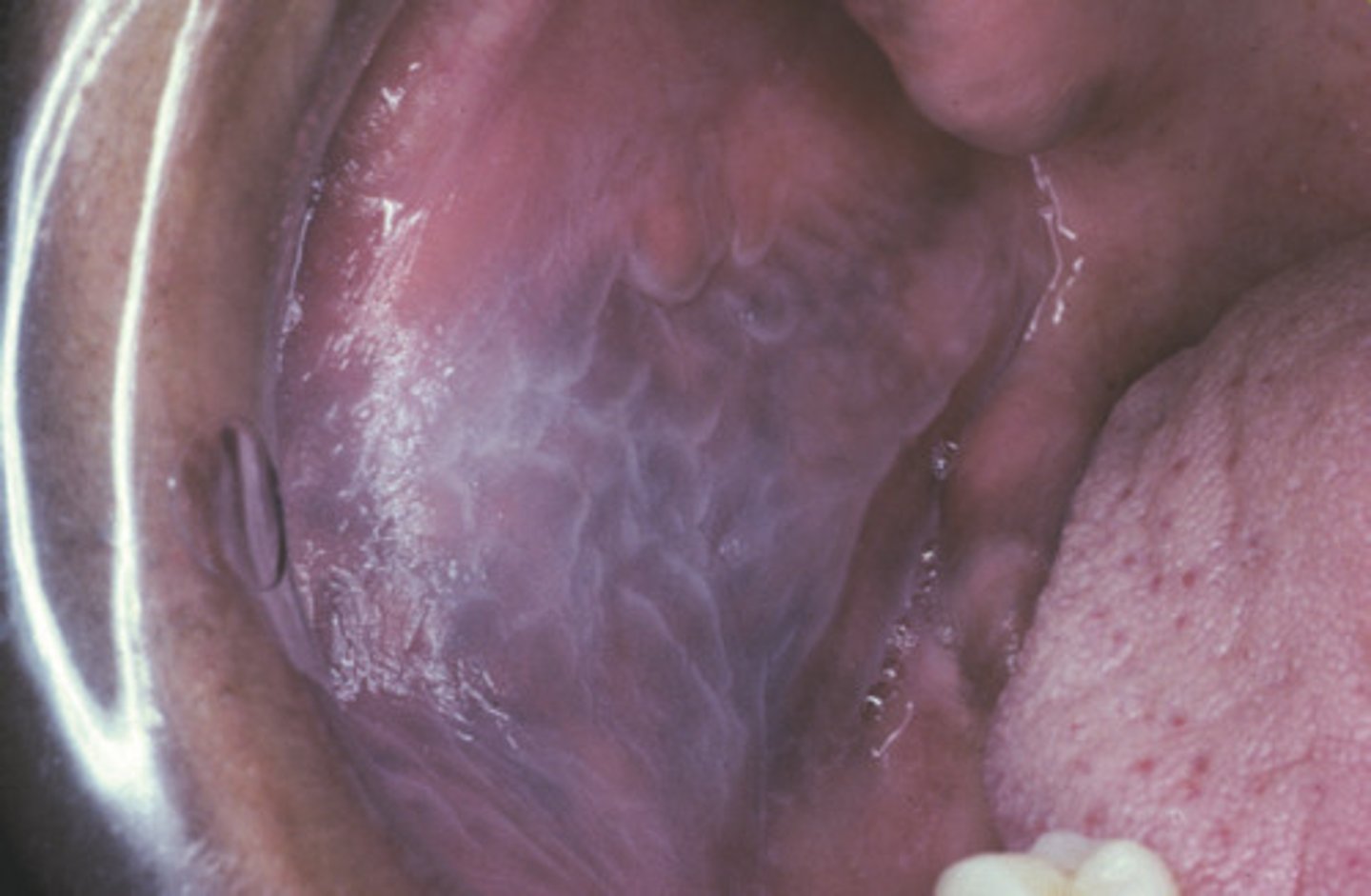
leukoedema
• Diffuse, gray-white, milky,
opalescent appearance of the
mucosa
• Surface appears folded/wrinkled
• Does not rub off
• Typically occurs bilaterally on the
buccal mucosa, mat extend to
labial mucosa
• White appearance greatly
diminishes or disappears when
the cheek is everted and stretched
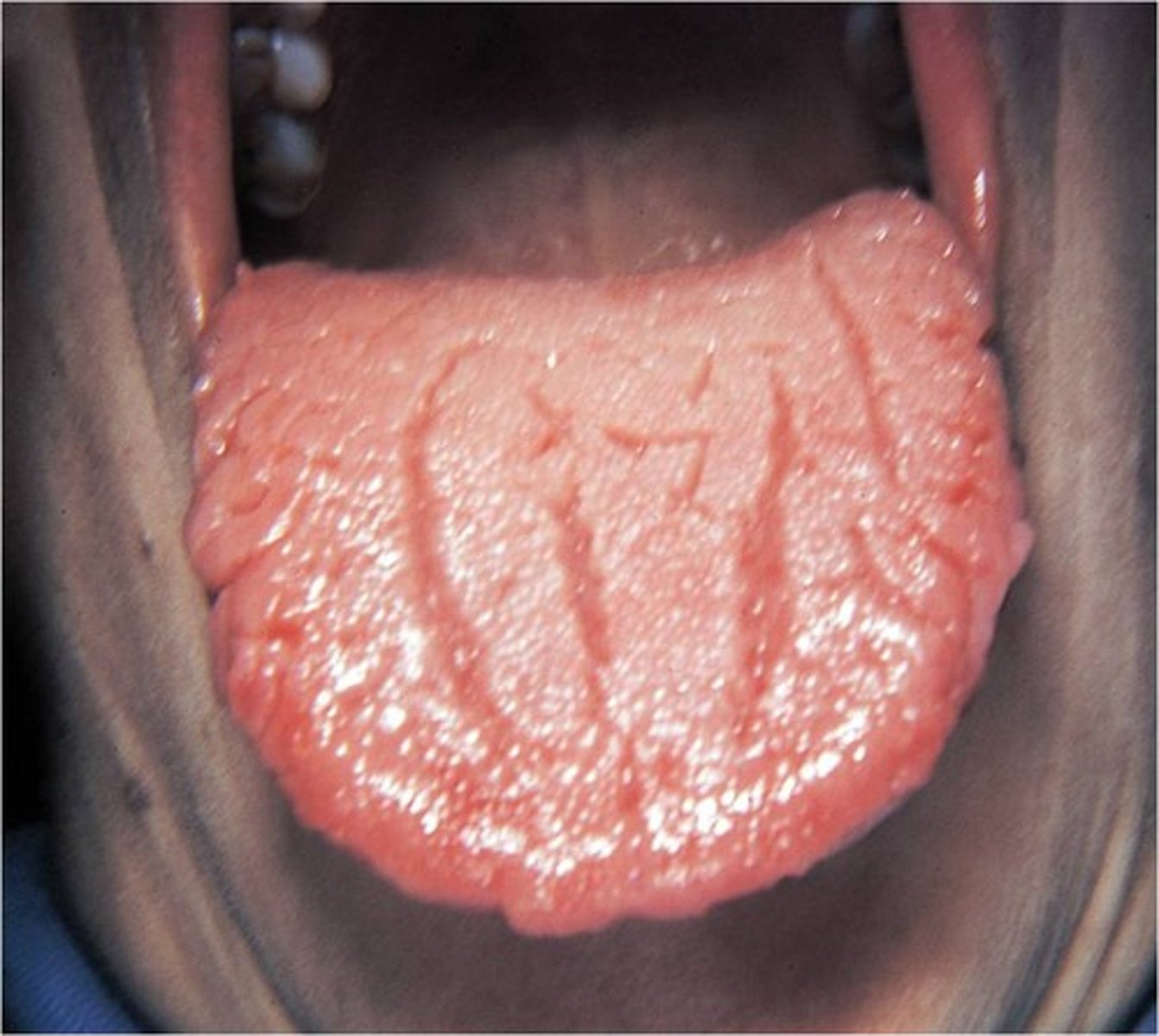
fissure tongue
• Presence of numerous grooves,
or fissures, on the dorsal tongue
surface
• Cause unknown, but heredity
appears to play a significant role
• Strong association between
fissured tongue and geographic
tongue
tori
• Localized bony protuberances that arise from the cortical plate
• May be related to stresses placed on the bone from the function of
teeth
• The best-known oral exostoses - the torus palatinus and the torus
mandibularis